Combined Application of Biochar and Calcium Superphosphate Can Effectively Immobilize Cadmium and Reduce Its Uptake by Cabbage
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Characterization
2.2. Experiment Design and Methods
2.3. Data Analysis
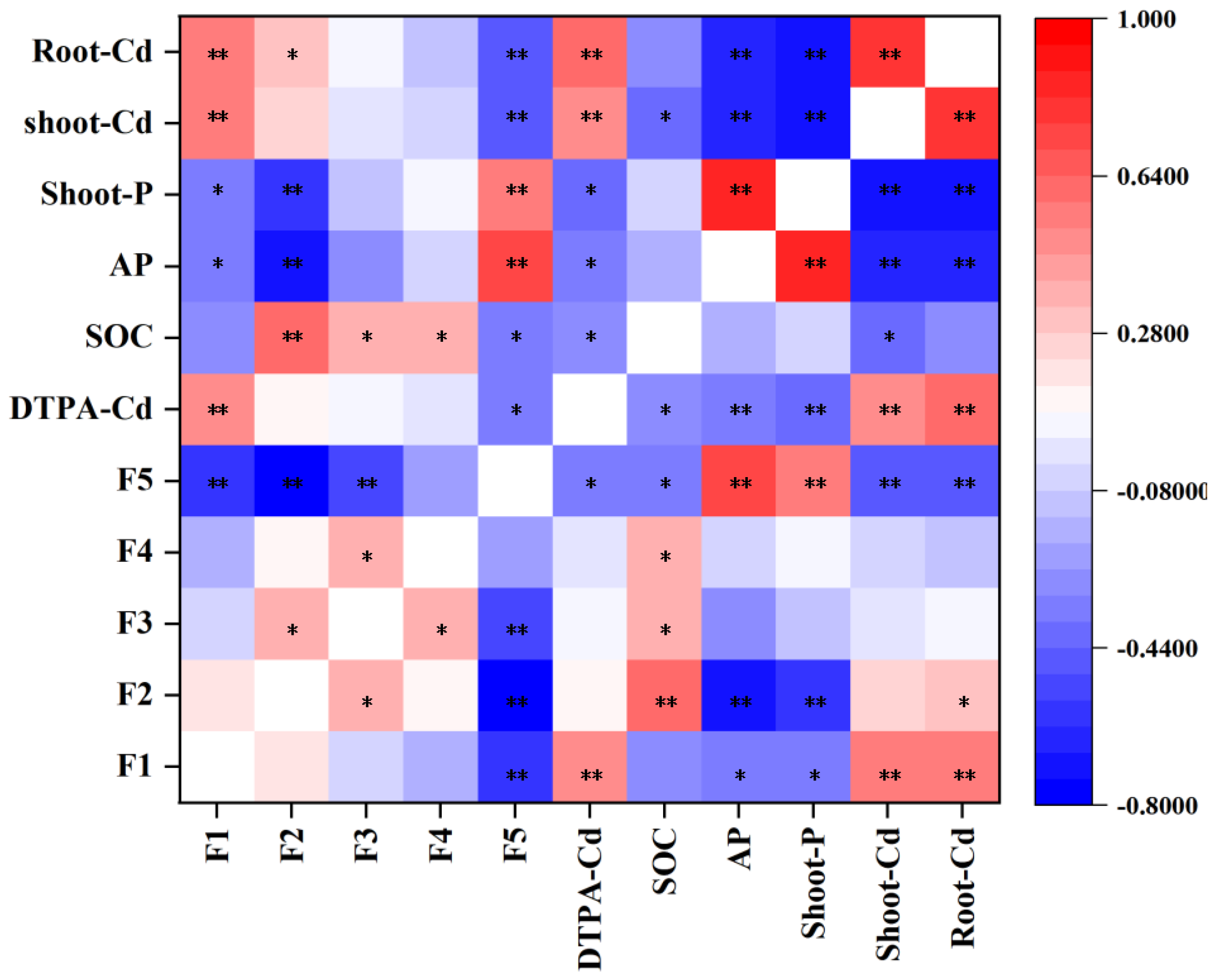
3. Results
3.1. Cd Uptake by Cabbage Under Amendment Application
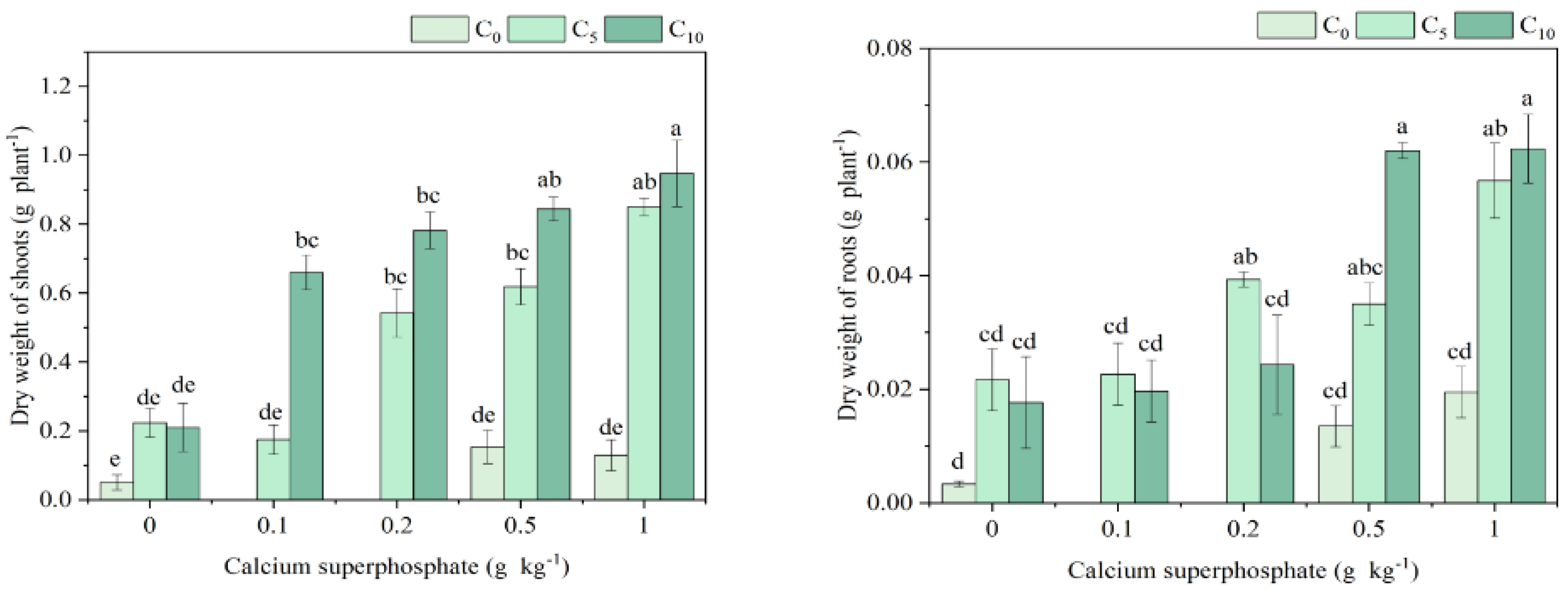
3.2. Plant Biomass Under Amendment Application
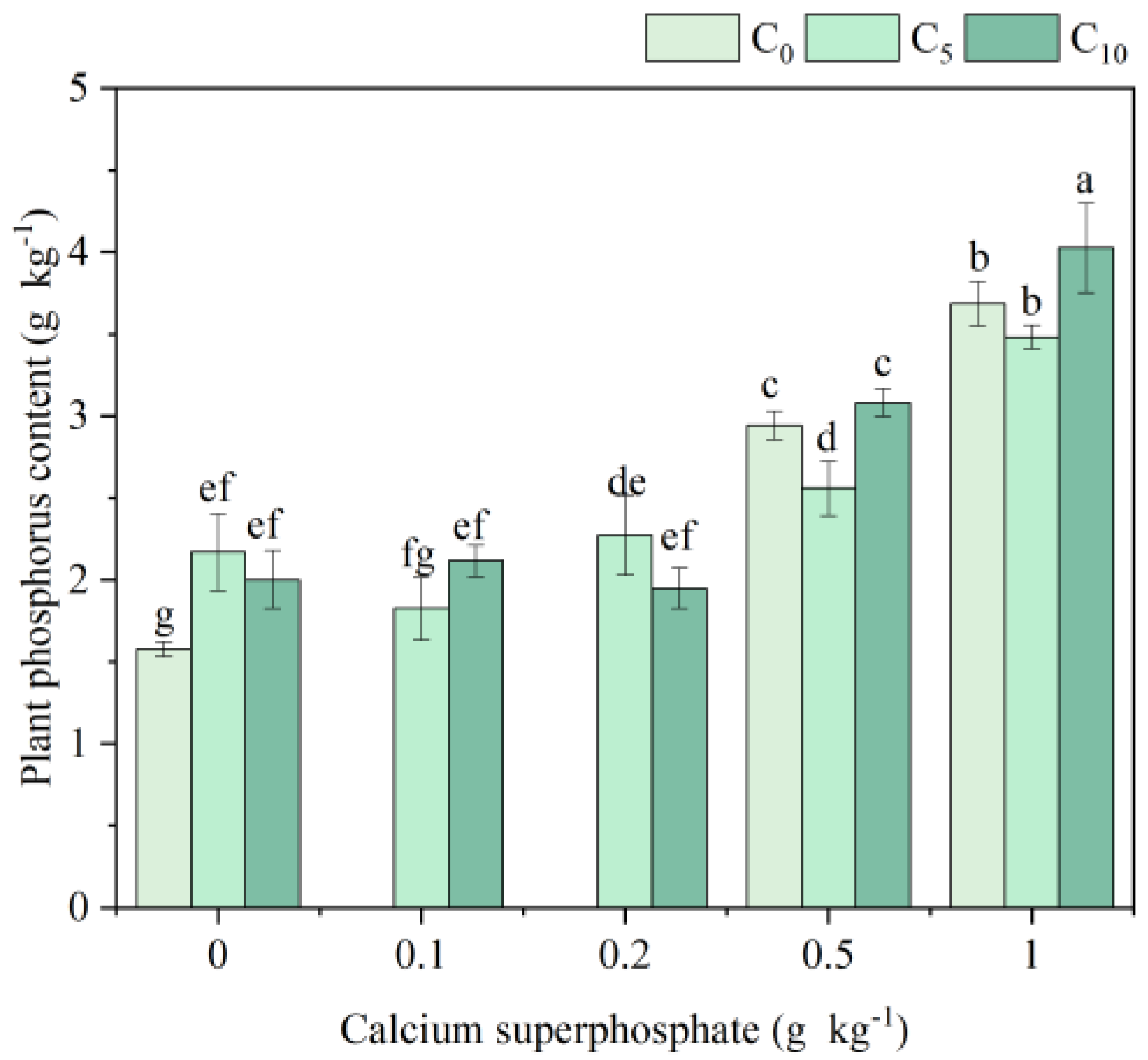
3.3. Physiological Indexes and Phosphorus Content of Cabbage Under Amendments Application
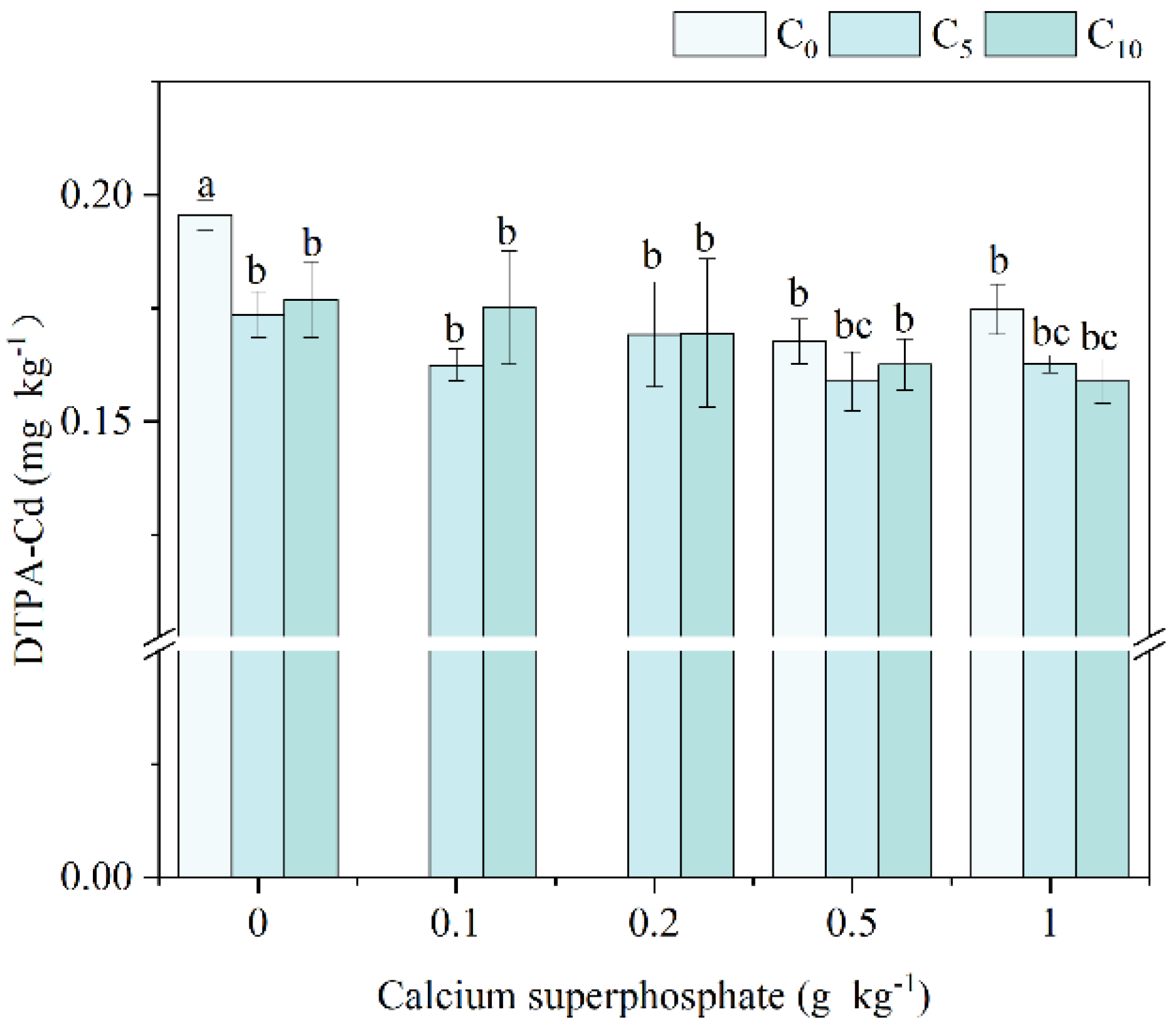
3.4. DTPA-Cd and Cd Fractionation for Contaminated Soil Under Amendments Application
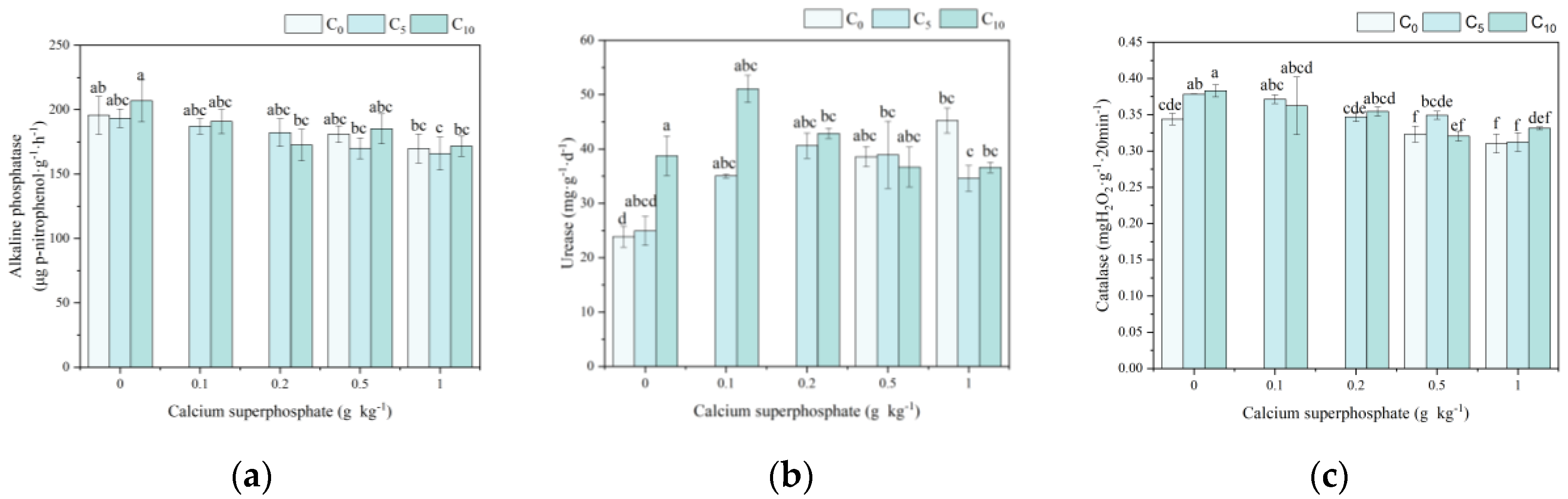
3.5. Chemical Properties of Soil Under Amendments Application
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jiang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Yi, X.T.; Zeng, P.; Liao, B.H.; Zhou, H.; Gu, J.F. Regulation of rhizosphere microenvironment by rice husk ash for reducing the accumulation of cadmium and arsenic in rice. J. Environ. Sci. 2023, 136, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.; Huang, D.; Liu, X.M.; Meng, J.; Tang, C.X.; Xu, J.M. Remediation of As(III) and Cd(II) co-contamination and its mechanism in aqueous systems by a novel calcium-based magnetic biochar. J. Hazard. Mater. 2018, 348, 10–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.H.; Xiao, C.F.; Wang, F.; Peng, L.; Zeng, Q.R. Assessment of the potential for phytoremediation of cadmium polluted soils by various crop rotation patterns based on the annual input and output fluxes. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 423, 127183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.J.; Tian, G.J.; Jiang, D.; Zhang, C.; Kong, L.Q. Cadmium (Cd) distribution and contamination in Chinese paddy soils on national scale. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 17941–17952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.Y.; Teng, Y.G.; Lu, S.J.; Wang, Y.Y.; Wang, J.S. Contamination features and health risk of soil heavy metals in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 512–513, 143–153. [Google Scholar]
