The Relationship between Soil Respiration and Plant Community Functional Traits in Ebinur Lake Basin
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
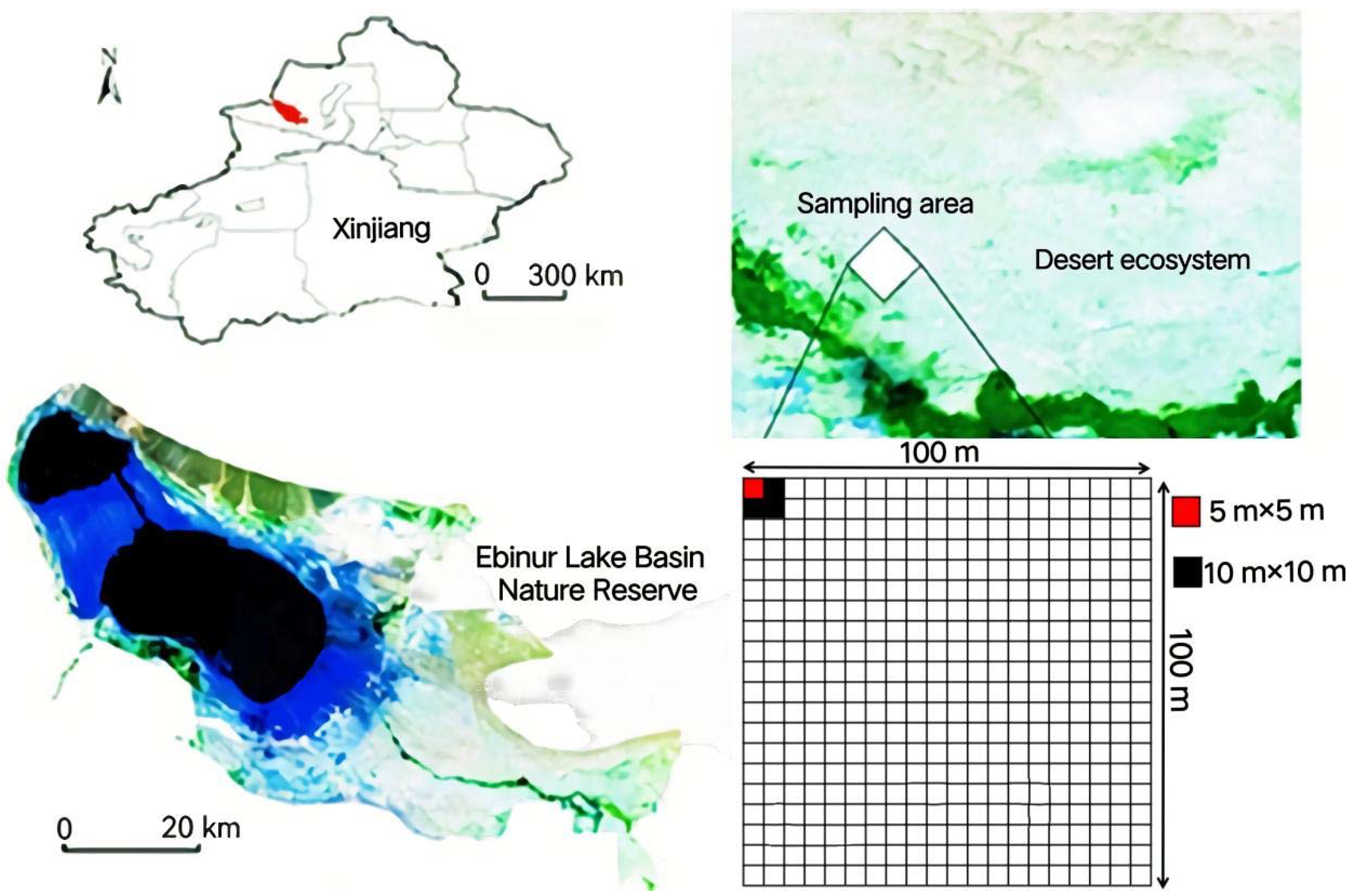
2.1. The Study Area
2.2. Sample Square Layout
2.3. Sample Collection and Determination
- (1)
- Determination of the soil respiration
- (2)
- Determination of environmental factors
- (3)
- Investigation, determination, and calculation of plant functional traits
| Plant Functional Traits | Unit | Ecological Significance |
|---|---|---|
| Maximum height, MH | cm | Reflects the light competitiveness of plants, such as growth form, position of the species in the vertical light, gradient of the vegetation, competitive vigour, reproductive size, whole-plant fecundity, potential lifespan [43] |
| Leaf length, LL | mm | LL is connect with the area of a leaf, which can be linked to allometric factors (plant size, twig size) and ecological strategy with respect to environmental nutrient stress [43] |
| Leaf width, LW | mm | LW is connect with the area of a leaf, which can be linked to allometric factors (plant size, twig size) and ecological strategy with respect to environmental nutrient stress [43] |
| Leaf thickness, LT | cm | Reflects the ability to resist physical damage [43] |
| Leaf dry matter content, LDMC | g·g−1 | Reflects the ability of plants to obtain resources and to resist physical damage [43,44] |
| Specific leaf area, SLA | cm2·g−1 | Reflects the ability of plants to obtain resources, correlated with photosynthetic intensity [43,45] |
| Leaf carbon content, LCC | mg·g−1 | Reflects the photosynthetic intensity [43] |
| Leaf nitrogen content, LNC | mg·g−1 | Reflects carbon sequestration and soil fertility maintenance capacity [46] |
| Leaf phosphorus content, LPC | mg·g−1 | Reflects the osmotic regulation ability, stress resistance, and adaptability of plants [47] |
2.4. Data Processing and Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Statistical Description of Soil Respiratory and Community Functional Traits
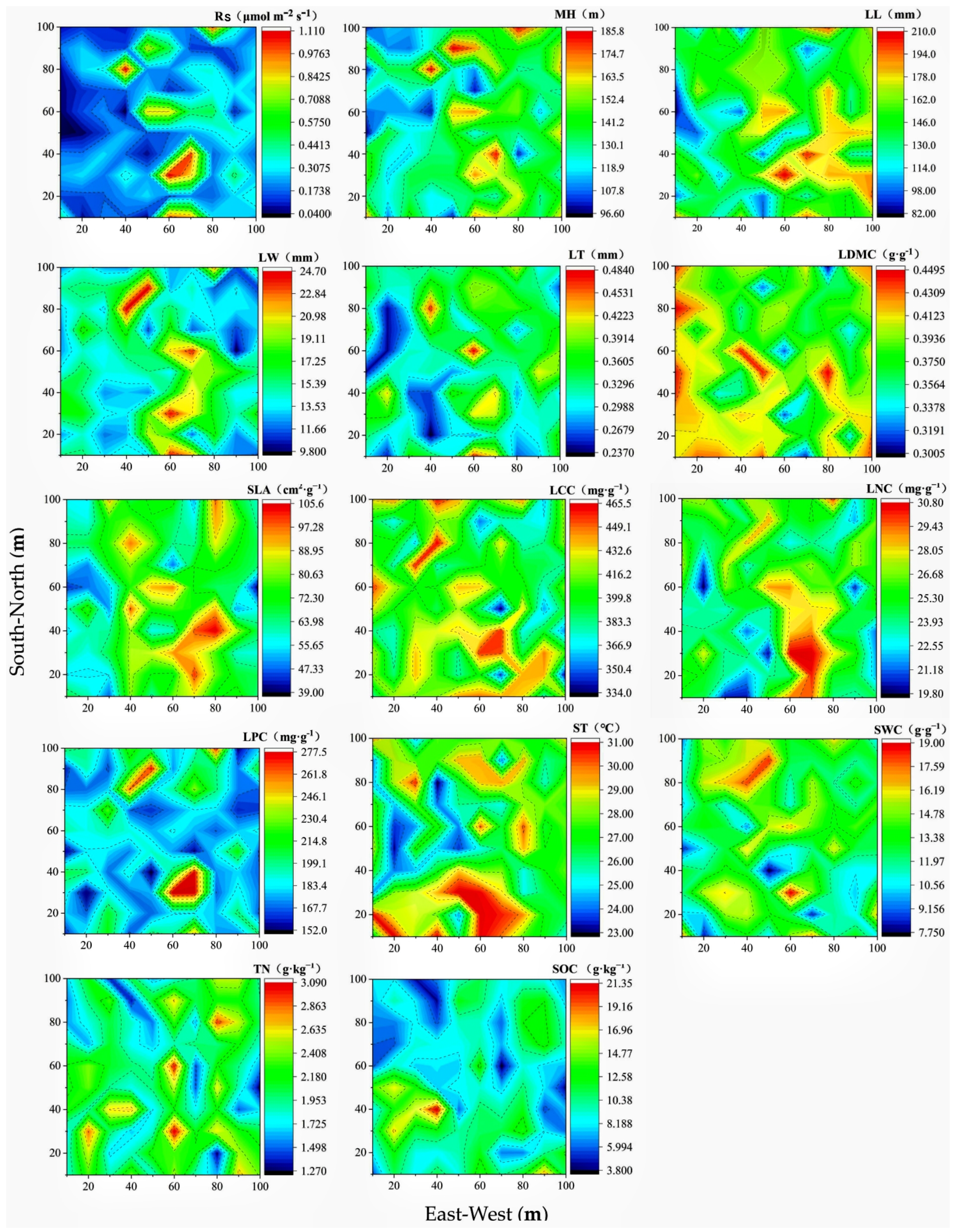
3.2. Spatial Distribution Rules of Soil Respiration, Community Functional Traits, and Environmental Factors
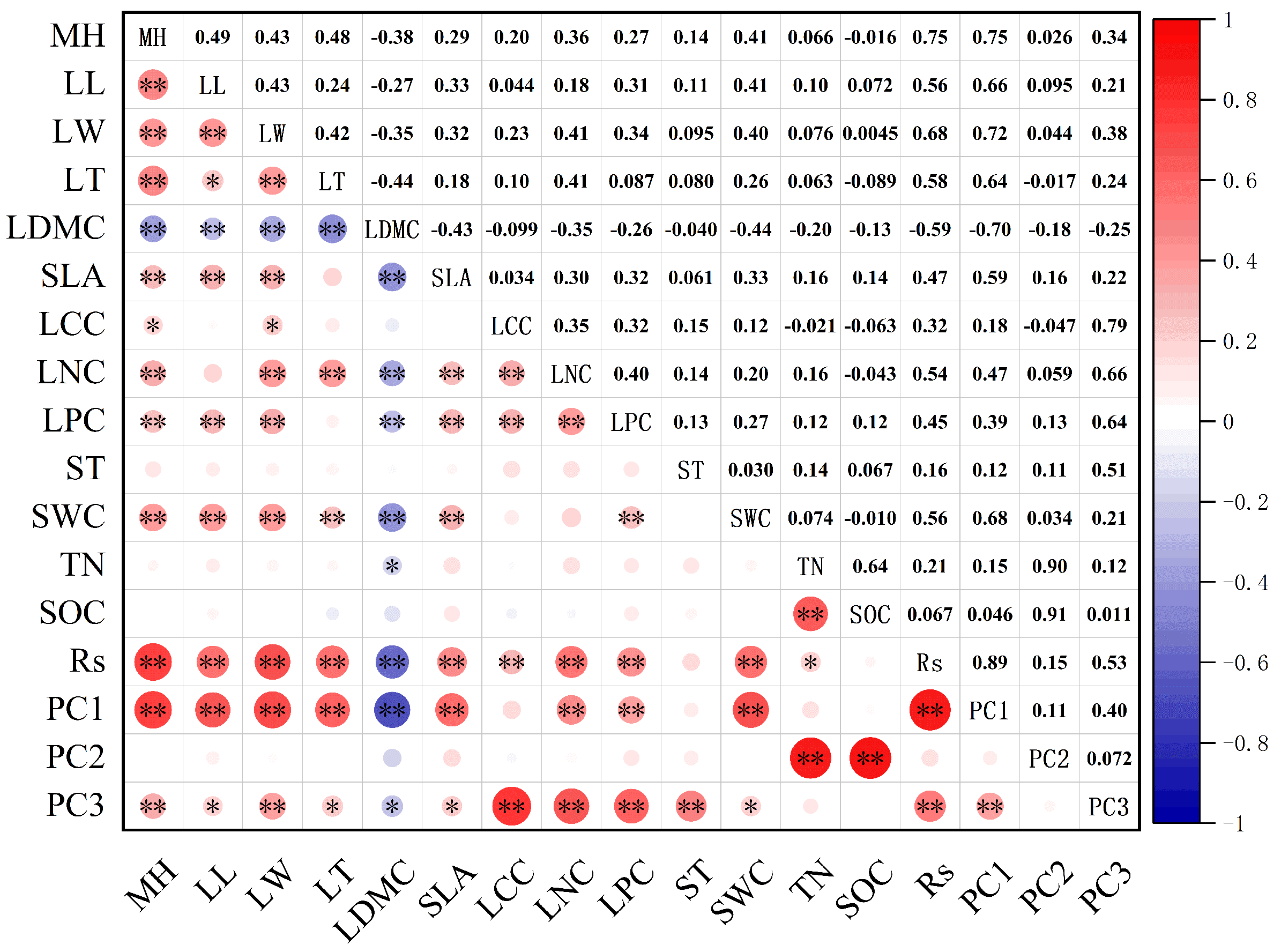
3.3. Relationship between Soil Respiration, Community Functional Traits, and Environmental Factors
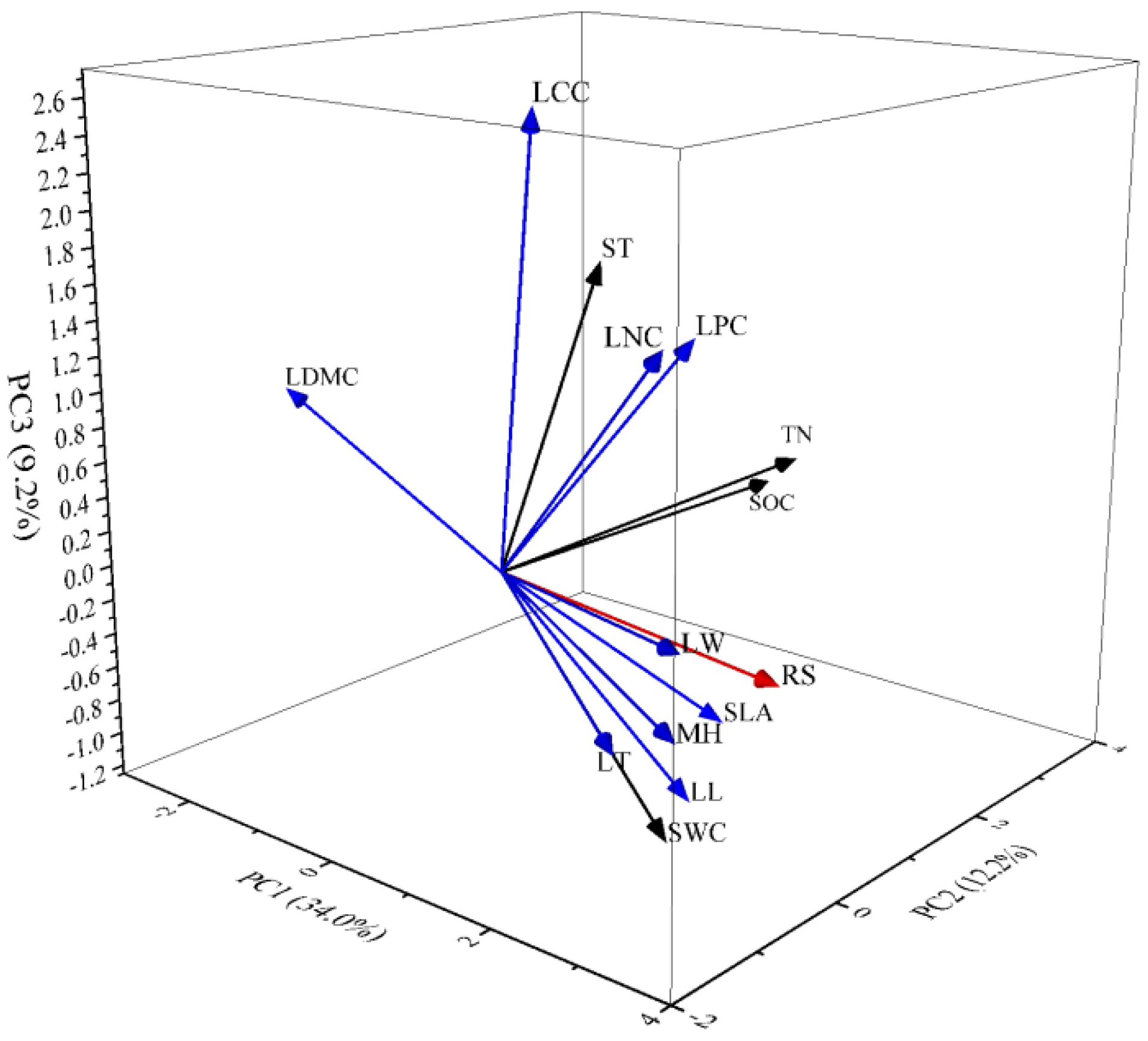
3.4. Multiple Regression Analysis of Soil Respiration (Rs) and Principal Components
4. Discussion
4.1. Spatial Distribution Characteristics of Soil Respiration Rates
4.2. Relationship between Soil Respiration and PC1
4.3. Relationship between Soil Respiration and PC2
4.4. Relationship between Soil Respiration and PC3
