Synergistic Matching and Influencing Factors of Grain Production and Cropland Net Primary Productivity in the Black Soil Region of Northeast China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
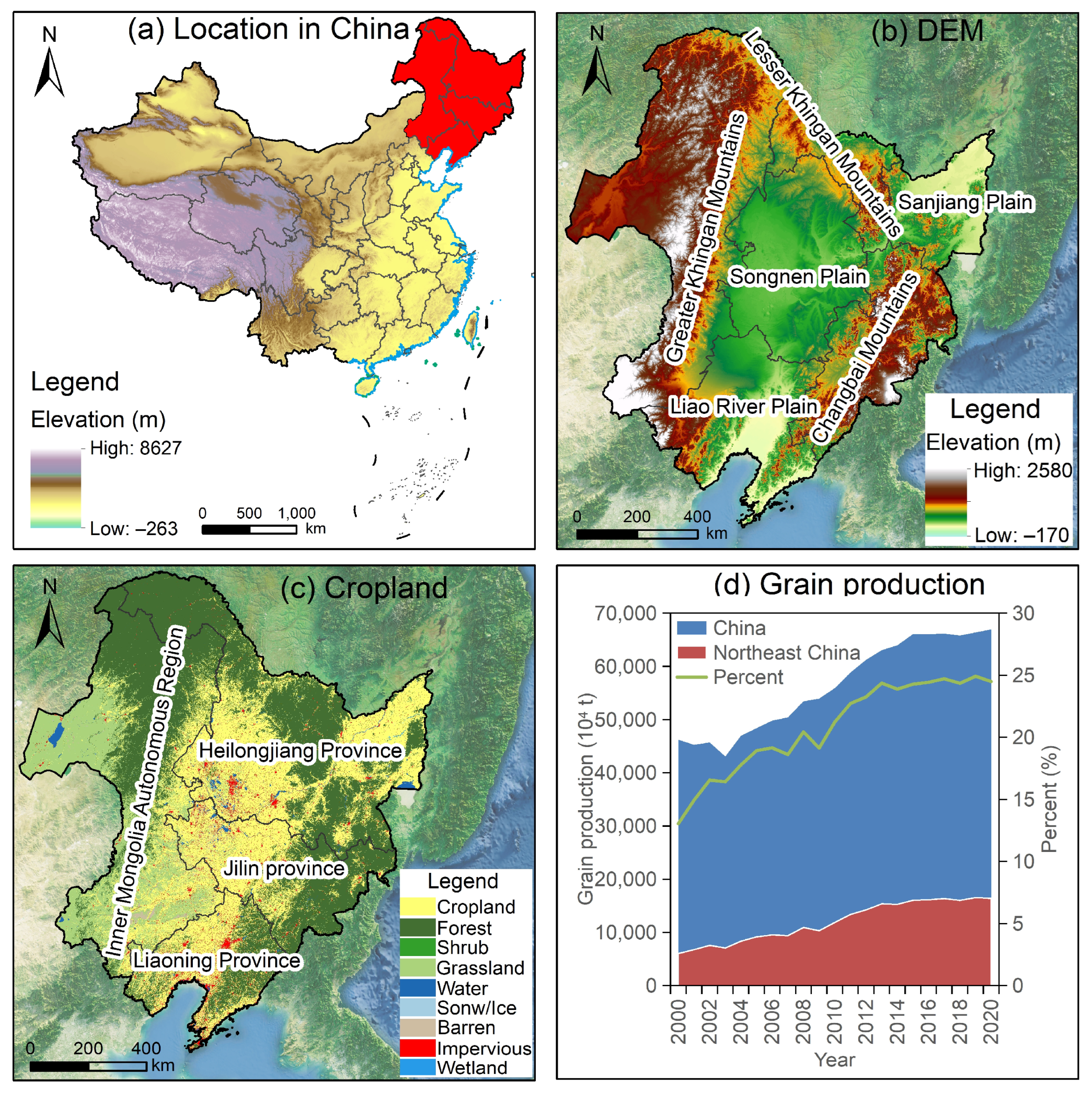
2.1. Overview of Study Area
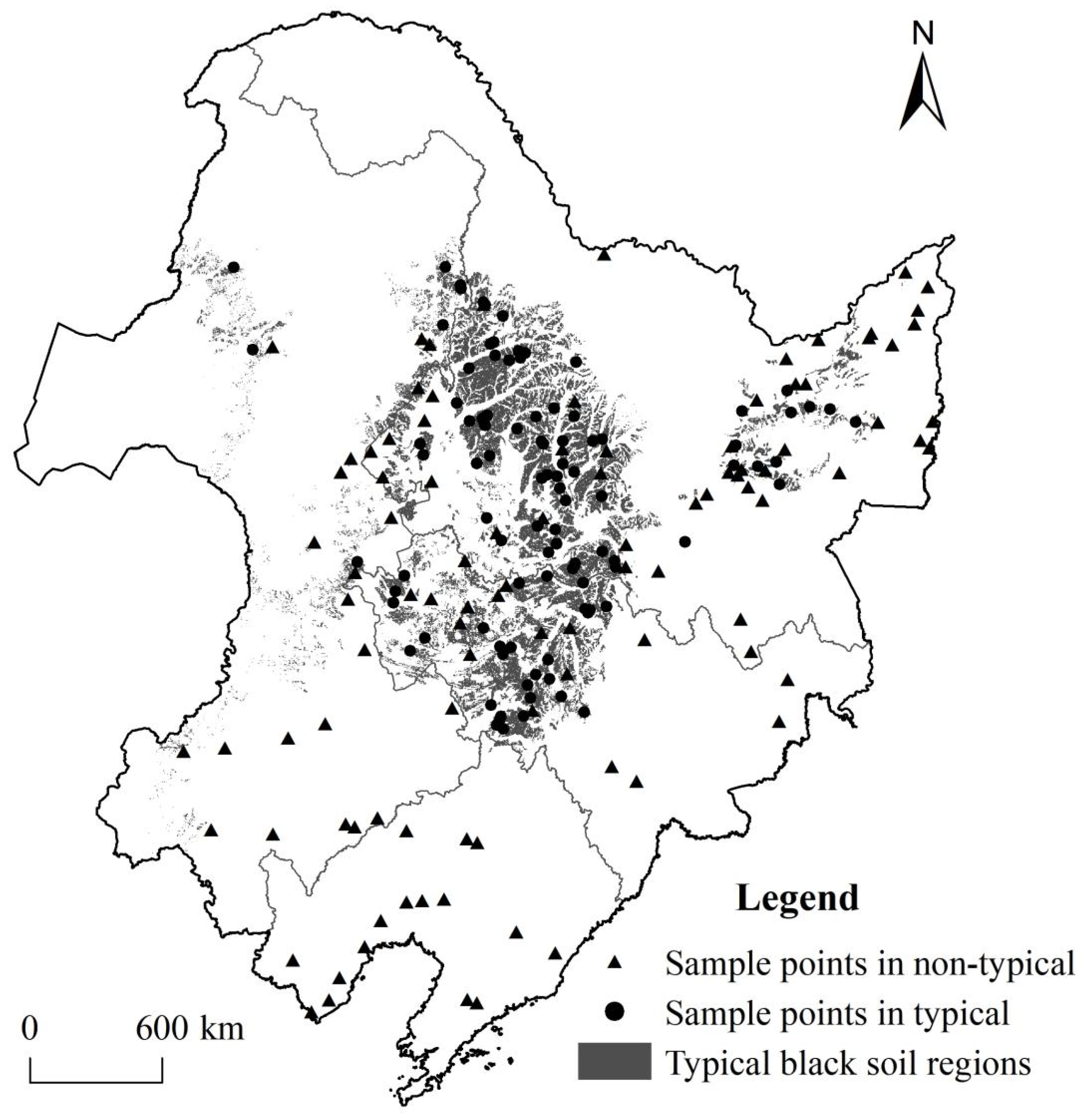
2.2. Data and Processing
2.3. Methods
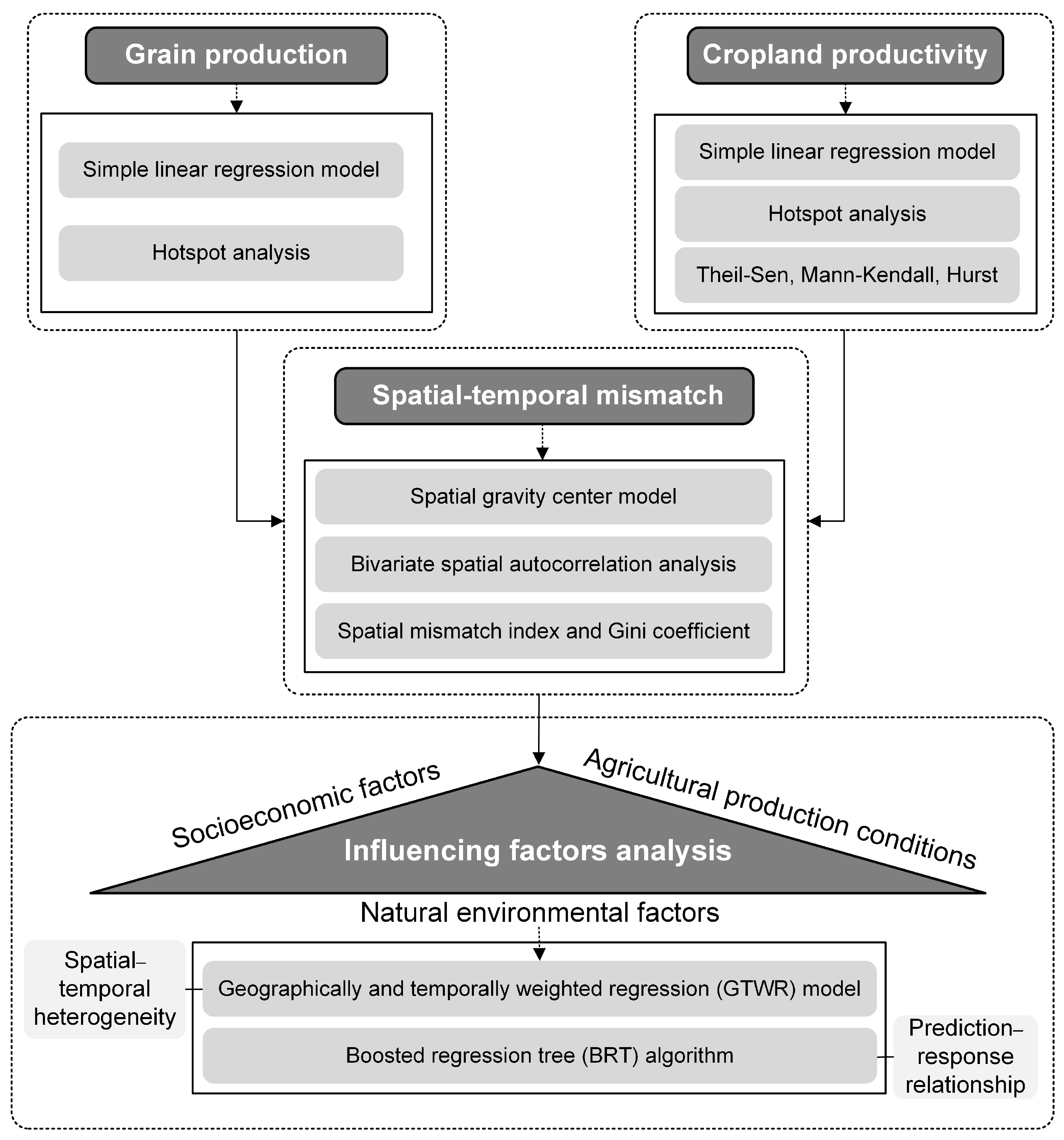
2.3.1. Methodological Framework
2.3.2. Statistical Analysis and Hotspot Analysis
2.3.3. Gravity Center Model
2.3.4. Bivariate Local Spatial Autocorrelation
2.3.5. Spatial Mismatch Analysis
2.3.6. Geographically and Temporally Weighted Regression (GTWR) Model
2.3.7. Boosted Regression Tree (BRT) Algorithm
2.3.8. Theil–Sen Estimator, Mann–Kendall Test, and Hurst Exponent
2.4. Explanatory Variables of Influencing Factors
3. Results
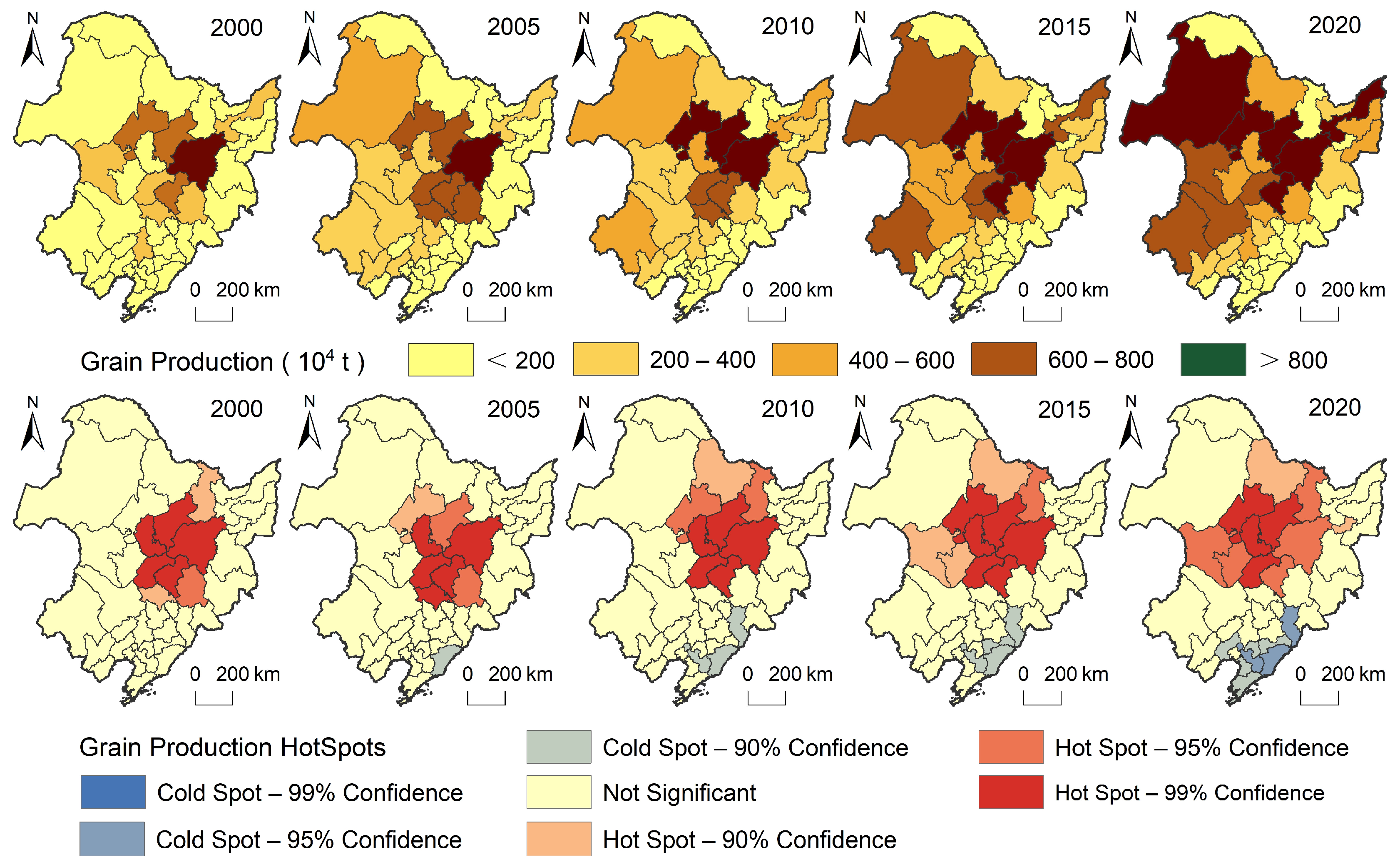
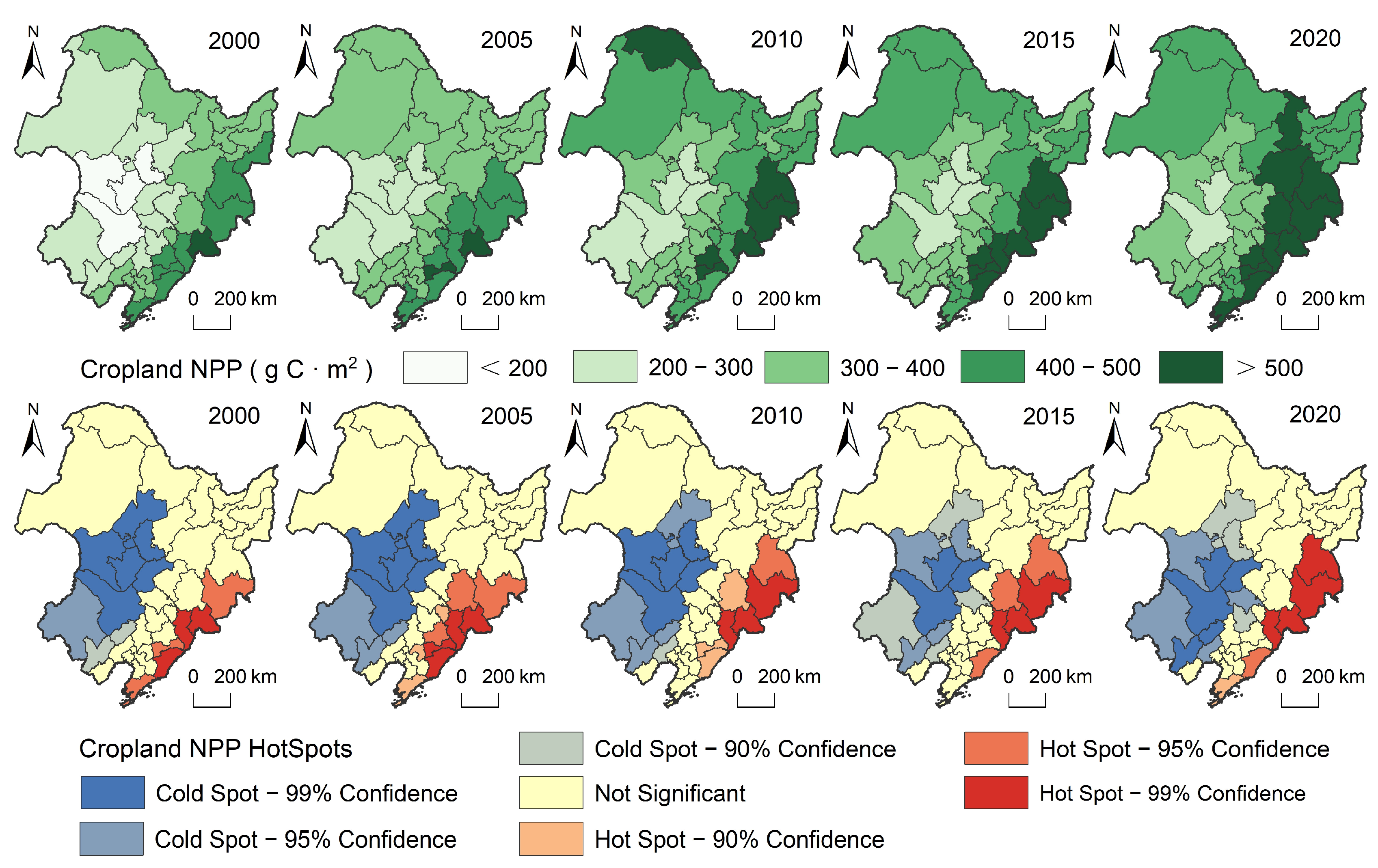
3.1. Hotspot Patterns of Grain Production and Cropland Productivity
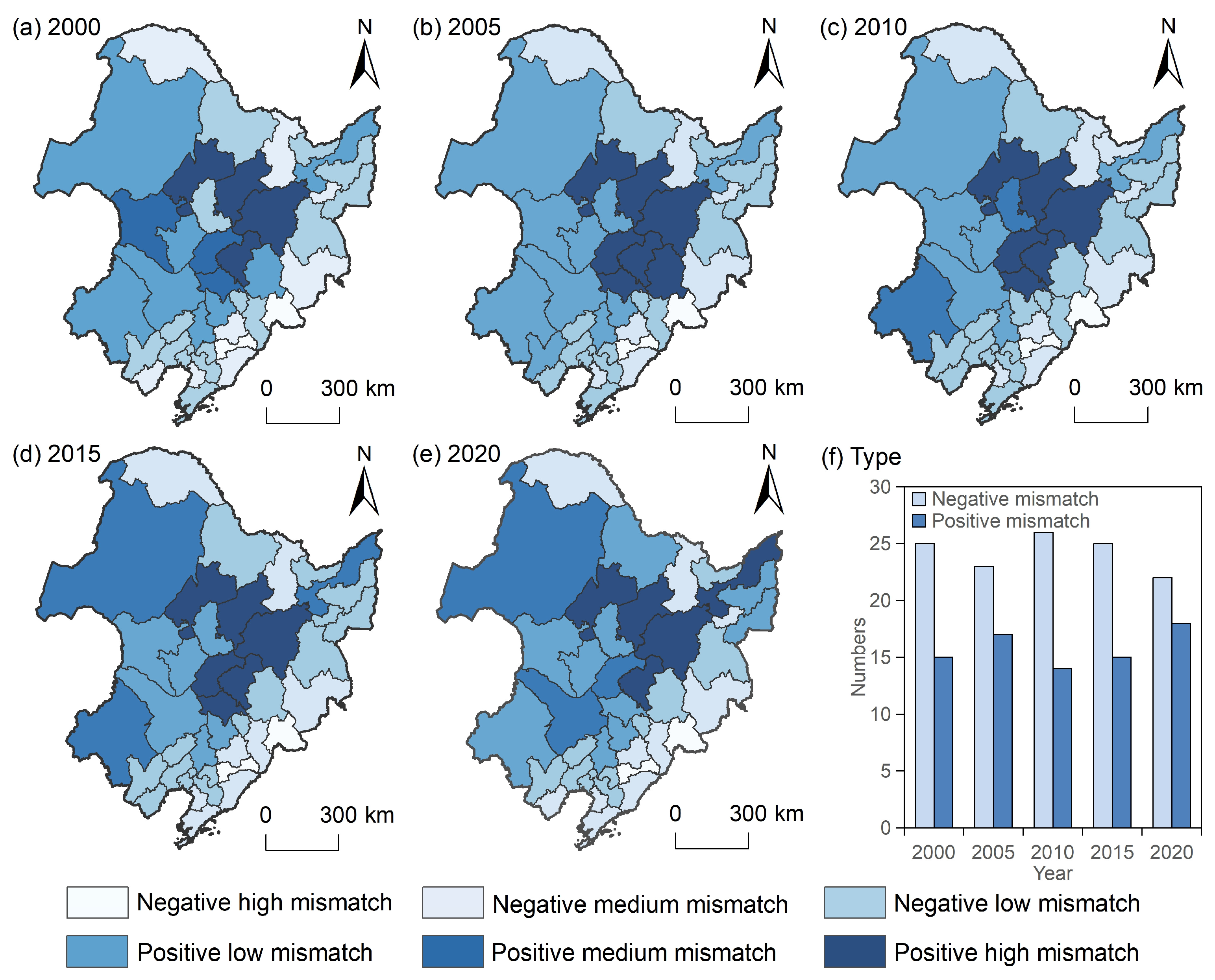
3.2. Spatial–Temporal Mismatch of Grain Production and Cropland Productivity
3.2.1. Variation Analysis of Spatial Gravity Center
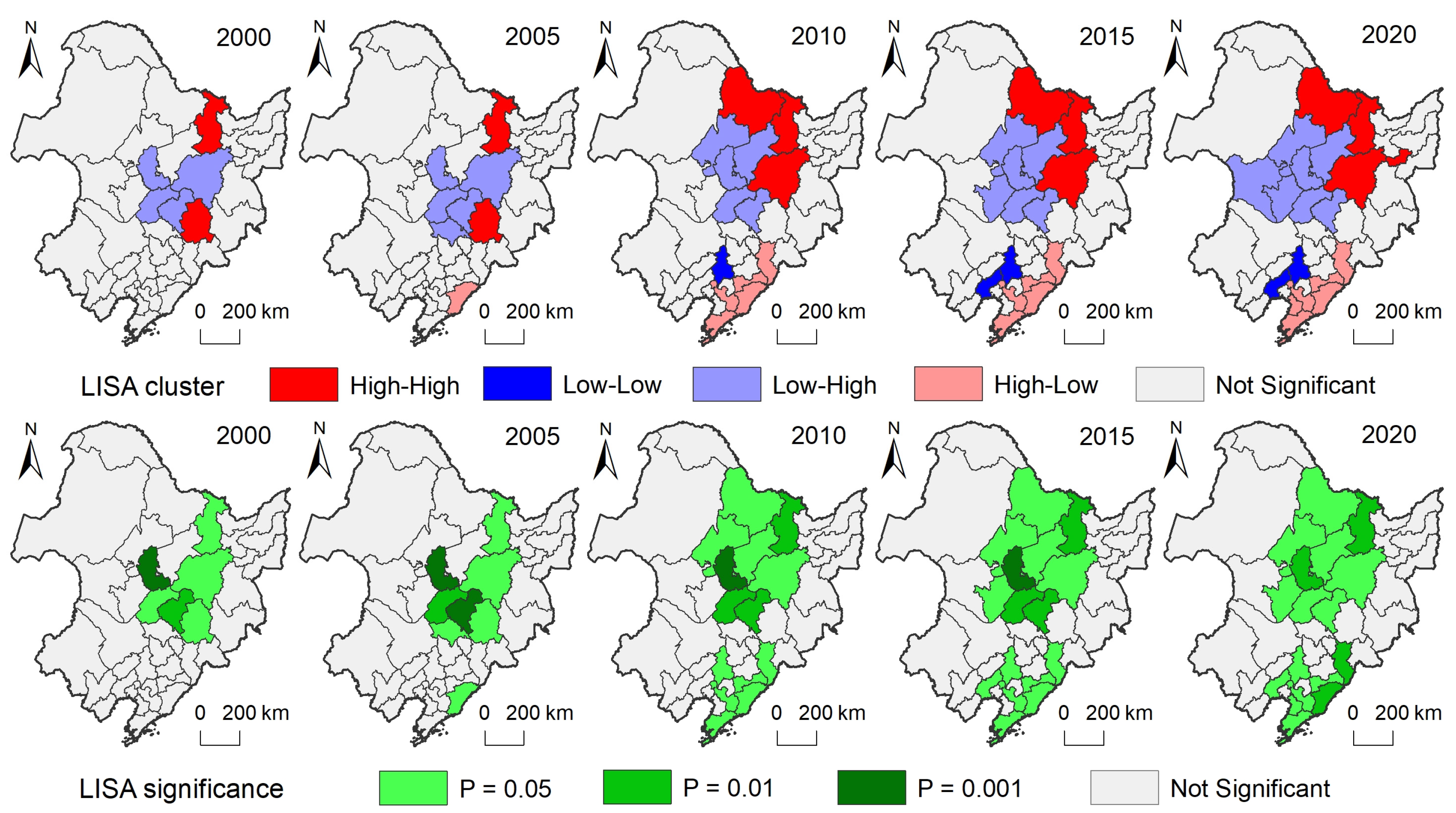
3.2.2. Spatial Interaction Pattern
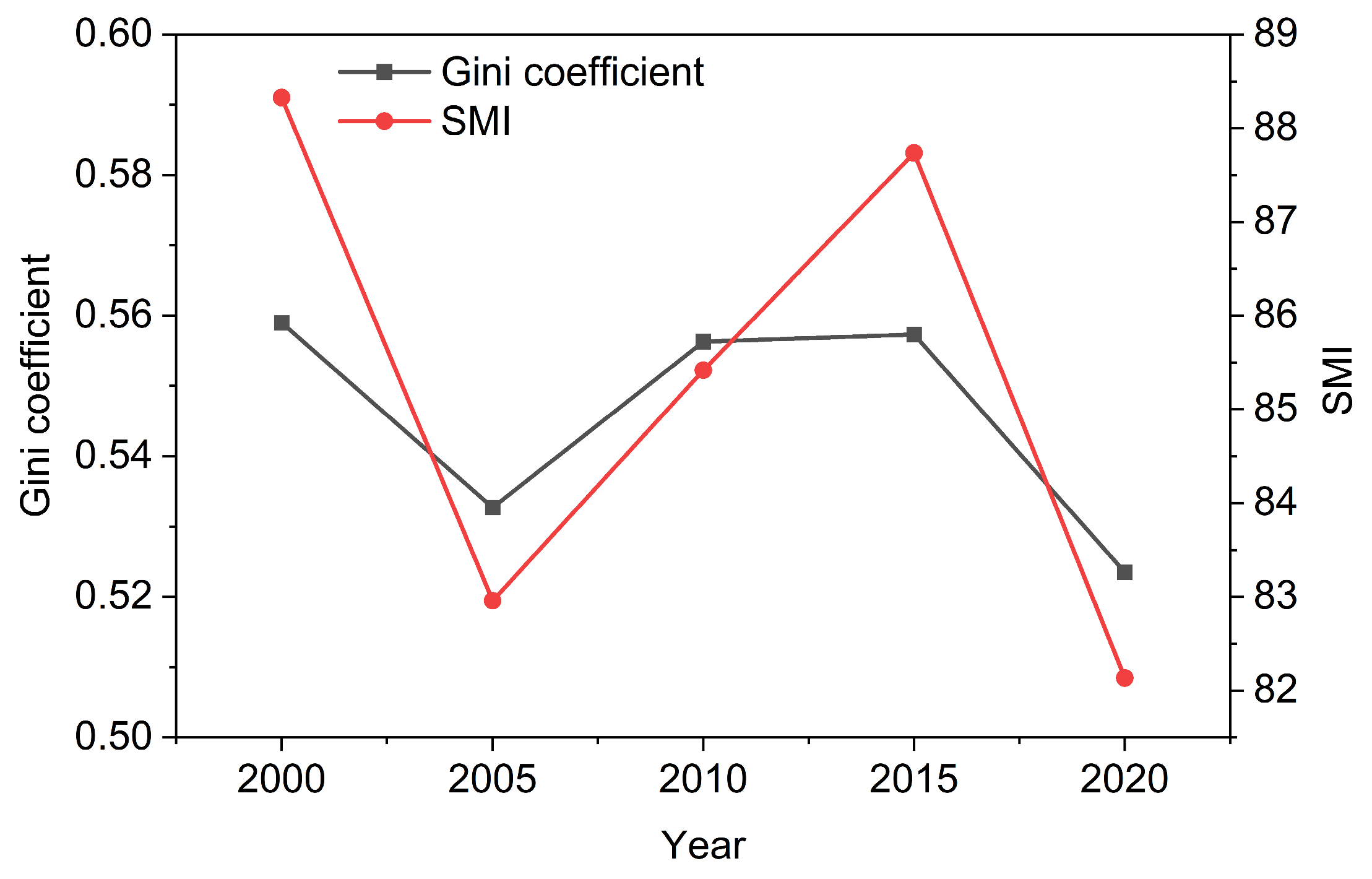
3.2.3. Spatial Mismatch Analysis
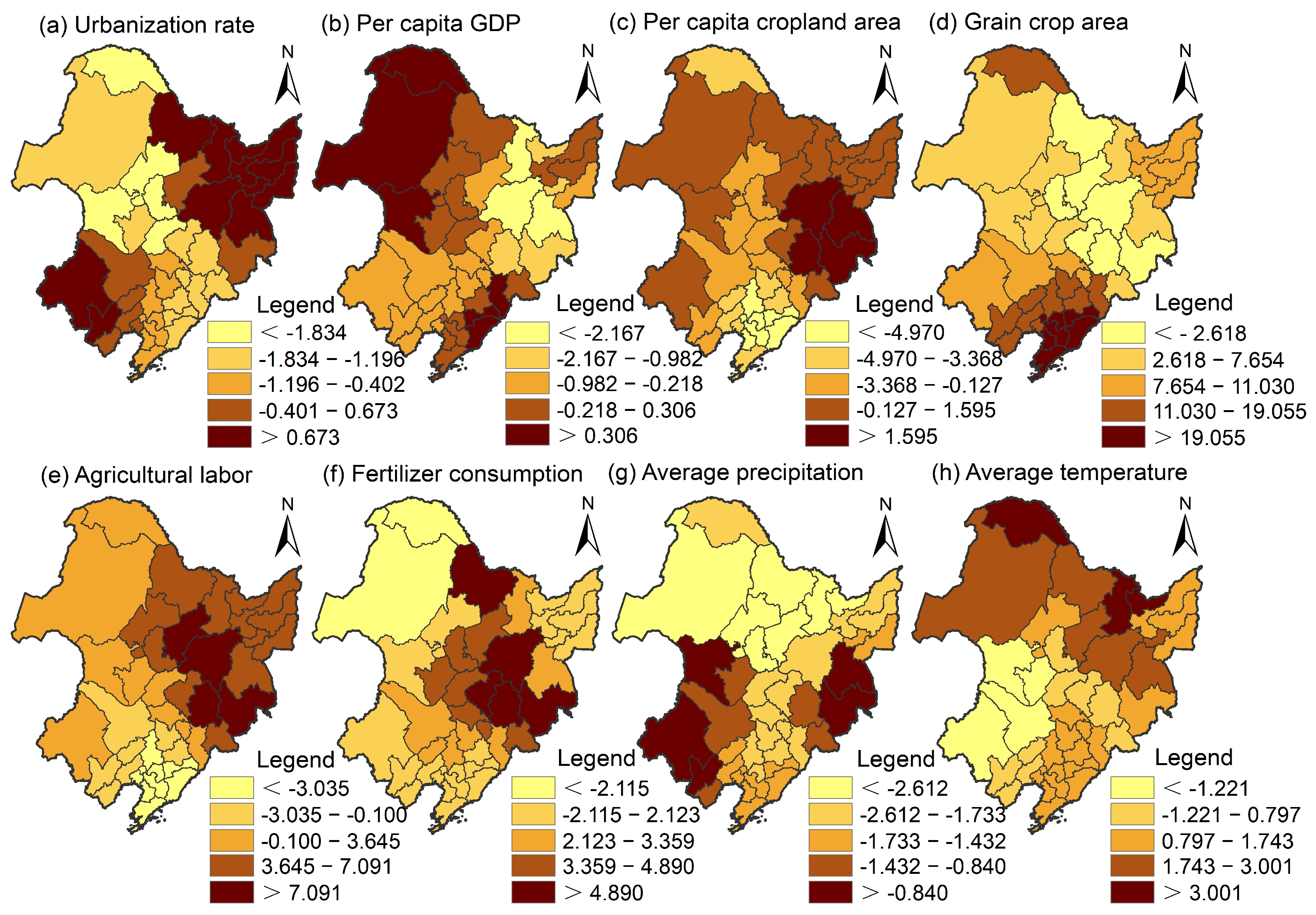
3.3. Spatial–Temporal Heterogeneity of Influencing Factors on Spatial Mismatch
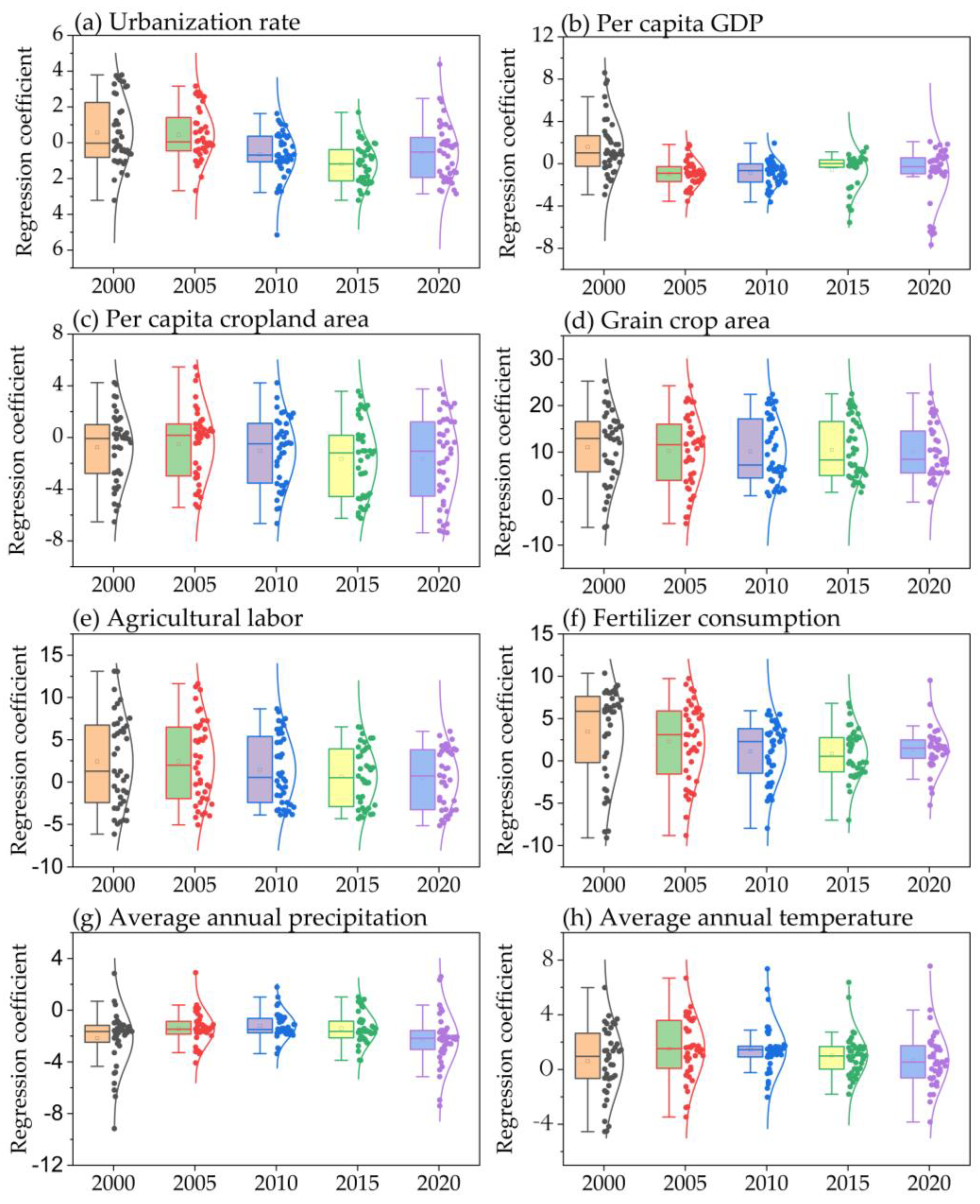
3.3.1. Model Selection and GTWR Regression Results
3.3.2. Changes in Influencing Factors over Time
3.3.3. Spatial Heterogeneity of Influencing Factors
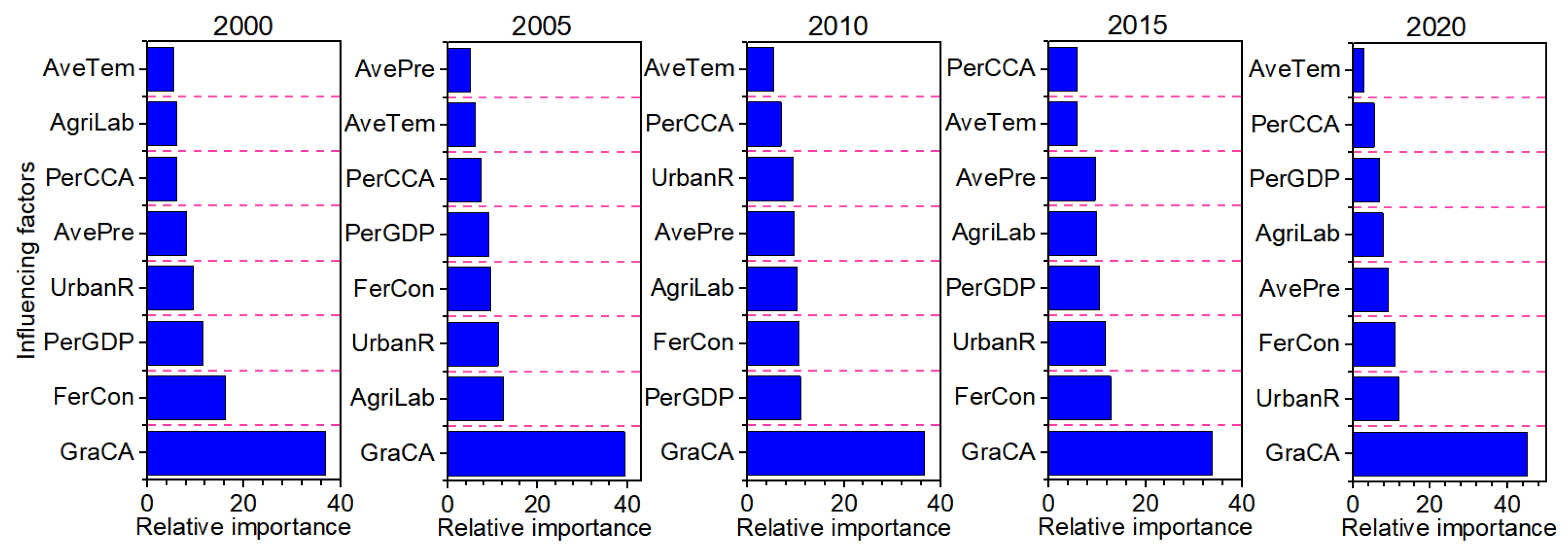
3.4. Predictor–Response Relationships of Influencing Factors on Spatial Mismatch
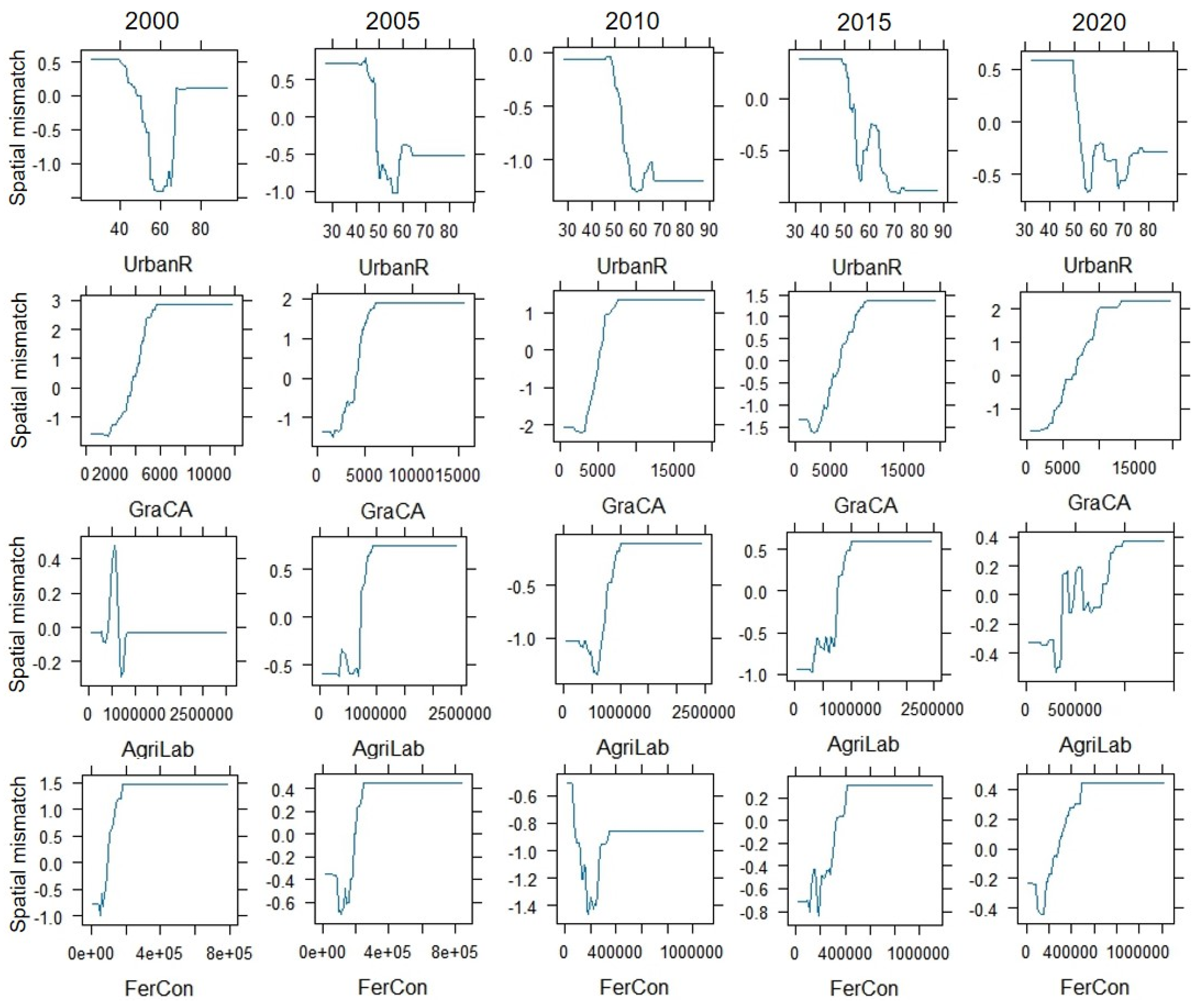
3.4.1. Relative Importance of Influencing Factors
3.4.2. Response Relationships of Key Influencing Factors
4. Discussion
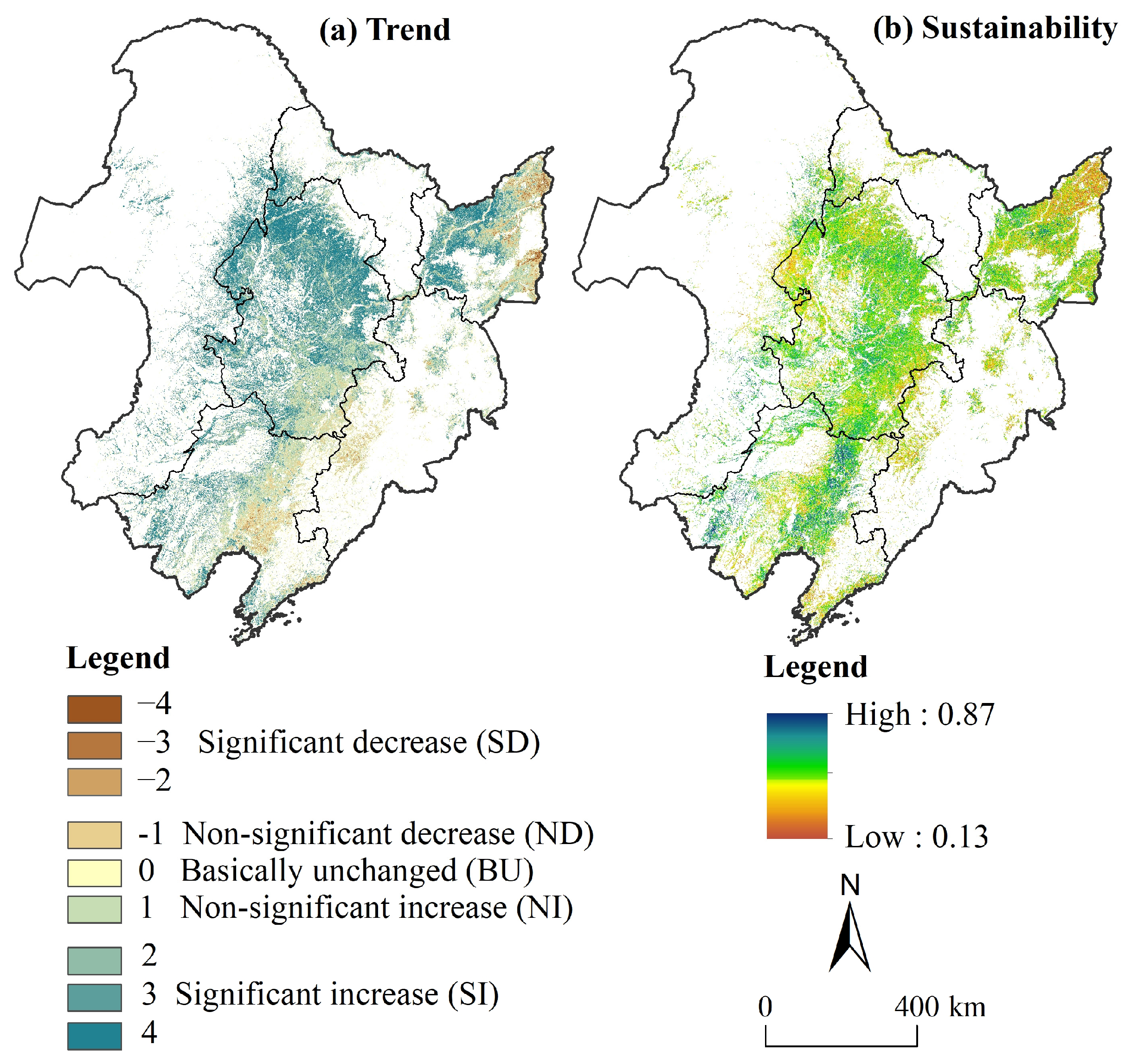
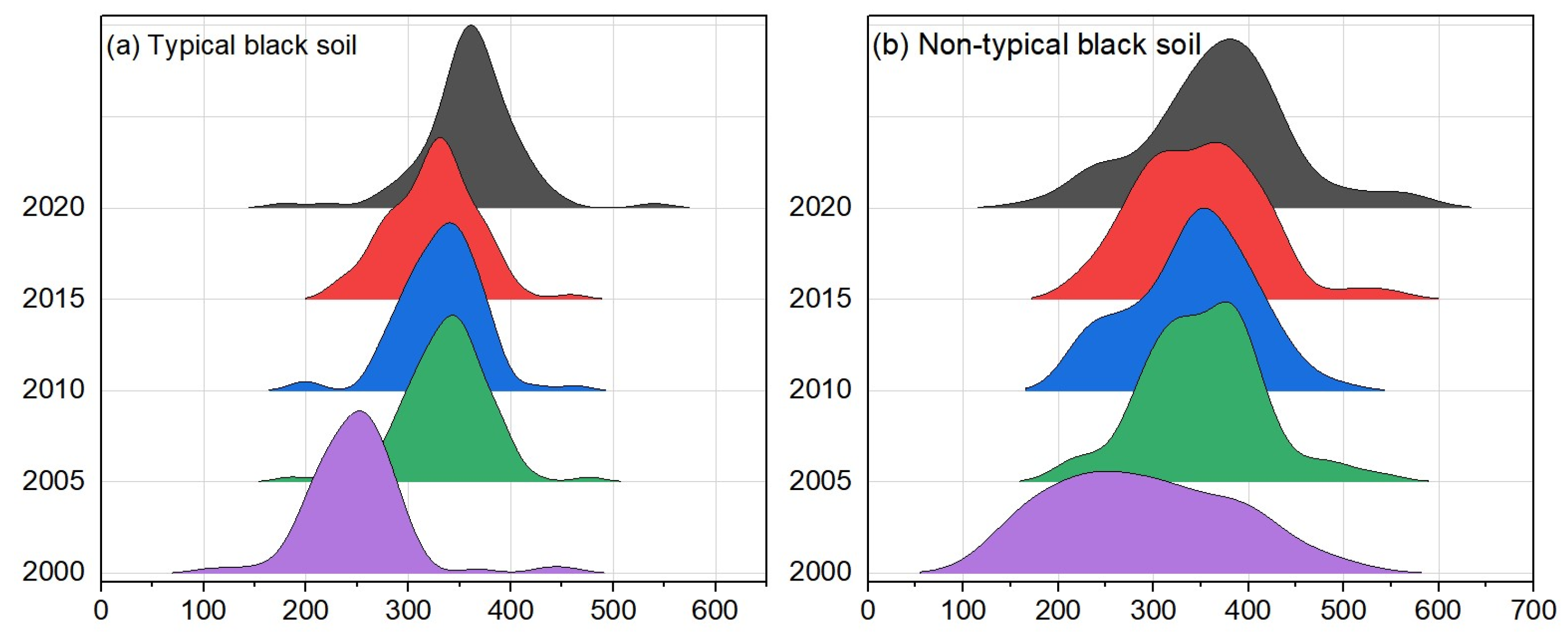
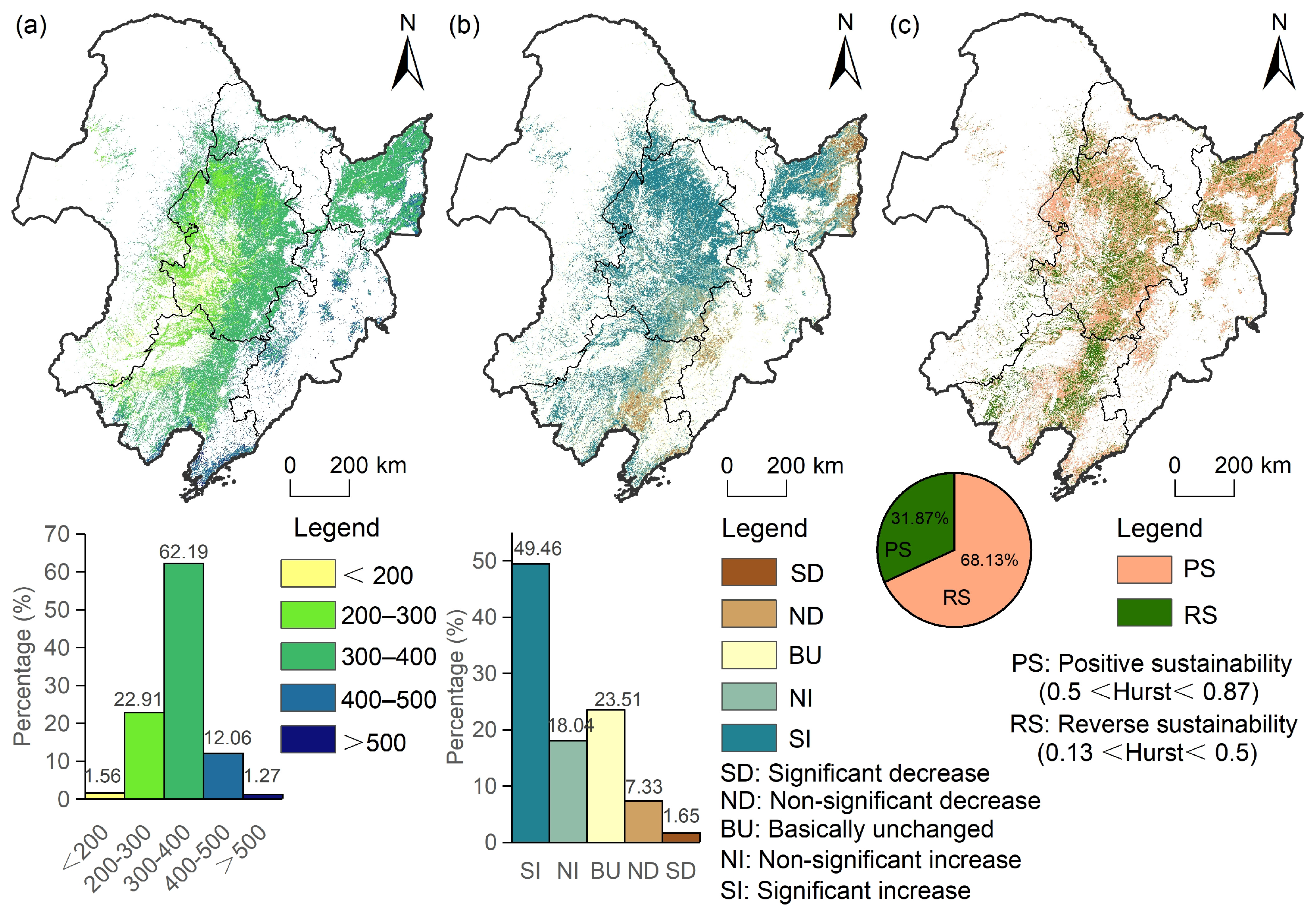
4.1. Historical Trend and Future Sustainability of Stable CNPP at Pixel Scale
4.2. Spatial–Temporal Synergistic Matching of Grain Production and CNPP
4.3. Interpretation of Spatial Mismatch Influencing Factors and Characteristics of GTWR and BRT
4.4. Implications for Sustainable Black Soil Cropland Protection and Food Supply Security
4.5. Limitations of the Study and Prospects in the Future
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| SCNPP | ZCNPP | Trend Code | Trend Types |
|---|---|---|---|
| SCNPP > 0 | 2.58 < ZCNPP | 4 | Significant increase (SI) |
| 1.96 < ZCNPP ≤ 2.58 | 3 | ||
| 1.65 < ZCNPP ≤ 1.96 | 2 | ||
| ZCNPP ≤ 1.65 | 1 | Non-significant increase (NI) | |
| SCNPP = 0 | ZCNPP | 0 | Basically unchanged (BU) |
| SCNPP < 0 | ZCNPP ≤ 1.65 | −1 | Non-significant decrease (ND) |
| 1.65 < ZCNPP ≤ 1.96 | −2 | Significant decrease (SD) | |
| 1.96 < ZCNPP ≤ 2.58 | −3 | ||
| ZCNPP ≤ 2.58 | −4 |
| Types | Influencing Factors | Description Calculation |
|---|---|---|
| Socioeconomic factors | Urbanization rate | Population urbanization rate, urban population/total population |
| Per capita GDP | GDP/total population | |
| Per capita cropland area | Cropland area/total population | |
| Agricultural production factors | Grain crop area | Grain crop area, obtained directly from statistical yearbooks |