- Gupta, D.K.; Pena, L.B.; Romero-Puertas, M.C.; Hernández, A.; Inouhe, M.; Sandalio, L.M. NADPH oxidases differentially regulate ROS metabolism and nutrient uptake under cadmium toxicity. Plant Cell Environ. 2017, 40, 509–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.Z.; Li, Z.T.; Huang, D.; Liu, X.M.; Tang, C.X.; Parikh, S.J.; Xu, J.M. A novel calcium-based magnetic biochar is effective in stabilization of arsenic and cadmium co-contamination in aerobic soils. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 387, 122010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bashir, S.; Hussain, Q.; Akmal, M.; Riaz, M.; Hu, H.H.; Ijaz, S.; Iqbal, M.; Abro, S.; Mehmood, S.; Ahmad, M. Sugarcane bagasse-derived biochar reduces the cadmium and chromium bio-availability to mash bean and enhances the microbial activity in contaminated soil. J. Soils Sediments 2018, 18, 874–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.K.; Wang, Q.; Zhou, Q.Y.; Ma, L.Y.; Wu, T.J.; Liu, Q.Z.; Wang, S.; Feng, Y. Cadmium uptake from soil and transport by leafy vegetables: A meta-analysis. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 264, 114677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, S.; Ji, X.; Xie, Y.; Liu, S.; Tian, F.; Liu, X. Influence of soil properties on cadmium accumulation in vegetables: Thresholds, prediction and pathway models based on big data. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 304, 119225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.F.; Liu, M.H.; Li, Y.; Che, Y.Y.; Xiao, Y. Effects of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi, biochar and cadmium on the yield and element uptake of Medicago sativa. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 655, 1150–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, F.; Liu, H.; Zhong, H.; Dong, L.; Tang, Y.; Ge, Y. Effects of biochar combined with nitrogen fertilizer on ryegrass remediation of cadmium-contaminated soil. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2024, 21, 4201–4212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zong, Y.; Chen, H.; Malik, Z.; Xiao, Q.; Lu, S. Comparative study on the potential risk of contaminated-rice straw, its derived biochar and phosphorus modified biochar as an amendment and their implication for environment. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 293, 118515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bashir, S.; Hussain, Q.; Shaaban, M.; Hu, H. Efficiency and surface characterization of different plant derived biochar for cadmium (Cd) mobility, bioaccessibility and bioavailability to Chinese cabbage in highly contaminated soil. Chemosphere 2018, 211, 632–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomes, F.P.; Soares, M.B.; Amoozegar, A.; Alleoni, L.R.F. How Does the Use of Biochar, Phosphate, Calcite, and Biosolids Affect the Kinetics of Cadmium Release in Contaminated Soil? Water Air Soil Pollut. 