Strategies for Regulating the Bioavailability and Mobility of Se and Cd in Cd-Contaminated Seleniferous Soils: Coupling the Bioavailable Se:Cd Molar Ratio with Soil Properties
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
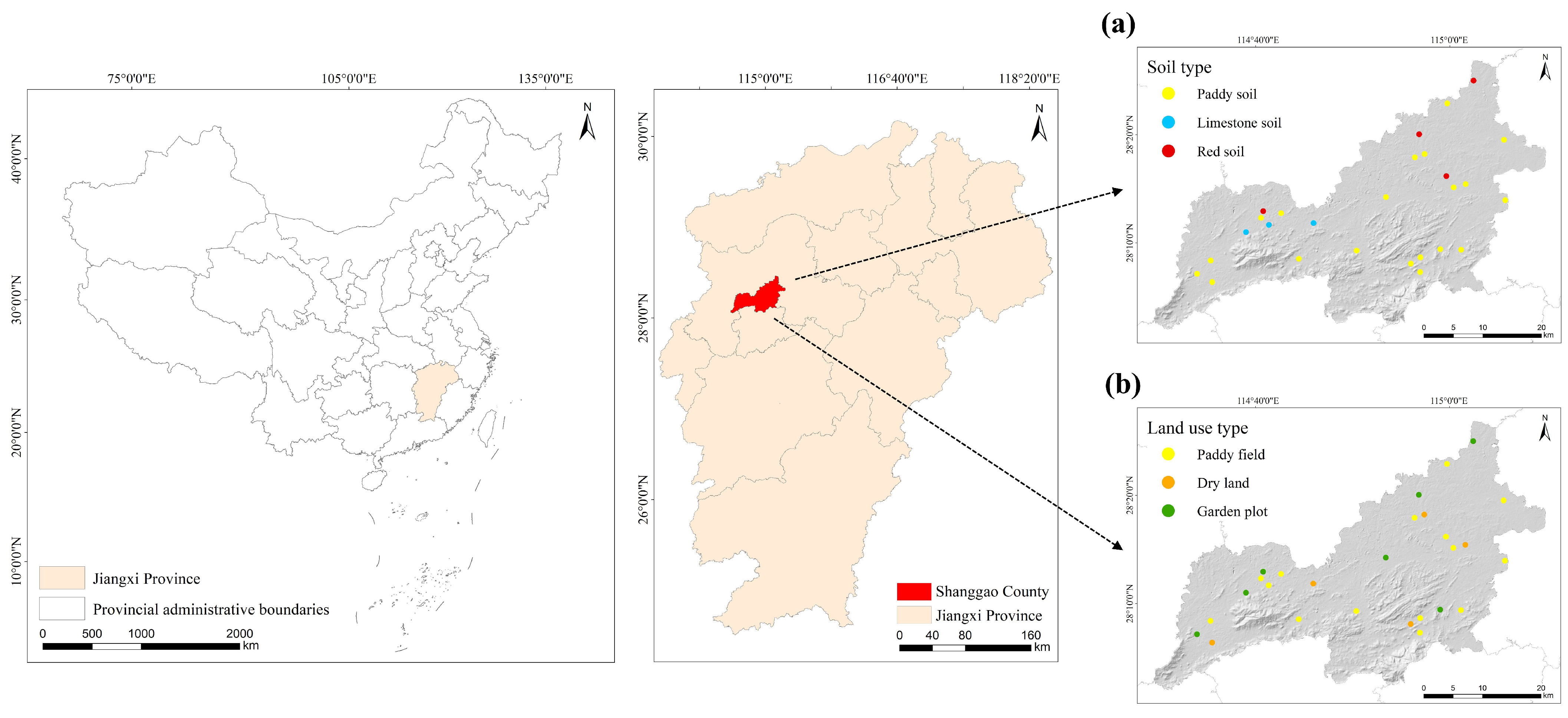
2.1. Overview of the Study Area
2.2. Sample Collection and Processing
2.3. Analysis and Test
2.4. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Physico-Chemical Properties of Soils in the Study Area
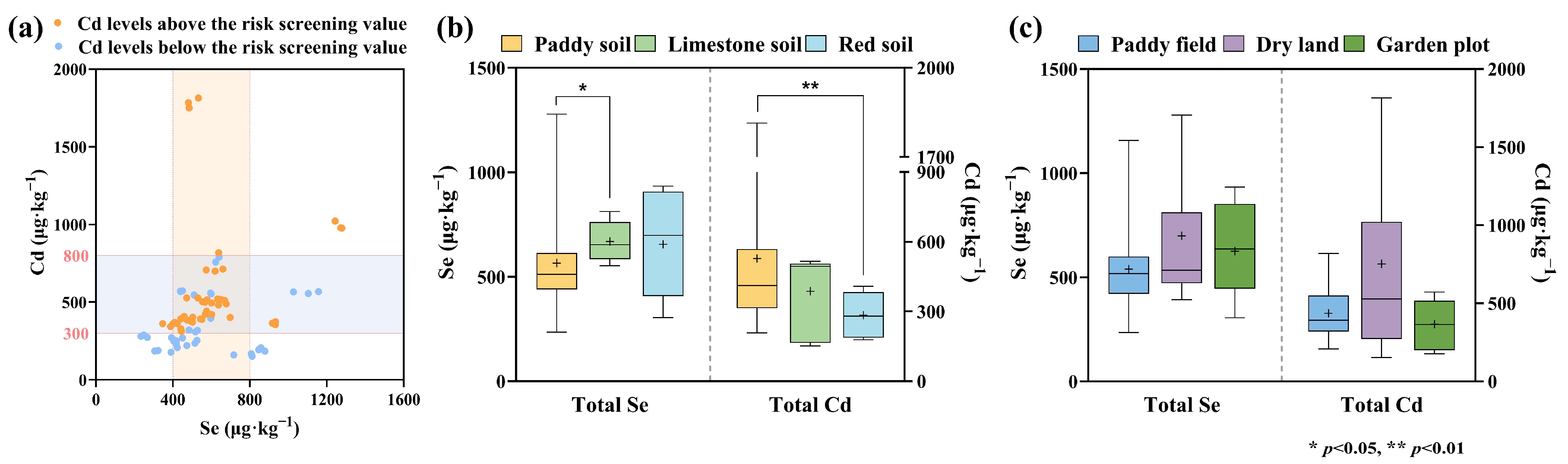
3.2. Characteristics of Total Se and Cd Distribution in the Study Area
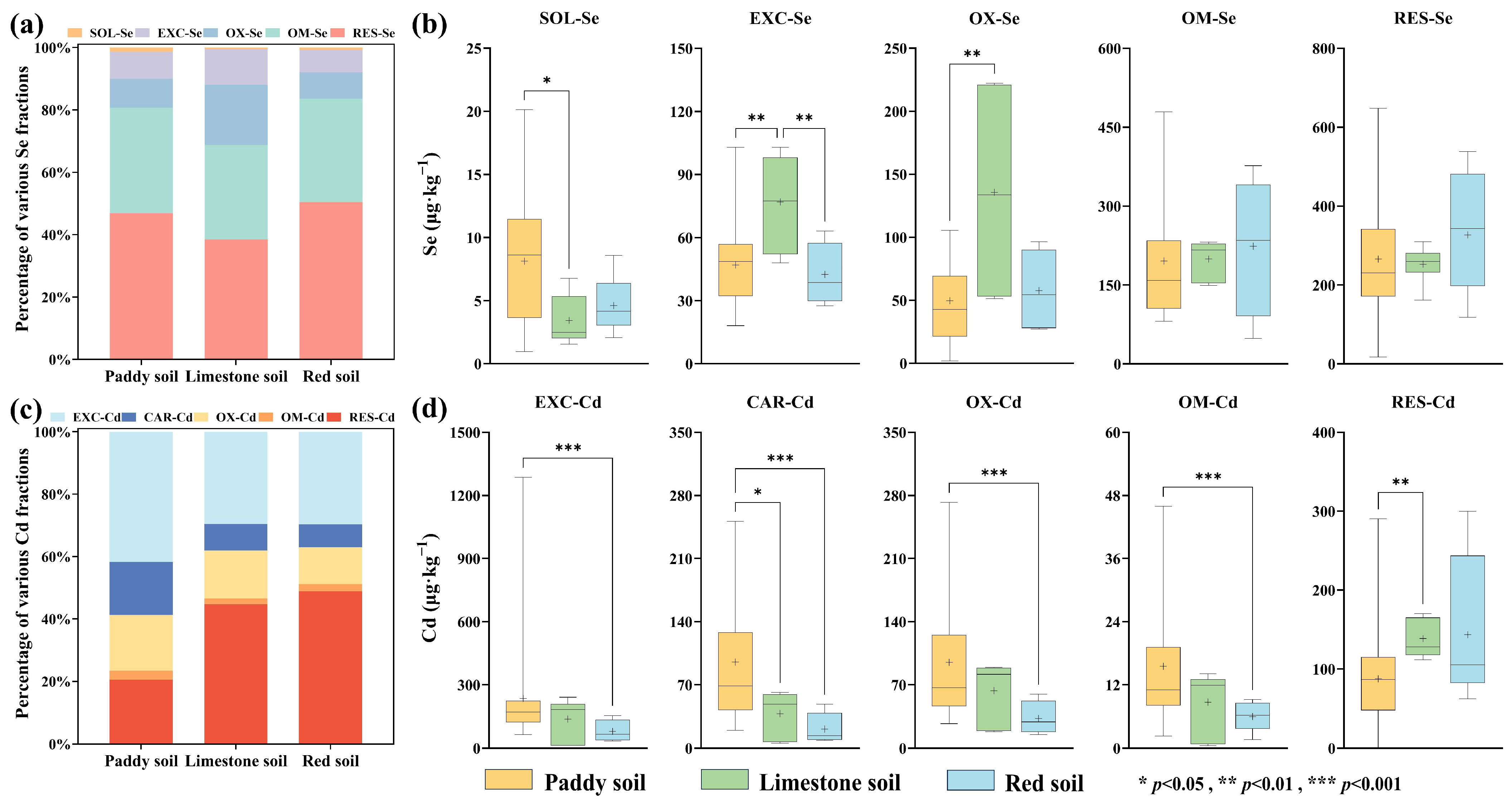
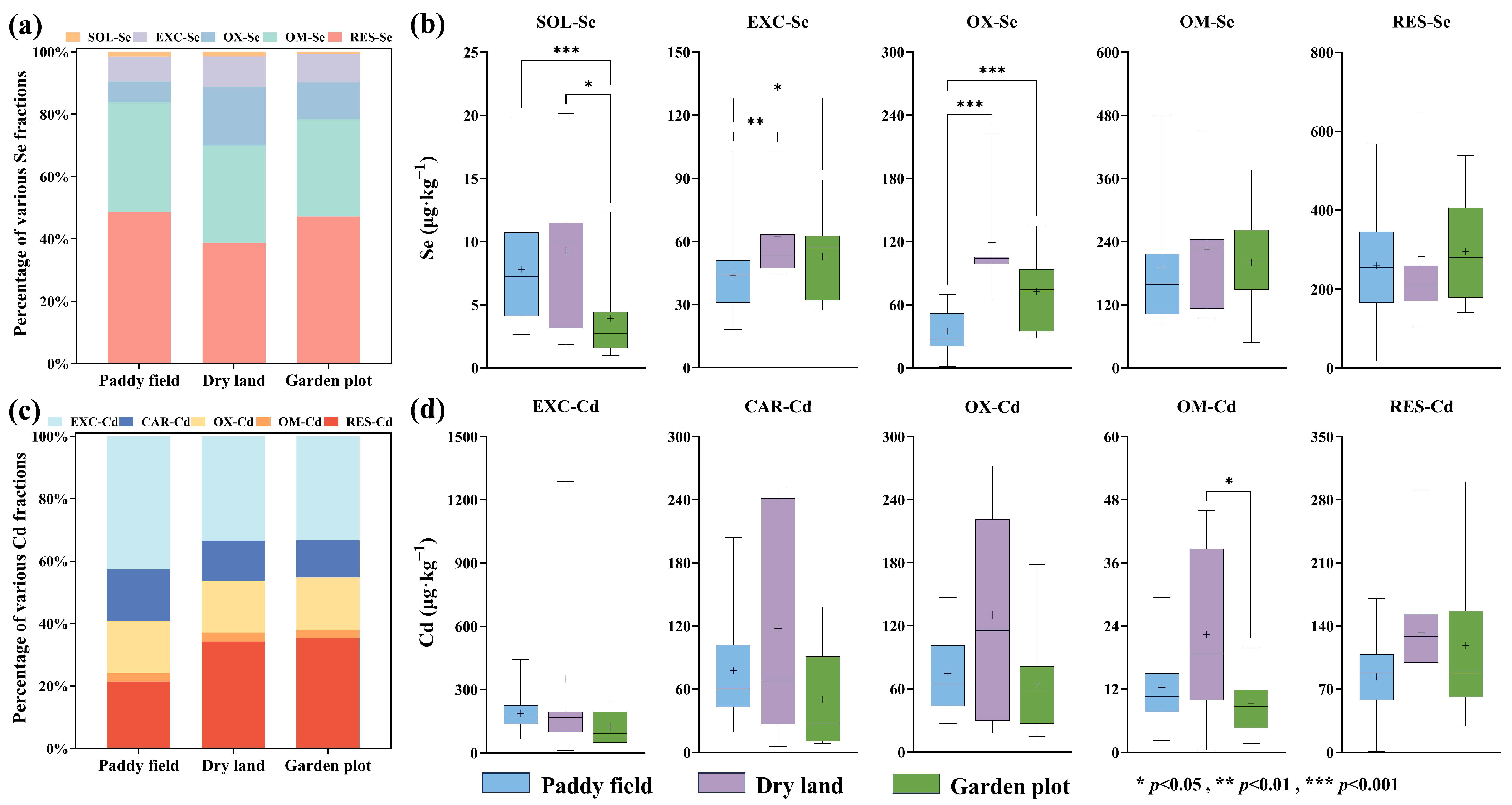
3.3. Characteristics of Distribution of Different Fractions of Se and Cd in Soils
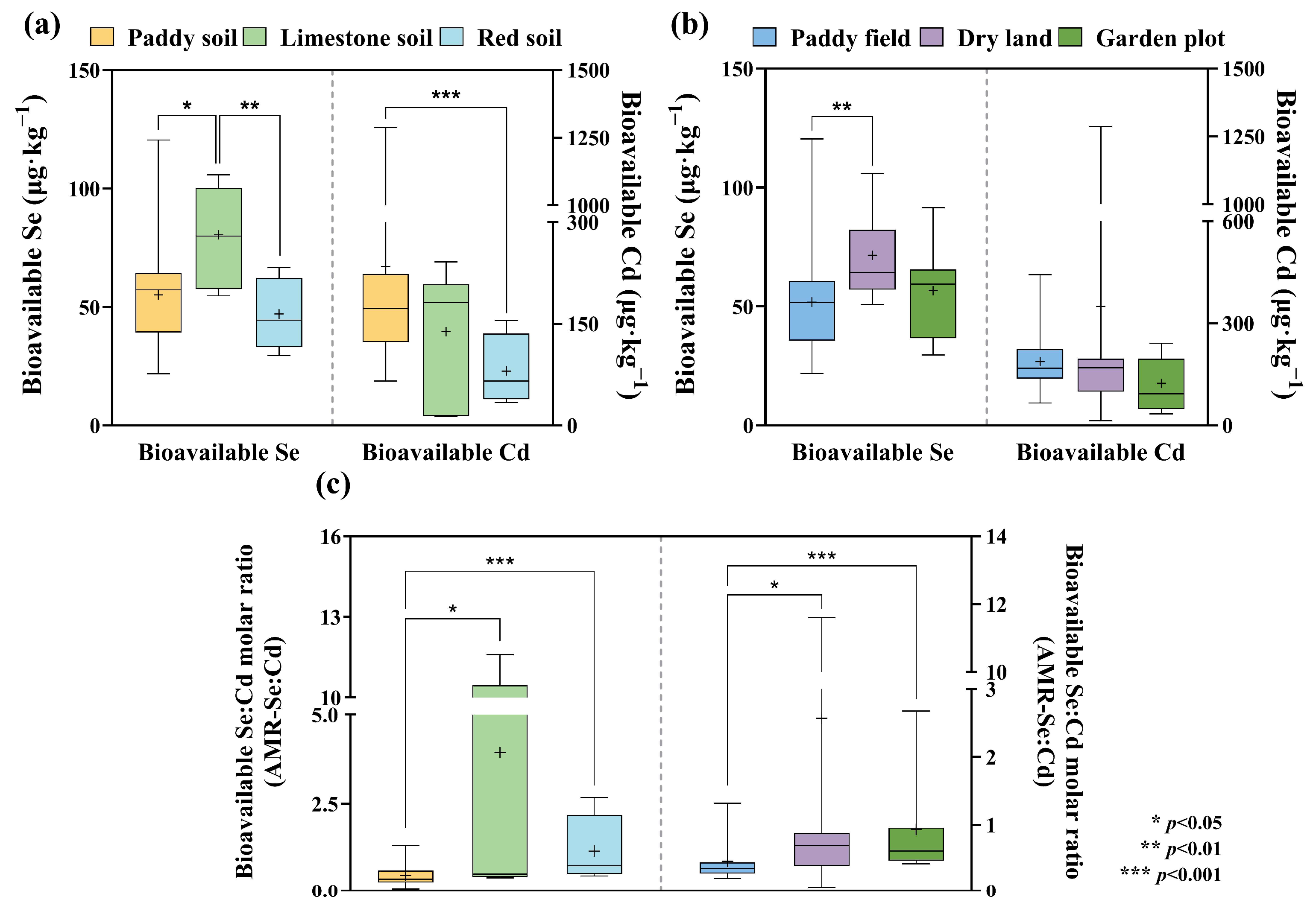
3.4. Characteristics of the Distribution of Bioavailable Se, Cd, and AMR-Se:Cd in Soils
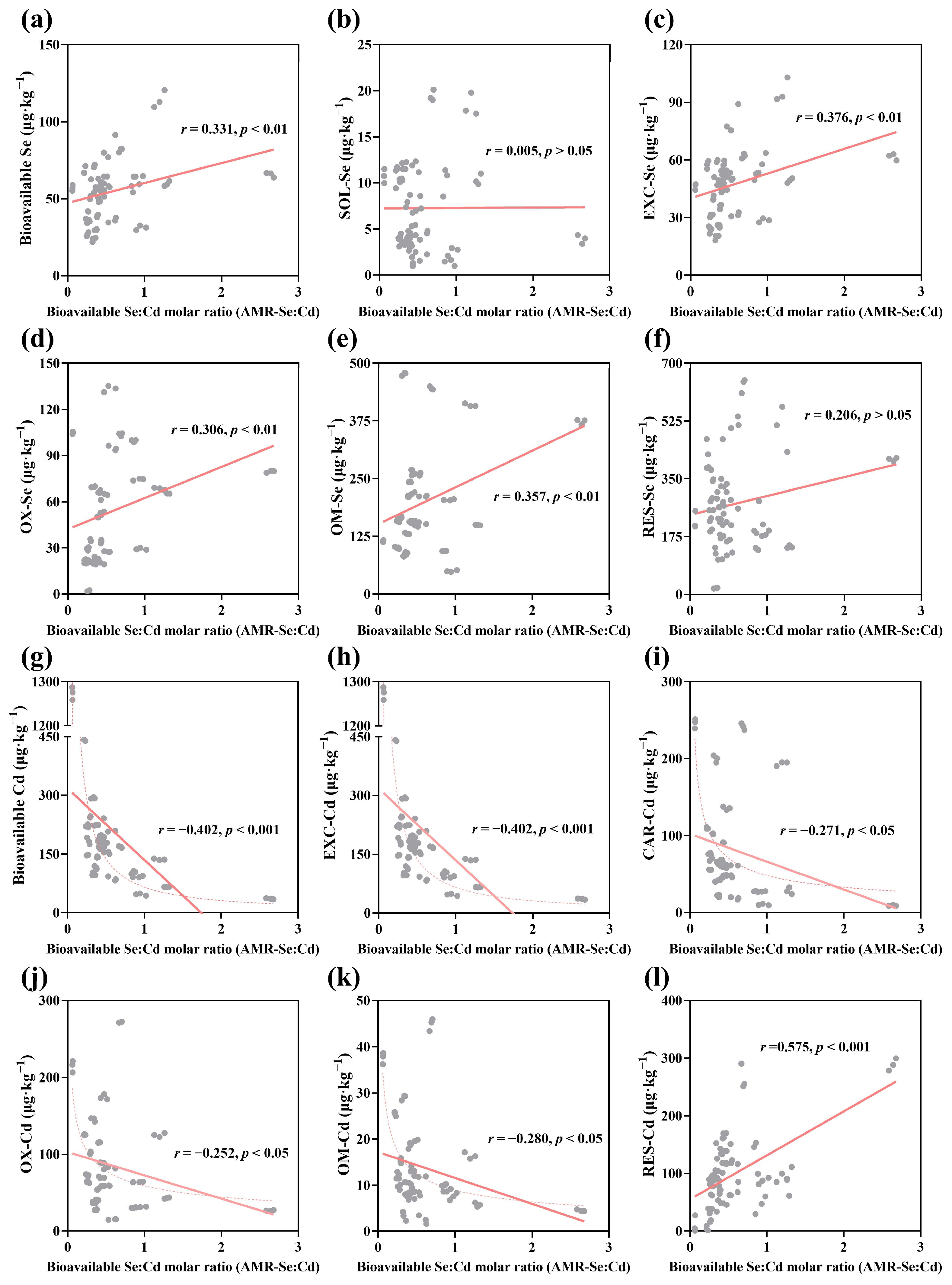
3.5. Relationship Between Soil AMR-Se:Cd and the Distribution of Se and Cd Fractions
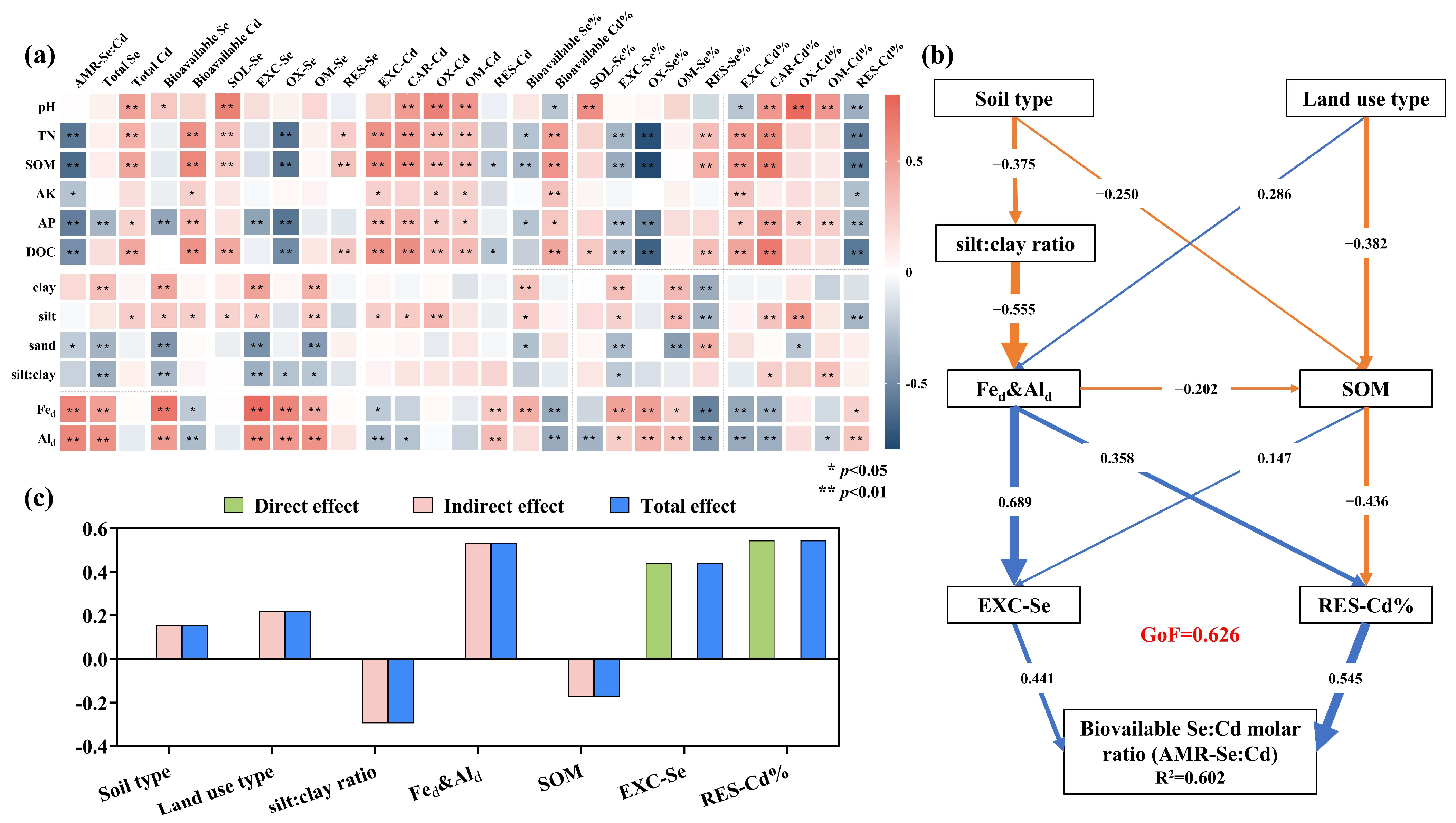
3.6. Influencing Factors of the Soil AMR-Se:Cd
4. Discussion
4.1. Effects of Different Soil Types and Land Use Types on the Distribution of Se and Cd
4.2. Relationship Between Soil AMR-Se:Cd and Se and Cd Transformation
4.3. Effects of Soil Properties on the AMR-Se:Cd
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dinh, Q.T.; Cui, Z.; Huang, J.; Tran, T.A.T.; Wang, D.; Yang, W.; Zhou, F.; Wang, M.; Yu, D.; Liang, D. Selenium Distribution in the Chinese Environment and Its Relationship with Human Health: A Review. Environ. Int. 2018, 112, 294–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, H.; Yang, X.; Ning, Z.; Kwon, S.Y.; Li, M.