Effects of Inequality of Access to Irrigation and Water Productivity on Paddy Yield in Nigeria
Abstract
1. Introduction
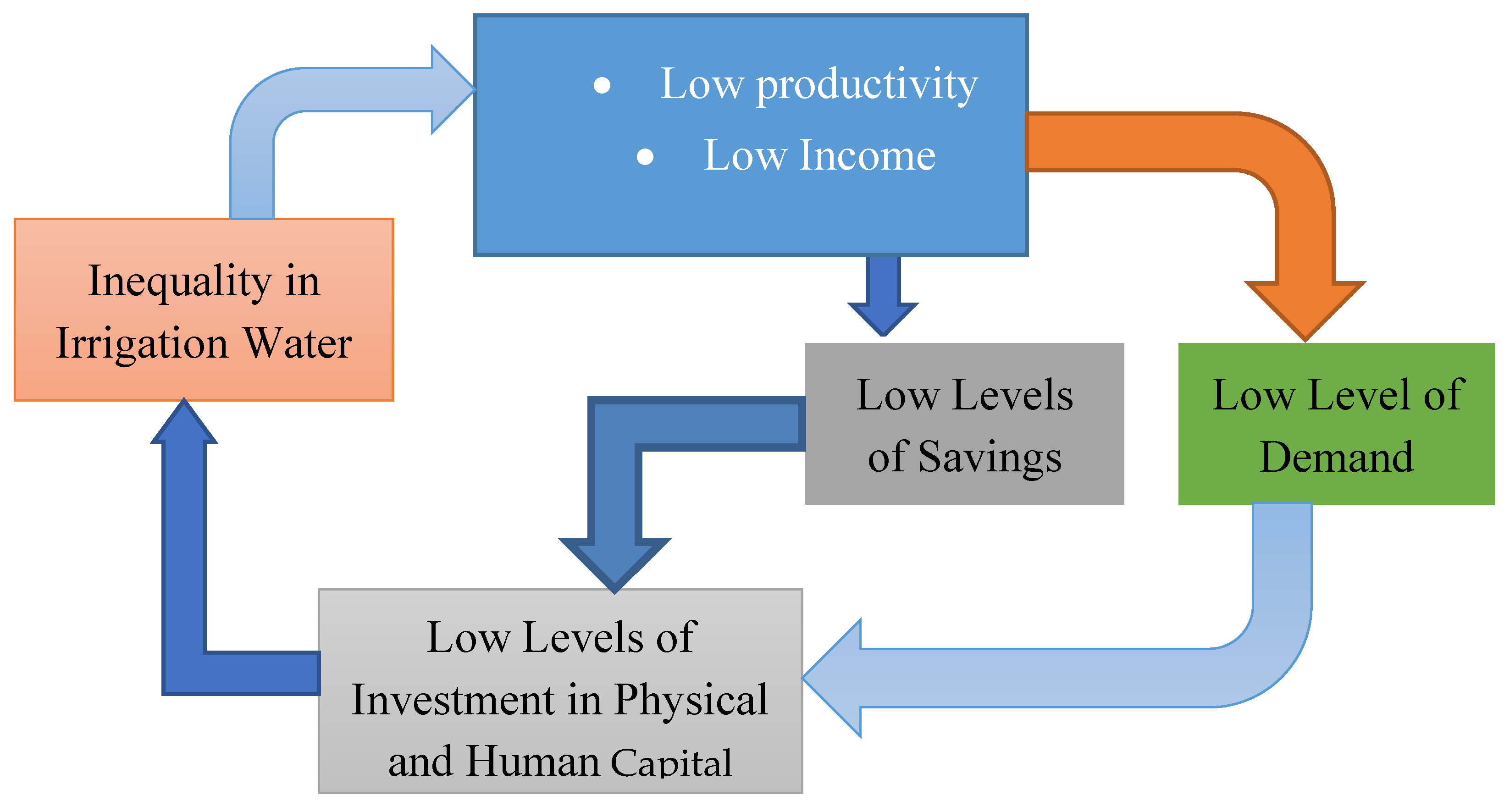
Conceptual Framework
2. Materials and Methods
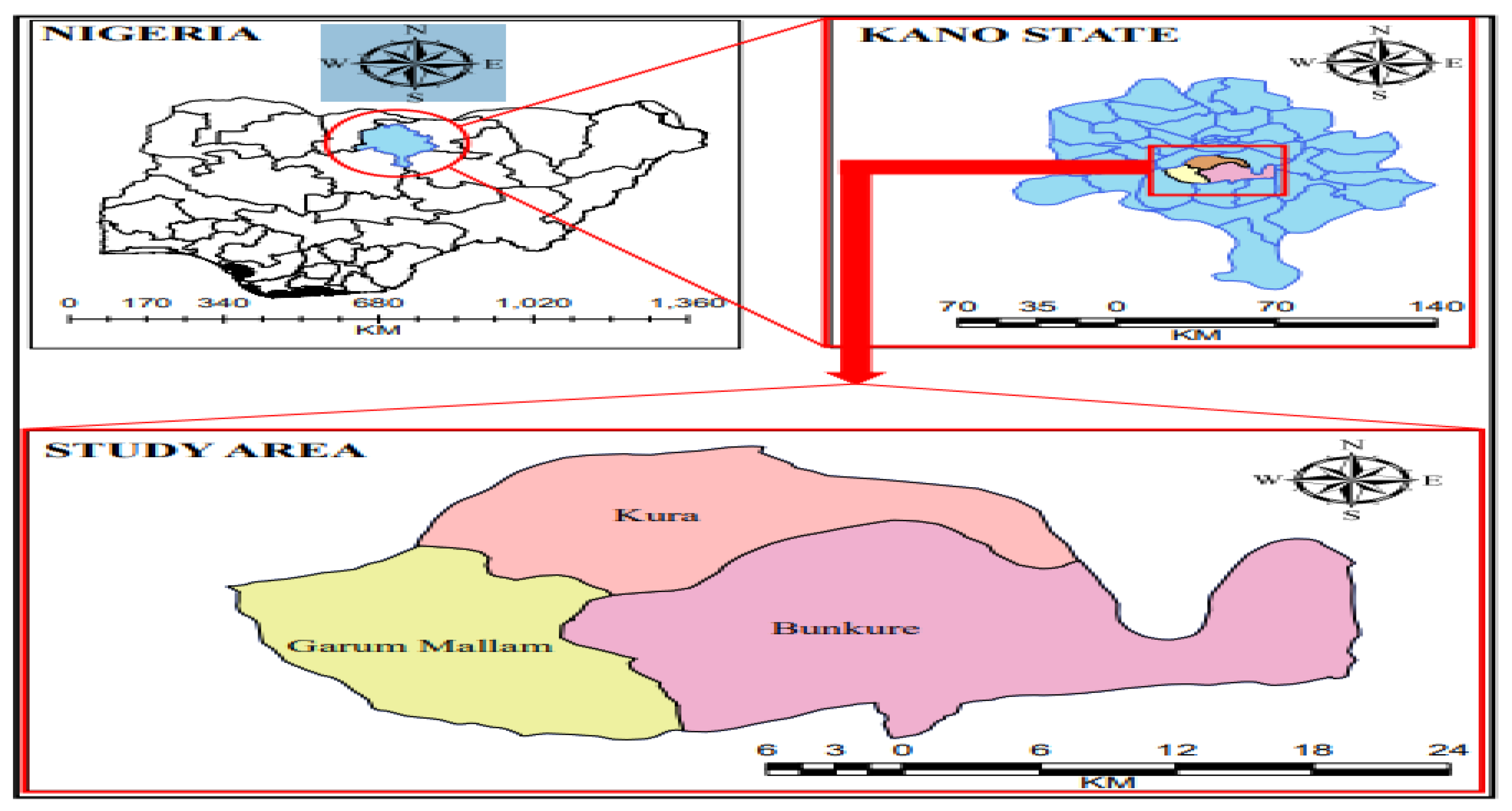
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Sampling Procedure
Measurement of Irrigation Water Use
2.3. Data Analysis
2.3.1. Kruskal–Wallis Test
2.3.2. Post Hoc Tukey–Kramer Test
2.3.3. Logistic Regression Analysis
2.3.4. Method Used to Measure Irrigation Water Accessibility
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Irrigation Water Used, Yield per Acre, and Water Productivity
3.2. Access to Irrigation Water
3.3. Kruskal–Wallis Test
3.4. Post-Hoc Test
3.5. Determinants of Paddy Output
4. Conclusions
5. Policy Recommendations
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hussain, I. Direct and indirect benefits and potential dis benefits of irrigation: Evidence and lessons. Irrig. Drain. J. Int. Comm. Irrig. Drain. 2007, 56, 179–194. [Google Scholar]
- Bardhan, P.; Dayton-Johnson, J. Unequal irrigators: Heterogeneity and commons management in large-scale multivariate research. Drama Commons 2002, 15, 87–112. [Google Scholar]
- Pariyar, B.; Lovett, J.C.; Snell, C. Inequality of access in irrigation systems of the mid-hills of Nepal. Area Dev. Policy 2018, 3, 60–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumari, B.; Thiruchelvam, S.; Dissanayake, K.; Lasantha, T. Crop diversification and income inequality in irrigation systems: The case of Minipe. Trop. Agric. Res. 2010, 21, 308–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shantha, A.; Ali, B.; Bandara, R. Efficiency and managerial ability of paddy farming under minor irrigation conditions: A frontior production function approach. J. Agric. Sci. Sri Lanka 2012, 7, 145–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yapa, L.; Rainis, R.; Abdullah, A.L.; Hemakumara, G. Upstream-downstream disparity in irrigation management in Sri Lanka: A review of empirical evidence. Geogr. Malays. J. Soc. Space 2020, 16, 45–55. [Google Scholar]
- Pollock, L.J. Integration of Aquaculture within Irrigation Systems: A Poverty-Focused Approach. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Stirling, Stirling, UK, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Aheeyar, M.M.M.; Padmajani, M.T.; Bandara, M.A.C.S. Farmer Participation in Irrigation System Management: Achievements and Drawbacks; Hector Kobbekaduwa Agrarian Research and Training Institute: Colombo, Sri Lanka, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Paranage, K. Understanding the relationship between water infrastructure and socio political configurations: A case study from Sri Lanka. Water 2018, 10, 1402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aida, T. Social capital as an instrument for common pool resource management: A case study of irrigation management in Sri Lanka. Oxf. Econ. Pap. 2019, 71, 952–978. [Google Scholar]