| Agricultural labor | Rural practitioners | |
| Fertilizer consumption | Total fertilizer application | |
| Natural factors | Average annual precipitation | Statistics based on precipitation and temperature raster datasets to administrative units (prefecture level) using ArcGIS 10.8 software |
| Average annual temperature |
References
- Abay, K.A.; Breisinger, C.; Glauber, J.; Kurdi, S.; Laborde, D.; Siddig, K. The Russia-Ukraine War: Implications for Global and Regional Food Security and Potential Policy Responses. Glob. Food Secur. Agric. Policy 2023, 36, 100675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhang, F.; Liu, Y.; Cheng, S.; Zhu, J.; Si, W.; Fan, S.; Gu, S.; Hu, B.; et al. New patterns of globalization and food security. J. Nat. Resour. 2021, 36, 1362–1380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.; Yang, R.; Xu, Q. Spatial mismatch evolution of global population and food and its influencing factors. J. Nat. Resour. 2021, 36, 1381–1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Zhong, H.; Li, Y.; Wen, Q.; Liu, X.; Jian, Y. Change in grain production in China and its impacts on spatial supply and demand distributions in recent two decades. J. Nat. Resour. 2021, 36, 1413–1425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saccone, D.; Vallino, E. Food Security in the Age of Sustainable Development: Exploring the Synergies between the SDGs. World Dev. 2022, 152, 105815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, X.; Liang, X.; Han, B.; Wang, S.; Hong, B.; Song, J. Theoretical analysis and geographical support framework of cultivated land protection for chinese-style modernization. Econ. Geogr. 2022, 42, 142–150. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, Z.; Sun, T.; Yang, Y. Study on the Spatiotemporal Patterns and Contribution Factors of China’s Grain Output Increase during 2003–2013. J. Nat. Resour. 2016, 31, 895–907. [Google Scholar]
- Gong, Y.; Zhang, Y. Influence of well-facilitated capital farmland construction policy on grain productivity. J. Huazhong Agric. Univ. 2023, 4, 175–190. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X.; Lin, C.; Hou, X.; Wu, Z.; Yan, G.; Zhu, C. The Impact of Land Consolidation on Arable Land Productivity: A Differentiated View of Soil and Vegetation Productivity. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2022, 326, 107781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Bai, Y.; Alatalo, J.M.; Wang, H.; Tong, J.; Liu, G.; Zhang, F.; Chen, J. Spatial-Temporal Pattern of Cultivated Land Productivity Based on Net Primary Productivity and Analysis of Influencing Factors in the Songhua River Basin. Land Degrad. Dev. 2022, 33, 1917–1932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, B.; Jin, X.; Yeting, F.; Chen, H.; Jin, J.; Xu, W.; Ren, J.; Zhou, Y. Trend and Spatial Pattern of Stable Cropland Productivity in China Based on Satellite Observations (2001−2020). Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 2023, 101, 107136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Ke, N.; Kuang, B. Regional differences and influencing factors of China’s grain production capacity. China Land Sci. 2020, 34, 53–62. [Google Scholar]
