Abstract
Soil extracellular enzyme activities play an important role in regulating the soil nitrogen (N) mineralization process in paddy fields. However, there is still a need to further study how N mineralization responds to different fertilizer management techniques and the soil extracellular enzyme activities for N mineralization in paddy fields. Therefore, the influence of different long-term (35 years) fertilizer regimes on soil N mineralization, hydrolysable N fractions—such as hydrolyzed unknown nitrogen (HUN), amino acid nitrogen (AAN), amino sugar nitrogen (ASN), ammonia nitrogen (AN), and total acid-hydrolyzed nitrogen (TAN)—and their extracellular enzyme activities (soil urease, L-glutaminase, β-glucosidase, arylamidase, and β-glucosaminidase) in a double-cropping rice field in southern China were investigated in this study. The field experiment included the following fertilizer regimes: rice straw and inorganic fertilizer (RF), 30% organic manure and 70% inorganic fertilizer (OM), inorganic fertilizer alone (MF), and no application of inorganic fertilizer as a control (CK). The results show that the soil ammonium N, amino sugar N, hydrolysable unidentified N, and amino acid N contents in the paddy field with RF treatment increased by 30.56%, 5.51%, and 62.74% compared with the CK treatment. The results show that the soil aerobic and anaerobic N mineralization rates in the paddy fields with OM and RF treatments increased by 22.92% and 18.27% compared with those with MF treatment. Moreover, soil extracellular enzyme activities under RF and OM treatments significantly increased, which indicated that the main substrate of microbial activity was effective. Correlation analysis indicated that the soil L-glutaminase activity, amino sugar N, amino acid N, and total acid-hydrolysable N contents were positively correlated with soil aerobic and anaerobic N mineralization rates in paddy fields. However, there was a negative correlation between the soil N mineralization rate and soil β-glucosaminidase activity in paddy fields. This finding shows that the yields of early rice and late rice under the RF and OM treatments were significantly higher than those under the MF and CK treatments. Compared with the MF treatment, the yields of double-cropping rice with RF and OM treatments increased by 9.84% and 11.37%, respectively. As a result, the application of straw or organic manure and inorganic fertilizer was effective for improving soil N mineralization, the soil acid-hydrolyzed N content, and extracellular enzyme activities in double-cropping rice fields.
1. Introduction
It is generally believed that soil nitrogen (N) provides the main nutrients for crop growth and yield. In recent years, the excessive use of inorganic N fertilizer has led to some problems in the process of agricultural production, such as soil degradation, irrigation water pollution, increases in nitrate leaching, and greenhouse gas emissions [1]. Some results show that effective management for increasing soil quality and soil fertility in paddy fields includes the application of organic manure and straw [2]. Therefore, practices for improving ecological environment in paddy fields would benefit from different fertilizer practices with improved N use efficiency from the fertilizer and controlled N mineralization.
It is generally accepted that organic compounds are the main components of the total N content in agricultural soil, and the other components exist in inorganic forms that are easily absorbed by crops [3]. The soil organic N fraction is clearly influenced by different fertilizer conditions; thus, soil fertility and crop growth are significantly affected [4]. In recent years, many studies have shown that easily hydrolysable soil N fractions (e.g., amino sugar N, hydrolysable NH4+-N, amine N, and amino acid N) are the main components of the soil-active N pool, which provides a soil available N source for crop growth [5,6]. Soil organic N fractions are significantly influenced by different cropping systems, fertilizer regimes, and tillage management practices [7,8]. Many results confirm that soil organic N fractions and N mineralization are enhanced by the long-term application of organic manure and inorganic fertilizer practices [2,9]. Some studies have proven that soil organic N fractions are not significantly impacted by inorganic fertilizer management [10]; at the same time, some studies found that inorganic fertilizer can reduce the total hydrolysable N fraction content of soil [11].
Meanwhile, it is generally believed that the process of soil N mineralization and soil enzyme activities in paddy fields are also significantly influenced by different fertilizer management techniques. Some studies have investigated the prediction of soil potential N mineralization according to the soil organic matter (SOM) fraction under laboratory incubation conditions [12,13]. Some results prove that anaerobic and aerobic N mineralization rates in the soil of paddy fields with organic matter management increased [14]. Other outcomes confirmed that rate of soil N mineralization is closely related to soil enzyme activity [15]. However, there was a negative relationship between soil variables and the aerobic N mineralization rate of soil in paddy fields. Therefore, anaerobic N mineralization in soil is mainly determined by the SOM content and other biotic or abiotic factors [14]. Soil enzyme activities play an important role in improving soil quality and soil fertility in paddy fields; it is generally considered that soil enzyme activities are early indicators of changes in the soil environment and soil fertility, which are sensitive to different fertilizer management regimes.
