Dynamic Change Patterns of Soil Surface Roughness and Influencing Factors under Different Tillage Conditions in Typical Mollisol Areas of Northeast China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
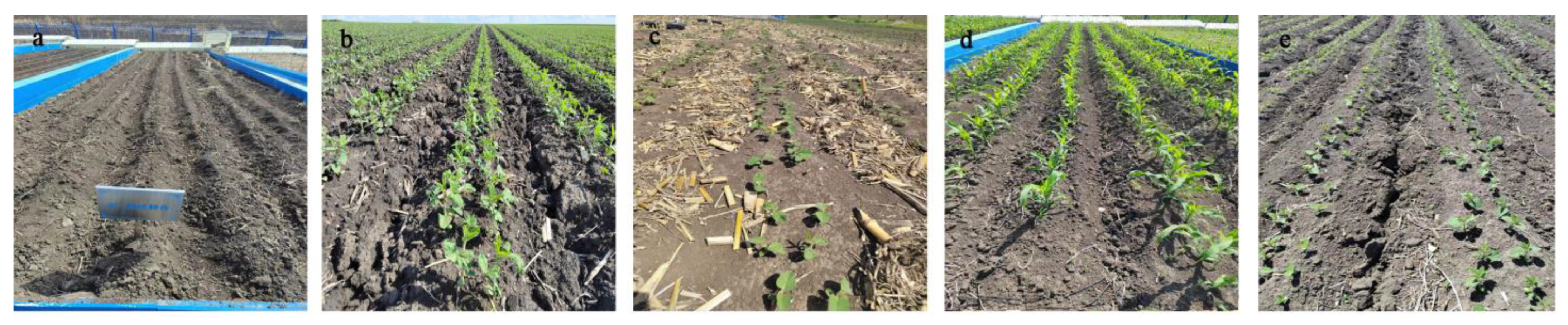
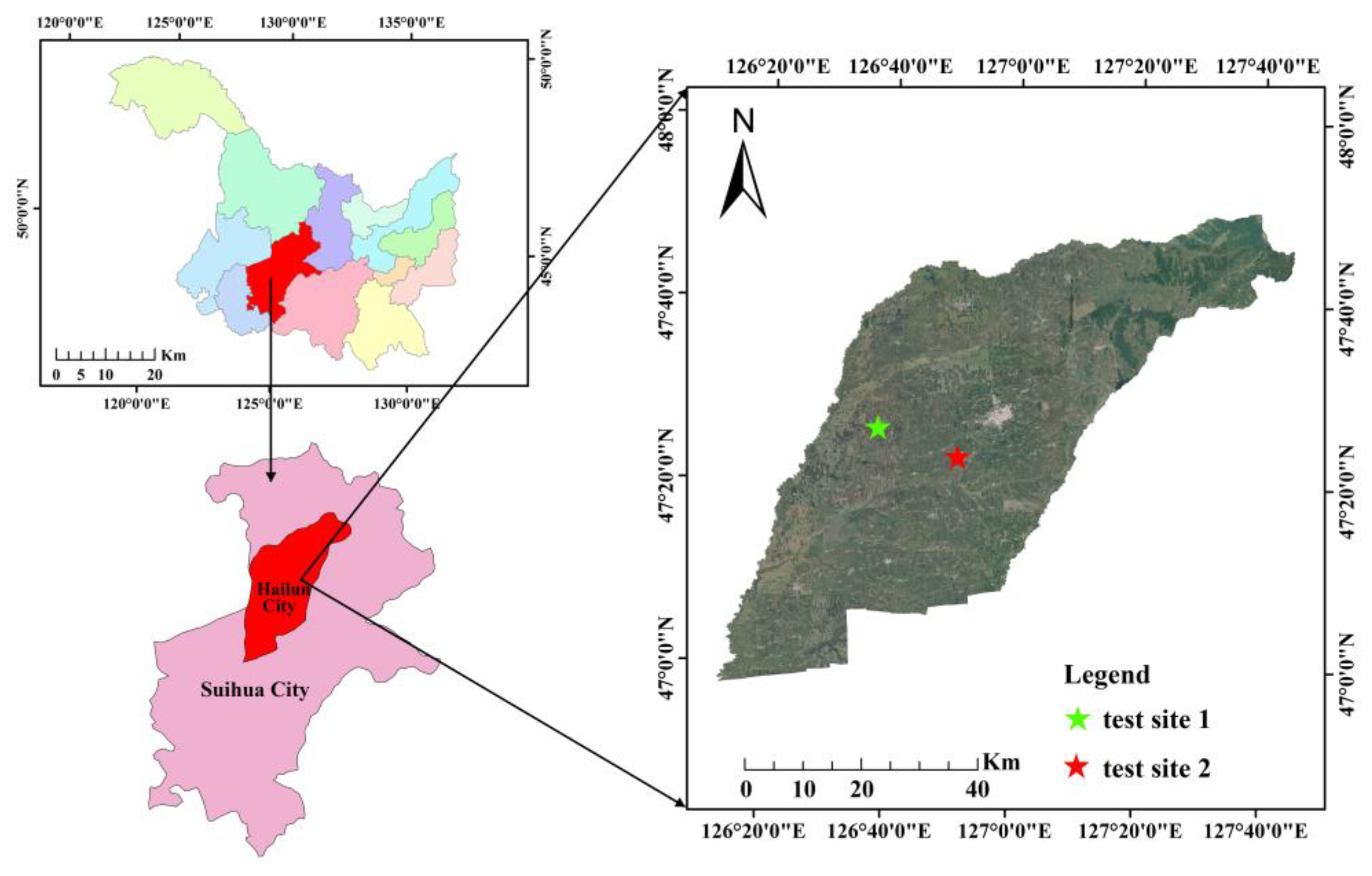
2.1. Experimental Design
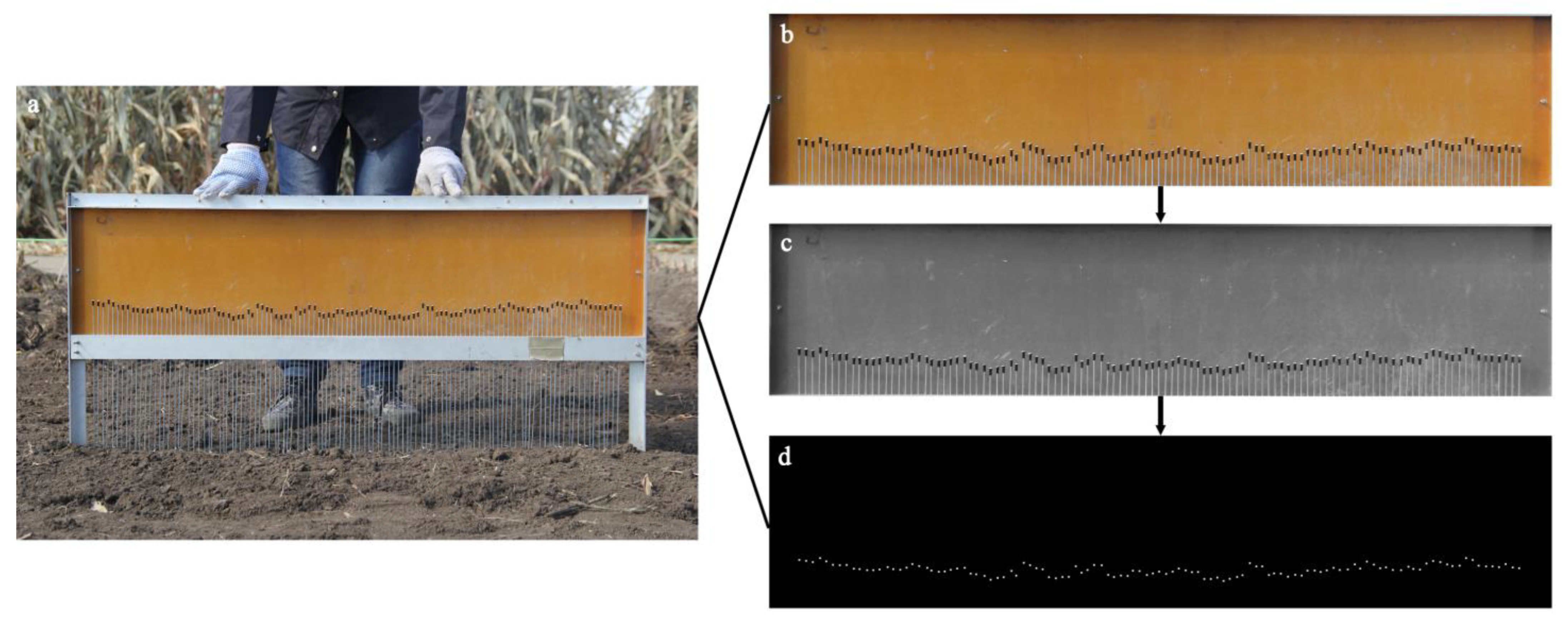
2.2. Extraction of Soil Surface Height
2.3. Calculations of Soil Surface Roughness
3. Results
3.1. Soil Surface Roughness Measurements
3.1.1. Statistical Results of Soil Surface Roughness under Sloping Land
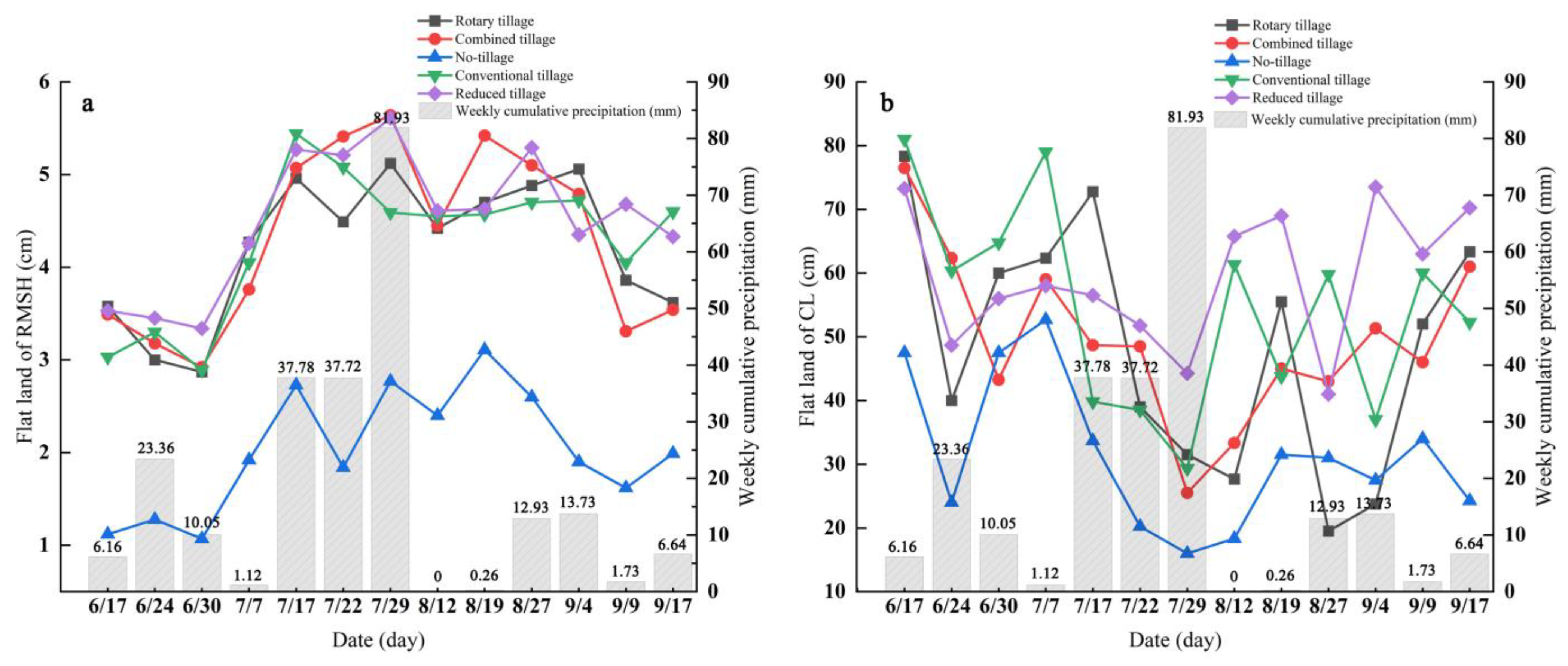
3.1.2. Statistical Results of Soil Surface Roughness under Flat Land
3.2. Soil Surface Roughness Variation Law on the Same Land
3.2.1. Variation Law of Soil Surface Roughness under Sloping Land
3.2.2. Variation Law of Soil Surface Roughness under Flat Land
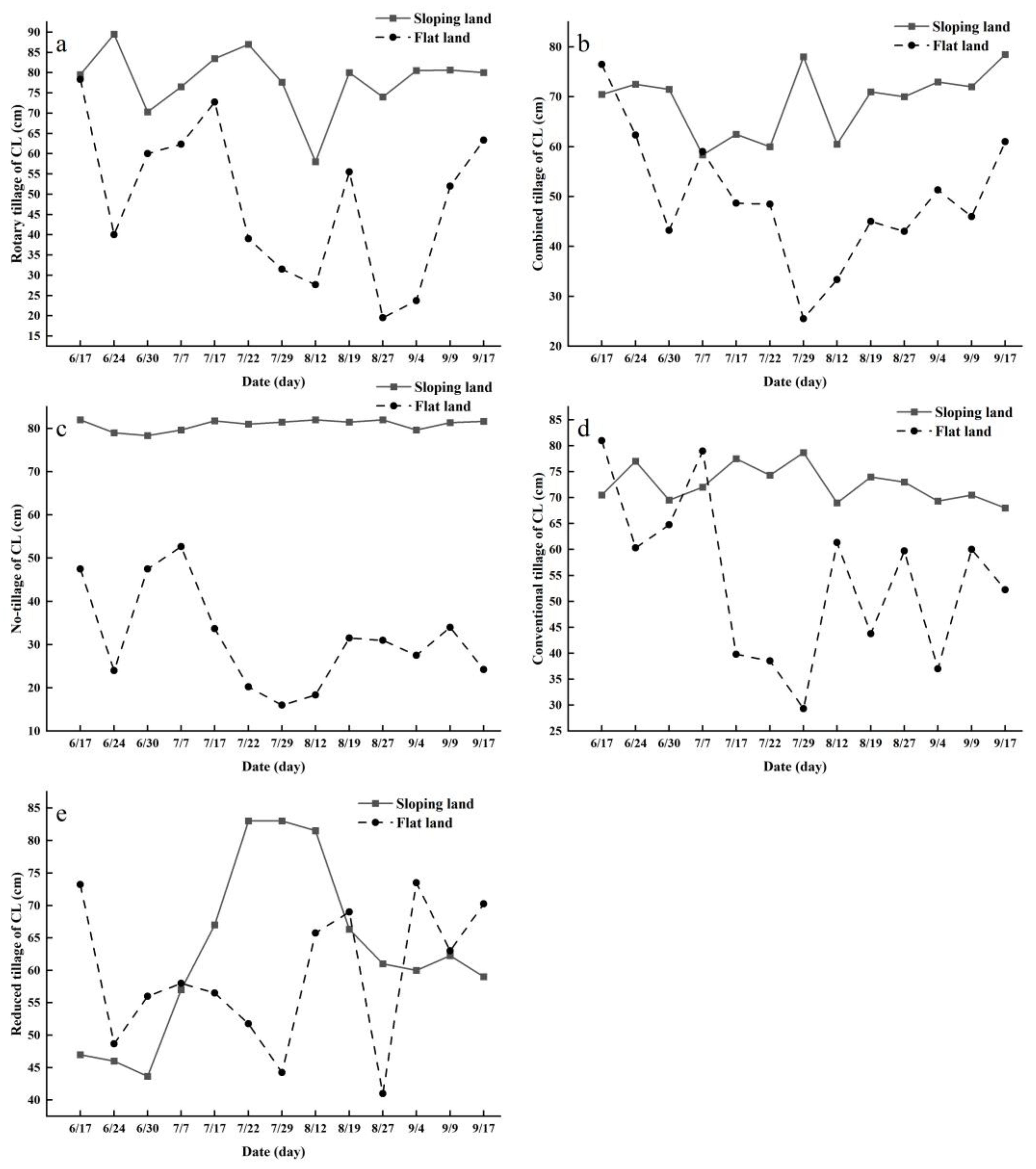
3.3. Comparison of the Variation in Soil Surface Roughness Parameters under Different Lands
3.3.1. Comparison of the Variation in the RMSH under Different Lands
3.3.2. Comparison of the Variation in CLs under Different Land Types
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Romkens, M.J.; Wang, J.Y. Effect of Tillage on Surface Roughness. Trans. ASAE 1986, 29, 429–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vázquez, E.V.; Miranda, J.G.V.; González, A.P. Characterizing anisotropy and heterogeneity of soil surface microtopography using fractal models. Ecol. Model. 2004, 182, 337–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Y.; Yuan, Z.; Zhuo, M.; Huang, B.; Nie, X.; Xie, Z.; Tang, C.; Li, D. Coupling effects of erosion and surface roughness on colluvial deposits under continuous rainfall. Soil Till. Res. 2019, 191, 98–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vermang, J.; Norton, L.D.; Huang, C.; Cornelis, W.M.; Silva, A.M.; Gabriels, D. Characterization of soil surface roughness effects on runoff and soil erosion rates under simulated rainfall. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2015, 79, 903–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Hou, R.; Wu, F.; Keesstra, S. Effect of soil surface roughness on infiltration water, ponding and runoff on tilled soils under rainfall simulation experiments. Soil Till. Res. 2018, 179, 47–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Planchon, O.; Darboux, F. A fast, simple and versatile algorithm to fill the depressions of digital elevation models. Catena 2002, 46, 159–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, P.; Zhang, G.; Wang, H.; Zhang, B.; Wang, X. Land surface roughness affected by vegetation restoration age and types on the Loess Plateau of China. Geoderma 2020, 366, 114240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Chu, X. Quantification of the spatio-temporal variations in hydrologic connectivity of small-scale topographic surfaces under various rainfall conditions. J. Hydrol. 2013, 505, 65–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, W.F.; Huang, C.H. Effects of soil surface roughness on interrill erosion processes and sediment particle size distribution. Geomorphology 2017, 295, 801–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Álvarez-Mozos, J.; Verhoest, N.E.C.; Larrañaga, A.; Casalí, J.; María, M.G. Influence of Surface Roughness Spatial Variability and Temporal Dynamics on the Retrieval of Soil Moisture from SAR Observations. Sensors 2009, 9, 463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.; Feng, Z.; Li, L.; Li, B.; Chen, S. Simultaneously estimating surface soil moisture and roughness of bare soils by combining optical and radar data. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. 2021, 100, 102345. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, Z.; He, S.; Wu, F. Changes of soil surface roughness under water erosion process. Hydrol. Process. 