The Use of Compost from Post-Consumer Wood Waste Containing Microbiological Inoculums on Growth and Flowering of Chrysanthemum (Chrysanthemum × grandiflorum Ramat./Kitam.)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Composts Preparation
2.2. Experimental Design
2.3. Morphological Features
2.4. Macronutrients and Micronutrients Determination
2.5. Statistical Analyses
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Van Gerrewey, T.; Ameloot, N.; Navarrete, O.; Vandecruys, M.; Perneel, M.; Boon, N.; Geelen, D. Microbial activity in peat-reduced plant growing media: Identifying influential growing medium constituents and physicochemical properties using fractional factorial desingn of experiments. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 256, 120323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gruda, N. Current and future perspective of growing media in Europe. Acta Hortic. 2012, 960, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kern, J.; Tameorg, P.; Shanskiy, M.; Sakrabani, R.; Knicker, H.; Kammann, C.; Tuhkanen, E.-M.; Smidt, G.; Prasad, M.; Tiilikkala, K.; et al. Syneristic use of peat and charred material in growing media- an option to reduce the pressure on peatlands? J. Environ. Eng. Landsc. Manag. 2017, 25, 160–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamczewska-Sowińska, K.; Sowiński, J.; Jamroz, E.; Bekier, J. Combining Willow compost and peat as media for juvenile tomato transplant production. Agronomy 2021, 11, 2089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tubiello, F.N.; Biancalani, R.; Salvatore, M.; Rossi, S.; Conchedda, G. A worldwide assessment of greenhouse gas emissions from drained organic soils. Sustainability 2016, 8, 371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irle, M.; Velez, G.; Belloncle, C.; Bonin, E.; Lahave, M. Recycling waste fibreboard. In Proceedings of the IPPS 2019, Llandudno, UK, 9–10 October 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Borazjani, H.; Diehl, S.V.; Stewart, H.A. Production of Compost from Furniture Manufacturing Woodwastes. For. Prod. J. 1997, 47, 47–48. [Google Scholar]
- Fengel, D.; Wegener, G. Wood: Chemistry, Ultrastructure, Reactions; Walter de Gruyter: Berlin, NY, USA, 1983. [Google Scholar]
