Zeolite as a Tool to Recycle Nitrogen and Phosphorus in Paddy Fields under Straw Returning Conditions
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
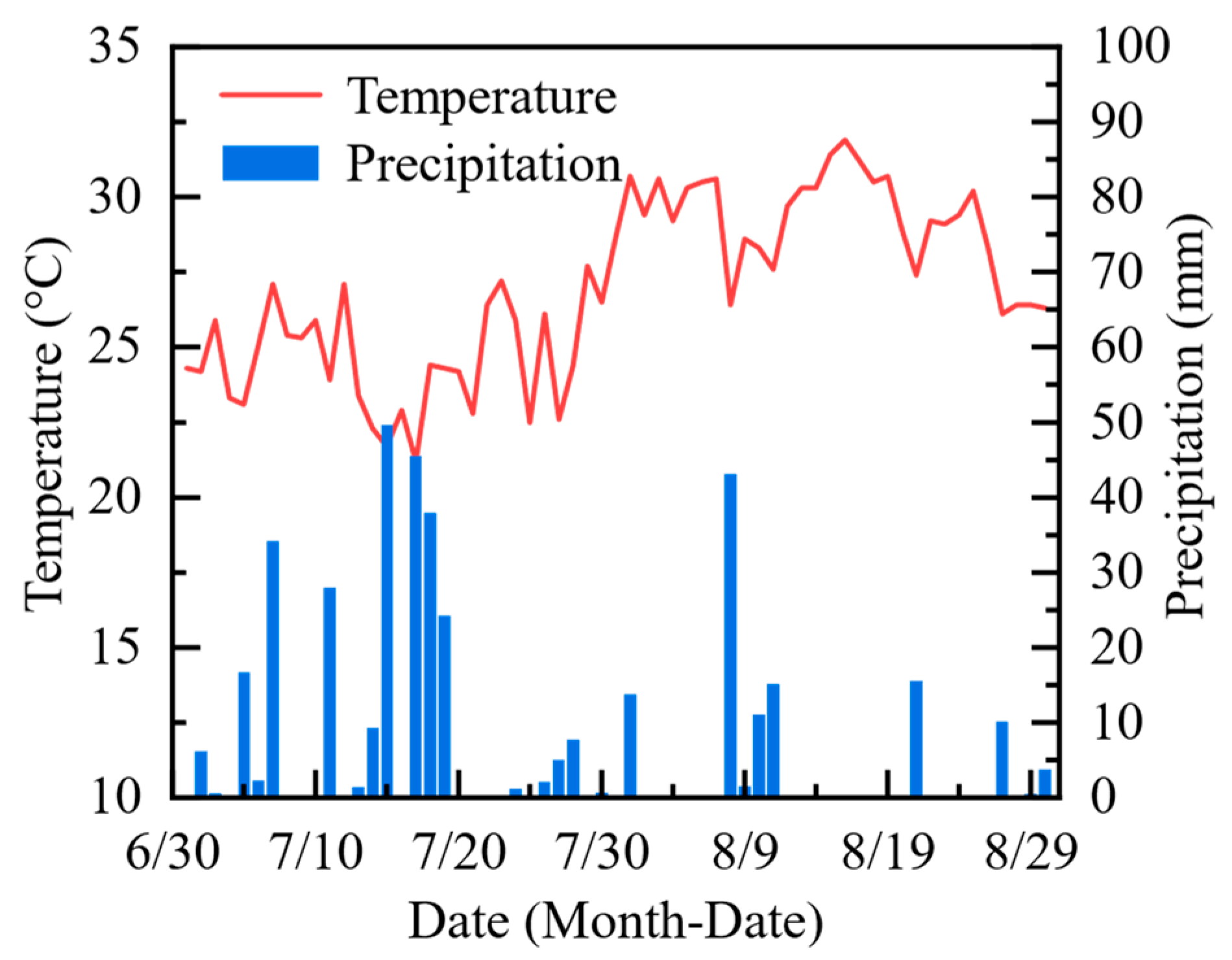
2.1. Site Description
2.2. Experimental Design and Sampling
