Abstract
The coastal saline-alkali soil in eastern China is an important reserve arable land resource. Adding exogenous organic material is an effective way to improve soil fertility and promote the conversion of saline-alkali soil to agricultural soil. In this study, a field plot experiment was used to investigate the influences of different organic materials (vinegar residue, VR; sewage sludge, SS; vermicompost, VC) on the reduction in salinity-alkalinity barrier factors, the accumulation of soil organic carbon (SOC), and the improvement in soil fertility in saline-alkali soil. The results indicated that applying different types of exogenous organic materials reduced soil electrical conductivity (EC) and pH, promoted SOC accumulation, and increased the barley yield. With the same application rate, VR application was more beneficial in reducing soil EC and pH, accumulating SOC, and increasing barley yield compared to SS and VC applications. In particular, the barley yield with VR application was higher than that with SS and VC applications by 18.4% and 26.6% on average, respectively, during the two-year experiment. Correlation and path analysis revealed that the barley yield was significantly negatively correlated with soil barrier factors (EC and pH), but EC in SS and VC-treated soils had an indirect negative effect on barley yield, while EC in VR-treated soil had a direct negative effect (−2.24). In addition, the direct (−4.46) and indirect (5.39) contributions of SOC to barley yield were higher with VR than those with SS and VC, while the direct contribution of soil aggregate to barley yield was lower with VR than that with SS and VC. Therefore, compared with SS and VC applications, VR application led to a fast reduction in soil barrier factors and the rapid accumulation of SOC, which were more beneficial for increasing barley yields in saline-alkali soil.
1. Introduction
Due to the shortage of arable land resources in China, it is of great strategic significance to use coastal saline-alkali soil comprehensively to ensure national food security. High salinity and high pH are the main barrier factors of saline-alkali soil. Additionally, due to its short period of reclamation, the tillage layer has not been formed, and the soil has a poor structure and low organic carbon pool and nutrient content, resulting in extremely low basic soil fertility in coastal saline-alkali soil [1]. Therefore, the key measures for improving saline-alkali soil are salinity reduction and soil fertility improvement. The salinity reduction process can be accelerated by diverting fresh water for irrigation and concentrating rainfall, and a key point in the rapid improvement in soil fertility is to increase the soil organic matter content [2,3,4]. Soil organic matter is closely related to improved soil fertility because it carries a large amount of negative charge, and its cation exchange capacity and water absorption rate are several times or even tens of times higher than those of soil clay, which can greatly improve the water storage and nutrient-retaining capacity of soil [5,6,7]. In addition, soil organic matter can promote the formation of soil aggregates, increase the noncapillary porosity, and cut off the capillaries while increasing the downward salt leaching channel, further promoting soil desalination and inhibiting soil resalinization [8,9,10]. However, the saline-alkali soils have very low organic matter content, and their own organic matter accumulation process is extremely slow under high salinity and high pH conditions. Therefore, on the basis of salinity reduction measures, anthropogenic input of large amounts of exogenous organic materials to drive the improvement in soil fertility is an effective way to promote the conversion of coastal saline-alkali soil to agricultural soil [11].
The accumulation of soil organic matter is the core of improving soil fertility in saline-alkali soil [2] and sufficient input of exogenous organic material is a necessary condition for the substantial accumulation of soil organic matter [4]. However, there may be differences in the ability of different organic materials to promote soil fertility. Jafari et al. [12] found that the effects of different organic materials (sewage sludge, livestock manure, and olive oil residue) on the accumulation of soil organic matter and nutrient varied significantly. Corbin et al. [13] reported that applying different types of organic materials (livestock manure and crop residue) could lead to a greater than 5-fold difference in the number of soil aggregates. Bowden et al. [14] found that different organic material applications resulted in a 2.3-fold difference in soil fertility (mainly soybean yield). However, the influences of different types of exogenous organic materials on soil fertility improvement in saline-alkali soil under high salinity and high pH conditions remain unclear.