2023, 234, 439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amirahmadi, E.; Ghorbani, M.; Moudrý, J. Effects of Zeolite on Aggregation, Nutrient Availability, and Growth Characteristics of Corn (Zea mays L.) in Cadmium-Contaminated Soils. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2022, 233, 436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Wang, L.; Qu, G.; Liu, X.; Lian, Y.; Hou, D. Soil health improvement in a karst area with geogenic Cd enrichment using biochar and clay-based amendments. J Soils Sediments 2024, 24, 230–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.; Yang, Z.X.; Tang, L.; Zeng, G.M.; Yu, M.; Li, X.D.; Wu, H.P.; Qian, Y.Y.; Li, X.M.; Luo, Y. Changes in heavy metal mobility and availability from contaminated wetland soil remediated with combined biochar-compost. Chemosphere 2017, 181, 281–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehmann, J.; Rillig, M.C.; Thies, J.; Masiello, C.A.; Hockaday, W.C.; Crowley, D. Biochar effects on soil biota—A review. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2011, 43, 1812–1836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, M.; Rajapaksha, A.U.; Lim, J.E.; Zhang, M.; Bolan, N.; Mohan, D.; Vithanage, M.; Lee, S. Biochar as a sorbent for contaminant management in soil and water: A review. Chemosphere 2014, 99, 19–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zong, Y.T.; Xiao, Q.; Lu, S.G. Biochar derived from cadmium-contaminated rice straw at various pyrolysis temperatures: Cadmium immobilization mechanisms and environmental implication. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 321, 124459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Chen, Z.; Xu, W.; Liao, Q.; Zhang, H.; Hao, S.; Chen, S. Pyrolysis of various phytoremediation residues for biochars: Chemical forms and environmental risk of Cd in biochar. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 299, 122581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, T.; Meng, J.; Jeyakumar, P.; Cao, T.; Liu, Z.; He, T.; Cao, X.; Chen, W.; Wang, H. Effect of pyrolysis temperature on the bioavailability of heavy metals in rice straw-derived biochar. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2021, 28, 2198–2208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiros, G.T.Y.; Hailu, A.M.; Asfaw, S.L.; Mekonnen, S.Y. The effect of brewery sludge biochar on immobilization of bio-available cadmium and growth of Brassica carinata. Heliyon 2020, 6, e05573. [Google Scholar]