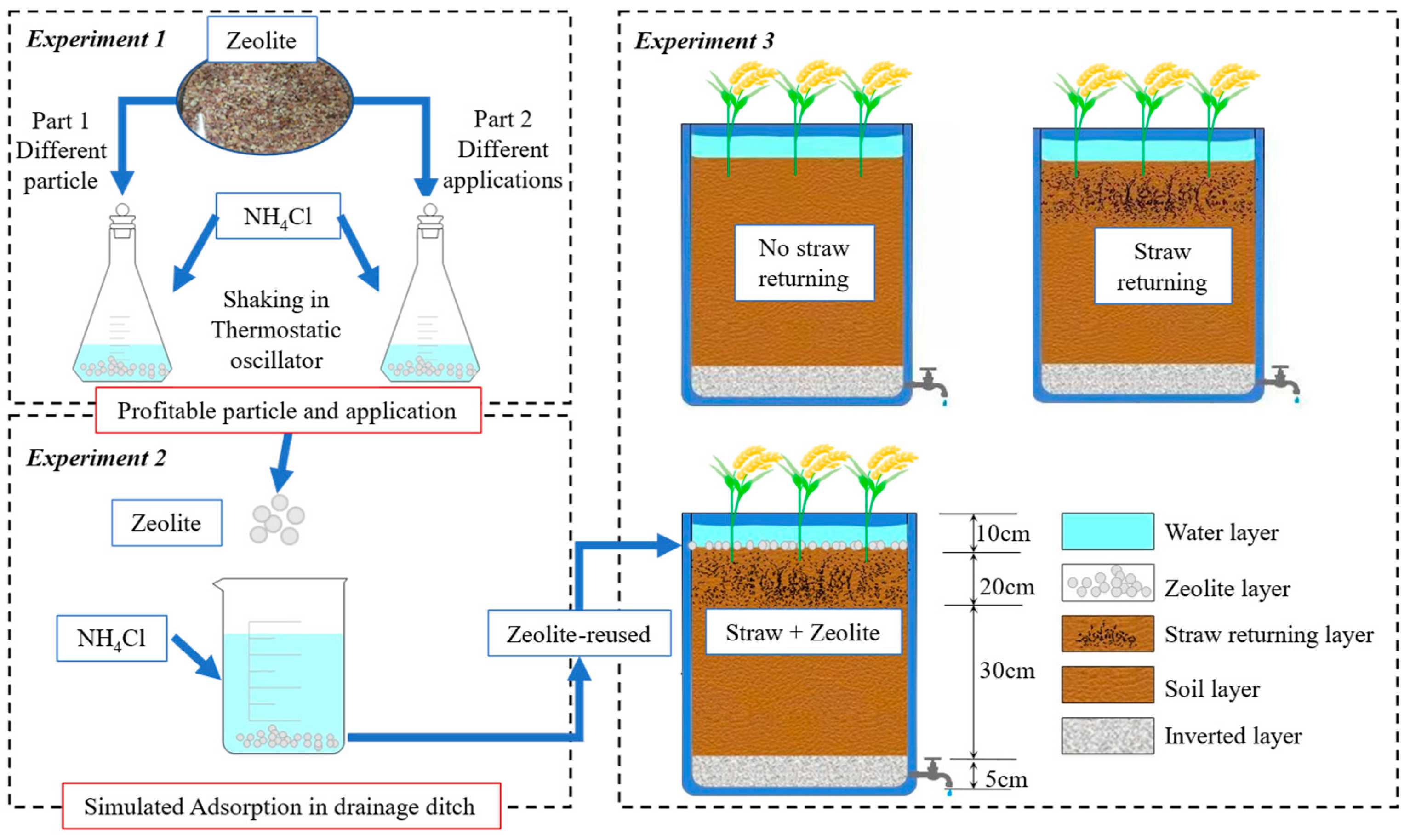
2.2.1. Experimental Design of N Adsorption Kinetics
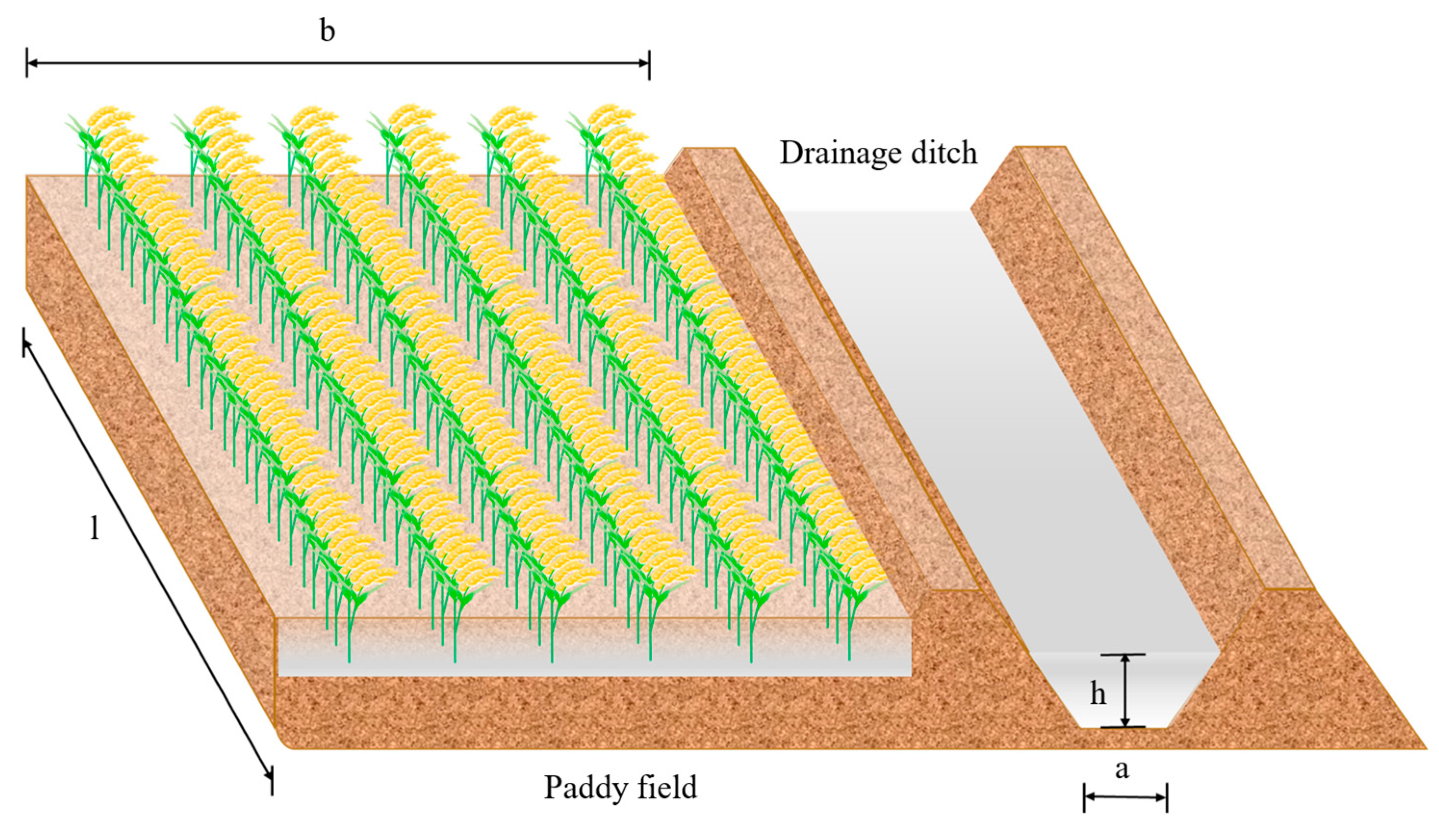
2.2.2. Experimental Design of NH4+-N Adsorption in Drainage Ditch Simulations
2.2.3. Pot Experimental Design of Excess N Recycling Using Zeolite
