Solar Radiation Prediction Model for the Yellow River Basin with Deep Learning
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Location and Data
- (1)
- If one or all of the measured meteorological data on a day is missing, the data of that day shall be deleted;
- (2)
- If Rs/Ra or n/N is greater than 1, we delete the data of that day to ensure that the data has real physical meaning (where Rs and Ra are global and extraterrestrial solar radiation (MJ/(M2 · d)), respectively; n represents the actual sunshine hours in a day; N represents the maximum sunshine hours on the same day);
- (3)
- If there are more than 10 missing data in a month, the data of that month will be deleted.
2.2. Ångström-Prescott Equation
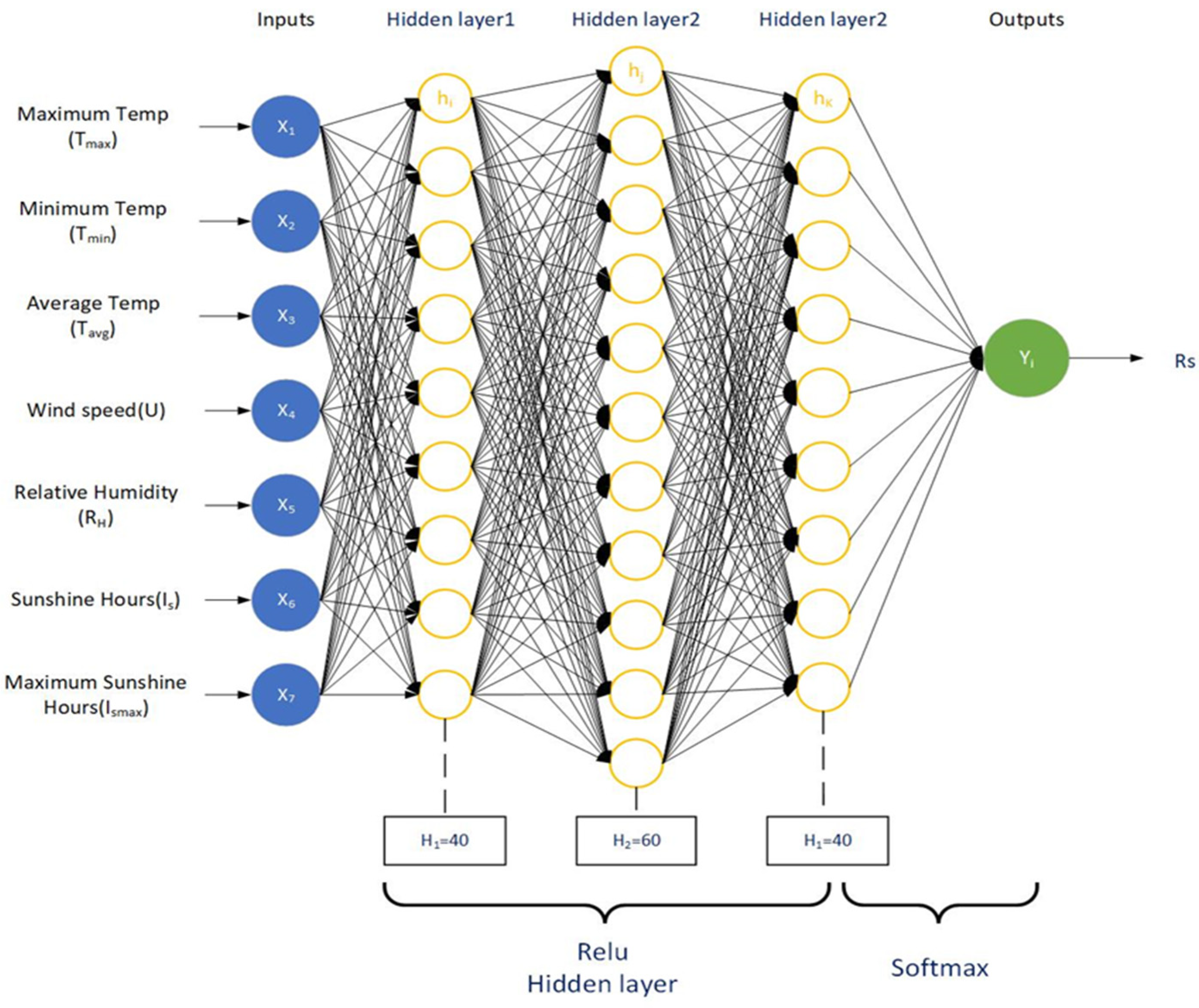
2.3. Deeping Learning Model
2.4. Model Evaluation Metrics
3. Results
3.1. Corrected Å-P Parameters and Performance Evaluation
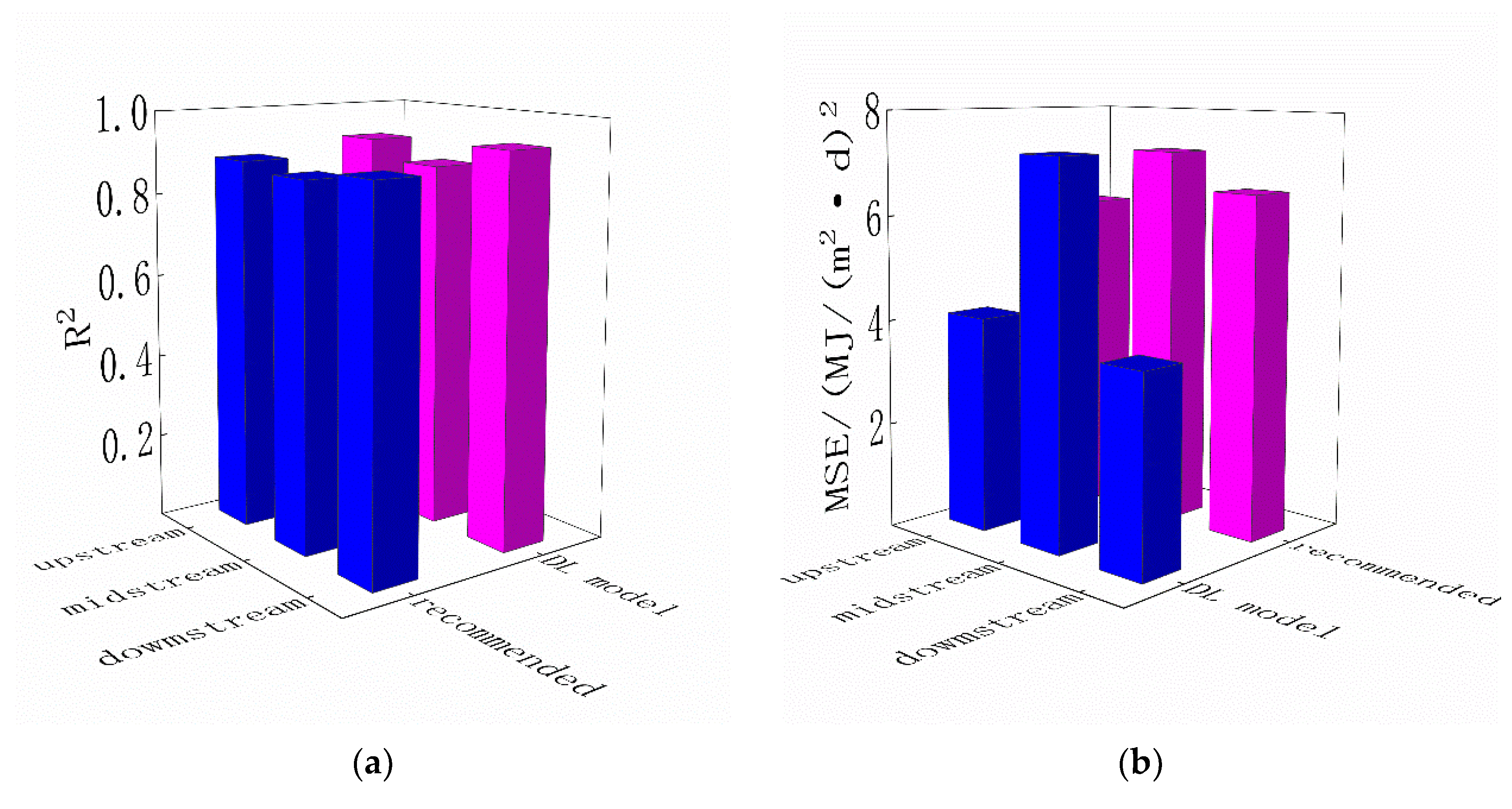
3.2. Comparison between the Recommended Values of Å-P Parameters and the Prediction Results of the DL Model
3.3. Comparison between the Prediction Results of Corrected Values of Å-P Parameters and Those of the DL Model
4. Discussion
4.1. Calibration of Å-P Parameters
4.2. Comparison between DL Model and Å-P Model
4.3. Comparison between DL Model and Other Machine Learning Models
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Adaramola, M.S. Estimating global solar radiation using common meteorological data in Akure, Nigeria. Renew. Energy 2012, 47, 38–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tymvios, F.S.; Jacovides, C.P.; Michaelides, S.C.; Scouteli, C. Comparative study of Angstroem’s and artificial neural networks’ methodologies in estimating global solar radiation. Sol. Energy 2005, 78, 752–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Xu, C.; Zhong, X.; Li, Y.; Yuan, X.; Cao, J. Comparison of 16 models for reference crop evapotranspiration against weighing lysimeter measurement. Agric. Water Manag. 2017, 184, 145–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vázquez, R. Effect of potential evapotranspiration estimates on effective parameters and performance of the MIKE SHE-code applied to a medium-size catchment. J. Hydrol. 2003, 270, 309–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labed, S.; Lorenzo, E. The impact of solar radiation variability and data discrepancies on the design of PV systems. Renew. Energy 2004, 29, 1007–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghoneim, A. Design optimization of photovoltaic powered water pumping systems. Energy Convers. Manag. 