Soil enzyme activities significantly change under different SOM biochemistry and physical soil conditions, and organic N mineralization in soil is mainly regulated by extracellular enzyme activities in soil [16]. It is generally accepted that the complex organic breakdown of N compounds into easily hydrolysable N fractions is the first step of soil N mineralization, and that the soil arylamidase and β-glucosaminidase activities play a significant role in regulating the process of soil N mineralization [17]. β-glucosidase activities in soil are usually regarded as an indicator of nutrient or energy flow, and are closely related to the provision of soil cellobiose hydrolase, energy, and carbon (C). L-glutaminase activities in soil are closely related to ammonification, with soil NH4+ being produced from amino acids [18]. Urease enzyme activities in soil play an important role in catalyzing hydroxyurea, urea, dihydroxyurea, and semicarbazid into NH3 and carbon dioxide (CO2) [19]. Therefore, some results indicate that there is a close relationship between soil urease, L-asparaginase, amidohydrolase activities, and soil mineralizable N [20].
Rice is the main grain crop in the Asia region, and a double-cropping rice system, which involves early and late rice planting patterns, is the main cropping system used in southern China [21]. The cultivation area of rice in China is 3.01 × 108 hm2, and the average yield of rice in China is 15,000 kg hm−2. The application of inorganic fertilizer and organic manure can maintain or improve soil quality and soil fertility in paddy fields. The results of our previous study show that the chemical and physical characteristics of the soil at the 0–20 cm layer in paddy fields significantly varied between different fertilizer practices, including the bulk density of soil, pH, soil organic carbon (SOC), and N contents [22]; thus, the soil quality and soil fertility also significantly changed. In our previous studies, these results showed that soil N content in paddy field was significantly influenced by different fertilizer regimes. However, the effects of different long-term fertilizer managements on soil N mineralization and its extracellular enzyme activities under a double-cropping rice system in southern China are still not clear. Therefore, a long-term (35 years) field fertilizer experiment was set up in paddy field under a double-cropping rice system, including rice straw and inorganic fertilizer (RF), 30% organic manure and 70% inorganic fertilizer (OM), inorganic fertilizer alone (MF), and no application of inorganic fertilizer as a control (CK). Therefore, the purpose of this study was: (1) to explore the characteristics of soil acid-hydrolysable N fractions in paddy fields under different long-term fertilizer conditions; (2) to investigate soil extracellular enzyme activities, soil anaerobic and aerobic N mineralization rates in paddy field; and (3) to analyze the correlation between soil extracellular enzyme activities and soil N mineralization and acidolytic N components in the double-cropping rice field.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Sites
The fertilizer field experiment was mainly located in a double-cropping rice region. The annual mean precipitation and potential evapotranspiration in this field experiment region were 1553 mm and 1354 mm, respectively. The monthly mean temperature in the field experiment region was 17.2 °C. At the beginning of this experiment, soil chemical characteristics at the 0–20 cm layer were determined, as shown in Table 1. There were three crops in each year: barley (Hordeum vulgare L.), early rice and late rice (Oryza sativa L.). More detailed additional information about the field experiment is provided by Tang et al. [23].

Table 1.
Soil chemical characteristics at 0–20 cm layer in paddy field beginning of this experiment.
2.2. Experimental Design
Four different fertilizer treatments were included in this field experiment, which began in 1986: rice straw and inorganic fertilizer (RF), 30% organic manure and 70% inorganic fertilizer (OM), inorganic fertilizer alone (MF), and no application of inorganic fertilizer as a control (CK). Each plot of all fertilizer treatments was arranged in paddy fields with a randomized block design, and each fertilizer treatment was replicated three times. Each plot area with all fertilizer treatments was 66.7 m2 (10 × 6.67 m). During the early rice and late rice growth period, the total amounts of N, P2O5, and K2O for MF, RF and OM treatments were 142.5, 54.0, 63.0 kg ha−1 and 157.5, 43.2, 81.0 kg ha−1, respectively. Additionally, the organic manure used for OM treatment was decomposed chicken manure. During the early rice and late rice growth period, the total amounts of organic manure for OM treatment were 2625 and 2670 kg ha−1, respectively. During the early rice and late rice growth period, the straw was buried with chemical fertilizer for RF treatment. Both early rice and late rice were artificially transplanted, with a spacing of 25.0 cm × 25.0 cm. Additional detailed information about fertilizer, tillage, rice varieties, irrigation, etc., is provided by Tang et al. [23].
2.3. Soil Sampling
Soil samples were collected at 0–20 cm layer in paddy field, at tillering stage of late rice in 2020. One composite soil sample was collected from each of the twenty points in the soil plot, and three composite soil samples were collected with every fertilizer treatment. Then, the mixed soil samples were divided into two parts: one part of the soil sample were stored at room temperature for the analysis of soil chemical characteristics, and the other soil samples were stored at 4 °C to investigate their extracellular enzyme activities (e.g., urease, arylamidase, L-glutaminase, β-glucosidase and β-glucosaminidase) and at −20 °C to measure their hydrolysable N fractions. Methods to determine the acid-hydrolyzed N components and extracellular enzyme activities of soil were introduced by Zhang et al. [24].