- Rowell, M.R.; Pettersen, R.; Tshabalala, M.A. Cell Wall Chemistry. In Handbook of Wood Chemistry and Wood Composites, 2nd ed.; Rowell, R.M., Ed.; CRC Press Taylor & Francis Group: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2012; pp. 34–70. [Google Scholar]
- Michel, F.C.; Rigot, J.; Tirado, S. Evaluation of the Compostability of Polymer-Coated Paperboard Packaging Materials; A report to the International Paper Packaging Development Center; 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Kirk, T.K. Lignin degradation: Basic research progress and aplications in soil remediation and biopulping. In Cellulosics: Pulp, Fibre and Environmental Aspects; Kennedy, J.F., Phillips, G.O., Williams, P.A., Eds.; Ellis Horwood: New York, NY, USA, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Healthy Soils—New EU Soil Strategy. Available online: https://ec.europa.eu/info/law/better-regulation/have-your-say/initiatives/12634-Healthy-soils-new-EU-soil-strategy_en (accessed on 19 April 2022).
- Hossain, M.Z.; Von Fragstein, P.; Von Niemsdorff, P.; Hes, J. Effect of Different Organic Wastes on Soil Propertie s and Plant Growth and Yield: A Review. Sci. Agric. Bohem. 2017, 48, 224–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolna-Maruwka, A.; Schroeter-Zakrzewska, A.; Borowiak, K.; Niewiadomska, A.; Piechota, T.; Swedrzyński, A.; Kosicka, D.; Zielewicz, W. The microbiological properties of substrates with sewage sludge composts in French Marigold (Tagetes patula L.) cultivation. Fresenius Environ. Bull. 2017, 26, 2822–2834. [Google Scholar]
- Zawadzińska, A.; Salachna, P. Ivy pelargonium response to media containing sewage sludge and potato pulp. Plant Soil Environ. 2018, 64, 180–185. [Google Scholar]
- Harris, C.N.; Dickson, R.W.; Fisher, P.R.; Jackson, B.E.; Poleatewich, A.M. Evaluating peat substrates amended with Pine wood fiber for Nitrogen immobilization and effects on plant performance with container grown petunia. HortTechnology 2020, 30, 107–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozik, E.; Wróblewska, H.; Bosiacki, M.; Wojciechowska, E. The use of composts from wood waste in the cultivation of selected species of ornamental plants. Apar. Badaw. Dydakt. 2010, 4, 75–81. (In Polish) [Google Scholar]