-L.; Tack, F.M.G.; Kwon, E.E.; Rinklebe, J.; Yin, R. The Beneficial and Hazardous Effects of Selenium on the Health of the Soil-Plant-Human System: An Overview. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 422, 126876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lyu, C.; Qin, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Liu, X. Characteristics of Selenium Enrichment and Assessment of Selenium Bioavailability Using the Diffusive Gradients in Thin-Films Technique in Seleniferous Soils in Enshi, Central China. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 273, 116507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.; Cui, Z.; Xue, M.; Peng, Q.; Zhou, F.; Wang, D.; Dinh, Q.T.; Liu, Y.; Liang, D. Assessing the Uptake of Selenium from Naturally Enriched Soils by Maize (Zea mays L.) Using Diffusive Gradients in Thin-Films Technique (DGT) and Traditional Extractions. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 689, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.; Rong, Q.; Guo, X.; Guo, J.; Chen, Y.; Chang, Y.; Chen, J.; Zhang, Q.; Zhou, C.; Cai, H.; et al. Land-Use Types Regulate Se:Cd Ratios of Natural Seleniferous Soil Derived from Different Parent Materials in Subtropical Hilly Areas. Forests 2023, 14, 656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Luo, K.; Ni, R.; Hussain, R. Selenium and Hazardous Elements Distribution in Plant–Soil–Water