Residual Effects of Pig Slurry Fertilization in a Mediterranean Rainfed Cereal System
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Design and Agronomic Management
2.2. Estimation of Mineral N Fertilizer Equivalence in Years Following Slurry Application
2.3. Estimation of Residual Effects
2.4. Nitrogen Use Efficiency
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Grain Yield and Whole-Plant Nitrogen Uptake
3.2. Mineral N Fertilizer Equivalence in Years Following Slurry Application
3.3. Residual Effects
3.4. Nitrogen Use Efficiencies
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sutton, M.A.; Cordovil, C.M.d.S.; Dalgaard, T.; Howard, C.M.; Amon, B.; Bittman, S.; Misselbrook, T.; Oenema, O. Chapter I: Overview for policymakers. In Nitrogen Opportunities for Agriculture, Food & Environment. UNECE Guidance Document on Integrated Sustainable Nitrogen Management; Sutton, M.A., Howard, C.M., Mason, K.E., Brownlie, W.J., Cordovil, C.M.d.S., Eds.; UK Centre for Ecology & Hydrology: Edinburgh, UK, 2022; pp. 1–8. Available online: https://unece.org/sites/default/files/2022-11/UNECE_NitroOpps%20red.pdf (accessed on 29 September 2024).
- De Vries, W.; Kros, J.; Kroeze, C.; Seitzinger, S.P. Assessing planetary and regional nitrogen boundaries related to food security and adverse environmental impacts. Curr. Opin. Environ. Sustain. 2013, 5, 392–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oenema, O.; Brentrup, F.; Lammel, J.; Bascou, P.; Billen, G.; Dobermann, A.; Erisman, J.W.; Garnett, T.; Hammel, M.; Haniotis, T.; et al. Nitrogen Use Efficiency (NUE): An Indicator for the Utilisation of Nitrogen in Agriculture and Food Systems; Wageningen University and Alterra: Wageningen, The Netherlands, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- A Farm to Fork Strategy for a Fair, Healthy and Environmentally-Friendly Food System. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/?uri=CELEX%3A52020DC0381 (accessed on 24 September 2024).
- Circular Economy: The EU Aims to Transition to a Circular Economy to Make Europe Cleaner and More Competitive. Available online: https://environment.ec.europa.eu/topics/circular-economy_en (accessed on 9 September 2024).
- Eurostat: Agriculture Database. Available online: https://ec.europa.eu/eurostat/web/agriculture/database (accessed on 24 September 2024).
- Instituto Nacional de Estadística: Anurario Estadístico de España. 2017. Available online: http://www.ine.es/prodyser/pubweb/anuarios_mnu.htm (accessed on 24 September 2024).
- Webb, J.; Sørensen, P.; Velthof, G.; Amon, B.; Pinto, M.; Rodhe, L.; Salomon, E.; Hutchings, N.; Burczyk, P.; Reid, J. An assessment of the variation of manure nitrogen efficiency throughout Europe and an appraisal of means to increase manure-N efficiency. Adv. Agron. 2013, 119, 371–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shakoor, A.; Bosch-Serra, À.D.; Lidón, A.; Ginestar, D.; Boixadera, J. Soil mineral nitrogen dynamics in fallow periods in a rainfed semiarid Mediterranean agricultural system. Pedosph 2022, 33, 622–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonanomi, G.; Sarker, T.C.; Zotti, M.; Cesarano, G.; Allevato, E.; Mazzoleni, S. Predicting nitrogen mineralization from organic amendments: Beyond C/N ratio by 13C-CPMAS NMR approach. Plant Soil 2019, 441, 129–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pratt, P.F.; Broadbent, F.E.; Martin, J.P. Using organic wastes as organic fertilizers. Calif. Agric. 1973, 27, 10–13. [Google Scholar]
- Beauchamp, E.G.; Paul, J.W. A simple model to predict manure N availability to crops in the field. In Nitrogen in Organic Wastes Applied to Soils; Hansen, J.A.A., Henriksen, K., Eds.; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1989; pp. 140–149. [Google Scholar]
- Sørensen, P.; Amato, M. Remineralisation and residual effects of N after application of pig slurry. Eur. J. Agron. 2002, 16, 81–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiménez-de-Santiago, D.E.; Lidón, A.; Bosch-Serra, À.D. Soil water dynamics in a rainfed Mediterranean agricultural system. Water 2019, 11, 799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yagüe, M.R.; Quílez, D. Residual effects of fertilization with pig slurry: Double cropping and soil. Agron. J. 2013, 105, 70–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schröder, J.J.; Uenk, D.; Hilhorst, G.J. Long-term nitrogen fertilizer replacement value of cattle manures applied to cut grassland. Plant Soil 2007, 299, 83–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klausner, S.D.; Kanneganti, V.R.; Bouldin, D.R. An approach for estimating a decay series for organic nitrogen in animal manure. Agron. J. 1994, 86, 897–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sørensen, P.; Thomsen, I.K. Separation of pig slurry, and plant utilization, and loss of nitrogen 15-labeled slurry nitrogen. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2005, 69, 1644–1651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuchs, M.; Frick, H.; Moinet, G.Y.K.; Mayer, M.; Bünemann, E.K. Residual nitrogen from slurry and mineral fertiliser two years after application: Fractionation and plant availability. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2023, 177, 108908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berntsen, J.; Petersen, B.M.; Sørensen, P.; Olesen, J.E. Simulating residual effects of animal manures using 15N isotopes. Plant Soil 2007, 290, 173–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soil Survey Staff. Keys to Soil Taxonomy, 12th ed.; USDA-Natural Resources Conservation Service: Washington, DC, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Porta Casanellas, J.; López-Acevedo Reguerín, M.; Rodríguez Ochoa, R. Técnicas y Experimentos en Edafología; Col·legi Oficial d’Enginyers Agrònoms de Catalunya: Barcelona, Spain, 1986; pp. 59–67. Available online: https://www.iec.cat/mapasols/Cas/Llibre.asp?Id=6 (accessed on 12 October 2024).
