Soil Ecoenzymatic Stoichiometry Reveals Microbial Metabolic Limitations in Apple Orchards with Cover Crop and Organic Fertilizer Incorporation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Site and Treatments
2.2. Soil Sample Collection
2.3. Soil Physiochemical Analysis
2.4. Quantification of Microbial Metabolic Limitation
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Changes in Soil Physicochemical Properties
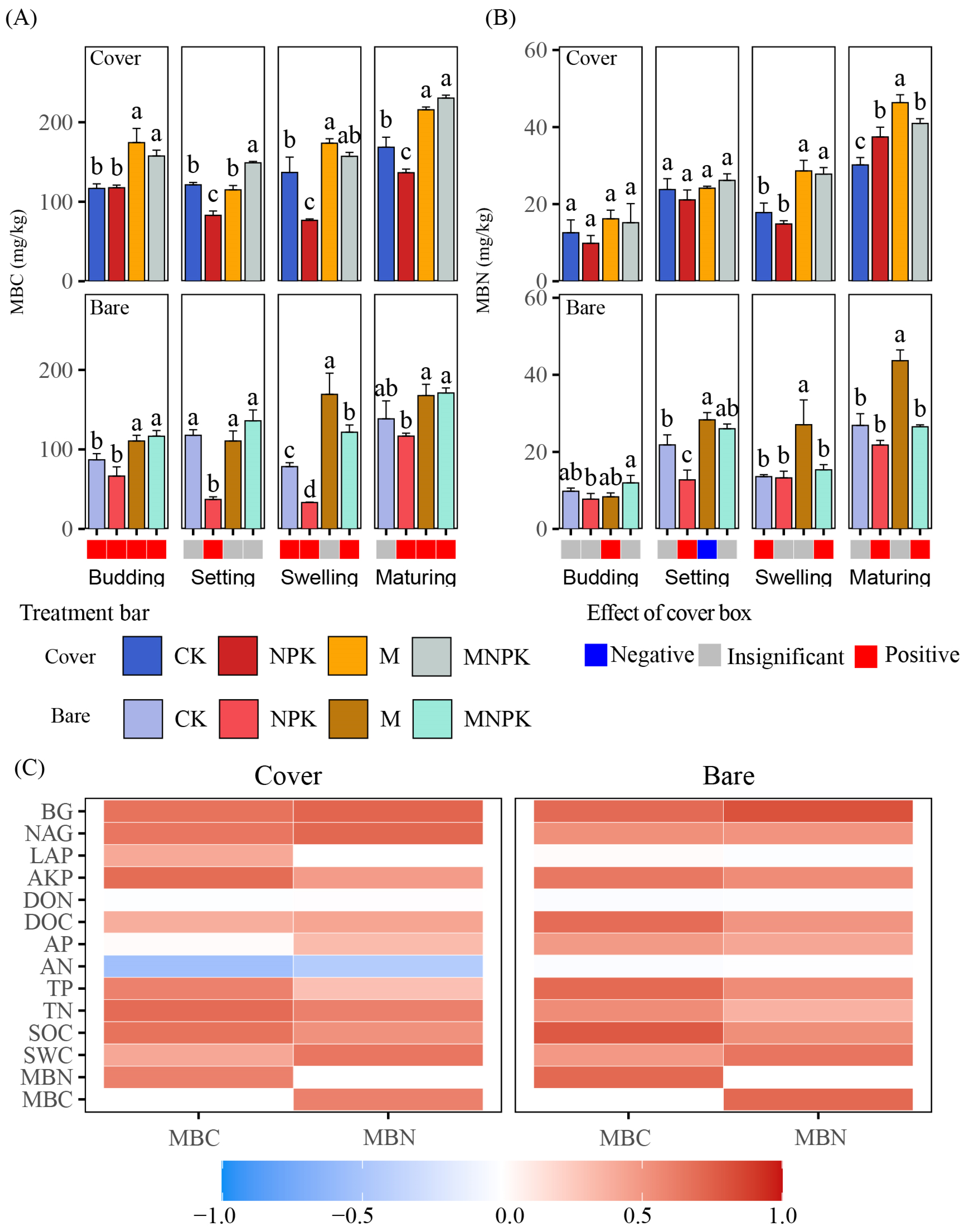
3.2. Changes in Soil Microbial Carbon and Nitrogen
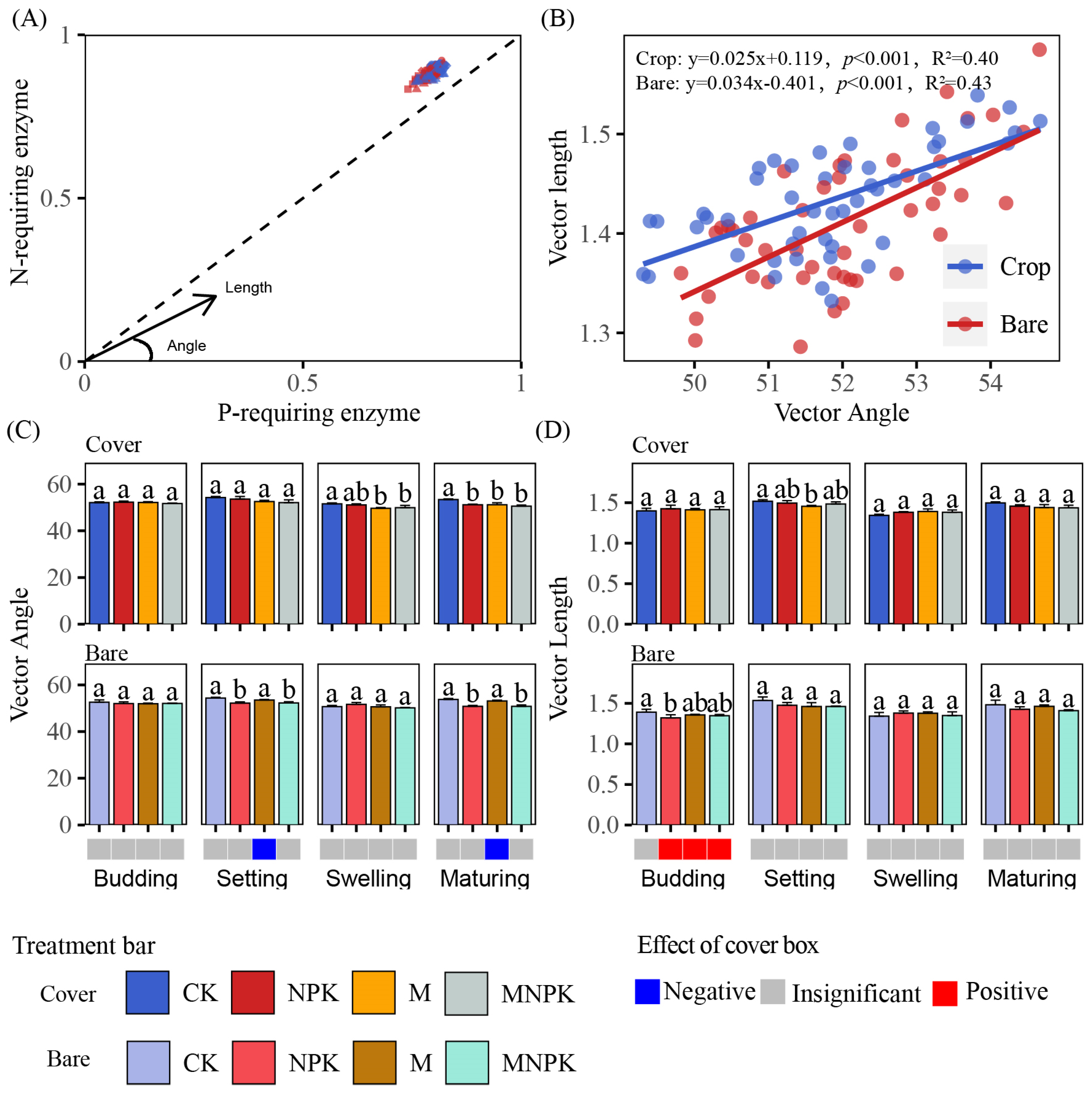
3.3. Changes in Soil Microbial Metabolic Limitations
4. Discussion
4.1. Effects of Cover Crop and Fertilizer Management on Soil Physicochemical Properties
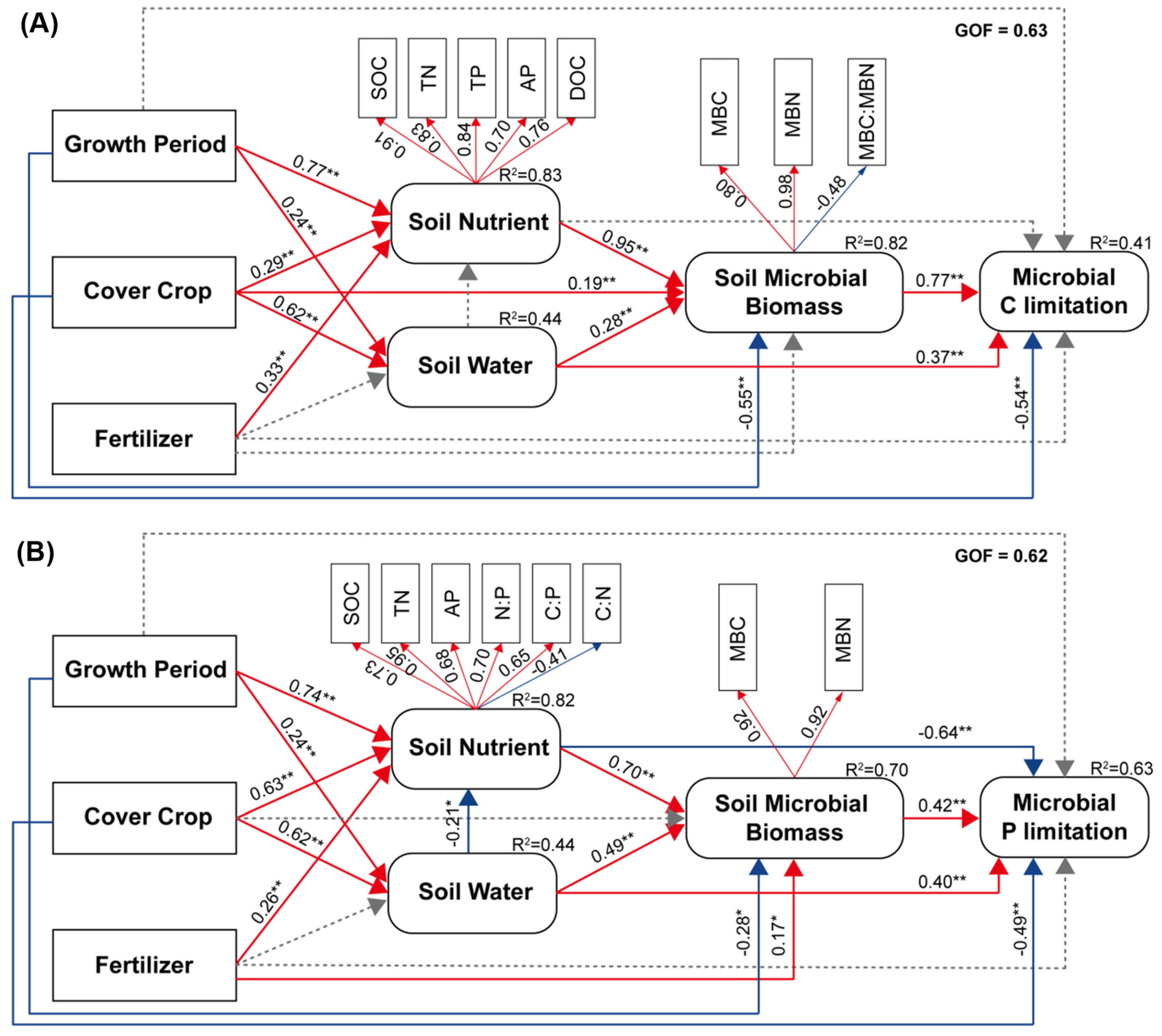
4.2. Effects of Cover Crop and Fertilizer Management on Microbial Metabolic Limitation
4.3. Mechanism of Microbial C and P Limitation Turn over in Cover Crop
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, M.; Guo, J.; Xu, C.; Lei, Y.; Li, J. Identifying Climatic Factors and Circulation Indices Related to Apple Yield Variation in Main Production Areas of China. Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 2018, 16, e00478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derpsch, R.; Franzluebbers, A.J.; Duiker, S.W.; Reicosky, D.C.; Koeller, K.; Friedrich, T.; Sturny, W.G.; Sá, J.C.M.; Weiss, K. Why Do We Need to Standardize No-Tillage Research? Soil Tillage Res. 2014, 137, 16–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mbuthia, L.W.; Acosta-Martínez, V.; DeBryun, J.; Schaeffer, S.; Tyler, D.; Odoi, E.; Mpheshea, M.; Walker, F.; Eash, N. Long Term Tillage, Cover Crop, and Fertilization Effects on Microbial Community Structure, Activity: Implications for Soil Quality. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2015, 89, 24–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Momesso, L.; Crusciol, C.A.C.; Cantarella, H.; Tanaka, K.S.; Kowalchuk, G.A.; Kuramae, E.E. Optimizing Cover Crop and Fertilizer Timing for High Maize Yield and Nitrogen Cycle Control. Geoderma 2022, 405, 115423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Freitas, P.L.; Landers, J.N. The Transformation of Agriculture in Brazil through Development and Adoption of Zero Tillage Conservation Agriculture. Int. Soil Water Conserv. Res. 2014, 2, 35–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Wang, Q.W.; Jin, Y.; Tang, J.; Lin, F.; Olatunji, O.A. Perennial