Impact of Short-Term Atmospheric Heat Transfer on the Survival of Granary Weevil in Stored Winter Wheat
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Insect Eradication Test
2.2. Germination Test
2.3. Determination of Compositional and Quality Parameters of Wheat
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
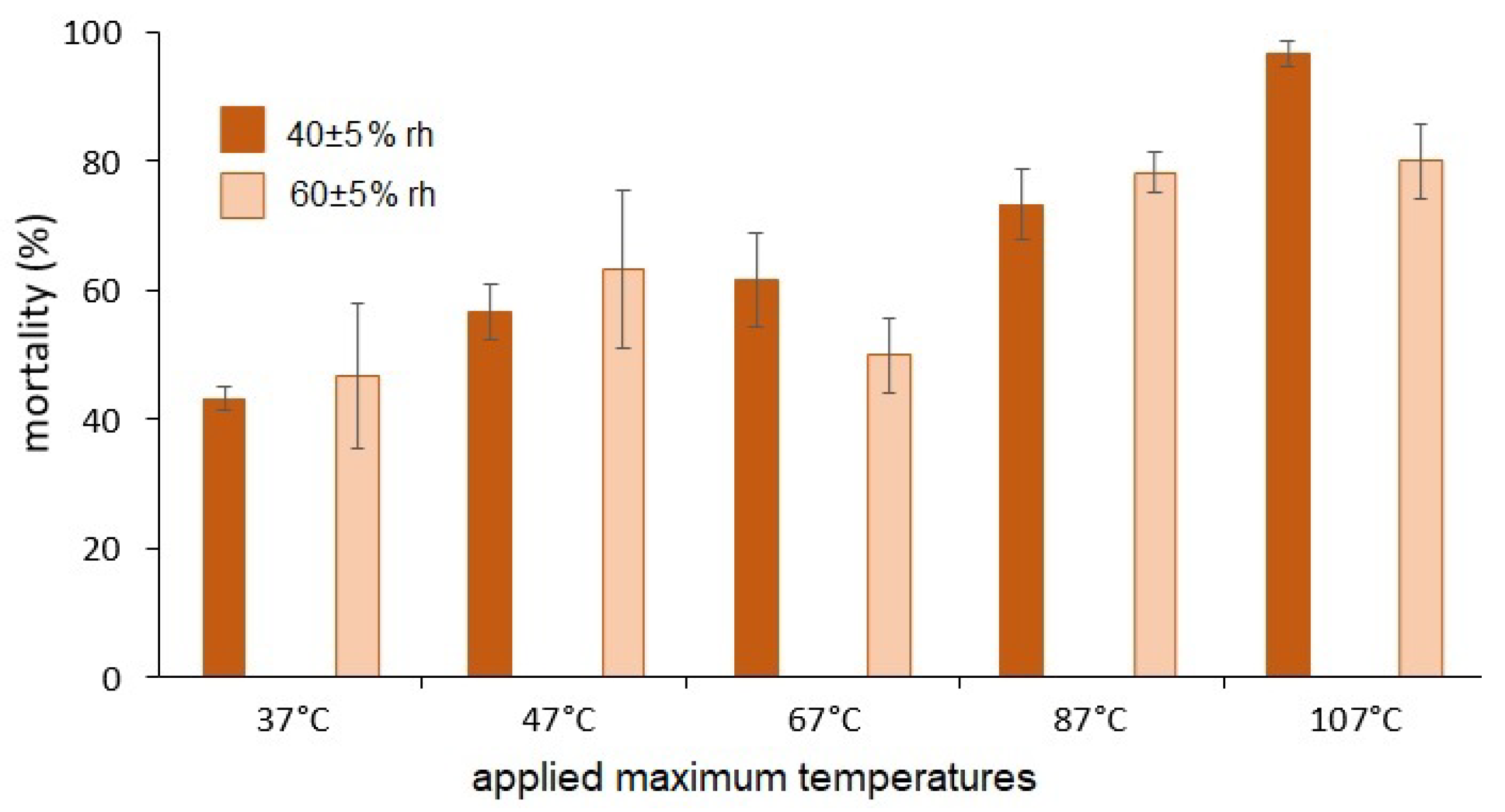
3.1. Insect Mortalities Triggered by 5 Minutes Heating
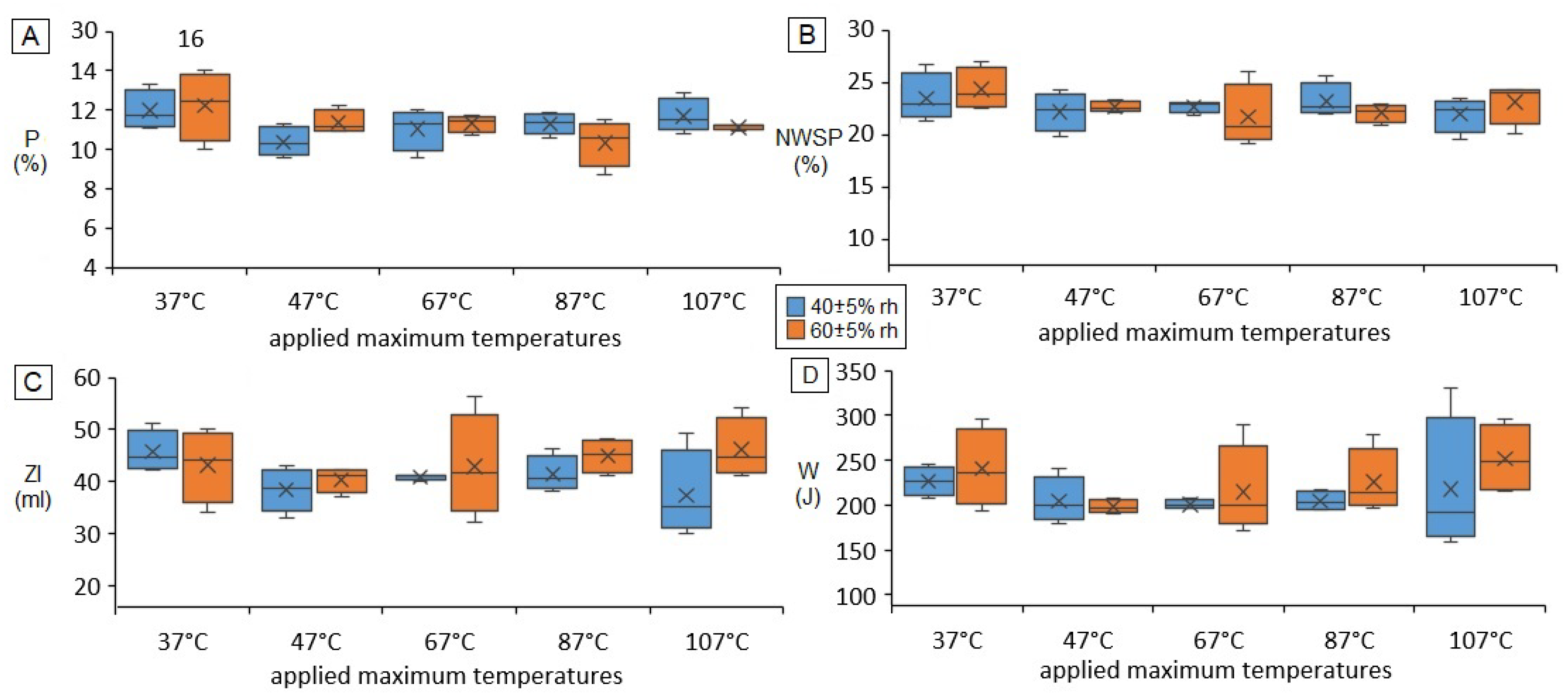
3.2. Germination, Compositional, and Quality Parameters of the Treated Wheat
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Longstaff, B.C. Biology of the grain pest species of the genus Sitophilus (Coleoptera: Curculionidae): A critical review. Prot. Ecol. 1981, 3, 83–130. [Google Scholar]
- Zettler, J.L.; Arthur, F.H. Chemical control of stored product insects with fumigants and residual treatments. Crop Prot. 2000, 19, 577–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammond, D. Heat Treatment for Insect Control: Developments and Applications; Elsevier: London, UK, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Hansen, J.D.; Johnson, J.A.; Winter, D.A. History and use of heat in pest control: A review. Int. J. Pest Manag. 2011, 57, 267–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youssef, M.O.; Youssef, A.D.; Hassan, R.A.; Mahmoud, A.M. Threshold temperature and heat unit requirements for the development of the granary weevil, Sitophilus granarius (L.). Arch. Phytopathol. Plant Prot. 2014, 47, 555–563. [Google Scholar]
- Adler, C. Efficacy of high temperatures against stored product insects. Mitt. Dtsch. Ges. Allg. Angew. Entomol. 2008, 16, 319–322. [Google Scholar]
- Murdock, L.L.; Shade, R.E. Eradication of cowpea weevil (Coleoptera: Bruchidae) in cowpeas by solar heating. Am. Entomol. 1991, 37, 228–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campolo, O.; Verdone, M.; Laudani, F.; Malacrinò, A.; Chiera, E.; Palmeri, V. Response of four stored products insects to a structural heat treatment in a flour mill. J. Stored Prod. Res. 2013, 54, 54–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrestha, B.; Yu, D.; Baik, O.D. Elimination of Criptolestes ferrungineus s. in wheat by radio frequency dielectric heating at different moisture contents. Prog. Electromagn. Res. 2013, 139, 517–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kljajić, P.; Andrić, G.; Perić, I. Impact of