- Namara, R.E.; Hanjra, M.A.; Castillo, G.E.; Ravnborg, H.M.; Smith, L.; Van Koppen, B. Agricultural water management and poverty linkages. Agric. Water Manag. 2010, 97, 520–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Praharaj, C.S.; Singh, U.; Singh, S.S.; Singh, N.P.; Shivay, Y.S. Supplementary and life-saving irrigation for enhancing pulses production, productivity and water-use efficiency in India. Indian J. Agron. 2016, 61, S249–S261. [Google Scholar]
- Barker, R.; Dawe, D.; Inocencio, A. Economics of water productivity in managing water for agriculture. In Water Productivity in Agriculture: Limits and Opportunities for Improvement; CABI Publishing: Wallingford, UK, 2003; pp. 19–35. [Google Scholar]
- Ezzahouani, A.; Valancogne, C.; Pieri, P.; Amalak, T.; Gaudillère, J.-P. Water economy by Italia grapevines under different irrigation treatments in a Mediterranean climate. OENO One 2007, 41, 131–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awel, S.M.; Tena Alamirew, T.T.; Michael, A.W. Performance assessment of community managed irrigation practices in the Wesha small-scale irrigation project, Southern Ethiopia. Irrig. Drain. Syst. Eng. 2018, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lashari, B.; Memon, Y.; Murray-Rust, H. Improving Equity of Water Distribution: The Challenge for Farmer Organizations in Sindh, Pakistan; Colorado State University: Fort Collins, CO, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Fujikura, R.; Nakayama, M.; Takesada, N. Lessons from Resettlement Caused by Large Dam Project: Case Studies from Japan, Indinesia and sri lanka. Water Resour. Dev. 2009, 25, 407–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, I.; Giordano, M.; Munir, H. Agricultural Water and Poverty Linkages: Case Studies on Large and Small Systems; International water Management Institute(IWMI): Colombo, Sri Lanka, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Bhattarai, M.; Sakthivadivel, R.; Hussain, I. Irrigation Impact on Incme Inequality and Pverty Alleviation: Plicy Issues and Ptions for Improved Management of Irrigation Systems; International Water Management Institute: Colmbo, Sri Lanka, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, L.E. Assessment of the Contribution of Irrigation to Poverty reduction and Sustainable Livelihoods. Water Resour. Dev. 2004, 20, 243–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, M.T.; Haie, N. Assessing the impacts of population growth and climate change on performance of water use systems and water allocation in Kano river basin, Nigeria. Water 2018, 10, 1766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Culas, R.J.; Baig, I.A. Impacts of irrigation water user allocations on water quality and crop productivity: The LCC irrigation system in Pakistan. Irrig. Drain. 