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hanson, P.J.; Edwards, N.T.; Garten, C.T.; Andrews, J.A. Separating root and soil microbial contributions to soil respiration: A review of methods and observations. Biogeochem 2000, 48, 115–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raich, J.W.; Potter, C.S. Global patterns of carbon dioxide emissions from soils. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 1995, 9, 23–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bond–Lamberty, B.; Thomson, A. A global database of soil respiration data. Biogeosciences 2010, 7, 1915–1926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fu, Y.; Zheng, Z.; Yu, G.; Hu, Z.; Sun, X.; Shi, P.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, X. Environmental influences on carbon dioxide fluxes over three grassland ecosystems in China. Biogeosciences 2009, 6, 2879–2893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- David, J.; Phoenix, G.K.; Grime, J.P. Plant community composition, not diversity, regulates soil respiration in grasslands. Biol. Lett. 2008, 4, 345–348. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, J.S.; Gupta, S.R. Plant decomposition and soil respiration in terrestrial ecosystems. Bot. Rev. 1977, 43, 449–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- James, W.R.; Aydin, T. Vegetation and soil respiration, Correlations and controls. Biogeochemistry 2000, 48, 71–90. [Google Scholar]
- Katayama, A.; Kume, T.; Komatsu, H.; Ohashi, M.; Nakagawa, M.; Yamashita, M.; Otsuki, K.; Suzuki, M.; Kumagai, T. Effect of forest structure on the spatial variation in soil respiration in a Bornean tropical rainforest. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2009, 49, 1666–1673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, M.W.; Liang, C.Z.; Bai, X.; Miao, B.L.; Wang, Y.S.; Bao, G.R.; Wang, X. Effects of annual plant functional group on biomass and soil respiration in a grazing community of a typical steppe grassland. Pratac. Sci. 2016, 33, 2407–2417. [Google Scholar]
- Buchmann, N. Biotic and abiotic factors controlling soil respiration rates in Picea abies stands. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2000, 32, 1625–1635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Wang, B.; Dai, W.; Li, P. Effects of tree growth and soil properties on soil respiration rate in Chinese fir plantations. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2011, 31, 0680–0688. [Google Scholar]
- Metcalfe, D.B.; Fisher, R.A.; Wardle, D.A. Plant communities as drivers of soil respiration, pathways, mechanisms, and significance for global change. Biogeosciences 2011, 8, 2047–2061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kang, S.Y.; Doh, S.; Lee, D. Topographic and climatic controls on soil respiration in six temperate mixed–hardwood forest slopes, Korea. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2003, 9, 1427–1437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, Y.; Han, S.J.; Hu, Y.L.; Dai, G.H. Effects of soil temperature and humidity on soil respiration rate under Pinus sylvestriformis forest. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2005, 16, 1581–1585. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.S.; Fan, J.; Zhao, X.H.; Xia, F.C.; Ni, R.Q.; Jin, G.Y.; Guo, Y.Q.; Li, H.S. Soil Respiration Components and Its Controlling Factors in a Pinus tabulaeformis Plantation in Taiyue Mountain. Sci. Silvae Sin. 2013, 49, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, T.; Han, F.G.; Guo, S.J.; Duan, X.F.; Zhang, Y.N. Spatial Heterogeneity of Soil Respiration of Nitraria Tangutorum Nebkhas During Different Growing Period in Arid Areas. B. Soil Water Conserv. 2016, 36, 102–109. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, Z. Simulation distribution of global forest soil respiration based on maximum entropy model. Agric. Technol. China 2021, 41, 41–45. [Google Scholar]