- Wróblewska, H. Studies on the effect of compost made of post-used wood waste on growth of willow plants. Mol. Cryst. Liq. Cryst. 2008, 483, 352–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wróblewska, H.; Czekała, J.; Piotrowska, M. Impact of different wood wastes on chemical properties of manufacutered composts. J. Res. Appl. Agric. Eng. 2009, 54, 185–189. [Google Scholar]
- Wróblewska, H.; Schroeter-Zakrzewska, A.; Głuchowska, K.; Wolna-Maruwka, A.; Kleiber, T. Application of post-consumer wood composts in canna lily (Canna × generaliis L.H.Bailey) cultivation. Drewno 2014, 57, 5–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schroeter-Zakrzewska, A.; Wolna-Maruwka, A.; Kleiber, T.; Wróblewska, H.; Głuchowska, K. Influence of compost from post-consumer wood on development, nutrition state of plants, microbiological and biochemical parameters of substrates in zonal pelargonium (Pelargonium zonale). Agronomy 2021, 11, 994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez, C. Lignocellulosic residues: Biodegradation and bioconversion by fungi. Biotechnol. Adv. 2009, 27, 185–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muttalib, S.A.A.; Ismail, S.N.S.; Praveena, S.M. Application of Effective Microorganism (EM) in food waste composting: A review. Asia Pac. Environ. Occup. Health J. 2016, 2, 37–47. [Google Scholar]
- Rostogi, M.; Nandal, M.; Khosla, B. Microbes as vital additives for soil waste composting. Heliyon 2020, 6, e03343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greff, B.; Szigeti, J.; Nagy, Á.; Lakatos, E.; Varga, L. Influence of microbial inoculants on co-composting of lignocellulosic crop residues with farm animal manure: A review. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 302 Pt B, 114088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higa, T. Proceedings of Effective Microorganisms: A biotechnology for mankind. In Proceeding of the First International Conference on Kyusei Nature Farming, Washington, DC, USA, 17–21 October 1991; pp. 8–14. [Google Scholar]
- Valarini, P.J.; Alvarez, M.C.D.; Gasco, J.M.; Guerrero, F.; Tokeshi, H. Assessment of soil properties by organic matter an EM-microorganism incorporation. Rev. Bras. Cienc. Solo 2003, 27, 519–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mbouobda, H.D.; Fotso, F.O.T.S.O.; Djeuani, C.A.; Baliga, M.O.; Omokolo, D.N. Comparative evaluation of enzyme activities and phenol content of Irish potato (Solanum tuberosum) grown under EM and IMO manures Bokashi. Int. J. Biol. Chem. Sci. 2014, 8, 