Site-Specific Management Zones Delineation Based on Apparent Soil Electrical Conductivity in Two Contrasting Fields of Southern Brazil
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
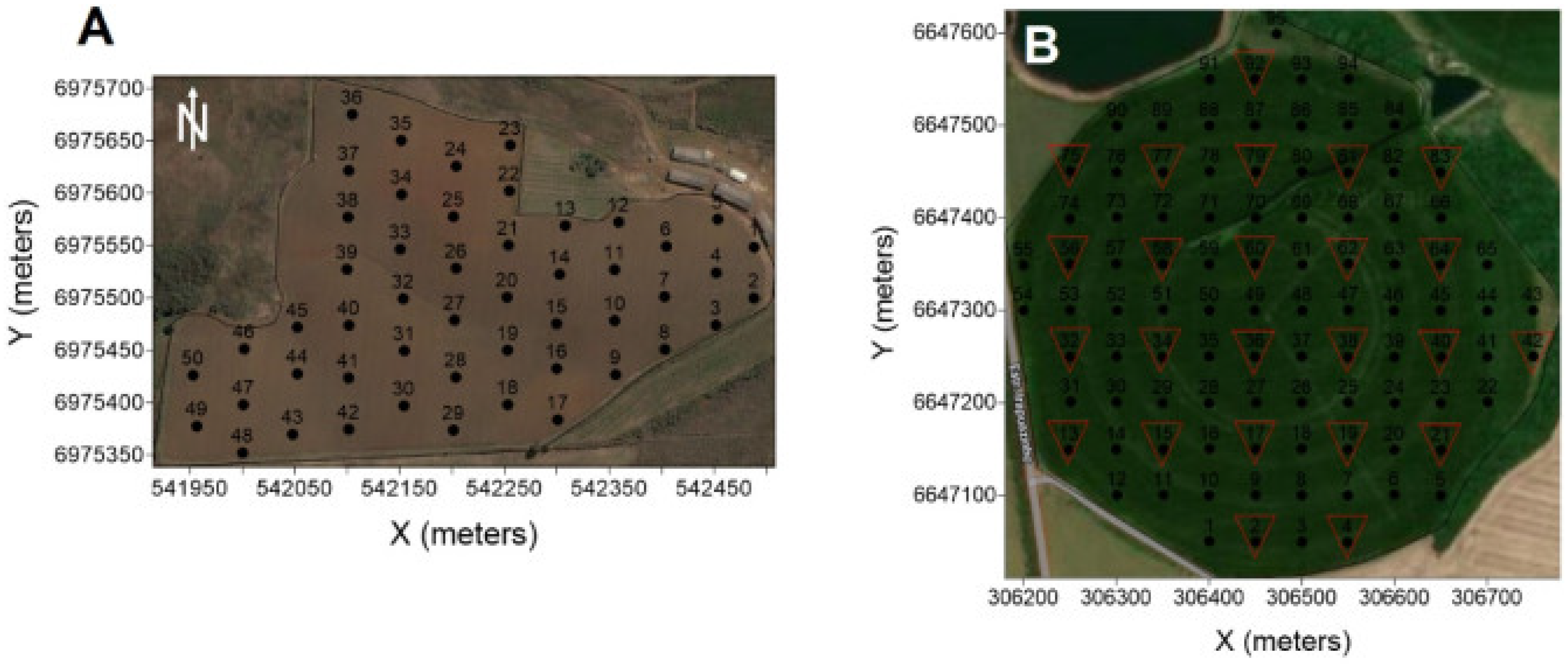
2.1. Experimental Areas
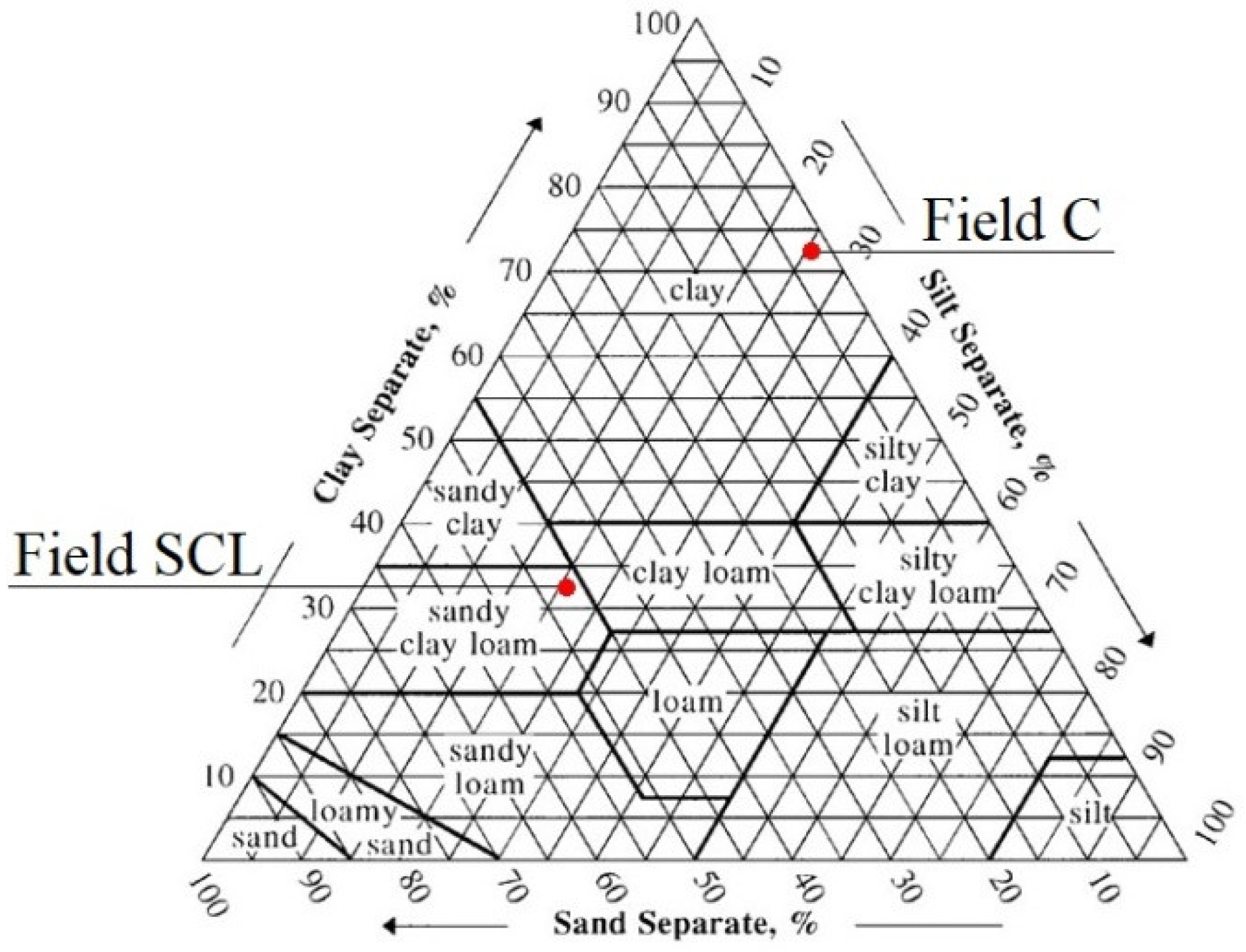
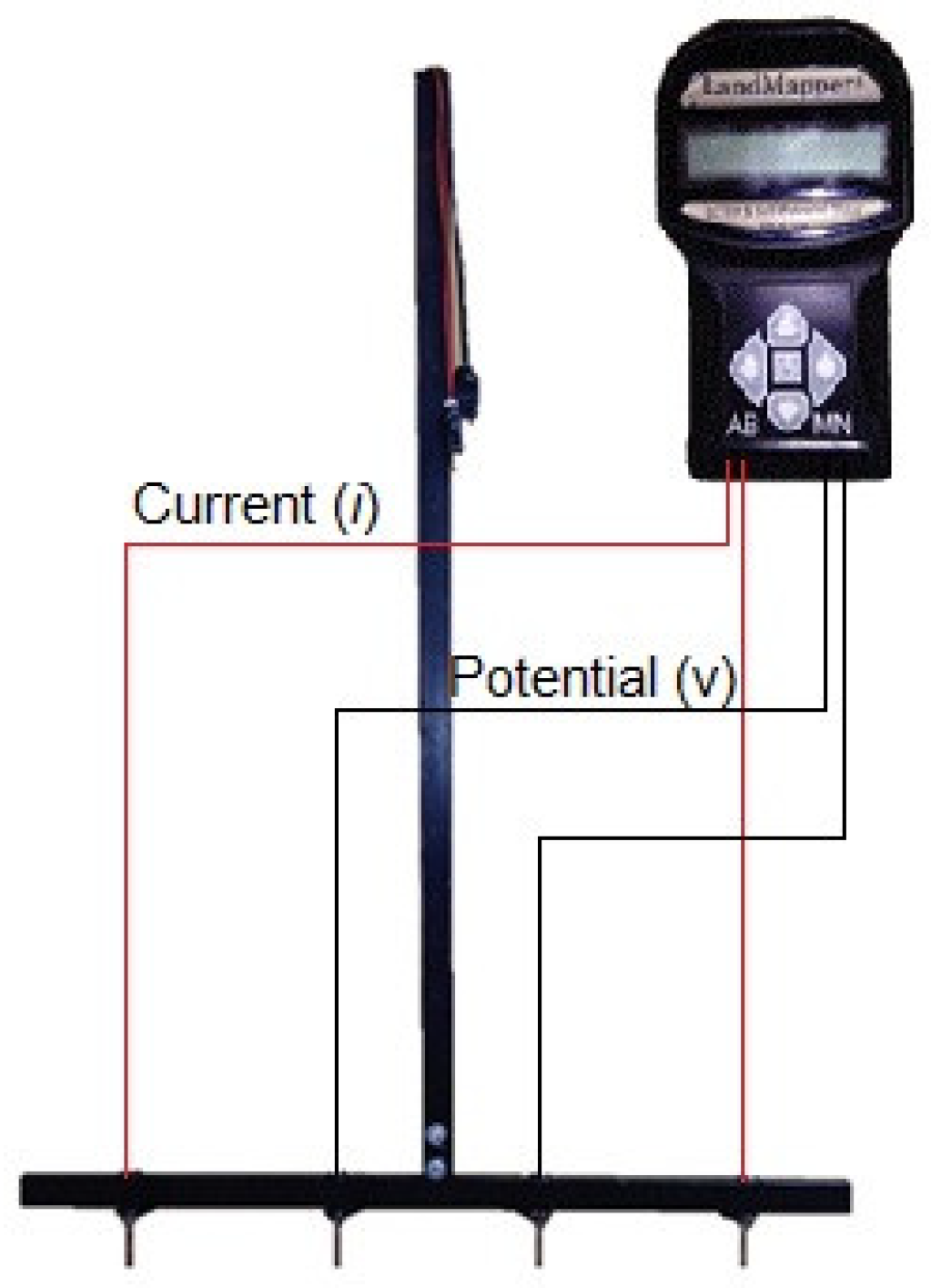
2.2. Apparent Soil Electrical Conductivity, Soil Samples, and Soybean Grain Yield
2.3. Geostatistical Analysis
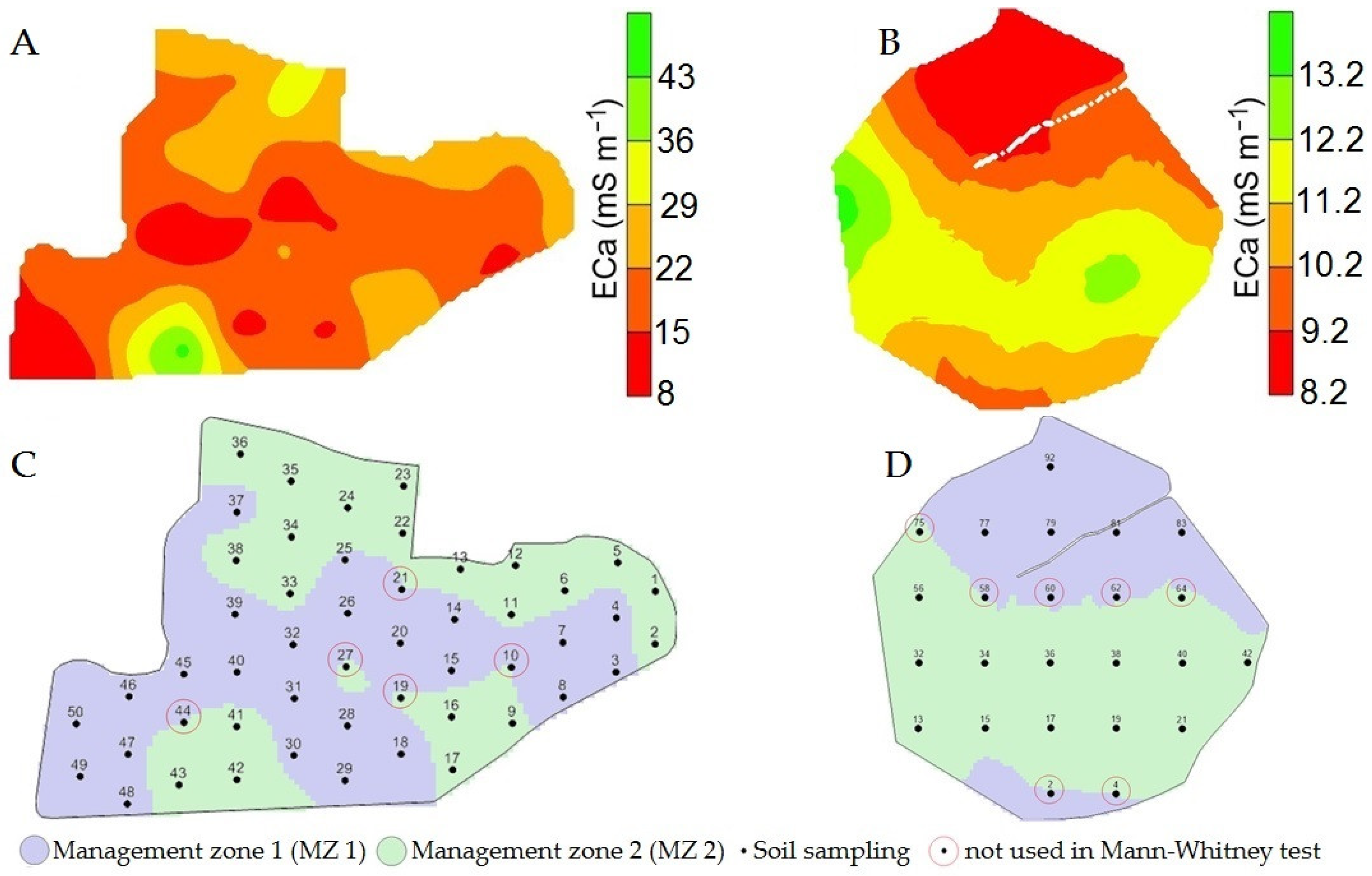
2.4. Management Zones and Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- CONAB (Companhia Nacional de Abastecimento). Acompanhamento da Safra Brasileira de Grãos; 12° Levantamento: Brasília, Brasil, 2020; pp. 1–68. [Google Scholar]
- Paterson, S.; Minasny, B.; McBratney, A. Spatial variability of Australian soil texture: A multiscale analysis. Geoderma 2018, 309, 60–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bottega, E.L.; Queiroz, D.M.; Pinto, F.A.C.; Valente, D.S.M.; Souza, C.M.A. Precision agriculture applied to soybean crop: Part II—Temporal stability of management zones. Aust. J. Crop Sci. 2017, 11, 676–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peralta, N.R.; Costa, J.L. Delineation of management zones with soil apparent electrical conductivity to improve nutrient management. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2013, 99, 218–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalchiavon, F.C.; Carvalho, M.P.; Andreotti, M.; Montanari, R. Variabilidade espacial de atributos da fertilidade de um Latossolo Vermelho Distroférrico sob Sistema Plantio Direto. Rev. Ciênc. Agron. 