2020, 69, 38–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ugalahi, U.B.; Adeoye, S.O.; Agbonlahor, M.U. Irrigation potentials and rice self-sufficiency in Nigeria: A review. Afr. J. Agric. Res. 2016, 11, 298–309. [Google Scholar]
- Adelodun, B.; Choi, K.-S. A review of the evaluation of irrigation practice in Nigeria: Past, present, and future prospects. Afr. J. Agric. Res. 2018, 13, 2087–2097. [Google Scholar]
- Smout, I.K.; Gorantiwar, S. Productivity and equity of different irrigation schedules under limited water supply. J. Irrig. Drain. Eng. 2006, 132, 349–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shantha, A.A.; Ali, B.A. The impact of uneven allocation of irrigation water on dynamics of agribusiness and income inequality: The case of mahaweli development project, sri lanka. Proc. Int. Conf. Bus. Manag. 2011, 8, 148–155. [Google Scholar]
- Herath, G. Irrigation Management—Does Bottom Up Work Better than Top Down in Sri Lanka? In Promise, Trust and Evolution: Managing the Commons of South Asia: Managing the Commons of South Asia; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2008; Volume 10, p. 191. [Google Scholar]
- Berundharshani, T.; Munasinghe, D. Drought Resilient Farming System through Crop Diversification: The Case of Huruluwewa. In Proceedings of the 6th Annual National Building Research Organization Symposium on Innovations for Resilient Environment, Colombo, Sri Lanka, 22 December 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Onyenweze, L.N. Evaluation of Participatory Poverty Reduction through Water Delivery Support of Local Empowerment and Environmental Management Project (LEEMP) in Rural Southeast Nigeria. Doctoral Dissertation, University of Nigeria, Nsukka, Nigeria, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Graham, W.B.R.; Bashar, Z.U. Irrigation performance and water productivity in small-holder lift irrigation systems in north-western Nigeria. Agric. Eng. Int. CIGR J. 2021, 23, 12–17. [Google Scholar]