Cover Crop Biomass Contributes to Regulating Soil P Availability More than Rhizosphere P-Mobilizing Capacity in Rubber-Based Agroforestry Systems. Geoderma 2021, 401, 115218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nevins, C.J.; Nakatsu, C.; Armstrong, S. Characterization of Microbial Community Response to Cover Crop Residue Decomposition. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2018, 127, 39–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lange, M.; Habekost, M.; Eisenhauer, N.; Roscher, C.; Bessler, H.; Engels, C.; Oelmann, Y.; Scheu, S.; Wilcke, W.; Schulze, E.-D.; et al. Biotic and Abiotic Properties Mediating Plant Diversity Effects on Soil Microbial Communities in an Experimental Grassland. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e96182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzola, M.; Hewavitharana, S.S.; Strauss, S.L. Brassica Seed Meal Soil Amendments Transform the Rhizosphere Microbiome and Improve Apple Production through Resistance to Pathogen Reinfestation. Phytopathology 2015, 105, 460–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fanin, N.; Fromin, N.; Bertrand, I. Functional Breadth and Home-Field Advantage Generate Functional Differences among Soil Microbial Decomposers. Ecology 2016, 97, 1023–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeLonge, M.S.; Miles, A.; Carlisle, L. Investing in the Transition to Sustainable Agriculture. Environ. Sci. Policy 2016, 55, 266–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comberti, C.; Thornton, T.F.; Wyllie de Echeverria, V.; Patterson, T. Ecosystem Services or Services to Ecosystems? Valuing Cultivation and Reciprocal Relationships between Humans and Ecosystems. Glob. Environ. Change 2015, 34, 247–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.; Fang, L.; Guo, X.; Wang, X.; Wang, Y.; Li, P.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, X. Responses of Soil Microbial Communities to Nutrient Limitation in the Desert-Grassland Ecological Transition Zone. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 642, 45–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, D.L.; Kielland, K.; Sinclair, F.L.; Dahlgren, R.A.; Newsham, K.K.; Farrar, J.F.; Murphy, D.V. Soil Organic Nitrogen Mineralization across a Global Latitudinal Gradient. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 2009, 23, GS1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burns, R.G.; DeForest, J.L.; Marxsen, J.; Sinsabaugh, R.L.; Stromberger, M.E.; Wallenstein, M.D.; Weintraub, M.N.; Zoppini, A. Soil Enzymes in a Changing Environment: Current Knowledge and Future Directions. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2013, 58, 216–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cenini, V.L.; Fornara, D.A.; McMullan, G.; Ternan, N.; Carolan, R.; Crawley, M.J.; Clément, J.C.; Lavorel, S. Linkages between Extracellular Enzyme Activities and the Carbon and Nitrogen Content of Grassland Soils. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2016, 96, 198–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinsabaugh, R.L.; Shah, J.J.F. Ecoenzymatic Stoichiometry and Ecological Theory. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Evol. Syst. 2012, 43, 313–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moorhead, D.L.; Sinsabaugh, R.L.; Hill, B.H.; Weintraub, M.N. Vector Analysis of Ecoenzyme Activities Reveal Constraints on Coupled C, N and P Dynamics. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2016, 93, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, W. Study on the Effects and Mechanisms of Different Fertilization Methods on Apple Yield and Quality and Water and Fertilizer Use Efficiency under Grass Coverage. Ph.D. Thesis, Northwest A&F University, Xianyang, China, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- He, L.; Lu, S.; Wang, C.; Mu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, X. Changes in Soil Organic Carbon Fractions and Enzyme Activities in Response to Tillage Practices in the Loess Plateau of China. Soil Tillage Res. 2021, 209, 104940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nevins, C.J.; Lacey, C.; Armstrong, S. The Synchrony of Cover Crop Decomposition, Enzyme Activity, and Nitrogen Availability in a Corn Agroecosystem in the Midwest United States. Soil Tillage Res. 2020, 197, 104518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, W.; Zhao, Z.; Lv, F.; Wang, R.; Gong, Q.; Zhai, B.; Wang, Z.; Zhao, Z.; Li, Z. Metagenomic Exploration of the Interactions between N and P Cycling and SOM Turnover in an Apple Orchard with a Cover Crop Fertilized for 9 Years. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2019, 55, 365–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bremner, J.M. Nitrogen-Total. In Methods of Soil Analysis; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1996; pp. 1085–1121. ISBN 978-0-89118-866-7. [Google Scholar]
