From Spatial Characterisation to Prediction Maps of the Naturally Occurring Radioactivity in Groundwaters Intended for Human Consumption of Duero Basin, Castilla y León (Spain)
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
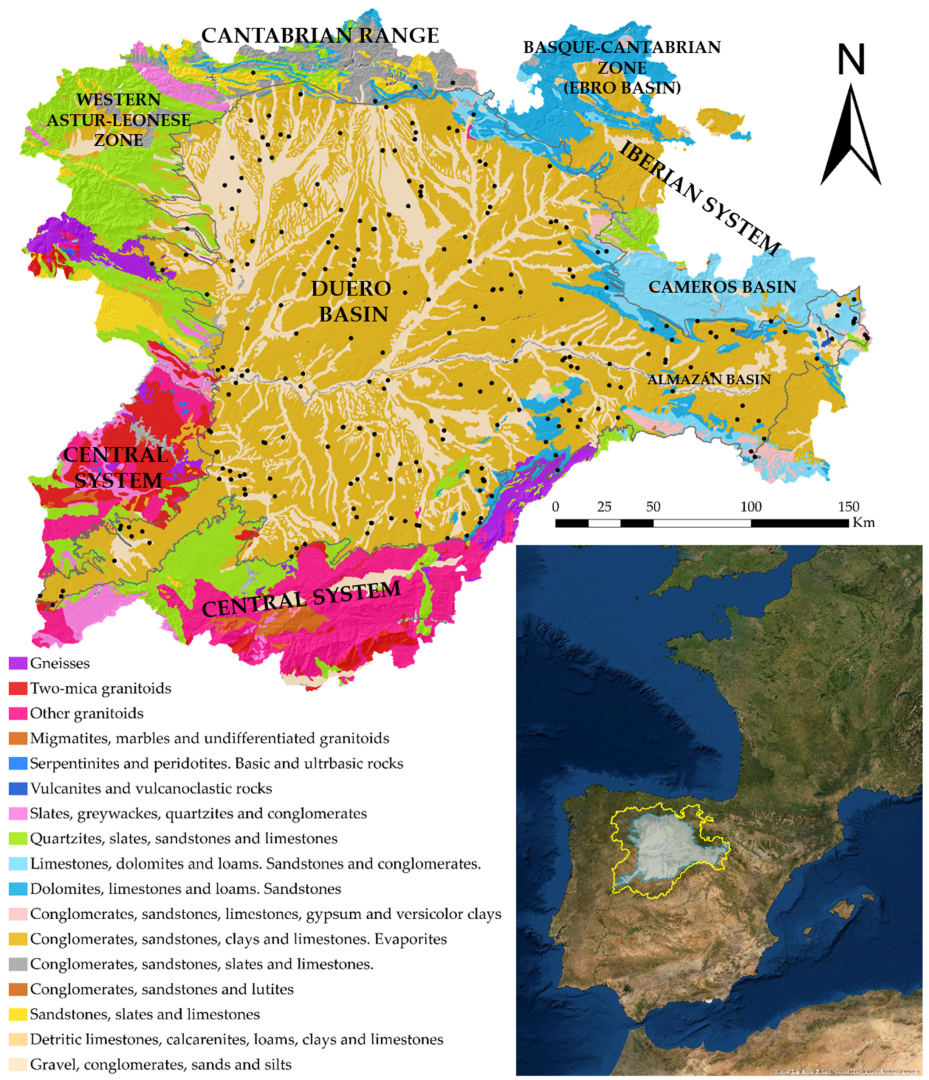
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Groundwater Samples
2.3. Radioactivity Measurements