2012, 43, 453–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues Junior, F.A.; Vieira, L.B.; Queiroz, D.M.; Santos, N.T. Geração de zonas de manejo para cafeicultura empregando-se sensor SPAD e análise foliar. Rev. Bras. Eng. Agríc. Ambient. 2011, 15, 778–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moral, F.J.; Terrón, J.M.; Rebollo, F.J. Site-specific management zones based on the Rasch model and geostatistical techniques. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2011, 75, 223–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiaohu, Z.; Li, J.; Xiaolei, Q.; Jianxiu, Q.; Juan, W.; Yan, Z. An improved method of delineating rectangular management zones using a semivariogram-based technique. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2016, 121, 74–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeraatpisheh, M.; Bakhshandeh, E.; Emadi, M.; Li, T.; Xu, M. Integration of PCA and fuzzy clustering for delineation of soil management zones and cost-efficiency analysis in a citrus plantation. Sustainability 2020, 12, 5809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moral, F.J.; Terrón, J.M.; Silva, J.R.M. Delineation of management zones using mobile measurements of soil apparent electrical conductivity and multivariate geostatistical techniques. Soil Tillage Res. 2010, 106, 335–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Pérez, J.R.; Plant, R.E.; Lambert, J.J.; Smart, D.R. Using apparent soil electrical conductivity (ECa) to characterize vineyard soils of high clay content. Precis. Agric. 