2.3. Analytical Methods
2.3.1. Parameter Analysis
2.3.2. Application Analysis
2.3.3. Statistical Analysis and Calculation
3. Results
3.1. N Adsorption Kinetics
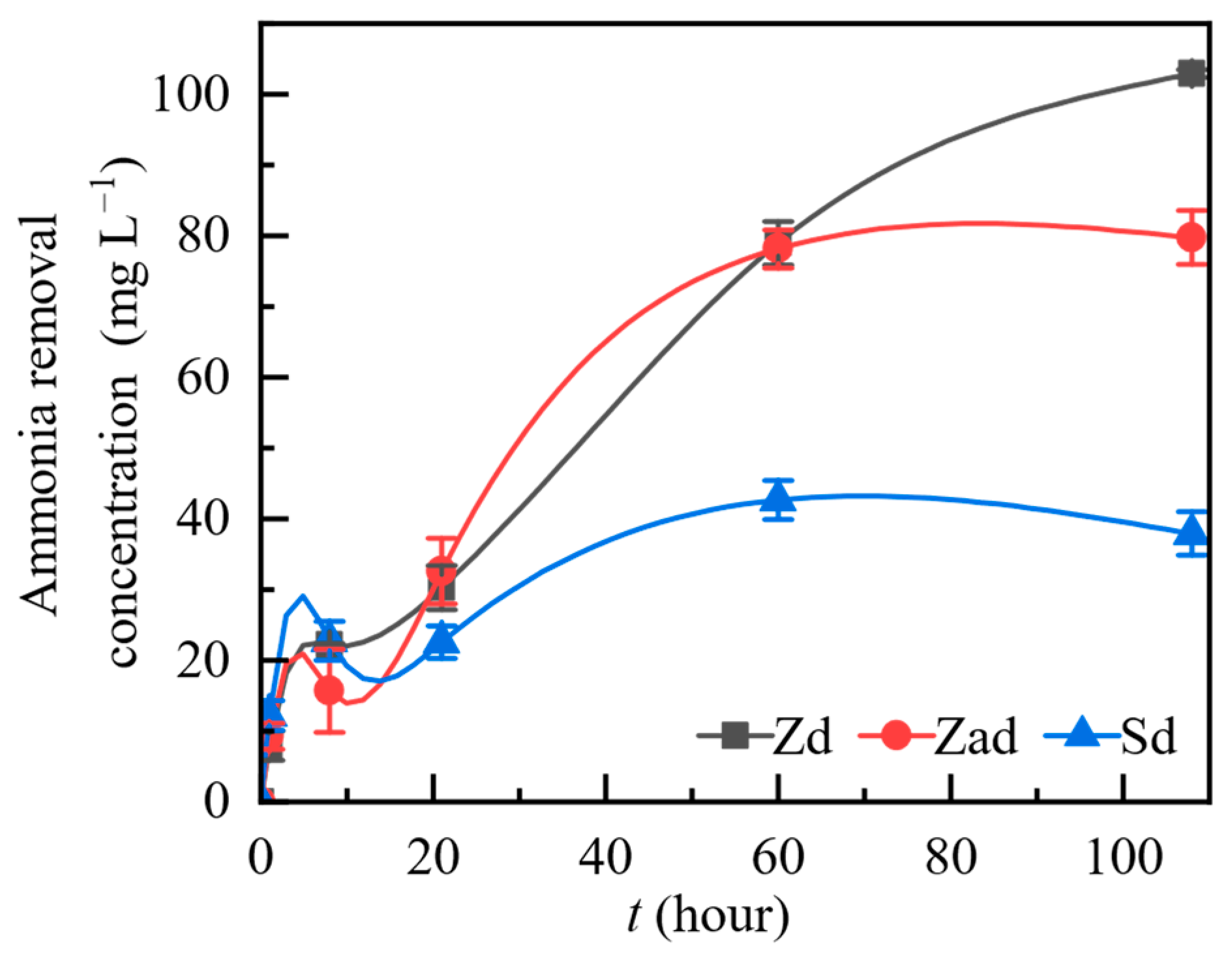
3.2. NH4+-N Adsorption in Drainage Ditch Simulations Using Zeolite