157–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Sharma, A.; Saha, T.N.; Arora, A.; Shah, R.; Nain, L. Efficient Microorganism compost benefits plant growth and improves soil health in Calendula and Marigold. Hortic. Plant J. 2017, 3, 67–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Jiang, Z.; Li, M.; Li, Q. Acompost-derived thermophilic microbal consortium enhances the humification proces and alters the microbial diversity during composting. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 243, 240–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zawadzińska, A.; Salachna, P.; Nowak, J.S.; Kowalczyk, W. Response of Interspecific Geraniums to Waste Wood Fiber Substrates and Additional Fertilization. Agriculture 2021, 11, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salachna, P.; Zawadzińska, A. Growth, flowering and bulb yield of Eucomis autumnalis (Mill.) Chitt. Treated with plant growth regulators. Folia Hortic. 2017, 29, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Schroeter-Zakrzewska, A.; Wolna-Maruwka, A.; Borowiak, K. The application of Effective Microorganism preparation in growing of zonal pelargonium (Pelargonium zonale). Ecol. Chem. Eng. A 2013, 20, 701–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolna-Maruwka, A.; Mocek-Płóciniak, A.; Schroeter-Zakrzewska, A.; Niewiadomska, A.; Piechota, T.; Swedrzyńska, D.; Kosicka, D.; Pilarska, A.A. The influence of a microbial inoculum on the enzymatic activity of peat and morphological features of the French Marigold. Nauka Przyr. Technol. 2015, 9, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Górski, R.; Kleiber, T. Effect of Effective Microorganism (EM) on nutrient contents in substrate and development and yielding of rose (Rosa hybrida) and gerbera (Gerbera jamesonii). Ecol. Chem. Eng. A 2010, 17, 505–513. [Google Scholar]
- Wróblewska, H.; Schroeter-Zakrzewska, A.; Zakrzewski, P. The use of compost obtained from post-consumer wood waste in the cultivation of zonal pelargonium (Pelargonium zonale) ‘Andria’. Apar. Badaw. Dydakt. 2013, 4, 365–372. [Google Scholar]
