Optimal Water and Nitrogen Regimes Increased Fruit Yield and Water Use Efficiency by Improving Root Characteristics of Drip-Fertigated Greenhouse Tomato (Solanum lycopersicum L.)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
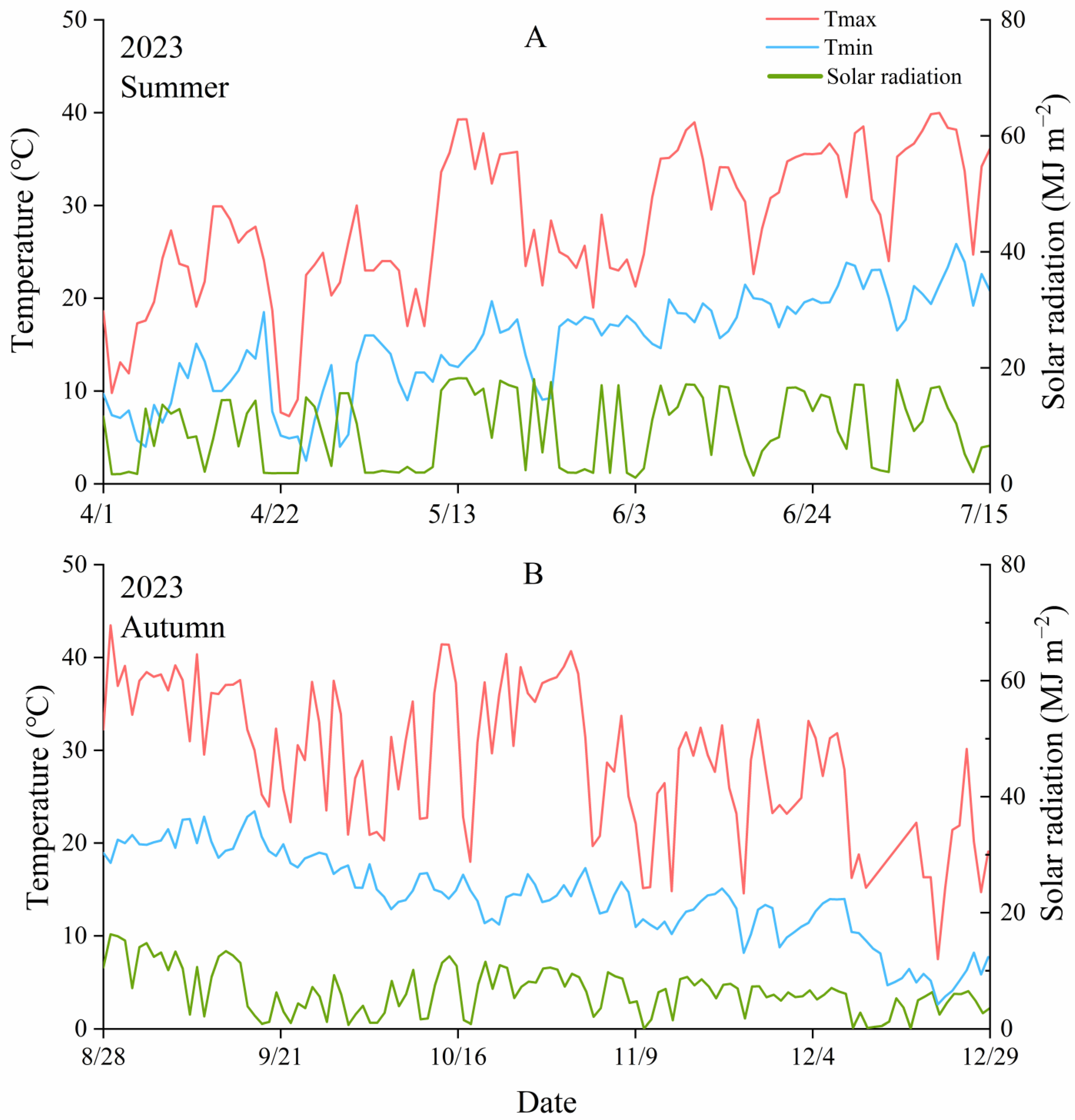
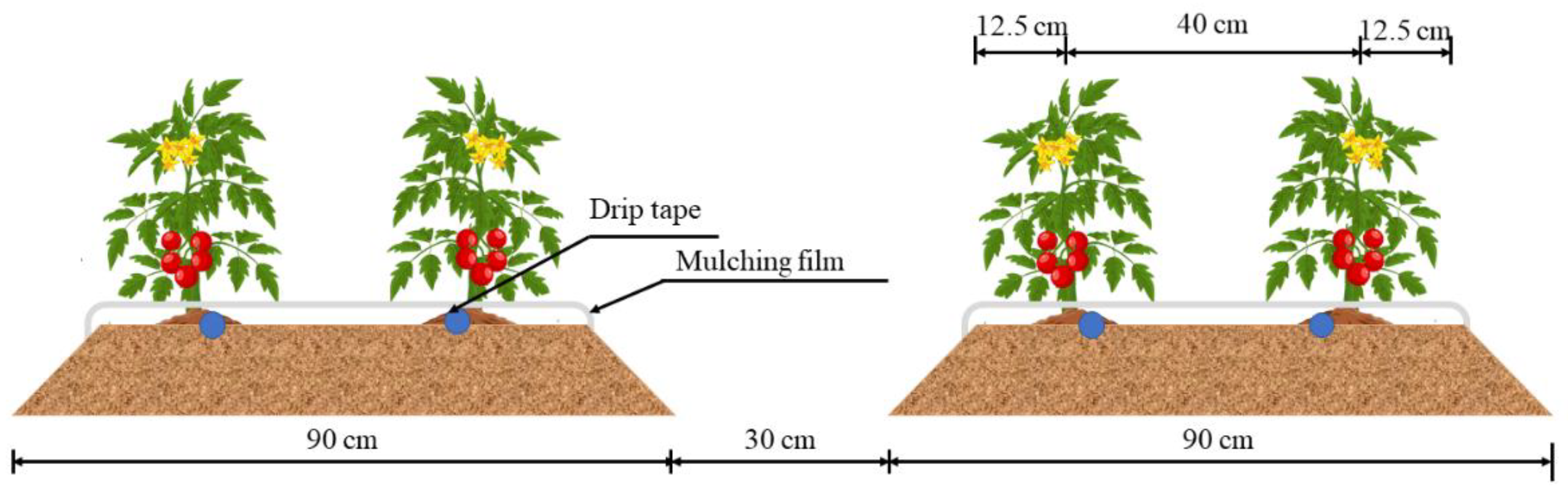
2.1. Description of Experimental Plots
2.2. Experimental Design and Crop Management
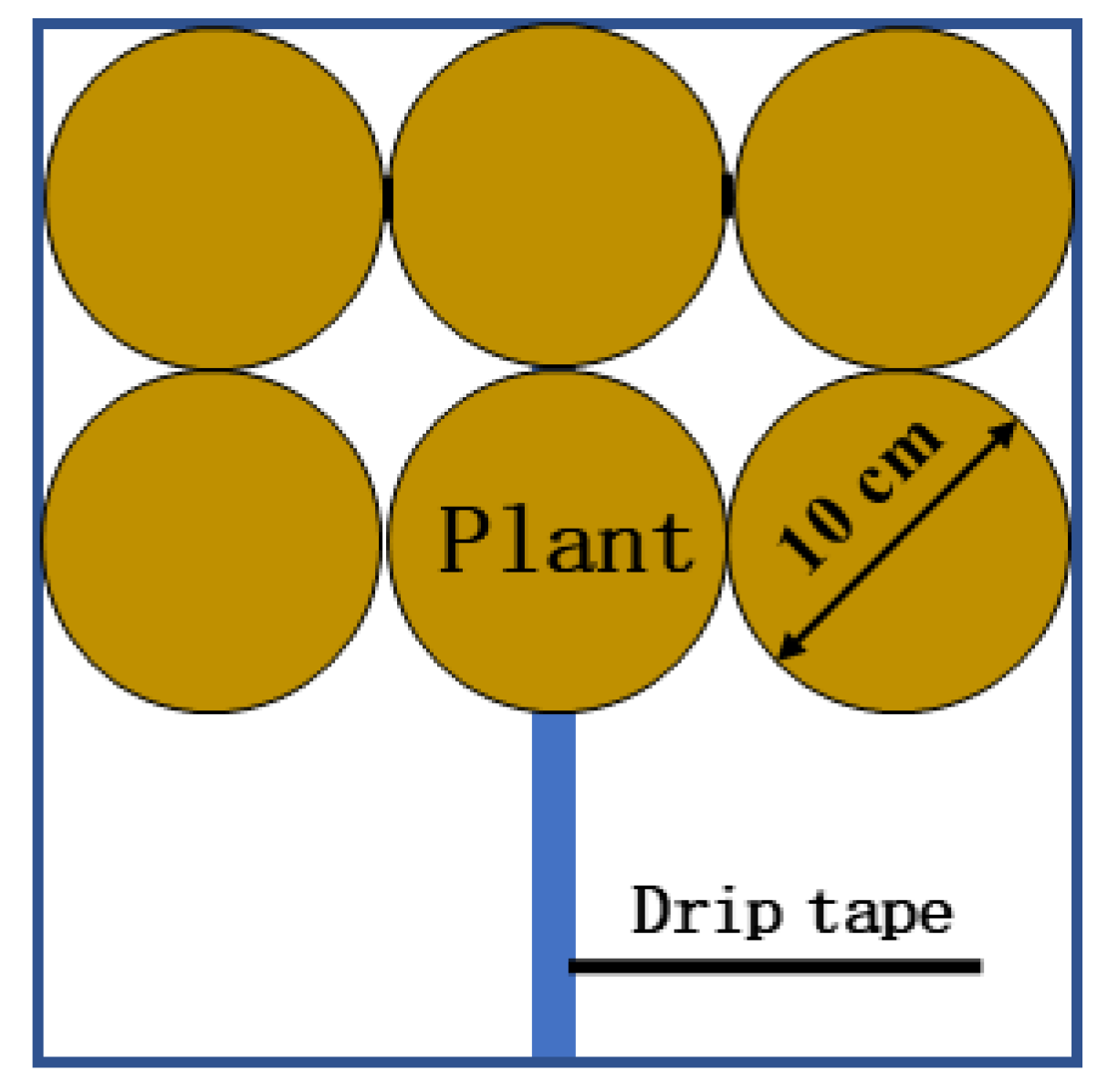
2.3. Sampling and Measurement
2.3.1. Root Characteristics
2.3.2. Fruit Yield (GY)
2.3.3. Water Use Efficiency
2.3.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
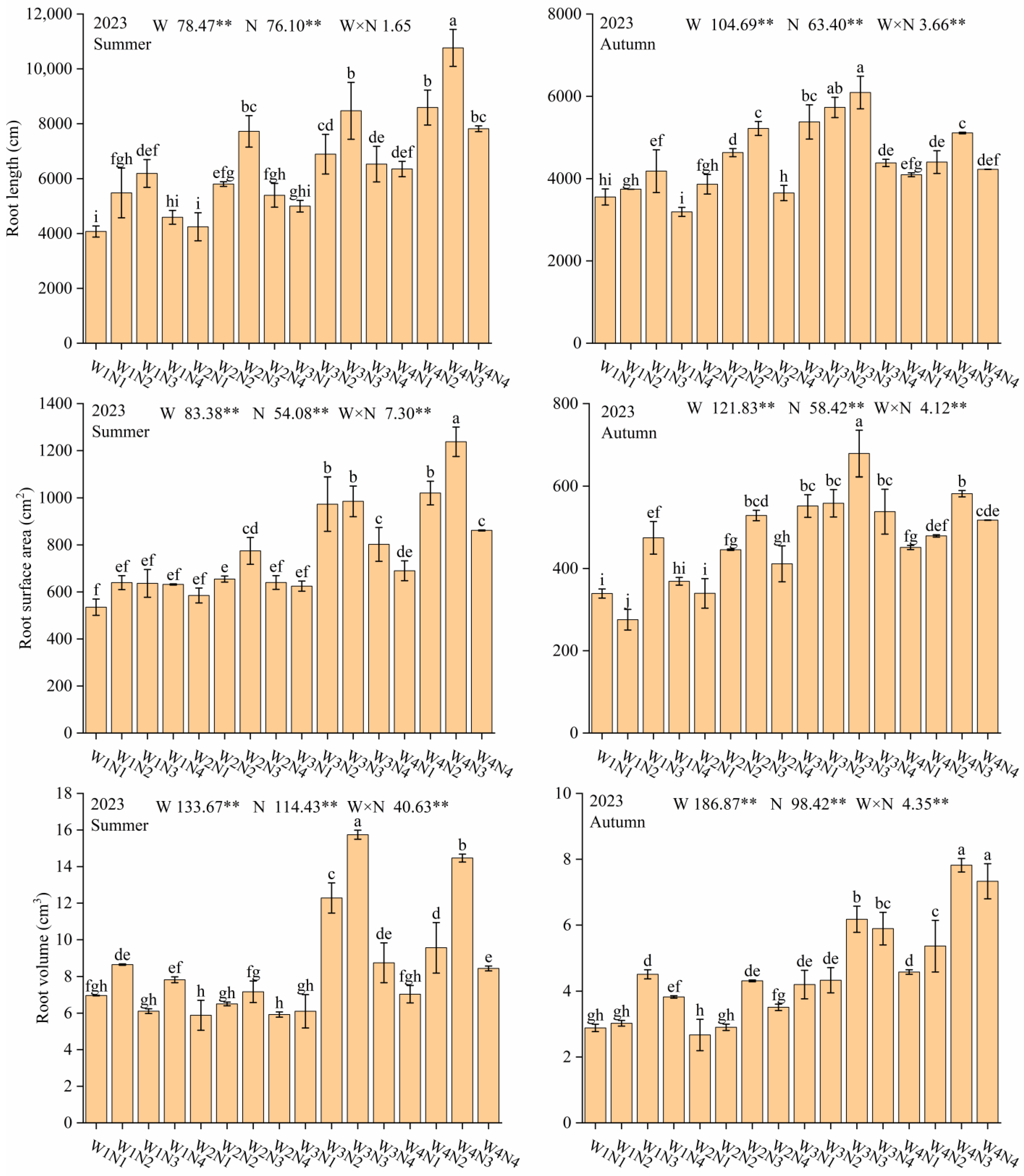
3.1. Total Root Characteristics
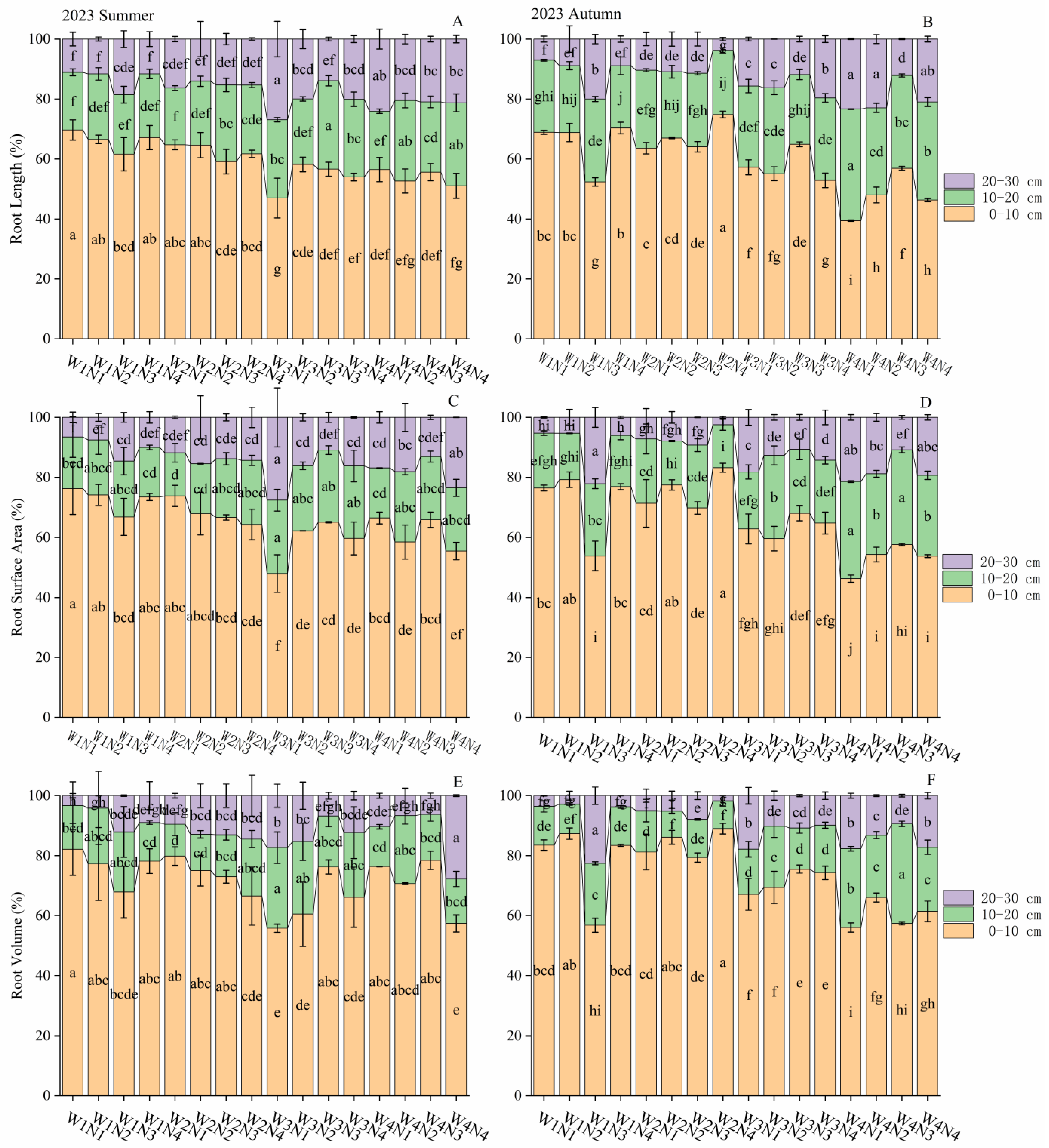
3.2. Root Characteristics in Each Soil Layer
3.3. Vertical Distribution of Roots
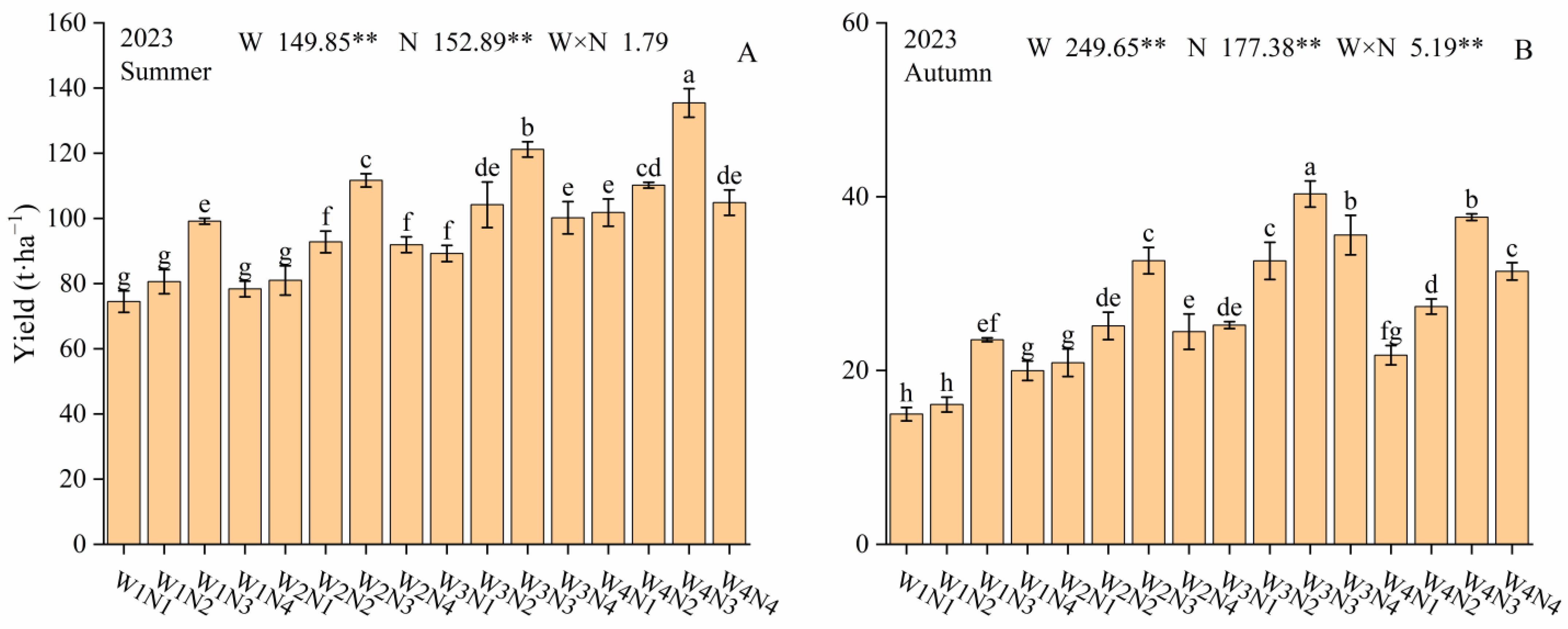
3.4. Fruit Yield
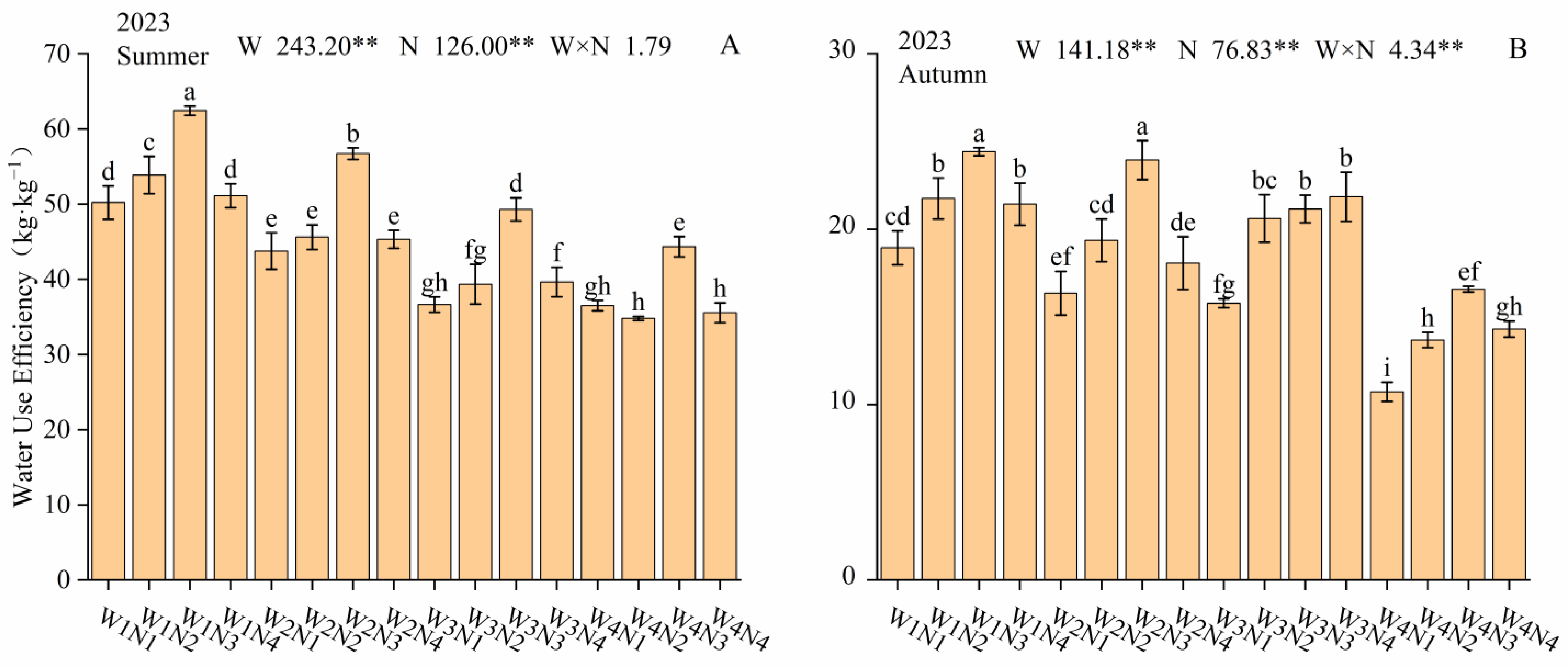
3.5. Water Use Efficiency
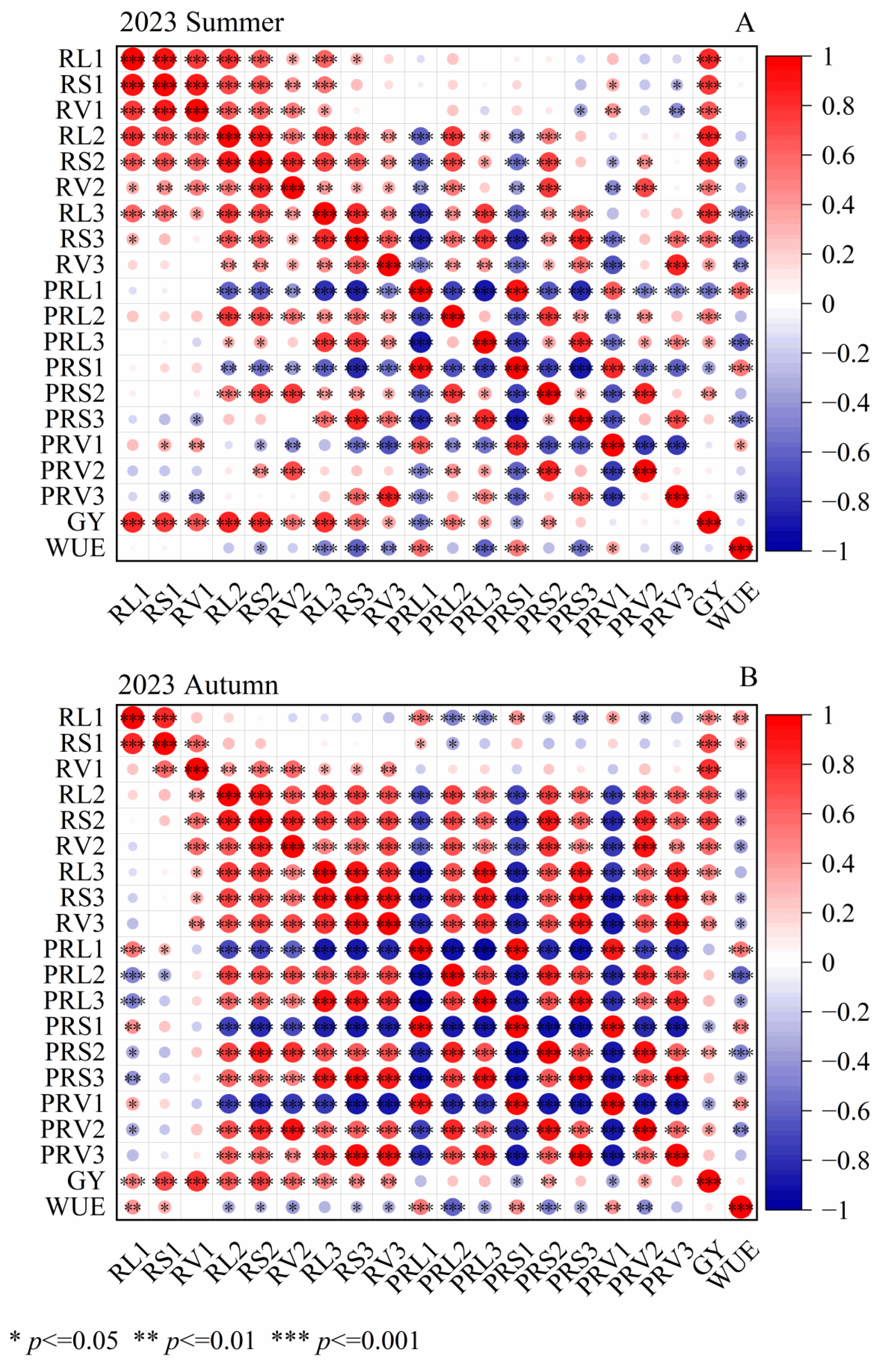
3.6. Correlation Analysis
4. Discussion
4.1. Effect of Water and Nitrogen Regulation on Total Root Characteristics
4.2. Impact of Water and Nitrogen Management on Root Distribution Each Soil Layers
4.3. Effect of Water and Nitrogen Regulation on Vertical Distribution of Roots
4.4. Effect of Water Nitrogen Regulation on Tomato Yield
4.5. Effect of Water and Nitrogen Regulation on WUE
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, X.; Tian, W.; Zheng, W.; Shah, S.; Li, J.; Wang, X.; Zhang, X. Quantitative relationships between salty water irrigation and tomato yield, quality, and irrigation water use efficiency: A meta-analysis. Agric. Water Manag. 2023, 280, 108213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Hou, X.; Bertin, N.; Ding, R.; Du, T. Quantitative responses of tomato yield, fruit quality and water use efficiency to soil salinity under different water regimes in Northwest China. Agric. Water Manag. 