2011, 12, 775–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corassa, G.M.; Amado, T.J.C.; Tabaldi, F.M.; Schwalbert, R.A.; Reimche, G.B.; Dalla Nora, D.; Alba, P.J.; Horbe, T.A.N. Espacialização em alta resolução de atributos da acidez de Latossolo por meio de sensoriamento em tempo real. Pesq. Agropec. Bras. 2016, 51, 1306–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Stadler, A.; Rudolph, S.; Kupisch, M.; Langensiepen, M.; Van Der Kruk, J.; Ewert, F. Quantifying the effects of soil variability on crop growth using apparent soil electrical conductivity measurements. Eur. J. Agron. 2015, 64, 8–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corwin, D.L.; Scudiero, E. Field-scale apparent soil electrical conductivity. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2020, 84, 1405–1441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, E.E.; Baio, F.H.R.; Teodoro, L.P.R.; Campos, C.N.S.; Plaster, O.B.; Teodoro, P.E. Variable-rate seeding in soybean according to soil attributes related to grain yield. Precis. Agric. 2022, 23, 35–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvares, C.A.; Stape, J.L.; Sentelhas, P.C.; Gonçalves, J.L.M.; Sparovek, G. Köppen’s climate classification map for Brazil. Meteorol. Z. 2013, 22, 711–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- USDA (United States Department of Agriculture). Online Soil Texture Calculator. Available online: https://www.nrcs.usda.gov/wps/portal/nrcs/detail/soils/survey/?cid=nrcs142p2054167 (accessed on 13 April 2022).