3.3. Paddy Field Water Quality Changes
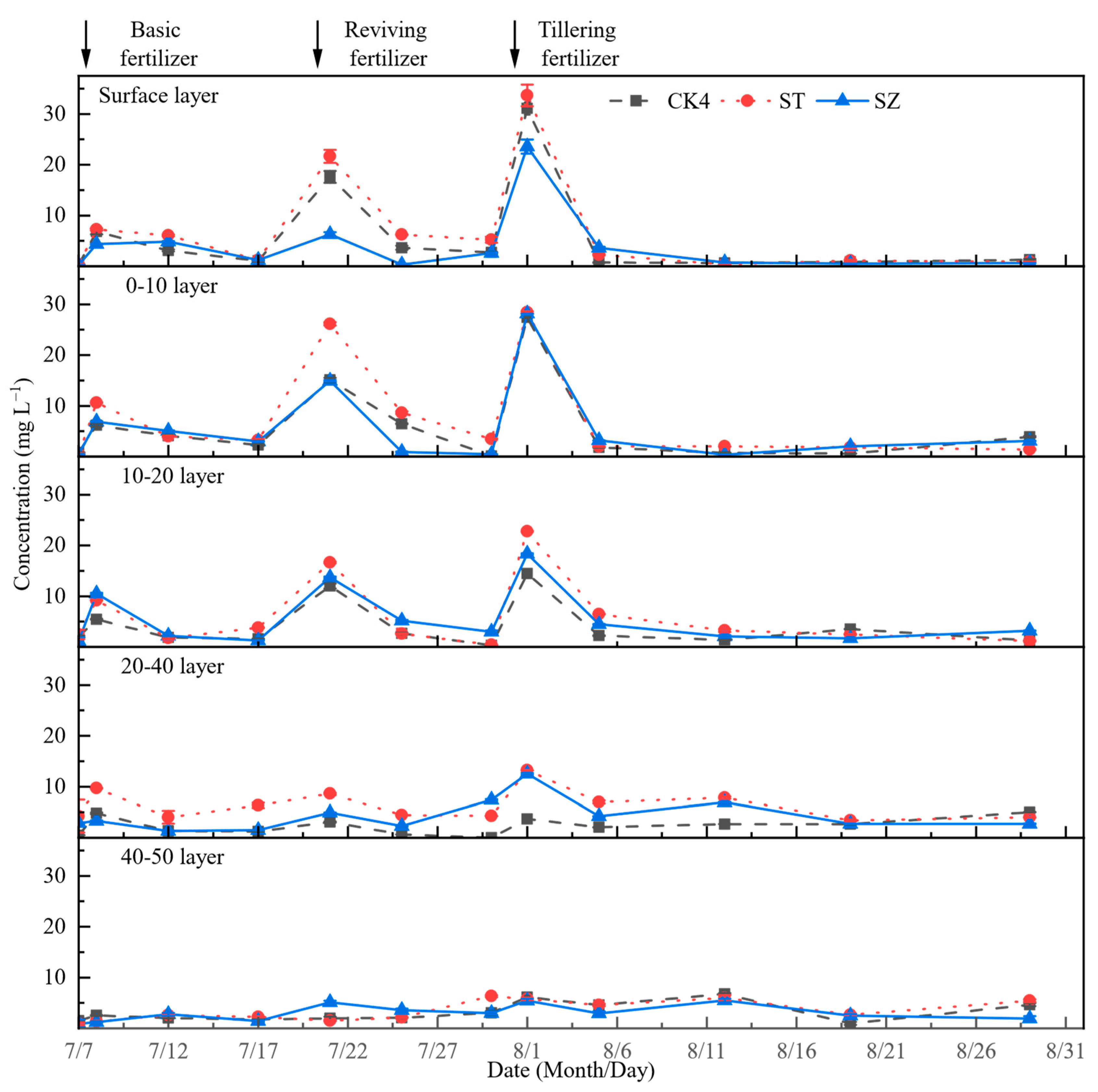
3.3.1. NH4+-N
3.3.2. NO3−-N
3.3.3. TN
3.3.4. TP
4. Discussion
4.1. Adsorption of NH4+-N by Zeolite in the Drainage Ditch
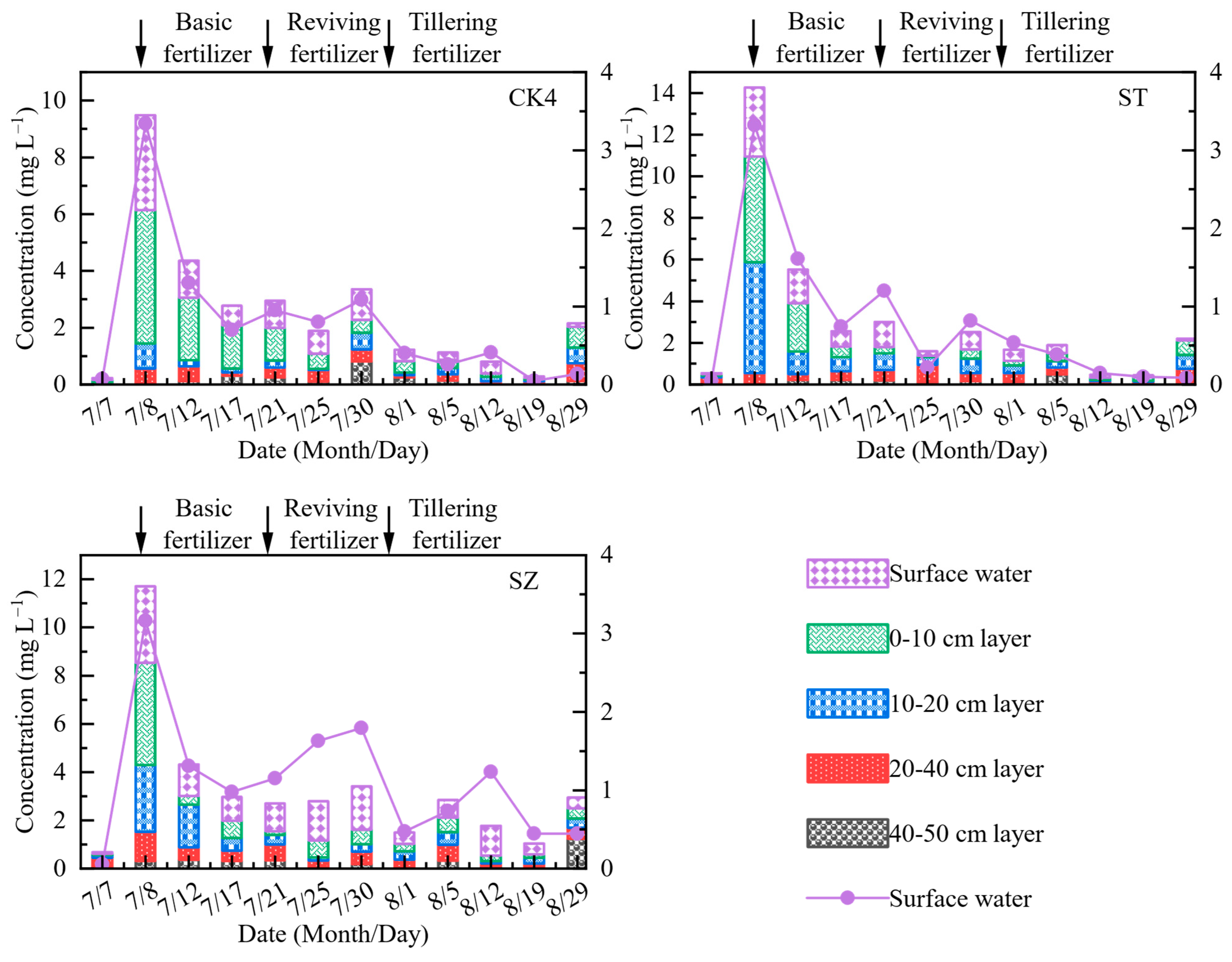
4.2. Effect of Zeolite Reuse on Water Quality under Straw Return Conditions
4.3. Suitable Zeolite Application
5. Conclusions
- (i)
- A quantity of 100 g L−1 of 3 mm heat-dried zeolite is appropriate for treating water in the drainage ditch, removing 74.23% of NH4+-N.