In this study, vinegar residue (VR), sewage sludge (SS), and vermicompost (VC) were used as exogenous organic materials to investigate the influences of different organic materials on soil barrier factors reduction, soil organic carbon (SOC) accumulation, and soil fertility improvement in saline-alkali soil. The aim of this study was to reveal the characteristics of soil fertility improvement driven by different organic materials, which can not only enrich the basic theory of soil fertility improvement, but also provide practical guidance for the improvement and utilization of coastal saline-alkali soils.
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Experimental Site and Materials
This experiment was performed from 2019 to 2021 in Fangling reclamation area (120°56′03″ E, 32°36′30″ N), Rudong County, Jiangsu Province, China. The experimental area was reclaimed in 2010 and the soil was sandy loam and coastal saline soil. Precipitation in the area is mainly concentrated in June to August. During the experiment, the average annual rainfall and temperature were 1074.6 mm and 15.1 °C, respectively. The groundwater in the topsoil of the experimental area belongs to the Quaternary pore phreatic water type, with a stratified distribution and an average burial depth of 0.8 m. The main sources of recharge are surface water and atmospheric precipitation.
The VR used in this study was obtained from Zhenjiang Hengshun Vinegar Co., Ltd., (Zhenjiang City, Jiangsu Province, China) and the SS and VC were obtained from Taizhou Chunguang Ecological Agriculture Development Co., Ltd., (Taizhou City, Jiangsu Province, China) and VC was obtained by digesting SS with earthworms. The SS was treated by stacking fermentation, with the corresponding indexes conforming to the Control Standards of Pollutants in Sludge for Agricultural Use (GB 4284-2018). The basic physiochemical properties of the saline-alkali soil, VR, SS, and VC are shown in Table 1.

Table 1.
Basic properties of saline-alkali soil and exogenous organic materials used in this study.
2.2. Experimental Design
A field randomized block experiment was performed, and each plot had an area of 16 m2 (4.0 m × 4.0 m). According to the dry-basis application rate of organic materials, five treatments (0, 25, 50, 100, and 200 t ha−1) were set up and each treatment was replicated three times, and the organic materials were applied only once during the whole experimental period. In October 2019, VR, SS, and VC were applied to each plot, and each organic material was mixed with the 0–20 cm topsoil using a rototiller. Barley (Hordeum vulgare L. Yangnongpi 5) was sown in November 2019 and November 2020 and harvested in May 2020 and May 2021, respectively, for yield measurements. Field weeds were controlled manually after barley sowing. Neither inorganic fertilizer nor additional freshwater irrigation was supplied in the whole barley growing season. Soil samples and aggregate samples were collected from the 0–20 cm topsoil on the day of barley harvest.
2.3. Soil Analysis
The soil samples were air-dried, crushed, and passed through 1 mm and 0.15 mm sieves to determine soil electrical conductivity (EC), pH, SOC, nitrogen (N), and phosphorus (P) contents. Soil EC and pH were measured at a soil-to-water ratio of 1:5 using a conductivity meter and a pH meter, respectively. SOC content was measured using the potassium dichromate external heating method [15]. Soil total N (TN), total P (TP), alkaline N (AN), and available P (AP) were measured using the semimicro-Kjeldahl method, sulfuric acid–perchloric acid digestion method, alkaline hydrolysis diffusion method, and sodium bicarbonate extraction (molybdenum-antimony anticolorimetric method) [15], respectively. Soil-water-stable aggregates (WSA) were measured using the wet sieving method [16].
2.4. Statistical Analysis
The data were statistically analyzed using Microsoft Excel (2019) and SPSS 19.0 statistical software, and the least significant difference (LSD) method was used to test the significance of differences at p < 0.05. The influences of related soil barrier factors (EC and pH) and fertility indicators (SOC, TN, AN, TP, AP, and WSA) in organic material-treated saline-alkali soil on barley yield were assessed using Pearson correlation analysis and path analysis, and the significance was set at p < 0.05.
