Evaluating the Effectiveness of the Biodegradable Superabsorbent Polymer (Fasal Amrit) on Soil Hydrological Properties: A Laboratory Rainfall Simulation Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area and Soil Sampling
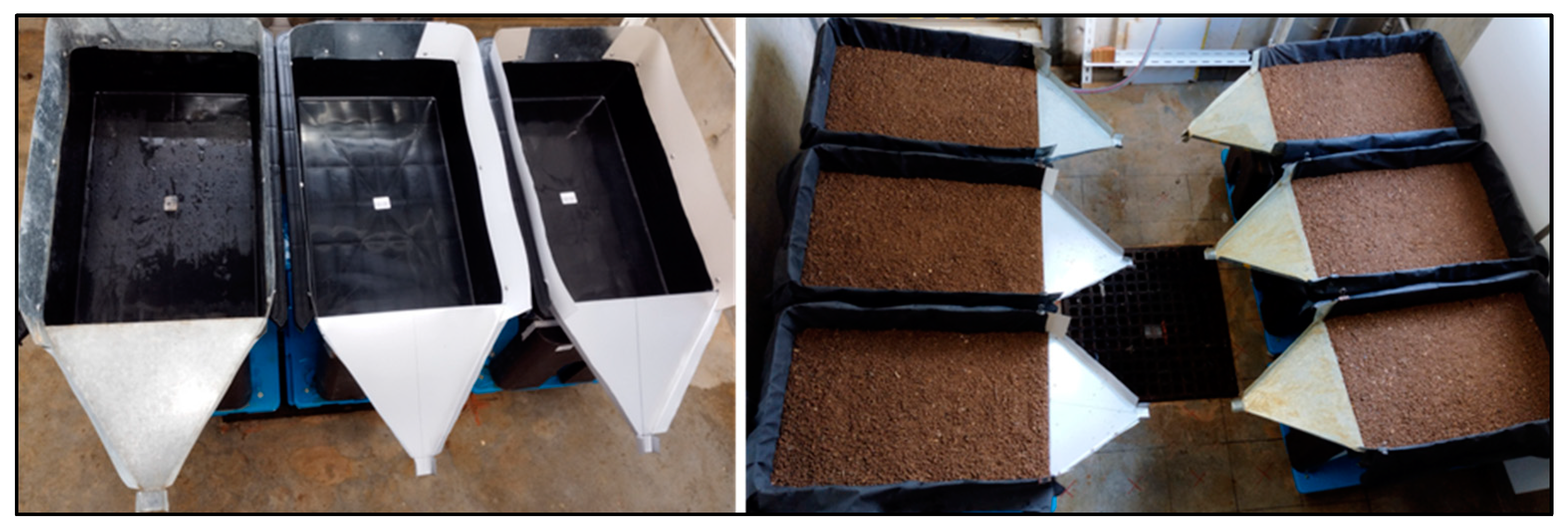
2.2. Experimental Setup and Treatments
2.3. Rainfall Simulation and Procedure
2.4. Evaluating the Effect of EFPs on Soil Hydrological and Erosional Responses
2.5. Evaluating the Effect of SAP Rates on Soil Properties
2.6. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Effect of the Application of EFP on Soil Properties
3.2. Effect of EFP Treatments on Hydrological Responses
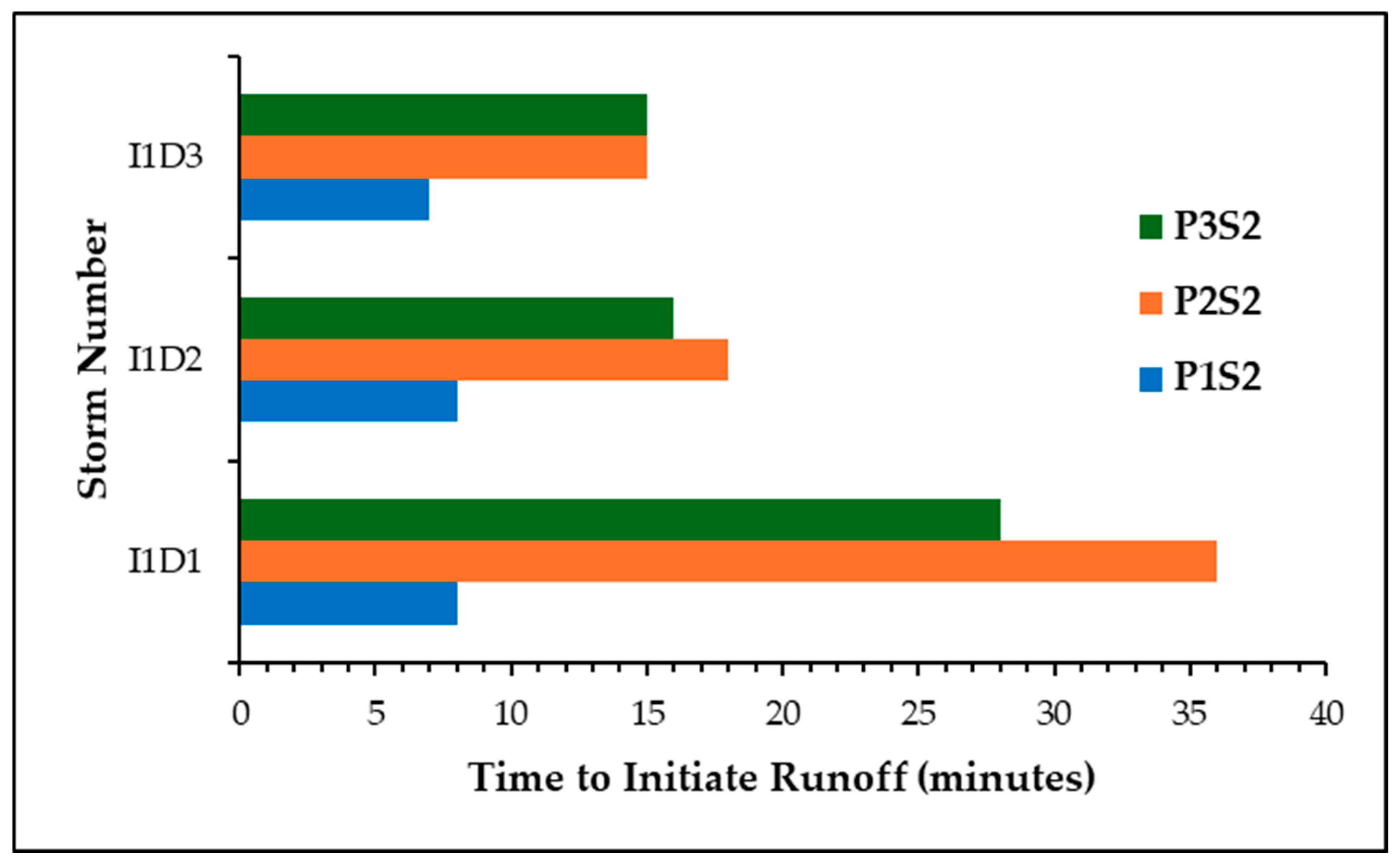
3.2.1. Time to Generate Runoff (TR)
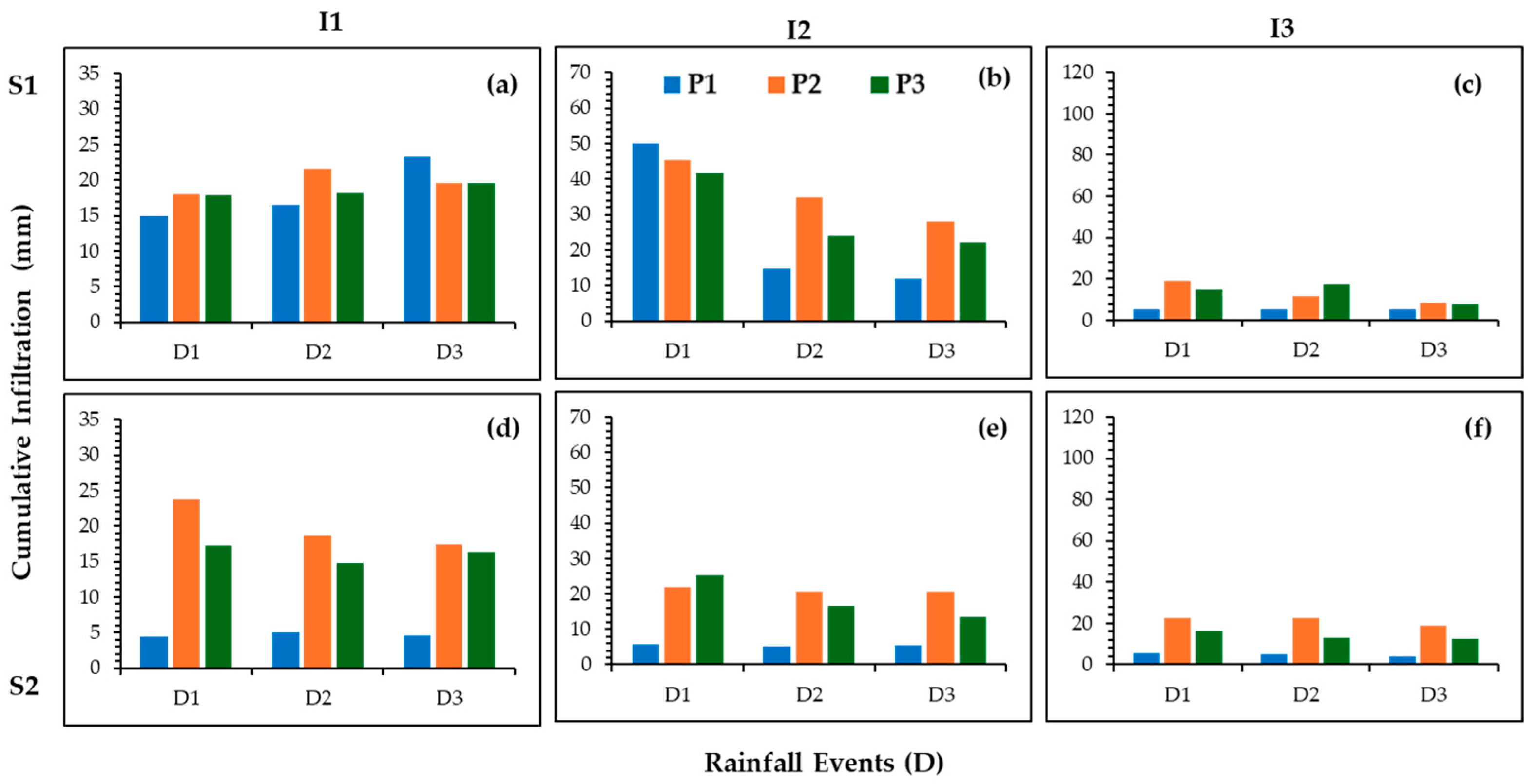
3.2.2. Infiltration (IR)
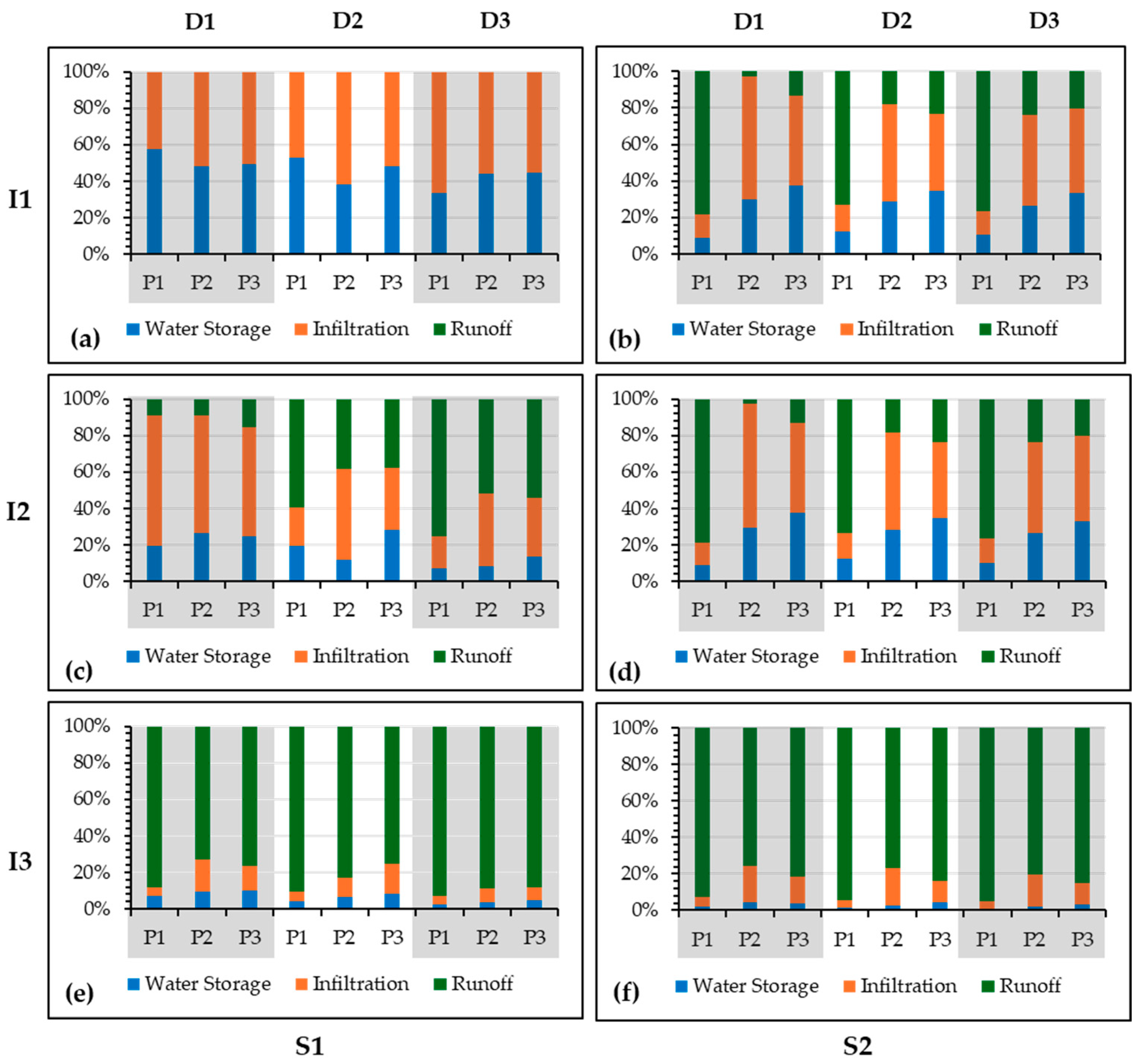
3.2.3. Surface Runoff (RO)
3.2.4. Water Storage (WS)
3.3. Effect of EFP Rates on Soil Erosional Responses
3.3.1. Soil Loss (SL)
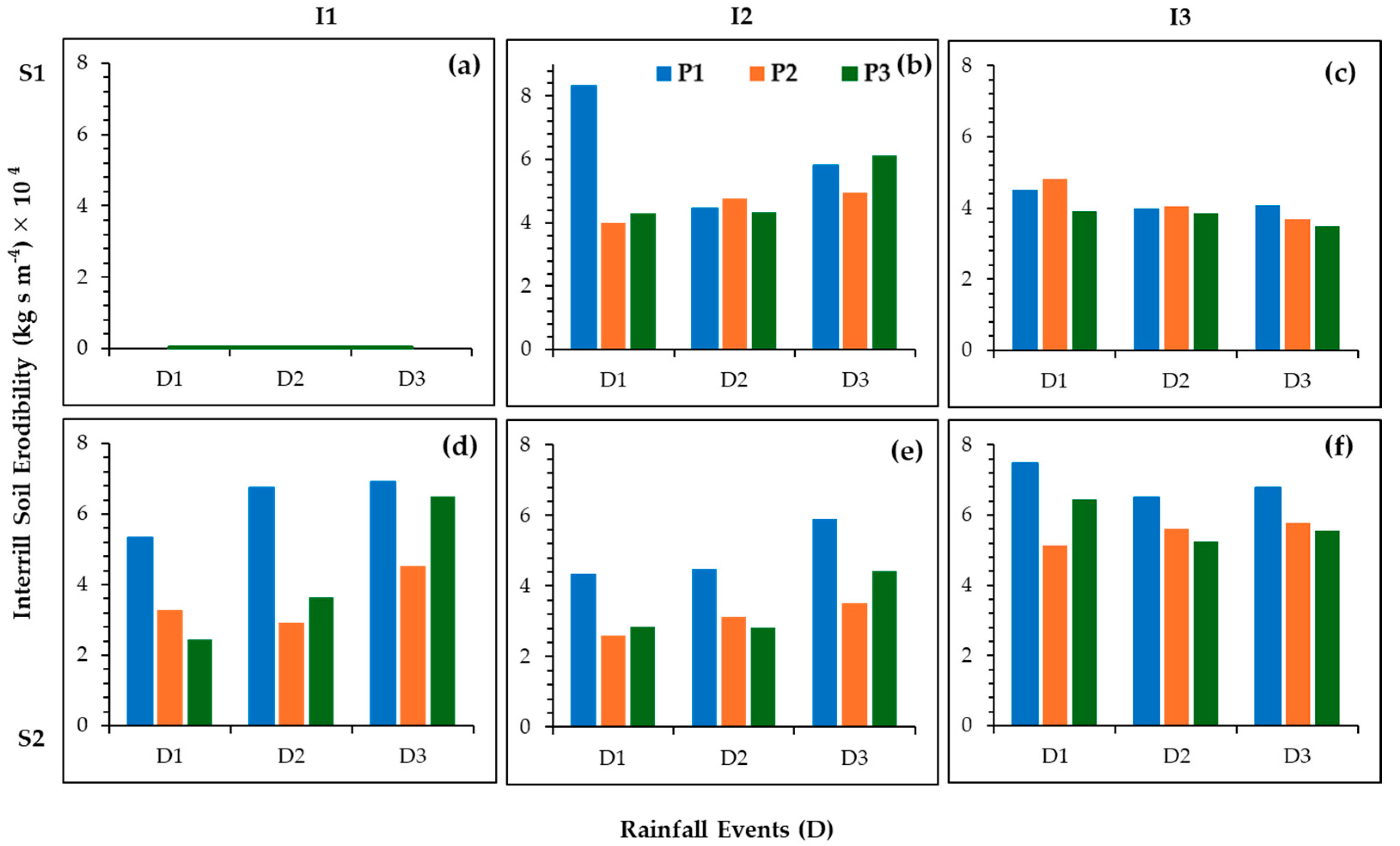
3.3.2. Interrill Soil Erodibility (Ki)
4. Discussion
4.1. Evaluating the Influence of EFP on Soil Properties
4.2. Evaluating the Influence of EFP on Hydrological Responses
4.2.1. Analysis of Time to Initiate Runoff
4.2.2. Analysis of Infiltration (IR)
4.2.3. Analysis of Surface Runoff (RO)
4.2.4. Analysis of Water Storage (WS)
4.3. Evaluating the Influence of EFP on Soil Erosional Responses
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- He, P.; Dai, W.; Luo, Y.; Ding, R.; Zheng, X. Towards Sustainable Development Goals: Study on the Consequences of Food Insecurity among Global Population—Worldwide, 2022. China CDC Wkly. 2022, 4, 583. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- FAO. How to Feed the World 2050: Global Agriculture Towards 2050. In Proceedings of the High-Level Expert Forum: How to Feed the World in 2050, Rome, Italy, 12–13 October 2009; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2009. Available online: http://www.fao.org/fileadmin/templates/wsfs/docs/Issues_papers/HLEF2050_Global_Agriculture.pdf (accessed on 2 August 2024).
- Tian, X.; Engel, B.A.; Qian, H.; Hua, E.; Sun, S.; Wang, Y. Will Reaching the Maximum Achievable Yield Potential Meet Future Global Food Demand? J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 294, 126285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandal, D.; Patra, S.; Sharma, N.K.; Alam, N.M.; Jana, C.; Lal, R. Impacts of Soil Erosion on Soil Quality and Agricultural Sustainability in the North-Western Himalayan Region of India. Sustainability 2023, 15, 5430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khosravi, K.; Rezaie, F.; Cooper, J.R.; Kalantari, Z.; Abolfathi, S.; Hatamiafkoueieh, J. Soil Water Erosion Susceptibility Assessment Using Deep Learning Algorithms. J. Hydrol. 