- Unal, H.; Asik, S.; Avci, M.; Yasar, S.; Akkuzu, E. Performance of water delivery system at tertiary canal level: A case study of the Menemen Left Bank Irrigation System, Gediz Basin, Turkey. Agric. Water Manag. 2004, 65, 155–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vos, J. Understanding water delivery performance in a large-scale irrigation system in Peru. Irrig. Drain. J. Int. Comm. Irrig. Drain. 2005, 54, 67–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gopalakrishnan, S.; Kumar, R.M.; Humayun, P.; Srinivas, V.; Kumari, B.R.; Vijayabharathi, R.; Somashekar, N. Assessment of different methods of rice (Oryza sativa. L) cultivation affecting growth parameters, soil chemical, biological, and microbiological properties, water saving, and grain yield in rice–rice system. Paddy Water Environ. 2014, 12, 79–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rowshon, M.K.; Mojid, M.A.; Amin, M.S.M.; Azwan, M.; Yazid, A.M. Improving irrigation water delivery performance of a large-scale rice irrigation scheme. J. Irrig. Drain. Eng. 2014, 140, 04014027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dejen, Z.A.; Schultz, B.; Hayde, L. Water delivery performance at Metahara large-scale irrigation scheme, Ethiopia. Irrig. Drain. 2015, 64, 479–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agide, Z.; Haileslassie, A.; Sally, H.; Erkossa, T.; Schmitter, P.S.; Langan, S.J.; Hoekstra, D. Analysis of Water Delivery Performance of Smallholder Irrigation Schemes in Ethiopia: Diversity and Lessons across Schemes, Typologies, and Reaches; International Livestock Research Institute: Nairobi, Kenya, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Nam, W.H.; Hong, E.M.; Choi, J.Y. Assessment of water delivery efficiency in irrigation canals using performance indicators. Irrig. Sci. 2016, 34, 129–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vera Delgado, J. The socio-cultural, institutional and gender aspects of the water transfer-agribusiness model for food and water security. Lessons learned from Peru. Food Secur. 2015, 7, 1187–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chukalla, A.D.; Krol, M.S.; Hoekstra, A.Y. Green and blue water footprint reduction in irrigated agriculture: Effect of irrigation techniques, irrigation strategies and mulching. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2015, 19, 4877–4891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suresh, A.; Raju, S.S.; Chauhan, S.; Chaudhary, K.R. Rainfed agriculture in India: An analysis of performance and implications. Indian J. Agric. Sci. 2014, 84, 1415–1422. [Google Scholar]
- Hussain, I.; Hanjra, M.A. Does irrigation water matter for rural poverty alleviation? Evidence from South and South-East Asia. Water Policy 2003, 5, 429–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, I. Pro-Poor Intervention Strategies in Irrigated Agriculture in Asia; International Water Management Institute: Colombo, Sri Lanka, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- You, L.; Ringler, C.; Wood-Sichra, U.; Robertson, R.; Wood, S.; Zhu, T.; Nelson, G.; Guo, Z.; Sun, Y. What is the irrigation potential for Africa? A combined biophysical and socioeconomic approach. Food Policy 2011, 36, 770–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ademola, A.E. Impact of agricultural financing on Nigeria economy. Asian J. Agric. Ext. Econ. Sociol. 