2023, 277, 108134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Fan, Y.; Qiu, Y.; Hao, X.; Li, S.; Kang, S. Response of yield and quality of greenhouse tomatoes to water and salt stresses and biochar addition in Northwest China. Agric. Water Manag. 2022, 270, 107736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, M.; Wang, H.; Fan, J.; Xiang, Y.; Tang, Z.; Pei, S.; Zeng, H.; Zhang, C.; Dai, Y.; Li, Z.; et al. Effects of nitrogen supply on tomato yield, water use efficiency and fruit quality: A global meta-analysis. Sci. Hortic. 2021, 290, 110553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, W.; Chang, N.; Zhang, J.; Li, G.; Zhang, J.; Ju, X.; Zhang, G.; Li, H. Optimized fertigation mitigates N2O and NO emissions and enhances NH3 volatilizations in an intensified greenhouse vegetable system. Agric. Water Manag. 2022, 272, 107797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, F.; Qiang, S.; Li, Z. Effects of irrigation and fertilization on growth, water and nitrogen use of tomato in greenhouse under fertigation. Agric. Res. Arid. Areas 2017, 35, 103–109. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Q.; Niu, W.; Du, Y.; Sun, J.; Cui, B.; Zhang, E.; Wang, Y.; Siddique, K.H. Effect of aerated drip irrigation and nitrogen doses on N2O emissions, microbial activity, and yield of tomato and muskmelon under greenhouse conditions. Agric. Water Manag. 2023, 283, 108321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, M.; Wang, H.; Fan, J.; Xiang, Y.; Liu, X.; Liao, Z.; Abdelghany, A.E.; Zhang, F.; Li, Z. Evaluation of AquaCrop model for greenhouse cherry tomato with plastic film mulch under various water and nitrogen supplies. Agric. Water Manag. 