2014, 28, 3919–3929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Agirre, A.; Álvarez-Mozos, J.; Giménez, R. Evaluation of surface roughness parameters in agricultural soils with different tillage conditions using a laser profile meter. Soil Till. Res. 2016, 161, 19–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vermang, J.; Norton, L.D.; Baetens, J.M.; Huang, C.; Cornelis, W.M.; Gabriels, D. Quantification of soil surface roughness evolution under simulated rainfall. Trans. ASAE 2013, 56, 505–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bullard, J.E.; Ockelford, A.; Strong, C.L.; Aubault, H. Impact of multi-day rainfall events on surface roughness and physical crusting of very fine soils. Geoderma 2018, 313, 181–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Xie, Z. Soil surface roughness decay under different topographic conditions. Soil Till. Res. 2019, 187, 92–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Nearing, M.A.; Nichols, M.H.; Polyakov, V.O.; Winter, C.L.; Cavanaugh, M.L. Temporal and spatial evolution of soil surface roughness on stony plots. Soil Till. Res. 2020, 200, 104526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, C.; Fang, H.; Wei, S. Review of land surface roughness parameterization study. Adv. Earth Sci. 2012, 27, 292–303. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.; Chen, N.; Perdok, U.D.; Hoogmoed, W.B. Characterisation of Soil Profile Roughness. Biosyst. Eng. 2005, 91, 369–377. [Google Scholar]
- Lv, J.; Xie, Y.; Luo, H. Erosion process and temporal variations in the soil surface roughness of spoil heaps under multi-day rainfall simulation. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 2192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Bi, Q.; Zhang, Q.; Tang, J.; Bi, D.; Chen, L. Evaluation method of soil surface roughness after ditching operation based on wavelet transform. Actuators 2022, 11, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.; Jiang, T.; Li, X.; Ding, Y.; Zhao, K. The temporal variation of farmland soil surface roughness with various initial surface states under natural rainfall conditions. Soil Till. Res. 2017, 170, 147–156. [Google Scholar]