- Olsen, S.R. Sommers Methods of Soil Analysis: Chemical and Microbiological Properties; American Society of Agronomy: Madison, WI, USA, 1982; ISBN 978-0-89118-072-2. [Google Scholar]
- Jones, D.L.; Willett, V.B. Experimental Evaluation of Methods to Quantify Dissolved Organic Nitrogen (DON) and Dissolved Organic Carbon (DOC) in Soil. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2006, 38, 991–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, F.; Zheng, W.; Zhai, B.; Li, Z. Cover Cropping and Chemical Fertilizer Seasonally Mediate Microbial Carbon and Phosphorus Metabolisms in an Apple Orchard: Evidence from the Enzymatic Stoichiometry Method. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2022, 178, 104579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinsabaugh, R.L.; Hill, B.H.; Follstad Shah, J.J. Ecoenzymatic Stoichiometry of Microbial Organic Nutrient Acquisition in Soil and Sediment. Nature 2009, 462, 795–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Liang, C.; Wang, Y.; Cheng, H.; An, S.; Chang, S.X. Soil Extracellular Enzyme Stoichiometry Reflects the Shift from P- to N-Limitation of Microorganisms with Grassland Restoration. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2020, 149, 107928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, A.; Zheng, Z.X.; Zhao, Z.Y.; Feng, T.Y.; Zheng, W.; Zhai, B.N. Effects of Long-term Combined Application of Organic and Inorganic Fertilizers on Soil Carbon Pool and Greenhouse Gas Emissions in Orchards. Huan Jing Ke Xue 2023, 44, 5823–5831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, R.; Dorodnikov, M.; Yang, S.; Zhang, Y.; Filley, T.R.; Turco, R.F.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, Z.; Li, H.; Jiang, Y. Responses of Enzymatic Activities within Soil Aggregates to 9-Year Nitrogen and Water Addition in a Semi-Arid Grassland. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2015, 81, 159–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Dong, L.; Liu, Y.; Wu, J.; Wang, J.; Shangguan, Z.; Deng, L. Soil Organic Carbon Variation Determined by Biogeographic Patterns of Microbial Carbon and Nutrient Limitations across a 3000-Km Humidity Gradient in China. Catena 2022, 209, 105849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, S.; Bai, G.; Yu, J. Soil Properties and Apricot Growth under Intercropping and Mulching with Erect Milk Vetch in the Loess Hilly-Gully Region. Plant Soil 2015, 390, 431–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Ghahramani, A.; Ali, A.; Erbacher, A. Cover Cropping Impacts on Soil Water and Carbon in Dryland Cropping System. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0286748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-García, L.B.; Korthals, G.; Brussaard, L.; Jørgensen, H.B.; De Deyn, G.B. Organic Management and Cover Crop Species Steer Soil Microbial Community Structure and Functionality along with Soil Organic Matter Properties. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2018, 263, 7–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sterner, R.W.; Elser, J.J. Ecological Stoichiometry: The Biology of Elements from Molecules to the Biosphere. In Ecological Stoichiometry; Princeton University Press: Princeton, NJ, USA, 2017; ISBN 978-1-4008-8569-5. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; Zhang, Y.Y.; Yang, S.; Wang, Z.; Feng, X.; Liu, H.; Jiang, Y. Variations in Soil Bacterial Taxonomic Profiles and Putative Functions in Response to Straw Incorporation Combined with N Fertilization during the Maize Growing Season. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2019, 283, 106578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Duan, C.; Wang, X.; Zhang, X.; Ju, W.; Chen, H.; Yue, S.; Wang, Y.; Li, S.; et al. Ecoenzymatic Stoichiometry Reveals Microbial Phosphorus Limitation Decreases the Nitrogen Cycling Potential of Soils in Semi-Arid Agricultural Ecosystems. Soil Tillage Res. 2020, 197, 104463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Li, D.; Xiao, K.; Wang, K. Soil Microbial Processes and Resource Limitation in Karst and Non-Karst Forests. Funct. Ecol. 2018, 32, 1400–1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.; Fang, L.; Deng, L.; Guo, X.; Han, F.; Ju, W.; Wang, X.; Chen, H.; Tan, W.; Zhang, X. Patterns of Soil Microbial Nutrient Limitations and Their Roles in the Variation of Soil Organic Carbon across a Precipitation Gradient in an Arid and Semi-Arid Region. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 658, 1440–1451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Cui, Y.; Wang, Y.; Duan, C.; Niu, Y.; Sun, R.; Shen, Y.; Guo, X.; Fang, L. Ecoenzymatic Stoichiometry Reveals Phosphorus Addition Alleviates Microbial Nutrient Limitation and Promotes Soil Carbon Sequestration in Agricultural Ecosystems. J. Soils Sediments 2022, 22, 536–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ladwig, L.M.; Sinsabaugh, R.L.; Collins, S.L.; Thomey, M.L. Soil Enzyme Responses to Varying Rainfall Regimes in Chihuahuan Desert Soils. Ecosphere 2015, 6, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tapia-Torres, Y.; Elser, J.J.; Souza, V.; García-Oliva, F. Ecoenzymatic Stoichiometry at the Extremes: How Microbes Cope in an Ultra-Oligotrophic Desert Soil. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2015, 87, 34–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, V.; Eriksen, J.; Jensen, L.S.; Thorup-Kristensen, K.; Magid, J. Towards Integrated Cover Crop Management: N, P and S Release from Aboveground and Belowground Residues. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2021, 313, 107392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, L.; Peng, C.; Huang, C.; Wang, K.; Liu, Q.; Liu, Y.; Hai, X.; Shangguan, Z. Drivers of Soil Microbial Metabolic Limitation Changes along a Vegetation Restoration Gradient on the Loess Plateau, China. Geoderma 2019, 353, 188–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwabiah, A.B.; Palm, C.A.; Stoskopf, N.C.; Voroney, R.P. Response of Soil Microbial Biomass Dynamics to Quality of Plant Materials with Emphasis on P Availability. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2003, 35, 207–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Ma, Y.; Zhang, A.; Chen, Y.; Zheng, Z.; Zheng, W.; Zhai, B. Response of Apple Orchard Bacteria Co-Occurrence Network Pattern to Long-Term Organic Fertilizer Input. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2023, 191, 105035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, C.; Zhao, F.; Kang, D.; Yang, G.; Han, X.; Tong, X.; Feng, Y.; Ren, G. Linkages of C:N:P Stoichiometry and Bacterial Community in Soil Following Afforestation of Former Farmland. For. Ecol. Manag. 2016, 376, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, L.; Chen, H.; Wang, Y.; Mao, Q.; Zheng, M.; Su, Y.; Xiao, K.; Wang, K.; Li, D. Responses of Soil Microbial Resource Limitation to Multiple Fertilization Strategies. Soil Tillage Res. 2020, 196, 104474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Treatment | Fertilizer (F) | Cover Crop (C) | Growth Period (G) | F×C | F×G | C×G | F×C×G |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| df | 3 | 1 | 3 | 3 | 9 | 3 | 9 |