- CQFS RS/SC (Comissão de Química e Fertilidade do Solo). Manual de Adubação e de Calagem Para os Estados do Rio Grande do Sul e de Santa Catarina, 10th ed.; Sociedade Brasileira de Ciência do Solo: Porto Alegre, Brasil, 2004; 400p. [Google Scholar]
- Corwin, D.L.; Hendrickx, J.M.H. Electrical Resistivity: Wenner Array. In Methods of Soil Analysis—Part 4 Physical Methods; Silva, J.S., Ed.; SSSA Book Series: Madison, WI, USA, 2002; pp. 1282–1287. [Google Scholar]
- Corwin, D.L.; Lesch, S.M. Apparent soil electrical conductivity measurements in agriculture. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2005, 46, 11–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliver, M.A.; Webster, R. A tutorial guide to geostatistics: Computing and modelling variograms and kriging. Catena 2014, 113, 56–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gamma Design Software, LLC. GS+ Geoestatistics for the Environmental Sciences, Version 7; Gamma Design Software, LLC.: Plainwell, MI, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Golden Software, INC. Surfer: Surface Mapping System, Version 10; Golden Software, INC.: Golden, CO, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Valente, D.S.M.; Queiroz, D.M.; Pinto, F.A.C.; Santos, N.T.; Santos, F.L. Definition of management zones in coffee production fields based on apparent soil electrical conductivity. Sci. Agric. 2012, 69, 173–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria. Available online: https://www.R-project.org/ (accessed on 10 November 2021).
