Amino Acids Content in Brassica napus L. and × Triticosecale Wittm. ex A. Camus on Soil Contaminated with Fluorine
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Growth Experiment
2.2. Analytical Methods
2.3. Statistical Analysis
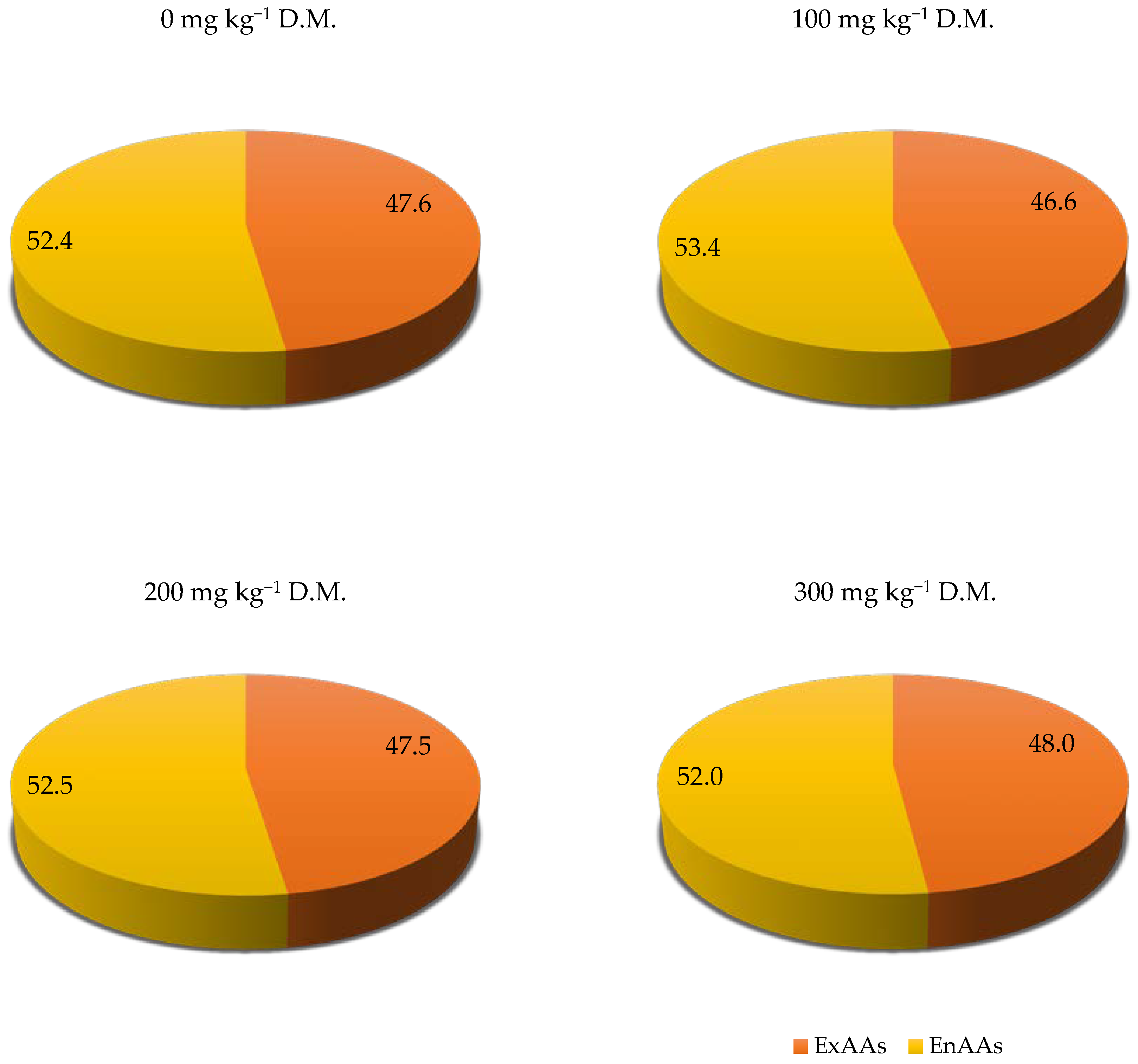
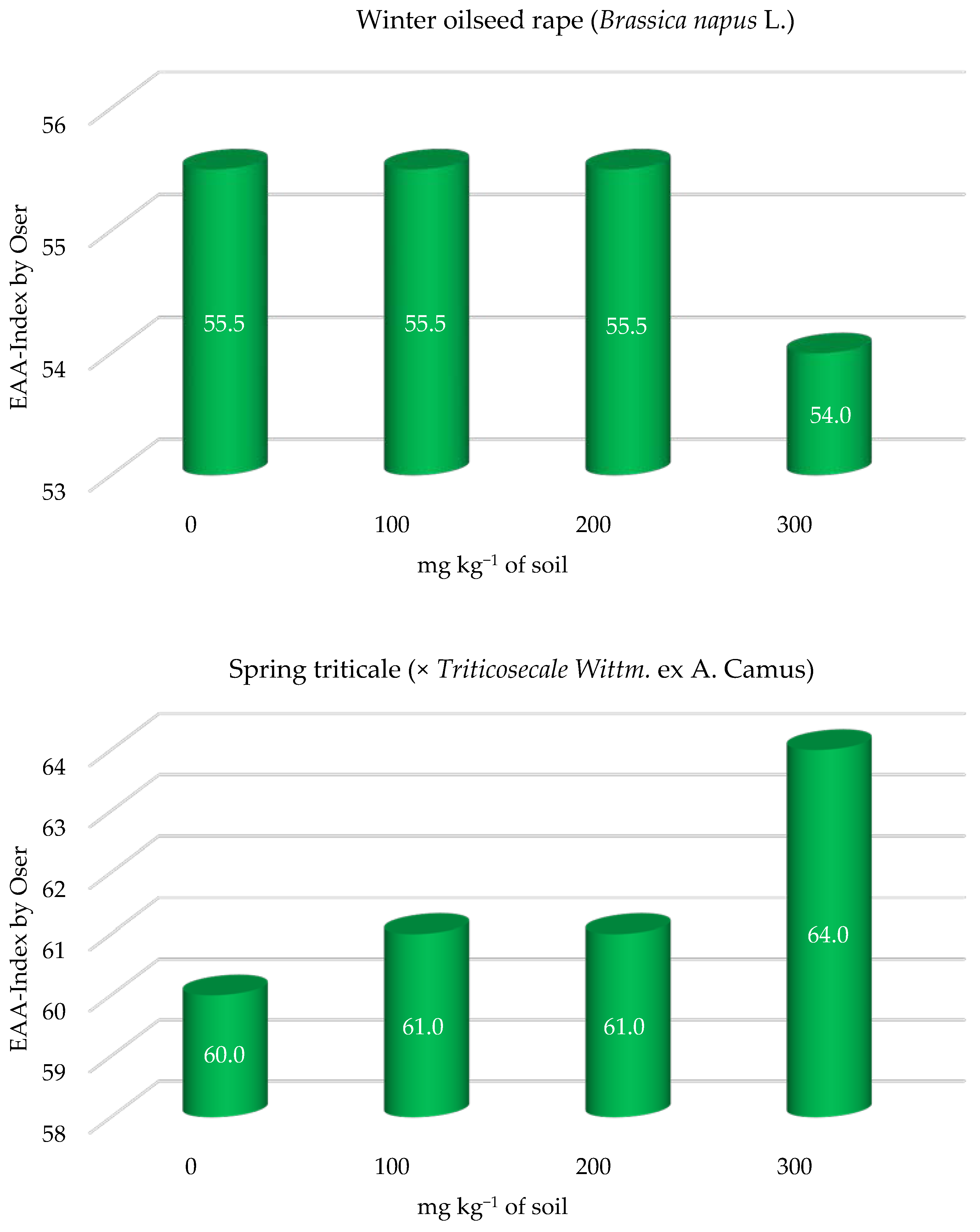
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kumar, R.; Sinha, R.; Sharma, P.K.; Ivy, N.; Kumar, P.; Kant, N.; Jha, A.; Jha, P.K.; Gupta, P.K.; Sharma, P.; et al. Bioaccumulation of fluoride in plants and its microbially assisted remediation: A review of biological processes and technological performance. Processes 2021, 9, 2154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, M.; Singh, G.; Jadeja, R. Fluoride contamination in groundwater, impacts, and their potential remediation techniques. In Groundwater Geochemistry: Pollution and Remediation Methods; John Wiley & Sons Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2021; pp. 22–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vithanage, M.; Rajapaksha, A.U.; Bootharaju, M.S.; Pradeep, T. Surface complexation of fluoride at the activated nano-gibbsite water interface. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2014, 462, 124–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarosz, Z.; Pitura, K. Fluoride toxicity limit—Can the element exert a positive effect on plants? Sustainability 2021, 13, 12065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Zhang, J.; Du, C.; Yang, H.; Ye, B.-C. Distribution and pollution evaluation of fluoride in a soil–water–plant system in Shihezi, Xinjiang, China. Hum. Ecol. Risk Assess. Int. J. 2018, 24, 445–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahab, S.; Mustafa, G.; Khan, I.; Zahid, M.; Yasinzai, M.; Ameer, N.; Asghar, N.; Ullah, I.; Nadhman, A.; Ahmed, A.; et al. Effects of Fluoride Ion Toxicity on Animals, Plants, and Soil Health: A Review. Fluoride 2017, 50, 393–408. Available online: https://www.fluorideresearch.org/504/files/FJ2017_v50_n4_p393-408_sfs.pdf (accessed on 12 December 2022).
