Maize-Straw Biochar Enhances Soil Properties and Grain Yield of Foxtail Millet in a Newly Reclaimed Land
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experiment Site Location
2.2. Experiment Design
2.3. Sample Collection and Soil Property Measurements
2.4. Data Statistics and Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Soil Bulk Density, pH, and Soil Water Content
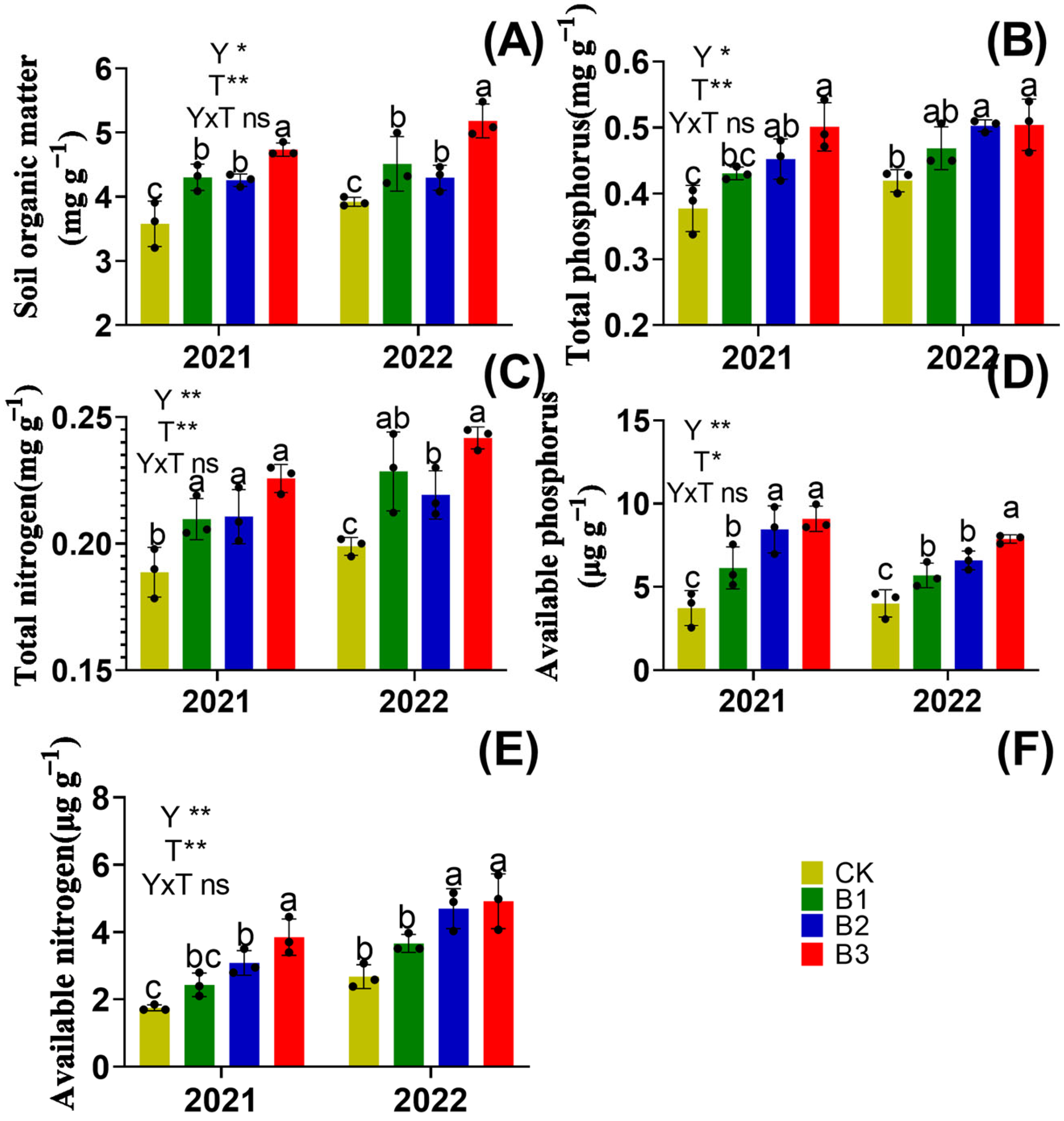
3.2. Soil Nutrients
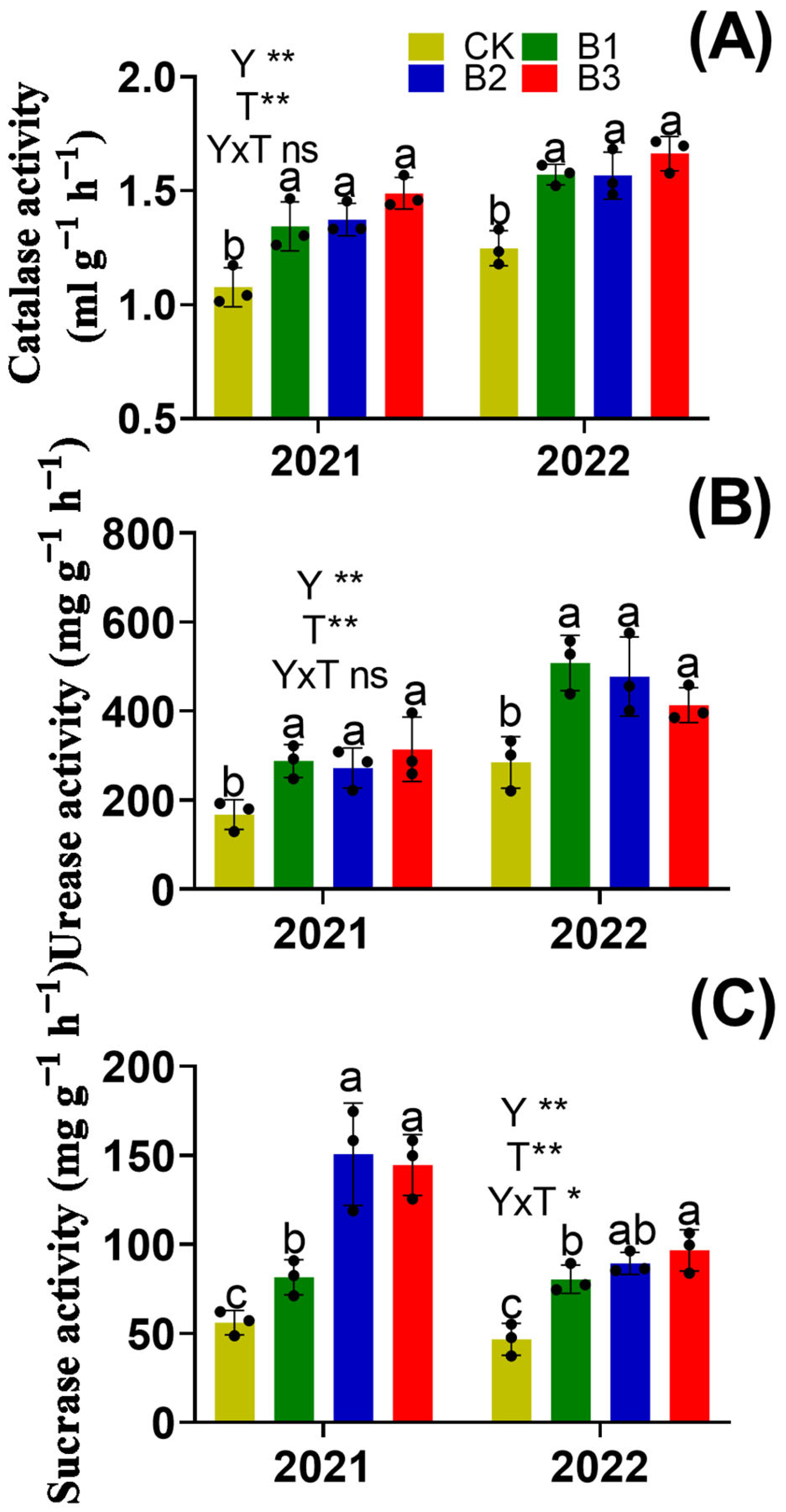
3.3. Soil Enzyme Activity and Organic Acids
3.4. Grain Yield
3.5. Relationships Among Soil Properties and Grain Yield
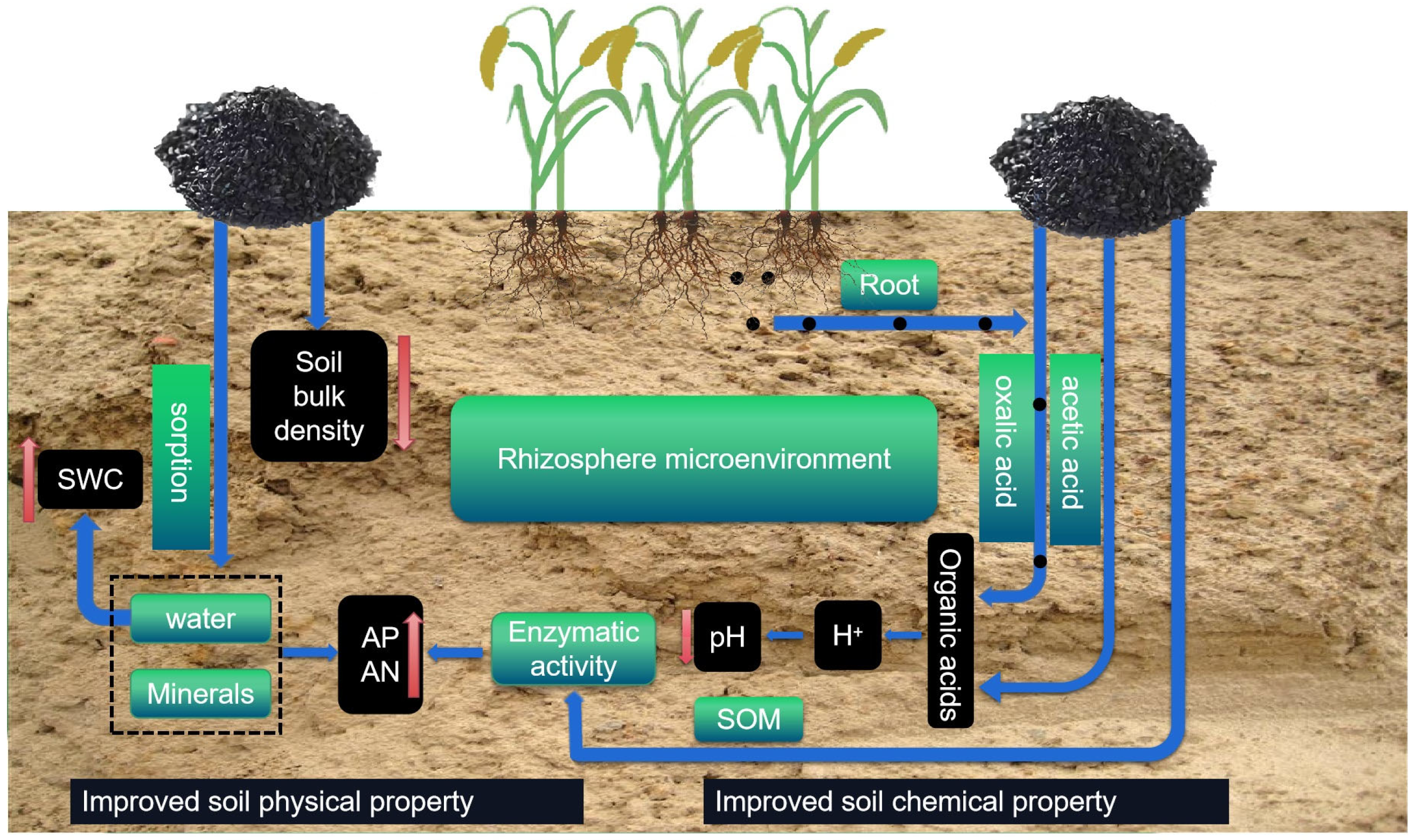
4. Discussion
4.1. Biochar Decreased Soil Bulk Density and Improved Soil Water Retention
4.2. Biochar Decreased Soil pH in Saline–Alkaline Soil
4.3. Biochar Application Improved Soil Fertility
4.4. Biochar Application Increased Millet Grain Yield
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- He, M.; Gao, X.; Zhao, Z.; Yang, H.; Huang, L.; Li, X.; Lei, J. Ecological Restoration and Countmeasures Against Desertification Crisis in Aral Sea Region. Bull. Chin. Acad. Sci. (Chin. Version) 2021, 36, 130–140. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Y.; Zhang, N.; Yan, J.; Zhang, S. Effects of soft rock and biochar applications on millet (Setaria italica L.) crop performance in sandy soil. Agronomy 2020, 10, 669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Han, J. Effect of soft rock amendment on soil hydraulic parameters and crop performance in Mu Us Sandy Land, China. Field Crops Res. 2018, 222, 85–93. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Wang, L.; Liu, L.; Zheng, Q. Preliminary study on soil moisture content in dried layer of sand dunes in the Mu Us sandland. Arid Zone Res. 2006, 23, 89–92. [Google Scholar]
- Saifullah; Saad, D.; Asif, N.; Zed, R.; Ravi, N. Biochar application for the remediation of salt-affected soils: Challenges and opportunities. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 625, 320–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Liu, C.; Zhang, F.; Han, H.; Wang, Z.; Yi, B.; Tang, L.; Meng, J.; Chi, D.; Wilson, L.T. Acid-modified biochar increases grain yield and reduces reactive gaseous N losses and N-related global warming potential in alternate wetting and drying paddy production system. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 377, 134451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, S.; Yang, S.; Lin, X.; Hu, J.; Jiang, Z.; Xu, Y. The long-term effectiveness of biochar in increasing phosphorus availability and reducing its release risk to the environment in water-saving irrigated paddy fields. Agric. Water Manag. 