Abstract
With a shortage of sulfur in the soil and an increasing world population and, thus, food consumption volume, the demand for this important nutrient is likely to increase, both globally and regionally. The purpose of this model incubation study was to evaluate the effect of fertilizer granule applications containing elemental sulfur, halloysite and phosphate rock on the content of the bioavailable form of sulfur and phosphorus, as well as dehydrogenase activity and pH value of two soils differing in granulometric composition and chemical parameters. In addition to the standard procedure of analysis of variance, the authors propose various methods of advanced statistical analysis: regression modeling, including simple regression and multiple regression, or multivariate methods of grouping objects and traits resulting in the creation of heatmaps. With respect to the control, the application of fertilizer granules generally had no significant effect on the content of available phosphorus and the activity of dehydrogenase, and had little effect on the degree of acidity of the soils tested. There was a greater effect of introducing fertilizer granules on the content of sulfate sulfur in heavy soil than in medium soil. Using advanced statistical techniques revealed relationships between the studied soil parameters and changes in their values as affected by the experimental factors.
1. Introduction
Sulfur is one of the most important nutrients determining the growth and development of plants and, thus, affecting the yield and quality of crops. It determines the nutritional value and taste qualities of agricultural and horticultural crops [1,2,3]. There is a strong connection between the nutritional status of plants in sulfur and nitrogen, since both elements participate in the formation of chlorophyll and are components of proteins. Soil sulfur deficiency results in reduced nitrogen utilization, lowering production effectiveness. Plants optimally supplied with sulfur take up nitrogen more intensively, resulting in reduced leaching of nitrates into deeper layers of the soil profile. This is of great importance both economically and environmentally. Sulfur is a component of many organic compounds in plants, including amino acids, proteins, vitamins and glucosinolates. The amount of sulfur accumulated in plant dry matter ranges from 0.2 to 0.5% (similar to phosphorus). This element increases plant resistance to diseases and pests, as well as environmental stress [4,5,6,7,8,9].
Human activity has a huge impact on the sulfur cycle in the environment. Over the years, there has been a shift in the global cycle of this element from a point where it was a threat to a point where it was intentionally introduced into the environment and significantly deficient in crop production. In the past, the atmosphere was a major source of sulfate in the soil, and the amounts of the deposited component substantially exceeded the nutritional needs of plants, and at one point, its excess in the environment threatened the health of humans, animals and plants. The situation changed after the introduction of controls on industrial emissions, resulting in a considerable reduction in the amount of sulfur returning to the environment. The current volume of sulfur deposition in Poland is annually within 10 kg ha−1, and in the US, it is 4–8 kg ha−1 [10,11]. At the same time, the intensification of crop production has resulted in an increased outflow of sulfur from crop fields. The export of the component with yields, depending on the species of crop grown, is at the level of 4–30 kg of S ha−1 [12]. In addition, the use of natural fertilizers has been reduced and the use of concentrated fertilizers devoid of ballast sulfur has increased. As a result of these changes, today, most (about 70%) of the cultivated soils in Poland, as well as in Europe and elsewhere in the world (North America, China, India), are characterized by a low content of sulfur, especially sulfate sulfur, which is the form directly available to plants. In view of the above, supplementing the deficiency of this element in the soil has become a necessity [1,13,14,15,16].
Balanced fertilization is an important part of proper management, both of crop production and of soil. More often than not, the nutrient reserves stored in the soil are insufficient to meet the nutritional requirements of plants. An imbalance in the nutrient content of soil is one of the main problems threatening its fertility and productivity. Plants take up sulfur throughout the growing season, and failure to include it in the fertilization plan can lead to reduced site functionality. On the other hand, well-maintained and fertile soil is the basis for achieving the best and most consistent production results over time. In crop production, the main source of sulfur is mineral fertilizers, which contain various chemical forms of this element (sulfate, thiosulfate, elemental). Regardless of the type of fertilizer used, efforts should be made to increase the efficiency of its use and reduce the loss of components from agro-ecosystems. Numerous fertilizers are available on the market, both single-component and multi-component products occurring in solid and liquid forms [14,17,18]. With the scarcity of sulfur in the soil environment and the increasing global population and, thus, the volume of food consumption, the demand for this important nutrient is likely to increase, both globally and regionally. According to the European Green Deal, regardless of the need to ensure food security for the human population, the food sector must become low-carbon and climate-neutral. Ensuring the implementation of these requirements will reduce the scale of the climate crisis and the processes of environmental degradation facing modern society. Elemental sulfur cannot be taken up by plants until it is converted to ionic form. The process of releasing the bioavailable form is spread out over time, which can be advantageous when the elemental form is used on soils prone to the leaching process. A thorough understanding of the effects of this material on soils characterized by different properties is an important aspect in terms of preserving their quality. This is an important issue in terms of sustainable development and maintaining this environmental element in good condition for present and future generations.
The purpose of this study was to verify the hypothesis, assuming that the application of new fertilizer granules containing elemental sulfur results in soil properties’ improvement. For this reason, the model incubation study was established using two soils differing in granulometric composition and chemical parameters. In order to assess the suitability of the mentioned products, the following properties of the tested soils were examined: sulfate sulfur content, pH value and dehydrogenase activity. With regard to the application of fertilizer granules SII and SIII, the content of bioavailable forms of phosphorus was also evaluated. In addition to the standard procedure of analysis of variance, we also used more advanced statistical procedures, such as regression modeling, including simple regression and multiple regression, and multivariate methods of grouping objects and traits resulting in the creation of heatmaps. In-depth analyses of this type give the possibility of a more complementary approach to the interpretation of the obtained data.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Establishing the Model Incubation Experiment
The incubation experiment was conducted on two soils taken from the 0–20 cm layer in southern Poland. A representative sample was taken in accordance with the requirements of PN-R-04031:1997 [19]. Medium and heavy soils were used, which, based on granulometric composition, were classified as sandy loam and clayey dust, respectively (Table 1). Prior to establishing the experiment, the soil was air-dried and sifted. Both soils were low in sulfate sulfur and total sulfur (Table 1), as determined using guidelines relating to sulfur limits in soils [20]. Selected properties of the soil material before the experiment are shown in Table 1.

Table 1.
Selected soil properties before establishing the experiment.
For each soil, the experimental scheme included 5 treatments (Table 2). Each treatment consisted of three replicates. Soil material without any additives and soil material with the addition of elemental sulfur were regarded as comparison points to treatments with fertilizer granulate addition.

Table 2.
Scheme of experimental design.
The doses of elemental sulfur and fertilizer granules (Figure 1) were determined based on their sulfur content, the sulfate sulfur content of the soil material before the start of the incubation experiment and the criteria set by Kabata-Pendias et al. [20]. The dose of sulfur introduced into all treatments (except the control) of medium and heavy soil was 15 mg kg−1 d.m. of soil and 20 mg kg−1 d.m. of soil, respectively. Prior to application, the test materials were crushed, and in addition, a rotary mixer was used to mix them evenly with the soil material.

Figure 1.
Materials used in the incubation experiment: (a)—fertilizer granulate I; (b)—fertilizer granulate II; (c)—fertilizer granulate III; (d)—fertilizer granulate IV.
The soil material was incubated in plastic containers (Figure 2). In each container, 200 g d.m. of medium or heavy soil was introduced and enriched with appropriate materials (according to the experimental scheme) (Table 2).

Figure 2.
Containers with soil material during the incubation experiment.