- Niu, Z.; Yan, H.; Liu, F. Decreasing Cropping Intensity Dominated the Negative Trend of Cropland Productivity in Southern China in 2000–2015. Sustainability 2020, 12, 10070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Xiao, X.; Qin, Y.; Yan, H.; Huang, J.; Wu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zou, Z.; Doughty, R.B. Large Spatial Variation and Stagnation of Cropland Gross Primary Production Increases the Challenges of Sustainable Grain Production and Food Security in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 811, 151408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Liu, Y.; Kong, X.; Chen, Y.; Pan, J. Spatial and temporal variation of grain production and its influencing factors at the county level in China. Econ. Geogr. 2018, 38, 142–151. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, D.; Liu, S.; Wen, X. Spatial-Temporal Evolution of Grain Production Structure in Northeast China. Econ. Geogr. 2019, 39, 163–170. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Q.; Zhang, F.; Wu, G.; Mai, Q. Spatial Spillover Effects of Grain Production Efficiency in China: Measurement and Scope. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 278, 121062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Si, X.; Wang, J. The measurement and its distribution dynamic evolution of grain production efficiency in China under the goal of reducing pollution emissions and increasing carbon sink. J. Nat. Resour. 2022, 37, 600–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Chen, Y.; Liu, Z. Spatiotemporal pattern and influencing factors of grain production resilience in China. Econ. Geogr. 2023, 43, 126–134. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Q.; Qu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Su, D.; Wei, C. Dynamic evolution and driving effects of carbon emissions from grain production in China. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2023, 78, 2186–2208. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, X.; Liu, J.; Wang, R.; Wang, X. Spatial-temporal coupling relationship between chemical fertilizer application and grain yield in China at city scale. J. Nat. Resour. 2019, 34, 1471–1482. [Google Scholar]
- Ge, D.; Long, H.; Zhang, Y.; Tu, S. Pattern and coupling relationship between grain yield and agricultural labor changes at county level in China. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2017, 72, 1063–1077. [Google Scholar]
- Fang, Y.; Liu, J. Coupled modes of grain yield and agricultural labor changes and rural development types at county level in Northeast China. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2020, 75, 2241–2255. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, K.; Ding, M.; Xin, L.; Chen, L. Spatial-temporal patterns of grain output and its spatial relationship with economic development at the county level in China. Econ. Geogr. 2021, 41, 167–175. [Google Scholar]
