Effect of Activated Water Irrigation on the Yield and Water Use Efficiency of Winter Wheat under Irrigation Deficit
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Site
2.2. Experimental Design and Management
2.2.1. Experimental Design
2.2.2. Experimental Management
2.2.3. Irrigation Water
2.3. Sampling and Measurements
2.3.1. Growth Characteristics
2.3.2. Physiological Characteristics
2.3.3. Yield Components, Total Water Consumption (TWC), and WUE
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Growth Characteristics
3.1.1. Plant Height
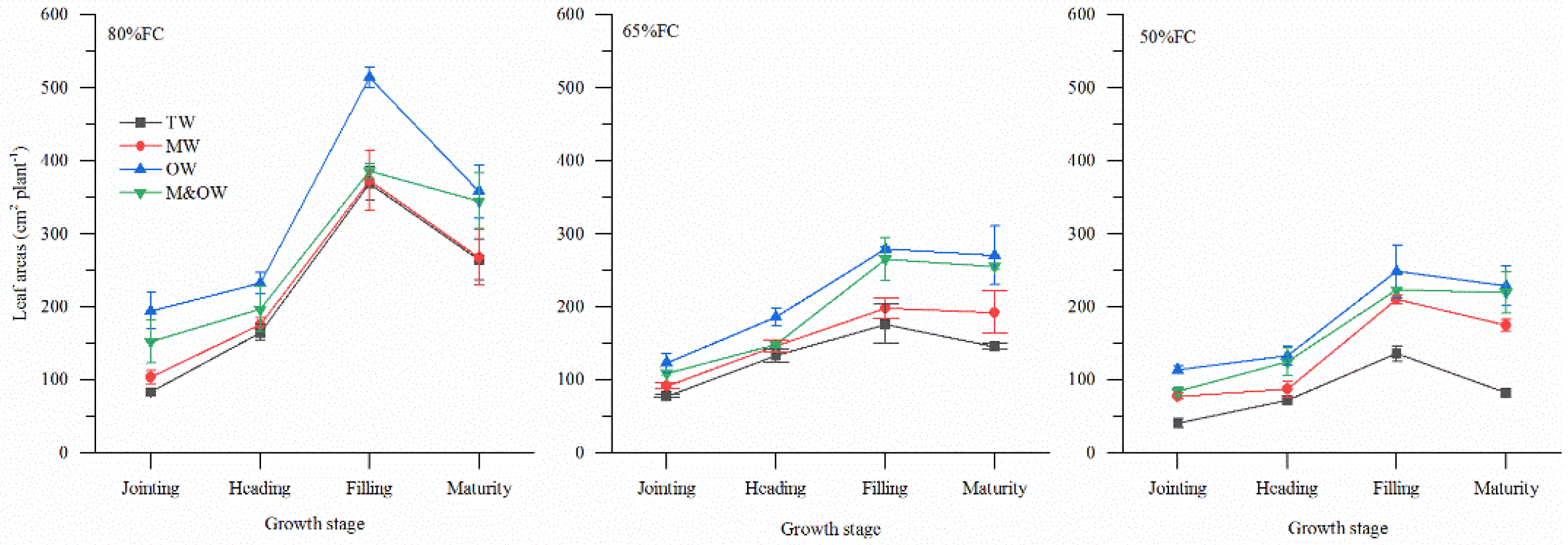
3.1.2. Leaf Area
3.1.3. Aboveground Biomass
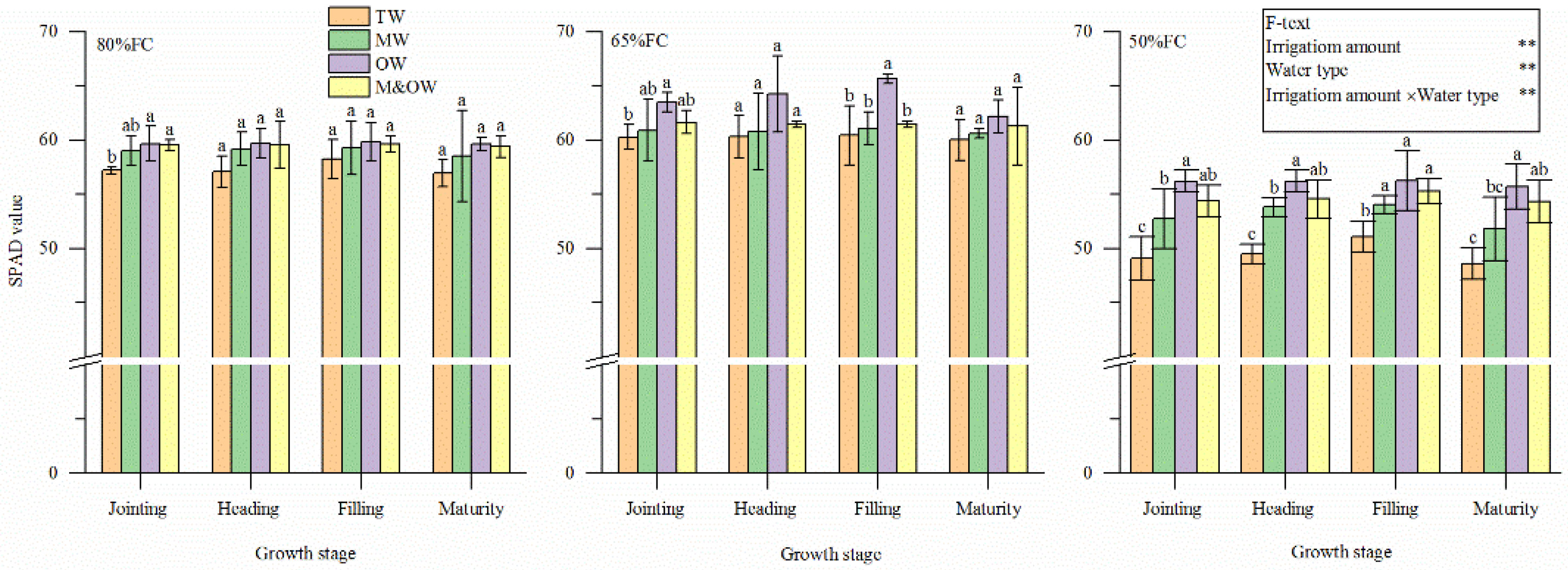
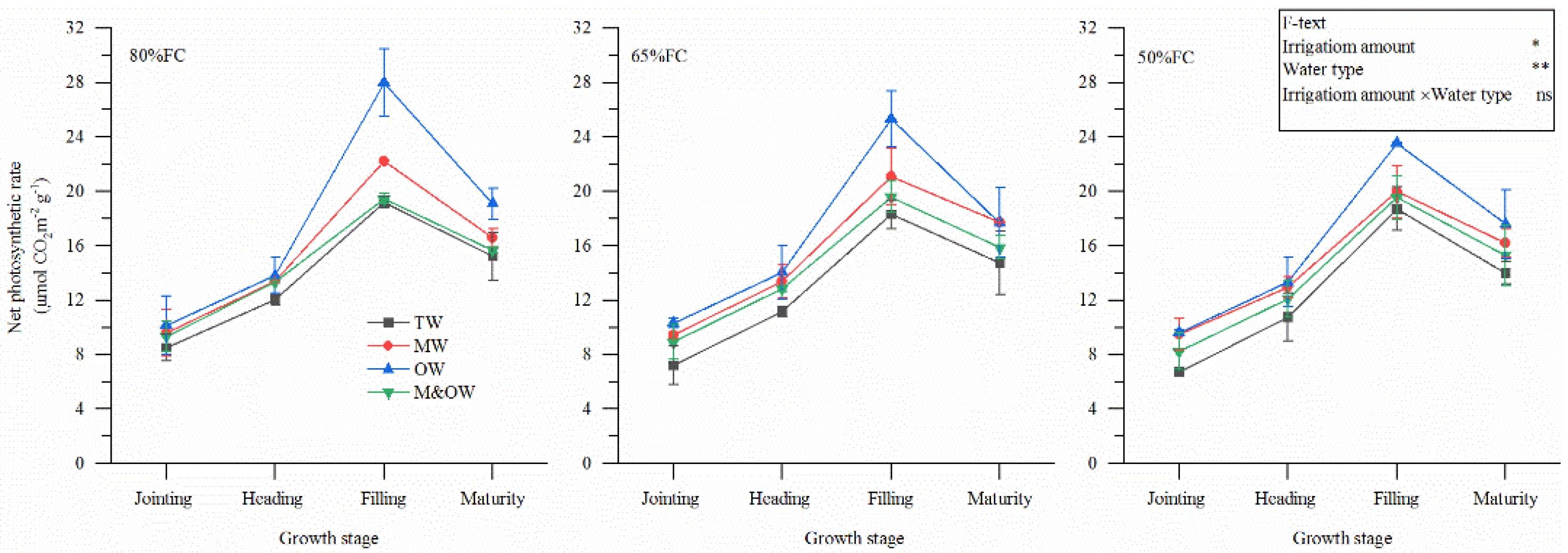
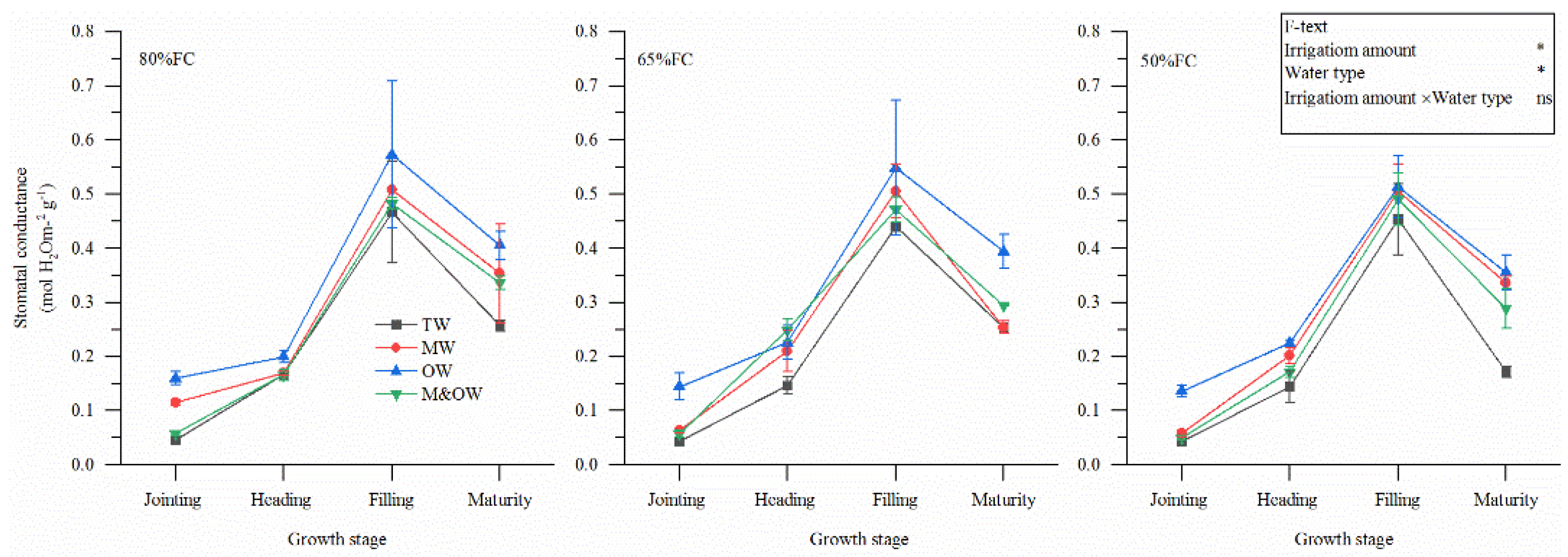
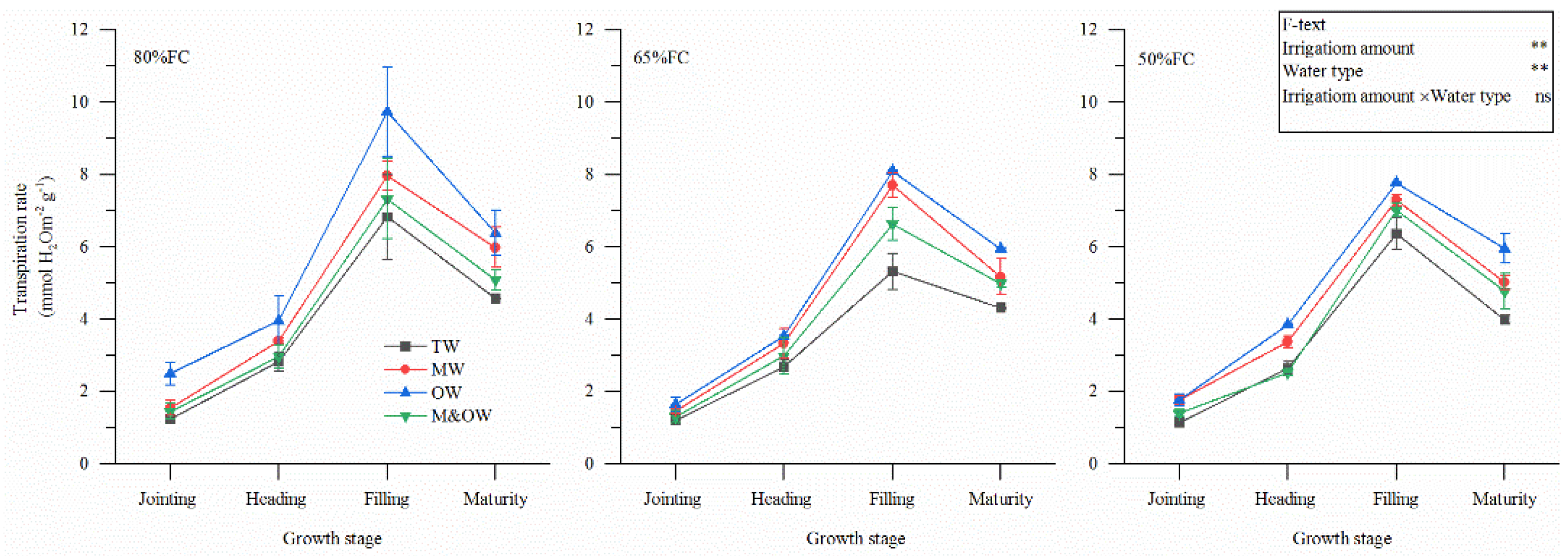
3.2. Physiological Characteristics
3.3. TWC, Wheat Yield, and WUE
4. Discussion
4.1. Response of Wheat Growth Traits to Irrigation Water Type and Irrigation Amount
4.2. Response of Yield, TWC, Biomass, and WUE to Irrigation Water Type and Irrigation Amount
4.3. Applicability Evaluation
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Schiermeier, Q. The parched planet: Water on tap. Nature 2014, 510, 326–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhao, C.; Liu, B.; Piao, S.; Wang, X.; Lobell, D.B.; Huang, Y.; Huang, M.T.; Yao, Y.T.; Bassu, S.; Ciais, P.; et al. Temperature increase reduces global yields of major crops in four independent estimates. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 9326–9331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hassani, A.; Azapagic, A.; Shokri, N. Global predictions of primary soil salinization under changing climate in the 21st century. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 6663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Viala, E. Water for food, water for life a comprehensive assessment of water management in agriculture. Irrig. Drain. Syst. 2008, 22, 127–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghose, B. Food security and food self–sufficiency in China: Form past to 2050. Food Energy Secur. 2004, 3, 86–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, X.P.; Shan, L.; Zhang, H.P.; Turner, N.C. Improving agricultural water use efficiency in arid and semi–arid areas of China. Agric. Water Manag. 2006, 80, 23–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, M.-D.; Fan, J.; Wang, Q.-J.; Dang, T.-H.; Guo, S.-L.; Wang, J.-J. Wheat Grain Yield and Yield Stability in a Long–Term Fertilization Experiment on the Loess Plateau. Pedosphere 2007, 17, 257–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, L.; Huang, Z.B.; Zhang, S.Q. Water–Saving Agriculture; Tsinghua University Press: Beijing, China, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Monreal, J.; Jiménez, E.; Remesal, E.; Morillo–Velarde, R.; García–Mauriño, S.; Echevarría, C. Proline content of sugar beet storage roots: Response to water deficit and nitrogen fertilization at field conditions. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2007, 60, 257–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tognetti, R.; Palladino, M.; Minnocci, A.; Delfine, S.; Alvino, A. The response of sugar beet to drip and low–pressure sprinkler irrigation in southern Italy. Agric. Water Manag. 2003, 60, 135–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, N.; Du, T.; Kang, S.; Li, F.; Hu, X.; Wang, M.; Li, Z. Relationship between stable carbon isotope discrimination and water use efficiency under regulated deficit irrigation of pear–jujube tree. Agric. Water Manag. 2009, 96, 1615–1622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bloch, D.; Hoffmann, C.M.; Märländer, B. Impact of water supply on photosynthesis, water use and carbon isotope discrimination of sugar beet genotypes. Eur. J. Agron. 2006, 24, 218–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geerts, S.; Raes, D. Deficit irrigation as an on–farm strategy to maximize crop water productivity in dry areas. Agric. Water Manag. 2009, 96, 1275–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ma, S.-C.; Duan, A.-W.; Wang, R.; Guan, Z.-M.; Yang, S.-J.; Shao, Y. Root–sourced signal and photosynthetic traits, dry matter accumulation and remobilization, and yield stability in winter wheat as affected by regulated deficit irrigation. Agric. Water Manag. 2015, 148, 123–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Z.; Du, T.; Zhang, J.; Xu, S.; Cambre, P.J.; Davies, W.J. Carbon isotope discrimination shows a higher water use efficiency under alternate partial root–zone irrigation of field–grown tomato. Agric. Water Manag. 2015, 165, 33–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haghverdi, A.; Yonts, C.D.; Reichert, D.L.; Irmak, S. Impact of irrigation, surface residue cover and plant population on sugarbeet growth and yield, irrigation water use efficiency and soil water dynamics. Agric. Water Manag. 2017, 180, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Jin, M.; Ferre, T.P.; Liu, Y.; Xian, Y.; Shan, T.; Ping, X. Spatial distribution of soil moisture, soil salinity, and root density beneath a cotton field under mulched drip irrigation with brackish and fresh water. Field Crops Res. 2018, 215, 207–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Dhungel, J.; Bhattarai, S.P.; Torabi, M.; Pendergast, L.; Midmore, D.J. Impact of oxygation on soil respiration, yield and water use efficiency of three crop species. J. Plant Ecol. 2010, 4, 236–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoshravesh–Miangoleh, M.; Kiani, A.-R. Effect of magnetized water on infiltration capacity of different soil textures. Soil Use Manag. 