2019, 31, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iheonu, C.; Urama, N.E. Addressing Poverty Challenges in Nigeria; African Heritage Institution: Enugu, Nigeria, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Sangari, D. An Evaluation of water and land uses in the kano River Project, Phase I, Kano State. J. Appl. Sci. Environ. Manag. 2007, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Mangiafico, S. How Should We Analyze Likert Item Data? J. NACAA 2019, 12, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Adunni Sanni, S.; Doppler, W. Socio-Economic Determinants of Household Fertilizer Use Intensity for Maize-based Production Systems in the Northern Guinea Savannah of Nigeria. J. Appl. Sci. 2007, 7, 1774–1779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Stevenson, J.; Vanlauwe, B.; Macours, K.; Johnson, N.; Krishnan, L.; Place, F.; Spielman, D.; Hughes, K.; Vlek, P. Farmer adoption of plot-and farm-level natural resource management practices: Between rhetoric and reality. Glob. Food Secur. 2019, 20, 101–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, S.; Martin, S.W.; Roberts, R.K.; Larson, J.A.; Hogan, R.J., Jr.; Johnson, J.L.; Paxton, K.W.; Reeves, J.M. Adoption of conservation-tillage practices and herbicide-resistant seed in cotton production. AgBioForum 2009, 12, 258–268. [Google Scholar]
- Bogale, A.; Shimelis, A. Household level determinants of food insecurity in rural areas of Dire Dawa, Eastern Ethiopia. Afr. J. Food Agric. Nutr. Dev. 2009, 9, 1914–1926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pieri, L.; Bittelli, M.; Wu, J.Q.; Dun, S.; Flanagan, D.C.; Pisa, P.R.; Ventura, F.; Salvatorelli, F. Using the Water Erosion Prediction Project (WEPP) model to simulate field-observed runoff and erosion in the Apennines mountain range, Italy. J. Hydrol. 2007, 336, 84–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paranage, K. Constructing the ‘legalities’ of encroachments in dam, canal, and stream reservations in the north-central province of Sri Lanka. Dev. Stud. Res. 2018, 5, 59–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onyeneke, R.U. Determinants of adoption of improved technologies in rice production in Imo State, Nigeria. Afr. J. Agric. Res. 2017, 12, 888–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nwaru, J.C.; Iheke, O.R. Comparative analysis of resource use efficiency in rice production systems in Abia State of Nigeria. J. Am. Sci. 2010, 6, 396–408. [Google Scholar]