2.4. Soil Laboratory Analysis
2.4.1. Chemical Characteristics and Acid-Hydrolysable N Fractions in Soil
Soil chemical properties of all soil samples were analyzed in the laboratory. The determination methods of SOC and soil pH and the measurement of total N, P contents are described by Zhao et al. [25]. Briefly, SOC content was measured using a Vario EL III Elemental Analyzer (Elementar, Langenselbold, Germany), soil pH was measured with a compound electrode (PE-10, Sartorious, Göttingen, Germany) using a soil-to-water ratio of 1:2.5, the total N content of soil was determined using a semi-micro version of the Kjeldahl method, and the total P content of soil was investigated using spectrophotometry (Lambda 25 UV/VIS spectrophotometer; PerkinElmer, Waltham, MA, USA) and the molybdenum blue method after fusion with NaOH in a muffle furnace. Soil ammonium nitrogen (NH4+-N) and nitrate nitrogen (NO3−-N) contents were measured using flow injection analysis according to the method introduced as by Berthrong et al. [26]. Different acid-hydrolysable N fractions of soil were measured according to the method described by Sekhon et al. [3], including hydrolyzed unknown N (HUN), amino acid N (AAN), amino sugar N (ASN), ammonia N (AN) and total acid-hydrolyzed N (TAN).
2.4.2. Soil N Mineralization Rate
The anaerobic and aerobic N mineralization rates of all soil samples were measured according to the method by Kader et al. [14]. Three replicate plot soils with each treatment were used to investigate N mineralization rate. Briefly, the removal of mineral N from soil solution using denitrification or immobilization was not considered and only net N mineralization was measured under incubation conditions (14 weeks).
Soil net aerobic N mineralization rate (mg N kg−1 d−1) was measured using following equation:
where N (t) is total number of mineral N during incubation time (t), t is incubation time (d), N0 is begin number of mineral N (mg N kg−1), and k0 is zero-order N mineralization rate (mg N kg−1 d−1).
N (t) = N0 + k0t
Soil anaerobic N mineralization data (mg N kg−1 d−1) were measured using following equation:
where NA is mineralizable N, k1 is a first-order rate parameter, and t is incubation time (d).
N (t) = NA (1 − e−k1t)
2.4.3. Extracellular Enzyme Activities in Soil
Extracellular enzyme activities in soil were investigated after one week of pre-incubation period (at 27 °C) following the method introduced by Zhang et al. [24], including soil arylamidase (EC 3.4.11.2), β-glucosidase (EC 3.2.1.21), β-glucosaminidase (EC 3.2.1.30), L-glutaminase (EC 3.5.1.2), and urease (EC 3.5.1.5). Briefly, substrates were added and then soil enzyme reactions were stopped as controls after culture experiments. Extracellular enzyme activities in soil were expressed based on the quality of dry soil. Moisture levels in soil samples were measured based on weight loss after drying at 105 °C for 48 h. Additionally, each investigated item was expressed as an average of three replicates using different fertilizer treatments.
2.4.4. Rice Yield
At the maturity stages of early rice and late rice in 2020, early rice and late rice were harvested from each plot subject to different fertilizer treatments and their yield was investigated. Rough (unhulled) rice with 14% moisture content was analyzed using a moisture instrument (QL-610B). The yield of the double-cropping rice encompassed the total yield of early rice and late rice.
2.5. Statistical Analysis
The survey indexes of all fertilizer treatments were expressed as mean and standard deviation. According to the probability level of 5%, the data of each investigated item with each fertilizer treatment were analyzed using a single-factor analysis of variance. All the data from each measured item in the present paper were analyzed using SAS 9.3 software package [27]. The correlation between acid-hydrolyzed N components and enzyme activities, as well as anaerobic and aerobic N mineralization rates, were analyzed by using Pearson’s correlation.
3. Results
3.1. Soil Acid-Hydrolysable N Fractions
Different fertilizer treatments had a significant impact on the content of total acid-hydrolyzed nitrogen of soil and its fractions in paddy fields (Table 2). The range of soil amino sugar nitrogen (ASN) content with different fertilizer treatments was from 51.02 to 62.35 mg kg−1. Compared with CK treatment, soil ASN content with MF, RF and OM treatments increased by 9.11%, 12.19% and 22.21%, respectively.

Table 2.
Effects of different long-term fertilizer treatments on soil acid-hydrolysable nitrogen fractions in the double-cropping rice field (mg kg−1).
This result indicates that soil amino acid nitrogen (AAN) content with RF and OM treatments significantly (p < 0.05) increased compared to MF and CK treatments. Soil AAN content with RF and OM treatments increased by 46.19% and 23.55%, compared to MF treatment, respectively. The ammonium nitrogen (AN) content of soil with RF and OM treatments was significantly (p < 0.05) higher than that of MF and CK treatments. The soil AN content with RF and OM treatments increased by 19.47% and 26.14%, compared to MF treatment, respectively.