Incubation was carried out in a greenhouse at 25 ± 2 °C. The moisture content of the soil material was kept constant at 60% of the maximum water holding capacity (PWmax). Samples for laboratory analysis were taken 4 times: on the day of fertilizer introduction, and 30 days, 60 days and 90 days after the establishment of the incubation. After collection, the soil material was brought to an air-dry state and sieved through a sieve with a mesh diameter of 1 mm in preparation for laboratory analyses (determination of dehydrogenase activity was performed using fresh material). The scope of analysis of the soil material included the determination of pH value, sulfate sulfur content, dehydrogenase activity and bioavailable forms of phosphorus (analysis when fertilizer granules SII and SIII, containing phosphate rock, were added to the soil material).
2.2. Methods of Laboratory Analysis
2.2.1. Soil pH
The pH value of soil material was determined through the potentiometric method in suspension of soil material in water and suspension of soil material in 1 mol L−1 (m/v 1:2.5) potassium chloride (KCl) (Chempur, Piekary Śląskie, Poland), using a multifunctional device CPC-502 (Elmetron, Zabrze, Poland) [21]. The average pH value of the soil material was calculated from the formula pH = −log[H+], after previously converting the pH values obtained for the repeats into hydrogen ion concentrations [H+] and determining the arithmetic mean concentration of these ions. The obtained value was converted into a pH value.
2.2.2. Available Sulfur and Phosphorus
The content of bioavailable forms of sulfur (sulfate, S-SO4) and phosphorus (P) were determined after the extraction of the samples with Mehlich 3 reagent (5 min, 40 rpm, m/v 1:10) [22]. Mehlich 3 is an extractant with a pH value of 2.5 ± 0.05, containing 0.2 mol L−1 CH3COOH (Chempur, Piekary Śląskie, Poland), 0.25 mol L−1 NH4NO3 (Chempur, Piekary Śląskie, Poland), 0.015 mol L−1 NH4F (Chempur, Piekary Śląskie, Poland), 0.013 mol L−1 HNO3 (Chempur, Piekary Śląskie, Poland) and 0.001 mol L−1 EDTA (POCH, Gliwice, Poland). The sulfur and phosphorus contents were quantitatively measured through inductively coupled plasma optical emission spectrometry (ICP-OES) using an Optima 7300 DV instrument (Perkin-Elmer, Waltham, MA, USA). The sulfur content was determined at 182 nm, while the phosphorus content was determined at 214 nm.
2.2.3. Dehydrogenase Activity
Dehydrogenase (DH) activity was determined by converting the colorless, water-soluble 2,3,5-triphenyltetrazolium chloride (TTC) into the insoluble 1,3,5-triphenylformazane (TPF) in water [23]. Soil material was incubated with 1.0% TTC, prepared in tris(hydroxymethyl) aminomethane hydrochloride buffer (TRIS-HCl) at a pH of 7.4. After incubation (1:1 m/v, 96 h, 30 °C), the resulting TPF was extracted with methyl alcohol and quantified using the colorimetric method at 485 nm on a UV/Vis DU 640 spectrophotometer (Beckman Instruments, Inc., Fullerton, CA, USA).
2.2.4. Properties of Soil Material before Establishing the Experiment
In order to determine the properties of the soil material before the incubation experiment, additional analyses were carried out. The granulometric composition of the soil material was determined using the Bouyoucos–Casagrande areometric method as modified by Proszynski [20,23,24]. This method was chosen because the method of evaluating the sulfur abundance of Polish soils is adapted to its results. The maximum water capacity of the soil material was determined through the weight method, by measuring the difference in the weight of the sample in the dry state and after moistening with water (due to capillary forces). The hydrolytic acidity of the soil material was determined using the Kappen method after extraction with a 1 mol L−1 sodium acetate solution (CH3COONa) (1 h, 40 rpm, 2:5 m/v). The nitrogen, carbon and total sulfur contents of the soil material were determined on a vario MAX cube CNS analyzer (Elementar Analysensysteme GmbH, Langenselbold, Germany). The determination included high-temperature combustion of the material with catalytic afterburning, purification of the gaseous combustion products, their separation and sequential detection of the signals in a thermal conductivity detector [25].
2.3. Statistical Analysis of the Results
The results obtained from the incubation experiment were statistically processed using Statistica 13.3 (TIBCO Software Inc., Palo Alto, CA, USA), providing values for the arithmetic mean and standard deviation (SD). The normality of distribution was determined in samples with Kolmogorov–Smirnov’s test and the homogeneity of variances was analyzed with Levene’s test. Next, differences between treatments, performed separately for the two soil types, were analyzed using ANOVA, followed by Duncan’s post hoc test. Homogeneous groups were determined at a significance level of p ≤ 0.05. The Pearson correlation coefficients (r) were used to study the relationships between various soil traits. Linear regression equations were developed and presented on the plots when r > 0.700 and with significance p ≤ 0.01, and they were also used for calculating the models’ coefficient of determination (R2). In two cases, it was reasonable to develop the polynomial models. Multiply regression analysis (general regression models—GRM) was used to study relationships between S-SO4 content as the dependent variable and each of the following traits as independent variables: pHH2O, P content and dehydrogenase activity. Simplified regression equations were characterized by the coefficient of determination (R2), adjusted coefficient of determination (R2adj.) and standard error of estimation (Se). The Generalized Linear/Nonlinear Model (GLZ) module was used to calculate the AIC (Akaike information criterion) and BIC (Bayesian information criterion) values. The initial assumptions were as follows: normal distribution, link function: log. The observed S-SO4 contents in medium and heavy soils versus predicted data are presented in the plots. Heatmap visualization was used to graphically represent numerical data and to increase the clarity about the relationships between them and the impact of experimental factors. Warmer colors indicate higher values and colder colors indicate lower values.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Value of Soil pH
On the day of the start of incubation, the value of pHH2O for medium soil did not differ significantly between the experimental treatments and ranged from 6.17 to 6.19 (Table 3). In the soil of the control (C), changes in the value of the pHH2O proceeded more slowly than in the soil treated with the addition of the tested fertilizer granules (SII, SIII, SIV) and elemental sulfur (SI). A significant increase in soil acidity in this object was found after 60 and 90 days of the experiment. On the other hand, in the soil with the addition of fertilizer granules, a substantial reduction in the pHH2O value was found after just 30 days of the experiment, which remained at a similar level for the next 30 days, and then decreased significantly. After 90 days, the value of pHH2O for medium soil in each site ranged from 6.04 to 6.07 (Table 3). Indeed, the highest value of this parameter was found in the soil with the addition of SIII and SIV granules.

Table 3.
Medium soil pHH2O value throughout the incubation experiment.
On the day incubation began, the value of pHH2O of heavy soil did not differ significantly between the experimental treatments and ranged from 6.32 to 6.34 (Table 4). After 30 days of the experiment, there was a significant reduction in the value of pHH2O for the soil of all treatments with the addition of the tested fertilizer granules (SII, SIII, SIV), elemental sulfur (SI) and the control object (C), and this reduction increased over time. For the first 60 days of the experiment, there were no significant differences in the pH values among all experimental treatments. On the day the incubation ended, the value of pHH2O of the heavy soil ranged from 5.98 to 6.02 (Table 4). Indeed, the highest pHH2O value was found in the soil of the control, while the variation among fertilized treatments was small, but the lowest pHH2O level was noted for the SII treatment.

Table 4.
Heavy soil pHH2O value throughout the incubation experiment.