2014, 30, 588–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; He, W.; Qi, S.; Wu, J.; Gu, X.S. A novel phytoremediation method assisted by magnetized water to decontaminate soil Cd based on harvesting senescent and dead leaves of Festuca arundinacea. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 383, 121115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higashitani, K.; Kage, A.; Katamura, S.; Imai, K.; Hatade, S. Effects of a Magnetic Field on the Formation of CaCO3 Particles. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1993, 156, 90–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amiri, M.; Dadkhah, A.A. On reduction in the surface tension of water due to magnetic treatment. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2006, 278, 252–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toledo, E.J.D.L.; Ramalho, T.; Magriotis, Z. Influence of magnetic field on physical–chemical properties of the liquid water: Insights from experimental and theoretical models. J. Mol. Struct. 2008, 888, 409–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.; Wang, Q.; Wu, L.; Zhang, P.; Zhao, G.; Liu, Y. A mathematical model for the transfer of soil solutes to runoff under water scouring. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 569–570, 332–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimokawa, I. Oxidative stress and calorie restriction. Geriatr. Gerontol. Int. 2004, 4, S149–S151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abuarab, M.; Mostafa, E.; Ibrahim, M. Effect of air injection under subsurface drip irrigation on yield and water use efficiency of corn in a sandy clay loam soil. J. Adv. Res. 2013, 4, 493–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ijaz, B. Changes in germination behavior of wheat seeds exposed to magnetic field and magnetically structured water. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2012, 11, 2927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grewal, H.S.; Maheshwari, B.L. Magnetic treatment of irrigation water and snow pea and chickpea seeds enhances early growth and nutrient contents of seedlings. Bioelectromagnetics 2010, 32, 58–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moussa, H.R. The impact of magnetic water application for improving common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) production. N. Y. Sci. J. 2011, 4, 15–20. [Google Scholar]
- Sadeghipour, O.; Aghaei, P. Improving the growth of cowpea (Vigna unguiculata L. Walp.) by magnetized water. J. Biodivers. Env. Sci. 2013, 3, 37–43. [Google Scholar]
