Abstract
Water ionization is an efficient physical water treatment technology, and crop water and nutrient use efficiencies can be improved using ionized water for irrigation. In order to explore the effect of ionized water on soil nitrification and nitrifying microorganisms, we conducted a laboratory soil incubation experiment with the addition of ionized water and ordinary water under different soil water contents (equal to 30%, 60%, 100% and 175% of the field capacity, θFC). During the soil incubation, we analyzed soil inorganic nitrogen transformation, ammonia oxidation gene abundances and nitrifying microbial community structure. The results showed that, no matter adding ordinary water or ionized water, the soil nitrification rate and the abundance of ammonia oxidizing bacteria in the 100%θFC treatment were significantly higher than those in other water conditions, while the abundance of ammonia oxidizing archaea was not affected by the soil water content. With the same soil water content, the nitrification rate of ionized water treatment was stronger than that of the ordinary water treatment. Although the absolute abundance of ammonia-oxidizing microorganisms in ionized water treatment was significantly lower than that of ordinary water (p < 0.05), the relative abundance of some dominant nitrifying microbial genera in the ionized water treatment was significantly higher (p < 0.05). The dominant genera may play a key role in the nitrification process. The results show that ionized water irrigation can significantly promote the nitrification of silt loam soil, especially under 100%θFC conditions, and may regulate soil nitrification by affecting some dominant nitrifying microorganisms. This study provides a theoretical basis for understanding the biological regulation mechanism of ionized water irrigation on soil nutrient transformation and for application of ionized water to field irrigation.
1. Introduction
With rapid economic development and continuous population growth, the water shortage has become a serious global challenge for the survival of humanity [1]. The contradiction between supply and demand of agricultural water resources is getting worse [2]. In order to achieve higher crop yields, large amounts of chemical fertilizers, especially nitrogen fertilizers, are used in agricultural production. However, excessive nitrogen fertilizer application not only causes serious economic loss but also causes a series of ecological and environmental problems, which further restricts the utilization of water resources [3]. The need to increase production versus water scarcity is increasingly prominent in agricultural production [4]. Therefore, in the context of water shortage, finding new ways to improve the efficiency of water and nitrogen fertilizer use is of great significance to the realization of sustainable agricultural development.
Water ionization is a simple, efficient and pollution-free physical water treatment technology, which was first proposed to use in industrial water and oil separation treatment in the United States and then gradually applied in agricultural production irrigation [5]. Studies have shown that ionized treatment could improve the physical and chemical properties of brackish water (i.e., surface tension, dissolved oxygen, pH and conductivity) and that irrigation with it improved soil water and salt transport characteristics and reduced soil salt stress [5]. Wang et al. [6] found that under the same irrigation level (180 mm), compared with ordinary water irrigation, ionized water irrigation significantly increased the growth rate of winter wheat in the Guanzhong Plain; despite its higher water consumption, its grain yield and water use efficiency were significantly increased by 17.8% and 15.1%, respectively; compared with no irrigation, the winter wheat yield of ionized water irrigation increased by 46.9%, which was significantly higher than that of ordinary water irrigation (24.7%). Zhu et al. [7] also found that ionized water irrigation significantly promoted the growth of tomato and improve its water use efficiency. Therefore, ionized water has great application potential in increasing agricultural production.
The transformation processes of soil nitrogen will directly affect the crop nutrient uptake and utilization. Nitrification is a key step in soil nitrogen transformation and determines the nitrogen availability to crops [8]. The ammonia oxidation process is the first and rate-limiting step in nitrification, which oxidizes ammonia to nitrite [9]. Ammonia-oxidizing microorganisms are the main players in this process, including ammonia-oxidizing bacteria (AOB) and ammonia-oxidizing archaea (AOA) [10]. Ammonia-oxidizing bacteria have long been considered to be the most important contributors to the aerobic ammonia oxidation process. In recent years, a large number of studies have found that ammonia-oxidizing archaea are abundant in soil [11] and play an important role in the ammonia oxidation process in different environments [12]. Changes in the number, diversity and community structure of ammonia-oxidizing microorganisms can affect the rate of soil nitrification [13]. Nitrifying microorganisms can oxidize ammonium produced by organic nitrogen mineralization or derived from fertilizers to nitrite/nitrate in soil, thereby reducing the loss of ammonia volatilization. However, the nitrate produced is easily lost by leaching or denitrification and has a negative impact on the water body and atmospheric environment [14]. The soil in the Xinjiang cotton-producing area in China is mostly weakly alkaline, and the area has strong evaporation and scarce rainfall all year round. Hence, ammonia volatilization is usually the main reason for the low nitrogen use efficiency in this area. Therefore, it is of great significance to study the effect of ionized water on the nitrification of soil in Xinjiang for the application of this technology.
In this study, we hoped to answer the following questions: (1) whether the addition of ionized water affected the soil nitrification rate, (2) whether ionized water affected soil nitrification by affecting the abundance of ammonia-oxidizing microbial functional genes, (3) whether ionized water affected soil nitrification by affecting the nitrifying microbial community structure and (4) whether the effects of ionized water on soil nitrification were consistent under different soil moisture conditions.