- (ii)
- Straw returning releases more N and P than it returns to the field. Zeolite adsorbs N and P to improve water quality during straw decomposition, then gradually releases them for reuse. The peak NH4+-N, TN, and TP values in the group with zeolite decreased by 30%, 19%, and 5%, respectively, relative to straw returning without zeolite.
- (iii)
- Combining all experimental results with conventional field layouts, 20 t ha−1 zeolite is the ideal application for recycling N and P.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yang, X.; Cheng, L.; Huang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Yin, C.; Lebailly, P. Incentive mechanism to promote corn stalk return sustainably in Henan, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 738, 139775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McKendry, P. Energy production from biomass (part 1): Overview of biomass. Bioresour. Technol. 2002, 83, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.; Ling, J.; Zhao, D.-Q.; Xu, Y.-P.; Liu, Z.-X.; Wen, Y.; Zhou, S.-L. Deep-injected straw incorporation improves subsoil fertility and crop productivity in a wheat-maize rotation system in the North China Plain. Field Crops Res. 2022, 286, 108612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Li, C.; Ristovski, Z.; Milic, A.; Gu, Y.; Islam, M.S.; Wang, S.; Hao, J.; Zhang, H.; He, C.; et al. A review of biomass burning: Emissions and impacts on air quality, health and climate in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 579, 1000–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, H.; Zhu, X.Q.; Heijman, W.; Zhao, K. The impact of land transfer and farmers’ knowledge of farmland protection policy on pro-environmental agricultural practices: The case of straw return to fields in Ningxia, China. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 277, 123701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T. Effects of Crop Residues Returning on Greenhouse Gas Emissions from Brown Red Soil. Master’s Thesis, Huazhong Agricultural University, Huazhong, China, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Nyberg, G.; Ekblad, A.; Buresh, R.; Högberg, P. Short-term patterns of carbon and nitrogen mineralisation in a fallow field amended with green manures from agroforestry trees. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2002, 36, 18–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.F.; Chen, J.G.; Jin, Z.X.; Guo, J.Y.; Yang, H.Q.; Zeng, Y.; Liu, Y. Simultaneous removal of phosphate and ammonium nitrogen from agricultural runoff by amending soil in lakeside zone of Karst area, Southern China. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2020, 289, 106745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.S.; Zhou, J.J.; Feng, J.X.; Zhai, S.L.; Chen, W.P.; Liu, J.; Bian, X.M. Ditch-buried straw return: A novel tillage practice combined with tillage rotation and deep ploughing in rice-wheat rotation systems. Adv. Agron. 2019, 154, 257–290. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.H.; Yang, H.S.; Liu, J.; Wu, J.S.; Chen, W.P.; Wu, J.; Zhu, L.Q.; Bian, X.M. Effects of ditch-buried straw return on soil organic carbon and rice yields in a rice-wheat rotation system. Catena 2015, 127, 56–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Chi, D.C.; Xia, G.M.; Chen, T.T.; Sun, Y.D.; Song, Y.H. Effects of Zeolite on Drought Resistance and Water-Nitrogen Use Efficiency in Paddy Rice. J. Irrig. Drain. Eng. 2019, 145, 04019024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.S.; Li, Y.F.; Zhai, S.L.; Fang, C.; Liu, J.; Zhang, Q. Long term ditch-buried straw return affects soil fungal community structure and carbon-degrading enzymatic activities in a rice-wheat rotation system. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2020, 155, 103660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Z.; Zheng, X.; Wang, R.; Xie, B.; Butterbach-Bahl, K.; Zhu, J. Nitrous oxide and methane fluxes from a rice–wheat crop rotation under wheat residue incorporation and no-tillage practices. Atmos. Environ. 2013, 79, 641–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabisa, E.W.; Gheewala, S.H. Potential of bio-energy production in Ethiopia based on available biomass residues. Biomass Bioenergy 2018, 111, 77–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Q.; Liu, X.; Hao, T.; Zeng, M.; Shen, J.; Zhang, F.; De Vries, W. Modeling soil acidification in typical Chinese cropping systems. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 613–614, 1339–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, X.; Zhou, Y.; Min, J.; Wang, S.Q.; Shi, W.M.; Xing, G.X. Nitrogen runoff dominates water nitrogen pollution from rice-wheat rotation in the Taihu Lake region of China. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2012, 156, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, X.; Shao, D.; Liu, H.; Yang, F.; Xiao, C.; Yang, H. Effects of alternate wetting and drying irrigation on percolation and nitrogen leaching in paddy fields. Paddy Water Environ. 