Based on this study, it was found that the applied fertilizer granules and elemental sulfur had a greater effect on the pH value of medium soil than that of heavy soil. In medium soil, the significant impact of the applied materials became apparent after 30 days of the experiment, and in heavy soil, it did so on the day of the end of incubation. At the same time, in conclusion, it should be noted that significant changes in the values of the parameter in question were small and affected only some experimental treatments or the sampling days of the soil material. Over the course of the experiment, soil pHH2O decreased, as a result of which the acidity status changed from slightly acidic to acidic. In medium soil, the change in reaction occurred on day 60 of the experiment, while in heavy soil, it occurred on day 30. Compared to control, the application of fertilizer granules SII, SIII and SIV and elemental sulfur (SI) had little effect on the change in the degree of acidity of the tested soils. In heavy soil, spontaneous changes in the value of pHH2O occurred more rapidly, and the effect of the applied fertilizer granules and elemental sulfur became apparent only on the day the experiment ended. The intensity of the effect of introduced sulfur on the state of soil acidity depends on climatic conditions, soil type and the size of the applied doses, as well as soil management practices. The negative effect of sulfur fertilization on soil pH can be reduced by performing a liming procedure [7,15,26]. The reduction in soil pH value is proportional to the intensity of the release of H+ ions due to the oxidation of elemental sulfur [27]. At the same time, it should be noted that the process of lowering the pH value in the soil occurs continuously and spontaneously, as can be seen in the soil of the control treatments of this study and also reported by Kulczycki [7]. Ye et al. [28] showed that the application of elemental sulfur at several different doses (0, 112, 224 and 448 kg S ha−1) had no effect on the pH value of the soil on different sampling days. The authors explained that this could be due to the introduction of too little sulfur and the high buffering capacity of the tested soil. According to Deubel et al. [29], the buffering process is often slower than the formation of sulfuric acid from elemental sulfur during its oxidation. Modaihsh et al. [30] found that the application of elemental sulfur at a dose of 0.5% significantly lowered the pH of soil incubated for 18 weeks, but higher doses (1.5 and 3.0%) caused no further change in pH, indicating that the rate of oxidation decreased as the dose of elemental sulfur increased. Jaggi et al. [27] showed that elemental sulfur application (at doses of 0 and 500 μg g−1) had no effect on the pH value of acidic (pH 4.9) and neutral (pH 7.1) soils under different conditions of their moisture content (40, 60, 120%) and a constant incubation temperature of 24 °C. On the other hand, in the case of alkaline soil (pH 10.2), the applied intervention lowered its pH value under aerobic conditions (moisturization at 40 and 60%). This was not observed in the case of complete flooding of the soil with water (moisture content 120%), which could be due to the cessation of the oxidation process of the introduced elemental sulfur [31]. Jaggi et al. [27] found that increasing the temperature from 12 °C to 36 °C did not cause significant changes in the value of the parameter in question in the incubated acidic soil (pH 4.9), in contrast to neutral (pH 7.1) and alkaline (pH 10.2) soil, where the pH value decreased with increasing the temperature of soil incubation. The authors emphasized that the intensity of changes in pH value depended on the pH of the incubated soils and was highest in alkaline soil, followed by neutral soil, reaching a minimum in acidic soil.
3.2. Content of Available Sulfur
On the day of the start of the incubation experiment, the sulfate sulfur content in the medium soil did not differ significantly between treatments and ranged from 7.79 to 9.92 mg S-SO4 kg−1 d.m. (Table 5). After 30 days, a significant increase in this content was found in the soil of all treatments. The same relationship was shown after another 30 days, except for the treatment with SI and SIV fertilizer granules, where no change was found with respect to the previous day. After 90 days of the experiment, the content of sulfate sulfur in the soil of individual treatments ranged from 16.11 to 20.16 mg SO4 kg−1 d.m. There were no significant differences between the treatments, with the content of the element in question in the soil of treatments with the addition of fertilizer granules SII, SIII and SIV determined on this day being significantly lower than the content determined on day 60.

Table 5.
Sulfate sulfur content in medium soil throughout the incubation experiment (mg S-SO4 kg−1 d.m. ± SD).
The sulfate sulfur content of the heavy soil was higher than that of the medium soil and on the day the experiment began, it ranged from 17.40 to 19.94 mg S-SO4 kg−1 d.m. (Table 6). After 30 days, there was a significant increase in this content in the soil of all treatments. The next 30 days resulted in a significant decrease in this content in the soil of all treatments, except for the soil with the addition of SIV fertilizer granules. After 90 days of the experiment, the content of sulfate sulfur in the soil of fertilized treatments ranged from 21.82 to 24.92 mg S-SO4 kg−1 d.m. with no statistically significant variation among individual fertilized treatments. On the day the experiment ended, the soil of the control had the lowest sulfate content.

Table 6.
Sulfate sulfur content in heavy soil throughout the incubation experiment (mg S-SO4 kg−1 d.m. ± SD).
The study showed little effect of the applied fertilizer granules on the content of sulfate in the medium soil. It is true that the determined content of this component in the soil of treatments fertilized on particular sampling days was generally higher than in the soil of the control, but the differences found were not statistically significant. A similar result was obtained when comparing the effect of applying elemental sulfur and the tested fertilizer materials. However, in heavy soil, the application of fertilizer granules and elemental sulfur caused a significant increase in the content of the component in question, relative to the control treatment. Throughout the experimental period, the soil of treatments fertilized with SII and SIII fertilizer granules was characterized by the highest sulfate content. In medium soil, the rate of the oxidation of elemental sulfur and, thus, the increase in sulfate content was observed until day 60 of incubation. In heavy soil, the oxidation process was faster and the highest sulfate sulfur content was found after 30 days of incubation. Additionally, Kulczycki [7], Modaihsh et al. [30], Wen et al. [32], Degryse et al. [33] and Malik et al. [34] found an increase in soil sulfate sulfur content after elemental sulfur application. In addition, Kulczycki [7], like Jaggi et al. [35], showed that sulfate content also increased over time in soil without elemental sulfur addition. Most of the sulfur in soil (95% of the total amount) is accumulated in organic form, and only 5% is sulfate form [36]. Hence, the increase in the content of the directly plant-available form (sulfate) in the soil of control treatments may be due to the mineralization of organic connections. As in our study, a decrease in S-SO4 after reaching a maximum level (on day 60 of incubation in medium soil and on day 30 of incubation in heavy soil) during the incubation experiment was also found by Jaggi et al. [35], which can be explained by the changing activity of soil microorganisms. The process of elemental sulfur transformation is controlled by organisms capable of carrying it out, and the intensity of oxidation increases with microbial biomass [37]. In parallel, during the oxidation process, there is also mineralization of sulfur accumulated in soil organic matter and its immobilization by soil microorganisms [38]. The results indicate that the effectiveness of applying the same materials to soils that differ in properties can produce different results. Wen et al. [32] stressed that sulfur oxidation as a biological transformation process depends on many factors and can be difficult to describe. Sulfur undergoes many transformations in the environment, as a result of which chemical compounds are formed that are on different oxidation levels from −2 to +6 [15]. The factors shaping the conditions of the environment in which sulfur is oxidized, that is, structure, temperature, humidity, pH value and abundance of organic matter, directly affect the activity of the organisms inhabiting it [32,35,39]. In sandy soils, characterized by poor structure, the oxidation efficiency of introduced sulfur is usually lower and increases with increasing content of clay fraction, which may be a consequence of variation in moisture and aeration conditions [40,41]. The process of sulfur oxidation ceases at low temperatures (<4 °C), and its intensity increases significantly with increasing temperature to a maximum of ~40 °C, with the temperature conducive to maximum oxidation efficiency being in the range of 30 °C to 40 °C [35,41]. Under both insufficient and excessive soil moisture conditions, the oxidation of elemental sulfur is limited, and a value close to the field capacity of the soil is considered optimal for its efficient conversion, as it allows for good soil aeration [31,41]. As the soil pH value decreases, the intensity of the process is reduced, reaching a minimum in acid soil [7,35]. A high concentration of ions (both anions and cations) in the soil solution inhibits the activity of organisms that oxidize the element in question. This is due to the effect of high osmotic pressure [42]. In contrast, the greater efficiency of this process in alkaline soil is due to the higher content of calcium carbonate (CaCO3) [43]. As the abundance of organic matter in the soil increases, the living conditions for microorganisms improve. Organic matter participates in the formation of soil structure, shaping the prevailing water, air and thermal conditions. It is also a source of energy and nutrients for microorganisms.
