The Fate and Challenges of the Main Nutrients in Returned Straw: A Basic Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Straw Types and Nutrients—An Overview
3. Straw Decomposition Effects and Nutrient Release Characteristics
3.1. Decomposition of Returned Straw
3.2. The Nutrient Release Characteristics of Returned Straw
4. The Fate of Straw Nutrients and Their Effects on Soil Nutrient Pools
4.1. The Fate of Straw C and Its Impact on C Pools in Soil
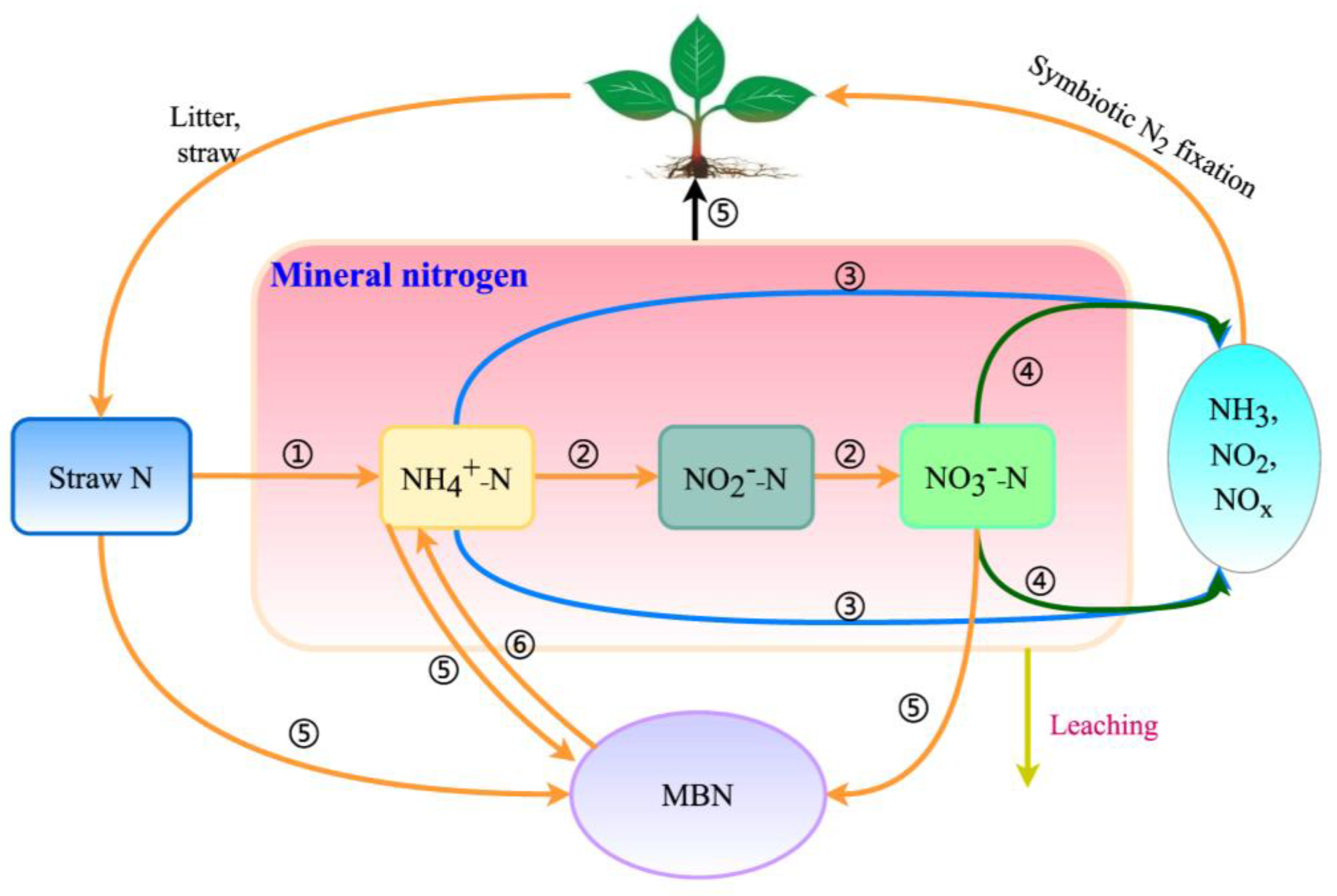
4.2. N Transformation Pathways in Straw and the Effects on Soil N Pools
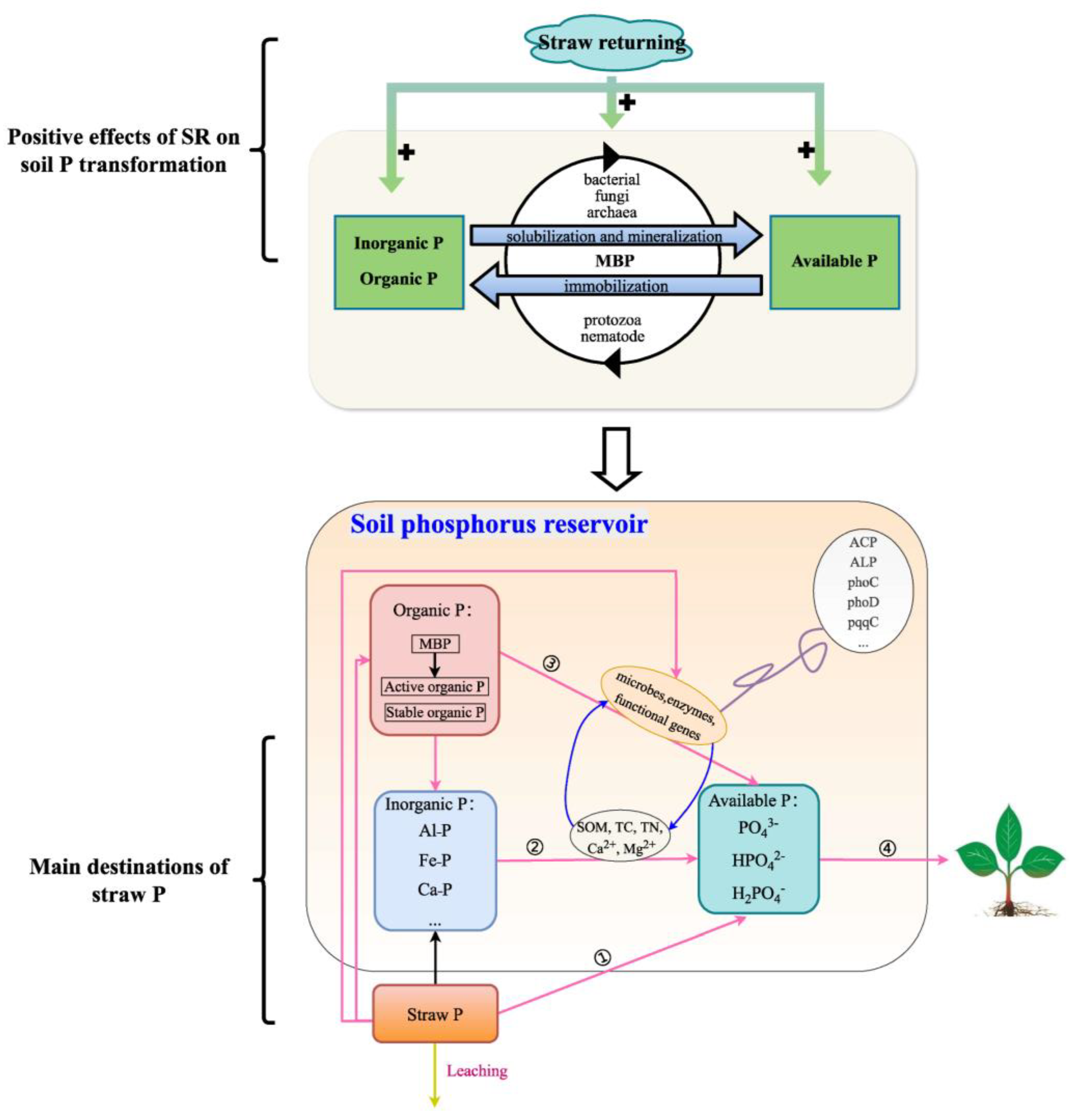
4.3. Straw P Conversion and Its Effects on Soil P Pools
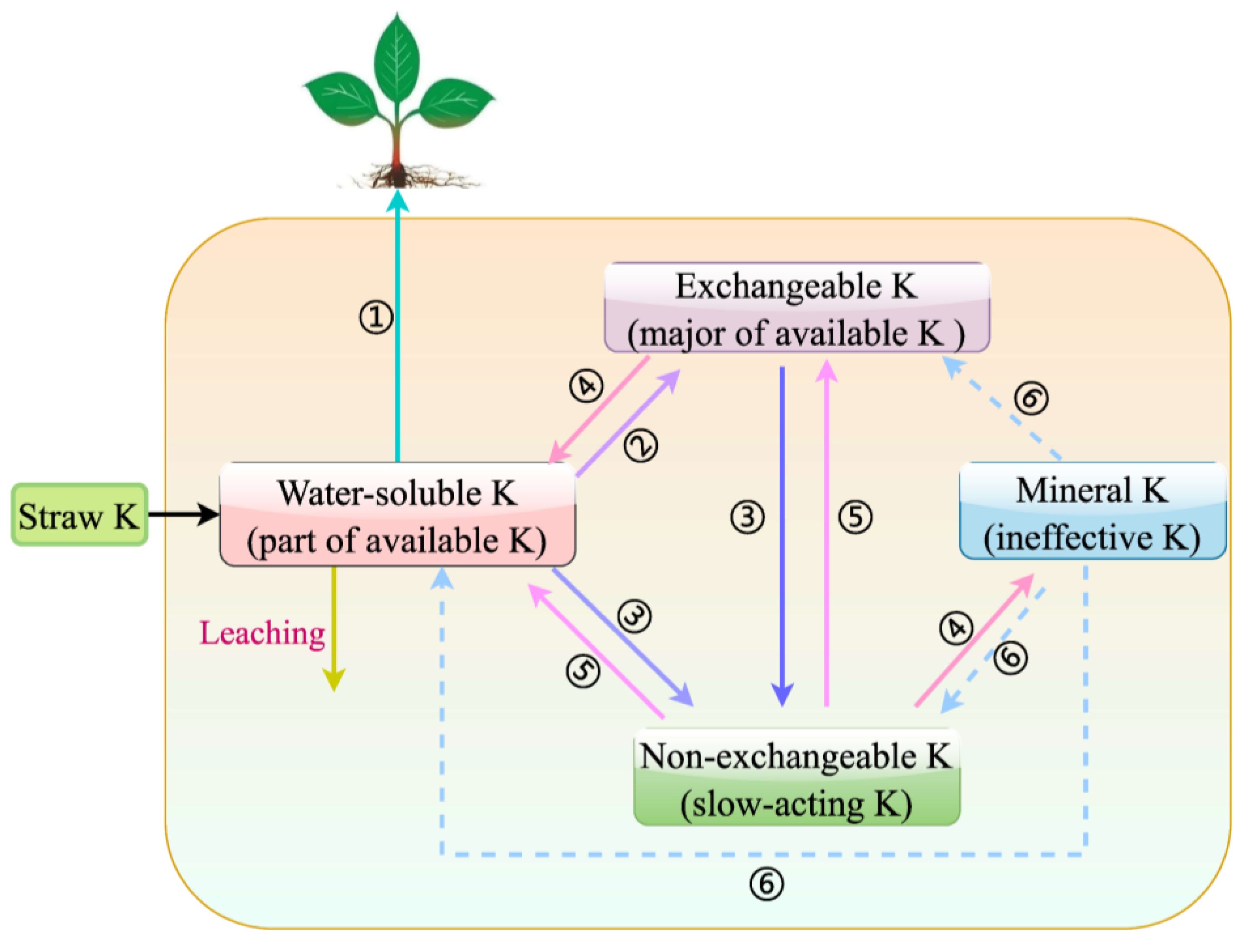
4.4. The Fate of K in Straw and Soil K Pool Responses to Straw Application
5. SR and Associated Challenges
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kubra, K.T.; Salman, M.S.; Hasan, M.N.; Islam, A.; Hasan, M.M.; Awual, M.R. Utilizing an alternative composite material for effective copper(II) ion capturing from wastewater. J. Mol. Liq. 2021, 336, 116325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubra, K.T.; Salman, M.S.; Hasan, M.N.; Islam, A.; Teo, S.H.; Hasan, M.M.; Sheikh, M.C.; Awual, M.R. Sustainable detection and capturing of cerium(III) using ligand embedded solid-state conjugate adsorbent. J. Mol. Liq. 2021, 338, 116667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, M.M.; Kubra, K.T.; Hasan, M.N.; Awual, M.E.; Salman, M.S.; Sheikh, M.C.; Rehan, A.I.; Rasee, A.I.; Waliullah, R.M.; Islam, M.S.; et al. Sustainable ligand-modified based composite material for the selective and effective cadmium(II) capturing from wastewater. J. Mol. Liq. 2023, 371, 121125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salman, M.S.; Hasan, M.N.; Hasan, M.M.; Kubra, K.T.; Sheikh, M.C.; Rehan, A.I.; Waliullah, R.M.; Rasee, A.I.; Awual, M.E.; Hossain, M.S.; et al. Improving copper(II) ion detection and adsorption from wastewater by the ligand-functionalized composite adsorbent. J. Mol. Struct. 2023, 1282, 135259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awual, M.R.; Hasan, M.N.; Hasan, M.M.; Salman, M.S.; Sheikh, M.C.; Kubra, K.T.; Islam, M.S.; Marwani, H.M.; Islam, A.; Khaleque, M.A.; et al. Green and robust adsorption and recovery of Europium(III) with a mechanism using hybrid donor conjugate materials. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2023, 319, 124088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Nayak, A.K.; Sharma, S.; Senapati, A.; Mitra, D.; Mohanty, B.; Prabhukarthikeyan, S.R.; Sabarinathan, K.G.; Mani, I.; Garhwal, R.S.; et al. Rice straw recycling: A sustainable approach for ensuring environmental quality and economic security. Pedosphere 2023, 33, 34–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Xiao, R.; Guo, Y.; Wang, Q.; Cui, Y.; Xiu, Y.; Ma, Z.; Zhang, M. Changes in soil microbial community composition during Phragmites australis straw decomposition in salt marshes with freshwater pumping. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 762, 143996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, T.; Yang, N.; Lu, C.; Qin, X.; Siddique KH, M. Soil organic carbon, total nitrogen, available nutrients, and yield under different straw returning methods. Soil Tillage Res. 2021, 214, 105171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wu, P.; Mei, F.; Ling, Y.; Qiao, Y.; Liu, C.; Leghari, S.J.; Guan, X.; Wang, T. Does continuous straw returning keep China farmland soil organic carbon continued increase? A meta-analysis. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 288, 112391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Dai, M.; Dai, S.; Dong, X. Current status and environment impact of direct straw return in China’s cropland—A review. Ecotox. Environ. Saf. 2018, 159, 293–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, S.; Ma, Z.; Wang, L.; Yan, C.; Liu, L.; Gong, Z.; Cui, G. Decomposition and nutrient release characteristics of incorporated soybean and maize straw in Northeast China. Ekoloji 2019, 28, 2119–2129. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, P.; Sui, P.; Lian, H.; Wang, Z.; Meng, G.; Sun, Y.; Wang, Y.; Su, Y.; Ma, Z.; Qi, H.; et al. Maize straw returning approaches affected straw decomposition and soil carbon and nitrogen storage in northeast China. Agronomy 2019, 9, 818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Yao, S.-H.; Jiang, H.; Ge, X.