- Dehbandi, R.; Moore, F.; Keshavarzi, B.; Abbasnejad, A. Fluoride hydrogeochemistry and bioavailability in groundwater and soil of an endemic fluorosis belt, central Iran. Environ. Earth. Sci. 2017, 76, 177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camargo, J.A. Fluoride toxicity to aquatic organisms: A review. Chemosphere 2003, 50, 251–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.; Zhang, J.; Dong, T. Removal of fluoride from contaminated field soil by anolyte enhanced electrokinetic remediation. Environ. Earth Sci. 2009, 59, 379–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ochoa-Herrera, V.; Banihani, Q.; Leon, G.; Khatri, C.; Fidel, A.J.; Sierra-Alvarez, R. Toxicity of fluoride to microorganisms in biological wastewater treatment systems. Water Res. 2009, 43, 3177–3186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozsvath, L.D. Fluoride and environmental health: A review. Rev. Environ. Sci. Biotechnol. 2009, 8, 59–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cape, N.J.; Fowler, D.; Davison, A. Ecological effects of sulfur dioxide, fluorides and minor air pollutants: Recent trends and research needs. Environ. Int. 2003, 29, 201–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, T.; Ujihara, K.; Matsumoto, O.; Yanagi, K.; Matsuo, N. Synthetic studies of fluorine containing compounds for household insecticides. J. Fluor. Chem. 2007, 128, 1174–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okibe, F.G.; Ekanem, E.J.; Paul, E.D.; Shallangwa, G.A.; Ekwumemgbo, P.A.; Sallau, M.S.; Abanka, O.C. Fluoride content of soil land vegetables from irrigation farms on the bank of river Galma, Zaria, Nigeria. Aust. J. Basic Appl. Sci. 2010, 4, 779–784. [Google Scholar]
- WHO. Fluorides. Environmental Health Criteria; World Health Organisation: Geneva, Switzerland, 2002; Volume 227, p. 268. Available online: https://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/handle/10665/42415/WHO_EHC_227.pdf (accessed on 18 January 2023).
- Malago, J.; Makoba, E.; Muzuka, A.N. Fluoride levels in surface and groundwater in Africa: A review. Am. J. Water Sci. Eng. 2017, 3, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranjith, M.; Sridevi, S.; Jeevanrao, K.; Ramesh, T. Fluoride contamination in the irrigation water, soil and crops of the Rangareddy District of Telangana State, India. Fluoride 2022, 55, 63–80. Available online: https://www.fluorideresearch.online/epub/files/144.pdf (accessed on 16 January 2023).
- Narsimha, A.; Sudarshan, V. Contamination of fluoride in groundwater and its effect on human health: A case study in hard rock aquifers of Siddipet, Telangana State, India. Appl. Water Sci. 2017, 7, 2501–2512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondal, D.; Gupta, S.; Reddy, D.; Nagabhushanam, P. Geochemical controls on fluoride concentrations in groundwater from alluvial aquifers of the Birbhum district, West Bengal, India. J. Geochem. Explor. 2014, 145, 190–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kłódka, D.; Musik, D.; Wójcik, K.; Telesiński, A. Fluorine content in selected vegetables grown within the area affected by emission of that element from the ‘Police’ Chemical Plant. Bromatol. Chem. Toksykol. 2008, 61, 964–969. [Google Scholar]
- Zakrzewska, H. Fluorine and its compounds in the natural environment and food. Bromatol. Chem. Toksykol. 1995, 4, 393–398. [Google Scholar]
- EFSA NDA Panel (EFSA Panel on Dietetic Products, Nutrition and Allergies). Scientific opinion on Dietary Reference Values for fluoride. EFSA J. 2013, 11, 3332–3378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smolik, B.; Telesiński, A.; Szymczak, J.; Zakrzewska, H. Assessing of humus usefulness in limiting of soluble fluoride content in soil. Environ. Prot. Nat. Resour. 2011, 49, 202–208. [Google Scholar]
- Bauthiyal, M.; Ranghar, S. Physiological and Biochemical Responses of Plants under Fluoride Stress: An Overview. Fluoride 2014, 47, 287–293. Available online: https://www.fluorideresearch.org/474/files/FJ2014_v47_n4_p287-293_sfs.pdf (accessed on 17 January 2023).