To answer the above questions, the silt loam soil from the cotton production area of Xinjiang was incubated with the addition of ionized water and ordinary water under different soil water contents (equal to 30%, 60%, 100% and 175% of the field capacity, θFC) in the laboratory. Soil samples were taken during incubation, and inorganic nitrogen concentration, ammonia oxidation gene abundances and the nitrifying microbial community structure were analyzed to explore the effects of ionized water on soil nitrification and nitrifying microorganisms. This study initially discussed the effect of ionized water irrigation on soil nitrification from the microbial level and provided an important theoretical basis for the development of efficient agricultural water utilization technology.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Soil Sampling
The soil was sampled from the Key Irrigation Experimental Station of Bazhou Xinjiang Bayingoleng Mongolian Autonomous Prefecture (86°10′ E, 41°35′ N) in 2019. The experimental station is in the flood plain belt of the Kongque River on the edge of the Tarim Basin and has an altitude of 901 m above the mean sea level. It has a temperate continental desert climate with sparse rainfall and strong evaporation. The rainy days are frequent in July and August, and the mean annual precipitation is 58 mm [15]. The mean annual temperature is 11.2 °C, and the annual maximum evaporation is 2788.2 mm. The soil samples were taken from the 0–20-cm cultivated layer of cotton farmland. The soil type was silt loam, which had 4.20% clay, 54.40% silt and 41.40% sand, with the bulk density of 1.56 g/cm3, the pH of 8.7, the organic carbon content of 3.4 g/kg, the total nitrogen content of 0.5 g/kg, the total carbon content of 15.7 g/kg, the ammonium nitrogen content of 3.52 mg/kg and the nitrate nitrogen content of 40 mg/kg. The field water holding capacity was 25% (volumetric moisture content). Plant roots, gravel and other debris were removed from the collected fresh soil; soil samples were mixed and air-dried thoroughly, and passed through a 2-mm sieve for subsequent experiments.
2.2. Experimental Design
The preparation of ionized water: Ionized water was made via the ionized treatment system installed on the irrigation pipes, which includes ionized processor, wire and ground electrode [6]. The ionized processor was produced by Korea Yameihua (Beijing, China) Environmental Technology Development Corporation. The model was W600DELF. The ionizer was equipped with a ground electrode with a resistance of 5 Ω, connected to the wire and plugged into the ground. When the water flew through the ionization processor, the ground electrode guided part of the electrons in the water into the ground, and the ions left in the water was dominated by positive ones, thereby making ionized water.
The laboratory soil incubation experiment was carried out at Xi’an University of Technology. The types of irrigation water used in the experiment included ordinary water (CK) and ionized water (DE). A soil sample equivalent to 200 g dry weight (dw) of soil from the prepared test soil was put into a 500-mL glass culture flask. Ammonium chloride was added into the soil to reach an N concentration of 200 mg N/kg dw soil. After that, ordinary water or ionized water was employed to adjust the soil moisture content to 30%, 60%, 100% and 175% (saturated moisture content) of the field capacity (θFC). Table 1 shows the eight treatments in total, and each treatment had three replicates. Next, all culture flasks were covered with plastic film to avoid the rapid evaporation of soil moisture, several small holes were pricked to ensure ventilation and the flasks were placed in an incubator at 20 ± 1 °C without light. Water was added during the incubation period to maintain the designed soil moisture content. Afterwards, 10 g soil samples were taken from each culture flask on days 0, 1, 2, 4, 6, 8, 12, 16 and 20 and stored at −20 °C for further analysis. For each sample, we used 8 g soil to determine the ammonium nitrogen (NH4+-N) and nitrate nitrogen (NO3−-N), and the rest was used for the microbial analysis.

Table 1.
Experimental treatment designs.
2.3. Measurements and Analysis Methods
2.3.1. Determination of Soil Mineral Nitrogen Concentration
Soil samples collected at each sampling time were analyzed uniformly to reduce the technical errors in detection. Soil samples weighting 8.00 g stored at −20 °C were added into a 100 mL bottle, and 40 mL of 2 M KCl solution was poured into each bottle to reach a soil–water ratio of 1:5. After shaking and extracting for 1 h at 180 r/min, the soil slurry was filtered, and the filtration was placed into an automatic discontinuous chemical analyzer (Smartchem450, AMS Alliance, Frépillon, France) to determine the contents of NH4+-N and NO3−-N [16].
2.3.2. Soil DNA Extraction
Soil total DNA was extracted from samples obtained on days 0, 6 and 16. FastDNA® SPIN Kit for Soil (MP Biomedicals, Santa Ana, CA, USA) was used according to the manufacturer’s instructions. The concentrations of the extracted DNA were determined by Qubit 3.0 Fluorometer (Invitrogen, Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA). DNA samples remain stored at −20 °C until gene quantification and sequence analysis.
2.3.3. Quantification of the Bacterial-amoA Gene and Archaeal-amoA Gene
Bacterial-amoA gene and archaeal-amoA gene as biomarkers were used to quantify the abundance of ammonia-oxidizing bacteria and ammonia-oxidizing archaea, respectively. The primers and the amplification procedures used in this study are listed in Table 2. Gene quantitation was performed with the StepOnePlus™ Real-Time PCR system (Applied Biosystems, Foster City, CA, USA). Each 25-μL reaction mixture was composed of 1 μL of DNA template, 0.5 μL of each primer, 0.5 μL of ROX Reference Dye (TaKaRa Bio, Otsu, Japan), 12.5 μL of SYBR Premix Ex Taq™ (TaKaRa Bio) and 10 μL of sterile ddH2O. With a negative control set in the experiment, the plasmid DNA of each target gene with a known copy number was diluted in a gradient to obtain a standard curve. Each sample was repeated three times.

Table 2.
Primers and amplification procedures used for qPCR in this study.