- Sigua, G.C.; Novak, J.M.; Watts, D.W.; Johnson, M.G.; Spokas, K. Efficacies of designer biochars in improving biomass and nutrient uptake of winter wheat grown in a hard setting subsoil layer. Chemosphere 2016, 42, 176–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, Q.; Zhao, J.W.; Li, J.X.; Liu, Y.K.; Luo, J.P.; Yuan, S.; Li, B.; Li, Q.Q.; Xu, X.F.; Huang, H.; et al. Unique root exudate tartaric acid enhanced cadmium mobilization and uptake in Cd-hyperaccumulator Sedum alfredii. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 383, 121177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, G.; Wan, J.; Huang, D.; Hu, L.; Huang, C.; Cheng, M.; Xue, W.; Gong, X.; Wang, R.; Jiang, D. Precipitation, adsorption and rhizosphere effect: The mechanisms for Phosphate-induced Pb immobilization in soils—A review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2017, 339, 354–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, M.; Zhao, Z.; Chen, L.; Wang, L.; Ji, L.; Xiao, Y. Influences of arbuscular mycorrhizae, phosphorus fertiliser and biochar on alfalfa growth, nutrient status and cadmium uptake—Sciencedirect. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 196, 110537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, M.; Shi, H.; Zhao, X.; Yu, Y.; Qu, B. Immobilization of Pb and Cd in contaminated soil using nano-crystallite hydroxyapatite. Procedia Environ. Sci. 2013, 18, 657–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.U.; Owens, V.N.; Kim, Y.G.; Lee, S.M.; Park, H.C.; Kim, K.K.; Joo, S.H.; Hong, C.O. Effect of phosphate addition on cadmium precipitation and adsorption in contaminated arable soil with a low concentration of cadmium. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2015, 95, 675–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Gong, J.L.; Zeng, G.M.; Niu, Q.Y.; Zhang, H.Y.; Niu, C.G.; Deng, J.H.; Yan, M. Adsorption of Cd (II) and Zn (II) from aqueous solutions using magnetic hydroxyapatite nanoparticles as adsorbents. Chem. Eng. J. 2010, 162, 487–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, W.W.; Wu, Y.Y.; Zhang, C.N.; Dilinuer, Y.; Pasang, L.; Lu, Y.Q.; Wang, Y.H.; Chen, H.M.; Li, C. Combination of Biochar and Phosphorus Solubilizing Bacteria to Improve the Stable Form of Toxic Metal Minerals and Microbial Abundance in Lead/Cadmium-Contaminated Soil. Agronomy 2022, 12, 