short-term heat pre-treatment at 50 °C on the toxicity of contact insecticides to adults of three Sitophilus granarius (L.) populations. J. Stored Prod. Res. 2009, 45, 272–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbar, S.; Sağlam, Ö.; Schilling, M.W.; Phillips, T.W. Efficacy of combining sulfuryl fluoride fumigation with heat to control the ham mite, Tyrophagus putrescentiae (Schrank) (Sarcoptiformes: Acaridae). J. Stored Prod. Res. 2018, 76, 7–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dowdy, A.K.; Fields, P.G. Heat combined with diatomaceous earth to control the confused flour beetle (Coleoptera: Tenebrionidae) in a flour mill. J. Stored Prod. Res. 2002, 38, 11–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziaee, M.; Ebadollahi, A.; Wakil, W. Integrating inert dusts with other technologies in stored products protection. Toxin Rev. 2021, 40, 404–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pradzynska, A. The role of higher temperatures to control of granary weevil [Sitophilus granarius L.]. J. Plant Prot. Res. 1995, 36, 119–127. [Google Scholar]
- Kovacs, M.I.P.; Fu, B.X.; Woods, S.M.; Khan, K. Thermal stability of wheat gluten protein: Its effect on dough properties and noodle texture. J. Cereal Sci. 2004, 39, 9–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schofield, J.D.; Bottomley, R.C.; Timms, M.F.; Booth, M.R. The effect of heat on wheat gluten and the involvement of sulphydryl-disulphide interchange reactions. J. Cereal Sci. 1983, 1, 241–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González, M.; Vernon-Carter, E.J.; Alvarez-Ramirez, J.; Carrera-Tarela, Y. Effects of dry heat treatment temperature on the structure of wheat flour and starch in vitro digestibility of bread. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 166, 1439–1447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortolan, F.; Steel, C.J. Protein characteristics that affect the quality of vital wheat gluten to be used in baking: A review. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2017, 16, 369–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Howe, R.W. A summary of estimates of optimal and minimal conditions for population increase of some stored products insects. J. Stored Prod. Res. 1965, 1, 177–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbott, W.S. A method of computing the effectiveness of an insecticide. J. Econ Entomol. 1925, 8, 265–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walter, G.H.; Hengeveld, R. Autecology: Organisms, Interactions and Environmental Dynamics; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA; Taylor & Francis Group: Abingdon, UK, 2014; p. 484. [Google Scholar]