- Rizzu, M.; Tanda, A.; Canu, L.; Masawe, K.; Mtei, K.; Deroma, M.A.; Roggeroa, P.P.; Seddaiu, G. Fluoride uptake and translocation in food crops grown in fluoride-rich soils. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2020, 100, 5498–5509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mezghani, I.; Elloumi, N.; Abdallah, F.B.; Chaieb, M.; Boukhris, M. Fluoride Accumulation by Vegetation in the Vicinity of a Phosphatate Fertilizer Plant in Tunisia. Fluoride 2005, 38, 69–75. Available online: https://www.fluorideresearch.org/381/files/38169-75.pdf (accessed on 17 January 2023).
- Szostek, R.; Ciećko, Z.; Rolka, E.; Wyszkowski, M. Content of amino acids in maize and yellow lupine after fluorine application to soil. Agriculture 2021, 11, 1120–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szostek, R.; Ciećko, Z. Effect of soil contamination with fluorine on the yield and content of nitrogen forms in the biomass of crops. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 8588–8601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szostek, R.; Wyszkowski, M.; Ciećko, Z.; Rolka, E. Sodium and sulphur content in plants after lime, charcoal, and loam application to soil contaminated with fluorine. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakrabarti, S.; Patra, K.P. Biochemical and Antioxidant Responses of Paddy (Oryza sativa L.) to Fluoride Stress. Fluoride 2015, 48, 56–61. Available online: https://www.fluorideresearch.org/481/files/FJ2015_v48_n1_p056-061_sfs.pdf (accessed on 7 January 2023).
- Hautala, E.L.; Holopainen, J.K. Gramine and free amino acids as indicators of fluoride-induced stress in barley and its consequences to insect herbivory. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 1995, 31, 238–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanson, A.D.; Nelson, C.E.; Everson, E.H. Evaluation of free proline accumulation as an index of drought resistance using, two contrasting barley cultivars. Crop Sci. 1977, 17, 720–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jędrusek-Golińska, A.; Korczak, J.; Gliszczyńska-Świgło, A.; Czaczyk, K.; Kmiecik, D. The protein concentrates from defatted rapeseed meal as a raw material for production of protein hydrolysates. Oilseed Crops 2005, 26, 249–259. [Google Scholar]
- Stankiewicz, C. Effect of the Sowing Density and Herbicides on the Composition of Amino Acids and Biological Value of Spring Triticale Protein. Acta Sci. Pol. Agri. 2005, 4, 127–139. Available online: http://old-agricultura.acta.utp.edu.pl/uploads/pliki/000010200500004000010012700139.pdf (accessed on 11 January 2023).
- Kabata-Pendias, A. Trace Elements in Soil and Plants, 4th ed.; CRS Press, Taylor and Francis Group: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2010; pp. 1–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oser, B.L. An Integrated Essential Amino Acid Index for Predicting Biological Value of Proteins; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1959; pp. 295–311. [Google Scholar]
- Research Procedure No. 29. Research Procedure; Chemical-Agricultural Station Instruction, II ed.; Chemical-Agricultural Station: Warsaw, Poland, 2008.
- Lityński, T.; Jurkowska, H.; Gorlach, E. Chemical and Agricultural Analysis; PWN Publishing House: Warsaw, Poland, 1976; pp. 129–132. [Google Scholar]
- Shimadzu. Shimadzu Analytical and Measuring Instruments; User’s Manual; Shimadzu Corporation: Kyoto, Japan, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- ISO 11261; Soil Quality—Determination of Total Nitrogen—Modified Kjeldahl Method. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 1995.
- Ostrowska, A.; Gawliński, S.; Szczubiałka, Z. Methods for Analysis and Evaluation of Soil and Plant Properties; Institute of Environmental Protection: Warsaw, Poland, 1991; pp. 1–334. [Google Scholar]
- Amino Acid Analyser AAA400, User Manual; Ingos S.R.O.: Prague, Czech Republic, 2007.
- Tibco Software Inc. Data Analysis Software System, Statistica Version 13.3; Tibco Software Inc.: Palo Alto, CA, USA, 2021. Available online: http://statistica.io (accessed on 23 December 2022).
- Ruan, J.; Ma, L.; Shi, Y.; Han, W. The impact of pH and calcium on the uptake of fluoride by tea plants (Camellia sinensis L.). Ann. Bot. 2004, 93, 97–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romar, A.; Gago, C.; Fernández-Marcos, L.M.; Álvarez, E. Influence of fluoride addition on the composition of solutions in Equilibrium with acid soils. Pedosphere 2009, 19, 60–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aslam, A.; Nawaz, H.; Khan, A.; Ghaffar, R.; Abbas, G. Effect of Exogenous Application of Citric Acid on Growth of Maize (Zea mays L.) under Sodium Fluoride Stress. Fluoride 2023, 1–29. Available online: https://www.fluorideresearch.online/epub/files/188.pdf (accessed on 10 November 2022).