- Verma, R.R.; Manjunath, B.L.; Singh, N.P.; Kumar, A.; Asolkar, T.; Chavan, V.; Srivastava, T.K.; Singh, P. Soil mapping and delineation of management zones in the Western Ghats of coastal India. Land Degrad. Dev. 2018, 29, 4313–4322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corá, J.E.; Araujo, A.V.; Pereira, G.T.; Beraldo, J.M.G. Variabilidade espacial de atributos do solo para adoção do sistema de agricultura de precisão na cultura de cana-de-açúcar. Rev. Bras. Ciênc. Solo 2004, 28, 1013–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michelon, C.J.; Carlesso, R.; Oliveira, Z.B.; Knies, A.E.; Petry, M.T.; Martins, J.D. Funções de pedotransferência para estimativa da retenção de água em alguns solos do Rio Grande do Sul. Cienc. Rural 2010, 40, 848–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Brevik, E.; Fenton, T.; Lazari, A. Soil electrical conductivity as a function of soil water content and implications for soil mapping. Precis. Agric. 2006, 7, 393–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peixoto, C.P.; Câmara, G.M.S.; Martins, M.C.; Marchiori, L.F.S.; Guerzoni, R.A.; Mattiazzi, P. Épocas de semeadura e densidade de plantas de soja: I. Componentes da produção e rendimento de grãos. Sci. Agric. 2000, 57, 89–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira Júnior, A.; Prochnow, L.I.; Klepker, D. Soybean yield in response to application of phosphate rock associated with triple superphosphate. Sci. Agric. 2011, 68, 376–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Pádua, G.P.; Zito, R.K.; Arantes, N.E.; França Neto, J.B. Influência do tamanho da semente na qualidade fisiológica e na produtividade da cultura da soja. Rev. Bras. Sementes 2010, 32, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Serafim, M.E.; Ono, F.B.; Zeviani, W.M.; Novelino, J.O.; Silva, J.V. Umidade do solo e doses de potássio na cultura da soja. Rev. Cienc. Agron. 2012, 43, 222–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Bender, R.R.; Haegele, J.W.; Below, F.E. Nutrient Uptake, Partitioning, and Remobilization in Modern Soybean Varieties. Agron. J. 2015, 107, 563–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soria, J.E.; Troleis, M.J.B.; Alves, M.R.; Montanari, R.; Andreotti, M. Influência do teor de argila nas relações entre os atributos químicos de solos no noroeste do estado de São Paulo. Cult. Agron. 