System and Human Health Risk Assessment of Lower Cambrian, Southern Shaanxi, China. Environ. Geochem. Health 2018, 40, 2049–2069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, R.; He, Y.; Luo, L.; Zhu, M.; Zan, S.; Guo, F.; Wang, B.; Yang, B. The Interaction between Selenium and Cadmium in the Soil-Rice-Human Continuum in an Area with High Geological Background of Selenium and Cadmium. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 222, 112516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Z.; Cai, S.; Yan, C.; Rao, S.; Cheng, S.; Xu, F.; Liu, X. Research Progress on the Physiological Mechanism by Which Selenium Alleviates Heavy Metal Stress in Plants: A Review. Agronomy 2024, 14, 1787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Mao, K.; Cao, H.; Ali, W.; Lei, D.; Teng, D.; Chang, C.; Yang, X.; Yang, Q.; Niazi, N.K.; et al. Exogenous Selenium (Cadmium) Inhibits the Absorption and Transportation of Cadmium (Selenium) in Rice. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 268, 115829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Li, R.; Lu, Y.; Bai, Z. Sustainable Management of Cadmium-Contaminated Soils as Affected by Exogenous Application of Nutrients: A Review. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 295, 113081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Yuan, L.; Qi, S.; Yin, X. The Threshold Effect between the Soil Bioavailable Molar Se:Cd Ratio and the Accumulation of Cd in Corn (Zea mays L.) from Natural Se-Cd Rich Soils. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 688, 1228–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Guan, D.-X.; Jiang, Y.-F.; Menezes-Blackburn, D.; Yu, T.; Yang, Z.; Ma, L.Q. Insight into the Availability and Desorption Kinetics of Se and Cd in Naturally-Rich Soils Using Diffusive Gradients in Thin-Films Technique. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 465, 133330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, K.; Tang, J.; Chen, H.; Li, D.; Liu, Y. Impact of Land Use/Land Cover Change on the Topsoil Selenium Concentration and Its Potential Bioavailability in a Karst Area of Southwest China. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 708, 135201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eger, A.; Koele, N.; Caspari, T.; Poggio, M.; Kumar, K.; Burge, O.R. Quantifying the Importance of Soil-Forming Factors Using Multivariate Soil Data at Landscape Scale. J. Geophys. Res. Earth Surf. 2021, 126, e2021JF006198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Zhang, N.; Li, Y.; Zhao, H.; Zhou, F.; Xue, M.; Lyu, L.; Yang, J.; Man, Y.B.; Wu, F.; et al. Differences in Selenium Concentration and Bioavailability between Paddy and Dryland Soils of China: A Study Based on Literature Collection and Field Sampling. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 445, 130467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Li, Y.; Li, H.; Wang, L.; Liao, X.; Wang, J.; Kong, C. Effects of Topography and Soil Properties on Soil Selenium Distribution and Bioavailability (Phosphate Extraction): A Case Study in Yongjia County, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 633, 240–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, F.; Wu, Y.; Islam, M.; Jiang, X.; Wang, B.; He, S.; Lin, X.; Sun, Y.; Chen, G.; Chen, X.; et al. Selenium Levels in Soil and Tea as Affected by Soil Properties in Jiangxi Province, China. BMC Plant Biol. 2024, 24, 1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, J.; Zhu, W.; Wang, W.; Li, R.; Hou, S.; Wang, D.; Yang, L. Selenium in Soil and Endemic Diseases in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2002, 284, 227–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB/T 17296-2009; Classification and Codes for Chinese Soil. General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of China, and Standardization Administration of China: Beijing, China, 2009; pp. 2–112.
- Lu, R.-K. Soil and Agro-Chemistry Analytical Methods; Agriculture Science and Technology Press of China: Beijing, China, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Meng, Q.; Diao, T.; Yan, L.; Sun, Y. Effects of Single and Combined Contamination of Microplastics and Cadmium on Soil Organic Carbon and Microbial Community Structural: A Comparison with Different Types of Soil. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2023, 183, 104763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zhao, Z.; Duan, B.; Hu, C.; Zhao, X.; Guo, Z. Effect of Applied Sulphur on the Uptake by Wheat of Selenium Applied as Selenite. Plant Soil 2015, 386, 35–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tessier, A.; Campbell, P.G.C.; Bisson, M. Sequential