3. Results
3.1. Barley Yield in Organic Material-Treated Saline-Alkali Soil
The barley yield in saline-alkali soil showed a gradual increase with the increasing application rates of exogenous organic materials (VR, SS, and VC) (Figure 1). In 2020, the barley yields in control treatments (without organic material application) were 1.81, 1.95, and 1.87 t ha−1, respectively, and the barley yields in treatments with the highest application rates (200 t ha−1) of VR, SS, and VC reached 4.63, 3.84, and 3.65 t ha−1, respectively, which were 156%, 96.6%, and 95.4% higher than the control soils, respectively. With the same application rate, the barley yields followed the order of VR > SS > VC. Specifically, the barley yields in VR-treated soil were 42.2%, 43.7%, 11.5%, and 20.8% higher than those with SS, respectively, and 27.5%, 51.2%, 20.4%, and 27.0% higher than those with VC, respectively, and the differences reached a significant level. The influences of different organic materials on barley yield in 2021 were similar to those in 2020.
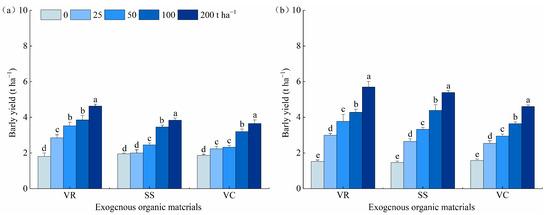
Figure 1.
Barley yield in response to the application of different exogenous organic materials in saline-alkali soil: (a,b), barley yield in 2020 and 2021, respectively; VR, vinegar residue; SS, sewage sludge; VC, vermicompost; OM, organic material. The vertical bars denote standard errors. Different small letters denote significant difference at p < 0.05.
3.2. Soil Barrier Factors
The application of organic materials (VR, SS, and VC) significantly decreased soil EC and pH (Figure 2). Specially, soil EC and pH in VR-, SS-, and VC-treated soils with 200 t ha−1 application rate decreased by 55.0%, 44.1%, 39.4%, and 0.95, 0.85, and 0.72 pH-units, respectively, in comparison to those in control soils. The changes in soil EC and pH in VR-, SS-, and VC-treated soils in 2021 were similar than those in 2020, and VR application was more beneficial for EC and pH reduction in saline-alkali soil compared to SS and VC.
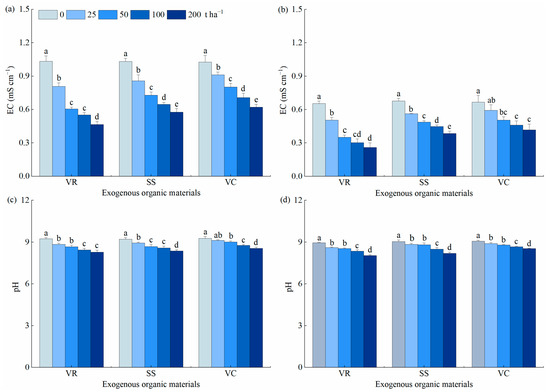
Figure 2.
Effect of different organic material application on soil EC and pH in saline-alkali soil: (a,b), soil EC in 2020 and 2021, respectively; (c,d), soil pH in 2020 and 2021, respectively; VR, vinegar residue; SS, sewage sludge; VC, vermicompost; OM, organic material; EC, electrical conductivity. The vertical bars denote standard errors. Different small letters denote significant difference at p < 0.05.
3.3. Soil Fertility
The application of organic materials significantly increased SOC content in saline-alkali soil (Figure 3). In 2020, SOC contents in VR-, SS-, and VC-treated soils with 200 t ha−1 application rate increased by 449%, 330%, and 255%, respectively, compared with the control soils. With the same application rate, the SOC contents in VR treatment increased by 51.2% and 59.3% on average compared to those in SS and VC treatments. Soil N and P contents in 2020 also increased with the increasing application rates of different organic materials (Table 2). With the same application rate, the contents of TN, AN, and AP in SS-treated soil were higher than those treated with VC and VR, and the TP content in VC-treated soil was higher than that treated with SS and VR. The trends in SOC, N, and P changes due to each treatment in 2021 were consistent with those in 2020.