2.3.4. High-Throughput Sequencing and Analysis of Nitrifying Microorganism Community
The bacterial 16S rRNA genes of V3 and V4 were amplified with the primers bac-341F (5′-CCT AYG GGR BGC ASC AG-3′) and bac-806R (5′-GGA CTACNVG GGT WTC TAA T-3′) during high-throughput sequencing. After purification, quantification and pooling, they were sequenced on an Illumina HiSeq PE250 platform (Novogene Bioinformatics Institute, Beijing, China). All raw sequence data were filtered via QIIME quality filters (http://www.qiime.org, accessed on: 5 January 2020), thus removing the low-quality sequence reads. The UCHIME algorithm was used to define the operational taxonomic units (OTUs) (http://www.drive5.com/usearch/manual/uchime_algo.html, accessed on: 8 January 2020) at 97% similarity. Each OTU was classified taxonomically based on the Silva database (http://www.arb-silva.de, accessed on: 15 January 2020). According to the results of the species annotations, OTUs related to nitrification were manually selected to analyze the community of nitrifying microorganism.
2.4. Data Processing and Statistical Analysis
For a quantitative description of the dynamic changes of the NH4+-N content over time and further speculation on the effects of different treatments on soil nitrification, Equation (1) was used to combine the experimental data, and the integral was expressed as an “S” curve [19].
Nt refers to the instantaneous residual amount of NH4+-N during the incubation period, mg/kg; S0 is the amount of NH4+-N addition (known), mg/kg; S represents the progressive value of NH4+-N consumption, mg/kg; t is the incubation time, day; e is the natural constant and a and b are the model parameters.
Equation (1) was derived to obtain the NH4+-N daily consumption rate, as in Equation (2). Equations (3)–(5) represent the initial NH4+-N consumption rate (V0), the maximum NH4+-N consumption rate (Vmax) and the time corresponding to the maximum consumption rate (TVmax) [20].
The data were sorted by Microsoft Excel 2016 software (Microsoft, Washington, DC, USA, https://www.microsoft.com, accessed on 5 January 2020), while the regression analysis was performed by MATLAB R2017a. Meanwhile, we used one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) in SPSS v.25.0 (IBM, Inc., Chicago, IL, USA) to analyze the significance of the difference.
3. Results
3.1. Dynamic Characteristics of Inorganic Nitrogen
The effect of ionized water (DE) on the change of the soil inorganic nitrogen content during soil incubation was different under different soil moisture conditions (Figure 1). With the progress of incubation, the content of NH4+-N in each treatment soil decreased gradually, and the content of NO3−-N increased gradually. Under the condition of 30%θFC, there was no significant difference in the soil NH4+-N and NO3−-N contents between the CK1 and DE1 treatments. When incubated under a 60%θFC condition for 12 days, the soil NH4+-N content in the DE2 treatment was significantly higher than that in the CK2 treatment (p < 0.05), while the soil NO3−-N content in the DE2 treatment was significantly lower than that in the CK2 treatment (p < 0.05). After incubating for 6 days under the 100%θFC condition, the soil NH4+-N and NO3−-N in the DE3 treatment were significantly lower than those in the CK3 treatment. After incubating for 4 days under the 175%θFC condition, the soil NH4+-N content in the DE4 treatment was significantly lower than that in the CK4 treatment (p < 0.05), but the soil NO3−-N content in the DE4 treatment was significantly higher than that in the CK4 treatment. Therefore, the DE treatment could significantly affect the dynamic changes of soil inorganic nitrogen during cultivation. With the increase of the soil moisture content, ionized water can significantly accelerate the consumption of soil NH4+-N and promote the generation of NO3−-N.
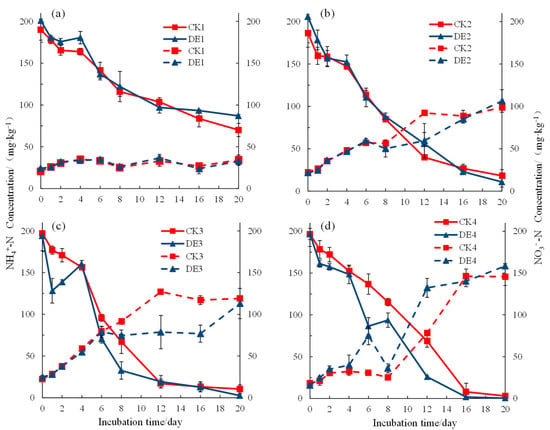
Figure 1.
Changes of the soil NH4+-N and NO3−-N concentrations under different treatments. Note: θFC, soil water content at field capacity; CK, ordinary water and DE, ionized water, (a) 30%θFC, (b) 60%θFC, (c) 100%θFC, (d) 175%θFC.
3.2. Quantitative Characterization of the Dynamic Changes of the Soil NH4+-N Content
The regression equation of the soil NH4+-N content and incubation time t under each treatment was calculated by Equation (1), and the model characteristic values are shown in Table 3. Figure 2 shows the soil NH4+-N daily consumption rate. The overall trends of the daily consumption rate of NH4+-N were relatively consistent under different treatments during incubation. There was always an initial consumption rate, which first increases to the maximum rate and then decreased before finally approaching 0. However, the characteristic values of NH4+-N dynamics under various treatments were different.

Table 3.
Characteristic values of the fitting model of the soil NH4+-N consumption in different treatments.
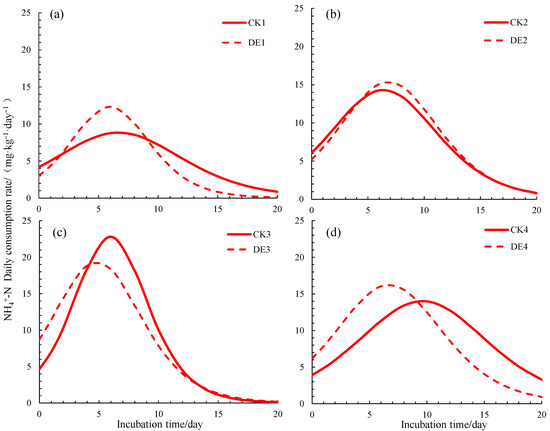
Figure 2.