2023, 618, 129229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Q.; Xu, Y.; Bennett, S.J.; Li, Y. Assessment of Soil Erosion Using RUSLE and GIS: A Case Study of the Yangou Watershed in the Loess Plateau, China. Environ. Earth Sci. 2015, 73, 1715–1724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Singh, D.; Kumar, A.; Kumar, M.; Giri, K.; Devi, K.; Singh, S. Estimation of Soil Erosion in the Indo-Gangetic Region Using Revised Universal Soil Loss Equation (RUSLE) Model and Geospatial Technology. Model. Earth Syst. Environ. 2023, 9, 1251–1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutta, S. Soil Erosion, Sediment Yield, and Sedimentation of Reservoirs: A Review. Model. Earth Syst. Environ. 2016, 2, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, S.; Abdo, H.G.; Szabo, S.; Pham, Q.B.; Holb, I.J.; Linh, N.T.T.; Anh, D.T.; Alsafadi, K.; Mokhtar, A.; Kbibo, I.; et al. Estimating Human Impacts on Soil Erosion Considering Different Hillslope Inclinations and Land Uses in the Coastal Region of Syria. Water 2020, 12, 2786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borrelli, P.; Robinson, D.A.; Fleischer, L.R.; Lugato, E.; Ballabio, C.; Alewell, C.; Meusburger, K.; Modugno, S.; Schütt, B.; Ferro, V.; et al. An Assessment of the Global Impact of 21st Century Land Use Change on Soil Erosion. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pimentel, D.; Burgess, M. Soil Erosion Threatens Food Production. Agriculture 2013, 3, 443–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marondedze, A.K.; Schütt, B. Assessment of Soil Erosion Using the RUSLE Model for the Epworth District of the Harare Metropolitan Province, Zimbabwe. Sustainability 2020, 12, 8531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nut, N.; Mihara, M.; Jeong, J.; Ngo, B.; Sigua, G.; Prasad, P.V.; Reyes, M.R. Land Use and Land Cover Changes and Its Impact on Soil Erosion in the Stung Sangkae Catchment of Cambodia. Sustainability 2021, 13, 9276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Mello, K.; Taniwaki, R.H.; de Paula, F.R.; Valente, R.A.; Randhir, T.O.; Macedo, D.R.; Leal, C.G.; Rodrigues, C.B.; Hughes, R.M. Multiscale Land Use Impacts on Water Quality: Assessment, Planning, and Future Perspectives in Brazil. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 270, 110879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dharmawan, I.W.S.; Pratiwi; Siregar, C.A.; Narendra, B.H.; Undaharta, N.K.E.; Sitepu, B.S.; Sukmana, A.; Wiratmoko, M.D.E.; Abywijaya, I.K.; Sari, N. Implementation of Soil and Water Conservation in Indonesia and Its Impacts on Biodiversity, Hydrology, Soil Erosion, and Microclimate. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 7648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, R.; Zheng, J.; Li, G.; Huang, Y.; Wang, J.; Qiu, F. Effects of Rainfall Characteristics and Sugarcane Growth Stage on Soil and Nitrogen Losses. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 87575–87587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samaraweera, W.G.R.L.; Dharmadasa, R.A.P.I.S.; Kumara, P.H.T.; Bandara, A.S.G.S. Evidence of Climate Change Impacts in Sri Lanka—A Review of Literature. Sri Lanka J. Econ. Res. 2024, 11, 69–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Silva, S.S.; Abeysingha, N.S.; Nirmanee, K.G.S.; Sandamali Pathirage, P.D.S.; Mallawatantri, A. Effect of Land Use–Land Cover and Projected Rainfall on Soil Erosion Intensities of a Tropical Catchment in Sri Lanka. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2023, 20, 9173–9188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deegala, D.M.B.M.; Abeysingha, N.S.; Muthuwatta, L.P.; Ray, R.L. Sustainable Growing Areas for Sugarcane in Sri Lanka Under a Changing Climate. Sugar Tech 2022, 24, 1801–1813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulasekara, B.R.; Ariyawansha, B.D.S.K.; Weerasinghe, H.A.S.; Kodithuwakku, K.A.D.; Kumarasiri, U.W.L.M. Response of Soil, Cane Yield, and Cane Quality Parameters to Zinc Fertiliser Under Alfisols Condition in Sri Lanka: A Preliminary Investigation. Sugar Tech 2024, 26, 915–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugarcane Research Institute. Statistics of the Sugarcane Industry. 2023. Available online: https://sugarres.lk/statistics-of-sugarcane-sri-lanka/ (accessed on 7 September 2024).
- Ariyawansha, T.; Abeyrathna, D.; Kodithuwakku, D.; Wijayawardhana, J.; Sewwandi, N.; Weerasinghe, A.; Pottawela, D.; Komoto, H.; Ahamed, T.; Noguchi, R. A Systematic Framework for Studying Two Sugarcane Harvesting Systems Based on National Policy Implementation in Sri Lanka. Sugar Tech 2023, 25, 846–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perera, K.H.K.; Udeshani, W.A.C.; Piyathilake, I.D.U.H.; Wimalasiri, G.E.M.; Kadupitiya, H.K.; Udayakumara, E.P.N.; Gunatilake, S.K. Assessing Soil Quality and Soil Erosion Hazards in the Moneragala District, Sri Lanka. SN Appl. Sci. 2020, 2, 