- Kuipers, H. A reliefmeter for soil cultivation studies. Neth. J. Agric. Sci. 1957, 5, 255–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jester, W.; Klik, A. Soil surface roughness measurement—Methods, applicability, and surface representation. Catena 2005, 64, 174–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.; Zhao, K.; Li, X.; Li, Y.; Ren, J. Improvements in farmland surface roughness measurement by employing a new laser scanner. Soil Till. Res. 2014, 143, 137–144. [Google Scholar]
- Turner, R.; Panciera, R.; Tanase, M.A.; Lowell, K.; Hacker, J.M.; Walker, J.P. Estimation of soil surface roughness of agricultural soils using airborne LiDAR. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 140, 107–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, H.; Chen, Q.; Li, Z.; Zeng, J.; Chen, X. Improvement of soil surface roughness measurement accuracy by close-range photogrammetry. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2017, 33, 162–167. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Allmaras, R.R.; Burwell, R.E.; Larson, W.E.; Holt, R.F. Total porosity and random roughness of the interrow zone as influenced by tillage. USDA 1966, 7, 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Zhao, K.; Zheng, X. Development of surface roughness tester based on laser triangulation method. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2012, 28, 116–121. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Y.; Sun, S.; Jin, X.; Wang, J.; Pang, A.; Yu, X.; Yu, K. Effects of different tillage measures on soil texture and maize yield. J. Maize Sci. 2022, 30, 97–106. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Deng, Z.; Huang, M.; Zhang, W.; Wang, G. Effects of conservation tillage on soil structure and bulk density under dryland. Chin. J. Soil Sci. 2023, 54, 46–55. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Hanson, R.L.D.R.J. Evolution of the plow over 10,000 years and the rationale for no-till farming. Soil Till. Res. 2006, 93, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Wu, F. Soil erosion resistance of sloping farmland under soybean cultivation relative to growth stage. Acta Pedol. Sin. 2016, 53, 1389–1398. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Hu, X.; Brierley, G.; Zhu, H.; Li, G.; Fu, J.; Mao, X.; Yu, Q.; Qiao, N. An exploratory analysis of vegetation strategies to reduce shallow landslide activity on loess hillslopes, onrtheast Qinghai-Tibet Plateau, China. J. Mt. Sci. 2013, 10, 668–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, W.; Guo, Q.; Cao, W.; Yin, Z.; Yan, Q.; Shan, Z.; Zheng, F. A new RUSLE slope length factor and its application to soil erosion assessment in a Loess Plateau watershed. Soil Till. Res. 2018, 182, 10–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Xu, M.; Ritsema, C. A study of soil surface characteristics in a small watershed in the hilly, gullied area on the Chinese Loess Plateau. Catena 2003, 54, 31–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nearing, M.A.; Polyakov, V.O.; Nichols, M.H.; Hernandez, M.; Armendariz, G. Slope–Velocity–Equilibrium and evolution of surface roughness on a stony hillslope. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2017, 21, 3221–3229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerdà, A.; Keesstra, S.D.; Rodrigo-Comino, J.; Novara, A.; Pereira, P.; Brevik, E.; Giménez-Morera, A.; Fernández-Raga, M.; Pulido, M.; Prima, S.D. Runoff initiation, soil detachment and connectivity are enhanced as a consequence of vineyards plantations. J. Environ. Manag. 2017, 202, 268–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, J.; Ge, W.; Hei, Z.; Cong, C.; Ma, C.; Xie, M.; Liu, B.; Feng, W.; Wang, F.; Jiao, J. Agricultural land use and management weaken the soil erosion induced by extreme rainstorms. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2020, 301, 10747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guzha, A.C. Effects of tillage on soil microrelief, surface depression storage and soil water storage. Soil Till. Res. 2003, 76, 105–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCool, D.K.; Brown, L.C.; Foster, G.R.; Mutchler, C.K.; Meyer, L.D. Revised Slope Steepness Factor for the Universal Soil Loss Equation. Trans. ASAE 1987, 30, 1387–1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gangan, M.; Guanglu, L.; Xudong, M.; Weiliang, H.; Yangyang, R.; Mingxi, Y. Effect of raindrop splashes on topsoil structure and infiltration characteristics. Catena 2022, 212, 106040. [Google Scholar]
- Busari, M.A.; Kukal, S.S.; Kaur, A.; Bhatt, R.; Dulazi, A.A. Conservation tillage impacts on soil, crop and the environment. Int. Soil Water Conserv. Res. 2015, 3, 119–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Liang, X.; Wu, F. Soil surface roughness change and its effect on runoff and erosion on the Loess Plateau of China. J. Arid. Land 2014, 6, 400–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Dalabay, N.; Lu, P.; Wu, F. Effects of tillage practices and slope on runoff and erosion of soil from the Loess Plateau, China, subjected to simulated rainfall. Soil Tillage Res. 2017, 166, 147–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callens, M.; Verhoest, N.E.C.; Davidson, M.W.J. Parameterization of tillage-induced single-scale soil roughness from 4-m profiles. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote. Sens. 2006, 44, 878–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Sun, Y.; Lammers, P.S. Short-term Changes of Soil Surface Roughness under Different Tillage Treatments. Chin. Agric. Sci. Bull. 2012, 28, 230–234. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Wang, Y.; Wang, J.; Lin, Q.; Wu, F. Effects of soil surface roughness on runoff generation mechanism on loess slop. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2018, 34, 120–128. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Laura, C.; Paolo, T.; Alessandra, C.; Paolo, N.; Nunzio, R.; Roberta, M. Evaluation of runoff and soil erosion under conventional tillage and no-till management: A case study in northeast Italy. Catena 2021, 197, 104972. [Google Scholar]