Daily consumption rate of soil NH4+-N under different treatments. Note: θFC, soil field capacity; CK, ordinary water and DE, ionized water, (a) 30%θFC, (b) 60%θFC, (c) 100%θFC, (d) 175%θFC. Numbers in the treatment labels: 1, 30%θFC; 2, 60%θFC; 3, 100%θFC and 4, 175%θFC.
With 30%θFC, the DE1 treatment had a lower V0, and then, the NH4+-N consumption rate increased significantly, reaching Vmax (12.32 mg/(kg·day)) on day 6, which was 1.4 times that of the CK1 treatment (p < 0.05). With 60%θFC, the soil NH4+-N consumption rate of the DE2 treatment was higher than that of the CK2 treatment in the middle stage of incubation (6~12 days). With the increase of the moisture content, with 100%θFC, the soil NH4+-N consumption rate of the DE3 treatment was significantly higher than that in CK3 (p < 0.05) at the initial stage of cultivation (0~4 days), reaching a maximum value of 19.36 mg/(kg day); meanwhile, the TVmax of DE3 was shortened by 20% compared with the CK3 treatment. With 175%θFC, the soil V0 in the DE4 treatment was 1.58 times that of CK4; before 10 days, the soil NH4+-N consumption rate of DE4 was significantly higher than that of CK4 and reached a maximum value of 16.24 mg/(kg day) at 6.7 days, which increased by 16% compared with the CK4 treatment. Therefore, it can be seen that the soil water content significantly affects the NH4+-N consumption characteristics. Under the condition of 100%θFC, the soil NH4+-N consumption rates of the CK3 and DE3 treatments both reached the maximum value in a short time, and soil nitrification was inhibited if the soil water content was too high or too low. However, ionized water could significantly reduce the difference caused by different water contents and increase the stability of the soil nitrification process.
3.3. Variation Characteristics of the Ammonia-Oxidizing Microorganism Abundance
Real-time quantitative PCR was used to analyze the copy number of the ammonia monooxygenase gene (amoA) of soil ammonia-oxidizing bacteria (AOB) and ammonia-oxidizing archaea (AOA) on day 0, day 6 and day 16 of the soil incubation (Figure 3). With the incubation time, the abundance of the ammonia-oxidizing bacteria in each treatment increased, while the abundance of the ammonia-oxidizing archaea decreased. Regardless of the difference in the water content or the addition of ionized water, ammonia-oxidizing bacteria were more sensitive to soil moisture changes than ammonia-oxidizing archaea; especially, the addition of ionized water would reduce the abundance of ammonia-oxidizing bacteria to a certain extent.
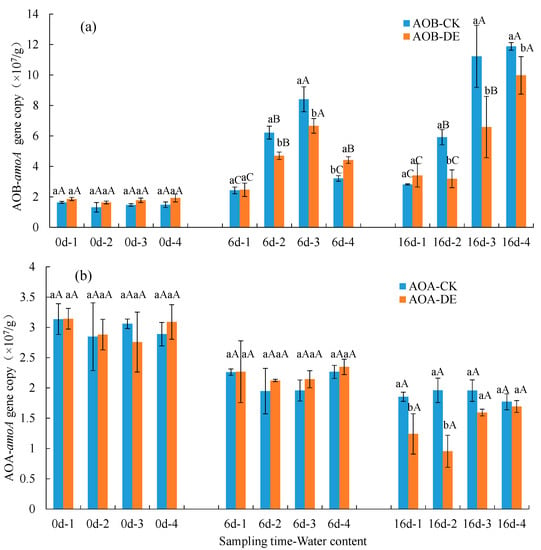
Figure 3.
Characteristics of the amoA gene abundance of ammonia-oxidizing microorganisms under different treatments. Note: (a) ammonia-oxidizing bacteria (AOB), (b) ammonia-oxidizing archaea (AOA). Different lowercase letters above the columns indicate significant differences under different water types with the same moisture content (p < 0.05), and different capital letters above the columns indicate significant differences under the same water type with different moisture contents (p < 0.05). θFC, soil water content at field capacity; CK, ordinary water and DE, ionized water. In the treatment labels: d, day; 1, 30%θFC; 2, 60%θFC; 3, 100%θFC and 4, 175%θFC.
Figure 3a shows the abundance of the bacterial-amoA gene in ammonia-oxidizing bacteria. At the beginning of the incubation (day 0), there was no significant difference in bacterial-amoA gene abundance among the treatments. On day 6, there was no significant difference between CK1 and DE1 under 30%θFC conditions; under 60%θFC and 100%θFC conditions, the abundance of bacterial-amoA gene in the soil of the DE treatment was significantly lower than that of the CK treatment (p < 0.05): DE2 decreased by 24.47% compared with CK2, and DE3 decreased by 20.82% compared with CK3; however, under the condition of 175%θFC, the abundance of the bacterial-amoA gene in the DE4 treatment was significantly higher than that in the CK4 treatment (p < 0.05). On day 16, under the condition of 30%θFC, there was still no significant difference in the soil bacterial-amoA gene abundance between the CK1 and DE1 treatments, but under the other water conditions, the soil bacterial-amoA gene abundances of the DE treatment were significantly lower than those of the CK treatment (p < 0.05). Overall, under the same water type treatment, with the extension of the culture time, the abundance of the bacterial-amoA gene showed a certain increasing trend, but it was also affected by the soil water content. When cultured for 6 days, the abundance of the bacterial-amoA gene increased with the increase of the soil water content, and the highest abundance appeared under the 100%θFC treatment. With a further increase of the water content to 175%θFC, the abundance of the bacterial-amoA gene decreased. When cultured for 16 days, the inhibitory effect of the bacterial-amoA gene abundance was weakened under the 175%θFC condition, and the bacterial-amoA gene abundance showed a trend of increasing with the increase of the water content.