- Karmakar, S.; Mukherjee, J.; Mukherjee, S. Removal of fluoride contamination in water by three aquatic plants. Int. J. Phytoremediat. 2016, 18, 222–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, C.K.; Mondal, K.N.; Bhaumik, R.; Banerjee, A.; Datta, K.J. Incorporation of Fluoride in Vegetation and Associated Biochemical Changes due to Fluoride Contamination in Water and Soil: A Comparative Field Study. Ann. Environ. Sci. 2012, 6, 123–139. Available online: https://openjournals.neu.edu/aes/journal/article/view/v6art7/v6p123-139 (accessed on 11 January 2023).
- Singh, U.P.; Rana Yashu, B.; Kumar, S.; Striastava, J.P. Biochemical responses of elevated level of fluoride in nutrient medium on wheat and barley. Int. J. Curr. Microbiol. Appl. Sci. 2020, 9, 3116–3123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eyini, M.; Sujanandini, K.; Pothiraj, C.; Jayakumar, M.; Kil, B.-S. Differental response of Azolla microphylla Kaulf. and Azolla filiculoides Lam. to sodium fluoride. J. Plant Biol. 1999, 42, 299–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.W. Effect of fluoride on ribosomes from corn roots. Changes with growth retardation. Physiol. Plant. 1970, 23, 536–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinha, S.; Saxena, R.; Singh, S. Fluoride removal from water by Hydrilla verticillata (I.f.) royle and its toxic effects. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2000, 65, 683–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, S.F.; Miller, G.W. Biochemical studies on the effect of fluoride on higher plants. 1. Metabolism of carbohydrates, organic acids and amino acids. Biochem. J. 1963, 88, 505–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, M.; Miller, G.W. Effect of fluoride on the respiration of leaves from higher plants. Plant Cell. Physiol. 1967, 8, 484–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.H.; Ni, D. Effect of Fluoride on the amino Acid Composition of tea Leaves. Fluoride 2016, 49, 274–278. Available online: https://fluorideresearch.org/493Pt1/files/FJ2016_v49_n3Pt1_p274-278_pq.pdf (accessed on 13 January 2023).
- Li, C.; Zheng, Y.; Zhou, J.; Xu, J.; Ni, D. Changes of leaf antioxidant system, photosynthesis and ultrastructure in tea plant under the stress of fluorine. Biol. Plantarum 2011, 55, 563–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maitra, A.; Datta, J.K.; Mondal, N.K. Amelioration of fluoride toxicity with the use of indigenous inputs. J. Stress Physiol. Biochem. 2013, 9, 207–219. [Google Scholar]
- Elloumi, N.; Ben Amor, A.; Zouari, M.; Belhaj, D.; Ben Abdallah, F.; Kallel, M. Adaptive Biochemical Responses of Punicagranatum to Atmospheric Fluoride Pollution. Fluoride 2016, 49, 357–365. Available online: https://www.fluorideresearch.org/493Pt2/files/FJ2016_v49_n3Pt2_p357-365_sfs.pdf (accessed on 9 January 2023).
- Elloumi, N.; Zouari, M.; Mezghani, I.; Abdallah, F.B.; Woodward, S.; Kallei, M. Adaptive biochemical and physiological responses of to fluoride air pollution. Ecotoxicology 2017, 26, 991–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mezghani, I.; Zouari, M.; Rouina, B.B.; Abdallah, F.B. Mulberry Leaves as a Bioindicator of Fluoride Pollution in the Vicinity of a Phosphate Fertilizer Factory Located in Sfax, Tunisia. Fluoride 2019, 52, 537–545. Available online: https://www.fluorideresearch.online/epub/files/051.pdf (accessed on 23 January 2023).
- Elloumi, N.; Zouari, M.; Chaari, L.; Abdallah, F.B.; Woodward, S.; Kallei, M. Effect of phosphogypsum on growth, physiology, and the antioxidative defense system in sunflower seedlings. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 22, 14829–14840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elloumi, N.; Belhaj, D.; Mseddi, S.; Zouari, M.; Abdallah, F.B.; Woodward, S.; Kallel, M. Response of Nerium oleander to phosphogypsum amendment and its potential use for phytoremediation. Ecol. Eng. 2017, 99, 164–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Datta, J.K.; Maitra, A.; Mondal, N.K.; Banerjee, A. Studies on the impact of fluoride toxicity on germination and seedling growth of gram seed (Cicer arietinum L. cv. Anuradha). J. Stress Physiol. Biochem. 2012, 8, 194–202. [Google Scholar]
- Gadi, B.R.; Verma, P.; Amra, R. Influence of NaF on seed germination, membrane stability and some biochemical content in Vigna seedlings. J. Chem. Biol. Phys. Sci. 2012, 2, 1371–1378. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmed, S.; Khalid, K.; Jabeen, F.; Ahmad, M.N.; Zia, A.; Haider, A.; Mujahid, M.; Zia, D.; Khan, N.P. The Effects of Fluoride Stress on Okra (Abelmoschus esculentus L.). Fluoride 2019, 52, 354–361. Available online: https://www.fluorideresearch.online/523Pt2/files/FJ2019_v52_n3Pt2_p354-361_sfs.pdf (accessed on 24 January 2023).