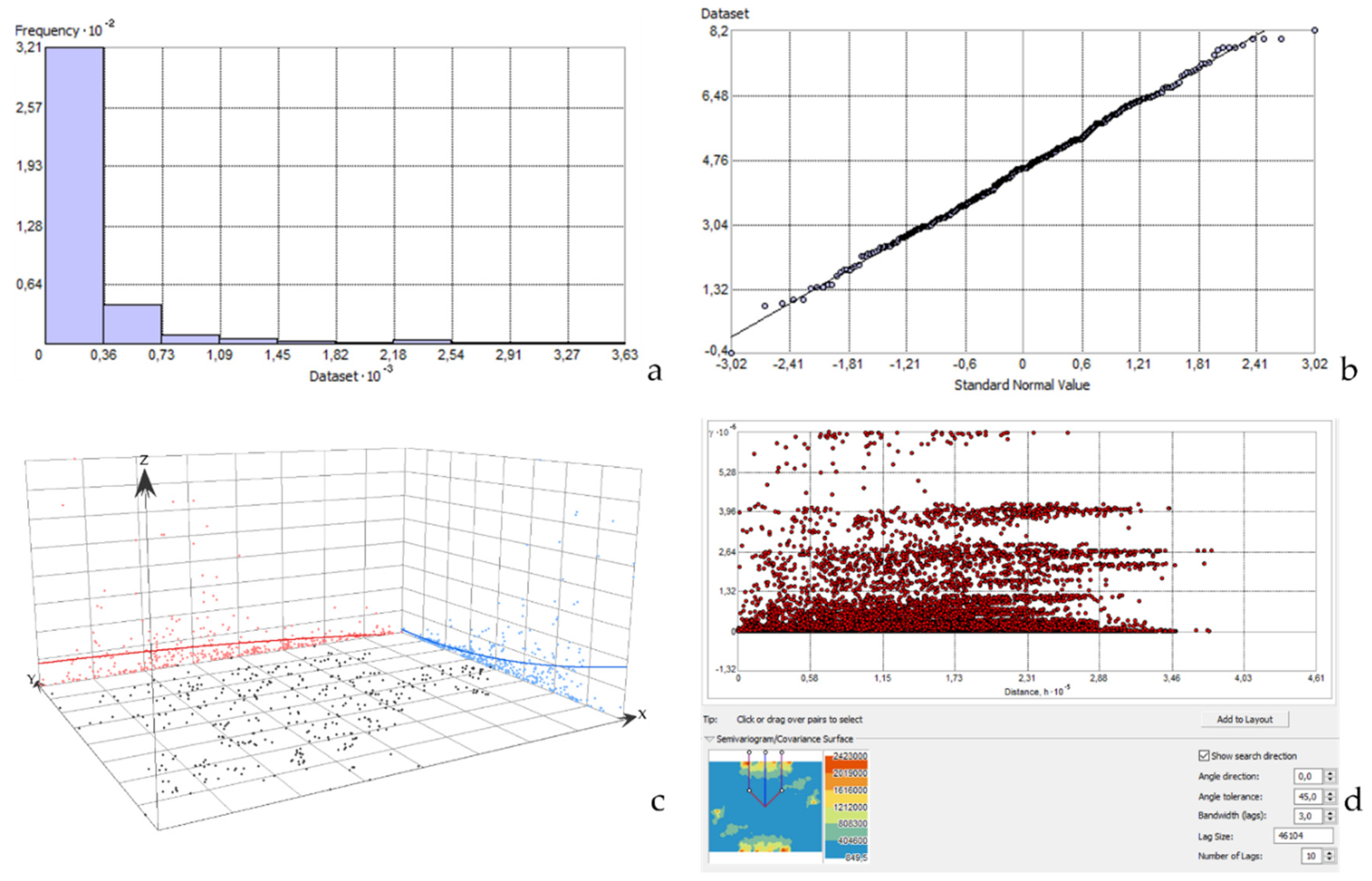
2.4. Statistical Analysis of the Samples
3. Results
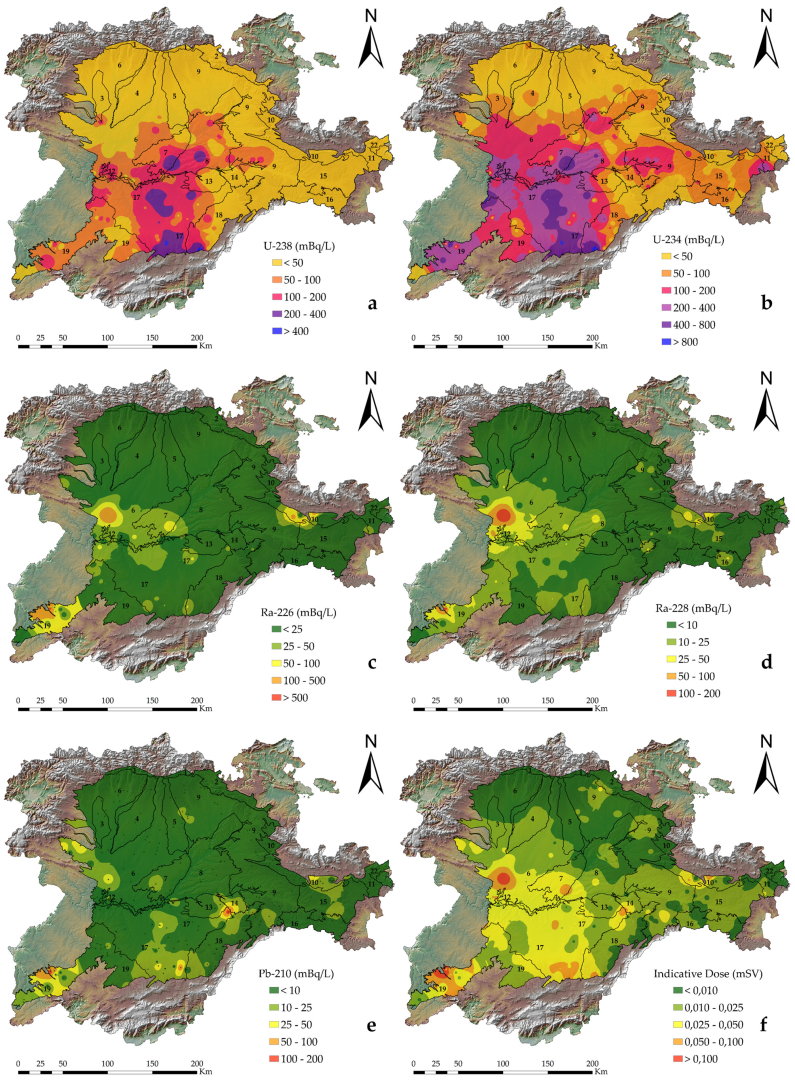
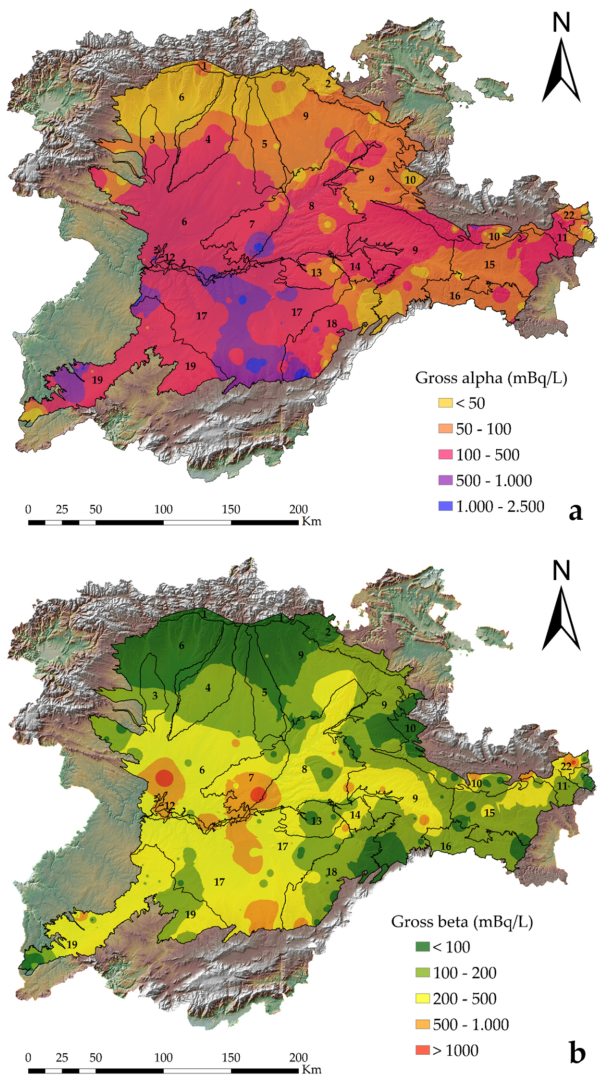
3.1. Radionuclide Analysis and Their Relationship with the Lithological Context and Permeability
- ▪
- In the central to the west of the Zamora province, and in the western area of the Esla-Valderaduey unit, 226Ra content in groundwaters from the marginal area of Tierra de Campos facies was formed by low to medium permeable detritic rocks, and varied from 100 to 250 mBq/L.
- ▪
- Extending through the southern areas of the Ciudad Rodrigo-Salamanca medium and low permeable detritic aquifers there was up to, or exceeding, 500 mBq/L in Gallegos de Argañan (Salamanca).