-L.; Zhang, Y.; Mao, J.; Dou, S.; Zhang, B. Effects of mixing maize straw with soil and placement depths on decomposition rates and products at two cold sites in the mollisol region of China. Soil Tillage Res. 2020, 197, 104519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Z.; Shah, T.; Zhang, L.; Liu, H.; Peng, S.; Nie, L. Effect of straw returning on soil organic carbon in rice-wheat rotation system: A review. Food Energy Secur. 2020, 9, e200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latifmanesh, H.; Deng, A.; Li, L.; Chen, Z.; Zheng, Y.; Bao, X.; Zheng, C.; Zhang, W. How incorporation depth of corn straw affects straw decomposition rate and C&N release in the wheat-corn cropping system. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2020, 300, 107000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, C.; Yan, S.-S.; Jia, T.-Y.; Dong, S.-K.; Ma, C.-M.; Gong, Z.-P. Decomposition characteristics of rice straw returned to the soil in northeast China. Nutr. Cycl. Agroecosyst. 2019, 114, 211–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Q.; Li, C.; Cao, C.; Huang, J.; Ding, H.; Yu, M.; Liu, J.; Liu, T. The rice-edible mushroom pattern promotes the transformation of composted straw-C to soil organic carbon. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2023, 353, 108560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Wang, H.; Liu, X.; Zhao, X.; Lu, D.; Zhou, J.; Li, C. Changes in soil microbial community and organic carbon fractions under short-term straw return in a rice-wheat cropping system. Soil Tillage Res. 2017, 165, 121–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubar, K.A.; Huang, L.; Lu, J.; Li, X.; Xue, B.; Yin, Z. Integrative effects of no-tillage and straw returning on soil organic carbon and water stable aggregation under rice-rape rotation. Chil. J. Agric. Res. 2018, 78, 205–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Li, X.; Zhu, W.; Chen, J.; Tian, X.; Shi, J. Does straw return strategy influence soil carbon sequestration and labile fractions? Agron. J. 2019, 111, 897–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Shen, Y.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, H.; Liu, L.; Wang, Z.; Gu, J. Effects of long-term straw returning on rice yield and soil properties and bacterial community in a rice-wheat rotation system. Field Crop. Res. 2023, 291, 108800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Guo, Y.; Li, C.; Cao, C.; Yuan, P.; Zou, F.; Wang, J.; Jia, P.; Wang, J. Effects of straw returning and feeding on greenhouse gas emissions from integrated rice-crayfish farming in Jianghan Plain, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 11710–11718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Liu, Y.; Jiao, X.; Li, J.; Liu, K.; Wu, T.; Zhang, Z.; Luo, D. Response of soil nutrients retention and rice growth to biochar in straw returning paddy fields. Chemosphere 2023, 312, 137244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, F.; Liang, X.; Zhang, H.; Tian, G. The influence of no-till coupled with straw return on soil phosphorus speciation in a two-year rice-fallow practice. Soil Tillage Res. 2019, 195, 104389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wang, L.; Zhu, P. Straw return with reduced nitrogen fertilizer maintained maize high yield in northeast China. Agronomy 2019, 9, 229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Ma, W.; Zhou, B.; Yang, X.; Salah, A.; Li, C.; Cao, C.; Zhan, M.; Zhao, M. Effects of straw-return method for the maize-rice rotation system on soil properties and crop yields. Agronomy 2020, 10, 461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spohn, M.; Kuzyakov, Y. Phosphorus mineralization can be driven by microbial need for carbon. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2013, 61, 69–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, Z.; Chen, R.; Wei, S.; Feng, Y.; Zhang, J.; Lin, X. Response and feedback of C mineralization to P availability driven by soil microorganisms. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2017, 105, 111–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, J.; Tcherkez, G. Potassium dependency of enzymes in plant primary metabolism. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2021, 166, 522–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Y.; Xu, X.; Kong, L.; Zhang, L.; Wang, L. The combination of straw return and appropriate K fertilizer amounts enhances both soil health and rice yield in northeast China. Agron. J. 2021, 113, 5424–5435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Cao, Y.; Wang, X.; Ge, X.; Li, B.; Jin, C. Evaluation on the production of food crop straw in China from 2006 to 2014. BioEnergy Res. 2017, 10, 949–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, R.; Lan, M.; Liu, J.; Gao, M. Soil aggregate and organic carbon distribution at dry land soil and paddy soil: The role of different straws returning. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 27942–27952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, L.; Zha, J.; Shen, M.; Wang, H.; Shi, L.; Tao, Y.; Zhou, X.; Lu, C. Effect of long-term straw returning on soil organic carbon fractions composition in rice-wheat rotation ecosystem. J. Agric. Sci. Technol. 2022, 24, 166–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.; Ran, C.; Liu, B.; Zhao, Z.; Bai, T.; Zhao, M.; Cheng, Z.; Chen, G.; Geng, Y. Effect of straw return with nitrogen fertilizer on photosynthetic characteristics and yield of rice in soda saline-alkali rice paddy fields. Cereal Res. Commun. 2022, 51, 509–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, N.; Wang, J.; Pang, J.; Hu, W.; Bai, H.; Zhou, Z.; Meng, Y.; Wang, Y. Straw retention coupled with mineral phosphorus fertilizer for reducing phosphorus fertilizer input and improving cotton yield in coastal saline soils. Field Crops Res. 2021, 274, 108309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, E.; Lin, X.; Tian, L.; Wang, X.; Ji, L.; Jin, F.; Tian, C. Effects of short-term rice straw return on the soil microbial community. Agriculture 2021, 11, 561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Fang, C.; Meng, Y.; Dai, Y.; Liu, J. Long-term ditch-buried straw return increases functionality of soil microbial communities. Catena 2021, 202, 105316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.; Yu, M.; Xi, H.; Lv, J.; Ma, Z.; Kou, C.; Shen, A. Soil microbial community shifts with long-term of different straw return in wheat-corn rotation system. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 6360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, J.; Li, D.; Yu, J.; Bai, X.; Cui, W.; Liu, R.; Zhuang, M. Environmental and economic benefits of substituting chemical potassium fertilizer with crop straw residues in China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 30, 30603–30611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, H.; Yang, B.; Dai, Y.; Xu, M.; Koide, R.T.; Wang, X.; Liu, J.; Bian, X. Soil nitrogen retention is increased by ditch-buried straw return in a rice-wheat rotation system. Eur. J. Agron. 2015, 69, 52–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, H.; Zhao, W.; Li, T.; Cheng, X.; Liu, Q. Balancing straw returning and chemical fertilizers in China: Role of straw nutrient resources. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2018, 81, 2695–2702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Li, S. Temporal and spatial distribution characteristics of crop straw nutrient resources and returning to farmland in China. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2017, 33, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Xia, J.; Xie, W.; Wei, S.; Cui, Q.; Shao, P.; Sun, J.; Dong, K.; Qi, X. Effects of straw returning and nitrogen addition on soil quality of a coastal saline soil: A field study of four consecutive wheat-maize cycles. Land Degrad. Dev. 2023, 34, 2061–2072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, A.; Liang, G.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, W.; Li, L.; Rui, Y.; Xu, M.; Luo, Y. Long-term straw decomposition in agro-ecosystems described by a unified three-exponentiation equation with thermal time. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 636, 699–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Zhong, Y.; Jia, X.; Yan, W.; Cao, J.; Shangguan, Z. Wheat straw decomposition patterns and control factors under nitrogen fertilization. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2021, 21, 3110–3121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Chen, L.; Li, Y.; Brookes, P.C.; Xu, J.; Luo, Y. Interactive effects of soil pH and substrate quality on microbial utilization. Eur. J. Soil Biol. 2020, 96, 103151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, H.; Chen, X.; Wei, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Chang, J.; Thompson, M.L. Decomposition dynamics and changes in chemical composition of wheat straw residue under anaerobic and aerobic conditions. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e158172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berhane, M.; Xu, M.; Liang, Z.; Shi, J.; Wei, G.; Tian, X. Effects of long-term straw return on soil organic carbon storage and sequestration rate in North China upland crops: A meta-analysis. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2020, 26, 2686–2701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Myers, R.; Palm, C.; Cuevas, E.; Gunatilleke, I.; Brossard, M. The Synchronisation of Nutrient Mineralisation and Plant Nutrient Eemand; John Wiley & Sons: Chichester, UK, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, S.; Fan, R.; Yang, X.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, X.; Liang, A. Decomposition of maize stover varies with maize type and stover management strategies: A microcosm study on a Black soil (Mollisol) in northeast China. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 234, 226–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Dou, S.; Ndzelu, B.S.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, X. Accumulation of straw-derived carbon and changes in soil humic acid structural characteristics during corn straw decomposition. Can. J. Soil Sci. 2021, 101, 452–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, C.; Zhong, W.; Han, C.; Deng, H.; Jiang, Y. Driving factors of soil organic carbon sequestration under straw returning across China’s uplands. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 335, 117590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, T.; Zhang, Q.; Ai, C.; Liang, G.; He, P.; Zhou, W. Nitrogen enrichment regulates straw decomposition and its associated microbial community in a double-rice cropping system. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 1847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- An, T.; Schaeffer, S.; Zhuang, J.; Radosevich, M.; Li, S.; Li, H.; Pei, J.; Wang, J. Dynamics and distribution of 13C-labeled straw carbon by microorganisms as affected by soil fertility levels in the Black Soil region of Northeast China. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2015, 51, 605–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.; He, Z.; Yang, Y.; Jia, S.; Yu, M.; Chen, X.; Shen, A. Linking soil microbial community dynamics to straw-carbon distribution in soil organic carbon. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 5526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, S.; Song, J.; Fan, J.; Yan, C.; Dong, S.; Ma, C.; Gong, Z. Changes in soil organic carbon fractions and microbial community under rice straw return in Northeast China. Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 2020, 22, e00962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, C.; Schimel, J.P.; Jastrow, J.D. The importance of anabolism in microbial control over soil carbon storage. Nat. Microbiol. 2017, 2, 17105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, D.; Cong, R.; Ren, T.; Lu, Z.; Lu, J.; Li, X. Straw incorporation improved the adsorption of potassium by increasing the soil humic acid in macroaggregates. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 310, 114665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia-Ruiz, R.; Carranza-Gallego, G.; Aguilera, E.; Gonzalez De Molina, M.; Guzman, G.I. C and N mineralisation of straw of traditional and modern wheat varieties in soils of contrasting fertility. Nutr. Cycl. Agroecosyst. 2019, 113, 167–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Song, C.; Xin, Z.; Fang, C.; Liu, Z.; Xu, Y. Agricultural management strategies for balancing yield increase, carbon sequestration, and emission reduction after straw return for three major grain crops in China: A meta-analysis. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 340, 117965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, P.; Xu, J.; Zhang, Z.; Nie, T.; Wang, K.; Guo, H. Where the straw-derived nitrogen gone in paddy field subjected to different irrigation regimes and straw placement depths? Evidence from 15N labeling. Agric. Water Manag. 2022, 273, 107921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Liu, E.; Tian, Q.; Yan, C.; Zhang, Y. Soil nitrogen dynamics and crop residues. A review. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2014, 34, 429–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, L.; Lam, S.K.; Wolf, B.; Kiese, R.; Chen, D.; Butterbach-Bahl, K. Trade-offs between soil carbon sequestration and reactive nitrogen losses under straw return in global agroecosystems. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2018, 24, 5919–5932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, D.; Bai, E.; Wang, S.; Zong, S.; Liu, Z.; Fan, X.; Zhao, C.; Hagedorn, F. Three-dimensional mapping of carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus in soil microbial biomass and their stoichiometry at the global scale. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2022, 28, 6728–6740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, Y.; Lv, J.L.; Yu, M.; Ma, Z.H.; Xi, H.; Kou, C.L.; He, Z.C.; Shen, A.L. Long-term decomposed straw return positively affects the soil microbial community. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2020, 128, 138–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Zhang, G.; Wang, D.; Liu, Q. Long-term straw return with N addition alters reactive nitrogen runoff loss and the bacterial community during rice growth stages. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 292, 112772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehtovirta-Morley, L.E. Ammonia oxidation: Ecology, physiology, biochemistry and why they must all come together. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2018, 365, fny058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Li, Y.; Ciampitti, I.A.; He, P.; Xu, X.; Qiu, S.; Zhao, S. Response of soil denitrification potential and community composition of denitrifying bacterial to different rates of straw return in north-central China. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2022, 170, 104312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Dong, W.; Jia, S.; Liu, Q.; Li, Y.; Hossain, M.E.; Liu, E.; Kuzyakov, Y. Transformations of N derived from straw under long-term conventional and no-tillage soils: A 15N labelling study. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 786, 147428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, M. Characteristics of Phosphorus Migration and Transformation after Straw Returning under Flooding Condition; Huazhong Agricultural University: Wuhan, China, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Maharajan, T.; Ceasar, S.A.; Krishna TP, A.; Ramakrishnan, M.; Duraipandiyan, V.; Abdulla, A.-D.N.; Ignacimuthu, S. Utilization of molecular markers for improving the phosphorus efficiency in crop plants. Plant Breed. 2018, 137, 10–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moro, H.; Park, H.-D.; Kunito, T. Organic phosphorus substantially contributes to crop plant nutrition in soils with low phosphorus availability. Agronomy 2021, 11, 903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Lu, S. Straw and straw biochar differently affect phosphorus availability, enzyme activity and microbial functional genes in an Ultisol. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 805, 150325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Q.; Hu, Y.; Chen, X.; Wei, X.; Shen, J.; Ge, T.; Su, Y. Flooding and straw returning regulates the partitioning of soil phosphorus fractions and phoD-harboring bacterial community in paddy soils. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2021, 105, 9343–9357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fei, C.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, L.; Ding, X. Straw is more effective than biochar in mobilizing soil organic phosphorus mineralization in saline-alkali paddy soil. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2023, 186, 104848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, J.; Jiang, N.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, L.; Huang, W.; Chen, L. Effects of various straw incorporation strategies on soil phosphorus fractions and transformations. GCB Bioenergy 2023, 15, 88–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, X.-K.; Wei, L.; Turner, N.C.; Ma, S.-C.; Yang, M.-D.; Wang, T.-C. Improved straw management practices promote in situ straw decomposition and nutrient release, and increase crop production. J. Clean Prod. 2020, 250, 119514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Liu, D.; Wu, M.; Xia, Y.; Zhang, F.; Fan, X. Long-term straw returning improve soil K balance and potassium supplying ability under rice and wheat cultivation. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 22260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sardans, J.; Penuelas, J. Potassium: A neglected nutrient in global change. Glob. Ecol. Biogeogr. 