This result indicates that soil hydrolysable unidentified nitrogen (HUN) content with OM treatment was significantly (p < 0.05) higher than that of MF, RF and CK treatments. Compared with CK treatment, soil HUN content with MF, RF and OM treatments increased by 11.56%, 5.51% and 27.72%, compared to MF treatment, respectively. Soil total acid-hydrolysable nitrogen (TAHN) content with RF and OM treatments were significantly (p < 0.05) higher than those of MF and CK treatments, but they were not significantly (p > 0.05) different in soil TAHN content between RF and OM treatments. Soil TAHN content with RF and OM treatments increased by 16.03% and 20.65%, compared to MF treatment, respectively (Table 2).
3.2. Soil Chemical Property and Soil Nitrogen Mineralization
This result indicates that fertilizer treatment has a significant impact on soil chemical characteristics in paddy fields (Table 3). The results show that the soil pH value in paddy fields with OM and RF treatments was significantly (p < 0.05) higher than that of CK treatment. Soil NO3−-N and NH4+-N contents with MF, RF and OM treatments were significantly (p < 0.05) higher than those of CK treatment. Compared with CK treatment, soil NO3−-N contents with MF, RF and OM treatments increased by 33.33%, 75.00% and 108.33%, and soil NH4+-N contents with MF, RF and OM treatments increased by 27.27%, 72.73% and 100.00%, respectively. The results show that soil total P, N, SOC contents in paddy fields with OM and RF treatments were significantly (p < 0.05) higher than those of MF and CK treatments (Table 3). However, there were no significant differences (p > 0.05) in soil C:N among MF, RF, OM and CK treatments.

Table 3.
Effects of different long-term fertilizer treatments on soil chemical characteristics in the double-cropping rice field.
The range of soil aerobic N mineralization rates with different fertilizer treatments was from 0.27 to 0.59 mg N kg−1 d−1. The soil aerobic N mineralization rates with OM treatment were significantly higher (p < 0.05) than those for RF, MF and CK treatments. At the same time, the soil anaerobic N mineralization rate with RF and MF treatments significantly (p < 0.05) increased compared to CK treatment. This result shows that soil aerobic and anaerobic N mineralization rates with MF and CK treatments significantly (p < 0.05) decreased compared to OM and RF treatments (Table 4). Compared with MF treatment, the soil aerobic N mineralization rates with RF and OM treatments increased by 12.50% and 22.92%, soil anaerobic N mineralization rates with RF and OM treatments increased by 10.58% and 18.27%, respectively.

Table 4.
Effects of different long-term fertilizer treatments on total N, SOC contents and N mineralization rates in the soil of a double-cropping rice field.
3.3. Soil Extracellular Enzyme Activities
This result indicated that soil β-glucosaminidase, β-glucosidase, urease, L-glutaminase and arylamidase activities significantly changed under different long-term fertilizer conditions (Table 5). The activities of soil β-glucosaminidase, urease and β-glucosidase with OM and RF treatments were significantly higher (p < 0.05) than those for MF and CK treatments. The activities of soil L-glutaminase and arylamidase with OM treatment were significantly higher (p < 0.05) than those of RF, MF and CK treatments. This result indicated that soil L-glutaminase, urease and arylamidase activities with OM treatment increased by 3.39, 1.88 and 1.74 times, compared with CK treatment, respectively. The order of soil L-glutaminase, β-glucosaminidase and arylamidase activities was CK < MF < RF < OM, and the order of soil urease activity was CK < MF < OM < RF.

Table 5.
Effects of different long-term fertilizer treatments on soil extracellular enzyme activities in a double-cropping rice field.
3.4. Correlation between Soil Extracellular Enzyme Activities and Soil Properties
This result show that there is a positive correlation between soil β-glucosaminidase activity and soil N, SOC contents (p < 0.01), and a positive correlation between soil β-glucosidase activity and SOC content (p < 0.01), C:N ratio (p < 0.05), respectively. Soil L-glutaminase and urease activities were negatively correlated with soil N, SOC contents and soil C:N ratio. Meanwhile, there was a significantly negative correlation between soil aromatic amidase activity and soil pH (p < 0.05) (Table 6).

Table 6.
Pearson’s correlation coefficient between extracellular enzyme activities and chemical characteristics of soil.
3.5. Correlation among Soil N Mineralization and Soil Extracellular Enzyme Activities, Soil Acid-Hydrolysable N Fractions
The Pearson correlation coefficient showed that soil L-glutaminase activity was positively correlated with soil aerobic (p < 0.01) and anaerobic (p < 0.05) N mineralization rates (Table 7). Furthermore, soil β-glucosaminidase, β-glucosidase and urease activities were significantly (p < 0.05) negatively correlated with soil aerobic and anaerobic N mineralization rates.

Table 7.
Pearson’s correlation coefficient between soil N mineralization rate and soil extracellular enzyme activities, soil acid-hydrolysable N fractions.
This results show that there was a significant (p < 0.01) positive correlation between soil AAN, TAHN contents and soil aerobic, anaerobic N mineralization rates. There was a significant (p < 0.05) positive correlation between soil ASN content and soil N mineralization rate. There was no significant (p > 0.05) correlation between soil HUN, AN contents and soil N mineralization rate.