- Hou, M.; Deng, Y.; Yao, S. Coordinated Relationship between Urbanization and Grain Production in China: Degree Measurement, Spatial Differentiation and Its Factors Detection. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 331, 129957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, Y. Spatial Shifts in Grain Production Increases in China and Implications for Food Security. Land Use Policy 2018, 74, 204–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Wu, J.; Song, W.; Li, Z.; Li, Z.; Kong, F. Spatial-Temporal Changes in Grain Production, Consumption and Driving Mechanism in China. J. Integr. Agric. 2013, 12, 374–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhi, J.; Cao, X.; Zhang, Z.; Qin, T.; Qu, L.; Qi, L.; Ge, L.; Guo, A.; Wang, X.; Da, C.; et al. Identifying the Determinants of Crop Yields in China since 1952 and Its Policy Implications. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2022, 327, 109216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.-C.; Zeng, M.; Luo, K. How Does Climate Change Affect Food Security? Evidence from China. Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 2024, 104, 107324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, H.; Liu, Z.; Wang, J. Understanding Impacts of Cropland Pattern Dynamics on Grain Production in China: A Integrated Analysis by Fusing Statistical Data and Satellite-Observed Data. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 313, 114988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, D.; Long, H.; Zhang, Y.; Ma, L.; Li, T. Farmland Transition and Its Influences on Grain Production in China. Land Use Policy 2018, 70, 94–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, A.; Yue, W.; Yang, J.; Xue, B.; Xiao, W.; Li, M.; He, T.; Zhang, M.; Jin, X.; Zhou, Q. Cropland Abandonment in China: Patterns, Drivers, and Implications for Food Security. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 418, 138154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Yang, F.; Li, F. The grain production space reconstruction in China since the reform and opening up. J. Nat. Resour. 2021, 36, 1426–1438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Qin, Z.; Liu, X.; Chen, Z.; Wei, X.; Zhang, Q.; Lei, M. Grain Production Space Reconstruction and Land System Function Tradeoffs in China. Geogr. Sustain. 2021, 2, 22–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, J.; Wang, Z.; Yang, J.; Zhang, L. Analysis for Spatial-Temporal Changes of Grain Production and Farmland Resource: Evidence from Hubei Province, Central China. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 207, 474–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Wang, G.; Cai, W.; Che, X.; Zhou, W.; Zhang, C.; Zeng, J. Spatiotemporal Mismatch of Global Grain Production and Farmland and Its Influencing Factors. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2023, 194, 107008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, G.; Li, Z.; Wang, Z.; Chu, X.; Li, Z. Impact of Land-Use Induced Changes on Agricultural Productivity in the Huang-Huai-Hai River Basin. Phys. Chem. Earth 2015, 79, 86–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, Z.; Yan, H.; Huang, M.; Hu, Y.; Chen, J. Agricultural productivity estimation with MODIS-OLI fusion data. J. Nat. Resour. 2016, 31, 875–885. [Google Scholar]