- Pansu, M.; Gautheyrou, J. Chapter 29. Phosphorus. In Handbook of Soil Analysis. Mineralogical, Organic and Inorganic Methods; Pansu, M., Gautheyrou, J., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2003; p. 809. [Google Scholar]
- APHA. Nitrogen (ammonia): 4500-NH3 B, preliminary distillation step and 4500-NH3 C, titrimetric method. In Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater, 22nd ed.; Rice, E.W., Bridgewater, L., Eds.; American Public Health Association, American Water Works Association, Water Environment Federation: Washington, DC, USA, 2012; p. 4-110-111. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, S.K.C. Protein analysis. 9.2.1. Kjeldalh method. In Food Analysis, 4th ed.; Nielsen, S.S., Ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2010; pp. 136–137. [Google Scholar]
- Muñoz, G.R.; Kelling, K.A.; Powell, J.M.; Speth, P.E. Comparison of estimates of first-year dairy manure nitrogen availability or recovery using nitrogen-15 and other techniques. J. Environ. Qual. 2004, 33, 719–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schröder, J.J.; Jansen, A.G.; Hilhorst, G.J. Long-term nitrogen supply from cattle slurry. Soil Use Manag. 2005, 21, 196–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cusick, P.R.; Kelling, K.A.; Powell, J.M.; Muñoz, G.R. Estimates of residual dairy manure nitrogen availability using various techniques. J. Environ. Qual. 2006, 35, 2170–2177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SAS Institute. Statistical Analysis System, SAS/TAT. Software V 9.4; SAS Institute: Cary, NC, USA, 2014.
- Yagüe, M.R.; Bosch-Serra, À.D.; Boixadera, J. Measurement and estimation of the fertiliser value of pig slurry by physicochemical models: Usefulness and constraints. Biosyst. Eng. 2012, 111, 206–2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menzi, H. Manure management in Europe: Results of a recent survey. In Proceedings of the 10th FAO/ESCORENA Network on Recycling Agricultural, Municipal and Industrial Residues in Agriculture (RAMIRAN), Štrbské, Pleso, Slovakia, 14–18 May 2002; Venglovský, J., Gréserová, G., Eds.; University of Veterinary Medicine: Košice, Slovakia, 2002; pp. 93–102. Available online: https://ramiran.uvlf.sk/index.php?page=content (accessed on 29 September 2024).
- Blum, A. Improving wheat grain filling under stress by stem reserve mobilisation. Euphyt 1998, 100, 77–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortiz, C.; Yagüe, M.R.; Valdez, A.S.; Molina, M.G.; Bosch-Serra, À.D. Sustainability of Organic Fertilizers Use in Dryland Mediterranean Agriculture. Agriculture 2024, 14, 1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedersen, B.N.; Christensen, B.T.; Bechini, L.; Cavalli, D.; Eriksen, J.; Sørensen, P. Nitrogen Fertilizer Value of Animal Slurries with Different Proportions of Liquid and Solid Fractions: A 3-Year Study under Field Conditions. J. Agric. Sci. 2020, 158, 707–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morell, F.J.; Lampurlanés, J.; Álvaro-Fuentes, J.; Cantero-Martínez, C. Yield and water use efficiency of barley in a semiarid Mediterranean agroecosystem: Long-term effects of tillage and N fertilization. Soil Tillage Res. 2011, 117, 76–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tambussi, E.A.; Bort, J.; Araus, J.L. Water use efficiency in C3 cereals under Mediterranean conditions: A review of physiological aspects. Ann. Appl. Biol. 2007, 150, 307–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, J.W.; Beauchamp, E.G. Nitrogen availability for corn in soils amended with urea, cattle slurry, and solid and composted manures. Can. J. Soil Sci. 1993, 73, 253–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yagüe, M.R.; Quílez, D. Direct, and residual response of wheat to swine slurry application method. Nutr. Cycl. Agroecosyst. 2010, 86, 161–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sørensen, P. Immobilisation, remineralisation, and residual effects in subsequent crops of dairy cattle slurry nitrogen compared to mineral fertiliser nitrogen. Plant Soil 2004, 267, 285–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fertilització de Cobertora en Cereal d’Hivern: Beneficis i Danys. Available online: https://ruralcat.gencat.cat/documents/20181/5961791/41_Fertilitzaci%C3%B3_cobertora_CH_Beneficis_danys_ACC.pdf/e304696e-a5d2-4441-9d53-fb8965bfd5bd (accessed on 30 September 2024).