Extraction Procedure for the Speciation of Particulate Trace Metals. Anal. Chem. 1979, 51, 844–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, C.; Chen, J.; Li, L.; Zhao, Z.; Liu, X. Characteristics of Se in Water-Soil-Plant System and Threshold of Soil Se in Seleniferous Areas in Enshi, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 827, 154372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lyu, C.; Qin, Y.; Chen, T.; Zhao, Z.; Liu, X. Microbial Induced Carbonate Precipitation Contributes to the Fates of Cd and Se in Cd-Contaminated Seleniferous Soils. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 423, 126977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Q.; Di, X.; Liu, Z.; Zhao, L.; Liang, X.; Sun, Y.; Qin, X.; Xu, Y. Mercapto-Palygorskite Efficiently Immobilizes Cadmium in Alkaline Soil and Reduces Its Accumulation in Wheat Plants: A Field Study. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2023, 266, 115559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, Z.; Li, Y.; Zhao, R.; Yang, Y.; Cai, Y.; Lu, H. Co-Enrichment of Selenium and Cadmium in Soils of Southern China and Its Implication for the Safe Utilisation of Selenium-Rich Lands. J. Geochem. Explor. 2024, 262, 107487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB 15618-2018; Soil Environmental Quality Risk Control Standard for Soil Contamination of Agricultural Land. Ministry of Ecology and Environment of China, and State Administration for Market Regulation of China: Beijing, China, 2018; p. 2.