- Raich, J.W.; Nadelhoffer, K.J. Belowground carbon allocation in forest ecosytems, Global trends. Ecology 1989, 70, 1346–1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, C.; Moncrieff, J.B. A model for soil CO2, production and transport, model development. Agric. For. Meteorol. 1999, 95, 225–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pries, J.A.; Koning, G.H.; Veldkam, A. Assessment of interactions between land use change and carbon and nut rient fluves in Ecuador. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2001, 85, 269–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gen, Y.B.; Zhang, S.; Dong, Y.S.; Meng, W.Q.; Qi, Y.C.; Chen, Z.Z.; Wang, Y.F. Carbon and nitrogen content in grassland soil and its correlation with greenhouse gas flux. ACTA Geogr. Sin. 2001, 56, 44–53. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, J.Y.; Wang, C.K. Soil carbon storage and flux of temperate forest ecosystems in northeastern China. ACTA Ecol. Sin. 2005, 25, 2875–2882. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, S.T.; Liu, Q.H.; Hu, Z.H.; Liu, Y.; Ren, J.Q.; Xie, W. Factors Influencing the Spatial Variability in Soil Respiration Under Different Land Use Regimes. Environ. Sci. 2013, 34, 1017–1025. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, M.K.; Hu, X.N.; Cao, J.H.; Wu, X.; Huang, F.; Wang, Q.G.; Min, J. Spatial Variability in Soil Respiration Under Different Land Use Patterns in Maocun Village, Guilin. Environ. Sci. 2019, 40, 924–933. [Google Scholar]
- Hao, L.Y.; Zhang, L.H.; Xie, Z.K.; Zhao, R.F.; Wang, J.F.; Guo, Y.F.; Gao, J.P. Influence of Precipitation Change on Soil Respiration in Desert Grassland. Environ. Sci. 2021, 42, 4527–4537. [Google Scholar]
- Han, D.; Li, Y.L.; Yang, H.L.; Ning, Z.Y.; Zhang, Z.Q. Effects of simulated warming and changing rainfall frequency on soil respiration in arid and semiarid regions. J. Desert Res. 2021, 41, 100–108. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, M.Y.; Lu, N.; Li, Q.L.; Fang, W.W.; Fu, B.J. Contribution of plant traits to the explanation of temporal variations in carbon and water fluxes in semiarid grassland patches. J. Plant Ecol. 2020, 13, 773–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legay, N.; Baxendale, C.; Grigulis, K.; Krainer, U.; Kastl, E.; Schloter, M.; Bardgett, R.D.; Arnoldi, C.; Bahn, M.; Dumont, M.; et al. Contribution of above–and below–ground plant traits to the structure and function of grassland soil microbial communities. Ann. Bot. 2014, 114, 1011–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Poorter, H.; Niinemets, Ü.; Poorter, L.; Wright, L.; Villar, R. Causes and consequences of variation in leaf mass per area (LMA), a meta–analysis. New Phytol. 