- ▪
- In carbonate aquifers of the Arlanza-Ucero-Albión unit, in the Cameros Basin, throughout the Lobos river canyon and the surrounding area of Cabrejas de Pinar, the 226Ra concentration values ranged between 100 and 120 mBq/L.
3.2. Radioactivity Parameters Used for Drinking Water Monitoring
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- De Stefano, L.; Martínez-Santos, P.; Villarroya, F.; Chico, D.; Martínez-Cortina, L. Easier said than done? The establishment of baseline groundwater conditions for the implementation of the water framework directive in Spain. Water Resour. Manag. 2013, 27, 2691–2707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos-Francés, F.; Gil-Pacheco, E.; Martínez-Graña, A.; Alonso-Rojo, P.; Ávila-Zarza, C.; García-Sanchez, A. Concentration of uranium in the soils of the west of Spain. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 236, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luque-Espinar, J.A.; Pardo-Igúzquiza, E.; Grima-Olmedo, J.; Grima-Olmedo, C. Multiscale analysis of the spatial variability of heavy metals and organic matter in soils and groundwater in Spain. J. Hydrol. 2018, 561, 348–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Su, Q.; Wang, S.; Gao, Z.; Liu, J. Spatial distribution and health risk assessment of dissolved heavy metals in groundwater of eastern China coastal zone. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 290, 118016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos-Francés, F.; Martínez-Graña, A.; Ávila-Zarza, C.; Criado, M.; Sáncez-Sánchez, Y. Soil quality and evaluation of spatial variability in a semi-arid ecosystem in a region of the southeasterrn Iberian Peninsula. Land 2022, 11, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godoy, J.M.; Godoy, M.L. Natural radioactivity in Brazilian groundwater. J. Environ. Radioact. 2006, 85, 71–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labidi, S.; Mahjoubi, H.; Essafi, F.; Ben Salah, R. Natural radioactivity levels in mineral, therapeutic and spring waters in Tunisia. Radiat. Phys. Chem. 2010, 79, 1196–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akweetelela, A.; Kgabi, N.; Zivuku, M.; Mashauri, D. Environmental radioactivity of groundwater and sediments in the Kuiseb and Okavango-Omatako basin in Namibia. Phys. Chem. Earth Parts A/B/C 2020, 120, 102911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rojas, L.V.; Santos Junior, J.A.; Corcho-Alvarado, J.A.; Amaral, R.S.; Rölin, S.; Milan, M.O.; Herrero, Z.; Francis, K.; Cavalcanti, M.; Santos, J.M.N. Quality and management status of the drinking water supplies in a semiarid region of Northeastern Brazil. J. Environ. Sci. Health Part A 2020, 55, 1247–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Moreno, S.M.; Guerrero, J.M.; Mosqueda, F.; Gázquez, M.J.; Bolívar, J.P. Hydrochemical behaviour of long-lived natural radionuclides in Spanish groundwaters. Catena 2020, 191, 104558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shabana, E.I.; Kinsara, A.A. Radioactivity in the groundwater of a high background radiation area. J. Environ. Radioact. 2014, 137, 181–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sherif, M.I.; Lin, J.; Poghosyan, A.; Abouelmagd, A.; Sultan, M.I.; Sturchio, N.C. Geological and hydrogeochemical controls on radium isotopes in groundwater of the Sinai Peninsula, Egypt. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 613, 877–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stackelberg, P.; Szabo, Z.; Jurgens, B.C. Radium mobility and the age of groundwater in public-drinking-water supplies from the Cambrian-Ordovician aquifer system, north-central USA. Appl. Geochem. 2018, 89, 34–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulrich, S.; Gillow, J.; Roberts, S.; Byer, G.; Sueker, J.; Farris, K. Hydrogeochemical and mineralogical factors influencing uranium in background area groundwater wells: Grants, New Mexico. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2019, 26, 100636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratia, J.M.; Hernando, A.P.; Aguilar, C.; Ballarín, F.B. Role of lithology in the presence of natural radioactivity in drinking water samples from Tarragona province. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 39333–39344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. Management of Radioactivity in Drinking Water; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Council Directive 2013/51/EURATOM of 22 October 2013 Laying down Requirements for the Protection of the Health of the General Public with Regard to Radioactive Substances in Water Intended for Human Consumption. Available online: http://data.europa.eu/eli/dir/2013/51/oj (accessed on 11 February 2022).