3.3. Content of Available Phosphorus
On the day of the start of the incubation experiment, the average content of available phosphorus in the soil generally did not differ significantly between treatments and ranged from 79.3 to 97.4 mg P kg−1 d.m. (Table 7). After 30 and 60 days of the experiment, a significant increase in the content of this element in the soil of the experimental treatments was observed, followed by a significant decrease after 90 days. The determined contents of available phosphorus ranged from 109.9 to 114.0 mg P kg−1 d.m. (no significant variation among treatments) and were significantly higher than on the day the experiment began.

Table 7.
Available phosphorus content in medium soil throughout the incubation experiment (mg P kg−1 d.m. ± SD).
The content of bioavailable forms of phosphorus in heavy soil on the day the experiment was set up was higher than in medium soil. On the day of the start of the incubation experiment, the content of this element in heavy soil did not differ significantly between treatments, ranging from 144.4 to 155.0 mg P kg−1 d.m. (Table 8). After 30 days of the experiment, this content was significantly higher in the soil of all experimental treatments. After 60 days, the content of bioavailable phosphorus was reduced only in the soil with SII fertilizer granules, and after 90 days of the experiment, in the soil of all treatments. On the day the experiment ended, the content of bioavailable forms of phosphorus in the soil of fertilized treatments ranged from 129.3 to 140.6 mg P kg−1 d.m. and was not significantly different among individual treatments.

Table 8.
Available phosphorus content in heavy soil throughout the incubation experiment (mg P kg−1 d.m. ± SD).
This study generally showed no effect of the applied elemental sulfur and its combination with phosphate rock on the content of available phosphorus in the two tested soils. It is likely that too low a dose of phosphorus in the form of fertilizer granules was applied, while at the same time, the abundance of this element in soils was relatively high. As in the case of sulfate sulfur, the increase in available phosphorus content in medium soil was observed until day 60 of incubation, and in heavy soil, until day 30. Similarly, Islam et al. [44] found that the effect of sulfur application on the content of available phosphorus in two different soils was not significant. However, the application of triple superphosphate in the cited study increased the available pool of the mentioned element and reduced the availability of sulfur. The small effect of applied elemental sulfur on the content of available phosphorus may be due to the higher abundance of soil with CaCO3, higher value of the ratio of CaCO3 to clay, higher pH value or higher phosphate retention capacity [30]. Modaihsh et al. [30] showed that the content of the bioavailable form of phosphorus in several soils with different properties increased significantly after the application of elemental sulfur at doses of 0.5, 1.5 and 3.0%. Higher contents of this element were recorded after 3–9 weeks of incubation. In contrast, after 18 weeks of the experiment, the content of available phosphorus in the tested soils decreased significantly. Karimizarchi et al. [26] highlighted that the effect of increasing the concentration of available phosphorus after the application of elemental sulfur was noted only during the initial period of the experiment, and the amount of the available form of this element decreased with time. In contrast, Jaggi et al. [27], testing the effect of elemental sulfur application under conditions of varying the moisture content and pH values of soils, showed an increase in phosphorus content during the 42-day incubation period by 8.5 μg and 16.5 μg P g−1 in acidic soil, 12.0 μg and 14.5 μg P g−1 in neutral soil and 7.5 μg and 13.0 μg P g−1 in alkaline soil at 40% and 60% moisture content, respectively. The increase in the content of available phosphorus after the application of elemental sulfur may be due to its displacement from the surface of soil colloids and replacement by sulfate ions formed due to sulfur oxidation. Another mechanism for increasing the concentration of this component in the soil solution is the increased solubility of its inorganic compounds, which occurs as the pH value decreases [27,45]. The pH value of the soil directly shapes the availability of nutrients to plants, since hydrogen ions H+ participate in the process of establishing ionic equilibrium in the soil solution [27]. In the case of phosphorus, this is particularly evident, and the availability of this element in an acidic environment can be reduced by up to 90% [46]. In neutral to alkaline soils, the pool of available phosphorus is shaped by the solubility of its mineral combinations with calcium, and in acidic conditions, by that with aluminum and iron [26,47]. Since most of the phosphorus in the soil is bound in organic form, the temperature and moisture content can have a significant impact on the content of the bioavailable form of this element by affecting the activity of soil microorganisms carrying out its transformation processes. Under optimal climatic conditions, the application of elemental sulfur can result in the release of a significant amount of bioavailable phosphorus. Jaggi et al. [27] showed that increasing the incubation temperature of soils promoted an increase in the stock of available phosphorus, which was due to the increased oxidation intensity of the applied elemental sulfur. The authors emphasized that the linear relationship between temperature and the concentration of this element in the tested soils suggested increasing its content by 0.24 μg g−1 for every 1 °C. A similar situation occurs with increasing levels of moisture content (40, 60, 120%). The cited authors found the highest content of the bioavailable form of this element in soil completely flooded with water (120% moisture content). However, as the amount of available oxygen decreases, the activity of soil organisms also declines. In view of this, the increase in the availability of phosphorus under conditions of total flooding of the soil may be due to both the activity of microorganisms and increased solubility of mineral combinations of this element [48].
3.4. Activity of Dehydrogenase
On the day of the start of the incubation, the activity of dehydrogenases in the medium soil was not statistically significantly different between the individual experimental treatments and ranged from 3.94 to 4.50 µg TPF g−1 d.m. 24 h−1 (Table 9). After 30 days of the experiment, there was a significant decrease in enzymatic activity in the soil of all experimental treatments, which intensified during the next sampling period and remained at a similar level until the end of the experiment. After 90 days of incubation, the activity of dehydrogenases in the soil of the experimental treatments ranged from 1.07 to 1.49 µg TPF g−1 d.m. 24 h−1. There was no significant variation in this parameter among individual treatments at that time.

Table 9.
Dehydrogenase activity in medium soil throughout the incubation experiment (µg TPF g−1 d.m. 24 h−1 ± SD).
The activity of dehydrogenases in heavy soil took on values higher than those found in medium soil. On the day of the start of the incubation, the activity of dehydrogenases in the heavy soil generally did not differ statistically significantly between the different experimental treatments and ranged from 7.68 to 9.53 µg TPF g−1 d.m. 24 h−1 (Table 10). After 30 days of the experiment, no significant changes in dehydrogenase activity were found in the soil of any of the experimental treatments. On the next sampling day, a significant reduction in the value of this parameter, with respect to the earlier day, was found in the soil of treatments with the addition of elemental sulfur (SI) and SII fertilizer granules. After 90 days of the experiment, a further significant reduction in the value of dehydrogenase activity was found in the soil of the experimental treatments. The determined activity ranged from 2.15 to 3.92 µg TPF g−1 d.m. 24 h−1 and generally did not vary significantly among individual treatments.

Table 10.