2023, 282, 108295. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, S.; Luthra, N.; Mandal, S.; Kushwaha, D.P.; Pathak, S.O.; Datta, D.; Sharma, R.; Pramanick, B. Distinct behavior of biochar modulating biogeochemistry of salt-affected and acidic soil: A review. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2023, 23, 2981–2997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; Yan, J.; Liu, P. Effect of bacterial manure on the properties of complex soil and growth of ryegrass. Agronomy 2021, 11, 568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghorbani, M.; Neugschwandtner, R.W.; Konvalina, P.; Asadi, H.; Kopecký, M.; Amirahmadi, E. Comparative effects of biochar and compost applications on water holding capacity and crop yield of rice under evaporation stress: A two-years field study. Paddy Water Environ. 2023, 21, 47–58. [Google Scholar]
- Ghorbani, M.; Amirahmadi, E.; Konvalina, P.; Moudrý, J.; Bárta, J.; Kopecký, M.; Teodorescu, R.I.; Bucur, R.D. Comparative influence of biochar and zeolite on soil hydrological indices and growth characteristics of corn (Zea mays L.). Water 2022, 14, 3506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alburquerque, J.A.; Salazar, P.; Barrón, V.; Torrent, J.; del Campillo, M.d.C.; Gallardo, A.; Villar, R. Enhanced wheat yield by biochar addition under different mineral fertilization levels. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2013, 33, 475–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haider, G.; Steffens, D.; Moser, G.; Müller, C.; Kammann, C.I. Biochar reduced nitrate leaching and improved soil moisture content without yield improvements in a four-year field study. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2017, 237, 80–94. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, C.; Tiwari, S.; Gupta, V.K.; Singh, J.S. The effect of rice husk biochar on soil nutrient status, microbial biomass and paddy productivity of nutrient poor agriculture soils. Catena 2018, 71, 485–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, D.; Rousk, J.; Edwards-Jones, G.; DeLuca, T.; Murphy, D. Biochar-mediated changes in soil quality and plant growth in a three year field trial. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2012, 45, 113–124. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, J.; Liu, P. Does complex soil enhance grain yield under cropping system? Agronomy 2021, 11, 1502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zadoks, J.C.; Chang, T.T.; Konzak, C.F. A decimal code for the growth stages of cereals. Weed Res. 1974, 14, 415–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.; Zhang, N.; Kang, F.; Wang, J.; Wang, X. Cultivar replacement increases water use efficiency in foxtail millet in Shaanxi Province, China. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2021, 164, 73–81. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, T.; Zhang, W.; Gulaqa, A.; Cui, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Weng, W.; Wang, X.; Liu, Q.; Jin, F. Effects of peanut shell biochar on soil nutrients, soil enzyme activity, and rice yield in heavily saline-sodic paddy field. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2021, 21, 655–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; Huang, S.; Lei, H.; Lei, X.; Liu, P.; Yan, J. Changes in soil quality over time focusing on organic acid content in restoration areas following coal mining. Catena 2022, 218, 106567. [Google Scholar]
- Gu, Y.; Wang, P.; Kong, C. Urease, invertase, dehydrogenase and polyphenoloxidase activities in paddy soil influenced by allelopathic rice variety. Eur. J. Soil Biol. 2009, 45, 436–441. [Google Scholar]
- Dam, R.; Mehdi, B.; Burgess, M.; Madramootoo, C.; Mehuys, G.; Callum, I. Soil bulk density and crop yield under eleven consecutive years of corn with different tillage and residue practices in a sandy loam soil in central Canada. Soil Tillage Res. 2005, 84, 41–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devau, N.; Le Cadre, E.; Hinsinger, P.; Jaillard, B.; Gérard, F. Soil pH controls the environmental availability of phosphorus: Experimental and mechanistic modelling approaches. Appl. Geochem. 2009, 24, 2163–2174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abalos, D.; Recous, S.; Butterbach-Bahl, K.; De Notaris, C.; Rittl, T.F.; Topp, C.F.; Petersen, S.O.; Hansen, S.; Bleken, M.A.; Rees, R.M. A review and meta-analysis of mitigation measures for nitrous oxide emissions from crop residues. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 828, 154388. [Google Scholar]
- Xiu, L.; Zhang, W.; Sun, Y.; Wu, D.; Meng, J.; Chen, W. Effects of biochar and straw returning on the key cultivation limitations of Albic soil and soybean growth over 2 years. Catena 2019, 173, 481–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heinonen, R. Towards “normal” soil bulk density. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1977, 41, 1214–1215. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Feng, H.; Chen, J.; Lu, J.; Wu, W.; Liu, X.; Li, C.; Siddique, K.H. Biochar incorporation increases winter wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) production with significantly improving soil enzyme activities at jointing stage. Catena 2022, 211, 105979. [Google Scholar]