- Gariglio, N.F.; Buyatti, M.A.; Bouzo, C.A.; Weber, M.E.; Pilatti, R.A. Use of willow (Salix sp.) sawdust as potting medium for calendula (Calendula officinalis) and marigold (Tagetes erecta) plant production. N. Z. J. Crop Hortic. Sci. 2004, 32, 147–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Brito, L.M.; Reis, M.; Mourao, I.; Coutinho, J. Use of Acacia waste compost as an alternative component for horticultural substrates. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 2015, 46, 1814–1826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, A.M.; Gilliam, C.H.H.; Fain, G.B.; Torbert, H.A.; Gallagher, T.V.; Sibley, J.L.; Boyer, C.H.R. Low-Value trees as alternative substrates in greenhouse production of three annual species. J. Environ. Hort. 2011, 29, 152–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bekier, J.; Jamroz, E.; Sowiński, J.; Adamczewska-Sowińska, K.; Kałuża-Haładyn, A. Effect of differently matured composts from willow on growth and development of Lettuce. Agronomy 2022, 12, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Picchoni, A.G.; Martinez, A.S.A.; Mexal, J.G.; VanLeeuwen, D.M. Vegetative growth and leaf nutrient status ‘Carpino’ chrysanthemum on a pecan wood-amended commercial substrate. HortScience 2016, 51, 177–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
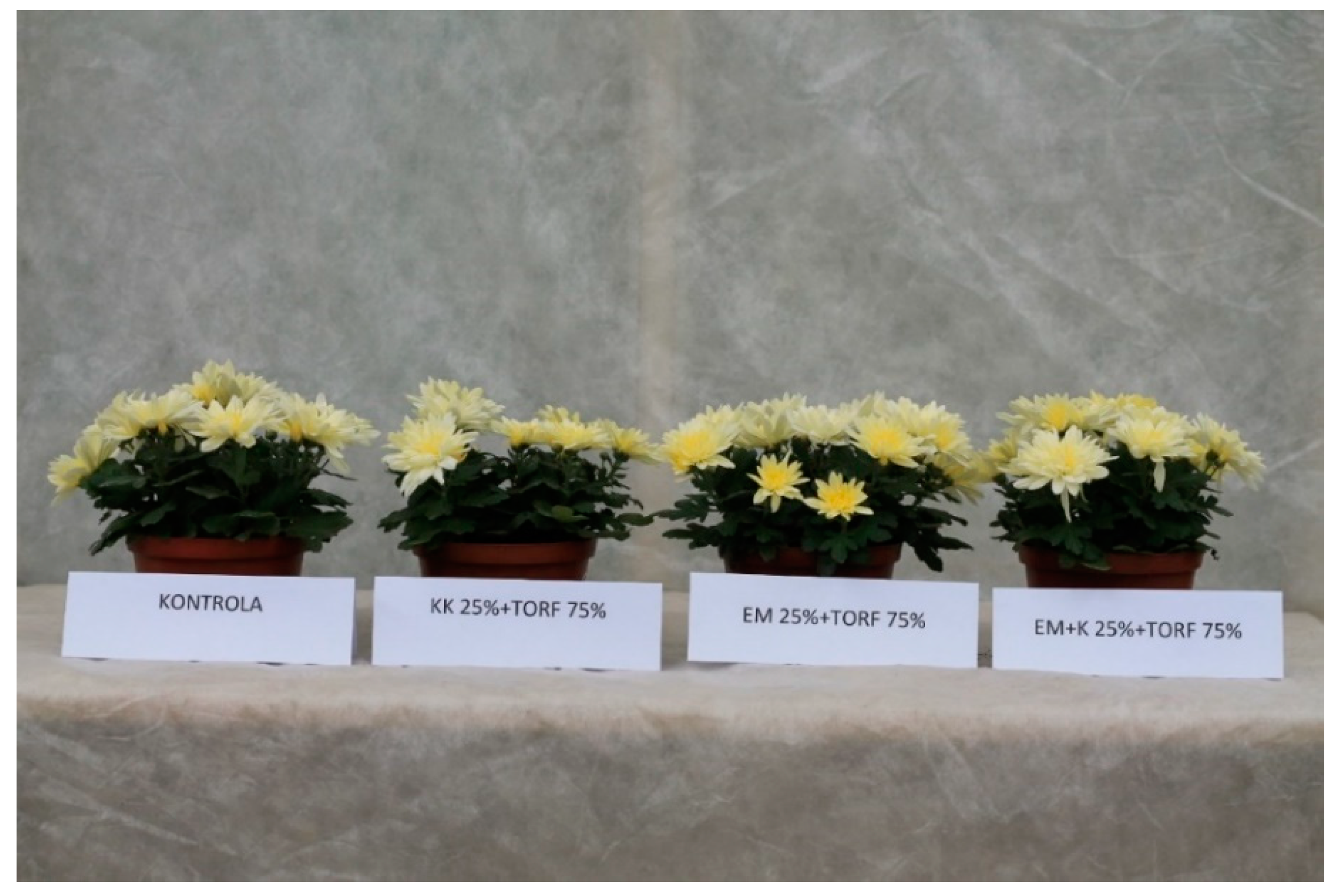
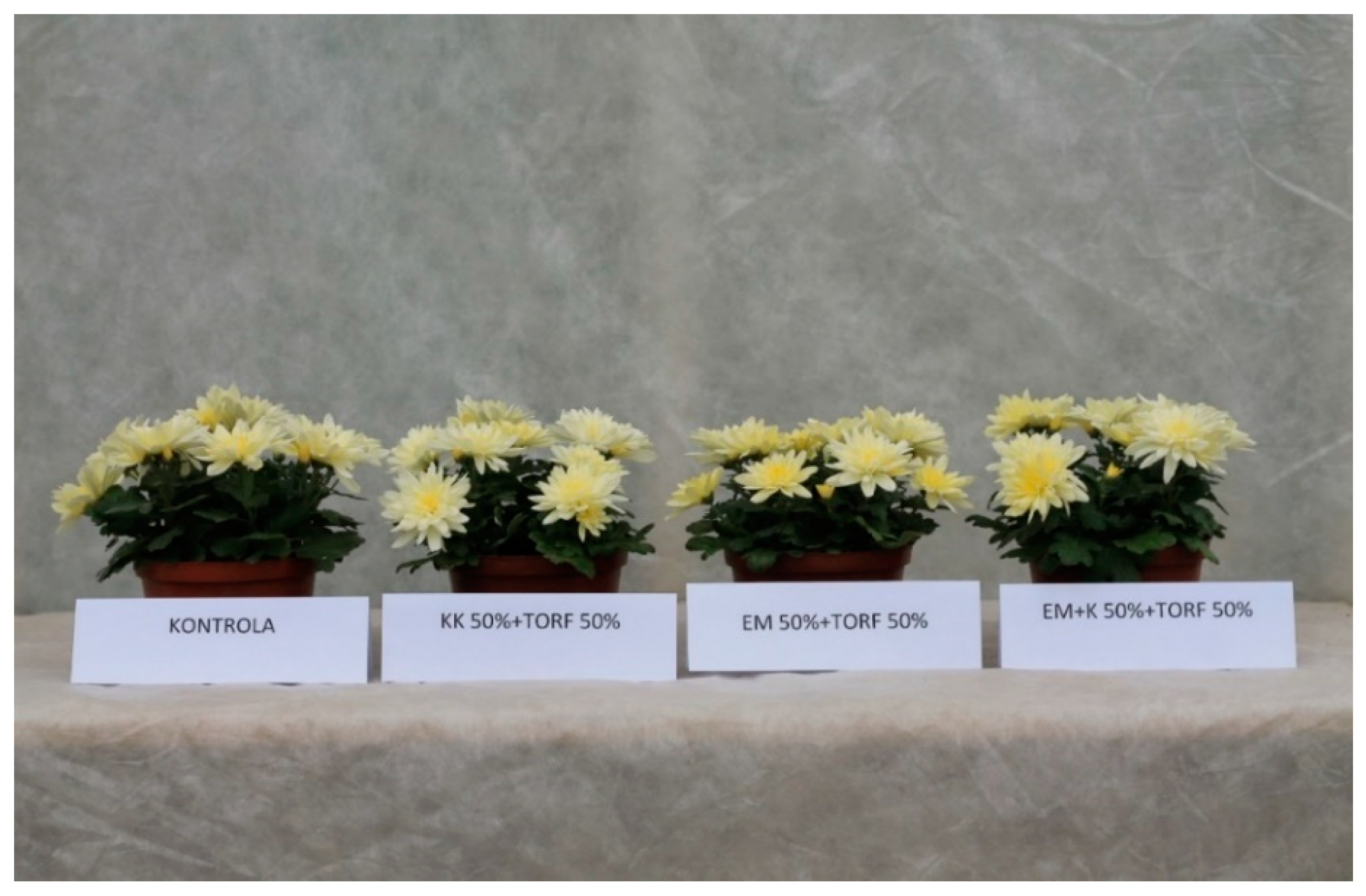
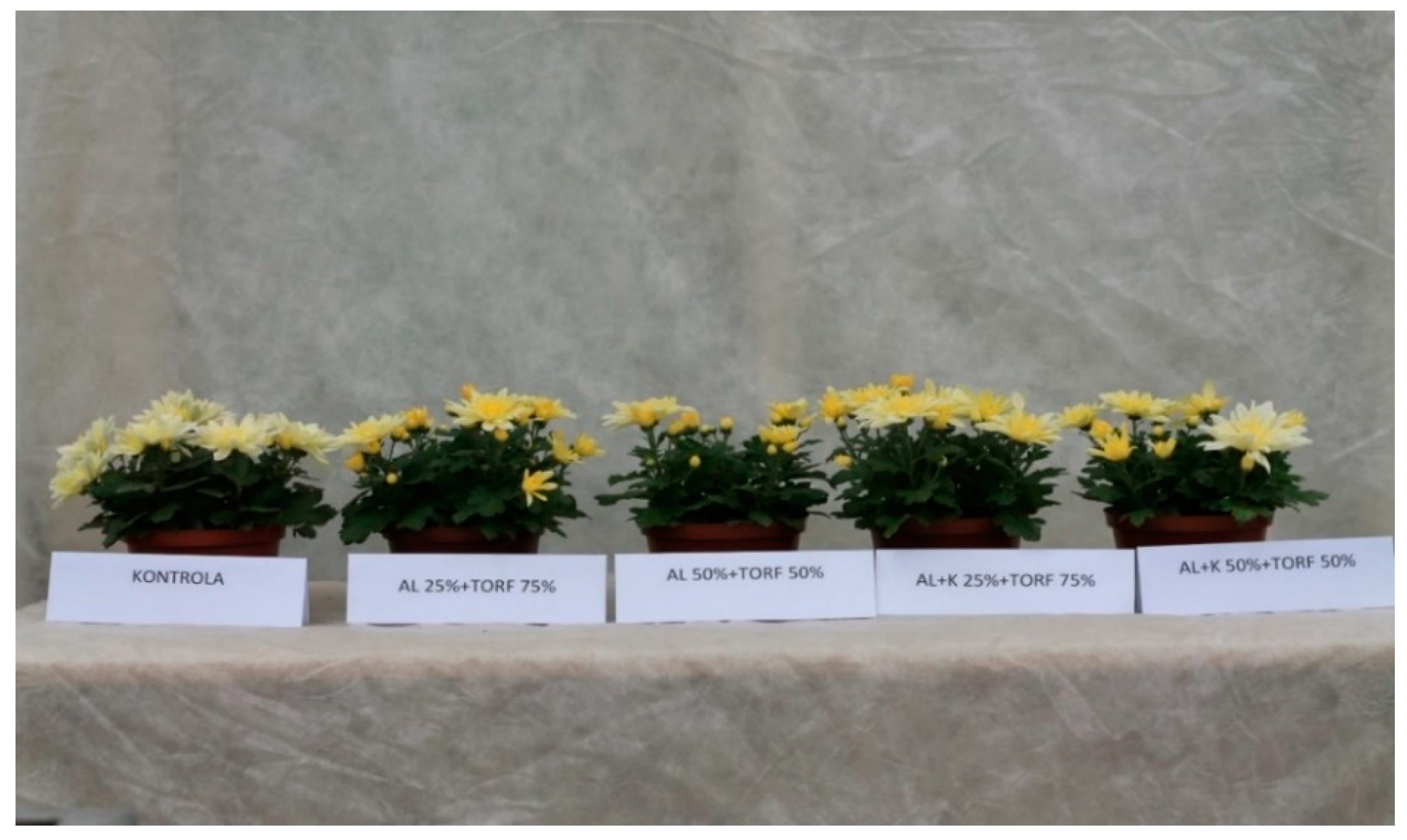
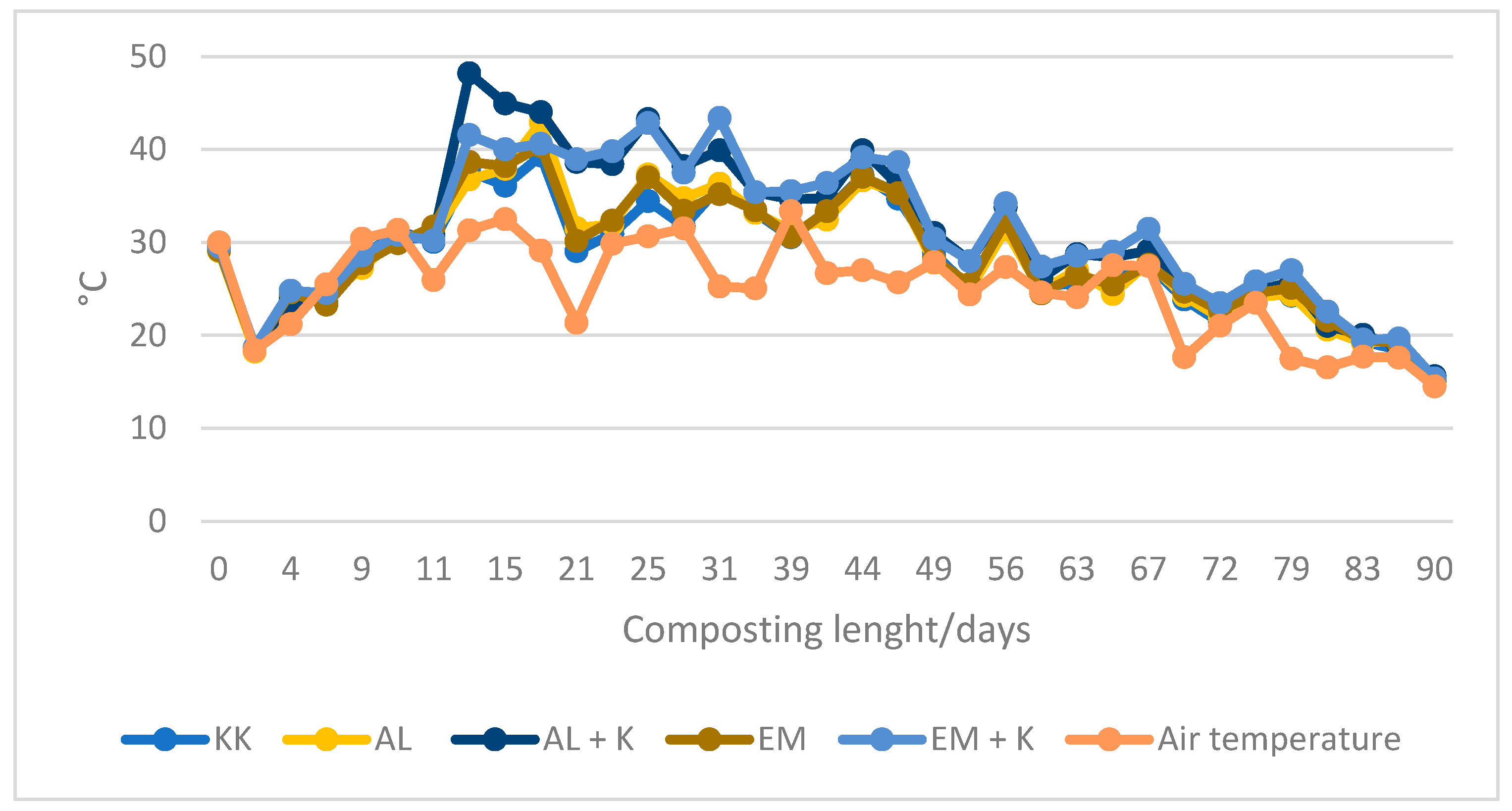
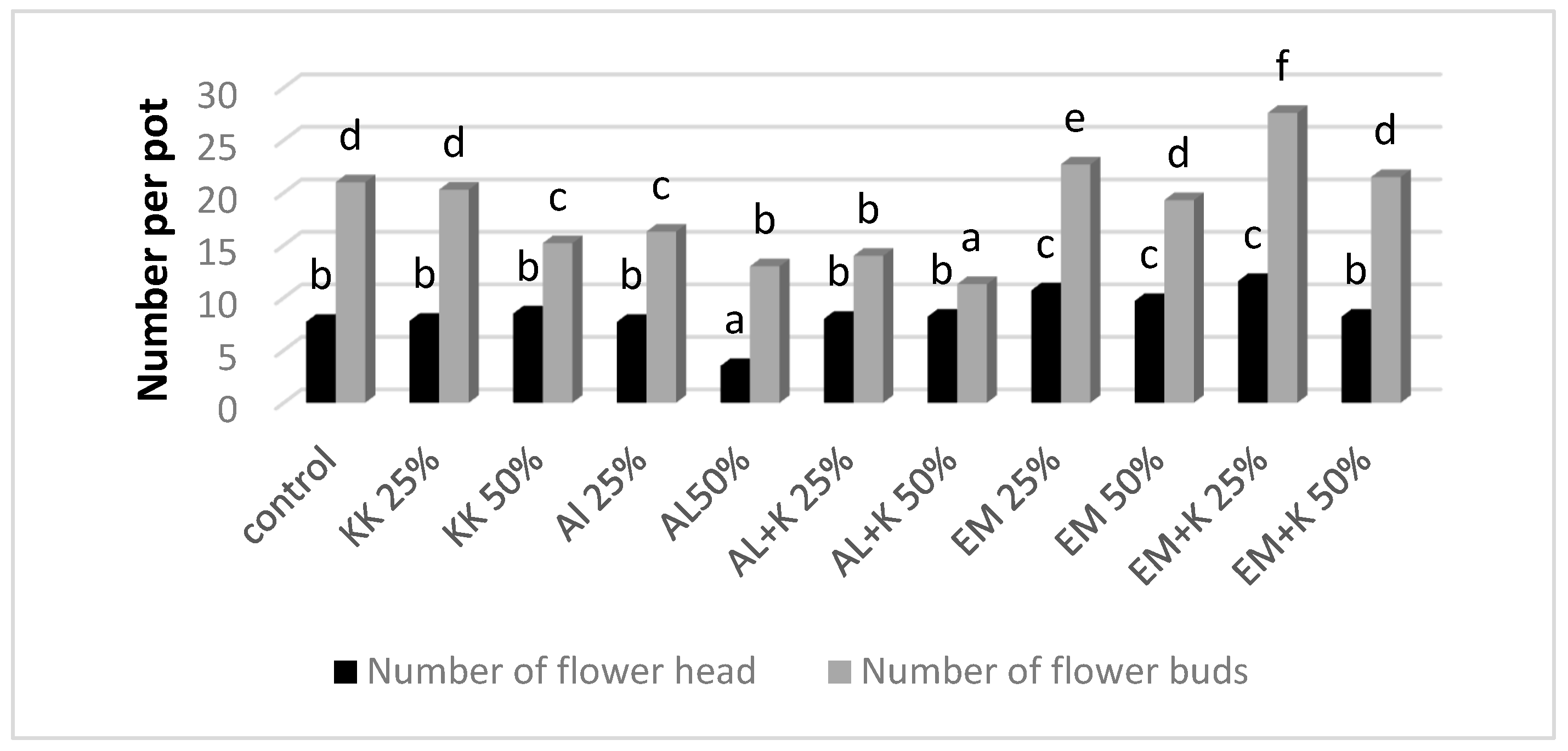



| Reactors Number | Name | Post-Consumer Wood Waste | Fibreboard Mature Compost | Protohumowit | Starch, Sugar, Corn Oil, Water | Activit Las 1200 mL | EM 250 mL | Bio Best |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | KK | √ | √ | √ | √ | |||
| 2 | KK | √ | √ | √ | √ | |||
| 3 | AL | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | ||
| 4 | AL | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | ||
| 5 | AL + K | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | |
| 6 | AL + K | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | |
| 7 | EM | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | ||
| 8 | EM | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | ||
| 9 | EM + K | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | |
| 10 | EM + K | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ |
| Name | Dry Mass | Ash | Density |
|---|---|---|---|
| % | g·dm3 | ||
| KK | 32.7 | 10.5 | 320 |
| AL | 32.2 | 11.5 | 330 |
| AL + K | 31.2 | 15.8 | 350 |
| EM | 32.8 | 11.4 | 382 |
| EM + K | 30.9 | 15.9 | 322 |