2022, 274, 107949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, X.; Li, X.; Li, Y.; Bo, G.; Qiu, R.; Huang, Z.; Gao, S.; Wang, S. An improved model to simulate soil water and heat: A case study for drip-irrigated tomato grown in a greenhouse. Agric. Water Manag. 2023, 277, 108121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Gu, F.; Chen, J.; Yang, H.; Jiang, J.; Du, T.; Zhang, J. Assessing the response of yield and comprehensive fruit quality of tomato grown in greenhouse to deficit irrigation and nitrogen application strategies. Agric. Water Manag. 2015, 161, 9–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; Huang, G.; Jia, D.; Wang, J.; Mota, M.; Pereira, L.S.; Huang, Q.; Xu, X.; Liu, H. Responses of drip irrigated tomato (Solanum lycopersicum L.) yield, quality and water productivity to various soil matric potential thresholds in an arid region of Northwest China. Agric. Water Manag. 2013, 129, 181–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Kang, S.; Du, T.; Qiu, R.; Guo, P.; Chen, R. Quantitative response of greenhouse tomato yield and quality to water deficit at different growth stages. Agric. Water Manag. 2013, 129, 152–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badr, M.A.; Abou-Hussein, S.D.; El-Tohamy, W.A. Tomato yield, nitrogen uptake and water use efficiency as affected by planting geometry and level of nitrogen in an arid region. Agric. Water Manag. 2016, 169, 90–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, Y.Y.; Zhang, F.C.; Zhang, Y.; Li, J.; Qiang, S.C.; Wu, L.F. Effect of Irrigation and Fertilizer Coupling on Greenhouse Tomato Yield, Quality, Water and Nitrogen Utilization Under Fertigation. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2015, 31 (Suppl. S1), 110–121. [Google Scholar]