| Type of Canal and Total Length | Upstream Area | Middle Area | Downstream Area |
|---|---|---|---|
| Main canal (25 km) | First 8.3 km | Between 8.4 and 16.6 km | Between 16.6 km and 25 km |
| Branch canal (27 km) | First 9 km | Between 9 and 18 km | Between 18.1 and 27 km |
| Distributary canal (204 km) | First 68 km from the branch canal | Between 68 and 136 km from the branch canal | Between 136 and 204 km from the branch canal |
| Variable | Explanation | Expected Sign of Variable |
|---|---|---|
| LCTN | Dummy variable of location (1 = upstream, 0 = otherwise) | + or − |
| WUA | Dummy variable of functional water users association (1 = yes, 0 = no) | + |
| IT | Dummy variable of illegal tapping (1 = yes, 0 = no) | − |
| CRC | Condition of the distr. canal (1 = yes, 0 = otherwise) | ? |
| EDU | Level of education of the farmers (continuous variable) | + or − |
| GEND | Dummy of gender (1 = male, 0 = female) | + or − |
| TWU | Dummy variable on training on water use (1 = yes, 0 = no) | + |
| AIW | Access to irrigation water (1 = high, 0 = low) | + |
| IWU | Quantity of irrigation water use in M3 (continuous variable) | + |
| FEXP | Farmer’s experience (continuous variable) | + or − |
| RECP | Adopting recommended practices (1 = yes, 0 = otherwise) | + |
| Location | Minimum | Maximum | Mean | Std. Deviation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Irrigation Water Used (m3) | ||||
| Upstream | 3041.98 | 9777.78 | 5258.73 | 2001.69 |
| Middle | 1498.51 | 5649.38 | 3654.14 | 1216.26 |
| Downstream | 1100.00 | 5703.70 | 2429.83 | 881.27 |
| Yield of Paddy/Acre (kg) | ||||
| Upstream | 1800 | 3000 | 2296.51 | 400.43 |
| Middle | 1125 | 2400 | 1978.51 | 343.81 |
| Downstream | 1050 | 2475 | 1625.25 | 265.35 |
| Physical Water Productivity | ||||
| Upstream | 0.44 kg/m3 | |||
| Middle | 0.53 kg/m3 | |||
| Downstream | 0.66 kg/m3 |
| Test Variables | Chi-Square | DF | Sig |
|---|---|---|---|
| Irrigation water use (upstream, middle, and downstream) | 95.461 | 2 | 0.000 *** |
| Access to irrigation water (upstream, middle, and downstream) | 111.164 | 2 | 0.000 *** |
| Paddy output (upstream, middle, and downstream) | 72.006 | 2 | 0.000 *** |
| Sample Comparison | T-Statistic | Std. Error | Std. Test Statistic | Sig | Adj. Sig |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Irrigation Water Use | |||||
| Downstream and middle | −43.995 | 10.161 | −4.330 | 0.000 | 0.000 *** |
| Downstream and upstream | −99.475 | 10.199 | −9.754 | 0.000 | 0.000 *** |
| Middle and upstream | −55.480 | 10.235 | −4.421 | 0.000 | 0.000 *** |
| Water Accessibility | |||||
| Downstream and middle | 45.964 | 10.032 | 4.582 | 0.000 | 0.000 *** |