2013, 11, 381–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.S.; Guo, L.J.; Liu, T.Q.; Li, C.F.; Cao, C.G. Effects of tillage practices and straw returning methods on greenhouse gas emissions and net ecosystem economic budget in rice–wheat cropping systems in central China. Atmos. Environ. 2015, 122, 636–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almutairi, A.; Weatherley, L.R. Intensification of ammonia removal from waste water in biologically active zeolitic ion exchange columns. J. Environ. Manag. 2015, 160, 128–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Li, H.; Zhu, J. A value-added step towards promoting the serviceability of fluidized bed bioreactor in treating wastewater with low carbon to nitrogen ratio. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 750, 141665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, D.P.; Smith, N.T. Anaerobic-ion exchange (AN-IX) process for local-scale nitrogen recovery from wastewater. Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 196, 324–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armbruster, T.; Gunter, M.E. Crystal structures of natural zeolites. Nat. Zeolites Occur. Prop. Appl. 2001, 45, 1–67. [Google Scholar]
- Mumpton, F.A. La roca magica: Uses of natural zeolites in agriculture and industry. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1999, 96, 3463–3470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bish, D.L. Chapter 13.2 Parallels and Distinctions between Clay Minerals and Zeolites. Dev. Clay Sci. 2006, 1, 1097–1112. [Google Scholar]
- Hermassi, M.; Valderrama, C.; Font, O.; Moreno, N.; Querol, X.; Batis, N.H.; Cortina, J.L. Phosphate recovery from aqueous solution by K-zeolite synthesized from fly ash for subsequent valorisation as slow release fertilizer. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 731, 139002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montalvo, S.; Huilinir, C.; Borja, R.; Sanchez, E.; Herrmann, C. Application of zeolites for biological treatment processes of solid wastes and wastewaters—A review. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 301, 122808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montalvo, S.; San Martina, J.; Huilinir, C.; Guerrero, L.; Borja, R. Assessment of a UASB reactor with high ammonia concentrations: Effect of zeolite addition on process performance. Process Biochem. 2014, 49, 2220–2227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.W.; Zhang, L.Y.; Xi, B.D.; Sun, W.J.; Xia, X.F.; Zhu, C.W.; He, X.S.; Li, M.X.; Yang, T.X.; Wang, P.F.; et al. Biogas production improvement and C/N control by natural clinoptilolite addition into anaerobic co-digestion of Phragmites australis, feces and kitchen waste. Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 180, 192–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noori, M.; Zendehdel, M.; Ahmadi, A. Using natural zeolite for the improvement of soil salinity and crop yield. Toxicol. Environ. Chem. 2006, 88, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.L.; Calvert, D.V.; Alva, A.K.; Li, Y.C.; Banks, D.J. Clinoptilolite zeolite and cellulose amendments to reduce ammonia volatilization in a calcareous sandy soil. Plant Soil 2002, 247, 253–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sha, Y.; Chi, D.; Chen, T.; Wang, S.; Zhao, Q.; Li, Y.; Sun, Y.; Chen, J.; Lærke, P.E. Zeolite application increases grain yield and mitigates greenhouse gas emissions under alternate wetting and drying rice system. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 838, 156067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campisi, T.; Abbondanzi, F.; Faccini, B.; Di Giuseppe, D.; Malferrari, D.; Coltorti, M.; Laurora, A.; Passaglia, E. Ammonium-charged zeolitite effects on crop growth and nutrient leaching: Greenhouse experiments on maize (Zea mays). Catena 2016, 140, 66–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, C.J.; Shyu, H.Y.; Xaba, L.; Bair, R.; Yeh, D.H. Performance and onsite regeneration of natural zeolite for ammonium removal in a field-scale non-sewered sanitation system. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 776, 145938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.D.; He, Z.L.; Wu, Q.; Zheng, J.L.; Li, Y.H.; Wang, Y.Z.; Chen, T.T.; Chi, D.C. Zeolite amendment enhances rice production, nitrogen accumulation and translocation in wetting and drying irrigation paddy field. Agric. Water Manag. 2020, 235, 106126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Shu, X.; Tu, Q.; Yang, Y.; Liu, C.; Fu, D.; Li, W.; Duan, C. Pollutant removal from agricultural drainage water using a novel double-layer ditch with biofilm carriers. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 310, 123344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guaya, D.; Mendoza, A.; Valderrama, C.; Farran, A.; Sauras-Yera, T.; Cortina, J.L. Use of nutrient-enriched zeolite (NEZ) from urban wastewaters in amended soils: Evaluation of plant availability of mineral elements. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 727, 138646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baghaie, A.H.; Aghili, F.; Jafarinia, R. Soil-indigenous arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi and zeolite addition to soil synergistically increase grain yield and reduce cadmium uptake of bread wheat (through improved nitrogen and phosphorus nutrition and immobilization of Cd in roots). Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2019, 26, 30794–30807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GhassemiSahebi, F.; Mohammadrezapour, O.; Delbari, M.; KhasheiSiuki, A.; Ritzema, H.; Cherati, A. Effect of utilization of treated wastewater and seawater with Clinoptilolite-Zeolite on yield and yield components of sorghum. Agric. Water Manag. 2020, 234, 106117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohan, S.; Dinesha, P.; Kumar, S. NOx reduction behaviour in copper zeolite catalysts for ammonia SCR systems: A review. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 384, 123253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinzato, M.C.; Wu, L.F.; Mariano, T.O.; Freitas, J.G.; Martins, T.S. Mineral sorbents for ammonium recycling from industry to agriculture. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2020, 27, 13599–13616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoud, A.W.M.; Abdeldaym, E.A.; Abdelaziz, S.M.; El-Sawy, M.B.I.; Mottaleb, S.A. Synergetic Effects of Zinc, Boron, Silicon, and Zeolite Nanoparticles on Confer Tolerance in Potato Plants Subjected to Salinity. Agronomy 2019, 10, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, D.P. Chabazite Biofilter for Enhanced Stormwater Nitrogen Removal. Water Environ. Res. 2011, 83, 373–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Li, M.; Zheng, F.; Wang, J.; Chen, L.; Hu, P.; Zhen, Q.; Bashir, S.; Liu, J.L. Efficient removal of water pollutants by hierarchical porous zeolite-activated carbon prepared from coal gangue and bamboo. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 325, 129322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seruga, P.; Krzywonos, M.; Pyzanowska, J.; Urbanowska, A.; Pawlak-Kruczek, H.; Niedzwiecki, L. Removal of Ammonia from the Municipal Waste Treatment Effluents using Natural Minerals. Molecules 2019, 24, 3633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, B.; Wang, X.; Li, S.; Liu, Y.; An, Y.; Zheng, X. Preferable Adsorption of Nitrogen and Phosphorus from Agricultural Wastewater Using Thermally Modified Zeolite–Diatomite Composite Adsorbent. Water 2019, 11, 2053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Guo, X.; Lu, J.; Wan, S.; Wang, Y.; Xu, Z.; Zhang, X. Decomposition characteristics of wheat straw and effects on soil biological properties and nutrient status under different rice cultivation. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2013, 33, 565–575. [Google Scholar]
- Scandelai, A.P.J.; Zotesso, J.P.; Jegatheesan, V.; Cardozo-Filho, L.; Tavares, C.R.G. Intensification of supercritical water oxidation (ScWO) process for landfill leachate treatment through ion exchange with zeolite. Waste Manag. 2020, 101, 259–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moussavi, G.; Talebi, S.; Farrokhi, M.; Sabouti, R.M. The investigation of mechanism, kinetic and isotherm of ammonia and humic acid co-adsorption onto natural zeolite. Chem. Eng. J. 2011, 171, 1159–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Component | Component | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Al2O3 (%) | 13.39 | Na2O (%) | 1.25 |
| SiO2 (%) | 68.30 | K2O (%) | 2.92 |
| Fe2O3 (%) | 1.06 | MgO (%) | 0.71 |
| Cao (%) | 3.42 | TiO2 (%) | 0.20 |
| CEC (cmol + kg−1) | 140 |
| Fertilizer | Type | Date | Application (kg/ha) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Basic fertilizer | Compound fertilizer (mineral and solid) N: P2O5: K2O = 15%: 15%: 15% | 7th July | 300 |
| Reviving fertilizer | Urea (mineral and solid): N ≧ 46.4% | 20th July | 150 |
| Tillering fertilizer | Urea (mineral and solid): N ≧ 46.4% | 31st July | 75 |
| Panicle fertilizer | Urea (mineral and solid): N ≧ 46.4% | 29th August | 150 |
| Size (mm) | Pseudo-First-Order Model | Pseudo-Second-Order Model | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
(min) | R2 | (mg g−1) | (g mg−1 min) | R2 | h (mg g−1 min) | ||
| 0.5–3 | 3.37 | 0.0175 | 0.8216 | 3.64 | 0.0076 | 0.9899 | 0.1016 |
| 3–5 | 2.77 | 0.0095 | 0.8549 | 3.26 | 0.0042 | 0.9677 | 0.0454 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hu, W.; Li, J.; Jiao, X.; Jiang, H. Zeolite as a Tool to Recycle Nitrogen and Phosphorus in Paddy Fields under Straw Returning Conditions. Agronomy 2023, 13, 327. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy13020327
Hu W, Li J, Jiao X, Jiang H. Zeolite as a Tool to Recycle Nitrogen and Phosphorus in Paddy Fields under Straw Returning Conditions. Agronomy. 2023; 13(2):327. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy13020327
Chicago/Turabian StyleHu, Weiyu, Jiang Li, Xiyun Jiao, and Hongzhe Jiang. 2023. "Zeolite as a Tool to Recycle Nitrogen and Phosphorus in Paddy Fields under Straw Returning Conditions" Agronomy 13, no. 2: 327. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy13020327
APA StyleHu, W., Li, J., Jiao, X., & Jiang, H. (2023). Zeolite as a Tool to Recycle Nitrogen and Phosphorus in Paddy Fields under Straw Returning Conditions. Agronomy, 13(2), 327. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy13020327