- Zhuang, Q.; Wu, S.; Huang, X.; Kong, L.; Yan, Y.; Xiao, H.; Li, Y.; Cai, P. Monitoring the Impacts of Cultivated Land Quality on Crop Production Capacity in Arid Regions. CATENA 2022, 214, 106263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rotllan-Puig, X.; Ivits, E.; Cherlet, M. LPDynR: A New Tool to Calculate the Land Productivity Dynamics Indicator. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 133, 108386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Wang, X.; Baiocchi, G.; Casazza, M.; Meng, F.; Cai, Y.; Hao, Y.; Wu, F.; Yang, Z. On the Accuracy of Official Chinese Crop Production Data: Evidence from Biophysical Indexes of Net. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 25434–25444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Ji, Q.; Liang, W.; Fu, B.; Lü, Y.; Yan, J.; Jin, Z.; Wang, Z.; Li, Y. Urbanization Does Not Endanger Food Security: Evidence from China’s Loess Plateau. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 871, 162053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, H.; Lu, X. Dynamic evolution and synergistic relationship between grain productivity capacity and vegetation primary productivity in the Middle Reaches of the Yangtze River. Econ. Geogr. 2022, 42, 103–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, F.; Zhang, X.; Yin, P.; Shen, Z. Spatial mismatch and problem type identification of agricultural transformation in resource-based city from the perspective of town scale: A case study of Xuzhou city. Econ. Geogr. 2022, 42, 152–161. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, T.; Zhang, C.; Kuang, W.; Luo, G.; Du, G.; DeMaeyer, P.; Yin, Z. A Large-Scale Shift of Cropland Structure Profoundly Affects Grain Production in the Cold Region of China. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 307, 127300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Liu, X.; Liu, Z. Effects of Climate Change on Paddy Expansion and Potential Adaption Strategies for Sustainable Agriculture Development across Northeast China. Appl. Geogr. 2022, 141, 102667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, D.; Cao, Y.; Cheng, J.; Lei, M.; Liao, Y.; Wang, L.; Zhao, J.; Kong, X. Spatiotemporal evolution and driving factors of black soil cultivated land within the framework of critical zones on the Earth. Resour. Sci. 2023, 45, 1856–1868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Shi, Z.; Xing, Z.; Wang, M.; Wang, M. Dynamic Evaluation of Cropland Degradation Risk by Combining Multi-Temporal Remote Sensing and Geographical Data in the Black Soil Region of Jilin Province, China. Appl. Geogr. 2023, 154, 102920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Xing, Q.; Tong, Y.; Wang, Z.; Li, B. Establish Governance Systems for Securing Black Soils in China Based on a New Law. Soil Secur. 2023, 13, 100112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Chu, L.; Xiao, Y.; Wang, C.; Tan, W.; Wang, T.; Cai, C. Spatiotemporal changes and driving forces of main grain crop planting types in Northeast China from 2017 to 2021. Resour. Sci. 2023, 45, 966–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Pei, J.; Li, S.; Zou, H.; Wang, J.; Zhang, J. Main characteristics and utilization countermeasures for black soils in different regions of Northeast China. Chin. J. Soil Sci. 2023, 54, 495–504. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, J.; Huang, X. The 30 m Annual Land Cover Dataset and Its Dynamics in China from 1990 to 2019. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2021, 13, 3907–3925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.; Jin, X.; Xu, X.; Chen, H.; Liu, J.; Yang, X.; Xu, W.; Sun, R.; Han, B.; Zhou, Y. Uncertainty in China’s Food Self-Sufficiency: A Dynamic System Assessment. Sustain. Prod. Consump. 