- Bosch-Serra, A.D.; Ortiz, C.; Yagüe, M.R.; Boixadera, J. Strategies to optimize nitrogen efficiency when fertilizing with pig slurries in dryland agricultural systems. Eur. J. Agron. 2015, 67, 27–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yagüe, M.R.; Valdez, A.S.; Bosch-Serra, A.D.; Ortiz, C.; Castellví, F. A short-term study to compare field strategies for ammonia emission mitigation. J. Environ. Qual. 2019, 48, 179–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Noor, H.; Noor, F.; Ding, P.; Sun, M.; Gao, Z. Effect of soil water and nutrient uptake on nitrogen use efficiency, and yield of winter wheat. Agronomy 2024, 14, 819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

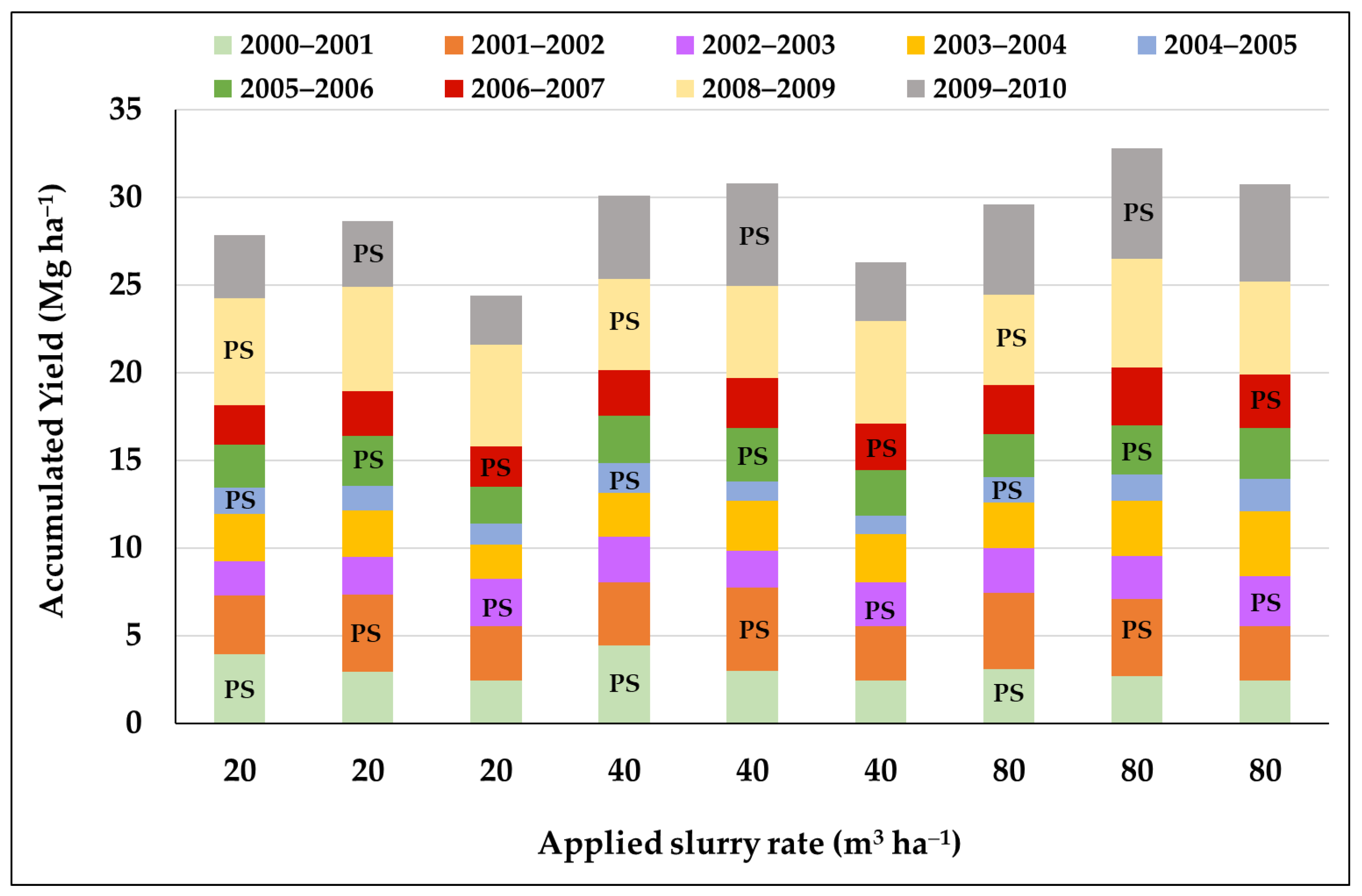
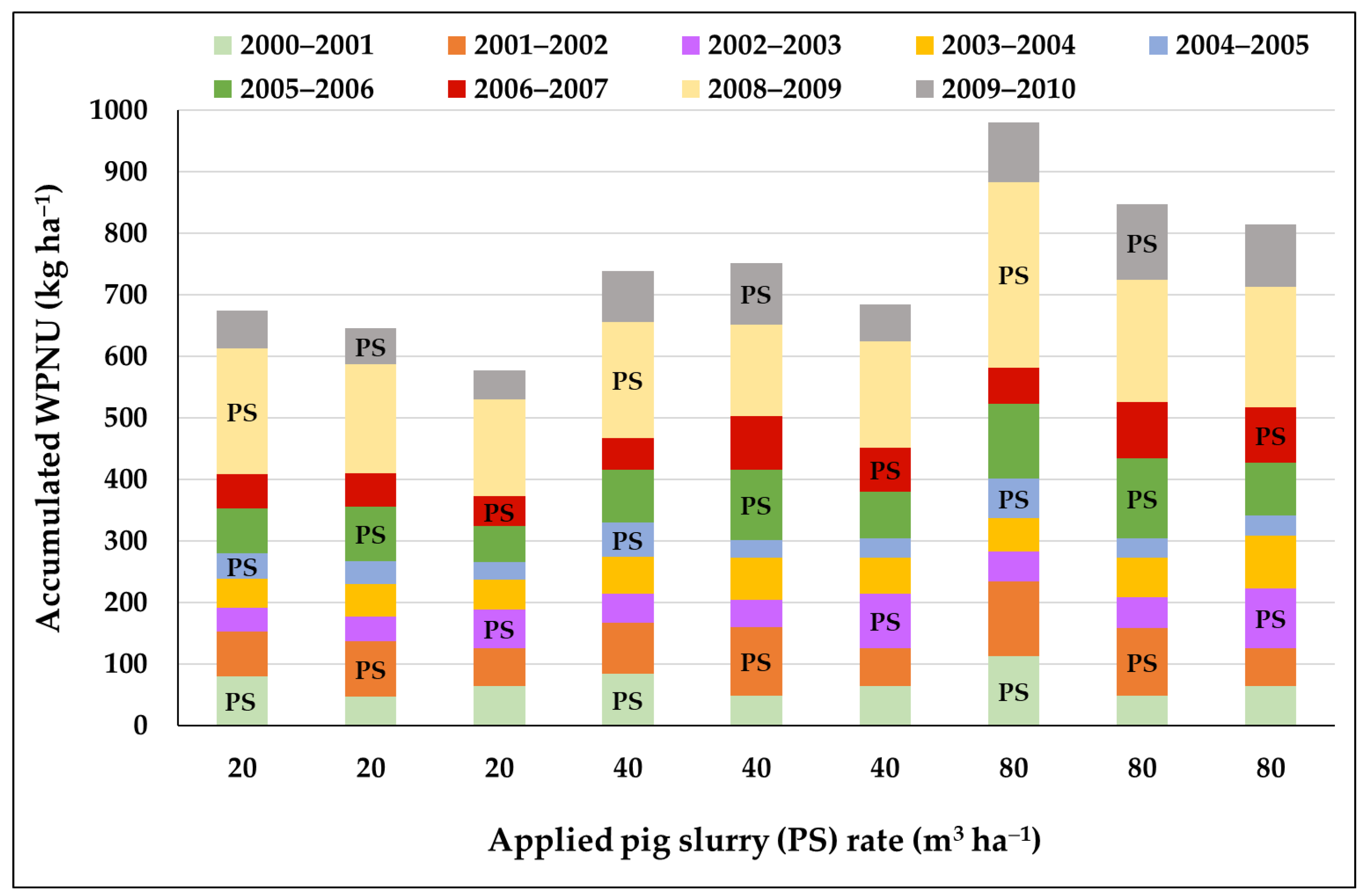
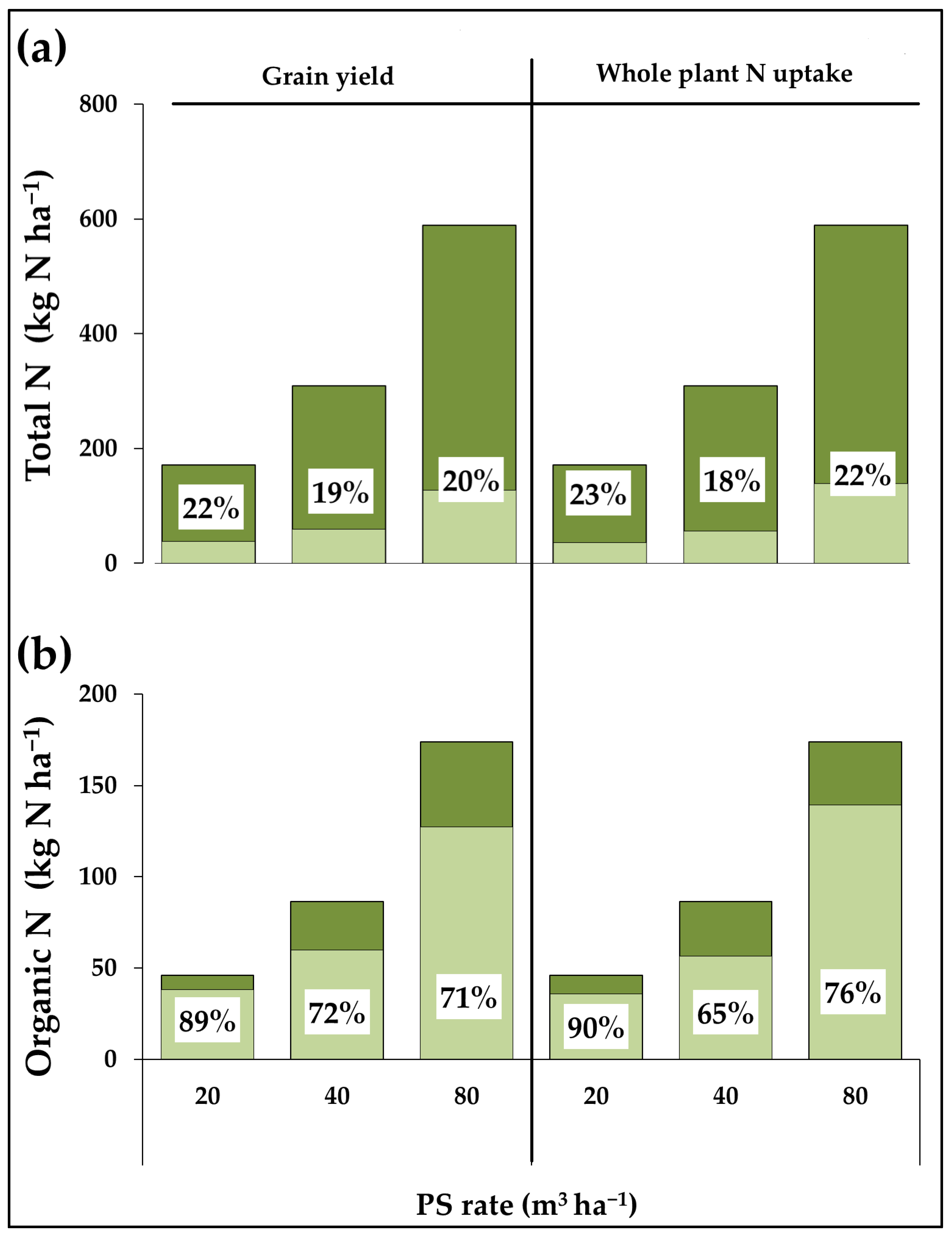
| Growing Season | 2000/01 | 2001/02 | 2002/03 | 2003/04 | 2004/05 | 2005/06 | 2006/07 | 2007/08 | 2008/09 | 2009/10 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Crop | Barley | Barley | Wheat | Barley | Barley | Wheat | Barley | Fallow | Wheat | Barley |
| Sowing | 05/11/00 | 08/11/01 | 31/10/02 | 30/10/03 | 16/11/04 | 04/11/06 | 04/11/06 | - | 10/11/08 | 03/11/09 |
| Harvest | 18/06/01 | 28/06/02 | 26/06/03 | 26/06/04 | 01/07/05 | 27/06/06 | 26/06/07 | - | 04/07/09 | 01/07/10 |
| Treatments | Growing Seasons | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2000/01 | 2001/02 | 2002/03 | 2003/04 | 2004/05 | 2005/06 | 2006/07 | 2007/08 | 2008/09 | 2009/10 | |
| MN 2 (kg of N ha−1) | 0 + 30 | 0 + 30 | 0 + 30 | 0 + 30 | 0 + 30 | 0 + 30 | 0 + 30 | F | 0 + 30 | 0 + 30 |