2006, 47, 1449–1463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iziomon, M.; Mayer, H. Assessment of some global solar radiation parameterizations. J. Atmos. Solar-Terrestrial Phys. 2002, 64, 1631–1643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trnka, M.; Žalud, Z.; Eitzinger, J.; Dubrovský, M. Global solar radiation in Central European lowlands es-timated by various empirical formulae. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2005, 131, 54–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Podestá, G.P.; Núñez, L.; Villanueva, C.A.; Skansi, M.A. Estimating daily solar radiation in the Argentine Pampas. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2004, 123, 41–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Tan, Q.; Pan, T. Determining the Parameters of the Ångström-Prescott Model for Estimating Solar Radiation in Different Regions of China: Calibration and Modeling. Earth Space Sci. 2019, 6, 1976–1986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Alawi, S.M.; Al-Hinai, H.A. An ANN-based approach for predicting global radiation in locations with no direct meas-urement instrumentation. Renew. Energy 1998, 14, 199–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohandes, M.; Rehman, S.; Halawani, T. Estimation of global solar radiation using artificial neural networks. Renew. Energy 1998, 14, 179–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, K.; Ranjan, M. Solar resource estimation using artificial neural networks and comparison with other correlation models. Energy Convers. Manag. 2003, 44, 2519–2530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yildiz, B.Y.; Sahin, M.; Şenkal, O.; Peştemalci, V.; Emrahoglu, N. A Comparison of Two Solar Radiation Models Using Artificial Neural Networks and Remote Sensing in Turkey. Energy Sources Part A Recover. Util. Environ. Eff. 2013, 35, 209–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.L.; Li, G.S.; Wu, S.J. Assessing the potential of support vector machine for estimating daily solar radi-ation using sunshine duration. Energy Convers. Manag. 2013, 75, 311–318. [Google Scholar]
- Ibrahim, I.A.; Khatib, T. A novel hybrid model for hourly global solar radiation prediction using random forests technique and firefly algorithm. Energy Convers. Manag. 2017, 138, 413–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucas, P.D.O.E.; Alves, M.A.; Silva, P.C.D.L.E.; Guimarães, F.G. Reference evapotranspiration time series forecasting with ensemble of convolutional neural networks. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2020, 177, 105700. [Google Scholar]