2175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Silva, A.L.C.; Wijayawardhana, L.M.J.R.; Witharama, W.R.G. Present Status of Research and Development on Climate Change Mitigation and Future Needs in the Sugarcane Sector in Sri Lanka. In Proceedings of the Workshop on Present Status of Research and Activities on Climate Change and Adaptation; Sri Lanka Council for Agricultural Research Policy: Colombo, Sri Lanka, 2016; pp. 101–112. [Google Scholar]
- Martinelli, L.A.; Filoso, S. Expansion of Sugarcane Ethanol Production in Brazil: Environmental and Social Challenges. Ecol. Appl. 2008, 18, 885–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paringit, E.C.; Nadaoka, K. Sediment Yield Modelling for Small Agricultural Catchments: Land-Cover Parameterization Based on Remote Sensing Data Analysis. Hydrol. Process. 2003, 17, 1845–1866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senanayake, S.S.; Munasinghe, M.A.K.; Wickramasinghe, W.M.A.D.B. Use of Erosion Hazard Assessments for Regional Scale Crop Suitability Mapping in the Uva Province. Ann. Sri Lanka Dep. Agric. 2013, 15, 127–141. [Google Scholar]
- Yakupoglu, T.; Rodrigo-Comino, J.; Cerdà, A. Potential Benefits of Polymers in Soil Erosion Control for Agronomical Plans: A Laboratory Experiment. Agronomy 2019, 9, 276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keesstra, S.D.; Rodrigo-Comino, J.; Novara, A.; Giménez-Morera, A.; Pulido, M.; Di Prima, S.; Cerdà, A. Straw Mulch as a Sustainable Solution to Decrease Runoff and Erosion in Glyphosate-Treated Clementine Plantations in Eastern Spain: An Assessment Using Rainfall Simulation Experiments. Catena 2019, 174, 95–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giménez-Morera, A.; Sinoga, J.R.; Cerdà, A. The Impact of Cotton Geotextiles on Soil and Water Losses from Mediterranean Rainfed Agricultural Land. Land Degrad. Dev. 2010, 21, 210–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, K.; Fullen, M.A.; Booth, C.A. A Pilot Project on the Potential Contribution of Palm-Mat Geotextiles to Soil Conservation. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2006, 31, 561–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jomaa, S.; Barry, D.A.; Heng, B.C.P.; Brovelli, A.; Sander, G.C.; Parlange, J.Y. Influence of Rock Fragment Coverage on Soil Erosion and Hydrological Response: Laboratory Flume Experiments and Modeling. Water Resour. Res. 2012, 48, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jomaa, S.; Barry, D.A.; Brovelli, A.; Heng, B.C.P.; Sander, G.C.; Parlange, J.Y.; Rose, C.W. Rain Splash Soil Erosion Estimation in the Presence of Rock Fragments. Catena 