| 30 + 30 | 30 + 30 | 30 + 30 | 30 + 30 | 30 + 30 | 30 + 30 | 30 + 30 | F | 30 + 30 | 30 + 30 | |
| 30 + 60 | 30 + 60 | 30 + 60 | 30 + 60 | 30 + 60 | 30 + 60 | 30 + 60 | F | 30 + 60 | 30 + 60 | |
| 30 + 120 | 30 + 120 | 30 + 120 | 30 + 120 | 30 + 120 | 30 + 120 | 30 + 120 | F | 30 + 120 | 30 + 120 | |
| PS 3 (m3 ha−1) | 20 (284/61) | RE1 | RE2 | RE3 | 20 (138/41) | RE1 | RE2 | F | 20 (105/27) | RE1 |
| 40 (495/117) | RE1 | RE2 | RE3 | 40 (250/83) | RE1 | RE2 | F | 40 (187/48) | RE1 | |
| 80 (851/210) | RE1 | RE2 | RE3 | 80 (534/194) | RE1 | RE2 | F | 80 (424/110) | RE1 | |
| 0 | 20 (179/31) | RE1 | RE2 | RE3 | 20 (143/41) | RE1 | F | RE3 | 20 (119/33) | |
| 0 | 40 (299/57) | RE1 | RE2 | RE3 | 40 (312/83) | RE1 | F | RE3 | 40 (239/67) | |
| 0 | 80 (498/108) | RE1 | RE2 | RE3 | 80 (633/194) | RE1 | F | RE3 | 80 (477/133) | |
| 0 | 0 | 20 (231/66) | RE1 | RE2 | RE3 | 20 (170/66) | F | RE2 | RE3 | |
| 0 | 0 | 40 (402/132) | RE1 | RE2 | RE3 | 40 (290/113) | F | RE2 | RE3 | |
| 0 | 0 | 80 (743/264) | RE1 | RE2 | RE3 | 80 (551/212) | F | RE2 | RE3 | |
| Parameter | 2000 | 2001 | 2002 | 2004 | 2005 | 2006 | 2008 | 2009 | Mean |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH (1:2.5) | 8.0 | 7.7 | 7.8 | 8.7 | 8.6 | 8.3 | 8.2 | 8.7 | 8.3 |
| DM (g kg−1) | 83 | 35 | 105 | 94 | 109 | 78 | 80 | 93 | 84 |
| Total N (kg of N m−3) | 8.3 | 4.7 | 6.8 | 8.8 | 8.9 | 8.1 | 7.3 | 6.7 | 7.7 |
| NH4+-N (kg of N m−3) | 6.1 | 3.6 | 4.2 | 6.1 | 6.9 | 5.0 | 5.4 | 5.0 | 5.4 |
| Organic N (kg of N m−3) | 2.2 | 1.1 | 2.6 | 2.7 | 2.0 | 3.1 | 1.9 | 1.7 | 2.3 |