- Saleh, A.A.H.; Abdel-Kader, D.Z. Metabolic responses of two Helianthus annuus cultivars to different fluoride concentrations during germination and seedling growth stages. Egypt. J. Exp. Biol. 2003, 5, 43–54. [Google Scholar]
- Das, C.; Dey, U.; Chakraborty, D.; Datta, J.K.; Mondal, N.K. Fluoride Toxicity Effects in Potato Plant (Solanum tuberosum L.) Grown in Contaminated Soils. Octa J. Environ. Res. 2015, 3, 136–143. Available online: http://sciencebeingjournal.com/sites/default/files/03-150606_0302_NKM.pdf (accessed on 20 January 2023).
- Dey, U.; Mondal, N.K.; Das, K.; Datta, J.K. Dual Effect of Fluoride and Calcium on the Uptake of Fluoride, Growth Physiology, Pigmentation and Biochemistry of Bengal Gram Seedlings (Cicer arietinum L.). Fluoride 2012, 45, 389–393. Available online: https://www.fluorideresearch.org/454/files/FJ2012_v45_n4_p389-393_pq.pdf (accessed on 20 January 2023).
- Zouari, M.; Ahmed, C.B.; Elloumi, N.; Rouina, B.B.; Labrousse, P.; Abdallah, F.B. Effects of Irrigation Water Fluoride on Relative Water Content, Photosynthetic Activity, and Proline Accumulation in Young Olive Trees (Olea europaea L. cv. chemlali) in Arid Zones. Fluoride 2016, 49, 303–372. Available online: https://fluorideresearch.org/493Pt2/files/FJ2016_v49_n3Pt2_p366-372_pq.pdf (accessed on 13 January 2023).
- Cai, H.; Dong, Y.; Li, Y.; Li, D.; Peng, C.; Zhang, Z.; Wan, X. Physiological and cellular responses to fluoride stress in tea (Camellia sinensis) leaves. Acta Physiol. Plant. 2016, 38, 144–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szostek, R.; Ciećko, Z. Content of Fluorine in Biomass of Crops Depending on Soil Contamination by This Element. Fluoride 2014, 47, 294–306. Available online: https://www.fluorideresearch.org/474/files/FJ2014_v47_n4_p294-306_sfs.pdf (accessed on 23 March 2023).
- Dirwai, T.L.; Senzanje, A.; Mabhaudhi, T. Calibration and evaluation of the FAO AquaCrop Model for Canola (Brassica napus) under varied moistube irrigation regimes. Agriculture 2021, 11, 410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zając, T.; Klimek-Kopyra, A.; Oleksy, A.; Lorenc-Kozik, A.; Ratajczak, K. Analysis of yield and plant traits of oilseed rape (Brassica napus L.) cultivated in temperate region in light of the possibilities of sowing in arid areas. Acta Agrobot. 2016, 69, 1696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feledyn-Szewczyk, B.; Nakielska, M.; Jończyk, K.; Berbeć, A.K.; Kopiński, J. Assessment of the suitability of 10 winter triticale cultivars (x Triticosecale Wittm. ex A. Camus) for organic agriculture: Polish case study. Agronomy 2020, 10, 1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Parameter | % or Value per kg−1 Soil |
|---|---|
| Grain size | |
| <0.002 | 1.89% |
| 0.002–0.050 | 18.61% |
| >0.050 | 79.50% |
| Hydrolytic acidity | 30.7 mM(+) |
| pH in H2O | 5.89 |
| pH in KCl | 4.43 |
| Available forms: | - |
| P | 43.2 mg |
| K | 124.5 mg |
| Mg | 30.0 mg |
| Total organic carbon | 6.0 g |
| Total nitrogen | 0.62 g |
| Total fluorine | 125 mg |
| Parameter | Method/Apparatus | |
|---|---|---|
| Soil | ||