Figure 3b shows the abundance of amoA genes in ammonia-oxidizing archaea. There was no significant difference in the abundance of archaeal-amoA among the treatments at day 0 and day 6. At day 16, only under the 30%θFC and 60%θFC treatments, the abundances of the archaeal-amoA gene in the soil of the DE treatments were significantly lower than that of the CK treatments (p < 0.05).
3.4. Changes in the Community Structure of Nitrifying Microorganisms
Figure 4 shows the changes in the relative abundance of the soil-nitrifying microorganisms. According to the high-throughput sequencing results, at the family level, the nitrifying microbial community consisted of Nitrosomonadaceae, Thermomicrobiaceae, Nitrospiraceae, Nitrososphaeraceae and unidentified Gammaproteobacteria. Among them, Nitrososphaeraceae had a higher relative abundance. Nitrososphaeraceae accounted for 19.67–40.00% of the total nitrifying microorganisms in all CK treatments and accounted for 36.40–61.55% of the total nitrifying microorganisms in all DE treatments. The relative abundance of some OTUs increased significantly with the culture time, such as OTU6893, OTU37 and OTU70 belonging to Nitrosomonadaceae; OTU2 belonging to Thermomicrobiaceae and all OTUs belonging to the unidentified Gammaproteobacteria and Nitrososphaeraceae.
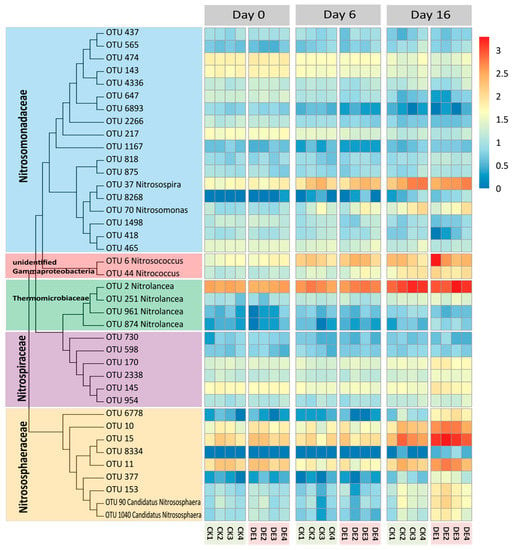
Figure 4.
Relative changes in the nitrifying microbial abundance during soil incubation. Note: CK, ordinary water, and DE, ionized water. Numbers in the treatment labels: 1, 30%θFC; 2, 60%θFC; 3, 100%θFC and 4, 175%θFC.
OTUs with a relative abundance > 5% in the nitrifying microorganisms were defined as dominant OTUs. By sorting the maximum relative abundances of the dominant OTUs in the samples, we selected six OTUs for further analysis. There was OTU2 belonging to Thermomicrobiaceae (the maximum relative abundance was 44.1%); OTU15 (34.1%), OTU11 (14.4%) and OTU10 (10.8%) belonging to Nitrososphaeraceae; OTU6 belonging to unidentified Gammaproteobacteria (31.1%) and OTU37 belonging to Nitrosomonadaceae (19.7%). Figure 5 shows the differences in the relative abundance of these six OTUs among the different treatments on day 16 of the incubation. Among these dominant OTUs, the DE treatment significantly increased the relative abundances of OTU15 and OTU10 under each soil water condition compared with the CK treatment. The DE treatment increased the relative abundance of OTU6 at 30%θFC and increased the relative abundance of OTU11 at 100%θFC. In contrast, the relative abundances of OTU2 and OTU37 were significantly reduced in the DE treatment. It shows that, although ionized water reduces the overall abundance of ammonia-oxidizing microorganisms, it obviously promotes the growth of some dominant nitrifying microorganisms and enhances their nitrification potential.
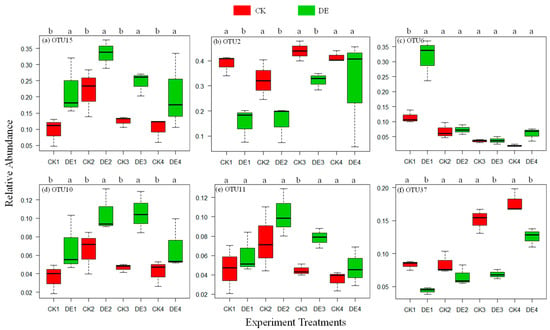
Figure 5.
Relative abundance of the dominant nitrifying microorganisms in different soil treatments on day 16 of incubation. Note: (a) OTU15, (b) OTU2, (c) OTU6, (d) OTU10, (e) OTU11, (f) OTU37. CK, ordinary water; DE, ionized water, θFC, soil water content at field capacity. Numbers in the treatment labels: 1, 30%θFC; 2, 60%θFC; 3, 100%θFC and 4, 175%θFC. Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences between different water treatments with the same moisture content (p < 0.05).
4. Discussion
In this study, the biological mechanism of the effect of ionized water on soil nitrification under different soil moisture conditions (30%WHC, 60%WHC, 100%WHC and 175%WHC) was elucidated based on the laboratory soil incubation experiment.