- Ndor, E.; Dauda, S.; Azagaku, E. Response of maize varieties (Zea mays) to biochar amended soil in Lafia, Nigeria. Am. J. Exp. Agric. 2014, 5, 525–531. [Google Scholar]
- Dempster, D.N.; Jones, D.L.; Murphy, D.V. Clay and biochar amendments decreased inorganic but not dissolved organic nitrogen leaching in soil. Soil Res. 2012, 50, 216–221. [Google Scholar]
- Faloye, O.; Alatise, M.; Ajayi, A.; Ewulo, B. Effects of biochar and inorganic fertiliser applications on growth, yield and water use efficiency of maize under deficit irrigation. Agric. Water Manag. 2019, 217, 165–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kannan, P.; Paramasivan, M.; Marimuthu, S.; Swaminathan, C.; Bose, J. Applying both biochar and phosphobacteria enhances Vigna mungo L. growth and yield in acid soils by increasing soil pH, moisture content, microbial growth and P availability. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2021, 308, 107258. [Google Scholar]
- Babalola, T.E.; Adabembe, B.A.; Faloye, O.T. Water use-yield relationship of maize as influenced by biochar and inorganic fertilizer applications in a tropical sandy clay loam soil. Agric. Water Manag. 2022, 271, 107801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Wu, P.; Feng, H.; Zhao, X.; Huang, J.; Zhuang, Z. Simulated experiment on effects of soil bulk density on soil water holding capacity. Acta Pedol. Sin. 2010, 47, 611–620. [Google Scholar]
- Günal, E.; Erdem, H.; Çelik, İ. Effects of three different biochars amendment on water retention of silty loam and loamy soils. Agric. Water Manag. 2018, 208, 232–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werner, W.; Sanderman, J.; Melillo, J. Decreased soil organic matter in a long-term soil warming experiment lowers soil water holding capacity and affects soil thermal and hydrological buffering. J. Geophys. Res. Biogeosci. 2020, 125, e2019JG005158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Q.; Liu, X.; Hao, T.; Zeng, M.; Shen, J.; Zhang, F.; De Vries, W. Modeling soil acidification in typical Chinese cropping systems. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 613, 1339–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houssou, A.A.; Jeyakumar, P.; Niazi, N.K.; Van Zwieten, L.; Li, X.; Huang, L.; Wei, L.; Zheng, X.; Huang, Q.; Huang, Y. Biochar and soil properties limit the phytoavailability of lead and cadmium by Brassica chinensis L. in contaminated soils. Biochar 2022, 4, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simmons, C.W.; Higgins, B.; Staley, S.; Joh, L.D.; Simmons, B.A.; Singer, S.W.; Stapleton, J.J.; VanderGheynst, J.S. The role of organic matter amendment level on soil heating, organic acid accumulation, and development of bacterial communities in solarized soil. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2016, 106, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, F.; Zhang, W.; Liang, Y.; Wang, K.; Jin, Z. Seasonal changes of soil organic acid concentrations in relation to available N and P at different stages of vegetation restoration in a karst ecosystem. Chin. J. Ecol. 2020, 39, 1112. [Google Scholar]
- Clarholm, M.; Skyllberg, U.; Rosling, A. Organic acid induced release of nutrients from metal-stabilized soil organic matter—The unbutton model. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2015, 84, 168–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nuss, R.F.; Loewus, F.A. Further studies on oxalic acid biosynthesis in oxalate-accumulating plants. Plant Physiol. 1978, 61, 590–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, X.; Liu, Z.; Liu, Z.; Xie, G.; Rookes, J.; An, F. Root secretion of oxalic and malic acids mitigates the rubber tree aluminum toxicity. J. Rubber Res. 2021, 24, 381–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulmatiski, A.; Beard, K.H.; Stevens, J.R.; Cobbold, S.M. Plant–soil feedbacks: A meta-analytical review. Ecol. Lett. 2008, 11, 980–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, M.B.; Zhou, J.L.; Ngo, H.H.; Guo, W. Insight into biochar properties and its cost analysis. Biomass Bioenergy 2016, 84, 76–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dari, B.; Nair, V.D.; Harris, W.G.; Nair, P.; Sollenberger, L.; Mylavarapu, R. Relative influence of soil- vs. biochar properties on soil phosphorus retention. Geoderma 2016, 280, 82–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Qu, Z.Y.; Zhang, R.X.; Yang, Y.X.; Jia, Y.L.; Gao, X.Y.; Gao, L.H. Effects of Drip-irrigation Schedule Under Film-mulching and Biochar Amount on Corn Growth and Water-Nitrogen Use Efficiency. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2023, 37, 313–322. [Google Scholar]