2023, 40, 135–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, P.; Chen, T.; Li, Y.; Liu, K.; Zhang, D.; Song, C. Comparison and Assessment of Different Land Cover Datasets on the Cropland in Northeast China. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 5134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, S.; Ding, Y.; Liu, W.; Li, Z. 1 Km Monthly Temperature and Precipitation Dataset for China from 1901 to 2017. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2019, 11, 1931–1946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Tan, S.; Chen, E.; Li, J. Spatio-Temporal Characteristics and Influencing Factors of Land Disputes in China: Do Socio-Economic Factors Matter? Ecol. Indic. 2024, 160, 111938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ord, J.K.; Getis, A. Local Spatial Autocorrelation Statistics: Distributional Issues and an Application. Geogr. Anal. 1995, 27, 286–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, B.; Wu, B.; Barry, M. Geographically and Temporally Weighted Regression for Modeling Spatio-Temporal Variation in House Prices. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2010, 24, 383–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, F.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Hu, M.; Gao, Y.; Zhu, J. Exploring Ecological Civilization Performance and Its Determinants in Emerging Industrialized Countries: A New Evaluation System in the Case of China. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 315, 128051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Tian, W.; Zhou, Q.; Shi, T. Spatiotemporal and Driving Forces of Ecological Carrying Capacity for High-Quality Development of 286 Cities in China. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 293, 126186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, M.; Li, C.; Wang, P.; Dai, X. Spatio-Temporal Variation and Future Sustainability of Net Primary Productivity from 2001 to 2021 in Hetao Irrigation District, Inner Mongolia. Agriculture 2024, 14, 613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, C.; Li, Z.; Yi, X. Driving effects of grain production change and its spatial differences in China. China Popul. Resour. Environ. 2016, 26, 72–81. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, D.; Yan, H.; Chi, H.; Geng, X.; Shao, Q. Research on spatiotemporal characteristics of farmland ecosystem NPP in Jianghan Plain from 2000 to 2015. J. Nat. Resour. 2020, 35, 845–856. [Google Scholar]
- Su, Y.; Qian, K.; Lin, L.; Wang, K.; Guan, T.; Gan, M. Identifying the Driving Forces of Non-Grain Production Expansion in Rural China and Its Implications for Policies on Cultivated Land Protection. Land Use Policy 2020, 92, 104435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, J.; Wang, B.; Zhang, C.; Li, W.; Wang, S. Mechanism of Regional Land Use Transition in Underdeveloped Areas of China: A Case Study of Northeast China. Land Use Policy 2020, 94, 104538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Cheng, Y. Spatio-temporal pattern and its driving factors of grain production in Heilongjiang Province. J. Nat. Resour. 2015, 30, 491–501. [Google Scholar]