| Control-Peat | 31.3 | 15.6 | 330 |
| Medium | N-NO3− | P | K | Ca | Mg | Fe | Mn | Zn | Cu | Cl | Salinity g NaCl·dm3 | pH |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| mg·dm−3 | ||||||||||||
| Control-peat | 209 | 71 | 210 | 963 | 101 | 86.4 | 23.8 | 6.5 | 1.7 | 42 | 1.56 | 5.3 |
| KK | 130 | 57 | 250 | 1022 | 113 | 53.6 | 16.5 | 374.0 | 2.2 | 51 | 1.64 | 5.5 |
| EM | 165 | 39 | 250 | 1012 | 114 | 67.5 | 18.9 | 322.0 | 2.1 | 56 | 1.67 | 5.4 |
| EM + K | 162 | 107 | 370 | 1101 | 137 | 57.6 | 18.6 | 314.5 | 2.0 | 89 | 1.86 | 5.4 |
| AL | 162 | 64 | 240 | 943 | 111 | 56.8 | 17.6 | 371.0 | 1.9 | 55 | 1.53 | 5.4 |
| AL + K | 161 | 93 | 335 | 873 | 118 | 52.4 | 19.3 | 276.5 | 2.0 | 91 | 1.48 | 5.5 |
| Substrate Treatments | Compost KK, AL, AL + K, EM, EM + K | Peat |
|---|---|---|
| I | 50% | 50% |
| II | 25% | 75% |
| Control | 100% |
| Medium | N-NO3- | P | K | Ca | Mg | Fe | Mn | Zn | Cu | Cl | Salinity g NaCl·dm3 | pH |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| mg·dm−3 | ||||||||||||
| beginning of the experiment | ||||||||||||
| Control-peat | 84 | 51 | 111 | 1707 | 228 | 24.14 | 1.53 | 17.73 | 1.65 | 106 | 1.50 | 6.5 |
| end of the experiment | ||||||||||||
| Control-peat | 891 | 114 | 519 | 2428 | 205 | 25.95 | 2.54 | 2.69 | 1.37 | 81 | 5.36 | 5.6 |
| KK beginning of the experiment | ||||||||||||
| 50% compost + 50% peat | 6 | 28 | 41 | 871 | 153 | 48.4 | 3.19 | 588.6 | 1.58 | 54 | 0.75 | 6.1 |
| 25% compost + 75% peat | 2 | 32 | 52 | 1068 | 183 | 37.0 | 2.24 | 401.3 | 1.79 | 46 | 0.83 | 6.5 |
| KK end of the experiment | ||||||||||||
| 50% compost + 50% peat | 980 | 70 | 265 | 1352 | 164 | 64.02 | 27.68 | 733.0 | 1.68 | 66 | 4.98 | 4.0 |
| 25% compost + 75% peat | 1155 | 78 | 340 | 1677 | 205 | 24.7 | 1.52 | 195.8 | 1.68 | 65 | 5.91 | 4.2 |
| EM beginning of the experiment | ||||||||||||
| 50% compost + 50% peat | 114 | 24 | 37 | 833 | 137 | 46.31 | 6.10 | 514.3 | 1.44 | 53 | 1.22 | 5.6 |
| 25% compost + 75% peat | 18 | 29 | 45 | 964 | 172 | 39.84 | 2.58 | 254.2 | 1.51 | 54 | 1.14 | 6.1 |
| EM end of the experiment | ||||||||||||
| 50% compost + 50% peat | 1530 | 67 | 285 | 1604 | 199 | 44.55 | 34.60 | 734.6 | 1.35 | 116 | 7.76 | 4.4 |
| 25% compost + 75% peat | 1045 | 66 | 302 | 1462 | 182 | 43.67 | 24.60 | 463.25 | 1.33 | 72 | 5.56 | 4.5 |
| EM + K beginning of the experiment | ||||||||||||