2009, 182, 565–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roa–Fuentes, L.L.; Templer, P.H.; Campo, J. Effects of precipitation regime and soil nitrogen on leaf traits in seasonally dry tropical forests of the Yucatan Peninsula, Mexico. Oecologia 2015, 179, 585–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchanan, S.W.; Attoye, T.M.; Dunfield, K.; Thevathasan, N.V.; Isaac, M.E. The role of plant functional traits and diversity in soil carbon dynamics within riparian agroforests. J. Environ. Qual. 2022, 51, 33–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reich, P.B.; Wright, I.J.; Cavender, J.M.; Craine, J.M.; Oleksyn, J.; Westoby, M.; Walters, M.B. The evolution of plant functional variation, Traits, spectra, and strategies. Int. J. Plant Sci. 2003, 164, S143–S164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, I.J.; Reich, P.B.; Westoby, M. Strategy shifts in leaf physiology, structure and nutrient content between species of high-and-low rainfall and high-and-low nutrient habitats. Funct. Ecol. 2001, 15, 423–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fang, J.Y.; Zhu, J.L.; Shi, Y. How will ecosystems respond to global warming. Sci. Bull. China 2018, 63, 136–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ran, Q.Y.; Lv, G.H.; Wei, X.F.; Liu, D.; Cui, N. Soil Enzyme Activities and Physicochemical Properties in Ebinur Lake Nature Reserve. Arid Zone Res. 2014, 31, 715–722. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.N.; Yang, X.D.; Lv, G.H. Diversity patterns and response mechanisms of desert plants to the soil environment along soil water and salinity gradients. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2016, 36, 3206–3215. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, X.D.; Lv, G.H.; Tian, Y.H.; Yang, J.; Zhang, X.M. Ecological groups of plants in Ebinur Lake Wetland Nature Reserve of Xinjiang. Chin. J. Ecol. 2009, 28, 2489–2494. [Google Scholar]
- Qin, L.; Fu, D.P.; Yang, J.; He, X.M.; Zhang, X.N.; Lv, G.H. Analysis on soil physical and chemical properties of typical communities in Ebinur Lake Wetland Nature Reserve. J. Arid Land Resour. Environ. 2011, 25, 144–151. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.X.; Yang, X.D.; Lv, G.H.; Liu, W.G. Distribution and Water Use Efficiency of Halophytes in Ebinur Lake Nature Reserve. Arid Zone Res. 2018, 35, 370–378. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.F. Plant Diversity and Ecosystem Functions in the Ebinur Lake Basin. Ph.D. Thesis, Xinjiang University, Urumqi, China, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.F.; Lv, G.H.; Zhou, Y.Z.; Cao, J. Effects of functional diversity and functional redundancy on the stability of desert plant communities under different water and salt gradients. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2017, 37, 7928–7937. [Google Scholar]
- Zhong, Y.M.; Wang, W.J.; Wang, J.M.; Wang, Y.C.; Li, J.W.; Yuan, D.; Fan, Y.Y.; Wei, X. Leaf functional traits of oasis plants in extremely arid areas and its response to soil water and salt factors. J. Beijing For. Univ. 2019, 41, 20–29. [Google Scholar]