- van Loon, M.P.; Adjei-Nsiah, S.; Descheemaeker, K.; Akotsen-Mensah, C.; van Dijk, M.; Morley, T.; van Ittersum, M.K.; Reidsma, P. Can Yield Variability Be Explained? Integrated Assessment of Maize Yield Gaps across Smallholders in Ghana. Field Crop. Res. 2019, 236, 132–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ha, T.T.V.; Fan, H.; Shuang, L. Climate Change Impact Assessment on Northeast China’s Grain Production. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 14508–14520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salmerón, R.; García, C.B.; García, J. Variance Inflation Factor and Condition Number in Multiple Linear Regression. J. Stat. Comput. Simul. 2018, 88, 2365–2384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potapov, P.; Turubanova, S.; Hansen, M.C.; Tyukavina, A.; Zalles, V.; Khan, A.; Song, X.-P.; Pickens, A.; Shen, Q.; Cortez, J. Global Maps of Cropland Extent and Change Show Accelerated Cropland Expansion in the Twenty-First Century. Nat. Food 2022, 3, 19–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arabameri, A.; Yamani, M.; Pradhan, B.; Melesse, A.; Shirani, K.; Tien Bui, D. Novel Ensembles of COPRAS Multi-Criteria Decision-Making with Logistic Regression, Boosted Regression Tree, and Random Forest for Spatial Prediction of Gully Erosion Susceptibility. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 688, 903–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Z.; Chu, L.; Wang, C.; Pan, Y.; Su, W.; Qin, Y.; Cai, C. What Drives the Spatial Heterogeneity of Cropping Patterns in the Northeast China: The Natural Environment, the Agricultural Economy, or Policy? Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 905, 167810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ao, M.; Zhang, X.; Guan, Y. Research and practice of conservation tillage technology in black soil of Northeast China. Bull. Chin. Acad. Sci. 2021, 36, 1203–1215. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, C.; Chen, W.; Ma, J.; Yun, W.; Gao, L.; Wang, H. Analysis on spatial-temporal changes of cultivated land productivity in Jilin Province from 2000 to 2019 based on EVI time series. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Mach. 2022, 53, 158–166. [Google Scholar]


| Type | Variable | Unit | VIF |
|---|---|---|---|
| Socioeconomic factors | Urbanization rate | % | 2.403 |
| Per capita GDP | yuan/person | 1.647 | |
| Per capita cropland area | km2/person | 2.475 | |
| Agricultural production factors | Grain crop area | km2 | 6.778 |
| Agricultural labor | person | 2.473 | |
| Fertilizer consumption | t | 4.545 | |
| Natural factors | Average annual precipitation | mm | 1.432 |
| Average annual temperature | °C | 1.857 |
| Period | Grain Production | CNPP | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Distance (km) | Direction (°) | Distance(km) | Direction (°) | |
| 2000–2005 | 35.73 | −179.41 | 17.54 | 137.21 |
| 2005–2010 | 59.72 | 53.57 | 28.12 | 55.43 |
| 2010–2015 | 10.42 | 111.41 | 5.78 | −106.06 |
| 2015–2020 | 41.80 | 21.88 | 5.86 | 12.44 |
| Year | 2000 | 2005 | 2010 | 2015 | 2020 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Moran’s I | −0.217 | −0.212 | −0.156 | −0.195 | −0.154 |
| p-Value | 0.003 | 0.004 | 0.024 | 0.009 | 0.018 |
| Z-Score | −2.860 | −2.856 | −2.099 | −2.558 | −2.068 |