- Anikwe, M.A.N.; Ubochi, J.N. Short-term changes in soil properties under tillage systems and their effect on sweet potato. Soil Res. 2007, 45, 351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palm, C.; Blanco-Canqui, H.; DeClerck, F.; Gatere, L.; Grace, P. Conservation agriculture and ecosystem services: An overview. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2014, 187, 87–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armand, R.; Bockstaller, C.; Auzet, A.-V.; Dijk, P.V. Runoff generation related to intra-field soil surface characteristics variability. Soil Till. Res. 2008, 102, 27–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Rotary Tillage | Combined Tillage | No Tillage | Conventional Tillage | Reduced Tillage | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RMSH | Minimum value (cm) | 0.55 | 0.85 | 2.50 | 1.72 | 2.19 |
| Maximum value (cm) | 1.66 | 1.46 | 3.46 | 2.53 | 3.84 | |
| Average value (cm) | 0.94 | 1.19 | 3.08 | 2.15 | 2.76 | |
| Standard deviation (cm) | 0.32 | 0.19 | 0.30 | 0.24 | 0.53 | |
| Coefficient of variation (%) | 34 | 16 | 10 | 11 | 19 | |
| Kurtosis | 1.54 | −1.14 | −0.86 | −0.74 | 0.06 | |
| Skewness | 0.33 | 0.20 | 0.31 | 0.25 | 0.55 | |
| CL | Minimum value (cm) | 58.00 | 58.33 | 78.33 | 68.00 | 43.67 |
| Maximum value (cm) | 89.50 | 78.50 | 82.00 | 78.67 | 83.00 | |
| Average value (cm) | 78.24 | 69.10 | 80.88 | 72.56 | 62.83 | |
| Standard deviation (cm) | 7.56 | 6.39 | 1.21 | 3.38 | 12.87 | |
| Coefficient of variation (%) | 10 | 9 | 2 | 5 | 20 | |
| Kurtosis | 3.08 | −0.95 | −0.40 | −1.05 | −0.79 | |
| Skewness | 7.87 | 6.65 | 1.26 | 3.52 | 13.40 |
| Rotary Tillage | Combined Tillage | No Tillage | Conventional Tillage | Reduced Tillage | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RMSH | Minimum value (cm) | 2.87 | 2.92 | 1.07 | 2.89 | 3.34 |
| Maximum value (cm) | 5.12 | 5.64 | 3.11 | 5.44 | 5.61 | |