1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.H.; Che, Y.Y.; Wang, L.Q.; Zhao, Z.J.; Zhang, Y.C.; Wei, L.L.; Xiao, X. Rice straw biochar and phosphorus inputs have more positive effects on the yield and nutrient uptake of Lolium multiflorum than arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi in acidic Cd-contaminated soils. Chemosphere 2019, 235, 32–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, S.; Hu, Z.; Huang, Y.; Hu, Y.; Pan, H. Evaluation of several phosphate amendments on rare earth element concentrations in rice plant and soil solution by X-ray diffraction. Chemosphere 2019, 236, 124322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, C.R.; Lei, W.X.; Wang, S.J.; Xie, G.X.; Qiu, D. Biochar and arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi promote rapid-cycling Brassica napus growth under cadmium stress. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 953, 953176034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.F.; Zhang, S.R.; Ding, X.D. Biochar combined with phosphate fertilizer application reduces soil cadmium availability and cadmium uptake of maize in Cd-contaminated soils. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 29, 25925–25938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.Z.; Peng, X.Y.; Lai, L.Y.; Li, H.; Zhang, X.Y.; Chen, H.X.; Xie, L.T. Phosphorus fertilization regimes and rates alter Cd extractability in rhizospheric soils and uptake in maize (Zea mays L.). Chemosphere 2022, 298, 134288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, K.P.; Yang, X.; Gielen, G.; Bolan, N.; Yong, O.S.; Niazi, N.K.; Xu, S.; Yuan, G.D.; Chen, X.; Zhang, X.K.; et al. Effect of bamboo and rice straw biochars on the mobility and redistribution of heavy metals (Cd, Cu, Pb and Zn) in contaminated soil. J. Environ. Manag. 2017, 186, 285–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.S.; Gao, R.; Gao, J.; Song, Z.T.; Ali, U.; Hu, H.Q. Cadmium, lead, and zinc immobilization in soil using rice husk biochar in the presence of citric acid. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 19, 567–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.S.; Kashem, M.A.; Moniruzzaman, M.; Parvin, A.; Das, S.; Hu, H.Q. Cadmium, lead, and zinc immobilization in the soil using a phosphate compound with citric acid present. Environ. Technol. 