- Du, Y.-D.; Niu, W.-Q.; Gu, X.-B.; Zhang, Q.; Cui, B.-J. Water- and nitrogen-saving potentials in tomato production: A meta-analysis. Agric. Water Manag. 2018, 210, 296–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Yun, J.; Shi, P.; Li, Z.; Li, P.; Xing, Y. Root Growth, Fruit Yield and Water Use Efficiency of Greenhouse Grown Tomato Under Different Irrigation Regimes and Nitrogen Levels. J. Plant Growth Regul. 2019, 38, 400–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Chen, J.; Chen, A.; Wang, L.; Guo, X.; Niu, Y.; Liu, S.; Mi, G.; Gao, Q. Reducing basal nitrogen rate to improve maize seedling growth, water and nitrogen use efficiencies under drought stress by optimizing root morphology and distribution. Agric. Water Manag. 2019, 212, 328–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Du, T.; Qiu, R.; Chen, J.; Wang, F.; Li, Y.; Wang, C.; Gao, L.; Kang, S. Improved water use efficiency and fruit quality of greenhouse crops under regulated deficit irrigation in northwest China. Agric. Water Manag. 2017, 179, 193–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.X.; Wang, C.Y.; He, D.X. Root of Wheat; China Agriculture Press: Beijing, China, 1999; pp. 1–10 and 136–142. [Google Scholar]
- Xue, L.H.; Duan, J.J.; Wang, Z.M.; Guo, Z.W.; Lu, L.Q. Effects of different irrigation regimes on spatial-temporal distribution of roots, soil water use and yield in winter wheat. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2010, 30, 5296–5305, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Luo, L.; Mei, H.; Yu, X.; Liu, H.; Feng, F. Water-saving and drought-resistance rice and its development strategy. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2011, 56, 804–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merrill, S.D.; Tanaka, D.L.; Hanson, J.D. Root Length Growth of Eight Crop Species in Haplustoll Soils. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2002, 66, 913–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, Z.; Fan, J.; Yang, R.; Xu, X.; Liu, L.; Li, S.; Zhang, F.; Li, Z. Interactive effects of plant density and nitrogen rate on grain yield, economic benefit, water productivity and nitrogen use efficiency of drip-fertigated maize in northwest China. Agric. Water Manag. 2022, 263, 107453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayankojo, I.T.; Morgan, K.T.; Kadyampakeni, D.M.; Liu, G.D. Tomato Growth, Yield, and Root Development, Soil Nitrogen and Water Distribution as Affected by Nitrogen and Irrigation Rates on a Florida Sandy Soil. HortScience 2020, 55, 1744–1755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, I.; Mao, H.; Rasool, G.; Gao, H.; Javed, Q.; Sarwar, A.; Khan, M.I. Effect of Deficit Irrigation and Reduced N Fertilization on Plant Growth, Root Morphology and Water Use Efficiency of Tomato Grown in Soilless Culture. Agronomy 2021, 11, 228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Khan, A.; Tan, D.K.Y.; Luo, H. Rational Water and Nitrogen Management Improves Root Growth, Increases Yield and Maintains Water Use Efficiency of Cotton under Mulch Drip Irrigation. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 912. Available online: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fpls.2017.00912 (accessed on 27 December 2023). [CrossRef]