- RD 314/2016. Real Decreto 314/2016, de 29 de julio, por el que se modifican el Real Decreto 140/2003, de 7 de febrero, por el que se establecen los criterios sanitarios de la calidad del agua de consumo humano, el Real Decreto 1789/2010, de 30 de diciembre, por el que se regula la explotación y comercialización de aguas minerales, naturales y aguas de manantial envasadas para consumo humano, y el Real Decreto 1799/2010, de 30 de diciembre, por el que se regula el proceso de elaboración y comercialización de aguas preparadas envasadas para el consumo humano. Boletín Oficial Estado 2016, 183, 53106–53126.
- Paul, R.; Brindha, K.; Gowrisankar, G.; Tan, M.L.; Singh, M.K. Identification of hydrogeochemical processes controlling groundwater quality in Tripura, Northeast India using evaluation indices, GIS, and multivariate statistical methods. Environ. Earth Sci. 2019, 78, 470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panneerselvam, B.; Paramasivam, S.K.; Karuppannan, S.; Ravichandran, N.; Selvaraj, P. A GIS-based evaluation of hydrochemical characterisation of groundwater in hard rock region, South Tamil Nadu, India. Arab. J. Geosci. 2020, 13, 837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keshavarzi, A.; Tuffour, H.O.; Brevik, E.C.; Ertunc, G. Spatial variability of soil mineral fractions and bulk density in Northern Ireland: Assessing the influence of topography using different interpolation methods and fractal analysis. Catena 2021, 207, 105646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asikainen, M.; Kahlos, H. Anomalously high concentrations of uranium, radium and radon in water from drilled wells in the Helsinki region. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1979, 43, 1681–1686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banks, D.; Royset, O.; Strand, T.; Skarphagen, H. Redioelement (U, Th, Rn) concentrations in Norwegian bedrock groundwaters. Environ. Geol. 1995, 25, 165–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegel, M.D.; Bryan, C.R. Radioactivity, Geochemistry, and Health. In Treatise on Geochemistry, 2nd ed.; Henrich, D.H., Turekian, K.T., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2014; Volume 11, pp. 191–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szabo, Z.; Stackelberg, P.E.; Cravotta III, C.A. Occurrence and geochemistry of lead-210 and polonium-210 radionuclides in public-drinking-water supplies from principal aquifers of the United States. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 7236–7249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, K.; Huang, Y.; Li, H.; Baoguo, L.; Chen, D.; White, R.E. Spatial variability of shallow groundwater level, electrical conductivity and nitrate concentration, and risk assessment of nitrate contamination in North China Plain. Environ. Int. 2005, 31, 896–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skeppström, K.; Olofsson, B. A prediction method for radon in groundwater using GIS and multivariate statistics. Sci. Total Environ. 2006, 367, 666–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valencia-Ortiz, J.A.; Martínez-Graña, A.M. A neural network model applied to landslide susceptibility analysis. Geomat. Nat. Hazards Risk 2018, 9, 1106–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, G.; Mattevada, S.; O’Bryant, S.E. Comparison of the accuracy of Kriging and IDW interpolations in estimating groundwater arsenic concentrations in Texas. Environ. Res. 2014, 130, 59–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, S.; Sangeetha, B. Assessment of groundwater quality in Madurai city by using geospatial techniques. Groundw. Sustain. Dev. 2020, 10, 100297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.C.; Charlet, J.M.; Poffijn, A. Radon risk mapping in southern Belgium: An application of geostatistical and GIS techniques. Sci. Total Environ. 