4.1. The Effect of Soil Moisture Condition on Nitrification and Ammonia-Oxidizing Microorganisms
There are many types of functional microorganisms involved during the nitrogen transformation in the soil. Among them, ammonia-oxidizing bacteria (AOB) and ammonia-oxidizing archaea (AOA) are the key microorganisms, which can regulate the transport and existence of nitrogen in the soil, thus affecting the efficient use of nitrogen fertilizer [21]. Ammonia-oxidizing microorganisms respond to many environmental factors [22], such as pH [23], temperature [24], NH3 molecular concentration [25] and moisture [26,27]. Among them, moisture is an important factor to its growth [28]. In this study, soil AOB was more sensitive to the changes in water conditions than AOA. Water addition stimulated the growth of AOB more obviously during the soil incubation, while the abundance of AOA had little effect on the soil water conditions. Ke and Lu [29] also found that the amount of AOB in the soil increased significantly after the submerged soil incubation of paddy soils sampled from Beijing and Hangzhou with different amounts of nitrogen input, but there was no significant change in the abundances of AOA. Gleeson et al. [30] investigated the effects of different water levels on the nitrification of semi-arid soils in Western Australia and found that the abundance of the bacterial-amoA gene in the soil first increased and then decreased with the increase of the soil moisture content. However, according to some other studies [31], AOA in forest soil was more sensitive to water, while AOB was less affected by water conditions but more sensitive to nitrogen application. This was also concluded by Bustamante et al. [32]. In summary, different groups of ammonia-oxidizing microorganisms have different requirements for water conditions and are closely related to soil physical and chemical properties.
The optimal water conditions for soil nitrification vary with the soil types. Most laboratory simulations [16,33] and field experiments [34] have shown that soil nitrification was most active with the moisture conditions at 50–60% of the field capacity (θFC). The results of this study showed that, under 100%θFC, soil NH4+-N was rapidly consumed and NO3−-N was rapidly accumulated, indicating that this water content could not only promote substrate diffusion and oxygen diffusion but could also meet the metabolic activity of ammonia-oxidizing microorganisms and promote AOB growth and reproduction; especially in the early and middle stages of soil incubation, it promoted the occurrence of soil nitrification.
4.2. Effect of Ionized Water on Nitrification and Ammonia-Oxidizing Microorganisms
This study showed that, with the extension of the incubation time, the abundance of the AOA in each treatment gradually decreased while the abundance of the AOB gradually increased, and the AOB/AOA value gradually increased. Therefore, AOB dominated the ammonia-oxidizing microorganisms in the soil of Xinjiang cotton fields. The pH value of the test soil in this study was about 8.7, which was relatively alkaline. This is consistent with the results of research conducted by Li et al. [35], finding that the abundance of AOB in alkaline sandy soil in Xinjiang was higher than that of AOA. However, some studies also found that AOA might be the dominant microbial population for soil nitrification in Xinjiang under saline irrigation conditions [36]. Possibly due to the freshwater irrigation in this study, AOB could grow better without salinity stress. Numerous studies have shown that AOA was more likely to survive in acidic soil (4.9–7.5) or under conditions with environmental stresses [37,38], while AOB preferred to live in alkaline soil (8~8.7) for survival [39,40]. This is because the oxidation of NH3 is the only energy source for the growth of ammonia-oxidizing microorganisms. In alkaline soils, the concentration of NH3 that can be dissociated from ammonium is higher, which is more conducive to the growth of AOB, with a relatively low affinity for NH3 [18].
This study found that ionized water would reduce the amount of soil AOA and AOB, but the change characteristics of the inorganic nitrogen content showed that ionized water could instead promote the occurrence of soil nitrification; that is, soil nitrification was not inhibited by the reduction in the number of ammonia-oxidizing microorganisms. Wang et al. [41] pointed out that the surface tension of water after ionization treatment was significantly reduced, the dissolved oxygen was significantly increased and the activity of the water molecules was further improved. Therefore, ionized water irrigation may enhance the functional activity of nitrifying microorganisms and improve their water and nitrogen utilization efficiency. Further analysis of the community structure of nitrifying microorganisms found that, although DE treatment reduced the number of AOA and AOB in the soil, the relative abundance of ammonia-oxidizing archaea Nitrososphaeraceae was significantly greater than that of CK, especially OTU15 and OTU10. There is a close relationship between the community structure of nitrifying microorganisms and the soil environment. We speculated that the soil environment after irrigating with ionized water could be changed in a direction that was favorable to the dominant groups, which was beneficial to their growth and function, and made them have a stronger competitive advantage over other groups.
4.3. Evaluation of the Effect of Ionized Water
Many studies have focused on the application of ionized water in agricultural production, but there is still little research on its effect on soil nitrogen transformation, especially on nitrification and ammonia-oxidizing microorganisms. Nitrification is a key process of the nitrogen cycle in farmland [42]. In this study, we found that ionized water irrigation could accelerate the soil nitrification rate and promote soil ammonium nitrogen transformation to nitrate nitrogen by changing the community structure of nitrifying microorganisms and enhancing the physiological activity of some key species. The soil used in this study was taken from a cotton field. Cotton usually prefers to absorb nitrate to ammonium [43]. After nitrate enters the cotton root system, it is transported, reduced and metabolized into amino acids and, finally, used by cotton plants [44]. Due to the dry climate in Xinjiang, China, the evaporation is much larger than the precipitation, and the leaching of NO3−-N is almost negligible. Therefore, after the application of urea or ammonium nitrogen fertilizer, irrigation ionized water can rapidly oxidize ammonium to nitrate nitrogen. This can increase the effective use of nitrogen by plants, thereby improving the nitrogen utilization.
At present, the research on the transformation of soil nitrogen by ionized water irrigation has just started, and this paper makes a preliminary investigation on it. The findings of this study show that there are still many scientific problems that need to be solved urgently in the research on the process of soil nitrogen transformation affected by ionized water. First of all, the number of soil microorganisms can reflect the soil quality and health status. Although ionized water irrigation promoted the nitrification and increased cotton yield [45], it reduced the number of soil microorganisms to a certain extent. Is this conducive to the improvement of soil fertility? Second, ionized water irrigation affected the relative abundance and community structure of the dominant species in the nitrifying microorganisms, which could explain the increase in the soil nitrification rate to a certain extent. However, how the dominant species adapted to the soil environment under the ionized water treatment is still unclear. In addition, further pot experiments and field experiments are needed to clarify the interaction and influence mechanisms among the crops, soil and microorganisms under ionized water irrigation.