| Granulometric composition | laser diffraction [37] Mastersizer 2000 Hydro G dispersion apparatus (Malvern, UK) | |
| pH in H2O and 1 M KCl | potentiometric [38] | |
| Hydrolytic acidity (HAC) | Kappen [38] | |
| Total organic carbon (TOC) | automatic Shimadzu TOC-L CSH/CNS analyser (Shimadzu Corporation, Kyoto, Japan) with the solid sample module SSM-5000A (Shimadzu Corporation, Kyoto, Japan) [39] | |
| Total nitrogen | Kjeldahl [40] | |
| Available phosphorus and potassium | Egner-Riehm [41] | |
| Available magnesium | Shachtschabel [41] | |
| Total fluorine | X-ray fluorescence spectrometry (XRF) Philips WD-XRF PW 2004 apparatus (Philips Research Corporation, Eindhoven, The Netherlands) | |
| Plants | ||
| Amino acids | ion-exchange chromatography with post-column derivatization with ninhydrin [42] automatic amino acid AAA400 analyser (INGOS, Praha, Czech Republic) | |
| Nutritive value of protein | Oser Index [36] | |
| Amino Acids | Fluorine Dose in mg kg−1 of Soil | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 100 | 200 | 300 | r | 0 | 100 | 200 | 300 | r | |
| g kg−1 DM | g 100 g−1 TotProt (16 g N) | |||||||||
| ExAAs | ||||||||||
| Arg | 12.81 | 13.97 | 14.07 | 13.71 | 0.63 * | 4.52 | 4.89 | 4.97 | 4.87 | 0.73 ** |
| Phe | 9.51 | 9.48 | 9.45 | 9.43 | −1.00 ** | 3.36 | 3.32 | 3.34 | 3.35 | −0.08 |
| His | 5.97 | 5.79 | 5.75 | 5.71 | −0.92 ** | 2.11 | 2.03 | 2.03 | 2.03 | −0.77 ** |
| Ile | 7.49 | 7.71 | 7.78 | 7.88 | 0.97 ** | 2.65 | 2.70 | 2.75 | 2.80 | 1.00 ** |
| Leu | 15.33 | 15.50 | 15.61 | 16.36 | 0.91 ** | 5.41 | 5.43 | 5.51 | 5.82 | 0.89 ** |
| Lys | 11.00 | 11.96 | 12.08 | 12.17 | 0.86 ** | 3.89 | 4.19 | 4.27 | 4.33 | 0.93 ** |
| Met | 1.30 | 1.20 | 1.17 | 0.97 | −0.95 ** | 0.46 | 0.42 | 0.41 | 0.34 | −0.96 ** |
| Thr | 10.03 | 9.99 | 9.71 | 9.66 | −0.95 ** | 3.54 | 3.50 | 3.43 | 3.43 | −0.95 ** |
| Tyr | 9.73 | 8.94 | 8.10 | 8.09 | −0.95 ** | 3.44 | 3.13 | 2.86 | 2.88 | −0.93 ** |
| Val | 11.13 | 11.49 | 11.53 | 11.58 | 0.88 ** | 3.93 | 4.02 | 4.07 | 4.12 | 0.99 ** |
| ExAAs sum | 94.30 | 96.03 | 95.25 | 95.56 | −0.53 | 33.31 | 33.62 | 33.64 | 33.98 | 0.96 ** |
| LSD0.01 | n.s. | n.s. | ||||||||
| EnAAs | ||||||||||
| Ala | 12.26 | 12.94 | 12.97 | 13.19 | 0.90 ** | 4.33 | 4.53 | 4.58 | 4.69 | 0.97 ** |
| Cys | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.00 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | 0.00 |
| Gly | 10.26 | 10.25 | 10.38 | 10.96 | 0.85 ** | 3.62 | 3.59 | 3.67 | 3.90 | 0.84 ** |
| Asp | 20.16 | 19.86 | 18.62 | 18.45 | −0.95 ** | 7.12 | 6.95 | 6.58 | 6.56 | −0.95 ** |
| Glu | 24.46 | 25.29 | 25.56 | 26.18 | 0.98 ** | 8.64 | 8.85 | 9.03 | 9.31 | 1.00 ** |
| Pro | 27.63 | 32.96 | 28.87 | 26.14 | −0.38 | 9.76 | 11.54 | 10.20 | 9.29 | −0.37 |
| Ser | 8.87 | 8.84 | 8.78 | 8.64 | −0.95 ** | 3.13 | 3.09 | 3.10 | 3.07 | −0.88 ** |
| EnAAs sum | 103.65 | 110.15 | 105.19 | 103.57 | 0.22 | 36.61 | 38.56 | 37.15 | 36.82 | −0.11 |
| LSD0.01 | n.s. | n.s. | ||||||||
| TotAAs sum | 197.95 | 206.18 | 200.44 | 199.13 | 0.08 | 69.92 | 72.19 | 70.80 | 70.80 | 0.17 |
| LSD0.01 | n.s. | n.s. | ||||||||