2019, 28, 111–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sana, R.S.; Anchinoni, I.; Brandão, Z.N.; Holzschuh, M.J. Variabilidade espacial de atributos físico-químicos do solo e seus efeitos na produtividade do algodoeiro. Rev. Bras. Eng. Agríc. Ambient. 2014, 18, 994–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Costa, M.M.; Queiroz, D.M.; Pinto, F.A.C.; Reis, E.F.; Santos, N.T. Moisture content effect in the relationship between apparent electrical conductivity and soil atributes. Acta Sci. Agron. 2014, 36, 395–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bortoluzzi, E.C.; Rheinheimer, D.S.; Petry, C.; Kaminski, J. Contribution of soil constituents to the cation exchange capacity obtained by different extraction methods. Rev. Bras. Ciênc. Solo 2009, 33, 507–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Briedis, C.; Sá, J.C.M.; Caires, E.F.; Navarro, J.F.; Inagaki, T.M.; Ferreira, A.O. Soil carbon and fertility attributes in response to surface liming in no-till. Pesqui. Agropecu. Bras. 2012, 47, 1007–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Peralta, N.R.; Costa, J.L.; Balzarini, M.; Angelini, H. Delineation of management zones with measurements of soil apparent electrical conductivity in the southeastern pampas. Can. J. Soil Sci. 2013, 93, 205–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Field | Geostatistical Parameters | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model | A (1) | C0 + C (2) | C0 (3) | RSS (4) | R2 (5) | |
| C | Spherical | 111.00 | 47.19 | 2.80 | 223 | 0.47 |
| SCL | Spherical | 467.80 | 5.93 | 2.72 | 0.105 | 0.98 |
| Cross-validation parameters | ||||||
| Regression coefficient | Y(6) | SEE(7) | R2 | |||
| C | 0.88 | 2.58 | 5.81 | 0.22 | ||
| SCL | 0.91 | 0.97 | 1.95 | 0.22 | ||
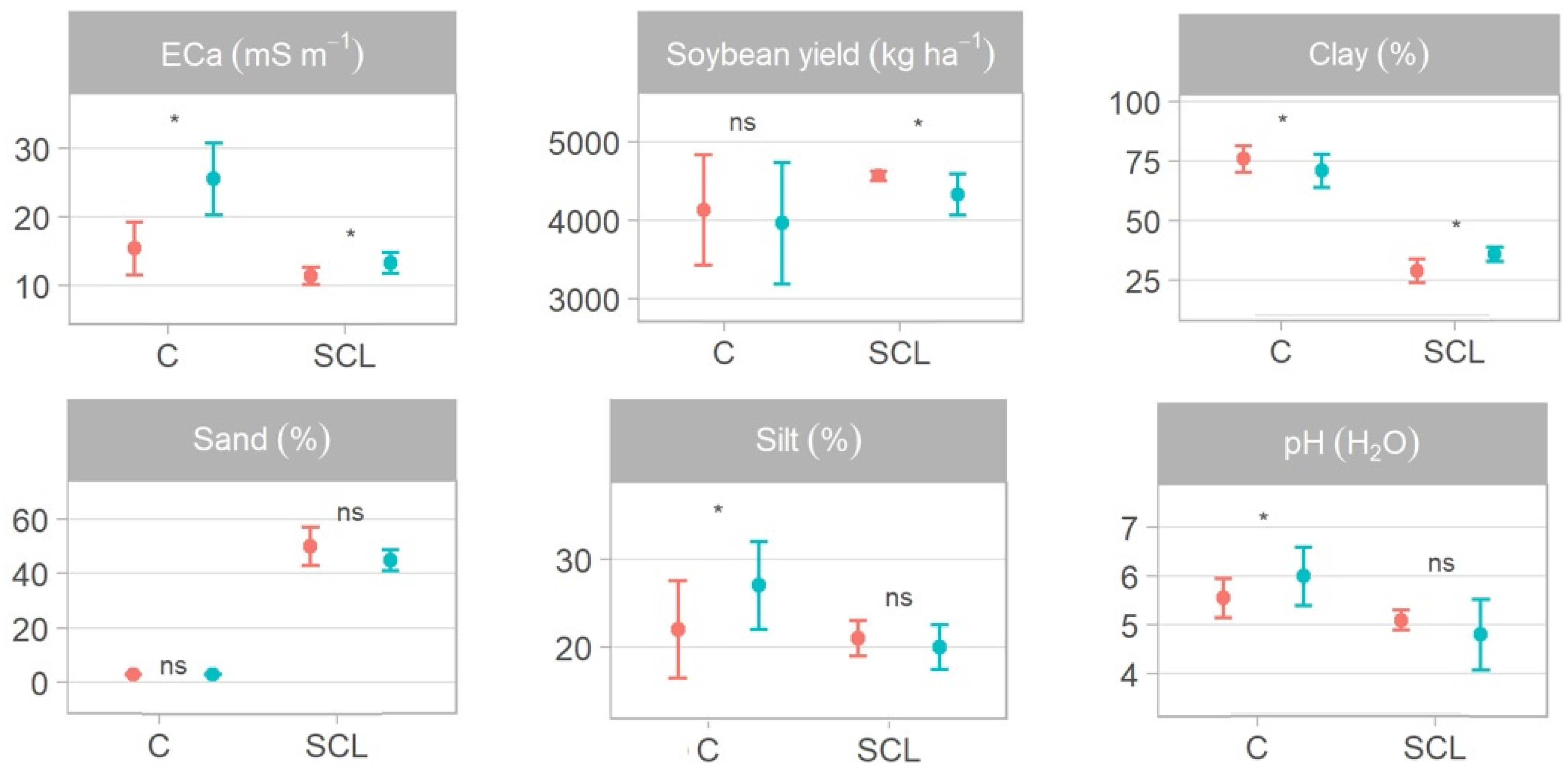
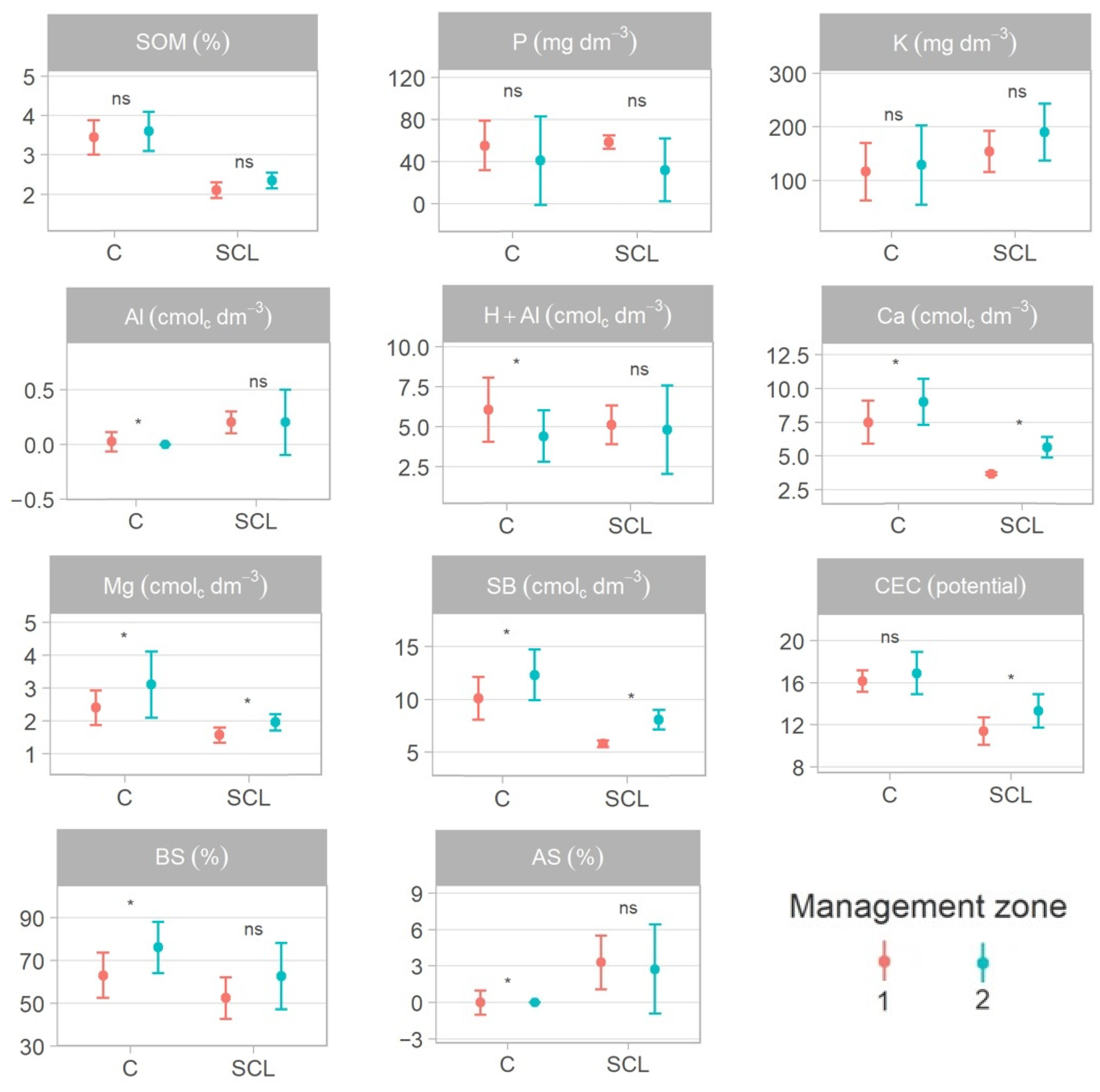
| Soil Attributes | Management Zone 1 (MZ 1) | Management Zone 2 (MZ 2) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Valid N | Mean | Minimum | Maximum | Std. Dev. | Valid N | Mean | Minimum | Maximum | Std. Dev. | |