2015, 24, 261–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Hu, W.; Ning, X.; Wei, W.; Tang, Y.; Gu, Y. Effects of potassium fertilizer and straw on maize yield, potassium utilization efficiency and soil potassium balance. Arch. Agron. Soil Sci. 2022, 69, 679–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Li, Y.; Wu, T.; Qu, C.; Ning, P.; Shi, J.; Tian, X. Potassium fertilization combined with crop straw incorporation alters soil potassium fractions and availability in northwest China: An incubation study. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e236634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Randhawa, M.K.; Dhaliwal, S.S.; Sharma, V.; Toor, A.S.; Sharma, S.; Kaur, M. Impact of integrated nutrient management on transformations of micronutrients and uptake by wheat crop in North-western India. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2021, 21, 2932–2945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhu, P.; Cui, X.; Han, X.; Xu, M.; Lu, C. The efficiency of long-term straw return to sequester organic carbon in Northeast China’s cropland. J. Integr. Agric. 2018, 17, 436–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, S.; Saha, B.; Seth, T.; Dasgupta, S.; Ray, M.; Pal, B.; Pati, S.; Mukhopadhyay, S.K.; Hazra, G. Micronutrients availability in soil-plant system in response to long-term integrated nutrient management under rice-wheat cropping system. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2019, 19, 712–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, F.; Li, B.; Ren, B.; Zhao, B.; Liu, P.; Zhang, J. Effects of residue management strategies on greenhouse gases and yield under double cropping of winter wheat and summer maize. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 687, 1138–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Li, J.; Jiao, X.; Li, H.; An, Y.; Liu, K. Effects of straw returning combine with biochar on water quality under flooded condition. Water 2020, 12, 1633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Li, J.; Jiao, X.; Li, H.; Hu, T.; Jiang, H.; Mahmoud, A. Effects of biochar on water quality and rice productivity under straw returning condition in a rice-wheat rotation region. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 819, 152063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, S.; Wang, Y.; Liu, R.; Xing, L.; Yang, Z. Improved crop yield and reduced nitrate nitrogen leaching with straw return in a rice-wheat rotation of Ningxia irrigation district. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 9458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Reichel, R.; Xu, Z.; Vereecken, H.; Brueggemann, N. Return of crop residues to arable land stimulates N2O emission but mitigates NO3− leaching: A meta-analysis. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2021, 41, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Kong, F.; Lv, X.; Wang, Z.; Zhou, Z.; Meng, Y. Responses of greenhouse gas emissions to different straw management methods with the same amount of carbon input in cotton field. Soil Tillage Res. 2021, 213, 105126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Yu, J.-G.; Zhao, Y.-H.; Chang, Z.-Z.; Shi, X.-X.; Ma, L.Q.; Li, H.-B. Straw enhanced CO2 and CH4 but decreased N2O emissions from flooded paddy soils: Changes in microbial community compositions. Atmos. Environ. 2018, 174, 171–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.; Kwong RW, M.; Tang, W.; Yang, Y.; Zhong, H. Straw return enhances the risks of metals in soil? Ecotox. Environ. Safe. 2021, 207, 111201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Chen, Z.; Wu, Y.; Zhong, H. Comparison of methylmercury accumulation in wheat and rice grown in straw-amended paddy soil. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 697, 134143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, R.; Wang, P.; Mi, S.; Ali, A.; Liu, X.; Li, Y.; Guan, W.; Li, R.; Zhang, Z. Effects of crop straw and its derived biochar on the mobility and bioavailability in Cd and Zn in two smelter-contaminated alkaline soils. Ecotox. Environ. Safe 2019, 181, 155–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, D.; Xue, M.-Y.; Wang, Y.-K.; Zhou, D.-Z.; Tang, L.; Cao, S.-Y.; Wei, Y.-H.; Yang, C.; Liang, D.-L. Effects of straw amendment on selenium aging in soils: Mechanism and influential factors. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 657, 871–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Z.; Liu, J.; Li, Y.; Jin, J.; Liu, X.; Wang, G. Impact of land use, fertilization and seasonal variation on the abundance and diversity of nirS-type denitrifying bacterial communities in a Mollisol in Northeast China. Eur. J. Soil Biol. 2018, 85, 4–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, F.; Peng, P.; Yang, K.; Shu, Y.; Wang, J. Straw return of maize and soybean enhances soil biological nitrogen fixation by altering the N-cycling microbial community. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2023, 192, 105094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, L.; Zhu, X.; Cui, H.; Ojika, M.; Wang, R.; Liu, H. Establishment of the straightforward electro-transformation system for Phytophthora infestans and its comparison with the improved PEG/CaCl2 transformation. J. Microbiol. Methods 2015, 112, 83–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shwe, A.; Ostbye, T.-K.K.; Krasnov, A.; Ramberg, S.; Andreassen, R. Characterization of differentially expressed miRNAs and their predicted target transcripts during smoltification and adaptation to seawater in head kidney of Atlantic salmon. Genes 2020, 11, 1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, G.; Jo, H.; Kim, H.-S.; Kwon, M.; Son, Y. Earthworm effects on soil biogeochemistry in temperate forests focusing on stable isotope tracing: A review. Appl. Biol. Chem. 2022, 65, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, K.; Zhou, C.; Li, H.; Zhou, Z.; Ni, G.; Yin, X. Effects of rumen microorganisms on straw returning to soil at different depths. Eur. J. Soil Biol. 2023, 114, 103454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Xia, S.; Qin, H.; Feng, C.; Bie, S. Influence of decomposition agent application and schedule in wheat straw return practice on soil quality and crop yield. Chem. Biol. Technol. Agric. 2023, 10, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lian, H.; Wang, Z.; Li, Y.; Xu, H.; Zhang, H.; Gong, X.; Qi, H.; Jiang, Y. Straw strip return increases soil organic carbon sequestration by optimizing organic and humus carbon in aggregates of Mollisols in Northeast China. Agronomy 2022, 12, 784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Zhai, L.; Guo, S.; Zhang, F.; Hua, L.; Liu, H. Returned straw reduces nitrogen runoff loss by influencing nitrification process through modulating soil C:N of different paddy systems. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2023, 354, 108438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Straw Type | Straw Return Approach | Soil Type | Study Method | Effects and Mechanisms | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Maize straw | Rotary tillage | Silty loam | Incubation study | Corn residues with higher levels of easily decomposable substrates were mineralized by microorganisms. Both soil dissolved organic C (DOC) content and N fixation were improved. | [11] |
| Rice straw | Burying | Phaeozem | Field study | Straw decomposition dynamics were fast and then slow. Straw return increased soil nutrient sources and appropriately reduced K and P fertilizer applications. | [16] |
| Maize straw | Nylon litterbags | Mollisol | Field study | Mixing straw with soil increased the relative abundance of stable aromatic C- and N-containing structures when compared with a straw-only treatment. In cold high-latitude regions, incorporating straw into soils enhanced maize straw decomposition and ensured more stable soil organic matter (SOM) formation. | [13] |
| Maize straw | Rotary and plow tillage | - | Field study | Fresh straw inputs and decomposition generated priming effects, increasing soil organic carbon (SOC) and soil total nitrogen (STN) concentrations and soil C/N. | [12] |
| Phragmites australis straw | Rotary tillage | Salt marshes | Indoor incubation study | Soil microorganisms elicited stress responses to short-term exogenous carbon addition, resulting in significant increases in microbial biomass (bacteria and fungi). | [7] |
| Corn straw | Rotary tillage | Fluvo-aquic soil | Plot study | Straw incorporation into the 0–10 cm topsoil layer decomposed faster in response to higher soil temperatures, microbial biomass C and N, and total soil porosity. | [15] |
| Rice and wheat straw | Rotary tillage | Loamy soil | Field positioning study | Straw addition increased the soil organic carbon (SOC) and enhanced rice yields, with rice straw showing superior enhancement effects when compared with wheat straw. | [33] |