- Geng, M.; Guan, S.; Meng, W.; Wang, X. Effects of straw returning and biochar application on soil organic matter and mitigate soil acidification of black soil. J. Jilin Agric. Univ. 2023, 45, 178–187. [Google Scholar]
- Acosta-Martinez, V.; Cano, A.; Johnson, J. Simultaneous determination of multiple soil enzyme activities for soil health-biogeochemical indices. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2018, 126, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Yang, Y.; Sun, Y.; Jiao, Y.; Wang, Y.; Chen, H.; Wu, Q.; Chi, D. Using nitrogen-loaded biochar for soil improvement to decrease applied nitrogen and stabilize rice yield under alternate wet-dry irrigation. Soil Tillage Res. 2022, 223, 105493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gömöryová, E.; Střelcová, K.; Škvarenina, J.; Gömöry, D. Responses of soil microorganisms and water content in forest floor horizons to environmental factors. Eur. J. Soil Biol. 2013, 55, 71–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogunkunle, C.O.; Falade, F.O.; Oyedeji, B.J.; Akande, F.O.; Vishwakarma, V.; Alagarsamy, K.; Ramachandran, D.; Fatoba, P.O. Short-term aging of pod-derived biochar reduces soil cadmium mobility and ameliorates cadmium toxicity to soil enzymes and tomato. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2021, 40, 3306–3316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, S.; Li, H.; Rengel, Z.; Du, Z.; Hu, N.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, A. Biochar application promotes crops yield through regulating root development and the community structure of root endophytic fungi in wheat-maize rotation. Soil Tillage Res. 2023, 234, 105827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Brutnell, T.P. Setaria viridis and Setaria italica, model genetic systems for the Panicoid grasses. J. Exp. Bot. 2011, 62, 3031–3037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Material | Soil Type | Sand (%) | Silt (%) | Clay (%) | pH | BD (g/cm3) | TN (‰) | TP (‰) | Organic Matter (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aeolian sandy soil | Sandy soil | 94.5 | 4.4 | 1.1 | \ | 1.72 | 0.07 | 0.23 | 0.15 |
| Loess | Loessial soil | 8.8 | 69.1 | 22.1 | \ | 1.62 | 0.12 | 0.32 | 0.25 |
| Biochar | \ | \ | \ | \ | 8.55 | 0.35 | 14 | 4.6 | 50.6 (Total C content) |
| Treatment | 2021 (kg ha−1) | 2022 (kg ha−1) |
|---|---|---|
| CK | 3410 ± 246 b | 3092 ± 175 c |
| B1 | 3827 ± 148 ab | 3931 ± 289 b |
| B2 | 4093 ± 458 a | 4246 ± 606 ab |
| B3 | 4250 ± 109 a | 4753 ± 433 a |
| Y | NS | |
| T | *** | |
| Y × T | NS | |