Dehydrogenase activity in heavy soil throughout the incubation experiment (µg TPF g−1 d.m. 24 h−1 ± SD).
The materials used generally had no effect on the activity of dehydrogenases in the two soils studied. With the passage of time, there was a significant decrease in the activity of the enzymes. At the same time, the greatest differences in the values of this parameter were already determined in medium soil in the first period of the study (up to the 30th day of incubation), while in heavy soil, these were determined in the last stage (between days 60 and 90 of incubation). A similar direction of changes in this parameter was also described in our previous works [38,49] and confirmed by Mierzwa-Hersztek [50]. Such a course of the experiment can be explained by the low content of organic matter in the tested soil material, which is not only a source of carbohydrates, proteins and mineral compounds, but also has protective and stabilizing functions against enzymes released from the cell after its degradation. In the heavy soil, the organic carbon content was higher than in the medium soil, hence the changes in dehydrogenase activity became apparent later in the incubation period. Various effects of sulfur application on the biological properties of soils are presented in the literature. Hammerschmiedt et al. [51] showed that elemental sulfur had a stimulating effect on the activity of dehydrogenases, and the intensity of the effect depended on the size of the particles applied. Filipek-Mazur et al. [52] found that applied mineral fertilization with NPKS had little effect on dehydrogenase activity in the soil of a two-year field experiment. In contrast, Gupta et al. [53] found a reduction in the activity of soil enzymes, including dehydrogenases, as an effect of several applications of elemental sulfur, with a concomitant reduction in soil pH values. Cooper and Warman [54], on the other hand, showed that it is possible to reduce the activity of dehydrogenases even when the pH value of the soil and its organic carbon stock are not reduced. Malik et al. [34] noted that the application of elemental sulfur had no significant effect on the value of the discussed parameter, while its combination with organic materials caused a significant increase in dehydrogenase activity. The application of fertilizers—mineral, organic and natural—can increase the population of microorganisms inhabiting the soil and, thus, its enzymatic activity.
Of the many enzymes present in the soil, dehydrogenases, which belong to the oxidoreductase group, play an important role in the initial stages of organic matter oxidation, and their activity can serve as an indicator of soil quality and the degree of soil degradation. The level of enzymatic activity in soils is variable in time and space. This is due to the fact that different habitats exhibit different characteristics. The abundance, diversity and activity of the microbial community are influenced by a number of factors shaped naturally and as a result of human activity (including pH value and soil type, electrolytic conductivity, nutrient availability, organic matter resources, climate, vegetation cover, mesofauna, soil erodibility status, applied fertilization and cropping system) [49,54,55,56]. As a rule, sandy soils have low enzymatic activity, clay soils have average enzymatic activity and strongly humus soils have high enzymatic activity [54,57]. This relationship is due to their properties. Soils with a higher organic carbon content are characterized by a higher abundance of inhabiting microorganisms, which, in turn, shape the flow of nutrients and the size of the pool available to plants [58,59]. Soil characterized by low cation exchange capacity is an environment with low dehydrogenase activity, which, in turn, increases with increasing soil sorption capacity and organic matter content. The factor that disrupts the balance of soil microorganisms can be both a deficiency and excess of macronutrients and trace elements [60,61]. Seasonal variation in dehydrogenase activity is shaped mainly by the level of soil moisture and temperature, an increase of which promotes the activity of the enzymes [62,63]. Many microorganisms are characterized by sensitivity to low soil pH (high concentration of hydrogen ions), so their abundance in an acidic environment will be low and, consequently, their enzymatic activity will also be low. As the pH value of the soil increases, the enzymatic activity of the soil rises. Dehydrogenase activity shows a maximum at a pH value of ~7 [57,64]. There are also relationships between the soil enzymes themselves. It was observed that dehydrogenase activity was significantly correlated with the activity (among others) of invertase, urease, arylsulfatase, protease and catalase in soil [51,52,58,65].
3.5. Relationships between Soil Parameters
The Pearson correlation analysis for medium soil showed a strong positive relationship between S-SO4 content and P availability (r = 0.8654) and negative relationship between S-SO4 content and dehydrogenase activity, where r = –0.9279 (Table 11). A negative correlation of dehydrogenase activity and P availability was also observed (r = –0.8211) for this type of soil, together with a positive correlation between dehydrogenase activity and pHH2O of the soil (r = 0.7061). A slight negative dependence for S-SO4 and pHH2O was also found (r = –0.5688). In heavy soil, only one strong and positive correlation was observed, i.e., between dehydrogenase activity and pHH2O (r = 0.8872). In two other cases, S-SO4 content with P availability and P availability with dehydrogenase activity, correlations were significant but much weaker (r = 0.6148 and r = 0.5721, respectively).

Table 11.
Pearson’s correlation coefficients for relationships among various soil traits.
The most notable correlations among the determined soil properties are presented in Figure 3. Simple regression analysis was performed and is expressed by the linear equation inserted in the particular plots with its corresponding coefficient of determination (R2). All these linear regression models presented in the plots turned out to be statistically significant. The coefficients of determination (R2) for the developed regression equations ranged from 0.4989 (equation involved dehydrogenase activity as y and pHH2O as x) to 0.8610 (S-SO4 content as y and dehydrogenase activity as x). Analyzing the location of the points on the plots, it can be suggested that the relationships between dehydrogenase activity (y) and pHH2O (x) could be better presented as polynomial regression for medium and heavy soil. In the case of medium soil, the calculated equations were y = 13,909.6184 − 4571.1813 ∗ x + 375.5812 ∗ x2 (R2 = 0.8277, p = 0.0001), while for heavy soil, they were y = –2294.5118 + 732.9312 ∗ x − 58.3127 ∗ x2 (R2 = 0.8568, p = 0.0001).
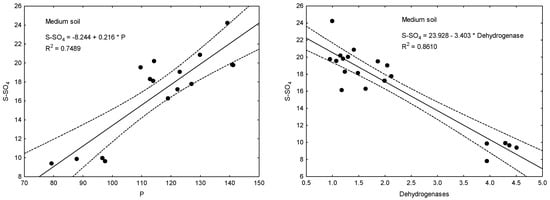
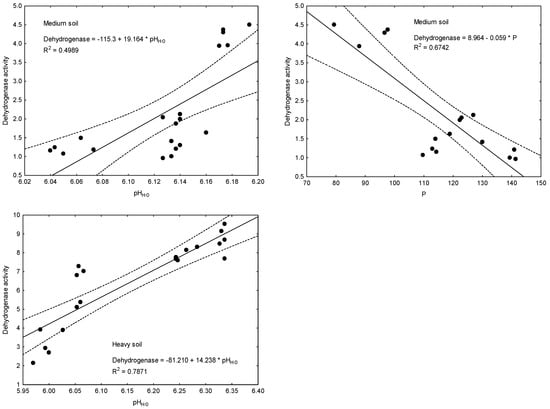
Figure 3.
Functional relationship between some soil traits with Pearson’s correlation coefficient r > 0.700 and with significance p ≤ 0.01 (see Table 10). R2—coefficients of determination for linear regression equations.