- Maheshwari, B.; Grewal, H.S. Magnetic treatment of irrigation water: Its effects on vegetable crop yield and water productivity. Agric. Water Manag. 2009, 96, 1229–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savostin, P.V. Magnetic growth relations in plants. Planta 1964, 12, 327. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Khazan, M.; Abdullatif, B.M.; Al-Assaf, N. Effects of magnetically treated water on water status, chlorophyll pigments and some elements content of Jojoba (Simmondsia chinensis L.) at different growth stages. Afr. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 5, 722–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mostafazadeh-Fard, B.; Khoshravesh, M.; Mousavi, S.-F.; Kiani, A.-R. Effects of Magnetized Water and Irrigation Water Salinity on Soil Moisture Distribution in Trickle Irrigation. J. Irrig. Drain. Eng. 2011, 137, 398–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrett-Lennard, E.G. The interaction between water–logging and salinity in higher plants: Causes, consequences and impli–cations. Plant Soil 2003, 253, 35–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grable, A.R. Soil Aeration and Plant Growth. Adv. Agron. 1966, 18, 57–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meek, B.D.; Ehlig, C.F.; Stolzy, L.H.; Graham, L.E. Furrow and Trickle Irrigation: Effects On Soil Oxygen and Ethylene and Tomato Yield. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1983, 47, 631–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattarai, S.P.; Huber, S.; Midmore, D.J. Aerated subsurface irrigation water gives growth and yield benefits to zucchini, vegetable soybean and cotton in heavy clay soils. Ann. Appl. Biol. 2004, 144, 285–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goorahoo, D.; Carstensen, G.; Zoldoske, D.F.; Norum, E.; Mazzei, A. Using air in subsurface drip irrigation (SDI) to increase yields in bell peppers. Int. Water Irrig. 2002, 22, 39–42. [Google Scholar]
- Ouyang, Z.; Tian, J.; Yan, X.; Shen, H. Effects of different concentrations of dissolved oxygen or temperatures on the growth, photosynthesis, yield and quality of lettuce. Agric. Water Manag. 2019, 228, 105896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, Z.; Tian, J.; Yan, X.; Shen, H. Effects of different concentrations of dissolved oxygen on the growth, photosynthesis, yield and quality of greenhouse tomatoes and changes in soil microorganisms. Agric. Water Manag. 2020, 245, 106579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pendergast, L.; Bhattarai, S.; Midmore, D. Evaluation of aerated subsurface drip irrigation on yield, dry weight partitioning and water use efficiency of a broad–acre chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.) in a vertosol. Agric. Water Manag. 2019, 217, 38–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattarai, S.P.; Pendergast, L.; Midmore, D.J. Root aeration improves yield and water use efficiency of tomato in heavy clay and saline soils. Sci. Hortic. 2006, 108, 278–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, T.; Pan, J.; Zhou, B.; Muhammad, T.; Zhou, C.; Li, Y. Micro–nano bubble water oxygation: Synergistically improving irrigation water use efficiency, crop yield and quality. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 222, 835–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, M.; Wang, Q.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, J. Effects of oxygenated brackish water on germination and growth characteristics of wheat. Agric. Water Manag. 2020, 245, 106520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhungel, J.; Bhattarai, S.P.; Midmore, D.J. Aerated water irrigation (oxygation) benefits to pineapple yield, water use efficiency and crop health. Adv. Hortic. Sci. 2012, 26, 3–16. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, G.; Mu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wang, L. Magnetization and oxidation of irrigation water to improve winter wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) production and water–use efficiency. Agric. Water Manag. 2021, 259, 107254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Fan, J.; Ge, J.; Luo, Z. Effect of Irrigation with Activated Water on Root Morphology of Hydroponic Rice and Wheat Seedlings. Agronomy 2022, 12, 1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Wei, T.; Cai, T.; Ali, S.; Han, Q.; Ren, X.; Jia, Z. Plastic–Film Mulching for Enhanced Water–Use Efficiency and Economic Returns from Maize Fields in Semiarid China. Front. Plant. Sci. 2017, 8, 512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Asghar, T.; Iqbal, M.; Jamil, Y.; Haq, Z.U.; Nisar, J.; Shahid, M. Comparison of HeNe laser and sinusoidal non–uniform magnetic field seed pre–sowing treatment effect on Glycine max (Var 90–I) germination, growth and yield. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 2016, 166, 212–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, B.; Gong, Z.; Gao, K.; Ou, Y.; Zhang, J. The effect of a static magnetic field on the hydrogen bonding in water using frictional experiments. J. Mol. Struct. 2013, 1052, 102–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, M.; Haq, Z.U.; Jamil, Y.; Nisar, J. Pre–sowing seed magnetic field treatment influence on germination, seedling growth and enzymatic activities of melon (Cucumis melo L.). Biocatal. Agric. Biotechnol. 2016, 6, 176–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Podleśna, A.; Gładyszewska, B.; Podleśny, J.; Zgrajka, W. Changes in the germination process and growth of pea in effect of laser seed irradiation. Int. Agrophysics 2015, 29, 485–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Racuciu, M.; Creanga, D.; Amoraritei, C. Biochemical changes induced by low frequency magnetized field exposure of vegetal organisms. Rom. J. Phys. 2007, 52, 645–651. [Google Scholar]