2023, 29, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.S.; Rezwan, F.; Kashem, M.A.; Moniruzzaman, M.; Parvin, A.; Das, S.; Hu, H.Q. Impact of a phosphate compound on plant metal uptake when low molecular weight organic acids are present in artificially contaminated soils. Environ. Adv. 2024, 15, 100468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Song, J.X.; Liu, Z.; Liu, Z.; Cui, J. Melatonin alleviates cadmium toxicity by reducing nitric oxide accumulation and IRT1 expression in Chinese cabbage seedlings. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 28, 15394–15405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lahori, A.H.; Zhang, Z.; Guo, Z.; Li, R.; Mahar, A.; Awasthi, M.K. Beneficial effects of tobacco biochar combined with mineral additives on (im)mobilization and (bio)availability of Pb, Cd, Cu and Zn from Pb/Zn smelter contaminated soils. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2017, 145, 528–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tessier, A.; Campbell, P.G.C.; Bisson, M. Sequential extraction procedure for the speciation of particulate trace metal. Anal. Chem. 1979, 51, 844–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, Z.L.; Liu, L.Q.; Chou, Z.Y.; Deng, S.; Tang, T.; Xiang, W.L.; Chen, X.J.; Li, Y. Efficient cadmium-resistant plant growth-promoting bacteria loaded on pig bone biochar has higher efficiency in reducing cadmium phytoavailability and improving maize performance than on rice husk biochar. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 249, 135609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.B.; Zhu, C.F.; Yang, H.F.; Zhang, X.W. Phosphate fertilizer affected rhizospheric soils: Speciation of cadmium and phytoremediation by Chlorophytum comosum. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 3934–3939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Li, M.; Li, Y.; Liu, Y.; Chen, Y.; Li, H. Hydroxyapatitemodified sludge-based biochar for the adsorption of Cu2+ and Cd2+: Adsorption behavior and mechanisms. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 321, 124413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Liu, B.; He, Z.; Pan, P.; Wu, L.; Lin, B.; Li, Q.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Z. The Synergistic Effect of Biochar-Combined Activated Phosphate Rock Treatments in Typical Vegetables in Tropical Sandy Soil: Results from Nutrition Supply and the Immobilization of Toxic Metals. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 19, 6431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, J.; Zhao, Z.X.; Ali, A.; Guan, W.D.; Xiao, R.; Wang, J.J.; Ma, S.R.; Guo, D.; Zhou, B.Y.; Zhang, Z.Q.; et al. Characterization of phosphorus engineered biochar and its impact on immobilization of Cd and Pb from smelting contaminated soils. J. Soils Sediments 2020, 20, 3041–3052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, R.; Li, Y.; Li, F.; Yin, X.; Li, R.; Wu, Z.; Li, Z. Phosphate fertilizers facilitated the Cd contaminated soil remediation by sepiolite: Cd mobilization, plant toxicity, and soil microbial community. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2022, 234, 113388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamid, Y.; Tang, L.; Sohail, M.I.; Cao, X.R.; Hussain, B.; Aziz, M.Z.; Usman, M.; He, Z.L.; Yang, X.E. An explanation of soil amendments to reduce cadmium phytoavailability and transfer to food chain. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 660, 80–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, T.; Wang, L.; Yang, J.X. Synergistic effects of combined application of biochar and arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi on the safe production of rice in cadmium contaminated soil. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 951, 175499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carvalho, M.E.A.; Piotto, F.A.; Franco, M.R.; Borges, K.L.; Gaziola, S.A.; Castro, P.R.; Azevedo, R.A. Cadmium toxicity degree on tomato development is associated with disbalances in B and Mn status at early stages of plant exposure. Ecotoxicology 2018, 27, 1293–1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Y.H.; Lin, H.; Jin, X.N.; Dong, Y.B.; Luo, M.K. Simultaneous reduction of arsenic and cadmium bioavailability in agriculture soil and their accumulation in Brassica chinensis L. by using minerals. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 198, 110660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, R.J.; Joseph, S.; Cui, L.Q.; Pan, G.X.; Li, L.Q.; Liu, X.Y.; Zhang, A.F.; Rutlidge, H.; Wong, S.W.; Chia, C.; et al. A three-year experiment confirms continuous immobilization of cadmium and lead in contaminated paddy field with biochar amendment. J. Hazard. Mater. 2014, 272, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shidan, B. Soil Agrochemical Analysis; China Agriculture Press: Beijing, China, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Xiaofang, L.; Zhiliang, Z. Plant Physiology Experiment Guidance; Higher Education Press: Beijing, China, 2016. [Google Scholar]


| Treatment | SOD (U g−1) | CAT (U g−1) | POD (U g−1) |
|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 103.89 ± 6.15abc | 0.96 ± 0.030a | 5.86 ± 0.88a |