- Huang, F.; Chen, L.; Zhou, Y.; Huang, J.; Wu, F.; Hu, Q.; Chang, N.; Qiu, T.; Zeng, Y.; He, H.; et al. Exogenous Selenium Promotes Cadmium Reduction and Selenium Enrichment in Rice: Evidence, Mechanisms, and Perspectives. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 476, 135043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, J.; Yang, J.; Wu, H.; Gao, J.; Tang, S.; Ma, S. Spatial Distribution and Environmental Impact Factors of Soil Selenium in Hainan Island, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 811, 151329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Ge, T.; Zhu, Z.; Liu, S.; Luo, Y.; Li, Y.; Wang, P.; Gavrichkova, O.; Xu, X.; Wang, J.; et al. Carbon Input and Allocation by Rice into Paddy Soils: A Review. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2019, 133, 97–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabos, M.B.; Alleoni, L.R.F.; Abreu, C.A. Background Levels of Selenium in Some Selected Brazilian Tropical Soils. J. Geochem. Explor. 2014, 145, 35–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Peng, Q.; Liang, D.; Liang, S.; Chen, J.; Sun, H.; Li, S.; Lei, P. Effects of Aging on the Fraction Distribution and Bioavailability of Selenium in Three Different Soils. Chemosphere 2016, 144, 2351–2359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Shi, Y.; Yang, X.; Zhou, W.; Li, Y.; Liu, C. Influence of Fe(II) on the Se(IV) Sorption under Oxic/Anoxic Conditions Using Bentonite. Chemosphere 2018, 193, 376–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, D.; Rensing, C.; Zheng, S. Microbial Reduction and Resistance to Selenium: Mechanisms, Applications and Prospects. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 421, 126684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, J.; Huang, X.; Jiang, D. Phosphorus Can Effectively Reduce Selenium Adsorption in Selenium-Rich Lateritic Red Soil. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 906, 167356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, P.; Chen, H.; Kopittke, P.M.; Zhao, F.-J. Cadmium Contamination in Agricultural Soils of China and the Impact on Food Safety. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 249, 1038–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Tian, X.; Liu, R.; Liu, S.; Zuza, A.V. Key Driving Factors of Selenium-Enriched Soil in the Low-Se Geological Belt: A Case Study in Red Beds of Sichuan Basin, China. Catena 2021, 196, 104926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, C.-L.; He, T.-B.; Liu, C.-Q.; Lu, X.-H. Effects of Land Use and Parent Materials on Trace Elements Accumulation in Topsoil. J. Environ. Qual 2013, 42, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Z.; He, S.; Li, C.; Men, W.; Yan, C.; Wang, F. Geochemical Characteristics of Soil Selenium and Evaluation of Se-Rich Land Resources in the Central Area of Guiyang City, China. Acta Geochim. 2017, 36, 240–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.; Sun, S.; Zhao, W.; Sheng, L.; Mao, H.; Yang, X.; Chen, Z. Metagenomics and Metabolomics Analysis Revealed That Se-Mediated Cd Precipitation and Nutrient Cycling Regulated Soil-Rice (Oryza sativa L.) Microenvironmental Homeostasis under Cadmium Stress. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2024, 228, 105958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, R.; Zhao, P.; Zhu, Y.; Yang, J.; Wei, X.; Yang, L.; Liu, H.; Rensing, C.; Ding, Y. Application of Inorganic Selenium to Reduce Accumulation and Toxicity of Heavy Metals (Metalloids) in Plants: The Main Mechanisms, Concerns, and Risks. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 771, 144776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, G.; Ding, C.; Guo, F.; Li, X.; Zhang, T.; Wang, X. Underlying Mechanisms and Effects of Hydrated Lime and Selenium Application on Cadmium Uptake by Rice (Oryza sativa L.) Seedlings. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 18926–18935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.; Xu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Qin, X.; Huang, R.; Liang, X. Selenium Application Alters Soil Cadmium Bioavailability and Reduces Its Accumulation in Rice Grown in Cd-Contaminated Soil. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 31175–31182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, X.; Zhao, P.; Liu, H.; Nie, Z.; Zhu, J.; Qin, S.; Li, C. Selenium Inhibits Cadmium Uptake and Accumulation in the Shoots of Winte Wheat by Altering the Transformation of Chemical Forms of Cadmium in Soil. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 8525–8537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, N.; Jiang, Z.; Li, X.; Liu, H.; Li, N.; Wei, S. Mitigation of Rice Cadmium (Cd) Accumulation by Joint Application of Organic Amendments and Selenium (Se) in High-Cd-Contaminated Soils. Chemosphere 2020, 241, 125106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, R.; Wei, C.; Tu, S.; Ding, Y.; Song, Z. A Dual Role of Se on Cd Toxicity: Evidences from the Uptake of Cd and Some Essential Elements and the Growth Responses in Paddy Rice. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2013, 151, 113–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, B.