- Saggi, M.K.; Jain, S. Reference evapotranspiration estimation and modeling of the Punjab Northern India using deep learning. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2018, 156, 387–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.Y.; Li, Y.Z. Effect of various Ångström–Prescott coefficients on reference crop evapotranspiration—A casestudy for the midstream of the Yellow River. Chin. Agro-Meteorol. 2007, 1, 29–35. [Google Scholar]
- Ngström, A. Solar and ter restrial radiation. Report to the international commission for solar research on actinometric in-vestigations of sola and atmospheric radiation. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 1924, 50, 121–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prescott, J.A. Evaporation from a water surface in relation to solar radiation. Trans. R. Soc. S. Aust. 1940, 64, 114–125. [Google Scholar]
- Rumelhart, D.E.; McClelland, J.L. (Eds.) Parallel Distributed Processing: Explorations in Themicrostructure of Cognition; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Hinton, G.E. Learning multiple layers of representation. Trends Cogn. Sci. 2007, 11, 428–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakirci, K. Correlations for estimation of daily global solar radiation with hours of bright sunshine in Turkey. Energy 2009, 34, 485–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Xu, Y.; Zhong, X.; Zhang, W.; Porter, J.R.; Liu, W. Assessing models for parameters of the Ångström–Prescott formula in China. Appl. Energy 2012, 96, 327–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Mei, X.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Q.; Jensen, J.R.; Porter, J.R. Calibration of the Ångström–Prescott coefficients (a, b) under different time scales and their impacts in estimating global solar radiation in the Yellow River basin. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2009, 149, 697–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.; Ersi, K.; Yang, J.; Lu, S.; Zhao, W. Validation of five global radiation models with measured daily data in China. Energy Convers. Manag. 2004, 45, 1759–1769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Persaud, N.; Lesolle, D.; Ouattara, M. Coefficients of the Angström–Prescott equation for estimating global irradiance from hours of bright sunshine in Botswana and Niger. Agric. For. Meteorol. 1997, 88, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richardson, C.W.; Wright, D.A. WGEN: A Model for Generating Daily Weather Variables; U.S. Department of Agriculture, Agricultural Research Service: Washington, DC, USA, 1984.