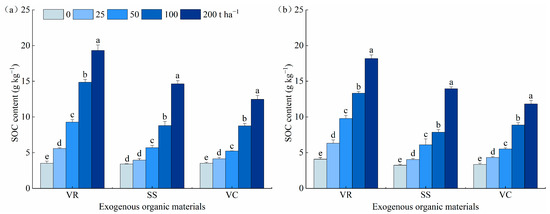
Figure 3.
The accumulation of soil organic carbon in different organic material-treated saline-alkali soils: (a,b), soil organic carbon contents in 2020 and 2021, respectively; VR, vinegar residue; SS, sewage sludge; VC, vermicompost; OM, organic material; SOC, soil organic carbon. The vertical bars denote standard errors. Different small letters denote significant difference at p < 0.05.

Table 2.
Effects of different organic material application on nitrogen and phosphorus contents in saline-alkali soil.
The application of SS and VC promoted soil aggregate formation (Figure 4). In 2020, in soils treated with 200 t ha−1 application rate of SS and VC, the percentages of >0.25 mm WSA increased by 195% and 227%, respectively, and the 0.106–0.25 mm WSA increased by 188% and 196%, respectively, compared with the control soils. The VR application had no significant influence on WSA in saline-alkali soil. With the same application rate, applying VC was more conducive to soil aggregate formation in saline-alkali soil than SS and VR.
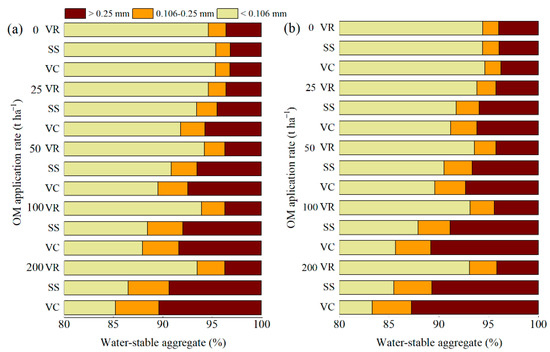
Figure 4.
The percentages of soil water-stable aggregate in response to the application of different organic materials in saline-alkali soil: (a,b), soil water-stable aggregate in 2020 and 2021, respectively; VR, vinegar residue; SS, sewage sludge; VC, vermicompost; OM, organic material.
3.4. Contribution Analysis for Saline-Alkali Soil Fertility
The correlation analysis indicated that barley yield was negatively correlated with soil barrier factors (p < 0.01) and positively correlated with soil fertility indicators (except soil water-stable aggregates in soil treated with VR) (p < 0.01) (Table 3). Path analysis further revealed that EC in SS- and VC-treated soils had direct effects of 0.70 and 0.24 on barley yield, respectively. Additionally, their indirect negative effects on barley yield through the TN, AN, AP, and WSA and through the SOC, TN, TP, and WSA, respectively, resulted in the combined indirect negative effects (SS: −1.55; VC: −1.17), which were greater than the direct positive effects. EC in VR-treated soil had a direct negative effect on barley yield (−2.24). Although the indirect positive effect on the yield through SOC, TN, and TP weakened the direct negative effect, it was still greater than the combined indirect positive effect. SOC in SS- and VR-treated soils had direct negative effects on barley yield, but their indirect positive effects on the yield through the TN, AN, AP, and WSA and through the AN, AP, pH, EC, and WSA, respectively, resulted in the combined indirect positive effects (SS: 2.85; VC: 7.55), which were greater than the direct negative effects. SOC in VC-treated soils had a direct positive effect on barley yield (1.09). Soil WSA in treatments using VR, SS, and VC primarily had direct positive effects on barley yield, and the direct positive effects of SS (0.97) and VC (0.81) treatments were greater than that of VR treatment (0.23).

Table 3.
Correlation and path analysis of barley yield and related soil barrier factors and fertility indicators in saline-alkali soil amended by different organic materials.