3.6. Rice Yield
This results indicate that the yields of early rice and late rice with RF and OM treatments were significantly higher (p < 0.05) than those for MF and CK treatments (Figure 1). Meanwhile, early rice yield with MF, RF and OM treatments increased by 2467.6, 2989.7 and 3310.4 kg hm−2 compared to CK treatment, respectively. Late rice yield with MF, RF and OM treatments increased by 2788.8, 3276.2 and 3112.5 kg hm−2, compared to CK treatments, respectively. The results show that the total yield of double-cropping rice (early rice and late rice) with RF and OM treatments was significantly higher (p < 0.05) than the yields of MF and CK treatments. Compared with MF treatment, the total yield of double-cropping rice with RF and OM treatments increased by 9.84% and 11.37%, respectively.
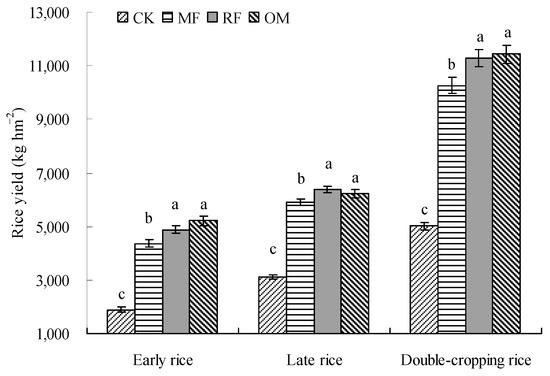
Figure 1.
Effects of different long-term fertilizer treatments on yields of early rice and late rice. MF: inorganic fertilizer; RF: rice straw and inorganic fertilizer; OM: 30% organic manure and 70% inorganic fertilizer; CK: no application of inorganic fertilizer as a control. Different lowercase letters were indicate a significant difference at the p < 0.05 level.
4. Discussion
4.1. Effects of Fertilization on Soil Acid-Hydrolysable N Fractions and N Mineralization
Soil total acid-hydrolysable nitrogen (N) (THAN) content in the double-cropping rice field without fertilizer input (CK) treatment was significantly lower than that of organic matter treatments (RF and OM), which may be due to the easy mineralization of acid-hydrolysable N in soil, which was generally regarded as an active N pool and mainly provided potentially available N for crop growth in soil [28]. At the same time, soil acid-hydrolysable N fractions (AN, AAN, ASN and HUN contents) in paddy fields with CK treatment were significantly lower than those for OM, RF and MF treatments, indicating that it should be measured to improve the status of organic N in soil of a double-cropping rice field under combined organic manure or rice straw and inorganic fertilizer conditions. In this study, soil acid-hydrolysable N fractions in the double-cropping rice field subject to inorganic fertilizer treatment (MF) were significantly lower than those for RF and OM treatments (Table 2). The reason may occur because the positive effects of rice straw and organic manure on soil N accumulation were significantly higher than those for inorganic fertilizer treatment. On the other hand, the long-term repeated addition of N and organic matter (rice straw and organic fertilizer) practices provide a larger organic N source for paddy field, which were consistent with previous founds [2,3]. Meanwhile, our results indicate soil acid-hydrolysable N fractions in paddy field with OM treatment were increased, compared with RF treatment. These results agreed with previous studies [29,30], suggesting that farm manure had a more positive effect on the accumulation of soil organic N in paddy field. Therefore, it were benefit practices for increasing soil acid-hydrolysable N fractions in the double-cropping rice field with organic matter input practices.
In the present study, our results show that soil aerobic and anaerobic N mineralization rates with RF, MF and OM treatments were higher than those for CK treatment possibly due to the poor quality of organic matter (SOM) and paddy soil under CK treatment. On the other hand, soil N, SOM quality, and soil chemical characteristics increase with the use of fertilizer input practices (Table 3 and Table 4), suggesting that organic matter provides more soil nutrients for paddy fields. Meanwhile, this finding proves that the soil N mineralization rate with RF and OM treatments were larger than that of MF treatment, indicating that the long-term application of inorganic fertilizer also changes soil N deficiency or SOM quality, as well as soil chemical properties (Table 3 and Table 4). Compared with RF treatment, the application of organic manure (OM) practices could significantly increase soil aerobic and anaerobic N mineralization rates in paddy fields. The reason for this may be that organic fertilizer contains a higher proportion of soluble N, and the active N pool in paddy field soil was larger; therefore, the long-term application of organic fertilizer practice can improve the quality of SOM [31]. The results of this study prove that there was a significant (p < 0.05) positive correlation between SOC, soil total N contents and soil N mineralization rate. This is consistent with previous results [12,13] suggesting that soil N mineralization rate was closely related to soil chemical characteristics (e.g., SOC, total N contents). SOC quality differences in fertilizer treatments were the main factors for regulating soil N mineralization and soil enzymatic activity in the double-cropping rice field. Therefore, soil N mineralization rates (aerobic and anaerobic) play a significant role in changing N mineralization and acid-hydrolysable N fractions in the soil of a double-cropping rice field.