- Pinker, R.; Frouin, R.; Li, Z. A review of satellite methods to derive surface shortwave irradiance. Remote Sens. Environ. 1995, 51, 108–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hay, J.E.; Suckling, P.W. An assessment of the net-works for measuring and modeling solar radiation in British Columbia and adjacent areas of western Canada. Can. Geogr. 1979, 23, 222–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bristow, K.L.; Campbell, G.S. On the relationship between incoming solar radiation and daily maximum and minimum temperature. Agric. For. Meteorol. 1984, 31, 159–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gueymard, C.A. Parameterized transmittance model for direct beam and circumsolar spectral irradiance. Sol. Energy 2001, 71, 325–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de La Casinière, A.; Bokoye, A.I.; Cabot, T. Direct Solar Spectral Irradiance Measurements and Updated Simple Transmittance Models. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 1997, 36, 509–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y. Computation of monthly mean daily global solar radiation in China using artificial neural networks and comparison with other empirical models. Energy 2009, 34, 1276–1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Z.; Yezheng, W.; Gang, Y. General formula for estimation of monthly average daily global solar radiation in China. Energy Convers. Manag. 2005, 46, 257–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Z.; Wang, Z.; Gui, K.; Yan, X.; Gao, M.; Luo, M.; Geng, H.; Liao, T.; Li, X.; An, J.; et al. Daily global solar radiation in China estimated from high-density me-teorological observations: A random forest model framework. Earth Space Sci. 2020, 7, e2019EA001058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, L.; Kang, J.; Wan, M.; Fang, L.; Zhang, C.; Zeng, Z. Solar Radiation Prediction Using Different Machine Learning Algorithms and Implications for Extreme Climate Events. Front. Earth Sci. 2021, 9, 202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghimire, S.; Deo, R.C.; Casillas-Pérez, D.; Salcedo-Sanz, S. Boosting solar radiation predictions with global climate models, observational predictors and hybrid deep-machine learning algorithms. Appl. Energy 2022, 316, 119063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, T.; Guo, Y.; Li, Z.; Wang, C. Solar Radiation Prediction Based on Convolution Neural Network and Long Short-Term Memory. Energies 2021, 14, 8498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, M.; Dash, P.B.; Nayak, J.; Naik, B.; Swain, S.K. Deep learning and wavelet transform integrated approach for short-term solar PV power prediction. Measurement 2020, 166, 108250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Site Name | Longitude | Latitude | Altitude | Average Temperature | Province | Data Period |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Yushu | 97.02 | 33.02 | 3681.2 | 3.59 | Qinghai | 1960–2016 |