- Selim, A.-F.H.; El-Nady, M.F. Physio–anatomical responses of drought stressed tomato plants to magnetic field. Acta Astronaut. 2011, 69, 387–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, Z.-H.; Cai, H.-J.; Chen, H.; Sun, Y.-N.; Li, L.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, X.-Y. Effect of Water–Fertilizer–Gas Coupling on Soil N2O Emission and Yield in Greenhouse Tomato. Environ. Sci. 2020, 41, 2924–2935. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, Y.; Cai, H.; Song, L.; Wang, X.; Shang, Z.; Sun, Y. Aerated Irrigation of Different Irrigation Levels and Subsurface Dripper Depths Affects Fruit Yield, Quality and Water Use Efficiency of Greenhouse Tomato. Sustainability 2020, 12, 2703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, F.; Sun, J.; Jiang, Y.; Hu, D.; Yang, X.; Dong, M.; Yu, K.; Yu, S. Effect of rhizosphere aeration by subsurface drip irrigation with tanks on the growth of ‘Red Globe’ grape seedling and its absorption, distribution and utilization of urea–15 N. Sci. Hortic. 2018, 236, 207–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.D.; Wang, C. Experimental study on the effect of direct oxygen supply on the growth of rice seedling root zone. Fresenius Environ. Bull. 2019, 28, 4745–4751. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, L.-F.; Yu, S.-M.; Jin, Q.-Y. Effects of Aerated Irrigation on Leaf Senescence at Late Growth Stage and Grain Yield of Rice. Rice Sci. 2012, 19, 44–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Hu, L.; Xia, Z. Impact of Groundwater Salinity on Bioremediation Enhanced by Micro–Nano Bubbles. Materials 2013, 6, 3676–3687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Liao, C.H.; Zhu, Y.Z.; Chen, H.J.; Jin, Q.F. Characteristics of micro–bubble and nano–bubble and their application in environmental pollution control. Chem. Ind. Eng. Progress. 2012, 31, 1333–1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.-D.; Gu, X.-B.; Wang, J.-W.; Niu, W.-Q. Yield and gas exchange of greenhouse tomato at different nitrogen levels under aerated irrigation. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 668, 1156–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.-D.; Niu, W.-Q.; Gu, X.-B.; Zhang, Q.; Cui, B.-J.; Zhao, Y. Crop yield and water use efficiency under aerated irrigation: A meta-analysis. Agric. Water Manag. 2018, 210, 158–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattarai, S.P.; Midmore, D.J. Oxygation Enhances Growth, Gas Exchange and Salt Tolerance of Vegetable Soybean and Cotton in a Saline Vertisol. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 2009, 51, 675–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pendergast, L.; Bhattarai, S.P.; Midmore, D.J. Benefits of oxygation of subsurface drip–irrigation water for cotton in a Vertosol. Crop Pasture Sci. 2013, 64, 1171–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, G.; Mu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wang, L. Response of winter–wheat grain yield and water–use efficiency to irrigation with activated water on Guanzhong Plain in China. Irrig. Sci. 2020, 39, 263–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, G.; Zhou, B.; Mu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wang, L. Irrigation with Activated Water Promotes Root Growth and Improves Water Use of Winter Wheat. Agronomy 2021, 11, 2459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, F.