| C0P5 | 108.78 ± 2.79ab | 0.04 ± 0.001h | 5.31 ± 0.82ab |
| C0P10 | 115.27 ± 7.35a | 0.04 ± 0.018h | 5.44 ± 0.55ab |
| C5P0 | 98.64 ± 9.58bcd | 0.12 ± 0.002ef | 4.84 ± 0.21b |
| C5P1 | 109.24 ± 7.48ab | 0.15 ± 0.038de | 2.25 ± 0.44def |
| C5P2 | 115.69 ± 7.48a | 0.16 ± 0.017d | 1.78 ± 0.47def |
| C5P5 | 99.19 ± 8.10bc | 0.09 ± 0.011fg | 1.49 ± 0.24f |
| C5P10 | 89.67 ± 6.98cd | 0.06 ± 0.023gh | 2.00 ± 0.29def |
| C10P0 | 92.43 ± 9.27cd | 0.32 ± 0.048b | 3.39 ± 0.37c |
| C10P1 | 85.07 ± 10.25de | 0.22 ± 0.013c | 2.58 ± 0.40d |
| C10P2 | 92.36 ± 10.98cd | 0.23 ± 0.020c | 3.42 ± 0.04c |
| C10P5 | 16.78 ± 4.45f | 0.06 ± 0.027gh | 2.48 ± 0.20de |
| C10P10 | 72.82 ± 6.31e | 0.04 ± 0.001h | 1.65 ± 0.46ef |
| Treatment | pH | Available Phosphorus (mg kg−1) |
|---|---|---|
| CK | 8.24 ± 0.01ab | 6.50 ± 0.49g |
| C0P5 | 8.24 ± 0.05ab | 20.36 ± 1.43b |
| C0P10 | 8.21 ± 0.05ab | 25.83 ± 1.88a |
| C5P0 | 8.24 ± 0.03ab | 8.99 ± 0.25f |
| C5P1 | 8.25 ± 0.03ab | 11.38 ± 0.65def |
| C5P2 | 8.25 ± 0.07ab | 11.94 ± 0.86de |
| C5P5 | 8.28 ± 0.04ab | 15.18 ± 0.51c |
| C5P10 | 8.23 ± 0.05ab | 24.07 ± 0.57a |
| C10P0 | 8.24 ± 0.06ab | 9.65 ± 0.54ef |
| C10P1 | 8.23 ± 0.06ab | 12.43 ± 0.24d |
| C10P2 | 8.18 ± 0.05ab | 12.05 ± 1.06d |
| C10P5 | 8.17 ± 0.02b | 17.19 ± 0.93c |
| C10P10 | 8.14 ± 0.03b | 21.17 ± 2.56b |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Peng, X.; Islam, M.S.; Li, Q.; Fu, Q.; Zhu, J.; Hu, H. Combined Application of Biochar and Calcium Superphosphate Can Effectively Immobilize Cadmium and Reduce Its Uptake by Cabbage. Agronomy 2024, 14, 2538. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14112538
Peng X, Islam MS, Li Q, Fu Q, Zhu J, Hu H. Combined Application of Biochar and Calcium Superphosphate Can Effectively Immobilize Cadmium and Reduce Its Uptake by Cabbage. Agronomy. 2024; 14(11):2538. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14112538
Chicago/Turabian StylePeng, Xinlei, Md. Shoffikul Islam, Qian Li, Qingling Fu, Jun Zhu, and Hongqing Hu. 2024. "Combined Application of Biochar and Calcium Superphosphate Can Effectively Immobilize Cadmium and Reduce Its Uptake by Cabbage" Agronomy 14, no. 11: 2538. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14112538
APA StylePeng, X., Islam, M. S., Li, Q., Fu, Q., Zhu, J., & Hu, H. (2024). Combined Application of Biochar and Calcium Superphosphate Can Effectively Immobilize Cadmium and Reduce Its Uptake by Cabbage. Agronomy, 14(11), 2538. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14112538