4.2. Effects of Fertilization on Extracellular Enzyme Activities in Soil
Our results show that soil β-glucosidase activity in paddy fields with MF and CK treatments were lower than those of RF and OM treatments. This may be attributed to the fact that N and glucosamine polymer contents in a microbial cell wall with organic manure and rice straw were higher, promoting the transformation of soil microorganisms [32,33,34]. This result proved that soil L-glutaminase activities with MF and CK treatments were lower than those of RF and OM treatments, indicating that the difference in protein N availability was the main factor in regulating soil L-glutaminase activity in paddy fields. Furthermore, with the increase in the amounts of organic fertilizer, crop root residues and exudates, soil chemical properties (e.g., SOC, total N, NO3−-N, NH4+-N contents) also increased (Table 3 and Table 4), providing more soil nutrients and energy for the activities of soil microorganisms. Compared with CK and MF treatments, soil arylamidase and urease activities with OM and RF treatments increased, indicating that aminohydrolase responded rapidly to changes in substrate levels [34]. The reason for this may be that soil chemical properties increased (Table 3), including SOC and soil N contents, in paddy fields subjected to rice straw and organic manure conditions, providing more soil C and N sources for the growth of soil arylamidase and urease [35]. On the other hand, the protective effect of soil enzymes on the extracellular pool in paddy fields was enhanced under higher SOC levels, providing more functional soil enzyme molecules for paddy fields [36]. Hence, these results indicate that microbial nutrients and environmental differences in fertilizer treatments were the main factors for regulating soil extracellular enzyme activities. This would benefit practices of increasing soil extracellular enzyme activities in a double-cropping rice field with organic matter input practices by regulating soil chemical properties and soil N mineralization.
The results of the present study show that rice yield with RF and OM treatments significantly increased compared to MF and CK treatments. This may be attributed to the increase in soil chemical properties in paddy fields that were subjected to rice straw and organic manure conditions, including SOC and soil N, P, NO3−-N, NH4+-N contents (Table 3 and Table 4), which provide more soil C and N sources for the growth of rice. On the other hand, soil extracellular enzyme activities in paddy fields subjected to rice straw and organic manure incorporation practices also increased and then accelerated soil nutrient decomposition and enhanced soil nutrient availability. Meanwhile, compared with OM treatment, RF treatment had a lower rice yield due to slower release of rice straw nutrients, especially during the early rice growth season under lower-temperature conditions, this result was consistent with those of previous studies [37]. This would benefit practices for increasing rice yield with organic matter input treatments under a double-cropping rice system by regulating the extracellular enzyme activities and chemical properties of soil.
4.3. Correlation between Soil N Mineralization Rate and Soil Extracellular Enzyme Activities, Acid-Hydrolysable N Fractions
Our results prove that there was a negative correlation between aerobic N mineralization rates and β-glucosidase activity in the soil of paddy fields, which was consistent with previous findings [16,38]. Meanwhile, this also indicated that there was a positive correlation (r = 0.82) between aerobic N mineralization rate and the activities of β-glucosidase and L-glutaminase enzymes in paddy fields (Table 7). Soil L-glutaminase activity was significantly positively correlated with soil anaerobic N mineralization rates in a double-cropping rice field (r = 0.63, p < 0.05), as supported by previous results [14,39]. Our results suggest that the disadvantage of the anaerobic N mineralization rate in soil was terminal amino acid-hydrolysis, which is expressed as soil NH4+-N accumulation. Meanwhile, the limitations of the early step of N mineralization and β-glucosaminidase activity in soil were related to the degradation of polypeptide glucan and chitin. There was a negative correlation between β-glucosidase activity and N mineralization rates (aerobic and anaerobic) in the soil of paddy fields (Table 7).
This result proved that there was a positively correlation between soil amino acid N, acid-hydrolhydrolysable N, total amino sugar N and soil N mineralization rates (Table 7), suggesting that soil amino sugar N, acid-hydrolhydrolysable N and total amino sugar N contents were the main sources of soil mineralized N in double-cropping rice fields. Therefore, soil amino sugar N, amino acid N and total acid-hydrolhydrolysable N contents play an important role in regulating soil N mineralization in double-cropping rice fields. In addition, hydrolysable N fractions are the main transport method of soil N and are active in the soil N transformation pool, suggesting that soil acid-hydrolysable N fractions significantly contribute to soil N mineralization in paddy fields.
5. Conclusions
In the present study, we explored beneficial practices for increasing early rice and late rice yield under the double-cropping rice system with rice straw and organic manure incorporation managements. Meanwhile, this result proves that soil acid N mineralization and hydrolysable N fractions in double-cropping rice fields subject to organic matter increased. Our results indicate that soil anaerobic nitrogen mineralization in the double-cropping rice field was mainly regulated by the cleavage of terminal amino acids rather than depolymerization. It is a beneficial practice for increasing soil N mineralization and its enzyme activities in double-cropping rice fields under the long-term application of organic matter conditions. Therefore, the anaerobic, aerobic nitrogen mineralization rates and extracellular enzyme activities of soil play an important role in regulating N mineralization and acid-hydrolysable N fractions in the soil of a double-cropping rice field. However, the dominant control factors in regulating proteinaceous nitrogen release in the double-cropping rice field still require further study.