| Year | Grain Yield (kg ha−1) | R2 | Whole-Plant N Uptake (kg ha−1) | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2000/01 | Y = 2575.12 + 25.0437x − 0.119107x2 | 0.68 | Y = 65.38 + 1.07x − 0.00438x2 | 0.76 |
| 2001/02 | Y = 2708.08 + 26.716x − 0.136887x2 | 0.58 | Y = 56.39 + 0.87x − 0.00326x2 | 0.84 |
| 2002/03 | Y = 1765.75 + 15.3512x − 0.0762058x2 | 0.61 | Y = 30.66 + 0.54x − 0.00097x2 | 0.83 |
| 2003/04 | Y = 2313.07 + 33.9637x − 0.178394x2 | 0.91 | Y = 65.34 + 0.69x − 0.00269x2 | 0.56 |
| 2004/05 | Y = 1215.7 + 11.8717x − 0.0739383x2 | 0.69 | Y = 29.37 + 0.36x − 0.00134x2 | 0.64 |
| 2005/06 | Y = 2182.53 + 11.166x − 0.0325398x2 | 0.91 | Y = 67.00 + 0.55x − 0.00202x2 | 0.51 |
| 2006/07 | Y = 1921.3 + 31.7152x − 0.201552x2 | 0.84 | Y = 40.76 + 1.21x − 0.00598x2 | 0.91 |
| 2007/08 | Fallow period | - | Fallow period | - |
| 2008/09 | Y = 4599.93 + 30.0266x − 0.164394x2 | 0.63 | Y = 123.41 + 2.23x − 0.01069x2 | 0.55 |
| 2009/10 | Y = 3238.4 + 79.0387x − 0.371552x2 | 0.86 | Y = 52.93 + 2.27x − 0.01235x2 | 0.84 |
| Year | PS Rate | MNFE Based on Grain Yield 1 | MNFE Based on Whole-Plant Nitrogen Uptake | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (m3 ha−1) | (kg of N ha−1) | (kg of N ha−1) | |||||||||||
| 2002 | 2004 | 2007 | 2010 | 2002 | 2003 | 2004 | 2005 | 2006 | 2007 | 2009 | 2010 | ||
| Yr1 | 20 | 28.7 | 2.7 | 24.3 | 6.5 | 22.3 | 17.1 | 0.0 | - | 25.5 | 11.9 | - | 5.2 |
| 40 | 55.8 | 20.2 | 36.7 | 21.9 | 39.4 | 21.7 | 2.6 | - | 49.8 | 44.7 | - | 14.3 | |
| 80 | 121.3 | 54.9 | 69.4 | 31.7 | 124.6 | 46.0 | 35.4 | - | 240.1 | 52.1 | - | 23.3 | |