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, P.; Jia, Z. Hydrothermal effects on maize productivity with different planting patterns in a rainfed farmland area. Soil Tillage Res. 2020, 205, 104794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, C.-L.; Zhang, X.-F.; Duan, H.-X.; Mburu, D.M.; Ren, H.-X.; Kavagi, L.; Dai, R.-Z.; Xiong, Y.-C. Dual plastic film and straw mulching boosts wheat productivity and soil quality under the El Nino in semiarid Kenya. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 738, 139808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Wei, T.; Han, Q.; Ren, X.; Jia, Z. Effects of different film mulching methods on soil water productivity and maize yield in a semiarid area of China. Agric. Water Manag. 2020, 241, 106382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kan, Z.-R.; Liu, Q.-Y.; He, C.; Jing, Z.-H.; Virk, A.L.; Qi, J.-Y.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, H.-L. Responses of grain yield and water use efficiency of winter wheat to tillage in the North China Plain. Field Crops Res. 2020, 249, 107760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Wu, G.; Mo, P.; Chen, S.; Wang, S.; Xiao, Y.; Ma, H.A.; Wen, T.; Guo, X.; Fan, G. The combined effects of maize straw mulch and no–tillage on grain yield and water and nitrogen use efficiency of dry–land winter wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Soil Tillage Res. 2019, 197, 104485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Ding, D.; Malone, R.W.; Chen, H.; Wei, Y.; Zhang, T.; Luo, X.; Li, C.; Chu, X.; Feng, H. When does plastic–film mulching yield more for dryland maize in the Loess Plateau of China? A meta-analysis. Agric. Water Manag. 2020, 240, 106290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Pan, Z.; Pan, F.; He, D.; Pan, Y.; Han, G.; Huang, N.; Zhang, Z.; Yin, W.; Zhang, J.; et al. The regional water–conserving and yield–increasing characteristics and suitability of soil tillage practices in Northern China. Agric. Water Manag. 2019, 228, 105883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, H.; Yan, C.; Liu, Q.; Ding, W.; Chen, B.; Li, Z. Effects of plastic mulching and plastic residue on agricultural production: A meta–analysis. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 651, 484–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.-D.; Zhang, Q.; Cui, B.-J.; Sun, J.; Wang, Z.; Ma, L.-H.; Niu, W.-Q. Aerated irrigation improves tomato yield and nitrogen use efficiency while reducing nitrogen application rate. Agric. Water Manag. 2020, 235, 106152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