Author Contributions
H.T. and X.X. designed the experiments. C.L., K.C., L.S. and L.W. performed the experiments. L.W. and W.L. analyzed the data, H.T. wrote the manuscript. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was supported by the Innovative Research Groups of the Natural Science Foundation of Hunan Province (2022CX75), Hunan Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China (2022JJ30352), Director Fund of Hunan Soil and Fertilizer Institute (2022tfs101), National Natural Science Foundation of China (U21A20187), Hunan science and technology talent lift project (2022TJ-N07).
Data Availability Statement
The data reported in this study are contained within the article.
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank the staff of Ningxiang Agricultural Technology Extension Center for field management.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Spiertz, J.H.J. Nitrogen, sustainable agriculture and food security. A review. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2010, 30, 43–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, L.; Wang, J.L.; Zhong, Z.Q.; Li, J.Q.; Deng, H. Immobilization of antimony in soil and groundwater using ferro-magnesium bimetallic organic frameworks. J. Environ. Sci. 2023, 125, 194–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sekhon, K.S.; Singh, J.P.; Mehla, D.S. Long-term effect of manure and mineral fertilizer application on the distribution of organic nitrogen fractions in soil under a rice–wheat cropping system. Arch. Agron. Soil Sci. 2011, 57, 705–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.; Daly, E.J.; Gorzelak, M.; Hernandez-Ramirez, G. Soil organic matter pools response to perennial grain cropping and nitrogen fertilizer. Soil Till. Res. 2022, 209, 105376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekambaram, S.P.; Aruldhas, J.; Srinivasan, A.; Erusappan, T. Modulation of NF-κB and MAPK signalling pathways by hydrolysable tannin fraction from Terminalia chebula fruits contributes to its anti-inflammatory action in RAW 264.7 cells. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2022, 74, 718–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Sun, J.; Kang, J.; Zhang, Z.; Shangguan, Z.; Wang, C. Influence of nitrogen addition on the changes in nitrogen and carbon fractions in soil profiles of wheat fields. Land Degrad. Dev. 2021, 32, 2540–2553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, Y.; Cheng, M.; Wen, Y.L.; Darboux, F. Soil organic carbon sequestration under long-term chemical and manure fertilization in a cinnamon soil, Northern China. Sustainability 2022, 14, 5109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wander, M.M.; Yun, W.; Goldstein, W.A.; Aref, S.; Khan, S.A. Organic N and particulate organic matter fractions in organic and conventional farming systems with a history of manure application. Plant Soil 2007, 291, 311–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.; Gao, T.; Liu, Z.; Ning, T. Rotary and subsoiling tillage rotations influence soil carbon and nitrogen sequestration and crop yield. Plant Soil Environ. 2022, 68, 89–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.C.; Shen, Q.R.; Ran, W. Content and distribution of forms of organic N in soil and particle size fractions after long-term fertilization. Chemosphere 2003, 50, 739–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, E.; Xia, N.; Tang, Y.; Guo, Z.; Guo, Y.; Wang, Y.; Vries, W.D. Anthropogenic and climatic shaping of soil nitrogen properties across urban-rural-natural forests in the Beijing metropolitan region. Geoderma 2022, 382, 115524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kader, M.A.; Sleutel, S.; Begum, S.A.; Moslehuddin, A.Z.M.; De Neve, S. Nitrogen mineralization in sub-tropical paddy soils in relation to soil mineralogy, management, pH, carbon, nitrogen and iron contents. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2013, 64, 47–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sleutel, S.; Kader, M.A.; Demeestere, K.; Walgraeve, C.; Dewulf, J.; De Neve, S. Subcritical water extraction to isolate kinetically different soil nitrogen fractions. Biogeosciences 2013, 10, 7435–7447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kader, M.A.; Yeasmin, S.; Solaiman, Z.M.; De, N.S.; Sleutel, S. Response of hydrolytic enzyme activities and nitrogen mineralization to fertilizer and organic matter application in subtropical paddy soils. Eur. J. Soil Biol. 2017, 80, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.F.; Hou, L.J.; Liu, M.; Lin, X.B.; Li, Y.; Li, S.W. Primary effects of extracellular enzyme activity and microbial community on carbon and nitrogen mineralization in estuarine and tidal wetlands. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2015, 99, 2895–2909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabatabai, M.A.; Ekenler, M.; Senwo, Z.N. Significance of enzyme activities in soil nitrogen mineralization. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 2010, 41, 595–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, R.; Tripathi, P.; Singh, R.P.; Khare, P. Assessment of soil enzymatic resilience in chlorpyrifos contaminated soils by biochar aided Pelargonium graveolens L. plantation. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2023, 30, 7040–7055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muruganandam, S.; Israel, D.W.; Robarge, W.P. Activities of nitrogenmineralization enzymes associated with soil aggregate size fractions of three tillage systems. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2009, 73, 751–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.; Mishra, J.S.; Naik, S.K.; Mondal, S.; Meena, R.S.; Kumar, S.; Dubey, A.K.; Makarana, G.; Jha, B.K.; Mali, S.S. Impact of crop establishment and residue management on soil properties and productivity in rice-fallow ecosystems in India. Land Degrad. Dev. 2022, 33, 798–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khorsandi, N.; Nourbakhsh, F. Prediction of potentially mineralizable N from amidohydrolase activities in a manure-applied, corn residue-amended soil. Eur. J. Soil Biol. 2008, 44, 341–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.Y.; Ren, W.D.; Sun, B.H.; Zhang, S.L. Effects of contrasting soil management regimes on total and labile soil organic carbon fractions in a loess soil in China. Geoderma 2012, 177–178, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, H.M.; Li, C.; Xiao, X.P.; Pan, X.C.; Cheng, K.K.; Shi, L.H. Effects of long-term fertiliser regime on soil organic carbon and its labile fractions under double cropping rice system of southern China. Acta Agric. Scand. Sect. B Soil Plant Sci. 2020, 70, 409–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, H.M.; Xiao, X.P.; Tang, W.G.; Li, C.; Wang, K.; Li, W.Y. Long-term effects of NPK fertilizers and organic manures on soil organic carbon and carbon management index under a double-cropping rice system in Southern China. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 2018, 49, 1976–1989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Liang, G.; Zhou, W.; Sun, J.; Wang, X.; He, P. Fatty-acid profiles and enzyme activities in soil particle-size fractions under long-term fertilization. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2016, 80, 97–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Zhang, R.; Xue, C.; Xun, W.; Sun, L.; Xu, Y. Pyrosequencing reveals contrasting soil bacterial diversity and community structure of two main winter wheat cropping systems in China. Microb. Ecol. 2014, 67, 443–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berthrong, S.T.; Buckley, D.H.; Drinkwater, L.E. Agricultural management and labile carbon additions affect soil microbial community structure and interact with carbon and nitrogen cycling. Microb. Ecol. 2013, 66, 158–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SAS. SAS Software of the SAS System for Windows, 3rd ed.; SAS Institute Inc.: Cary, NC, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez-Prieto, S.J.; Jocteur-Monrozier, L.; Hetier, J.M.; Carballad, T. Changes in the soil organic N fractions of tropical alfisol fertilized with 15N-urea and cropped to maize or pasture. Plant Soil 1997, 195, 151–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santhy, P.; Jaysreesankar, S.; Muthuvel, P.; Selvi, D. Long term fertilizers experiments status of N, P and K fractions in soil. J. Indian Soc. Soil Sci. 1998, 46, 395–398. [Google Scholar]
- Mohanty, M.; Reddy, S.K.; Probert, M.E.; Dalal, R.C.; Rao, S.A.; Menzies, N.W. Modelling N mineralization from green manure and farmyard manure from a laboratory incubation study. Ecol. Model. 2011, 222, 719–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartz, T.K.; Mitchell, J.P.; Giannini, C. Nitrogen and carbon mineralization dynamics of manures and composts. Hortic. Sci. 2000, 35, 209–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Sun, S.; Zhou, T.; Du, Z.; Wang, J.; Li, B.; Wang, J.; Zhu, L. Effects of pyroxsulam on soil enzyme activity, nitrogen and carbon cycle-related gene expression, and bacterial community structure. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 355, 131821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.Y.; Xie, D.; Ge, X.G.; Dong, W.; Luan, J.W. Altered diversity and functioning of soil and root-associated microbiomes by an invasive native plant. Plant Soil 2022, 473, 235–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burns, R.G.; DeForest, J.L.; Marxsen, J.; Sinsabaugh, R.L.; Stromberger, M.E.; Wallenstein, M.D. Soil enzymes in a changing environment: Current knowledge and future directions. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2013, 58, 216–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, D.; Agrawal, M.; Bohra, J.S. Effects of conventional tillage and no tillage permutations on extracellular enzyme activities and microbial biomass under rice cultivation. Soil Till. Res. 2014, 136, 51–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nannipieri, P.; Sequi, P.; Fusi, P. Humus and enzyme activity. In Humic Substances in Terrestrial Ecosystems; Piccolo, A., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1996; pp. 293–327. [Google Scholar]
- Lehmann, J.; Pereira da Silva, J.; Steiner, C.; Nehls, T.; Zech, W.; Glaser, B. Nutrient availability and leaching in an archaeological Anthrosol and a Ferralsol of the Central Amazon basin: Fertilizer, manure and charcoal amendments. Plant Soil 2003, 249, 343–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, X.Q.; Jarvie, S.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, Q.F.; Yan, Y.Z.; Su, N.; Han, P.; Li, F.S. Community assembly of plant, soil bacteria, and fungi vary during the restoration of an ecosystem threatened by desertification. J. Soil Sediment. 2023, 23, 459–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinsabaugh, R.L.; Hill, B.H.; Follstad, J.J. Ecoenzymatic stoichiometry of microbial organic nutrient acquisition in soil and sediment. Nature 2009, 462, 795–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).