- Giuliani, M.M.; Nardella, E.; Gagliardi, A.; Gatta, G. Deficit Irrigation and Partial Root-Zone Drying Techniques in Processing Tomato Cultivated under Mediterranean Climate Conditions. Sustainability 2017, 9, 2197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Xu, F.; Zhu, J.R.; Wang, R.F.; Xu, Z.H.; Shu, L.Z.; Xu, W.W. Nitrogen forms affect root growth, photosynthesis, and yield of tomato under alternate partial root-zone irrigation. J. Plant Nutr. Soil Sci. 2016, 179, 104–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.Y.; Ma, Y.X. Ecological and Physiological effects on root systems of wheat under different soil water conditions. Acta Agri. Boreali-Sin. 1992, 7, 1–8, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.; Liu, W.; Li, Q.; Ma, D.; Lu, H.; Feng, W.; Xie, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Guo, T. Effects of different irrigation and nitrogen regimes on root growth and its correlation with above-ground plant parts in high-yielding wheat under field conditions. Field Crops Res. 2014, 165, 138–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, D.; Ning, S.; Sun, X.; Zhang, J.; Zhu, H.; Tang, J.; Xu, Y. Agricultural use of deserted saline land through an optimized drip irrigation system with mild salinized water. Agric. Water Manag. 2023, 281, 108261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, X.; Deng, T.; Xiao, Y.; Jin, C.; Lyu, W.; Wu, Z.; Wang, W.; Wang, X.; He, Q.; Yang, H. Emerging Alternaria and Fusarium mycotoxins in tomatoes and derived tomato products from the China market: Occurrence, methods of determination, and risk evaluation. Food Control. 2023, 145, 109464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Yan, S.; Fan, J.; Zhang, F.; Zhao, W.; Zheng, J.; Guo, J.; Xiang, Y.; Wu, L. Combined effects of irrigation level and fertilization practice on yield, economic benefit and water-nitrogen use efficiency of drip-irrigated greenhouse tomato. Agric. Water Manag. 