- Schowalter, T.D. Insect Ecology: An Ecosystem Approach, 5th ed.; Academic Press: London, UK, 2022; p. 928. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, L.; Wang, S. Industrial-scale radio frequency treatments to control Sitophilus oryzae in rough, brown, and milled rice. J. Stored Prod. Res. 2016, 68, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramírez-Rojas, N.Z.; Cerón-García, A.; Salas-Araiza, M.D.; Estrada-García, H.J.; Rojas-Laguna, R.; Sosa-Morales, M.E. Radio frequency heating against Sitophilus zeamais Motschulsky in white maize. J. Stored Prod. Res. 2020, 89, 101730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keszthelyi, S.; Lukács, H.; Pál-Fám, F. Effects of different infra-red irradiations on the survival of granary weevil Sitophilus granarius: Bioefficacy and sustainability. Insects 2021, 12, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duangkhamchan, W.; Phomphai, A.; Wanna, R.; Wiset, L.; Laohavanich, J.; Ronsse, F.; Pieters, J.G. Infrared heating as a disinfestation method against Sitophilus oryzae and its effect on textural and cooking properties of milled rice. Food Bioproc. Technol. 2017, 10, 284–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Qiu, C.; Xiong, S.; Cheng, X. A thermal lethal model of rice weevils subjected to microwave irradiation. J. Stored Prod. Res. 2007, 43, 430–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keszthelyi, S.; Nyári, A.; Pál-Fám, F. Assessment of short-term mortality of granary weevil, Sitophilus granarius (Coleoptera: Curculionidae) triggered by different microwave irradiation powers. Int. J. Pest Manag. 2020, 66, 222–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleurat-Lessard, F.; Dupuis, S.A. Comparative analysis of upper thermal tolerance and CO2 production rate during heat shock in two different European strains of Sitophilus zeamais (Coleoptera: Curculionidae). J. Stored Prod. Res. 2010, 46, 20–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.; Ikediala, J.N.; Wang, S.; Hansen, J.D.; Cavalieri, R.P. High-temperature-short-time thermal quarantine methods. Postharv. Biol. Technol. 