2001, 272, 203–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobya, Y.; Taşkin, H.; Yeşilkanat, C.M.; Çevik, U.; Karahan, G.; Çakir, B. Radioactivity survey and risk assessment study for drinking water in the Artvin province, Turkey. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2015, 226, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Junta de Castilla y León. Mapa Geológico y Minero de Castilla y León, Escala 1:400.000; SIEMCALSA: Valladolid, Spain, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- IGME. Mapa Geológico de la Peninsula Ibérica, Baleares y Canarias a Escala 1:1.000.000; IGME: Madrid, Spain, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Del Pozo Gómez, M. Mapa Litoestratigráfico, de Permeabilidad e Hidrogeológico βde España Continuo Digital a Escala 1:200.000. Convenio de Colaboración Entre el Ministerio de Medio Ambiente y el Instituto Geológico y Minero de España para la Realización de Trabajos Técnicos en Relación con la Aplicación de la Directiva Marco del Agua en Materia de Agua Subterránea; IGME: Madrid, Spain, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Borrego-Alonso, D.; Quintana, B.; Lozano, J.C. Revisiting methods for the naturally-occurring radioactivity assessment in drinking waters. Appl. Radiat. Isot. 2022. submitted. [Google Scholar]
- García-Talavera, M.; Neder, H.; Daza, M.J.; Quintana, B. Towards a proper modelling of detector and source characteristics in Monte Carlo simulations. Appl. Radiat. Isot. 2000, 52, 777–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daza, M.J.; Quintana, B.; García-Talavera, M.; Fernández, F. Efficiency calibration of an HPGe detector in the 46.54–2000 keV energy range for the measurement of environmental samples. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. A 2001, 470, 520–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quintana, B.; Pedrosa, M.C.; Vázquez-Canelas, L.; Santamaría, R.; Sanjuán, M.A.; Puertas, F. A method for the complete analysis of NORM building materials by y-ray spectrometry using HPGe detectors. Appl. Radiat. Isot. 2018, 134, 470–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quintana, B.; Fernández, F. Gamma-ray spectral analysis with the COSPAJ continuum fitting routine. Appl. Radiat. Isot. 1998, 49, 9–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LNHB. Nucléide-Lara, Library for Gamma and Alpha Emissions. 2020. Available online: http://www.nucleide.org/Laraweb/ (accessed on 11 February 2022).
- Hallstadius, L. A method for the electrodeposition of actinides. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. 1984, 223, 266–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horwitz, E.P.; Dietz, M.L.; Chiarizia, R.; Diamond, H.; Essling, A.M.; Graczyk, D. Separation and preconcentration of uranium from acidic media by extraction chromatography. Anal. Chim. Acta 1998, 266, 25–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flynn, W.W. The determination of low levels of polonium-210 in environmental materials. Anal. Chim. Acta 1968, 43, 221–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Férnandez, P.L.; Gómez, J.; Ródenas, C. Evaluation of uncertainty and detection limits in 210Pb and 210Po measurement in water by alpha spectrometry using 210Po spontaneous deposition onto silver disk. Appl. Radiat. Isot. 2012, 70, 758–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Organization of Health. Guidelines for Drinking Water Quality: 4th ed Incorporating the First Addendum; World Organization of Health: Geneva, Switzerland, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- ESRI. Creating, Editing and Managing Geodatabases for ArcGis Desktop; Virtual Campus, ESRI Educational Service, Environmental Systems Research Institute, Inc.: Redlands, CA, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Heap, A.D. A review of comparative studies of spatial interpolation methods in environmental sciences: Performances and impact factors. Ecol. Inform. 