2012, 92, 38–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, S.; Wang, Z.; Hu, Y.; Liu, B.; Liu, J. Effectiveness and Durability of Polyacrylamide (PAM) and Polysaccharide (Jag C 162) in Reducing Soil Erosion Under Simulated Rainfalls. Water 2018, 10, 257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garg, A.; Wani, I.; Kushvaha, V. Application of Artificial Intelligence for Predicting Erosion of Biochar Amended Soils. Sustainability 2022, 14, 684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tümsavaş, Z.; Kara, A. The Effect of Polyacrylamide (PAM) Applications on Infiltration, Runoff, and Soil Losses Under Simulated Rainfall Conditions. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2011, 10, 2894–2903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kebede, B.; Tsunekawa, A.; Haregeweyn, N.; Tsubo, M.; Mulualem, T.; Mamedov, A.I.; Meshesha, D.T.; Adgo, E.; Fenta, A.A.; Ebabu, K.; et al. Effect of Polyacrylamide Integrated with Other Soil Amendments on Runoff and Soil Loss: Case Study from Northwest Ethiopia. Int. Soil Water Conserv. Res. 2022, 10, 487–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moslemi, Z.; Habibi, D.; Asgharzadeh, A.; Ardakani, M.R.; Mohammadi, A.; Sakari, A. Effects of Super Absorbent Polymer and Plant Growth Promoting Rhizobacteria on Yield and Yield Components of Maize Under Drought Stress and Normal Conditions. Afr. J. Agric. Res. 2011, 6, 4471–4476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elshafie, H.S.; Camele, I. Applications of Absorbent Polymers for Sustainable Plant Protection and Crop Yield. Sustainability 2021, 13, 3253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lertsarawut, P.; Rattanawongwiboon, T.; Tangthong, T.; Laksee, S.; Kwamman, T.; Phuttharak, B.; Romruensukharom, P.; Suwanmala, P.; Hemvichian, K. Starch-Based Super Water Absorbent: A Promising and Sustainable Way to Increase Survival Rate of Trees Planted in Arid Areas. Polymers 2021, 13, 1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Wang, A. Synthesis, Swelling Behaviors, and Slow-Release Characteristics of a Guar Gum-g-Poly (Sodium Acrylate)/Sodium Humate Superabsorbent. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2009, 112, 2102–2111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Q.; Fu, B.; Tang, X.; Ren, H. Effects of Land Use on Phosphorus Loss in the Hilly Area of the Loess Plateau, China. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2008, 139, 195–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krasnopeeva, E.L.; Panova, G.G.; Yakimansky, A.V. Agricultural Applications of Superabsorbent Polymer Hydrogels. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 11534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sroka, K.; Sroka, P. Superabsorbent Hydrogels in the Agriculture and Reclamation of Degraded Areas. Sustainability 2024, 16, 2945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damiri, F.; Salave, S.; Vitore, J.; Bachra, Y.; Jadhav, R.; Kommineni, N.; Karouach, F.; Paiva-Santos, A.C.; Varma, R.S.; Berrada, M. Properties and Valuable Applications of Superabsorbent Polymers: A Comprehensive Review. Polym. Bull. 2024, 81, 6671–6701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu-Zreig, M. Control of Rainfall-Induced Soil Erosion with Various Types of Polyacrylamide. J. Soils Sediments 2006, 6, 137–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Wang, B.; Guo, H.; Xiao, H.; Wei, T. The Effect of Super Absorbent Polymers on Soil and Water Conservation on the Terraces of the Loess Plateau. Ecol. Eng. 2017, 102, 270–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thombare, N.; Mishra, S.; Siddiqui, M.Z.; Jha, U.; Singh, D.; Mahajan, G.R. Design and Development of Guar Gum Based Novel, Superabsorbent and Moisture Retaining Hydrogels for Agricultural Applications. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 185, 169–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khushbu, S.G.W.; Warkar, A.; Kumar, A. Synthesis and Assessment of Carboxymethyl Tamarind Kernel Gum Based Novel Superabsorbent Hydrogels for Agricultural Applications. Polymer 2019, 182, 121823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y. Properties and Development of Hydrogels. In Hydrogels Based on Natural Polymers; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; pp. 3–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Cen, R.; Feng, W.; Liu, J.; Qu, Z.; Miao, Q. Effects of Super-Absorbent Polymer on Soil Remediation and Crop Growth in Arid and Semi-Arid Areas. Sustainability 2020, 12, 8785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EF Polymer Pvt Ltd. EF Polymer | Reimagining Sustainable Agriculture. 2023. Available online: https://efpolymer.com/ (accessed on 28 August 2024).
- Meena, C.B.; Pilania, S.; Singh, V.; Jat, G.; Surolia, D.K.; Bairwa, H.L.; Kumari, M.; Singh, R. Effect of Ball Culture in Seed Germination of Ridge Gourd. Curr. J. Appl. Sci. Technol. 2022, 41, 16–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Japan Meteorological Agency. Tables of Monthly Climate Statistics. Available online: https://www.data.jma.go.jp/stats/data/en/smp/index.html (accessed on 15 August 2024).