- Pérez-Harguindeguy, N.; Díaz, S.; Garnier, E.; Lavorel, S.; Poorter, H.; Jaureguiberry, P.; Bret-Harte, M.S.; Cornwell, W.K.; Craine, J.M.; Gurvich, D.E.; et al. New handbook for standardised measurement of plant functional traits worldwide. Aust. J. Bot. 2013, 61, 167–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Májeková, M.; Bello, F.D.; Doležal, J.; Lepš, J. Plant functional traits as determinants of population stability. Bull. Ecol. Soc. Am. 2016, 95, 2369–2374. [Google Scholar]
- Poorter, L. Growth responses of 15 rain–forest tree species to a light gradient, the relative importance of morphological and physiogical traits. Funct. Ecol. 1999, 13, 396–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osborne, B.B.; Nasto, M.K.; Soper, F.M.; Asner, G.P.; Balzotti, C.S.; Cleveland, C.C.; Tavlor, P.G.; Townsend, A.R.; Porder, S. Leaf litter inputs reinforce islands of nitrogen fertility in a lowland tropical forest. Biogeochem 2020, 147, 293–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.D.; Meng, T.T.; Ni, J.; Su, H.X.; Xie, Z.Q.; Zhang, S.R.; Zheng, Y.R.; Xiao, C.W. Within–leaf allometric relationships of mature forests in different bioclimatic zones vary with plant functional types. J. Plant Ecol. 2011, 35, 687–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Bagousse-Pinguet, Y.; Gross, N.; Maestre, F.T.; Maire, V.; de Bello, F.; Fonseca, C.R.; Kattge, J.; Valencia, E.; Leps, J.; Liancourt, P. Testing the environmental filtering concept in global drylands. J. Ecol. 2017, 105, 1058–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lei, Z.D.; Yang, S.X.; Xie, S.Z. Soil Water Dynamics; Tsing-Hua University Press: Beijing, China, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, B.; Mao, R.Z.; Cao, J.; Wang, Y.Z.; Gao, Y.F.; Li, D.M. Spatial variability of heavy metal content in farmland in Haihe low plain–A Case Study of Feixiang County. Hebei Prov. Ecol. 2006, 26, 4082–4090. [Google Scholar]
- Li, R.P.; Jiang, Y.D.; Li, G.D.; Zhou, N.N.; Yu, C.; Hou, C.D. Spatial distribution of heavy metals in farmland soil based on GIS–A Case Study of Tai'an City, Shandong Province. J. Shandong Agric. Univ. 2012, 43, 232–238. [Google Scholar]
- Cambardella, C.A.; Moorman, T.B.; Novak, J.M.; Parkin, T.B.; Konopka, A.E. Field-scale variability of soil properties in central iowa soils. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1994, 58, 1501–1511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, M.F.; Zhang, X.S.; Zhou, G.S. Spatial heterogeneity of soil respiration in Populus balsamifera plantation at different developmental stage. Chin. J. Ecol. 2013, 32, 1378–1384. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, J.X.; Liang, Y.N.; Li, H.J.; Li, J.J. Spatial Heterogeneity of Soil Respiration in a Larch Plantation of North China at Different Sampling Scales. Environ. Sci. 2015, 36, 4591–4599. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.H.; Li, H.J.; Rong, Y.M.; Yan, J.X.; Li, J.J. Study on spatial heterogeneity of soil respiration in Taiyuan Basin. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2010, 30, 6606–6612. [Google Scholar]