4. Discussion
High salinity and high pH are the main barrier factors limiting the improvement in soil fertility in saline-alkali soil. In this study, the application of different types of exogenous organic materials (VR, SS, and VC) significantly reduced soil salinity and pH. The high salinity in saline-alkali soil is primarily attributed to the accumulation of subsurface salts to the surface soil with capillary action due to the dense capillary pores in the soil [17]. In this study, applying VR was more beneficial to soil salinity reduction than SS and VC. This result is possibly due to the loose structure of the VR, which is more conducive to increasing soil noncapillary pores and promoting the downward leaching of salt in the topsoil. A similar result showed that saline-alkali soil treated with VR had a higher salinity reduction efficiency than those treated with sulfuric acid, gypsum, and crop straw [18]. The humic acid-like substances released during the decomposition of exogenous organic materials are the main cause of the decrease in the pH of saline-alkali soil [19]. This study demonstrated that applying VR was more effective at reducing soil pH than SS and VC, possibly due to the low pH of the VR itself (Table 1).
Promoting soil aggregate formation in saline-alkali soil is an effective way to increase soil noncapillary porosity, cut off the capillary while increasing the salt leaching channels, and inhibit the salt accumulation in the surface soil. In this study, soil WSA increased with increasing application rates of SS and VC. The formation and stability of soil aggregates are related to “binder” and “dispersant” functions [20]. SOM, which is an important material basis that promotes aggregate formation, is generally considered a “binder” for soil aggregate formation [21,22]. SS and VC, which are rich in organic matter, have a large negative charge and can improve the aggregation of soil particles and effectively promote soil aggregate formation [6,7,23,24]. The high salinity is recognized as a “dispersant” that destroys aggregate stability in saline-alkali soil [22,25]. The application of exogenous organic materials (VR, SS, and VC) reduced the EC in saline-alkali soil, which was conductive to the increase in soil aggregate stability. In this study, applying VC and SS both promoted soil aggregate formation, while applying VR had no significant influence on soil aggregate formation. This result occurred because SS and VC are rich in the organic cementing substances required for soil aggregate formation, while VR is primarily cellulose and has few organic cementing substances [26,27]. Previous studies have also confirmed that applying different organic materials can lead to more than a 5-fold difference in the amount of soil aggregates formed [13]. This result may be due to the differences in the ability of different organic materials to bind to soil minerals, and the percentage of different organic materials adsorbed by the same soil can range from 1% to 86% [28,29]. In addition, the formation and stability of soil aggregates are closely related to microorganisms [22,30]. The different intermediate products produced by microbial decomposition of different exogenous organic materials entering the soil are also one of the reasons for the differences in the formation and stability of soil aggregates [31].
SOC accumulation is an important prerequisite for improving soil fertility in saline-alkali soil. The application of different types of exogenous organic materials (VR, SS, and VC) significantly increased SOC contents in saline-alkali soil. The correlation analysis revealed that the SOC content was significantly positively correlated with VR, SS, and VC application rates, with the following fitted equations: y = −0.0004x2 + 0.1571x + 2.9214 (R2 = 0.993, p < 0.01), y = 0.0002x2 + 0.1337x + 3.0948 (R2 = 0.999, p < 0.01), and y = −0.0002x2 + 0.1309x + 3.1058 (R2 = 0.985, p < 0.01), respectively. However, the effects of different organic materials on SOC accumulation varied significantly in saline-alkali soil. In this study, applying VR was more beneficial to SOC accumulation than applying SS and VC, mainly due to the higher organic carbon content of VR. In addition, the differences in C/N ratio and organic carbon composition directly affect the mineralization rate of organic carbon [32,33,34]. Therefore, the high C/N ratio of VR is not conducive to organic carbon mineralization, thus reducing the loss of organic carbon in saline-alkali soil.