| Yr2 | 20 | - | 11.2 | 18.0 | - | - | 14.9 | 0.0 | 0.0 | - | 17.8 | 19.8 | - |
| 40 | - | 12.6 | 27.2 | - | - | 31.2 | 3.3 | 14.8 | - | 9.3 | 26.3 | - | |
| 80 | - | 20.8 | 40.4 | - | - | 38.0 | 0.0 | Nd | - | 17.3 | 46.7 | - | |
| Yr3 | 20 | - | 16.1 | - | 0.0 | - | - | 0.0 | 26.5 | 3.5 | - | 27.7 | 0.0 |
| 40 | - | 5.6 | - | 6.8 | - | - | 0.7 | 7.7 | 23.4 | - | 16.0 | 6.2 | |
| 80 | - | 19.3 | - | 35.5 | - | - | 6.8 | 13.1 | 38.9 | - | 50.1 | 25.1 | |
| Year | PS Rate | RE Based on GY | RE Based on WPNU | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (RE) | (m3 ha−1) | (%, Over Total N Applied) | (%, Over Total N Applied) | ||||||||||||
| 2002 | 2004 | 2007 | 2010 | Mean | 2002 | 2003 | 2004 | 2005 | 2006 | 2007 | 2009 | 2010 | Mean | ||
| Yr1 | 20 | 10.1 | 1.1 | 16.9 | 6.7 | 8.7 | 7.9 | 9.6 | 0.0 | - | 20.8 | 9.1 | - | 5.6 | 8.8 |
| (RE1) | 40 | 11.3 | 5.0 | 12.2 | 11.7 | 10.0 | 7.9 | 7.3 | 0.6 | - | 19.9 | 14.9 | - | 7.6 | 9.7 |
| 80 | 13.8 | 7.4 | 11.0 | 8.3 | 10.1 | 14.4 | 9.3 | 4.8 | - | 42.9 | 8.3 | - | 6.0 | 14.3 | |
| Yr2 | 20 | - | 6.2 | 14.7 | - | 10.4 | - | 5.2 | 0.0 | 0.0 | - | 14.6 | 13.2 | - | 6.6 |
| (RE2) | 40 | - | 4.2 | 10.8 | - | 7.5 | - | 6.3 | 1.1 | 3.7 | - | 3.6 | 9.1 | - | 4.8 |
| 80 | - | 4.2 | 7.8 | - | 6.0 | - | 4.3 | 0.0 | Nd | - | 3.3 | 8.5 | - | 4.0 | |
| Yr3 | 20 | - | 5.7 | - | 0.0 | 2.8 | - | - | 0.0 | 14.8 | 1.5 | - | 19.6 | 0.0 | 7.2 |
| (RE3) | 40 | - | 1.1 | - | 2.2 | 1.7 | - | - | 0.1 | 2.6 | 6.0 | - | 4.6 | 2.1 | 3.1 |
| 80 | - | 2.2 | - | 6.4 | 4.3 | - | - | 0.8 | 2.6 | 5.2 | - | 7.4 | 4.5 | 4.1 | |