| Guoluo | 100.25 | 34.47 | 3719 | 0.04 | Qinghai | 1993–2016 |
| Gangcha | 100.13 | 37.33 | 3301.5 | 0.05 | Qinghai | 1993–2016 |
| Geermu | 94.9 | 36.42 | 2807.7 | 5.75 | Qinghai | 1957–2016 |
| Xining | 101.77 | 36.62 | 2261.2 | 6.09 | Qinghai | 1959–2016 |
| Ganzi | 100 | 31.62 | 3393.5 | 5.98 | Sichuan | 1994–2016 |
| Hongyuan | 102.55 | 32.8 | 3491.6 | 1.75 | Sichuan | 1994–2016 |
| Wuwei | 102.67 | 37.92 | 1530.9 | 8.54 | Gansu | 1961–2016 |
| Minqin | 103.08 | 38.63 | 1367 | 8.78 | Gansu | 1957–2016 |
| Yuzhong | 104.15 | 35.87 | 1874.1 | 6.99 | Gansu | 2005–2016 |
| Guyuan | 106.27 | 36 | 1752.2 | 6.95 | Ningxia | 1985–2016 |
| Yinchuan | 106.22 | 38.48 | 1111.4 | 9.51 | Ningxia | 1959–2016 |
| Huhehaote | 111.68 | 40.82 | 1063 | 7.13 | Neimenggu | 1959–2016 |
| Erlianhaote | 111.97 | 43.65 | 964.7 | 4.56 | Neimenggu | 1957–2016 |
| Wulatezhongqi | 108.52 | 41.57 | 1288.2 | 5.73 | Neimenggu | 1992–2016 |
| Dongsheng | 109.98 | 39.83 | 1460.4 | 6.67 | Neimenggu | 1992–2016 |
| Taiyuan | 112.55 | 37.78 | 777.9 | 10.38 | Shanxi | 1959–2016 |
| Datong | 113.33 | 40.1 | 1067.2 | 7.21 | Shanxi | 1960–2016 |
| Houma | 111.37 | 35.65 | 433.7 | 13.04 | Shanxi | 1959–2016 |
| Yanan | 109.5 | 36.6 | 957.8 | 10.21 | Shanxi | 1990–2016 |
| Jinghe | 108.97 | 34.43 | 410 | 14.90 | Shanxi | 2006–2016 |
| Ankang | 109.03 | 32.72 | 290.8 | 15.86 | Shanxi | 1990–2016 |
| Nanyang | 112.58 | 33.03 | 129.2 | 15.22 | Henan | 1990–2016 |
| Zhengzhou | 113.65 | 34.72 | 110.4 | 14.84 | Shanxi | 1957–2016 |
| Anyang | 114.37 | 36.12 | 75.5 | 14.15 | Shanxi | 1960–2016 |
| Fushan | 121.25 | 37.5 | 32.6 | 12.77 | Shandong | 1992–2016 |
| Jinan | 116.98 | 36.68 | 51.6 | 14.77 | Shandong | 1959–2016 |
| Juxian | 118.83 | 35.58 | 107.4 | 12.66 | Shandong | 1990–2016 |
| Watershed Distribution | Site Name | Province | a | b | R2 | RMSE | RE | MAE | d |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Upstream | Yushu | Qinghai | 0.20 | 0.61 | 0.74 | 3.309 | 0.20 | 2.265 | 0.93 |
| Upstream | Guoluo | Qinghai | 0.25 | 0.58 | 0.87 | 2.451 | 0.14 | 1.835 | 0.96 |
| Upstream | Gangcha | Qinghai | 0.20 | 0.62 | 0.93 | 1.705 | 0.10 | 1.269 | 0.98 |
| Upstream | Geermu | Qinghai | 0.26 | 0.57 | 0.96 | 1.518 | 0.08 | 1.106 | 0.99 |
| Upstream | Xining | Qinghai | 0.18 | 0.61 | 0.92 | 1.896 | 0.12 | 1.399 | 0.98 |
| Upstream | Ganzi | Sichuan | 0.29 | 0.54 | 0.88 | 2.127 | 0.11 | 1.630 | 0.96 |
| Upstream | Hongyuan | Sichuan | 0.18 | 0.68 | 0.81 | 3.766 | 0.24 | 2.763 | 0.93 |
| Upstream | Wuwei | Gansu | 0.13 | 0.69 | 0.89 | 2.960 | 0.16 | 2.290 | 0.97 |
| Upstream | Minqin | Gansu | 0.20 | 0.53 | 0.95 | 1.595 | 0.09 | 1.168 | 0.99 |
| Upstream | Yuzhong | Gansu | 0.17 | 0.58 | 0.95 | 2.027 | 0.13 | 1.692 | 0.98 |