-B.; Yang, C.; Shao, Z.-Y.; Wang, H.; Zan, S.-T.; Zhu, M.; Zhou, S.-B.; Yang, R.-Y. Selenium (Se) Does Not Reduce Cadmium (Cd) Uptake and Translocation in Rice (Oryza sativa L.) in Naturally Occurred Se-Rich Paddy Fields with a High Geological Background of Cd. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2019, 103, 127–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Liang, D.; Peng, Q.; Cui, Z.; Huang, J.; Lin, Z. Interaction between Selenium and Soil Organic Matter and Its Impact on Soil Selenium Bioavailability: A Review. Geoderma 2017, 295, 69–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Q.; Ding, Z.; Li, R.; Shi, Z. Kinetics of Cadmium (Cd), Nickel (Ni), and Lead (Pb) Release from Fulvic Acid: Role of Re-Association Reactions and Quantitative Models. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 843, 156996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Wang, Z.; Song, Q.; Hong, J.; Jin, T.; Huang, H.; Zheng, Z. Potential Mechanism of Humic Acid Attenuating Toxicity of Pb2+ and Cd2+ in Vallisneria natans. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 864, 160974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yong, Y.; Yang, T.; Wang, Y.; Xu, Y.; Huang, Q.; Liang, X.; Sun, Y.; Wang, L. Mercapto–Palygorskite Decreases the Cd Uptake of Wheat by Changing Fe and Mn Fraction in Cd Contaminated Alkaline Soil. Geoderma 2024, 441, 116751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Xia, Y.; He, X.; Yuan, L.; Li, W.; He, C.; Xia, K. Research Progress of Cd Form Transformation and the Effective Environmental Factors in Soil Based on Tessier Analysis. Chin. J. Soil Sci. 2021, 52, 1505–1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Indicators | Soil Type | Land Use Type | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Paddy Soil | Limestone Soil | Red Soil | Paddy Field | Dry Land | Garden Plot | |
| pH | 5.76 (5.19, 7.10) a | 4.69 (4.60, 5.98) b | 5.11 (4.72, 5.67) b | 5.80 (5.18, 6.30) | 5.51 (5.19, 5.71) | 5.06 (4.61, 5.95) |
| TN/% | 0.19 (0.14, 0.27) a | 0.15 (0.10, 0.17) ab | 0.07 (0.04, 0.17) b | 0.20 (0.18, 0.28) a | 0.14 (0.10, 0.15) b | 0.13 (0.06, 0.17) b |
| SOM/g·kg−1 | 31.69 (20.78, 42.48) a | 20.13 (14.11, 24.09) b | 11.21 (4.94, 27.43) b | 32.21 (28.14, 43.09) a | 18.67 (13.92, 21.23) b | 18.29 (9.83, 24.09) b |
| AK/mg·kg−1 | 101.60 (68.74, 140.10) a | 85.30 (73.99, 110.50) ab | 71.82 (45.65, 96.49) b | 95.33 (70.99, 110.50) b | 125.3 (104.30, 402.00) a | 56.32 (45.32, 97.48) c |
| AP/mg·kg−1 | 27.77 (19.78, 52.52) a | 8.63 (0.47, 16.64) b | 0.45 (0.00, 17.93) b | 28.06 (20.20, 53.39) a | 15.05 (7.98, 52.27) a | 7.12 (0.00, 21.59) b |
| DOC/mg·kg−1 | 162.60 (94.44, 222.90) a | 103.60 (53.18, 133.20) b | 87.96 (36.77, 137.80) b | 179.60 (117.50, 236.00) a | 71.73 (60.48, 93.83) b | 117.40 (54.73, 134.60) b |
| Sand/% | 38.81 (28.75, 50.29) | 36.26 (13.48, 46.62) | 47.25 (21.71, 82.74) | 35.47 (28.44, 46.21) | 46.18 (36.26, 54.18) | 46.56 (20.51, 65.81) |
| Silt/% | 38.34 (30.66, 43.53) a | 36.16 (31.77, 38.25) ab | 18.80 (9.16, 36.33) b | 38.72 (30.66, 43.65) a | 35.70 (30.55, 38.25) ab | 30.50 (17.09, 42.07) b |
| Clay/% | 25.50 (17.86, 28.16) | 25.50 (21.61, 50.36) | 23.83 (8.10, 51.87) | 25.61 (23.02, 28.21) | 20.31 (15.27, 25.50) | 20.36 (17.09, 36.01) |
| Fed/g·kg−1 | 27.63 (24.20, 37.42) b | 45.44 (44.81, 59.20) a | 37.76 (20.57, 75.64) ab | 26.57 (21.78, 40.68) b | 32.41 (30.69, 38.56) ab | 34.95 (26.32, 60.06) a |
| Ald/g·kg−1 | 5.35 (3.39, 6.29) b | 10.42 (8.30, 16.29) a | 7.41 (4.18, 11.86) ab | 5.56 (3.20, 6.58) | 6.11 (4.87, 10.11) | 7.61 (4.20, 12.91) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tan, Z.; Rong, Q.; Wang, W.; Jiang, H.; Yu, L.; Hu, J.; Chen, J.; Liang, X.; Zhao, X.; Zhou, C. Strategies for Regulating the Bioavailability and Mobility of Se and Cd in Cd-Contaminated Seleniferous Soils: Coupling the Bioavailable Se:Cd Molar Ratio with Soil Properties. Agronomy 2024, 14, 2941. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14122941
Tan Z, Rong Q, Wang W, Jiang H, Yu L, Hu J, Chen J, Liang X, Zhao X, Zhou C. Strategies for Regulating the Bioavailability and Mobility of Se and Cd in Cd-Contaminated Seleniferous Soils: Coupling the Bioavailable Se:Cd Molar Ratio with Soil Properties. Agronomy. 2024; 14(12):2941. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14122941
Chicago/Turabian StyleTan, Zebin, Qinlei Rong, Wenfeng Wang, Haiyan Jiang, Luyao Yu, Jingrui Hu, Jie Chen, Xuefeng Liang, Xiaomin Zhao, and Chunhuo Zhou. 2024. "Strategies for Regulating the Bioavailability and Mobility of Se and Cd in Cd-Contaminated Seleniferous Soils: Coupling the Bioavailable Se:Cd Molar Ratio with Soil Properties" Agronomy 14, no. 12: 2941. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14122941
APA StyleTan, Z., Rong, Q., Wang, W., Jiang, H., Yu, L., Hu, J., Chen, J., Liang, X., Zhao, X., & Zhou, C. (2024). Strategies for Regulating the Bioavailability and Mobility of Se and Cd in Cd-Contaminated Seleniferous Soils: Coupling the Bioavailable Se:Cd Molar Ratio with Soil Properties. Agronomy, 14(12), 2941. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14122941