| ECa | 5 | 9.52 | 8.28 | 10.23 | 1.84 | 12 | 11.47 | 10.85 | 13.42 | 3.05 |
| Soybean | 5 | 4563.25 | 4451.97 | 4636.95 | 70.90 | 12 | 4308.82 | 3755.41 | 5474.38 | 461.30 |
| Clay | 5 | 30.60 | 26.00 | 37.00 | 4.39 | 12 | 35.50 | 33.00 | 37.00 | 1.57 |
| Sand | 5 | 48.60 | 41.00 | 55.00 | 5.59 | 12 | 45.08 | 41.00 | 50.00 | 2.91 |
| Silt | 5 | 20.80 | 19.00 | 22.00 | 1.30 | 12 | 19.42 | 15.00 | 22.00 | 2.23 |
| pH | 5 | 5.08 | 4.70 | 5.40 | 0.26 | 12 | 4.98 | 4.40 | 5.60 | 0.43 |
| SOM | 5 | 2.14 | 1.70 | 2.50 | 0.30 | 12 | 2.38 | 2.10 | 2.70 | 0.17 |
| P | 5 | 53.26 | 22.00 | 72.90 | 18.92 | 12 | 37.25 | 14.20 | 82.40 | 20.73 |
| K+ | 5 | 162.20 | 110.00 | 204.00 | 36.99 | 12 | 195.25 | 140.00 | 310.00 | 47.64 |
| Al3+ | 5 | 0.22 | 0.10 | 0.50 | 0.16 | 12 | 0.26 | 0.00 | 0.70 | 0.22 |
| H+ + Al3+ | 5 | 5.32 | 4.10 | 6.40 | 0.93 | 12 | 5.10 | 3.00 | 8.60 | 1.87 |
| Ca2+ | 5 | 3.92 | 3.50 | 5.10 | 0.66 | 12 | 5.65 | 4.60 | 6.90 | 0.68 |
| Mg2+ | 5 | 1.66 | 1.33 | 2.16 | 0.31 | 12 | 2.02 | 1.62 | 2.54 | 0.29 |
| SB | 5 | 6.00 | 5.10 | 7.80 | 1.05 | 12 | 8.18 | 6.90 | 9.90 | 0.96 |
| CEC | 5 | 6.24 | 5.60 | 7.90 | 0.95 | 12 | 8.44 | 7.40 | 10.00 | 0.83 |
| BS | 5 | 53.12 | 44.40 | 61.30 | 6.94 | 12 | 62.35 | 46.20 | 76.80 | 10.22 |
| AS | 5 | 3.84 | 1.30 | 8.80 | 2.98 | 12 | 3.25 | 0.00 | 8.80 | 2.75 |
| Soil Attributes | Management Zone 1 (MZ 1) | Management Zone 2 (MZ 2) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Valid N | Mean | Minimum | Maximum | Std. Dev. | Valid N | Mean | Minimum | Maximum | Std. Dev. | |
| ECa | 24 | 15.23 | 8.00 | 18.93 | 2.78 | 21 | 26.44 | 21.27 | 45.45 | 5.38 |
| Soybean | 24 | 4221.91 | 3257.33 | 5295.20 | 577.01 | 21 | 4061.01 | 3141.33 | 5525.20 | 599.20 |
| Clay | 24 | 74.28 | 65.50 | 85.50 | 4.46 | 21 | 69.81 | 63.00 | 78.00 | 3.78 |
| Sand | 24 | 2.99 | 2.50 | 3.70 | 0.30 | 21 | 3.00 | 2.00 | 5.00 | 0.63 |
| Silt | 24 | 22.73 | 12.00 | 31.50 | 4.34 | 21 | 27.57 | 19.00 | 35.00 | 3.94 |
| pH | 24 | 5.58 | 4.90 | 6.30 | 0.32 | 21 | 6.09 | 5.40 | 6.90 | 0.38 |
| SOM | 24 | 3.51 | 3.10 | 4.30 | 0.32 | 21 | 3.60 | 2.80 | 4.30 | 0.39 |
| P | 24 | 54.99 | 20.00 | 95.00 | 20.18 | 21 | 53.71 | 22.00 | 122.00 | 28.59 |