Applying exogenous organic materials improved soil fertility and increased barley yield in saline-alkali soil. The correlation analysis indicated that barley yield was significantly positively correlated with the application rates of VR, SS, and VC, with the following fitted equations: y = −8 × 10−5x2 + 0.0292x + 2.0103 (R2 = 0.930, p < 0.001), y = −4 × 10−5x2 + 0.0192x + 1.7587 (R2 = 0.934, p < 0.001), and y = −3 × 10−5x2 + 0.0157x + 1.8231 (R2 = 0.945, p < 0.001), respectively. Numerous studies reported that applying VR, SS, and VC increased the yields of various crops, such as rice [35], maize [36], and wheat [37,38]. In this study, the increase in barley yield was attributed to reduced soil barrier factors (EC and pH), improved soil physical property (soil aggregate), and increased soil fertility (SOC, N, and P contents) under the application of exogenous organic materials, thus providing a good root growth environment for barley growth in saline-alkali soil. Bowden et al. [14] found that applying different organic materials resulted in a 2.3-fold difference in soil fertility (mainly soybean yield). In this study, applying VR was more effective at increasing barley yield than applying SS and VC. The reason may be that applying VR is more conducive to the reduction in soil salinity and pH and the accumulation of SOC in saline-alkali soil. Correlation and path analysis revealed that barley yield was negatively correlated with soil barrier factors (EC and pH), where the effect of EC on barley yield was indirectly negative in SS and VC treatments, and directly negative in VR treatment. One possible reason for these results is that the loose structure of VR is more conducive to increasing soil noncapillary pores and thus promoting the downward leaching of surface soil salts, while applying SS and VC is more inclined to promote soil aggregate formation and thus reduce soil EC. Compared with SS and VC treatments, both direct and indirect contribution of SOC to barley yield were higher in VR treatment, and the contributions were dominated by the indirect positive effect, indicating that the relationship between exogenous carbon input and barley yield in saline-alkali soil was not simply linear, and high carbon input tended to affect other soil physicochemical indicators, thus affecting barley yields. Applying SS and VC is more beneficial to soil aggregate formation in saline-alkali soil, resulting in a significantly higher direct positive effect on barley yield than VR treatment.
5. Conclusions
This study demonstrated that applying VR, SS, and VC promoted the reduction in soil barrier factors (EC and pH), the improvement in soil physical property (soil aggregate), and the increase in soil fertility (SOC, N, and P contents), thus increasing barley yield in saline-alkali soil. With the same application rate, VR application was more effective than that of SS and VC at increasing barley yield, mainly because of the higher reduction in soil salinity and pH and the higher accumulation of SOC. Correlation analysis indicated that barley yield was significantly negatively correlated with soil barrier factors (EC and pH) and positively correlated with various indicators of soil fertility (SOC, TN, AN, TP, AP, and WSA). Path analysis further revealed that soil EC and pH in SS and VC treatments had indirect negative effects on barley yield, while VR treatment had a direct negative effect. The SOC in SS and VR treatments had indirect positive effects, while VC treatment had a direct positive effect on barley yield, and both the direct and indirect contributions of SOC to barley yield were higher with VR application than with SS and VC applications. In addition, the direct contribution of soil aggregate to the yield was significantly lower with VR application than with SS and VC applications. In summary, VR application was more conducive to the reduction in soil barrier factors, the accumulation of SOC, and the increase in barley yield in saline-alkali soil than SS and VC applications.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Y.B. and Y.S.; methodology, W.Z. and L.X.; formal analysis, investigation and data curation, L.X., M.Q., S.Y., Y.W., C.S. and Y.Z.; writing—original draft preparation, W.Z. and L.X.; writing—review and editing, W.Z., Y.B., Y.L. and C.G. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (41977089 and 31872179), China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (2021M692722), the Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province (BK20210793), the Fund for Key Laboratory of Organic Geochemistry, GIGCAS (SKLOG202118), Fund for State Key Laboratory of Pollution Control and Resource Utilization (PCRRF21036), Research Fund for Jiangsu Agricultural Industry Technology System (JATS[2020]311, JATS[2021]348, and JATS[2022]352), and the Blue-Blue Project and High-Rank Talent of Yangzhou University and Jiangsu Province.