- Gang, L.; Rei, S.; Quan, W. Spatial Variations of Soil Respiration in Arid Ecosystems. Open J. Ecol. 2016, 6, 192–205. [Google Scholar]
- Vojtech, E.; Loreau, M.; Yachi, S.; Spehn, E.M.; Hector, A. Light partitioning in experimental grass Communities. Oikos 2008, 117, 1351–1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, R.T.; Dong, X.M.; Jin, S.S.; Hu, L.P.; Yan, D.F. Effects of thinning on the functional traits of understory Vitex negundo var.heterophylla in Quercus variabilis plantation. J. Zhejiang Univ. Agric. Life Sci. 2021, 38, 567–576. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, L.; Shan, L.S.; Xie, T.T.; Chong, P.F.; Yang, J.; Shi, Y.T. Variation in Plant Functional Traits of Two Typical Desert Plant Based on Common Garden Experiment. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2022, 30, 701–711. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, C.; Chen, X.F.; Zhou, B.; Zhang, C.L.; Li, J.J.; Zhang, J.; Dai, J. Effects of vermicompost application on soil microbial characteristics and enzyme activities. Soils 2014, 46, 70–75. [Google Scholar]
- Cornelissen, J.H.C.; Lavorel, S.; Garnier, E.; Díaz, S.; Buchmann, N.; Gurvich, D.E. A handbook of protocols for standardised and easy measurement of plant functional traits worldwide. Aust J. B. 2003, 51, 335–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qi, J.; Ma, K.M.; Zhang, Y.X. Comparisons on leaf traits of Quercus liaotungensis Koidz. on different slope positions in Dongling Moutain of Beijing. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2008, 28, 122–128. [Google Scholar]
- Li, S.J.; Su, P.X.; Zhang, H.N.; Zhou, Z.J.; Xie, T.T. Characteristics and Relationships of Foliar Water and Leaf Functional Traits of Desert Plants. Plant Physiol. J. 2013, 49, 153–160. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.H.; Zeng, D.H.; Don, K.L. Leaf traits and their interrelationships of main plant species in southeast Horqin sandy land. Chin. J. Ecol. 2006, 25, 921–925. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, X.; Zuo, X.A.; Zhao, X.Y.; Liu, C.; Lv, P. Plant functional traits and interrelationships of 34 plant species in south central Horqin Sandy Land, China. J. Desert Res. 2015, 35, 1489–1495. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, R.L.; Yu, G.R.; He, N.P.; Wang, Q.F.; Zhao, N.; Xu, Z.W. Latitudinal variation of leaf morphological traits from species to communities along a forest transect in eastern China. J. Geogr. Sci. 2016, 26, 15–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, F.; Guo, S.J.; Fan, B.L.; Zhang, W.X.; Wang, F.L.; Han, F.G.; Zhang, Y.N.; Sun, T. Variation in leaf functional traits of different–aged Haloxylon ammodendron communities, and the relationship with soil factors. Pratac. Sci. 2020, 37, 2486–2496. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, P.F.; Zhou, H.R.; Liu, H.X. Spatial distribution characteristics of soil physical and chemical properties in Baiyang River–Alik Lake wetland. Arid Zone Res. 2008, 25, 406–412. [Google Scholar]