| Downstream and upstream | 108.101 | 10.286 | 10.510 | 0.000 | 0.000 *** |
| Middle and upstream | 62.137 | 10.111 | 6.146 | 0.000 | 0.000 *** |
| Paddy output | |||||
| Downstream and middle | −4.167 | 10.153 | −0.410 | 0.681 | 1.00 NS |
| Downstream and upstream | 0.77.164 | 10.329 | −7.471 | 0.000 | 0.000 *** |
| Middle and upstream | 0.72.996 | 10.074 | −7.246 | 0.000 | 0.000 *** |
| Predictor | β | Se β | Wald’s χ2 | DF | p. Value | EXP (β) | Tolerance | VIF |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Constant | −4.032 | 2.067 | 3.804 | 1 | 0.051 ** | 0.018 | ||
| Location (upstream) | 0.937 | 0.607 | 4.609 | 1 | 0.000 *** | 2.939 | 0.433 | 2.311 |
| Water user’s association | 0.089 | 0.564 | 0.025 | 1 | 0.875 | 1.093 | 0.875 | 1.143 |
| Illegal tapping | −0.587 | 0.570 | 1.061 | 1 | 0.303 | 0.556 | 0.928 | 1.077 |
| Condition of the distr. canal | −0.924 | 0.535 | 2.980 | 1 | 0.084 * | 0.397 | 0.948 | 1.055 |
| Education | −0.018 | 0.056 | 0.099 | 1 | 0.754 | 0.983 | 0.898 | 1.113 |
| Gender | −1.883 | 0.933 | 4.074 | 1 | 0.044 ** | 0.152 | 0.903 | 1.108 |
| Training on water use | 0.407 | 0.694 | 0.344 | 1 | 0.557 | 1.502 | 0.863 | 1.159 |
| Access to irrigation water | 0.185 | 0.075 | 5.978 | 1 | 0.014 ** | 1.203 | 0.302 | 3.309 |
| Irrigation water use | 0.977 | 0.517 | 3.573 | 1 | 0.059 ** | 2.657 | 0.348 | 2.872 |
| Experience | 0.001 | 0.023 | 0.001 | 1 | 0.978 | 1.001 | 0.935 | 1.069 |
| Recommended practices | 0.139 | 0.176 | 0.625 | 1 | 0.429 | 1.149 | 0.704 | 1.142 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wudil, A.H.; Ali, A.; Usman, M.; Radulescu, M.; Sass, R.; Prus, P.; Musa, S. Effects of Inequality of Access to Irrigation and Water Productivity on Paddy Yield in Nigeria. Agronomy 2023, 13, 2195. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy13092195
Wudil AH, Ali A, Usman M, Radulescu M, Sass R, Prus P, Musa S. Effects of Inequality of Access to Irrigation and Water Productivity on Paddy Yield in Nigeria. Agronomy. 2023; 13(9):2195. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy13092195
Chicago/Turabian StyleWudil, Abdulazeez Hudu, Asghar Ali, Muhammad Usman, Magdalena Radulescu, Roman Sass, Piotr Prus, and Salihu Musa. 2023. "Effects of Inequality of Access to Irrigation and Water Productivity on Paddy Yield in Nigeria" Agronomy 13, no. 9: 2195. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy13092195
APA StyleWudil, A. H., Ali, A., Usman, M., Radulescu, M., Sass, R., Prus, P., & Musa, S. (2023). Effects of Inequality of Access to Irrigation and Water Productivity on Paddy Yield in Nigeria. Agronomy, 13(9), 2195. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy13092195