| City | SMI | Change Direction | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2000 | 2005 | 2010 | 2015 | 2020 | ||
| Jixi | −1.17 | −1.08 | −0.72 | −0.69 | 0.76 | Negative → Positive |
| Shuangyashan | −1.64 | −1.17 | −0.98 | −0.81 | 0.79 | Negative → Positive |
| Daqing | −0.02 | 0.48 | 2.14 | 1.89 | 0.85 | Negative → Positive |
| Heihe | −0.86 | −0.84 | −0.76 | −0.43 | 0.57 | Negative → Positive |
| Jilin | 1.33 | 3.17 | −0.16 | −0.07 | −0.38 | Positive → Negative |
| Tieling | 0.74 | 0.30 | −0.03 | 0.34 | 0.20 | Positive → Negative |
| Chaoyang | −1.50 | 0.02 | −0.50 | −0.87 | −0.64 | Negative → Positive → Negative |
| Model Parameters | OLS | GWR | GTWR |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bandwidth | 592.984 | 0.150 | 0.140 |
| Residual Squares | 207.548 | 52.658 | 27.488 |
| Sigma | — | 0.513 | 0.371 |
| AICc | — | 442.980 | 482.061 |
| R2 | 0.855 | 0.963 | 0.981 |
| Model | Factors | Minimum | Maximum | Mean | Standard Deviation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GWR | Urbanization rate | −5.152 | 4.380 | −0.281 | 1.637 |
| Per capita GDP | −7.674 | 8.602 | −0.347 | 2.209 | |
| Per capita cropland area | −7.372 | 5.459 | −1.119 | 2.935 | |
| Grain crop area | −6.208 | 25.238 | 10.365 | 6.952 | |
| Agricultural labor | −6.157 | 13.096 | 1.495 | 4.396 | |
| Fertilizer consumption | −9.108 | 10.367 | 1.814 | 4.037 | |
| Average annual precipitation | −9.159 | 2.900 | −1.699 | 1.615 | |
| Average annual temperature | −4.541 | 7.551 | 1.063 | 2.056 | |
| GTWR | Urbanization rate | −4.877 | 2.236 | −0.371 | 1.344 |
| Per capita GDP | −4.185 | 1.981 | −0.992 | 1.202 | |
| Per capita cropland area | −6.300 | 3.796 | −0.870 | 2.663 | |
| Grain crop area | −0.374 | 22.757 | 9.836 | 6.494 | |
| Agricultural labor | −4.027 | 9.008 | 1.879 | 4.182 | |
| Fertilizer consumption | −6.420 | 6.068 | 1.208 | 2.972 | |
| Average annual precipitation | −3.594 | 1.879 | −1.347 | 0.951 | |
| Average annual temperature | −2.434 | 5.797 | 1.286 | 1.843 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Q.; Ren, J.; Zhang, M.; Sui, H.; Li, X. Synergistic Matching and Influencing Factors of Grain Production and Cropland Net Primary Productivity in the Black Soil Region of Northeast China. Agronomy 2024, 14, 2932. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14122932
Wang Q, Ren J, Zhang M, Sui H, Li X. Synergistic Matching and Influencing Factors of Grain Production and Cropland Net Primary Productivity in the Black Soil Region of Northeast China. Agronomy. 2024; 14(12):2932. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14122932
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Quanxi, Jun Ren, Maomao Zhang, Hongjun Sui, and Xiaodan Li. 2024. "Synergistic Matching and Influencing Factors of Grain Production and Cropland Net Primary Productivity in the Black Soil Region of Northeast China" Agronomy 14, no. 12: 2932. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14122932
APA StyleWang, Q., Ren, J., Zhang, M., Sui, H., & Li, X. (2024). Synergistic Matching and Influencing Factors of Grain Production and Cropland Net Primary Productivity in the Black Soil Region of Northeast China. Agronomy, 14(12), 2932. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14122932