2022, 262, 107401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dou, Z.; Feng, H.; Zhang, H.; Abdelghany, A.E.; Zhang, F.; Li, Z.; Fan, J. Silicon application mitigated the adverse effects of salt stress and deficit irrigation on drip-irrigated greenhouse tomato. Agric. Water Manag. 2023, 289, 108526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Liu, H.; Gong, X.; Li, S.; Pang, J.; Chen, Z.; Sun, J. Optimizing irrigation and nitrogen management strategy to trade off yield, crop water productivity, nitrogen use efficiency and fruit quality of greenhouse grown tomato. Agric. Water Manag. 2021, 245, 106570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, Y.; Zhang, F.; Zhang, Y.; Li, J.; Qiang, S.; Li, Z.; Gao, M. Irrigation and fertilization coupling of drip irrigation under plastic film promotes tomato’s nutrient uptake and growth. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2014, 30, 70–80. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, M.; Zhang, Y.; Hu, W.; Hu, G.; Li, Q.; Yao, Y.; Gao, Y. Effects of different nitrogen rates on nutrition absorption, distribution and yield in tomato. J. Plant Nutr. Fertil. 2010, 16, 1238–1245. [Google Scholar]
- Lahoz, I.; Pérez-de-Castro, A.; Valcárcel, M.; Macua, J.I.; Beltrán, J.; Roselló, S.; Cebolla-Cornejo, J. Effect of water deficit on the agronomical performance and quality of processing tomato. Sci. Hortic. 2016, 200, 55–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Truu, M.; Truu, J.; Heinsoo, K. Changes in soil microbial community under willow coppice: The effect of irrigation with secondary-treated municipal wastewater. Ecol. Eng. 2009, 35, 1011–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Replication I | Replication II | Replication III | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| W1 | W2 | W3 | W4 | W1 | W2 | W3 | W4 | W1 | W2 | W3 | W4 |