- Bellido, J.; Sakai, K.; Nakamura, S.; Kazuro, M.; Okamoto, K.; Nakandakari, T. N2O Emissions from Shimajiri-Maji (Calcaric Dark Red Soil) after Applying Two Chemical Fertilizers. Appl. Ecol. Environ. Res. 2015, 13, 339–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durner, W.; Iden, S.C. The Improved Integral Suspension Pressure Method (ISP+) for Precise Particle Size Analysis of Soil and Sedimentary Materials. Soil Tillage Res. 2021, 213, 105086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klute, A. Physical and Mineralogical Methods of Soil Analysis; American Society of Agronomy: Madison, WI, USA, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Kojima, R.; Osawa, K.; Matsuura, M.; Fujisawa, H.; Tomisaka, M.; Matsui, H. Identification of Soil Erodibilities for an Application of WEPP Model with Biological Ground Cover by Algae and Fungi. J. Jpn. Soc. Civ. Eng. Ser. G Environ. Res. 2018, 74, I_233–I_239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christiansen, J.E. Irrigation by Sprinkling; University of California: Berkeley, CA, USA, 1942; Volume 4. [Google Scholar]
- Tu, A.; Xie, S.; Mo, M.; Song, Y.; Li, Y. Water Budget Components Estimation for a Mature Citrus Orchard of Southern China Based on HYDRUS-1D Model. Agric. Water Manag. 2021, 243, 106426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinnell, P.I.A. Runoff as a Factor Influencing Experimentally Determined Interrill Erodibilities. Aust. J. Soil Res. 1993, 31, 333–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.B.; Wang, Z.L.; Yang, M.Y. Validating and Improving Interrill Erosion Equations. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e88275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kemper, W.D.; Rosenau, R.C. Aggregate Stability and Size. In Methods of Soil Analysis, Part 1—Physical and Mineralogical Methods; ASA/SSSA: Madison, WI, USA, 1986; Volume 9, pp. 425–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Igwe, C.A.; Nwokocha, D. Influence of Soil Properties on the Aggregate Stability of a Highly Degraded Tropical Soil in Eastern Nigeria. Int. Agrophysics 2005, 19, 131–139. [Google Scholar]
- Abrisham, E.S.; Jafari, M.; Tavili, A.; Rabii, A.; Zare Chahoki, M.A.; Zare, S.; Egan, T.; Yazdanshenas, H.; Ghasemian, D.; Tahmoures, M. Effects of a Super Absorbent Polymer on Soil Properties and Plant Growth for Use in Land Reclamation. Arid Land Res. Manag. 2018, 32, 407–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, W.; Zhang, H.; Liu, B.; Wu, Y.; Song, J.Q. Effects of Super-Absorbent Polymers on the Physical and Chemical Properties of Soil Following Different Wetting and Drying Cycles. Soil Use Manag. 2010, 26, 253–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.G.; Yang, P.L.; Luo, Y.P.; Ren, S.M.; Zhang, L.X.; Xu, L. Porosity Change Model for Watered Super Absorbent Polymer-Treated Soil. Environ. Earth Sci. 2010, 61, 1197–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Wu, J.; Zhao, S.; Gao, C.; Pan, X.; Tang, D.W.; van der Ploeg, M. Effects of Long-Term Super Absorbent Polymer and Organic Manure on Soil Structure and Organic Carbon Distribution in Different Soil Layers. Soil Tillage Res. 2021, 206, 104781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhardwaj, A.K.; Shainberg, I.; Goldstein, D.; Warrington, D.N.; Levy, G.J. Water Retention and Hydraulic Conductivity of Cross-Linked Polyacrylamides in Sandy Soils. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2007, 71, 406–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Yu, X.; Yang, P.; Li, B.; Xu, L.; Wang, C. Dynamic Study on Water Diffusivity of Soil with Super-Absorbent Polymer Application. Environ. Earth Sci. 2013, 69, 289–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahid, S.A.; Qidwai, A.A.; Anwar, F.; Ullah, I.; Rashid, U. Improvement in the Water Retention Characteristics of Sandy Loam Soil Using a Newly Synthesized Poly(acrylamide-co-acrylic Acid)/AlZnFe2O4 Superabsorbent Hydrogel Nanocomposite Material. Molecules 2012, 17, 9397–9412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Shao, M.; Horton, R. Effect of Polyacrylamide Applications on Soil Hydraulic Characteristics and Sediment Yield of Sloping Land. Procedia Environ. Sci. 2011, 11, 763–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.N.; Gong, Y.; Hu, T.; Lal, R.; Zheng, J.; Justine, M.F.; Azhar, M.; Che, M.; Zhang, H. Effect of Slope, Rainfall Intensity and Mulch on Erosion and Infiltration under Simulated Rain on Purple Soil of South-Western Sichuan Province, China. Water 2016, 8, 528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Z.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, X.C.; Li, Z.; Li, P.; Zhou, Z.Z. Sand Cover Enhances Rill Formation under Laboratory Rainfall Simulation. Catena 2021, 205, 105472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trout, T.J.; Sojka, R.E.; Lentz, R.D. Polyacrylamide Effect on Furrow Erosion and Infiltration. Trans. Am. Soc. Agric. Eng. 1995, 38, 761–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Li, D.; Zhuo, M.; Guo, T.; Liao, Y.; Xie, Z. Effects of Rainfall Intensity and Slope Gradient on Erosion Characteristics of the Red Soil Slope. Stoch. Environ. Res. Risk Assess. 2015, 29, 609–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandal, U.K.; Bhardwaj, A.K.; Warrington, D.N.; Goldstein, D.; Bar Tal, A.; Levy, G.J. Changes in Soil Hydraulic Conductivity, Runoff, and Soil Loss Due to Irrigation with Different Types of Saline-Sodic Water. Geoderma 2008, 144, 509–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ran, Q.; Su, D.; Li, P.; He, Z. Experimental Study of the Impact of Rainfall Characteristics on Runoff Generation and Soil Erosion. J. Hydrol. 