| Year | PS Rate | RE Based on GY | RE Based on WPNU | ||||||||||||
| (RE) | (m3 ha−1) | (%, Over the Organic N Applied) | (%, Over the Organic N Applied) | ||||||||||||
| 2002 | 2004 | 2007 | 2010 | Mean | 2002 | 2003 | 2004 | 2005 | 2006 | 2007 | 2009 | 2010 | Mean | ||
| Yr1 | 20 | 47.1 | 3.8 | 58.2 | 26.5 | 33.9 | 36.5 | 55.6 | 0.0 | - | 68.7 | 31.4 | - | 21.9 | 35.7 |
| (RE1) | 40 | 47.8 | 15.4 | 45.8 | 45.3 | 38.6 | 33.7 | 38.1 | 1.8 | - | 65.7 | 55.9 | - | 29.5 | 37.4 |
| 80 | 55.2 | 21.0 | 35.9 | 32.1 | 36.1 | 58.4 | 42.8 | 13.7 | - | 141.4 | 27.0 | - | 23.3 | 51.1 | |
| Yr2 | 20 | - | 36.3 | 48.3 | - | 42.3 | - | 24.4 | 0.0 | 0.0 | - | 48.0 | 37.8 | - | 22.1 |
| (RE2) | 40 | - | 22.1 | 35.6 | - | 28.8 | - | 26.7 | 5.8 | 11.7 | - | 12.0 | 24.3 | - | 16.1 |
| 80 | - | 19.3 | 25.5 | - | 22.4 | - | 16.8 | 0.0 | Nd | - | 10.8 | 21.2 | - | 12.2 | |
| Yr3 | 20 | - | 26.3 | - | 0.0 | 13.2 | - | - | 0.0 | 86.0 | 5.5 | - | 67.5 | 0.0 | 31.8 |
| (RE3) | 40 | - | 4.8 | - | 5.2 | 5.0 | - | - | 0.6 | 13.4 | 18.7 | - | 17.1 | 5.3 | 11.0 |
| 80 | - | 8.5 | - | 16.6 | 12.6 | - | - | 3.1 | 11.9 | 14.7 | - | 23.5 | 11.8 | 13.0 | |
| Time | PS Rate | NUEs at Different Harvests | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (m3 ha−1) | 2001 | 2002 | 2003 | 2004 3 | 2005 | 2006 | 2007 | 2008 | 2009 | 2010 | |
| Yr0 | 20 | 0.28 | 0.50 | 0.27 | - | 0.31 | 0.62 | 0.32 | Fallow | 2.03 | 0.50 |
| 40 | 0.17 | 0.37 | 0.22 | - | 0.22 | 0.36 | 0.25 | Fallow | 1.00 | 0.42 | |
| 80 | 0.13 | 0.22 | 0.13 | - | 0.12 | 0.18 | 0.17 | Fallow | 0.73 | 0.26 | |