- Davidson, E.A.; Verchot, L.V.; Cattanio, J.H.; Ackerman, I.L.; Carvalho, J.E. Effects of soil water content on soil respiration in forests and cattle pastures of eastern Amazonia. Biochem 2000, 48, 53–69. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, Y.; Zhou, X. Soil Respiration and the Environment, 1st ed.; Academic Press: Amsterdam, The Netherlands; London, UK, 2006; p. 328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, L.; Lv, G.H.; Zhang, X.N.; He, X.M.; Wang, H.L. Spatial heterogeneity of soil respiration in arid Ebinur Lake Basin. Arid Land Geol. 2014, 37, 704–712. [Google Scholar]
- Gong, X.W.; Lv, G.H.; Ma, Y.; Zhang, X.N.; He, X.M.; Guo, Z.J. Ecological Stoichiometry Characteristics in the Soil under Crown and Leaves of Two Desert Halophytes with Soil Salinity Gradients in Ebinur Lake Basin. Sci. Silvae Sin. 2017, 53, 28–36. [Google Scholar]
- Abliz, A.; Lv, G.H.; Zhang, X.N.; Gong, Y.M. Carbon, nitrogen and phosphorus stoichiometry of photosynthetic organs across Ebinur Lake Wetland Natural Reserve of Xinjiang, Northwest China. Chin. J. Ecol. 2015, 34, 2123–2130. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, J.W.; Luo, L.Y.; Li, S.Y.; Wang, G.J.; He, G.X.; Wen, S.Z. Response of Phoebe bournei leaf functional traits and phenotypic plasticity to its mixture with the Chinese fir. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2021, 41, 2855–2866. [Google Scholar]
- Wildung, R.E.; Garland, T.R.; Buschbom, R.L. The interdependent effects of soil temperature and water content on soil respiration rate and plant root decomposition in arid grassland soils. Soil Biol. Biochem. 1975, 7, 373–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornwell, W.K.; Schwilk, D.W.; Ackerly, D.D. A trait–based test for habitat filtering, convex hull volume. Ecology 2006, 87, 1465–1471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Scientific Name of Plant | Family | Genus | Biotype |
|---|---|---|---|
| Populus euphratica Oliv. 1807 | Salicaceae | Populus | arbor |
| Haloxylon ammodendron (C. A. Mey.) Bunge. 1851 | Chenopodiaceae | Haloxylon | dungarunga |
| Halimodendron halodendron (Pall.) Voss. 1896 | Leguminosae | Halimodendron | bush |
| Nitraria tangutorum Bobr. 1946 | Zygophyllaceae | Nitraria | bush |
| Lycium ruthenicum Murray. 1780 | Solanaceae | Lycium | bush |
| Apocynum venetum Linn. 1753 | Apocynaceae | Apocynum | fruticuli |
| Alhagi sparsifolia Shap. 1933 | Leguminosae | Alhagi | fruticuli |
| Reaumuria soongorica (Pall.) Maxim. 1889 | Tamaricaceae | Reaumuria | fruticuli |
| Phragmites australis (Cav.) Trin. 1841 | Gramineae | Phragmites | herbaceous |
| Suaeda microphylla (C. A. Mey.) Pall. 1803 | Chenopodiaceae | Suaeda | herbaceous |
| Achnatherum splendens (Trin.) Nevski. 1937 | Gramineae | Achnatherum | herbaceous |
| Salsola collina Pall. 1803 | Chenopodiaceae | Salsola | herbaceous |
| Mulgedium tataricum (Linn.) DC. 1838 | Compositae | Mulgedium | herbaceous |