| 50% compost + 50% peat | 415 | 107 | 89 | 1413 | 242 | 44.55 | 34.60 | 734.6 | 1.35 | 127 | 2.75 | 5.7 |
| 25% compost + 75% peat | 1045 | 66 | 302 | 1462 | 718.3 | 43.43 | 5.43 | 463.25 | 1.80 | 72 | 5.56 | 4.5 |
| EM + K end of the experiment | ||||||||||||
| 50% compost + 50% peat | 1855 | 280 | 892 | 2208 | 338 | 44.55 | 34.60 | 734.6 | 1.35 | 242 | 8.58 | 4.5 |
| 25% compost + 75% peat | 1270 | 190 | 612 | 1898 | 272 | 46.37 | 28.91 | 530.75 | 1.72 | 140 | 6.82 | 4.5 |
| AL beginning of the experiment | ||||||||||||
| 50% compost + 50% peat | 166 | 30 | 34 | 820 | 130 | 53.99 | 9.20 | 683.62 | 1.85 | 54 | 1.42 | 5.3 |
| 25% compost + 75% peat | 5 | 23 | 21 | 917 | 161 | 41.80 | 2.78 | 452.0 | 1.55 | 40 | 0.81 | 6.1 |
| AL end of the experiment | ||||||||||||
| 50% compost + 50% peat | 1085 | 69 | 242 | 1379 | 162 | 63.84 | 31.70 | 825.38 | 1.78 | 107 | 5.11 | 4.1 |
| 25% compost + 75% peat | 1000 | 74 | 280 | 1531 | 185 | 52.64 | 28.86 | 553.63 | 1.68 | 104 | 4.90 | 4.3 |
| AL + K beginning of the experiment | ||||||||||||
| 50% compost + 50% peat | 372 | 137 | 85 | 1327 | 220 | 46.74 | 6.86 | 834.5 | 2.17 | 102 | 2.52 | 5.5 |
| 25% compost + 75% peat | 59 | 75 | 41 | 1344 | 224 | 35.33 | 2.34 | 368.0 | 1.82 | 60 | 1.39 | 6.3 |
| AL + K end of the experiment | ||||||||||||
| 50% compost + 50% peat | 1980 | 272 | 853 | 2117 | 323 | 46.88 | 42.75 | 817.63 | 1.60 | 262 | 8.80 | 4.6 |
| 25% compost + 75% peat | 1350 | 214 | 600 | 1954 | 282 | 46.11 | 29.77 | 474.00 | 1.68 | 170 | 6.55 | 4.5 |
| Medium | Height of Plants (cm) | Diameter of Plants (cm) | Diameter of Shoot (mm) | Fresh Weight (g)/per pot | Dry Weight (g)/per pot | Diameter of Flower Head (cm) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control-peat | 13.0 c * | 22.7 b | 3.0 c | 66.7 c | 27.3 ab | 7.0 bc | |
| KK | 25% compost + 75% peat | 11.4 a | 20.2 a | 2.5 a | 50.5 b | 20.6 a | 7.4 c |
| 50% compost + 50% peat | 10.4 a | 20.0 a | 2.6 ab | 47.2 a | 20.4 a | 6.7 b | |
| AL | 25% compost + 75% peat | 13.0 c | 21.7 a | 3.2 d | 57.1 b | 23.1 a | 6.6 b |
| 50% compost + 50% peat | 11.0 a | 19.6 a | 2.9 b | 44.1 a | 38.2 b | 5.6 a | |
| AL + K | 25% compost + 75% peat | 13.2 c | 23.2 c | 2.8 b | 62.6 c | 45.5 c | 7.1 c |
| 50% compost + 50% peat | 12.2 b | 22.0 b | 2.3 a | 55.1 b | 41.7 c | 7.5 c | |
| EM | 25% compost + 75% peat | 12.6 b | 23.1 c | 2.9 b | 77.1 d | 30.6 b | 7.1 c |