5. Conclusions
This study showed that, compared with ordinary water, ionized water irrigation was beneficial to promote soil nitrification and accelerated the conversion process of soil ammonium to nitrate. Although ionized water decreased the abundance of ammonia-oxidizing microorganisms, especially ammonia-oxidizing bacteria, it increased the relative abundance and functional activity of some dominant nitrifying microorganisms. This study supplemented the possible reasons why ionized water irrigation promoted the crop yield in field experiments from the biological mechanism of the soil nutrient transformation, which is helpful for deepening the understanding and application of ionized water irrigation technology.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization and methodology, Z.Q., M.L. and Q.W.; formal analysis, Z.Q. and M.L.; investigation, Z.Q., M.L., Y.S., Y.W. and J.L.; data curation, J.L.; writing—original draft preparation, Z.Q. and M.L.; writing—review and editing, Q.W. and funding acquisition, Z.Q., Y.S. and Q.W. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 41830754, 41977043, 41907010 and 41501258) and the Project funded by the China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (2019M653708).
Data Availability Statement
The data are presented in the article.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Islam, M.R.; Eneji, A.E.; Ren, C.; Hu, Y.G.; Xue, X.Z. Oat-based crop-ping system for sustainable agricultural development in arid regions of northern China. Agric. Biotechnol. Ecol. 2010, 3, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, T.; Dong, Z.; Zhang, C.; Ali, S.; Han, Q.; Zhang, F.; Jia, Z.; Zhang, P.; Ren, X. Effects of rainwater harvesting planting combined with deficiency irrigation on soil water use efficiency and winter wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) yield in a semiarid area. Field Crops Res. 2018, 218, 231–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Davidson, E.A.; Mauzerall, D.L.; Searchinger, T.D.; Dumas, P.; Shen, Y. Managing nitrogen for sustainable development. Nature 2015, 528, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, X.X.; Zhang, M.; Li, J.P.; Liu, Z.Q.; Zhao, Z.G.; Zhang, Y.H.; Zhou, S.L.; Wang, Z.M. Improving water use efficiency and grain yield of winter wheat by optimizing irrigations in the North China Plain. Field Crop Res. 2018, 221, 219–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.J.; Xu, Z.Y.; Shan, Y.Y.; Zhang, J.H. Effect of salinity of de-electronic brackish water on characteristics of water and salt movement in soil. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2018, 34, 125–132. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.H.; Zhao, G.Q.; Wang, Q.J.; Wang, L. Effects of irrigation with de-electronic water on growth and water use of winter wheat. J. Agro-Environ. Sci. 2020, 39, 953–963. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, M.; Li, B. Effects of irrigation with de-electronic water on yield, quality and water use efficiency of tomato grown in greenhouse. Water Sav. Irrig. 2020, 11, 20–24. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Yao, H.; Gao, Y.; Nicol, G.W.; Campbell, C.D.; Singh, B.K. Links between ammonia oxidizer community structure, abundance, and nitrification potential in acidic soils. Appl. Environ. Microb. 2011, 77, 4618–4625. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kowalchuk, G. Ammonia-oxidizing bacteria: A model for molecular microbial ecology. Annu Rev. Microbio. 2001, 55, 485–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, Y.C.; Lu, L.; Wang, B.Z.; Lin, X.G.; Zhu, J.; Cai, Z.C.; Yan, X.Y.; Jia, Z.J. Long-Term Field Fertilization Significantly Alters Community Structure of Ammonia-Oxidizing Bacteria rather than Archaea in a Paddy Soil. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2011, 75, 1431–1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konneke, M.; Bernhard, A.E.; Torre, D.L.; José, R.; Walker, C.B.; Waterbury, J.B.; Stahl, D.A. Isolation of an autotrophic ammonia-oxidizing marine archaeon. Nature 2005, 437, 543–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Norton, J.M.; Stark, J.M. Regulation and measurement of nitrification in terrestrial systems. Methods Enzymol. 2011, 486, 343–368. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, Y.Y.; Chapman, S.J.; Nicol, G.W.; Yao, H.Y. Nitrification and nitrifiers in acidic soils. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2018, 116, 290–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.P.; Duan, Y.H.; Xu, M.G.; Zhang, S.Q.; Wang, X.L. Nitrification potential in Fluvo-aquic soils different in fertility and its influencing factors. Acta Pedol. Sin. 2019, 56, 124–134. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, S. Study on Soil Water Amd Salt Regulation and Cotton Growth Characteristics under Film-Mulched Drip Irrigation with Brackish Water. Ph.D. Thesis, Xi’an Technological University, Xi’an, China, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Qu, Z.; Li, M.J.; Wang, Q.J.; Sun, Y.; Su, L.J.; Li, J. Effect of micro-nano oxygenated water addition on nitrification of Xinjiang sandy loam soil under controlled conditions. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2020, 36, 189–196. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Francis, C.A.; Roberts, K.J.; Beman, J.M.; Santoro, A.E.; Oakley, B.B. Ubiquity and diversity of ammonia-oxidizing archaea in water columns and sediments of the ocean. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 14683–14688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rotthauwe, J.H.; Witzel, K.P.; Liesack, W. The ammonia monooxygenase structural gene amoA as a functional marker: Molecular fine-scale analysis of natural ammonia-oxidizing populations. Appl. Environ. Microb. 1997, 63, 4704–4716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, G.Z.; Li, S.Q. Three kinds of ammonium nitrogen fertilizer on nitrification and model analysis. Agric. Res. Arid. Areas 2007, 6, 177–182+211. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, G.Z.; Huang, Z.B.; Li, S.Q.; Deng, Z.Y.; Zhang, Q.S. Effects of different exogenous nitrogen sources on nitrification in limy soil and its kinetic analysis. Plant Nutr. Fertil. Sci. 2011, 17, 1147–1155. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Jan, M.T.; Roberts, P.; Tonheim, S.K.; Jones, D.L. Protein breakdown represents a major bottleneck in nitrogen cycling in grassland soils. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2009, 41, 2272–2282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilmour, J.T. The Effects of Soil Properties on Nitrification and Nitrification Inhibition. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1985, 49, 1262–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernie, J.Z.; Thomas, A.F.; Claudia, G. Effect of soil acidification on nitrification in soil. Can. J. Soil Sci. 2015, 95, 359–363. [Google Scholar]