| GY | OA | AA | CA | SBD | pH | Cat | Ur | Su | AN | AP | SOM | TP | TN | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OA | 0.824 ** | |||||||||||||
| AA | 0.641 ** | 0.752 ** | ||||||||||||
| CA | 0.553 ** | 0.691 ** | 0.947 ** | |||||||||||
| SBD | −0.612 ** | −0.742 ** | −0.706 ** | −0.664 ** | ||||||||||
| pH | −0.640 ** | −0.470 * | −0.04 | 0.034 | 0.263 | |||||||||
| Cat | 0.639 ** | 0.856 ** | 0.812 ** | 0.725 ** | −0.741 ** | −0.232 | ||||||||
| Ur | 0.476 * | 0.691 ** | 0.756 ** | 0.661 ** | −0.593 ** | −0.04 | 0.820 ** | |||||||
| Su | 0.519 ** | 0.551 ** | 0.062 | −0.003 | −0.216 | −0.727 ** | 0.363 | 0.065 | ||||||
| AN | 0.712 ** | 0.847 ** | 0.869 ** | 0.802 ** | −0.738 ** | −0.174 | 0.852 ** | 0.712 ** | 0.324 | |||||
| AP | 0.679 ** | 0.729 ** | 0.289 | 0.217 | −0.467 * | −0.619 ** | 0.551 ** | 0.241 | 0.777 ** | 0.542 ** | ||||
| SOM | 0.699 ** | 0.811 ** | 0.628 ** | 0.528 ** | −0.589 ** | −0.327 | 0.786 ** | 0.553 ** | 0.427 * | 0.678 ** | 0.686 ** | |||
| TP | 0.633 ** | 0.769 ** | 0.678 ** | 0.621 ** | −0.799 ** | −0.245 | 0.788 ** | 0.542 ** | 0.456 * | 0.805 ** | 0.647 ** | 0.689 ** | ||
| TN | 0.643 ** | 0.811 ** | 0.736 ** | 0.639 ** | −0.600 ** | −0.172 | 0.801 ** | 0.617 ** | 0.402 | 0.760 ** | 0.576 ** | 0.884 ** | 0.753 ** | |
| SWC | 0.617 ** | 0.776 ** | 0.900 ** | 0.888 ** | −0.687 ** | −0.001 | 0.811 ** | 0.785 ** | 0.076 | 0.865 ** | 0.381 | 0.688 ** | 0.753 ** | 0.711 ** |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hou, X.; He, W.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, N.; Yan, J.; Chen, Y. Maize-Straw Biochar Enhances Soil Properties and Grain Yield of Foxtail Millet in a Newly Reclaimed Land. Agronomy 2024, 14, 2465. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14112465
Hou X, He W, Zhang Y, Zhang N, Yan J, Chen Y. Maize-Straw Biochar Enhances Soil Properties and Grain Yield of Foxtail Millet in a Newly Reclaimed Land. Agronomy. 2024; 14(11):2465. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14112465
Chicago/Turabian StyleHou, Xuyan, Wei He, Yi Zhang, Ningning Zhang, Jiakun Yan, and Yinglong Chen. 2024. "Maize-Straw Biochar Enhances Soil Properties and Grain Yield of Foxtail Millet in a Newly Reclaimed Land" Agronomy 14, no. 11: 2465. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14112465
APA StyleHou, X., He, W., Zhang, Y., Zhang, N., Yan, J., & Chen, Y. (2024). Maize-Straw Biochar Enhances Soil Properties and Grain Yield of Foxtail Millet in a Newly Reclaimed Land. Agronomy, 14(11), 2465. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14112465