| Upstream | Guyuan | Ningxia | 0.16 | 0.61 | 0.93 | 2.028 | 0.14 | 1.528 | 0.98 |
| Upstream | Yinchuan | Ningxia | 0.20 | 0.57 | 0.93 | 2.023 | 0.13 | 1.435 | 0.98 |
| Upstream | Huhehaote | Neimenggu | 0.18 | 0.61 | 0.91 | 2.142 | 0.13 | 1.522 | 0.98 |
| Upstream | Erlianhaote | Neimenggu | 0.20 | 0.60 | 0.93 | 2.236 | 0.13 | 1.658 | 0.98 |
| Upstream | Wulatezhongqi | Neimenggu | 0.23 | 0.55 | 0.94 | 2.011 | 0.12 | 1.459 | 0.98 |
| Upstream | Dongsheng | Neimenggu | 0.16 | 0.58 | 0.93 | 2.542 | 0.17 | 1.707 | 0.97 |
| Midstream | Taiyuan | Shanxi | 0.16 | 0.59 | 0.86 | 2.823 | 0.20 | 2.122 | 0.96 |
| Midstream | Datong | Shanxi | 0.17 | 0.60 | 0.92 | 2.119 | 0.14 | 1.610 | 0.98 |
| Midstream | Houma | Shanxi | 0.16 | 0.58 | 0.86 | 2.664 | 0.22 | 1.981 | 0.96 |
| Midstream | Yanan | Shanxi | 0.14 | 0.58 | 0.82 | 3.296 | 0.24 | 2.340 | 0.95 |
| Midstream | Jinghe | Shanxi | 0.19 | 0.50 | 0.87 | 3.739 | 0.29 | 2.988 | 0.94 |
| Midstream | Ankang | Shanxi | 0.16 | 0.54 | 0.88 | 2.621 | 0.23 | 1.883 | 0.97 |
| Midstream | Nanyang | Henan | 0.19 | 0.53 | 0.86 | 2.748 | 0.23 | 2.070 | 0.96 |
| Downstream | Zhengzhou | Shanxi | 0.17 | 0.55 | 0.89 | 2.594 | 0.22 | 1.983 | 0.96 |
| Downstream | Anyang | Shanxi | 0.16 | 0.52 | 0.85 | 2.657 | 0.21 | 2.025 | 0.96 |
| Downstream | Fushan | Shandong | 0.16 | 0.56 | 0.95 | 1.736 | 0.12 | 1.323 | 0.98 |
| Downstream | Jinan | Shandong | 0.11 | 0.60 | 0.88 | 2.759 | 0.23 | 2.039 | 0.96 |
| Downstream | Juxian | Shandong | 0.21 | 0.53 | 0.94 | 1.715 | 0.12 | 1.289 | 0.98 |
| Site | Model | R2 | MSE | RMSE | MAE | Site | Model | R2 | MSE | RMSE | MAE |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Yushu | Recommended | 0.77 | 9.347 | 3.057 | 2.335 | Wulatezhongqi | Recommended | 0.92 | 5.090 | 2.256 | 1.590 |
| DL prediction | 0.90 | 5.018 | 2.240 | 1.728 | DL prediction | 0.95 | 3.273 | 1.809 | 1.435 | ||
| Guoluo | Recommended | 0.87 | 7.383 | 2.717 | 2.111 | Dongsheng | Recommended | 0.92 | 4.324 | 2.079 | 1.456 |
| DL prediction | 0.88 | 7.343 | 2.710 | 2.207 | DL prediction | 0.91 | 6.990 | 2.644 | 1.685 | ||
| Gangcha | Recommended | 0.91 | 4.698 | 2.167 | 1.735 | Taiyuan | Recommended | 0.87 | 6.333 | 2.516 | 1.878 |
| DL prediction | 0.94 | 2.647 | 1.627 | 1.243 | DL prediction | 0.89 | 9.559 | 3.092 | 2.216 | ||
| Geermu | Recommended | 0.93 | 5.999 | 2.449 | 1.984 | Datong | Recommended | 0.90 | 5.086 | 2.255 | 1.708 |
| DL prediction | 0.96 | 2.033 | 1.426 | 1.029 | DL prediction | 0.93 | 3.686 | 1.920 | 1.485 | ||
| Xining | Recommended | 0.88 | 5.605 | 2.368 | 1.728 | Houma | Recommended | 0.89 | 5.979 | 2.445 | 1.835 |
| DL prediction | 0.93 | 4.017 | 2.004 | 1.519 | DL prediction | 0.89 | 6.495 | 2.549 | 2.070 | ||
| Ganzi | Recommended | 0.89 | 6.954 | 2.637 | 2.172 | Yanan | Recommended | 0.87 | 8.986 | 2.998 | 2.235 |
| DL prediction | 0.85 | 4.559 | 2.135 | 1.704 | DL prediction | 0.87 | 7.068 | 2.659 | 1.855 | ||