2011, 6, 228–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osmond, J.K.; Cowart, J.B. U-series nuclides as tracers in groundwater hydrology. In Environmental Tracers in Subsurface Hydrology; Cook, P.G., Herczeg, A.L., Eds.; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 2000; pp. 145–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giménez-Forcada, E.; Smedley, P.L. Geological factors controlling occurrence and distribution of arsenic in groundwaters from the southern margin of the Duero Basin, Spain. Environ. Geochem. Health 2014, 36, 1029–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sturchio, N.C.; Banner, J.L.; Binz, C.M.; Heraty, L.B.; Musgrove, M. Radium geochemistry of groundwaters in Palaeozoic carbonate aquifers, midcontinent, USA. Appl. Geochem. 2001, 16, 109–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vengosh, A.; Coyte, R.M.; Podgorski, J.; Johnson, T.M. A critical review on the occurrence and distribution of the uranium- and thorium-decay nuclides and their effects on the quality of groundwater. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 808, 151914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jurgens, B.C.; Parkhurst, D.L.; Belitz, K. Assessing the lead solubility potential of untreated groundwater of the United States. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 3095–3103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]

| Radionuclide | 210Pb | 226Ra | 228Ra | 234U | 238U |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Derived concentration (Bq/L) | 0.2 | 0.5 | 0.2 | 2.8 | 3.0 |
| 234U | 238U | 226Ra | 228Ra | 210Pb | ID | aα | aβ | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ) | 131 | 58.2 | 24.04 | 9.62 | 16.1 | 20.8 | 215 | 228 |
| Median (Me) | 51.4 | 21.8 | 5.30 | 4.10 | 4.84 | 11.6 | 108.0 | 132 |
| Minimum (min) | 0.07 | 0.04 | 0.13 | 0.03 | 0.37 | 0.33 | 0.67 | 1.83 |
| Maximum (max) | 1616 | 705 | 1162 | 196 | 512 | 318 | 2407 | 1547 |
| Standard deviation (S) | 208 | 91.1 | 86.80 | 18.9 | 47.4 | 28.5 | 323.3 | 254 |
| Kurtosis | 20.0 | 16.8 | 101.08 | 58.4 | 64.7 | 53.1 | 20.184 | 9.45 |
| Skewness | 3.57 | 3.25 | 9.16 | 6.59 | 7.14 | 5.72 | 3.64 | 2.35 |
| HU | 238U | 234U | 228Ra | 226Ra | 210Pb | ID | aα | aβ | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| mBq/L | mBq/L | mBq/L | mBq/L | mBq/L | μSv | mBq/L | mBq/L | ||
| 1 | Min–Max | 0.91–36.8 | 1.53–66.8 | 0.36–11.2 | 0.18–11.6 | 0.84–5.9 | 0.48–12.9 | 11.1–91.6 | 17.5–241 |
| Median | 12.4 | 49.4 | 6.5 | 5.5 | 2.8 | 5.5 | 51.6 | 57.0 | |
| 2 | Min–Max | 3.69–7.89 | 3.94–6.61 | 0.39–0.43 | 0.25–0.31 | 0.84–2.16 | 1.03–1.92 | 14.3–19.5 | 21.7–35.0 |
| Median | 5.79 | 5.28 | 0.41 | 0.28 | 1.50 | 1.47 | 16.9 | 28.4 | |
| 3 | Min–Max | 0.72–37.0 | 1.48–91.7 | 2.10–6.26 | 0.92–5.96 | 3.88–8.60 | 4.88–11.12 | 7.12–115 | 30.1–150 |
| Median | 12.5 | 28.3 | 3.82 | 2.95 | 4.39 | 7.39 | 43.1 | 96.7 | |
| 4 | Min–Max | 0.3–42.2 | 0.86–81.3 | 0.49–9.28 | 0.66–24.8 | 1.52–6.56 | 5.03–13.6 | 28.9–117 | 50.4–175 |
| Median | 24.4 | 33.9 | 4.57 | 3.86 | 4.08 | 12.3 | 112 | 134 | |
| 5 | Min–Max | 0.92–37.5 | 1.99–53.1 | 0.42–3.90 | 1.40–3.36 | 1.12–9.76 | 2.04–10.6 | 8.95–107 | 46.0–136.0 |
| Median | 18.6 | 20.7 | 1.2 | 1.95 | 5.3 | 6.57 | 42.7 | 74.4 | |
| 6 | Min–Max | 0.04–169.8 | 0.07–247 | 0.17–196 | 0.41–251 | 1.16–166 | 2.46–172 | 6.68–817 | 20.0–1547 |
| Median | 21.6 | 44.6 | 5.2 | 11.8 | 4.52 | 12.1 | 127 | 134 | |