Multiple regression analysis using stepwise selection was applied to identify independent variables and their contribution to S-SO4 availability separately for medium and heavy soils. The initial multiple linear regression equation for both types of soil was as follows: y = b0 + b1×1 + b2×2 + b3×3, where b0 was the intercept, b1, b2 and b3 were regression coefficients and x1, x2 and x3 were pHH2O, P availability and dehydrogenase activity, respectively. The regression analyses were performed with a backward elimination procedure and the results are presented in Table 12. The first regression model for medium soil covered only one of the tested soil parameters, namely dehydrogenase activity, as the most significant variable in predicting the content of S-SO4. This was somewhat surprising, especially eliminating pH as a variable from the equation. The p-values for the coefficients indicate the very high significance of the model. The coefficient of determination (R2) meant that variation in the predictor variable can explain variation in the response variable by more than 90%. The standard error of estimation (Se) for the model showed that we made an error of 1.8248 mg S-SO4 kg−1 d.m. of the prediction value for y relative to the observed value. A different situation was observed in the development of the regression model for heavy soil. All initial independent variables were left in the equation. Despite this, the fit of the model was lower compared to that obtained for medium soil, when R2 was equal to 0.7793 and the adjusted coefficient of determination (R2adj.) was only slightly higher than 0.7000. However, the model was statistically significant and the p-value was very low. The error of estimation calculated for the model for heavy soil showed that we made an error of 2.1376 mg S-SO4 kg−1 d.m. during the estimation of observed values. Lower AIC or BIC values for the regression model developed for S-SO4 content in medium soil indicate a better fit.

Table 12.
Estimated equation parameters and statistics for stepwise multiple regression of S-SO4 in different soil types.
Figure 4 shows the observed S-SO4 contents plotted against the fitted values calculated on the basis of the regression equations developed for medium and heavy soils. The data points for the medium soil model are much closer to the projected regression line, although they are not evenly distributed along the entire line. In the case of the heavy soil model, the data are more scattered along the line, but also distributed more regularly along the line with a few points quite far beyond the confidence intervals.
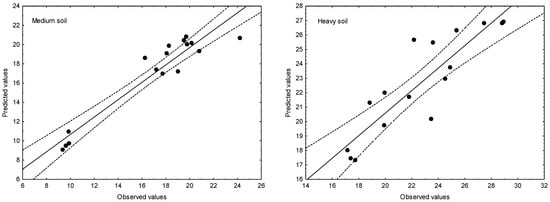
Figure 4.
Observed S-SO4 contents in medium and heavy soils versus predicted data generated using the developed simplified regression equations.
Heatmaps obtained for the four determined soil parameters (i.e., soil pH, dehydrogenase activity, S-SO4 and P contents) are presented in Figure 5 for medium and heavy soil separately. The colors reflect the values of soil parameters depending on the treatments, as well as the incubation time. In the case of medium soil, high pH values at the beginning of the experiment are clearly visible, corresponding to the high activity of dehydrogenase, which decreased over time similarly to the soil pH. The availability of S-SO4 was lowest at the beginning of the experiment, but gradually increased, reaching a maximum after 60 days of incubation. The amount of P was also low initially. P availability was the highest after 60 days of incubation, then slightly decreased. It can be clearly seen that the SII treatment increased the availability of S-SO4 in medium soil, especially on the 30th and 60th day of incubation. Initially, SI treatment caused the lowest P availability in the soil, and on the 60th day of incubation, the SIII treatment reduced its content the most. For heavy soil, changes in pH and dehydrogenase activity over time were quite similar to those for light soil, although the high pH lasted longer and dehydrogenase activity decreased more quickly. S-SO4 and P availability was the highest after 30 days of incubation. The high bioavailability of P was maintained for the next 30 days, but then (on the 90th day of incubation) it decreased significantly. On the other hand, the S-SO4 content, after a certain decrease observed on the 60th day of incubation, increased again on the 90th day. The SI, SII and SIII treatments caused the highest availability of S-SO4 on the 30th day of incubation, which was repeated for these treatments after 90 days. There were some differences between the treatments in terms of the availability of P in heavy soil, especially on day 0 of incubation, when slightly more of this element was present in the SI treatment, and the lowest P content was noted in the control after 90 days. After 60 and 90 days of incubation, the lowest dehydrogenase activity was observed for the SII treatment.
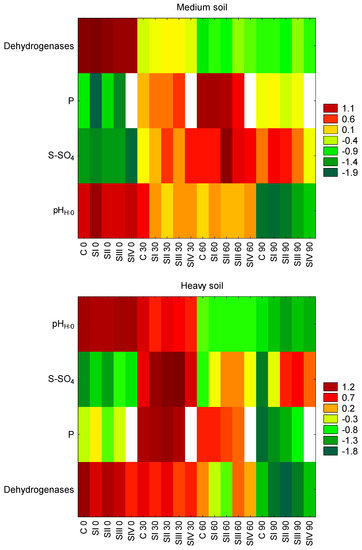
Figure 5.
Heatmaps of selected soil parameters (pHH2O, dehydrogenase activity, S-SO4 and P contents in medium and heavy soil. Blank—no data.
4. Conclusions
The tested fertilizer granules SII, SIII and SIV contained elemental sulfur in their composition, which is not directly available to plants. Two of them (SII, SIII) contained small amounts of phosphorus in the form of phosphate rock. The rate of change of the studied parameters depended on the granulometric composition of the tested soils. In general, the application of fertilizer granules had no statistically significant effect on the content of available phosphorus and the activity of dehydrogenase, and had a minor effect on the degree of acidity of the soils tested. There was a higher effect of applied fertilizer granules on the content of available sulfur in heavy soil than in medium soil. A little effect of introduced fertilizer granules on the tested soils properties could result from its low doses. It should be noted that transformation of materials introduced into soil depends on various factors, hence the possibility of unapparent results occurring.
In the analysis of research data, advanced statistical techniques were used to explore the hidden insights and better understand the relationships between the studied soil parameters and changes in their values as affected by the experimental factors. These types of statistical modules are useful for visualizing multidimensional data and showing the relationships between them, making complex data easier to understand. This allowed for a clear summary of the research results in this manuscript.