| Hongyuan | Recommended | 0.83 | 10.373 | 3.221 | 2.559 | Jinghe | Recommended | 0.84 | 8.333 | 2.887 | 2.283 |
| DL prediction | 0.88 | 6.340 | 2.518 | 1.836 | DL prediction | 0.89 | 9.502 | 3.083 | 2.518 | ||
| Wuwei | Recommended | 0.84 | 9.619 | 3.101 | 2.311 | Ankang | Recommended | 0.84 | 10.803 | 3.287 | 2.489 |
| DL prediction | 0.91 | 5.849 | 2.418 | 1.757 | DL prediction | 0.81 | 9.493 | 3.081 | 1.880 | ||
| Minqin | Recommended | 0.90 | 4.983 | 2.232 | 1.597 | Nanyang | Recommended | 0.87 | 5.009 | 2.238 | 1.729 |
| DL prediction | 0.96 | 2.165 | 1.471 | 1.036 | DL prediction | 0.85 | 4.979 | 2.231 | 1.592 | ||
| Yuzhong | Recommended | 0.91 | 3.708 | 2.418 | 1.403 | Zhengzhou | Recommended | 0.88 | 5.487 | 2.342 | 1.736 |
| DL prediction | 0.95 | 2.224 | 1.491 | 1.131 | DL prediction | 0.95 | 2.148 | 1.466 | 1.136 | ||
| Guyuan | Recommended | 0.91 | 4.270 | 2.066 | 1.486 | Anyang | Recommended | 0.87 | 9.739 | 3.121 | 2.481 |
| DL prediction | 0.93 | 3.430 | 1.852 | 1.368 | DL prediction | 0.89 | 9.722 | 3.118 | 2.644 | ||
| Yinchuan | Recommended | 0.91 | 4.232 | 2.057 | 1.407 | Fushan | Recommended | 0.94 | 4.574 | 2.139 | 1.640 |
| DL prediction | 0.94 | 2.629 | 1.621 | 1.163 | DL prediction | 0.96 | 1.973 | 1.405 | 1.043 | ||
| Huhehaote | Recommended | 0.90 | 5.497 | 2.345 | 1.733 | Jinan | Recommended | 0.86 | 9.697 | 3.114 | 2.368 |
| DL prediction | 0.90 | 3.645 | 1.909 | 1.346 | DL prediction | 0.92 | 3.064 | 1.750 | 1.320 | ||
| Erlianhaote | Recommended | 0.91 | 6.024 | 2.454 | 1.866 | Juxian | Recommended | 0.92 | 3.105 | 1.762 | 1.344 |
| DL prediction | 0.94 | 3.308 | 1.819 | 1.671 | DL prediction | 0.95 | 1.636 | 1.279 | 0.957 |
| Site | Model | R2 | MSE | RMSE | MAE | Site | Model | R2 | MSE | RMSE | MAE |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Yushu | Corrected | 0.78 | 8.926 | 2.988 | 2.209 | Wulatezhongqi | Corrected | 0.92 | 4.556 | 2.135 | 1.448 |
| DLprediction | 0.90 | 5.018 | 2.240 | 1.728 | DLprediction | 0.95 | 3.273 | 1.809 | 1.435 | ||
| Guoluo | Corrected | 0.87 | 5.085 | 2.255 | 1.608 | Dongsheng | Corrected | 0.92 | 3.831 | 1.957 | 1.391 |
| DLprediction | 0.88 | 7.343 | 2.710 | 2.207 | DLprediction | 0.91 | 6.990 | 2.644 | 1.685 | ||
| Gangcha | Corrected | 0.92 | 3.285 | 1.812 | 1.314 | Taiyuan | Corrected | 0.88 | 5.476 | 2.340 | 1.750 |
| DLprediction | 0.94 | 2.647 | 1.627 | 1.243 | DLprediction | 0.89 | 9.559 | 3.092 | 2.216 | ||
| Geermu | Corrected | 0.94 | 3.226 | 1.796 | 1.290 | Datong | Corrected | 0.90 | 4.989 | 2.234 | 1.698 |
| DLprediction | 0.96 | 2.033 | 1.426 | 1.029 | DLprediction | 0.93 | 3.686 | 1.920 | 1.485 | ||
| Xining | Corrected | 0.88 | 5.449 | 2.334 | 1.687 | Houma | Corrected | 0.89 | 5.040 | 2.245 | 1.654 |
| DLprediction | 0.93 | 4.017 | 2.004 | 1.519 | DLprediction | 0.89 | 6.495 | 2.549 | 2.070 | ||