| N4 | N1 | N3 | N2 | N2 | N2 | N1 | N3 | N4 | N4 | N1 | N3 |
| N2 | N3 | N2 | N1 | N1 | N3 | N3 | N2 | N3 | N2 | N2 | N2 |
| N1 | N4 | N1 | N4 | N4 | N1 | N4 | N4 | N2 | N1 | N3 | N1 |
| N3 | N2 | N4 | N3 | N3 | N4 | N2 | N1 | N1 | N3 | N4 | N4 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Feng, H.; Dou, Z.; Jiang, W.; Mahmood, H.; Liao, Z.; Li, Z.; Fan, J. Optimal Water and Nitrogen Regimes Increased Fruit Yield and Water Use Efficiency by Improving Root Characteristics of Drip-Fertigated Greenhouse Tomato (Solanum lycopersicum L.). Agronomy 2024, 14, 2439. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14102439
Feng H, Dou Z, Jiang W, Mahmood H, Liao Z, Li Z, Fan J. Optimal Water and Nitrogen Regimes Increased Fruit Yield and Water Use Efficiency by Improving Root Characteristics of Drip-Fertigated Greenhouse Tomato (Solanum lycopersicum L.). Agronomy. 2024; 14(10):2439. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14102439
Chicago/Turabian StyleFeng, Hanlong, Zhiyao Dou, Wenhui Jiang, Hemat Mahmood, Zhenqi Liao, Zhijun Li, and Junliang Fan. 2024. "Optimal Water and Nitrogen Regimes Increased Fruit Yield and Water Use Efficiency by Improving Root Characteristics of Drip-Fertigated Greenhouse Tomato (Solanum lycopersicum L.)" Agronomy 14, no. 10: 2439. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14102439
APA StyleFeng, H., Dou, Z., Jiang, W., Mahmood, H., Liao, Z., Li, Z., & Fan, J. (2024). Optimal Water and Nitrogen Regimes Increased Fruit Yield and Water Use Efficiency by Improving Root Characteristics of Drip-Fertigated Greenhouse Tomato (Solanum lycopersicum L.). Agronomy, 14(10), 2439. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14102439