- Duan, P.P.; Wu, Z.; Zhang, Q.Q. Thermodynamic responses of ammonia-oxidizing archaea and bacteria explain N2O production from greenhouse vegetable soils. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2018, 120, 37–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kits, K.D.; Sedlacek, C.J.; Lebedeva, E.V. Kinetic analysis of a complete nitrifier reveals an oligotrophic lifestyle. Nature 2017, 549, 269–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Agehara, S.; Warncke, D.D. Soil moisture and temperature effects on nitrogen release from organic nitrogen Sources. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2005, 69, 1844–1855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, R.X.; He, J.Z.; Zhang, L.M. Response of nitrification/denitrification and their associated microbes to soil moisture change in paddy soil. Environ. Sci. 2014, 35, 4275–4283. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Li, G.; Lai, X.; Song, X.L.; Zhao, J.N.; Yang, D.L. Effects of nitrogen and water addition on the community structure of soil ammonium oxidizing microorganisms in Stipa Baikal Steppe. J. Resour. Ecol. 2015, 6, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Ke, X.B.; Lu, Y.H. Adaptation of ammonia-oxidizing microorganisms to environment shift of paddy field soil. Fems Microbiol. Ecol. 2012, 80, 87–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gleeson, D.B.; Müller, C.; Banerjee, S.; Ma, W.; Siciliano, S.D.; Murphy, D.V. Response of ammonia oxidizing archaea and bacteria to changing water filled pore space. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2010, 42, 1888–1891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szukics, U.; Hackl, E.; Zechmeister-Boltenstern, S.; Sessitsch, A. Rapid and dissimilar response of ammonia oxidising archaea and bacteria to nitrogen and water amendment in two temperate forest soils. Microbiol. Res. 2012, 167, 103–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bustamante, M.; Verdejo, V.; Zúniga, C.; Espinosa, F.; Orlando, J.; Carú, M. Comparison of water availability effect on ammonia-oxidizing bacteria and archaea in microcosms of a Chilean semiarid soil. Front. Microbiol. 2012, 282, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, S.L.; Yang, X.Y.; Lv, D.Q.; Tong, Y.A. Effect of soil moisture, temperature and different nitrogen fertilizers on nitrification. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2002, 22, 2147–2153. [Google Scholar]
- Linn, D.M.; Doran, J.W. Effect of water-filled pore space on carbon dioxide and nitrous oxide production in tilled and nontilled soils. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1984, 48, 1267–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, C.H.; Jia, Z.J.; Tang, L.S.; Wu, Y.C.; Li, Y. Effect of model of fertilization on microbial abundance and enzyme activities in oasis farmland soil. Acta Pedol. Sin. 2012, 49, 567–574. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Ma, L.J.; Zhang, H.M.; Hou, Z.A.; Min, W. Effects of long-term saline water drip irrigation on the abundance and community structure of ammonia oxidizers. J. Agro-Environ. Sci. 2019, 38, 2797–2807. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- He, J.Z.; Hu, H.W.; Zhang, L.M. Current insights into the autotrophic thaumarchaeal ammonia oxidation in acidic soils. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2012, 55, 146–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicol, G.W.; Leininger, S.; Schleper, C. The influence of soil pH on the diversity, abundance and transcriptional activity of ammonia oxidizing archaea and bacteria. Environ. Microbiol. 2008, 10, 2966–2978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goloran, J.B.; Chen, C.R.; Phillips, I.R.; Liu, X.C. Pathways of different forms of nitrogen and role of ammonia-oxidizing bacteria in alkaline residue sand from bauxite processing. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2015, 66, 942–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhu, G.; Song, L.; Wang, S.; Yin, C. Manure fertilization alters the population of ammonia-oxidizing bacteria rather than ammonia-oxidizing archaea in a paddy soil. J. Basic Microb. 2014, 54, 190–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.J.; Zhang, J.H.; Men, Q.; Tan, S.; Zhou, L.W.; Liu, X.Y. Experiment on physical and chemical characteristics of activated brackish water by magnetization or ionization. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2016, 32, 60–66. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Fabian, B.; Hans, M.; Tom, B. Nitrification in agricultural soils: Impact, actors and mitigation. Curr. Opin. Biotech. 2018, 50, 166–173. [Google Scholar]
- Pate, J.S. Uptake, assimilation and transport of nitrogen compounds by plants. Soil Biol. Biochem. 1973, 5, 109–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marschner, P. Marschner’s mineral nutrition of higher plants. Sci. Press Beijing 2013, 50, 71–84. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, K.; Zhang, J.H.; Wang, Q.J.; Guo, Y.; Mu, W.Y. Irrigation with ionized brackish water affects cotton yield and water use efficiency. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2022, 175, 114244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).