2000, 21, 129–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eastham, L.E.S.; McCully, S.B. The oviposition responses of Calandra granaria L. Exp. Biol. 1943, 20, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azizoglu, U.; Yilmaz, S.; Karaborklu, S.; Ayvaz, A. Ovicidal activity of microwave and UV radiations on Mediterranean flour moth Ephestia kuehniella Zeller, 1879 (Lepidoptera: Pyralidae). Turk. J. Entomol. 2011, 35, 437–446. [Google Scholar]
- Hrušková, M.; Faměra, O. Prediction of wheat and flour Zeleny sedimentation value using NIR technique. Czech J. Food Sci. 2003, 21, 91–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]


| Treatments | No. Progeny | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| control | 7.25 ± 0.75 | ||||||
| applied maximum temperatures | 37 °C | 47 °C | 67 °C | 87 °C | 107 °C | p | |
| exposure times | 5 min | 4.25 ± 0.47 | 4.00 ± 1.08 | 4.00 ± 0.49 | 2.50 ± 0.50 | 2.50 ± 0.28 | 0.317 |
| 6 min | 4.00 ± 1.35 | 2.00 ± 0.71 | 2.50 ± 0.50 | 0.50 ± 0.50 | 0.50 ± 0.28 | 0.047 | |
| 7 min | 2.50 ± 0.50 | 1.50 ± 0.86 | 2.25 ± 0.69 | 1.50 ± 0.64 | 0.75 ± 0.25 | 0.004 | |
| p | 0.075 | 0.429 | 0.056 | 0.280 | 0.068 | ||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lukács, H.; Pál-Fám, F.; Varga-Visi, É.; Rolbiecki, R.; Percze, A.; Keszthelyi, S. Impact of Short-Term Atmospheric Heat Transfer on the Survival of Granary Weevil in Stored Winter Wheat. Agronomy 2022, 12, 1313. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12061313
Lukács H, Pál-Fám F, Varga-Visi É, Rolbiecki R, Percze A, Keszthelyi S. Impact of Short-Term Atmospheric Heat Transfer on the Survival of Granary Weevil in Stored Winter Wheat. Agronomy. 2022; 12(6):1313. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12061313
Chicago/Turabian StyleLukács, Helga, Ferenc Pál-Fám, Éva Varga-Visi, Roman Rolbiecki, Attila Percze, and Sándor Keszthelyi. 2022. "Impact of Short-Term Atmospheric Heat Transfer on the Survival of Granary Weevil in Stored Winter Wheat" Agronomy 12, no. 6: 1313. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12061313
APA StyleLukács, H., Pál-Fám, F., Varga-Visi, É., Rolbiecki, R., Percze, A., & Keszthelyi, S. (2022). Impact of Short-Term Atmospheric Heat Transfer on the Survival of Granary Weevil in Stored Winter Wheat. Agronomy, 12(6), 1313. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12061313