2012, 424–425, 99–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, T.X.; Band, L.E.; Vertessy, R.A. Continuous Modeling of Intermittent Stormflows on a Semi-Arid Agricultural Catchment. J. Hydrol. 1999, 226, 11–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assouline, S.; Ben-Hur, M. Effects of Rainfall Intensity and Slope Gradient on the Dynamics of Interrill Erosion During Soil Surface Sealing. Catena 2006, 66, 211–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misiewicz, J.; Datta, S.S.; Lejcuś, K.; Marczak, D. The Characteristics of Time-Dependent Changes of Coefficient of Permeability for Superabsorbent Polymer-Soil Mixtures. Materials 2022, 15, 4465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inbar, A.; Ben-Hur, M.; Sternberg, M.; Lado, M. Using Polyacrylamide to Mitigate Post-Fire Soil Erosion. Geoderma 2015, 239, 107–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abrol, V.; Shainberg, I.; Lado, M.; Ben-Hur, M. Efficacy of Dry Granular Anionic Polyacrylamide (PAM) on Infiltration, Runoff and Erosion. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2013, 64, 699–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Lei, T.; Shainberg, I.; Mamedov, A.I.; Levy, G.J. Infiltration and Erosion in Soils Treated with Dry PAM and Gypsum. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2003, 67, 630–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben-Hur, M. Seal Formation Effects on Soil Infiltration and Runoff in Arid and Semiarid Regions under Rainfall and Sprinkler Irrigation Conditions. In Environmental Science and Engineering; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2008; pp. 430–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Shao, M.; Li, Y. The Characteristics of Soil Water Cycle and Water Balance on Steep Grassland under Natural and Simulated Rainfall Conditions in the Loess Plateau of China. J. Hydrol. 2008, 360, 242–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, M.; Huang, Z.; Ji, H.; Qiu, F.; Zhao, D.; Bredar, A.R.; Farnum, B.H. Simultaneous Control of Soil Erosion and Arsenic Leaching at Disturbed Land Using Polyacrylamide Modified Magnetite Nanoparticles. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 702, 134997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berninger, T.; Dietz, N.; González López, Ó. Water-Soluble Polymers in Agriculture: Xanthan Gum as Eco-Friendly Alternative to Synthetics. Microb. Biotechnol. 2021, 14, 1881–1896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, W.F.; Zhang, X.C. An Evaluation on Using Soil Aggregate Stability as the Indicator of Interrill Erodibility. J. Mt. Sci. 2016, 13, 831–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Soil Type | Particle Size Distribution (%) | pH | EC (µs cm−1) | SOM (%) | BD (g cm−3) | Ks (cm s−1) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Clay | Silt | Sand | ||||||
| Shimajiri-maji | 55 | 30 | 15 | 7.995 | 128.93 | 0.063 | 1.12 | 3.27 × 10−3 |
| Soil Parameter | P1 | P2 | P3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bulk density—BD (g cm−3) | 1.123 a | 1.073 b | 1.109 ab |
| Porosity % | 52.72 b | 56.79 a | 54.16 b |
| Organic Matter (%) | 0.063 c | 0.837 b | 1.253 a |
| Hydraulic conductivity Ks (mm/h) | 117.72 a | 112.32 b | 96.12 c |
| Mean weight Diameter—MWD (mm) | 0.716 b | 0.862 a | 0.854 a |
| Slope | Treatment | Total Runoff | Runoff Reduction Effect Compared to the Control (%) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| I1 | I2 | I3 | I1 | I2 | I3 | ||
| S1 | Control | - | 100.92 | 299.31 | - | ||
| P2 | - | 69.44 | 268.82 | - | 31.19 | 10.21 | |
| P3 | - | 75.42 | 264.0 | - | 25.28 | 11.79 | |
| S2 | Control | 80.03 | 186.68 | 310.32 | |||
| P2 | 15.55 | 134.95 | 256.39 | 80.57 | 27.71 | 17.37 | |
| P3 | 19.85 | 138.57 | 275.9 | 75.19 | 25.77 | 11.08 | |
| Erosion Plot | Total Soil Loss (g/m−2) | Reduction Effect Compared to the Control (%) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| I1 | I2 | I3 | I1 | I2 | I3 | ||
| S1 | Control | - | 228.01 | 822.30 | - | ||
| P2 | - | 138.52 | 730.82 | - | 39.25 | 11.12 | |
| P3 | - | 164.29 | 645.71 | - | 27.95 | 21.47 | |
| S2 | Control | 146.38 | 531.459 | 1954.8 | |||
| P2 | 17.14 | 241.02 | 1288.62 | 88.29 | 54.65 | 34.08 | |
| P3 | 25.20 | 273.67 | 1440.71 | 82.78 | 48.51 | 26.30 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ruwanpathirana, P.P.; Sakai, K.; Nakandakari, T.; Yuge, K. Evaluating the Effectiveness of the Biodegradable Superabsorbent Polymer (Fasal Amrit) on Soil Hydrological Properties: A Laboratory Rainfall Simulation Study. Agronomy 2024, 14, 2467. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14112467
Ruwanpathirana PP, Sakai K, Nakandakari T, Yuge K. Evaluating the Effectiveness of the Biodegradable Superabsorbent Polymer (Fasal Amrit) on Soil Hydrological Properties: A Laboratory Rainfall Simulation Study. Agronomy. 2024; 14(11):2467. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14112467
Chicago/Turabian StyleRuwanpathirana, P. P., Kazuhito Sakai, Tamotsu Nakandakari, and Kozue Yuge. 2024. "Evaluating the Effectiveness of the Biodegradable Superabsorbent Polymer (Fasal Amrit) on Soil Hydrological Properties: A Laboratory Rainfall Simulation Study" Agronomy 14, no. 11: 2467. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14112467
APA StyleRuwanpathirana, P. P., Sakai, K., Nakandakari, T., & Yuge, K. (2024). Evaluating the Effectiveness of the Biodegradable Superabsorbent Polymer (Fasal Amrit) on Soil Hydrological Properties: A Laboratory Rainfall Simulation Study. Agronomy, 14(11), 2467. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14112467