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Guo, K.; Liu, X. Reclamation effect of freezing saline water irrigation on heavy saline-alkali soil in the Hetao Irrigation District of North China. Catena 2021, 204, 105420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Chen, R.; Hu, J.; Zhao, F.; Wang, J.; Chu, H.; Zhang, J.; Dolfing, J.; Lin, X. Bacillus asahii comes to the fore in organic manure fertilized alkaline soils. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2015, 81, 186–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, X.; Zhang, J.; Zhu, A.; Zhang, C. Effects of long-term (23 years) mineral fertilizer and compost application on physical properties of fluvo-aquic soil in the North China Plain. Soil Till. Res. 2016, 156, 166–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Ding, W.; Yu, H.; He, X. Linking organic carbon accumulation to microbial community dynamics in a sandy loam soil: Result of 20 years compost and inorganic fertilizers repeated application experiment. Biol. Fert. Soils 2014, 51, 137–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fooladmand, H.R. Estimating cation exchange capacity using soil textural data and soil organic matter content: A case study for the south of Iran. Arch. Agron. Soil Sci. 2008, 54, 381–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.X.; Liu, H.T.; Wu, S.B. Humic substances developed during organic waste composting: Formation mechanisms, structural properties, and agronomic functions. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 662, 501–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Wang, T.; Liu, K.S.; Wang, L.; Wang, K.; Zhou, Y. Effects of different amendments for the reclamation of coastal saline soil on soil nutrient dynamics and electrical conductivity responses. Agr. Water Manag. 2015, 159, 115–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grosbellet, C.; Vidal-Beaudet, L.; Caubel, V.; Charpentier, S. Improvement of soil structure formation by degradation of coarse organic matter. Geoderma 2011, 162, 27–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mierzwa-Hersztek, M.; Gondek, K.; Lahori, A.H.; KopeĆ, M.; Mazurek, R.; Zaleski, T.; GŁĄB, T.; Wieczorek, J. Soil micromorphological and physical properties after application of composts with polyethylene and biocomponent-derived polymers added during composting. Pedosphere 2021, 31, 560–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celik, I.; Gunal, H.; Budak, M.; Akpinar, C. Effects of long-term organic and mineral fertilizers on bulk density and penetration resistance in semi-arid Mediterranean soil conditions. Geoderma 2010, 160, 236–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.; Tao, T.; Gu, C.; Wang, L.; Feng, K.; Shan, Y. Mudflat soil amendment by sewage sludge: Soil physicochemical properties, perennial ryegrass growth, and metal uptake. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2013, 59, 942–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jafari Tarf, O.; Akça, M.O.; Donar, Y.O.; Bilge, S.; Turgay, O.C.; Sınağ, A. The short-term effects of pyro-and hydrochars derived from different organic wastes on some soil properties. Biomass Convers. Bior. 2021, 12, 129–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corbin, A.T.; Thelen, K.D.; Robertson, G.P.; Leep, R.H. Influence of cropping systems on soil aggregate and weed seedbank dynamics during the organic transition period. Agron. J. 2010, 102, 1632–1640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowden, C.L.; Evanylo, G.K.; Zhang, X.; Ervin, E.H.; Seiler, J.R. Soil carbon and physiological responses of corn and soybean to organic amendments. Compost Sci. Util. 2010, 18, 162–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, S. Soil and Agro-Chemistry Analysis; China Agriculstural Press: Beijing, China, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Zuo, W.; Gu, C.; Zhang, W.; Xu, K.; Wang, Y.; Bai, Y.; Shan, Y.; Dai, Q. Sewage sludge amendment improved soil properties and sweet sorghum yield and quality in a newly reclaimed mudflat land. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 654, 541–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jorenush, M.H.; Sepaskhah, A.R. Modelling capillary rise and soil salinity for shallow saline water table under irrigated and non-irrigated conditions. Agr. Water Manage. 2003, 61, 125–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, H.; Wang, L.; Cheng, W.; Zhao, J.; Pan, J.; Lu, W. Effect of different regulating materials on fast desalination of coastal saline soil. Acta Technol. Boreali-Sinica 2016, 31, 121–126. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno, J.L.; García, C.; Hernández, T.; Ayuso, M. Application of composted sewage sludges contaminated with heavy metals to an agricultural soil. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 1997, 43, 565–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Six, J.; Bossuyt, H.; Degryze, S.; Denef, K. A history of research on the link between (micro)aggregates, soil biota, and soil organic matter dynamics. Soil Till. Res. 2004, 79, 7–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, X.; Fan, H.; Wang, J.; Ippolito, J.; Li, Y.; Feng, S.; An, M.; Zhang, F.; Wang, K. Effect of polymer materials on soil structure and organic carbon under drip irrigation. Geoderma 2019, 340, 94–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bronick, C.J.; Lal, R. Soil structure and management: A review. Geoderma 2005, 124, 3–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheshire, M.V.; Sparling, G.P.; Mundie, C.M. Effect of periodate treatment of soil on carbohydrate constituents and soil aggregation. J. Soil Sci. 1983, 34, 105–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lax, A.; Garcia-Orenes, F. Carbohydrates of municipal solid wastes as aggregation factor of soils. Soil Technol. 1993, 6, 157–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.C.; Zhang, Z.B.; Zhou, H.; Rahman, M.T.; Wang, D.Z.; Guo, X.S.; Li, L.J.; Peng, X.H. Long-term animal manure application promoted biological binding agents but not soil aggregation in a Vertisol. Soil Till. Res. 2018, 180, 232–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, P.; Hu, W.; Feng, W.; Dai, D. Fermentation conditions of monascus pigments with vinegar wastes. China Brewing 2015, 34, 71–74. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Tisdall, J.M.; Oades, J.M. Organic matter and water-stable aggregates in soils. J. Soil Sci. 1982, 33, 141–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikutta, R.; Mikutta, C.; Kalbitz, K.; Scheel, T.; Kaiser, K.; Jahn, R. Biodegradation of forest floor organic matter bound to minerals via different binding mechanisms. Geochim. Cosmochim. Ac. 2007, 71, 2569–2590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaiser, K.; Guggenberger, G.; Zech, W. Sorption of DOM and DOM fractions to forest soils. Geoderma 1996, 74, 281–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Li, T.; Zheng, Z.; Chen, H.Y.H. Soil aggregate-associated bacterial metabolic activity and community structure in different aged tea plantations. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 654, 1023–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashid, M.I.; Mujawar, L.H.; Shahzad, T.; Almeelbi, T.; Ismail, I.M.; Oves, M. Bacteria and fungi can contribute to nutrients bioavailability and aggregate formation in degraded soils. Microbiol. Res. 2016, 183, 26–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prescott, C.E. Litter decomposition: What controls it and how can we alter it to sequester more carbon in forest soils? Biogeochemistry 2010, 101, 133–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, G.; Badejo, M.A.; Okoh, A.I.; Ishida, F.; Kolawole, G.O.; Hayashi, Y.; Salako, F.K. Effects of residue quality and climate on plant residue decomposition and nutrient release along the transect from humid forest to Sahel of West Africa. Biogeochemistry 2007, 86, 217–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, X.; Wu, J.; Li, J.; Hu, J.; Zhang, L. Effect of exogenous organic carbon on organic carbon and particulate organic carbon of black soil. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2017, 31, 278–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, W.; Bai, Y.; Lv, M.; Tang, Z.; Ding, C.; Gu, C.; Shan, Y.; Dai, Q.; Li, M. Sustained effects of one-time sewage sludge addition on rice yield and heavy metals accumulation in salt-affected mudflat soil. Environ. Sci. Pollut. R. 2021, 28, 7476–7490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamali, M.K.; Kazi, T.G.; Arain, M.B.; Afridi, H.I.; Memon, A.R.; Jalbani, N.; Shah, A. Use of sewage sludge after liming as fertilizer for maize growth. Pedosphere 2008, 18, 203–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kizilkaya, R.; Hepsen Turkay, F.S.; Turkmen, C.; Durmus, M. Vermicompost effects on wheat yield and nutrient contents in soil and plant. Arch. Agron. Soil Sci. 2012, 58, S175–S179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, G.; Zhu, K.; Zhang, P.; Lu, J.; Ma, H. Effect of vinegar residue mulching on soil and wheat yield-related traits in saline soil. J. Anhui Agr. Sci. 2021, 49, 2. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).