| Ganzi | Corrected | 0.89 | 3.467 | 1.862 | 1.408 | Yanan | Corrected | 0.88 | 5.871 | 2.423 | 1.718 |
| DLprediction | 0.85 | 4.559 | 2.135 | 1.704 | DLprediction | 0.86 | 7.068 | 2.659 | 1.855 | ||
| Hongyuan | Corrected | 0.84 | 7.648 | 2.765 | 1.994 | Jinghe | Corrected | 0.83 | 7.641 | 2.764 | 2.007 |
| DLprediction | 0.88 | 6.340 | 2.518 | 1.836 | DLprediction | 0.89 | 9.502 | 3.083 | 2.518 | ||
| Wuwei | Corrected | 0.81 | 12.101 | 2.960 | 2.760 | Ankang | Corrected | 0.83 | 7.185 | 2.680 | 1.871 |
| DLprediction | 0.91 | 5.849 | 2.418 | 1.757 | DLprediction | 0.81 | 9.493 | 3.081 | 1.880 | ||
| Minqin | Corrected | 0.90 | 4.684 | 2.164 | 1.614 | Nanyang | Corrected | 0.88 | 4.448 | 2.109 | 1.506 |
| DLprediction | 0.96 | 2.165 | 1.471 | 1.036 | DLprediction | 0.85 | 4.979 | 2.231 | 1.592 | ||
| Yuzhong | Corrected | 0.91 | 3.661 | 2.418 | 1.485 | Zhengzhou | Corrected | 0.89 | 4.685 | 2.165 | 1.615 |
| DLprediction | 0.95 | 2.224 | 1.491 | 1.131 | DLprediction | 0.95 | 2.148 | 1.466 | 1.136 | ||
| Guyuan | Corrected | 0.92 | 3.859 | 1.964 | 1.427 | Anyang | Corrected | 0.88 | 4.657 | 2.158 | 1.597 |
| DLprediction | 0.93 | 3.430 | 1.852 | 1.368 | DLprediction | 0.89 | 9.722 | 3.118 | 2.644 | ||
| Yinchuan | Corrected | 0.92 | 4.201 | 2.050 | 1.381 | Fushan | Corrected | 0.94 | 2.528 | 1.590 | 1.205 |
| DLprediction | 0.94 | 2.629 | 1.621 | 1.163 | DLprediction | 0.96 | 1.973 | 1.405 | 1.043 | ||
| Huhehaote | Corrected | 0.90 | 4.967 | 2.229 | 1.595 | Jinan | Corrected | 0.86 | 6.647 | 2.578 | 1.835 |
| DLprediction | 0.90 | 3.645 | 1.909 | 1.346 | DLprediction | 0.92 | 3.064 | 1.750 | 1.320 | ||
| Erlianhaote | Corrected | 0.91 | 5.108 | 2.260 | 1.584 | Juxian | Corrected | 0.93 | 2.848 | 1.688 | 1.266 |
| DLprediction | 0.94 | 3.308 | 1.819 | 1.671 | DLprediction | 0.95 | 1.636 | 1.279 | 0.957 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, Q.; Tian, X.; Zhang, P.; Hou, L.; Peng, Z.; Wang, G. Solar Radiation Prediction Model for the Yellow River Basin with Deep Learning. Agronomy 2022, 12, 1081. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12051081
Zhang Q, Tian X, Zhang P, Hou L, Peng Z, Wang G. Solar Radiation Prediction Model for the Yellow River Basin with Deep Learning. Agronomy. 2022; 12(5):1081. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12051081
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Qian, Xiaoxu Tian, Peng Zhang, Lei Hou, Zhigong Peng, and Gang Wang. 2022. "Solar Radiation Prediction Model for the Yellow River Basin with Deep Learning" Agronomy 12, no. 5: 1081. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12051081
APA StyleZhang, Q., Tian, X., Zhang, P., Hou, L., Peng, Z., & Wang, G. (2022). Solar Radiation Prediction Model for the Yellow River Basin with Deep Learning. Agronomy, 12(5), 1081. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12051081