| SOC (g·kg−1) | 72.31 *** | 27.06 *** | 7.50 *** | 1.53 *** | 3.24 *** | 0.95 ** | 1.59 *** |
| TN (g·kg−1) | 0.66 *** | 0.41 *** | 0.39 *** | 0.06 *** | 0.04 *** | 0.03 *** | 0.02 *** |
| TP (g·kg−1) | 0.19 *** | 0.13 *** | 0.01 | 0.01 * | 0.01 ** | 0.01 ** | 0.01 |
| DOC (mg·kg−1) | 1254.31 *** | 124.97 *** | 546.14 *** | 32.28 *** | 90.72 *** | 49.28 *** | 16.26 *** |
| DON (mg·kg−1) | 3894.2 *** | 3.5 | 2618.5 *** | 3.9 | 904.6 *** | 86.3 *** | 25.0 *** |
| AN (mg·kg−1) | 2113.92 *** | 855.99 *** | 2239.46 *** | 58.60 *** | 418.01 *** | 554.30 *** | 69.83 *** |
| AP (mg·kg−1) | 1270.76 *** | 472.15 *** | 371.16 *** | 106.50 *** | 75.59 *** | 40.36 *** | 19.21 *** |
| DOC:DON | 31.68 *** | 0.06 | 16.27 *** | 1.44 *** | 8.79 *** | 6.40 *** | 1.94 *** |
| C:N | 6.26 *** | 0.62 | 14.17 *** | 0.96 | 4.75 *** | 3.90 *** | 3.51 *** |
| C:P | 10.29 *** | 0.01 | 4.42 *** | 3.41 ** | 2.39 ** | 2.47 * | 1.03 |
| N:P | 0.13 *** | 0.02 | 0.52 *** | 0.12 *** | 0.13 *** | 0.19 *** | 0.08 *** |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cai, S.; Zheng, B.; Zhao, Z.; Zheng, Z.; Yang, N.; Zhai, B. Soil Ecoenzymatic Stoichiometry Reveals Microbial Metabolic Limitations in Apple Orchards with Cover Crop and Organic Fertilizer Incorporation. Agronomy 2024, 14, 581. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14030581
Cai S, Zheng B, Zhao Z, Zheng Z, Yang N, Zhai B. Soil Ecoenzymatic Stoichiometry Reveals Microbial Metabolic Limitations in Apple Orchards with Cover Crop and Organic Fertilizer Incorporation. Agronomy. 2024; 14(3):581. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14030581
Chicago/Turabian StyleCai, Shibiao, Bangyu Zheng, Zhiyuan Zhao, Zhaoxia Zheng, Na Yang, and Bingnian Zhai. 2024. "Soil Ecoenzymatic Stoichiometry Reveals Microbial Metabolic Limitations in Apple Orchards with Cover Crop and Organic Fertilizer Incorporation" Agronomy 14, no. 3: 581. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14030581
APA StyleCai, S., Zheng, B., Zhao, Z., Zheng, Z., Yang, N., & Zhai, B. (2024). Soil Ecoenzymatic Stoichiometry Reveals Microbial Metabolic Limitations in Apple Orchards with Cover Crop and Organic Fertilizer Incorporation. Agronomy, 14(3), 581. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14030581