Together with the intensification of crop production, the demand for new fertilizers containing key nutrients is likely to increase. Therefore, understanding the effect of new products on soils characterized by different properties constitutes an important issue in terms of preserving their quality. New formulations of fertilizers are being developed in response to emerging environmental problems. However, while increasing the efficiency of crop production, caring for the environment and food safety should also constitute one of the key goals.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, A.L., B.F.-M. and A.K. (Andrzej Kalisz); methodology, A.L., B.F.-M., O.G., A.K. (Agnieszka Kowalczyk) and A.K. (Andrzej Kalisz); software, A.L., B.F.-M., A.K. (Andrzej Kalisz), O.G. and A.K. (Agnieszka Kowalczyk); validation, A.L., B.F.-M. and A.K. (Andrzej Kalisz); formal analysis, A.L., B.F.-M., A.K. (Andrzej Kalisz) and O.G.; investigation, A.L., B.F.-M., O.G. and A.K. (Andrzej Kalisz); resources, A.L., B.F.-M., A.K. (Agnieszka Kowalczyk) and O.G.; data curation, A.L., B.F.-M. and A.K. (Andrzej Kalisz); writing—original draft preparation, A.L., B.F.-M., A.K. (Andrzej Kalisz), A.K. (Agnieszka Kowalczyk) and O.G.; writing—review and editing, A.L., B.F.-M., A.K. (Andrzej Kalisz) and O.G.; visualization, A.L., B.F.-M. and A.K. (Andrzej Kalisz); supervision, A.L., B.F.-M. and A.K. (Andrzej Kalisz); project administration, A.L., B.F.-M., A.K. (Andrzej Kalisz), O.G. and A.K. (Agnieszka Kowalczyk); funding acquisition, A.L., B.F.-M., A.K. (Agnieszka Kowalczyk) and O.G. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This publication was financed by a subsidy granted to the University of Agriculture in Krakow by the Ministry of Science and Education of the Republic of Poland and the Institute of Technology and Life Sciences, National Research Institute.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Prasad, R. Major sulphur compounds in plants and their role in human nutrition and health—An overview. Proc. Indian Natl. Sci. Acad. 2014, 80, 1045–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crespo, C.; Wyngaard, N.; Sainz Rozas, H.; Barbagelata, P.; Barraco, M.; Gudelj, V.; Barbieri, P. Improving soil organic nitrogen and sulfur pools by cover cropping and crop fertilization in soybean-based cropping systems. Soil Tillage Res. 2021, 213, 105138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santana, M.M.; Dias, T.; Gonzalez, J.M.; Cruz, C. Transformation of organic and inorganic sulfur—Adding perspectives to new players in soil and rhizosphere. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2021, 160, 108306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lal, R. Restoring soil quality to mitigate soil degradation. Sustainability 2015, 7, 5875–5895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuentes-Lara, L.O.; Medrano-Macías, J.; Pérez-Labrada, F.; Rivas-Martínez, E.N.; García-Enciso, E.L.; González-Morales, S.; Juárez-Maldonado, A.; Rincón-Sánchez, F.; Benavides-Mendoza, A. From elemental sulfur to hydrogen sulfide in agricultural soils and plants. Molecules 2019, 24, 2282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baikhamurova, M.O.; Sainova, G.A.; Akbasova, A.D.; Anarbekova, G.D.; Ozler, M.A. The influence of the mixture of vermicompost and sulphur-perlite-containing waste on the yield and the quality of crops. J. Water Land Dev. 2021, 49, 213–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulczycki, G. The effect of elemental sulfur fertilization on plant yields and soil properties. Adv. Agron. 2021, 167, 105–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcinkowska, M.A.; Jeleń, H.H. Role of sulfur compounds in vegetable and mushroom aroma. Molecules 2022, 27, 6116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olson, R. Is Sulphur the Missing Ingredient? TSI Review. The Sulphur Institute. 2021. Available online: https://www.sulphurinstitute.org/pub/?id=BE62AA02-1866-DAAC-99FB-4AE5712BF1C7 (accessed on 18 February 2023).
- Liana, E.; Kolanek, A.; Pobudejski, M.; Miszuk, B.; Rawa, W. Monitoring Chemizmu Opadów Atmosferycznych i Ocena Depozycji Zanieczyszczeń do Podłoża w Latach 2021–2022; Raport Roczny z Badań Monitoringowych; IMGW-PIB: Warszawa, Poland, 2022; p. 493. [Google Scholar]
- National Atmospheric Deposition Program. National Atmospheric Deposition Program, 2021 Annual Summary; Wisconsin State Laboratory of Hygiene, University of Wisconsin-Madison: Madison, WI, USA, 2021; p. 28. Available online: https://nadp.slh.wisc.edu/wp-content/uploads/2022/11/2021as.pdf (accessed on 18 February 2023).
- Zhao, F.J.; McGrath, S.P.; Blake-Kalff, M.M.A.; Link, A.; Tucker, M. Crop Responses to Sulphur Fertilisation in Europe; International Fertiliser Society: Colchester, UK, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Engardt, M.; Simpson, D.; Schwikowski, M.; Granat, L. Deposition of sulphur and nitrogen in Europe 1900-2050. Model calculations and comparison to historical observations. Tellus B Chem. Phys. Meteorol. 2017, 69, 1328945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Sarkar, D.; Mehjabeen; Bhudevi, M.; Rakesh, S.; Singh, R.K.; Kar, S.; Rakshit, A. Advanced forms of sulphur formulations for improving use efficiency in crop species. Annu. Res. Rev. Biol. 2018, 27, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinckley, E.L.S.; Crawford, J.T.; Fakhraei, H.; Driscoll, C.T. A shift in sulfur-cycle manipulation from atmospheric emissions to agricultural additions. Nat. Geosci. 2020, 13, 597–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Sulphur Institute. Learn More About Sulphur. 2023. Available online: https://go.nature.com/32OHX87 (accessed on 18 February 2023).
- Johnston, F.; McAmish, L. A study of the rates of sulfur production in acid thiosulfate solutions using S-35. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1973, 42, 112–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Degryse, F.; Ajiboye, B.; Baird, R.; da Silva, R.C.; McLaughlin, M.J. Oxidation of elemental sulfur in granular fertilizers depends on the soil-exposed surface area. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2016, 80, 294–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Analiza Chemiczno-Rolnicza Gleby—Pobieranie Próbek. Opracowana na Podstawie PN-R-04031:1997. Available online: http://oschr-bydgoszcz.pl/Dokumenty/Instrukcja%20pobierania%20probek%20glebowych.pdf (accessed on 16 February 2023).
- Kabata-Pendias, A.; Piotrowska, M.; Motowicka-Terelak, T.; Maliszewska-Kordybach, B.; Filipiak, K.; Krakowiak, A.; Pietruch, C. Podstawy Oceny Chemicznego Zanieczyszczenia Gleb. Metale Ciężkie, Siarka i WWA. Biblioteka Monitoringu Środowiska; PIOŚ, IUNG: Warszawa, Poland, 1995; p. 41. [Google Scholar]
- Ostrowska, A.; Gawliński, S.; Szczubiałka, Z. Metody Analizy i Oceny Właściwości Gleb i Roślin: Katalog; Instytut Ochrony Środowiska: Warszawa, Poland, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Mehlich, A. Mehlich 3 soil test extractant: A modification of Mehlich 2 extractant. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 1984, 15, 1409–1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thalmann, A. Methods of dehydrogenase activity determination with triphenyltetrazoliumchlorid (TTC). Landwirtsch. Forsch. 1968, 21, 249–258. [Google Scholar]
- Warzyński, H.; Sosnowska, A.; Harasimiuk, A. Effect of variable content of organic matter and carbonates on results of determination of granulometric composition by means of Casagrande’s areometric method in modification by Prószyński. Soil Sci. Annu. 2018, 69, 39–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Operating Instructions Vario MAX Cube Analyzer. Elementar Analysensysteme GmbH; Version 12.11.2013; Mechanical Engineer: Langenselbold, Germany, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Karimizarchi, M.; Aminuddin, H.; Khanif, M.Y.; Radziah, O. Effect of elemental sulphur timing and application rates on soil P release and concentration in maize. Pertanika J. Trop. Agric. Sci. 2016, 39, 235–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaggi, R.C.; Aulakh, M.S.; Sharma, A.R. Impacts of elemental S applied under various temperature and moisture regimes on pH and available P in acidic, neutral and alkaline soils. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2005, 41, 52–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, R.; Wright, A.L.; McCray, J.M. Seasonal changes in nutrient availability for sulfur-amended everglades soils under sugarcane. J. Plant Nutr. 2011, 34, 2095–2113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deubel, A.; Braune, H.; Tanneberg, H.; Merbach, W. Conversion and acidifying effect of elemental sulphur in an alkaline loess soil. Arch. Agron. Soil Sci. 2007, 53, 161–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Modaihsh, A.S.; Al-Mustafa, W.A.; Metwally, A.I. Effect of elemental sulphur on chemical changes and nutrient availability in calcareous soils. Plant Soil 1989, 116, 95–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aulakh, M.S.; Jaggi, R.C.; Sharma, R. Mineralization-immobilization of soil organic S and oxidation of elemental S in subtropical soils under flooded and nonflooded conditions. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2002, 35, 197–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, G.; Schoenau, J.J.; Yamamoto, T.; Inoue, M. A model of oxidation of an elemental sulfur fertilizer in soil. Soil Sci. 2001, 166, 607–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Degryse, F.; da Silva, R.C.; Baird, R.; Beyrer, T.; Below, F.; McLaughlin, M.J. Uptake of elemental or sulfate-S from fall- or spring-applied co-granulated fertilizer by corn—A stable isotope and modeling study. Field Crops Res. 2018, 221, 322–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, K.M.; Khan, K.S.; Billah, M.; Akhtar, M.S.; Rukh, S.; Alam, S.; Munir, A.; Mahmood Aulakh, A.; Rahim, M.; Qaisrani, M.M.; et al. Organic amendments and elemental sulfur stimulate microbial biomass and sulfur oxidation in alkaline subtropical soils. Agronomy 2021, 11, 2514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaggi, A.C.; Aulakh, M.S.; Sharma, R. Temperature effects on soil organic sulphur mineralization and elemental sulphur oxidation in subtropical soils of varying pH. Nutr. Cycl. Agroecosyst. 1999, 54, 175–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kertesz, M.A.; Mirleau, P. The role of soil microbes in plant sulphur nutrition. J. Exp. Bot. 2004, 55, 1939–1945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawrence, J.R.; Germida, J.J. Relationship between microbial biomass and elemental sulfur oxidation in agricultural soils. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1988, 52, 672–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabak, M.; Lisowska, A.; Filipek-Mazur, B. Bioavailability of sulfur from waste obtained during biogas desulfurization and the effect of sulfur on soil acidity and biological activity. Processes 2020, 8, 863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucheta, A.R.; Lambais, M.R. Sulfur in agriculture. Rev. Bras. Ciênc. Solo 2012, 36, 1369–1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fawzi, M.A. Rate of elemental sulfur oxidation in some soils of Egypt as affected by the salinity level, moisture, texture, temperature and inoculation. Beitr. Trop. Landwirtsch. Veterinarmed. 1976, 14, 179–185. [Google Scholar]
- Germida, J.J.; Janzen, H.H. Factors affecting the oxidation of elemental sulfur in soils. Fertil. Res. 1993, 35, 101–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harahuc, L.; Lizama, H.M.; Suzuki, I. Selective inhibition of the oxidation of ferrous iron or sulfur in Thiobacillus ferrooxidans. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2000, 66, 1031–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lettl, A.; Langkramer, O.; Lochman, V. Some factors influencing production of sulphate by oxidation of elemental sulphur and thiosulphate in upper horizons of spruce forest soils. Folia Microbiol. 1981, 26, 158–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.D.; Akmal, M.; Khan, M.A. Effect of phosphorus and sulphur application on soil nutrient balance under chickpea (Cicer arietinum) monocropping. Rom. Agric. Res. 2013, 30, 223–232. [Google Scholar]
- Pasricha, N.S.; Baddesha, H.S.; Aulakh, M.S.; Nayyar, V.K. The zinc quantity-intensity relationships in four different soils as influenced by phosphorus. Soil Sci. 1987, 143, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fageria, N.K.; Baligar, V.C. Ameliorating soil acidity of tropical oxisols by liming for sustainable crop production. Adv. Agron. 2008, 99, 345–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelazeem, S.A.E.M.; Al-Werwary, S.M.; Mehana, T.A.E.; El-Hamahmy, M.A.; Kalaji, H.M.; Rastogi, A.; Elsheery, N.I. Use of plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria isolates as a potential biofertiliser for wheat. J. Water Land Dev. 2022, 99–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vig, A.C.; Bahl, G.S.; Chand, M. Phosphorus—Its transformation and management under rice-wheat system. Fert. News 1999, 44, 33–46. [Google Scholar]
- Lisowska, A.; Filipek-Mazur, B.; Komorowska, M.; Niemiec, M.; Bar-Michalczyk, D.; Kuboń, M.; Tabor, S.; Gródek-Szostak, Z.; Szeląg-Sikora, A.; Sikora, J.; et al. Environmental and production aspects of using fertilizers based on waste elemental sulfur and organic materials. Materials 2022, 15, 3387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mierzwa-Hersztek, M.; Wolny-Koładka, K.; Gondek, K.; Gałązka, A.; Gawryjołek, K. Effect of coapplication of biochar and nutrients on microbiocenotic composition, dehydrogenase activity index and chemical properties of sandy soil. Waste Biomass Valor. 2020, 11, 3911–3923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammerschmiedt, T.; Holatko, J.; Huska, D.; Kintl, A.; Skarpa, P.; Bytesnikova, Z.; Pekarkova, J.; Kucerik, J.; Mustafa, A.; Radziemska, M.; et al. Impact of smart combinations of graphene oxide and micro/nanosized sulfur particles on soil health and plant biomass accumulation. Chem. Biol. Technol. Agric. 2022, 9, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filipek-Mazur, B.; Gorczyca, O.; Tabak, M. The effect of sulphur-containing fertilizers on soil biological properties. Water Environ. Rural Areas 2017, 17, 69–81. [Google Scholar]
- Gupta, V.V.S.R.; Lawrence, J.R.; Germida, J.J. Impact of elemental sulfur fertilization on agricultural soils. I. Effects on microbial biomass and enzyme activities. Can. J. Soil Sci. 1988, 68, 463–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooper, J.M.; Warman, P.R. Effects of three fertility amendments on soil dehydrogenase activity, organic C and pH. Can. J. Soil Sci. 1997, 77, 281–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bielińska, E.J.; Futa, B.; Mocek-Płóciniak, A. Soil Enzymes as Bio-Indicators of Soil Health and Quality; Towarzystwo Wydawnictw Naukowych Libropolis: Lublin, Poland, 2014; p. 107. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, B.; Adachi, Y.; Sugiyama, S. Soil productivity and structure of bacterial and fungal communities in unfertilized arable soil. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0204085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mocek-Płóciniak, A. Utilisation of enzymatic activity for the evaluation of the impact of anthropogenic changes caused by heavy metals in soil environment. Nauka Przyr. Technol. Uniw. Przyr. W Pozn. 2010, 4, 86. [Google Scholar]
- Frankenberger, W.T.; Dick, W.A. Relationships between enzyme activities and microbial growth and activity indices in soil. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1983, 47, 945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goyal, S.; Mishra, M.M.; Dhankar, S.S.; Kapoor, K.K.; Batra, R. Microbial biomass turnover and enzyme activities following the application of farmyard manure to field soils with and without previous long-term applications. Biol. Fertil. Soils 1993, 15, 60–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jośko, I.; Oleszczuk, P.; Futa., B. The efect of inorganic nanoparticles (ZnO, Cr2O3, CuO and Ni) and their bulk counterparts on enzyme activities in diferent soils. Geoderma 2014, 232, 528–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Różyło, K.; Bohacz, J. Microbial and enzyme analysis of soil after the agricultural utilization of biogas digestate and mineral mining waste. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 17, 1051–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brzezińska, M.; Stępniewska, Z.; Stępniewski, W. Soil oxygen status and dehydrogenase activity. Soil Biol. Biochem. 1998, 30, 1783–1790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ros, M. Soil microbial activity after restoration of a semiarid soil by organic amendments. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2003, 35, 463–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ross, D.J. Some factors influencing the estimation of dehydrogenase activities of some soils under pasture. Soil Biol. Biochem. 1971, 3, 97–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcıa-Gil, J.C.; Plaza, C.; Soler-Rovira, P.; Polo, A. Long-term effects of municipal solid waste compost application on soil enzyme activities and microbial biomass. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2000, 32, 1907–1913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).