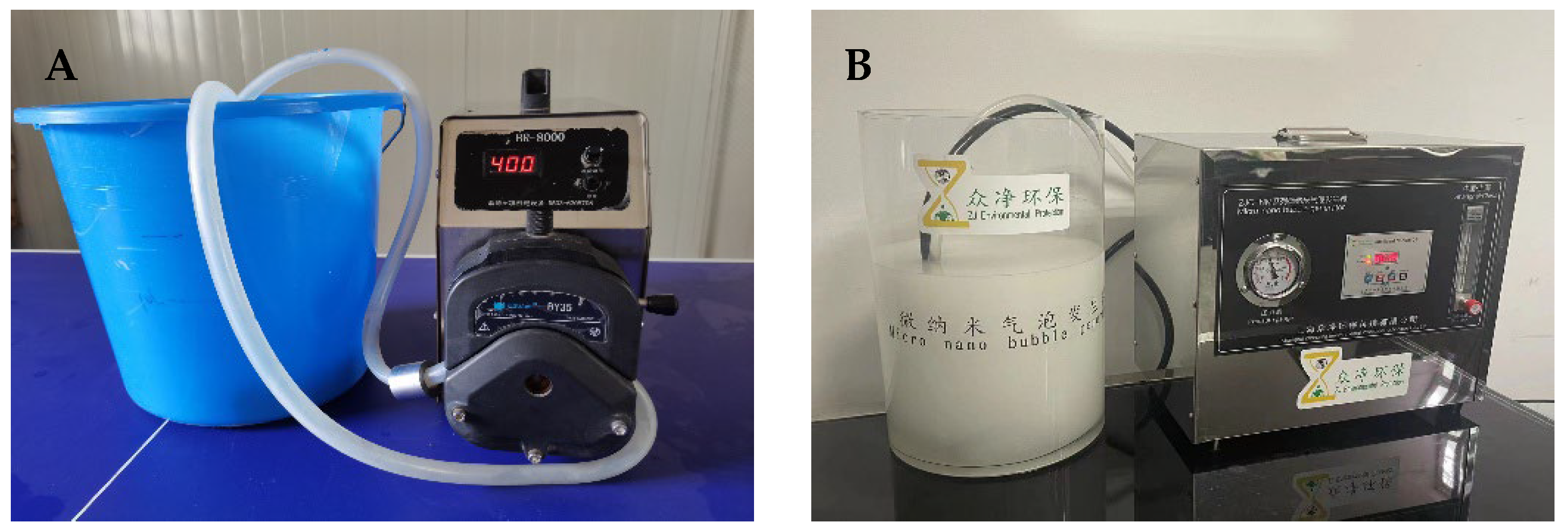



| Treatment | Irrigation Water Type | Irrigation Amount |
|---|---|---|
| TW80 | Tap water | 80%FC |
| TW65 | Tap water | 65%FC |
| TW50 | Tap water | 50%FC |
| MW80 | Magnetized water | 80%FC |
| MW65 | Magnetized water | 65%FC |
| MW50 | Magnetized water | 50%FC |
| OW80 | Oxygenated water | 80%FC |
| OW65 | Oxygenated water | 65%FC |
| OW50 | Oxygenated water | 50%FC |
| M&OW80 | Magnetized and oxygenated water | 80%FC |
| M&OW65 | Magnetized and oxygenated water | 65%FC |
| M&OW50 | Magnetized and oxygenated water | 50%FC |
| Irrigation Amount | Treatment | Spikes per Pot | Kernels per Pot | Yield (×10−3 kg pot−1) | WUE (kg ha−1 mm−1) | HI (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 80%FC | TW80 | 14.0 ± 1.0 a | 304.0 ± 29.1 b | 7.0 ± 1.3 b | 2.6 bc | 23.0 a |
| MW80 | 16.3 ± 2.5 a | 417.7 ± 15.7 a | 9.5 ± 0.9 a | 4.0 a | 22.9 a | |
| OW80 | 17.3 ± 0.6 a | 354.7 ± 40.0 b | 7.8 ± 0.5 ab | 3.2 ab | 22.9 a | |
| M&OW80 | 16.7 ± 2.3 a | 144.7 ± 19.1 c | 5.1 ± 1.0 c | 2.2 c | 13.9 b | |
| 65%FC | TW65 | 12.0 ± 1.7 b | 123.3 ± 7.6 c | 4.1 ± 0.1 b | 2.7 b | 15.9 b |
| MW65 | 13.0 ± 1.0 ab | 262.0 ± 21.5 a | 5.9 ± 0.3 a | 3.7 a | 22.0 a | |
| OW65 | 15.7 ± 1.5 a | 167.0 ± 2.7 b | 6.0 ± 0.7 a | 3.7 a | 23.7 a | |
| M&OW65 | 13.3 ± 1.5 ab | 187.7 ± 16.0 b | 4.7 ± 0.2 b | 3.0 b | 15.8 b | |
| 50%FC | TW50 | 7.3 ± 0.6 b | 114.3 ± 5.1 b | 2.2 ± 0.2 b | 2.9 c | 17.9 c |
| MW50 | 7.3 ± 0.6 b | 84.3 ± 3.1 c | 1.8 ± 0.2 b | 2.2 c | 17.0 c | |
| OW50 | 8.3 ± 0.6 b | 117.0 ± 9.5 b | 3.9 ± 0.8 a | 4.1 b | 21.9 b | |
| M&OW3 | 10.7 ± 0.6 a | 181.3 ± 27.6 a | 4.9 ± 0.7 a | 5.1 a | 24.7 a | |
| Irrigation amount | ** | ** | ** | ** | ns | |
| Water type | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** | |
| Irrigation amount × Water type | ns | ** | ** | ** | ** | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, H.; Fan, J.; Fu, W. Effect of Activated Water Irrigation on the Yield and Water Use Efficiency of Winter Wheat under Irrigation Deficit. Agronomy 2022, 12, 1315. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12061315
Wang H, Fan J, Fu W. Effect of Activated Water Irrigation on the Yield and Water Use Efficiency of Winter Wheat under Irrigation Deficit. Agronomy. 2022; 12(6):1315. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12061315
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Huan, Jun Fan, and Wei Fu. 2022. "Effect of Activated Water Irrigation on the Yield and Water Use Efficiency of Winter Wheat under Irrigation Deficit" Agronomy 12, no. 6: 1315. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12061315
APA StyleWang, H., Fan, J., & Fu, W. (2022). Effect of Activated Water Irrigation on the Yield and Water Use Efficiency of Winter Wheat under Irrigation Deficit. Agronomy, 12(6), 1315. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12061315