| Yr0+1 | 20 | - | 0.54 | 0.69 | 1.00 | - | 0.83 | 1.05 | Fallow | - | 2.64 |
| 40 | - | 0.36 | 0.53 | 0.77 | - | 0.57 | 0.61 | Fallow | - | 1.45 | |
| 80 | - | 0.28 | 0.33 | 0.38 | - | 0.35 | 0.32 | Fallow | - | 0.97 | |
| Yr0+1+2 | 20 | - | - | 0.67 | 1.00 | 1.65 | - | 1.23 | Fallow | 1.46 | - |
| 40 | - | - | 0.45 | 0.76 | 1.22 | - | 0.76 | Fallow | 0.85 | - | |
| 80 | - | - | 0.33 | 0.45 | Nd | - | 0.46 | Fallow | 0.49 | - | |
| Yr0+1+2+3 | 20 | - | - | - | 0.84 | 1.20 | 2.62 | - | Fallow | - | 1.77 |
| 40 | - | - | - | 0.57 | 0.86 | 1.87 | - | Fallow | - | 1.05 | |
| 80 | - | - | - | 0.40 | 0.52 | Nd | - | Fallow | - | 0.67 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ortiz, C.; Boixadera, J.; Bosch-Serra, À.D. Residual Effects of Pig Slurry Fertilization in a Mediterranean Rainfed Cereal System. Agronomy 2024, 14, 2552. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14112552
Ortiz C, Boixadera J, Bosch-Serra ÀD. Residual Effects of Pig Slurry Fertilization in a Mediterranean Rainfed Cereal System. Agronomy. 2024; 14(11):2552. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14112552
Chicago/Turabian StyleOrtiz, Carlos, Jaime Boixadera, and Àngela D. Bosch-Serra. 2024. "Residual Effects of Pig Slurry Fertilization in a Mediterranean Rainfed Cereal System" Agronomy 14, no. 11: 2552. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14112552
APA StyleOrtiz, C., Boixadera, J., & Bosch-Serra, À. D. (2024). Residual Effects of Pig Slurry Fertilization in a Mediterranean Rainfed Cereal System. Agronomy, 14(11), 2552. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14112552