| Glycyrrhiza uralensis Fisch. 1825 | Leguminosae | Glycyrrhiza | herbaceous |
| Sonchus oleraceus Linn. 1753 | Compositae | Sonchus | herbaceous |
| Research Variables | Means ± Standard Deviation | Coefficient of Variation (%) | Variogram Model Type | Range (m) | Nugget Values C0/(C + C0) | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Soil respiration (μmol m−2·s−1) | 0.29 ± 0.25 | 86.21 | Exponential | 25.50 | 0.11 | 0.60 |
| Maximum strain height (cm) | 135.74 ± 21.12 | 15.56 | Exponential | 21.60 | 0.06 | 0.61 |
| Leaf length (mm) | 148.11 ± 29.30 | 19.78 | Exponential | 19.50 | 0.07 | 0.37 |
| Leaf width (mm) | 15.31 ± 3.32 | 21.69 | Exponential | 27.60 | 0.16 | 0.84 |
| Leaf thickness (cm) | 0.33 ± 0.05 | 15.15 | Spherical | 17.10 | 0.03 | 0.89 |
| Leaf dry matter content (g·g−1) | 0.39 ± 0.28 | 8.21 | Exponential | 18.30 | 0.07 | 0.71 |
| Specific leaf area (cm2·g−1) | 70.60 ± 14.23 | 20.16 | Gaussian | 19.75 | 0.11 | 0.96 |
| Leaf carbon content (mg·g−1) | 407.09 ± 30.27 | 7.44 | Linear | 52.97 | 1.00 | 0.03 |
| Leaf nitrogen content (mg·g−1) | 25.20 ± 2.46 | 9.76 | Exponential | 30.90 | 0.15 | 0.86 |
| Leaf phosphorus content (mg·g−1) | 2.24 ± 0.22 | 9.82 | Spherical | 16.80 | 0.04 | 0.37 |
| Soil temperature (°C) | 27.36 ± 2.05 | 7.49 | Exponential | 25.50 | 0.16 | 0.65 |
| Soil water content (g·g−1) | 13.12 ± 2.33 | 17.76 | Exponential | 15.00 | 0.08 | 0.64 |
| Total nitrogen (g·kg−1) | 2.05 ± 0.39 | 19.02 | Exponential | 8.10 | 0.09 | 0.01 |
| Soil organic content (g·kg−1) | 9.57 ± 3.11 | 32.50 | Exponential | 30.00 | 0.11 | 0.91 |
| Component | Initial Eigen Values | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Total | Variance % | Cumulative % | |
| 1 | 4.76 | 34.02 | 34.02 |
| 2 | 1.71 | 12.23 | 46.25 |
| 3 | 1.29 | 9.23 | 55.48 |
| 4 | 1.02 | 7.31 | 62.79 |
| 5 | 0.96 | 6.84 | 69.63 |
| 6 | 0.79 | 5.62 | 75.25 |
| 7 | 0.69 | 4.92 | 80.17 |
| 8 | 0.57 | 4.10 | 84.27 |
| 9 | 0.54 | 3.83 | 88.10 |
| 10 | 0.47 | 3.36 | 91.46 |
| 11 | 0.41 | 2.95 | 94.41 |
| 12 | 0.37 | 2.63 | 97.04 |
| 13 | 0.30 | 2.15 | 99.19 |
| 14 | 0.11 | 0.81 | 100.00 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sheng, H.; Wang, J.; He, X.; Lv, G. The Relationship between Soil Respiration and Plant Community Functional Traits in Ebinur Lake Basin. Agronomy 2022, 12, 966. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12040966
Sheng H, Wang J, He X, Lv G. The Relationship between Soil Respiration and Plant Community Functional Traits in Ebinur Lake Basin. Agronomy. 2022; 12(4):966. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12040966
Chicago/Turabian StyleSheng, Huiyi, Jinlong Wang, Xuemin He, and Guanghui Lv. 2022. "The Relationship between Soil Respiration and Plant Community Functional Traits in Ebinur Lake Basin" Agronomy 12, no. 4: 966. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12040966
APA StyleSheng, H., Wang, J., He, X., & Lv, G. (2022). The Relationship between Soil Respiration and Plant Community Functional Traits in Ebinur Lake Basin. Agronomy, 12(4), 966. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12040966