| 50% compost + 50% peat | 11.5 a | 21.7 a | 2.9 b | 57.4 b | 24.3 a | 7.1 c | |
| EM + K | 25% compost + 75% peat | 12.4 b | 22.5 b | 3.1 c | 77.9 d | 31.4 b | 7.5 c |
| 50% compost + 50% peat | 11.5 a | 21.0 a | 3.1 c | 64.4 c | 26.8 ab | 6.7 b | |
| Medium | Number of Leaves | Greening Index of Leaves (SPAD) | Leaf Area (cm2) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control-peat | 140.7 c * | 51.4 c | 12.3 b | |
| KK | 25% compost + 75% peat | 160.7 d | 51.5 c | 11.6 a |
| 50% compost + 50% peat | 133.2 b | 43.4 a | 11.4 a | |
| AL | 25% compost + 75% peat | 125.2 b | 40.2 a | 11.8 a |
| 50% compost + 50% peat | 95.5 a | 47.1 b | 11.7 a | |
| AL + K | 25% compost + 75% peat | 137.2 b | 41.5 a | 12.5 b |
| 50% compost + 50% peat | 138.2 b | 42.1 a | 12.1 b | |
| EM | 25% compost + 75% peat | 76.8 a | 48.5 b | 14.4 c |
| 50% compost + 50% peat | 156.2 d | 49.0 b | 14.9 cd | |
| EM + K | 25% compost + 75% peat | 156.7 d | 48.9 b | 14.7 cd |
| 50% compost + 50% peat | 138.0 b | 46.8 b | 14.0 c | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Schroeter-Zakrzewska, A.; Komorowicz, M. The Use of Compost from Post-Consumer Wood Waste Containing Microbiological Inoculums on Growth and Flowering of Chrysanthemum (Chrysanthemum × grandiflorum Ramat./Kitam.). Agronomy 2022, 12, 1274. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12061274
Schroeter-Zakrzewska A, Komorowicz M. The Use of Compost from Post-Consumer Wood Waste Containing Microbiological Inoculums on Growth and Flowering of Chrysanthemum (Chrysanthemum × grandiflorum Ramat./Kitam.). Agronomy. 2022; 12(6):1274. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12061274
Chicago/Turabian StyleSchroeter-Zakrzewska, Anita, and Magdalena Komorowicz. 2022. "The Use of Compost from Post-Consumer Wood Waste Containing Microbiological Inoculums on Growth and Flowering of Chrysanthemum (Chrysanthemum × grandiflorum Ramat./Kitam.)" Agronomy 12, no. 6: 1274. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12061274
APA StyleSchroeter-Zakrzewska, A., & Komorowicz, M. (2022). The Use of Compost from Post-Consumer Wood Waste Containing Microbiological Inoculums on Growth and Flowering of Chrysanthemum (Chrysanthemum × grandiflorum Ramat./Kitam.). Agronomy, 12(6), 1274. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12061274