| Rice straw | Rotary tillage | Soda saline-alkali soil | Plot study | Straw application significantly increased photosynthetic capacity in rice canopies and reduced mineral fertilizer use without compromising yields in soda saline–alkali rice areas. | [34] |
| Cotton and barley straws | Rotary tillage | Coastal saline soil | Field study | Straw return improved P availability in the soil as evidenced by higher P apparent recovery efficiency and soil P activation coefficients. Thus, straw return reduced P fertilizer levels while maintaining high seed cotton yields. | [35] |
| Rice straw | Mulching | Mollisol with clay soil quality | Field study | Microbial network complexity was increased when large amounts of straw were returned to fields, which contributed to C and iron cycling processes to some extent. | [36] |
| Rice straw; wheat straw | Ditch-buried | Sandy loamy soil | Plot study | Ditch-buried straw return significantly increased overall functional activity (fluorescein diacetate hydrolase) and growth activity (respiration rate) in 10–20 cm and 20–30 cm soils. Additionally, β-glucosidase, lipase, acid phosphatase, and arylsulphatase activities were significantly increased in different soil layers. | [37] |
| Wheat straw; corn straw | Rotary tillage | - | Field study | Soil organic carbon (SOC), total nitrogen (TN), available K (AK), and available P (AP) contents were higher when double-season straw return was compared with single-season straw return. Copiotrophic bacteria were better represented in soils upon corn straw return, while oligotrophic groups were better represented in wheat-straw-returned soils. | [38] |
| Crops Straws | Total N, P, and K Content (g kg−1) | N (%) | P (%) | K (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rice | 28.5 | 28.77 | 4.56 | 66.67 |
| Wheat | 17.9 | 30.17 | 5.03 | 64.80 |
| Maize | 19.9 | 44.72 | 5.53 | 49.75 |
| Sorghum | 27.2 | 44.12 | 5.51 | 50.37 |
| Millet | 22.7 | 25.55 | 4.41 | 70.04 |
| Barley | 29.9 | 17.06 | 4.35 | 78.60 |
| Other cereals | 29.3 | 19.11 | 4.10 | 76.79 |
| Soybeans | 16.2 | 54.94 | 5.56 | 39.51 |
| Mung bean | 25.9 | 54.44 | 8.49 | 37.07 |
| Peas | 33.6 | 64.58 | 5.06 | 30.36 |
| Broad bean | 28.6 | 43.71 | 3.15 | 53.15 |
| Beans | 38 | 56.05 | 5.26 | 38.68 |
| Other beans | 36.3 | 57.02 | 5.51 | 37.47 |
| Sweet potato | 43.3 | 45.50 | 9.93 | 44.57 |
| Potato | 56 | 41.96 | 8.75 | 49.29 |
| Peanut | 33.5 | 48.96 | 4.48 | 46.57 |
| Rapeseed | 27.8 | 23.02 | 4.68 | 72.30 |
| Sesame | 20.5 | 52.20 | 23.41 | 24.39 |
| Flaxseed | 24 | 47.08 | 2.92 | 50.00 |
| Sunflower | 54 | 15.00 | 6.30 | 78.70 |
| Other oil crops | 31.9 | 27.27 | 5.02 | 67.71 |
| Cotton | 27 | 31.48 | 8.15 | 60.37 |
| Lint | 17.9 | 69.83 | 3.35 | 26.82 |
| Sugarcane | 21.4 | 46.73 | 6.07 | 47.20 |
| Sugarbeet | 21.4 | 46.73 | 6.07 | 47.20 |
| Tobacco | 31.1 | 41.80 | 4.82 | 53.38 |
| Leafy vegetables | 88.5 | 44.86 | 5.76 | 49.38 |
| Rhizome vegetables | 69.1 | 63.24 | 4.49 | 32.27 |
| Fruits and vegetables | 51.8 | 48.07 | 5.79 | 46.14 |
| Average of vegetables | 64.3 | 47.59 | 5.91 | 46.50 |
| Banana leaves | 66.6 | 43.39 | 3.45 | 53.15 |
| Banana fake stems | 65.5 | 17.86 | 2.29 | 79.85 |
| Pineapple leaves | 28.6 | 31.82 | 3.15 | 65.03 |
| Pineapple stems | 18.4 | 34.78 | 3.26 | 61.96 |
| Main Nutrient Elements | Forms of Existence | Release Rate |
|---|---|---|
| C | Organic | K > P > C > N |
| N | ||
| P | Inorganic P (60%) and recalcitrant organic P | |
| K | Ionic |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, H.; Li, J.; Jiao, X.; Jiang, H.; Liu, Y.; Wang, X.; Ma, C. The Fate and Challenges of the Main Nutrients in Returned Straw: A Basic Review. Agronomy 2024, 14, 698. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14040698
Li H, Li J, Jiao X, Jiang H, Liu Y, Wang X, Ma C. The Fate and Challenges of the Main Nutrients in Returned Straw: A Basic Review. Agronomy. 2024; 14(4):698. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14040698
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Huandi, Jiang Li, Xiyun Jiao, Hongzhe Jiang, Yong Liu, Xinglang Wang, and Chao Ma. 2024. "The Fate and Challenges of the Main Nutrients in Returned Straw: A Basic Review" Agronomy 14, no. 4: 698. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14040698
APA StyleLi, H., Li, J., Jiao, X., Jiang, H., Liu, Y., Wang, X., & Ma, C. (2024). The Fate and Challenges of the Main Nutrients in Returned Straw: A Basic Review. Agronomy, 14(4), 698. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14040698