| K+ | 24 | 120.71 | 62.40 | 198.90 | 41.16 | 21 | 134.46 | 58.50 | 261.30 | 58.50 |
| Al3+ | 24 | 0.09 | 0.00 | 1.03 | 0.21 | 21 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.09 | 0.02 |
| H+ + Al3+ | 24 | 6.14 | 3.70 | 9.40 | 1.39 | 21 | 4.18 | 2.30 | 6.90 | 1.17 |
| Ca2+ | 24 | 7.49 | 4.60 | 9.40 | 1.22 | 21 | 9.11 | 7.40 | 11.20 | 1.07 |
| Mg2+ | 24 | 2.30 | 1.50 | 3.30 | 0.43 | 21 | 3.13 | 2.40 | 4.30 | 0.57 |
| SB | 24 | 10.09 | 6.30 | 12.50 | 1.58 | 21 | 12.60 | 10.20 | 15.60 | 1.60 |
| CEC | 24 | 16.22 | 14.30 | 18.70 | 1.07 | 21 | 16.78 | 14.80 | 19.00 | 1.37 |
| BS | 24 | 62.11 | 40.00 | 77.00 | 8.61 | 21 | 75.00 | 61.00 | 85.00 | 6.71 |
| AS | 24 | 1.15 | 0.00 | 14.00 | 2.91 | 21 | 0.05 | 0.00 | 1.00 | 0.22 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bottega, E.L.; Safanelli, J.L.; Zeraatpisheh, M.; Amado, T.J.C.; Queiroz, D.M.d.; Oliveira, Z.B.d. Site-Specific Management Zones Delineation Based on Apparent Soil Electrical Conductivity in Two Contrasting Fields of Southern Brazil. Agronomy 2022, 12, 1390. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12061390
Bottega EL, Safanelli JL, Zeraatpisheh M, Amado TJC, Queiroz DMd, Oliveira ZBd. Site-Specific Management Zones Delineation Based on Apparent Soil Electrical Conductivity in Two Contrasting Fields of Southern Brazil. Agronomy. 2022; 12(6):1390. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12061390
Chicago/Turabian StyleBottega, Eduardo Leonel, José Lucas Safanelli, Mojtaba Zeraatpisheh, Telmo Jorge Carneiro Amado, Daniel Marçal de Queiroz, and Zanandra Boff de Oliveira. 2022. "Site-Specific Management Zones Delineation Based on Apparent Soil Electrical Conductivity in Two Contrasting Fields of Southern Brazil" Agronomy 12, no. 6: 1390. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12061390
APA StyleBottega, E. L., Safanelli, J. L., Zeraatpisheh, M., Amado, T. J. C., Queiroz, D. M. d., & Oliveira, Z. B. d. (2022). Site-Specific Management Zones Delineation Based on Apparent Soil Electrical Conductivity in Two Contrasting Fields of Southern Brazil. Agronomy, 12(6), 1390. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12061390