| 7 | Min–Max | 15.5–400 | 19.9–786 | 2.10–27.2 | 2.41–73.0 | 2.90–15.6 | 6.32–72.3 | 71.8–1174 | 82–1425 |
| Median | 66.2 | 79.4 | 9.92 | 45.2 | 6.36 | 28.5 | 157 | 492 | |
| 8 | Min–Max | 5.60–321 | 7.94–434 | 0.46–33.1 | 1.32–32.0 | 0.96–10.1 | 3.01–29.4 | 17.3–481 | 20.9–909 |
| Median | 29.1 | 49.7 | 3.42 | 7.20 | 2.44 | 6.93 | 93.7 | 160 | |
| 9 | Min–Max | 0.13–146 | 0.46–251 | 0.31–18.8 | 0.17–25.2 | 0.88–24.1 | 2.05–74.5 | 19.8–436 | 29.1–792 |
| Median | 16.7 | 25.3 | 3.14 | 3.96 | 3.98 | 10.16 | 70.8 | 100 | |
| 10 | Min–Max | 1.20–31.3 | 1.05–124 | 0.40–48.1 | 0.54–122 | 0.85–51.8 | 0.89–76.7 | 24.7–672 | 28.0–956 |
| Median | 13.0 | 27.3 | 6.76 | 6.29 | 6.01 | 6.54 | 41.2 | 80.3 | |
| 11 | Min–Max | 4.97–50.3 | 22.1–372 | 1.61–13.1 | 1.48–39.6 | 0.78–11.6 | 5.17–27.1 | 38.5–452 | 52.0–1191 |
| Median | 16.9 | 31.8 | 2.18 | 1.86 | 3.27 | 7.96 | 81.95 | 160 | |
| 12 | Min–Max | 17.6–170 | 108–487 | 3.10–53.0 | 4.58–77.2 | 1.20–15.0 | 13.1–63.4 | 174–681 | 312–819 |
| Median | 152 | 296 | 9.75 | 6.48 | 8.56 | 30.8 | 482 | 600 | |
| 13 | Min–Max | 12.1–18.4 | 14.9–72.3 | 1.85–2.92 | 4.36–7.13 | 1.44–10.7 | 5.95–12.2 | 28.8–65.0 | 37.0–141 |
| Median | 16.6 | 15.8 | 2.09 | 4.86 | 1.72 | 10.4 | 60.5 | 77.0 | |
| 15 | Min–Max | 9.62–22.6 | 40.3–66.8 | 2.42–11.2 | 3.10–11.6 | 1.20–4.80 | 8.17–12.9 | 51.6–91.7 | 57.6–241 |
| Median | 13.9 | 50.7 | 7.05 | 8.58 | 2.58 | 9.37 | 74.0 | 129 | |
| 16 | Min–Max | 9.76–48.6 | 13.2–106 | 0.88–27.1 | 0.48–16.9 | 1.45–24.0 | 2.39–23.1 | 26.5–128 | 37.7–198 |
| Median | 15.9 | 47.0 | 1.61 | 3.29 | 2.43 | 4.89 | 92.6 | 100 | |
| 17 | Min–Max | 5.84–705 | 7.52–1616 | 0.03–34.4 | 1.76–61.2 | 1.08–122 | 6.73–94.9 | 70.8–2407 | 59.5–1325 |
| Median | 94.3 | 237 | 6.28 | 15.1 | 6.32 | 32.4 | 300 | 310 | |
| 18 | Min–Max | 8.24–485 | 11.0–1100 | 0.51–29.7 | 0.70–62.4 | 0.72–23.1 | 1.86–69.0 | 12.5–1847 | 49–781 |
| Median | 18.5 | 45.4 | 3.84 | 2.32 | 3.68 | 8.86 | 74.0 | 112 | |
| 19 | Min–Max | 1.76–199 | 2.07–891 | 0.37–164 | 0.16–738 | 1.76–156 | 8.74–318 | 6.07–1223 | 51.4–1015 |
| Median | 43.6 | 136 | 11.7 | 16.2 | 7.12 | 23.2 | 254 | 189 | |
| 20 | Min–Max | 0.21–48.2 | 0.48–69.4 | 0.26–4.45 | 0.13–17.5 | 1.92–6.08 | 0.33–10.6 | 0.67–158 | 1.83–179 |
| Median | 5.56 | 5.97 | 1.66 | 0.72 | 2.32 | 2.34 | 4.10 | 25.8 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Borrego-Alonso, D.; Martínez-Graña, A.M.; Quintana, B.; Lozano, J.C. From Spatial Characterisation to Prediction Maps of the Naturally Occurring Radioactivity in Groundwaters Intended for Human Consumption of Duero Basin, Castilla y León (Spain). Agronomy 2022, 12, 2059. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12092059
Borrego-Alonso D, Martínez-Graña AM, Quintana B, Lozano JC. From Spatial Characterisation to Prediction Maps of the Naturally Occurring Radioactivity in Groundwaters Intended for Human Consumption of Duero Basin, Castilla y León (Spain). Agronomy. 2022; 12(9):2059. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12092059
Chicago/Turabian StyleBorrego-Alonso, David, Antonio M. Martínez-Graña, Begoña Quintana, and Juan Carlos Lozano. 2022. "From Spatial Characterisation to Prediction Maps of the Naturally Occurring Radioactivity in Groundwaters Intended for Human Consumption of Duero Basin, Castilla y León (Spain)" Agronomy 12, no. 9: 2059. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12092059
APA StyleBorrego-Alonso, D., Martínez-Graña, A. M., Quintana, B., & Lozano, J. C. (2022). From Spatial Characterisation to Prediction Maps of the Naturally Occurring Radioactivity in Groundwaters Intended for Human Consumption of Duero Basin, Castilla y León (Spain). Agronomy, 12(9), 2059. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12092059