| Amino Acids | Fluorine Dose in mg kg−1 of Soil | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 100 | 200 | 300 | r | 0 | 100 | 200 | 300 | r | |
| g kg−1 DM | g 100 g−1 TotProt (16 g N) | |||||||||
| ExAAs | ||||||||||
| Arg | 6.40 | 7.49 | 8.04 | 8.53 | 0.98 ** | 5.36 | 5.52 | 5.74 | 5.91 | 1.00 ** |
| Phe | 4.78 | 5.83 | 6.39 | 7.02 | 0.99 ** | 4.00 | 4.30 | 4.56 | 4.86 | 1.00 ** |
| His | 2.64 | 3.25 | 3.46 | 3.70 | 0.96 ** | 2.21 | 2.40 | 2.47 | 2.56 | 0.97 ** |
| Ile | 3.49 | 3.70 | 4.22 | 4.46 | 0.99 ** | 2.92 | 2.73 | 3.01 | 3.09 | 0.66 * |
| Leu | 7.16 | 8.14 | 9.16 | 9.88 | 1.00 ** | 6.00 | 6.00 | 6.54 | 6.84 | 0.95 ** |
| Lys | 3.93 | 4.41 | 4.56 | 4.90 | 0.98 ** | 3.29 | 3.25 | 3.26 | 3.39 | 0.63 * |
| Met | 1.65 | 1.54 | 1.42 | 1.30 | −1.00 ** | 1.38 | 1.14 | 1.01 | 0.90 | −0.98 ** |
| Thr | 3.67 | 3.98 | 4.19 | 5.07 | 0.95 ** | 3.07 | 2.93 | 2.99 | 3.51 | 0.68 * |
| Tyr | 2.55 | 3.01 | 3.23 | 3.59 | 0.99 ** | 2.14 | 2.22 | 2.31 | 2.49 | 0.98 ** |
| Val | 4.93 | 7.54 | 6.80 | 6.70 | 0.53 | 4.13 | 5.56 | 4.86 | 4.64 | 0.18 |
| ExAAs sum | 41.20 | 48.89 | 51.47 | 55.15 | 0.97 ** | 34.51 | 36.05 | 36.76 | 38.20 | 0.99 ** |
| LSD0.01 | 6.78 | n.s. | ||||||||
| EnAAs | ||||||||||
| Ala | 4.34 | 4.81 | 5.17 | 5.50 | 1.00 ** | 3.64 | 3.55 | 3.69 | 3.81 | 0.77 ** |
| Cys | 0.71 | 0.90 | 1.00 | 0.79 | 0.35 | 0.60 | 0.66 | 0.71 | 0.55 | −0.19 |
| Gly | 4.67 | 5.31 | 5.70 | 6.32 | 1.00 ** | 3.91 | 3.92 | 4.07 | 4.38 | 0.92 ** |
| Asp | 6.41 | 7.52 | 8.10 | 8.89 | 0.99 ** | 5.37 | 5.54 | 5.79 | 6.16 | 0.99 ** |
| Glu | 25.43 | 30.08 | 39.03 | 44.83 | 0.99 ** | 21.30 | 22.18 | 27.88 | 31.05 | 0.97 ** |
| Pro | 13.84 | 16.64 | 19.02 | 21.75 | 1.00 ** | 11.59 | 12.27 | 13.59 | 15.06 | 0.99 ** |
| Ser | 5.36 | 6.36 | 6.92 | 7.28 | 0.97 ** | 4.49 | 4.69 | 4.94 | 5.04 | 0.99 ** |
| EnAAs sum | 60.76 | 71.62 | 84.94 | 95.36 | 1.00 ** | 50.90 | 52.81 | 60.67 | 66.05 | 0.98 ** |
| LSD0.01 | 10.86 | 7.94 | ||||||||
| TotAAs sum | 101.96 | 120.51 | 136.41 | 150.51 | 1.00 ** | 85.41 | 88.86 | 97.44 | 104.25 | 0.99 ** |
| LSD0.01 | 17.63 | 12.92 | ||||||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Szostek, R.; Wyszkowski, M.; Ciećko, Z. Amino Acids Content in Brassica napus L. and × Triticosecale Wittm. ex A. Camus on Soil Contaminated with Fluorine. Agronomy 2023, 13, 1038. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy13041038
Szostek R, Wyszkowski M, Ciećko Z. Amino Acids Content in Brassica napus L. and × Triticosecale Wittm. ex A. Camus on Soil Contaminated with Fluorine. Agronomy. 2023; 13(4):1038. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy13041038
Chicago/Turabian StyleSzostek, Radosław, Mirosław Wyszkowski, and Zdzisław Ciećko. 2023. "Amino Acids Content in Brassica napus L. and × Triticosecale Wittm. ex A. Camus on Soil Contaminated with Fluorine" Agronomy 13, no. 4: 1038. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy13041038
APA StyleSzostek, R., Wyszkowski, M., & Ciećko, Z. (2023). Amino Acids Content in Brassica napus L. and × Triticosecale Wittm. ex A. Camus on Soil Contaminated with Fluorine. Agronomy, 13(4), 1038. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy13041038