| Average value (cm) | 4.22 | 4.31 | 2.03 | 4.27 | 4.50 | |
| Standard deviation | 0.74 | 0.94 | 0.63 | 0.75 | 0.71 | |
| Coefficient of variation (%) | 17 | 22 | 31 | 18 | 16 | |
| Kurtosis | −0.92 | −1.78 | −1.07 | −0.41 | −0.91 | |
| Skewness | 0.77 | 0.98 | 0.66 | 0.78 | 0.74 | |
| CL | Minimum value (cm) | 19.50 | 25.50 | 16.00 | 29.33 | 41.00 |
| Maximum value (cm) | 78.33 | 76.50 | 52.67 | 81.00 | 73.50 | |
| Average value (cm) | 48.13 | 49.49 | 31.40 | 54.37 | 59.30 | |
| Standard deviation | 18.44 | 12.63 | 11.22 | 15.39 | 10.44 | |
| Coefficient of variation (%) | 2.87 | 2.92 | 1.07 | 2.89 | 3.34 | |
| Kurtosis | −1.28 | 0.64 | −0.62 | −0.80 | −1.13 | |
| Skewness | 19.19 | 13.14 | 11.68 | 16.02 | 10.87 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhou, S.; Ren, J.; Chen, Q.; Zhang, Z. Dynamic Change Patterns of Soil Surface Roughness and Influencing Factors under Different Tillage Conditions in Typical Mollisol Areas of Northeast China. Agronomy 2023, 13, 1817. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy13071817
Zhou S, Ren J, Chen Q, Zhang Z. Dynamic Change Patterns of Soil Surface Roughness and Influencing Factors under Different Tillage Conditions in Typical Mollisol Areas of Northeast China. Agronomy. 2023; 13(7):1817. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy13071817
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhou, Shuang, Jianhua Ren, Qiang Chen, and Zhuopeng Zhang. 2023. "Dynamic Change Patterns of Soil Surface Roughness and Influencing Factors under Different Tillage Conditions in Typical Mollisol Areas of Northeast China" Agronomy 13, no. 7: 1817. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy13071817
APA StyleZhou, S., Ren, J., Chen, Q., & Zhang, Z. (2023). Dynamic Change Patterns of Soil Surface Roughness and Influencing Factors under Different Tillage Conditions in Typical Mollisol Areas of Northeast China. Agronomy, 13(7), 1817. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy13071817







