Recovery Characteristics of Cry1Ac Endotoxin Expression and Related Physiological Mechanisms in Bt Transgenic Cotton Squares after High-Temperature Stress Termination
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Materials and Field Design
2.2. Preparation of Plant Material
2.3. Physiological Measurements
2.3.1. Cry1Ac Protein Concentration Assay
2.3.2. Free Amino Acid and Soluble Protein Content Analyses
2.3.3. Glutamic Pyruvic Transaminase (GPT) and Glutamate Oxaloacetate Transaminase (GOT) Assays
2.3.4. Protease and Peptidase Activity Analyses
2.4. Statistics Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Changes of Cry1Ac Endotoxin Contents in Cotton Squares after Critical High-Temperature Stress Termination
3.2. Physiological Characteristics of Nitrogen Metabolism in Bt Cotton Squares after Critical High-Temperature Stress Termination
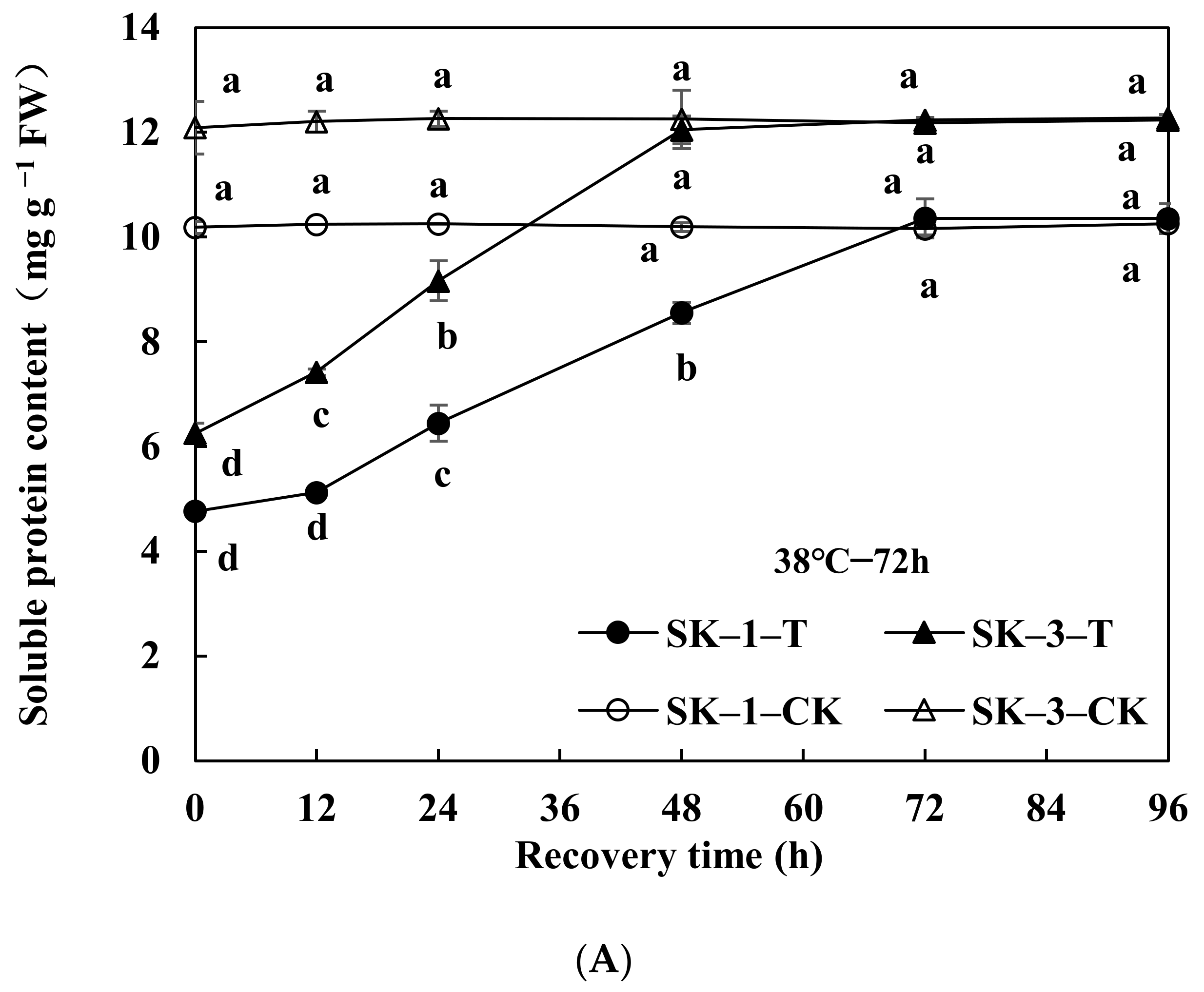
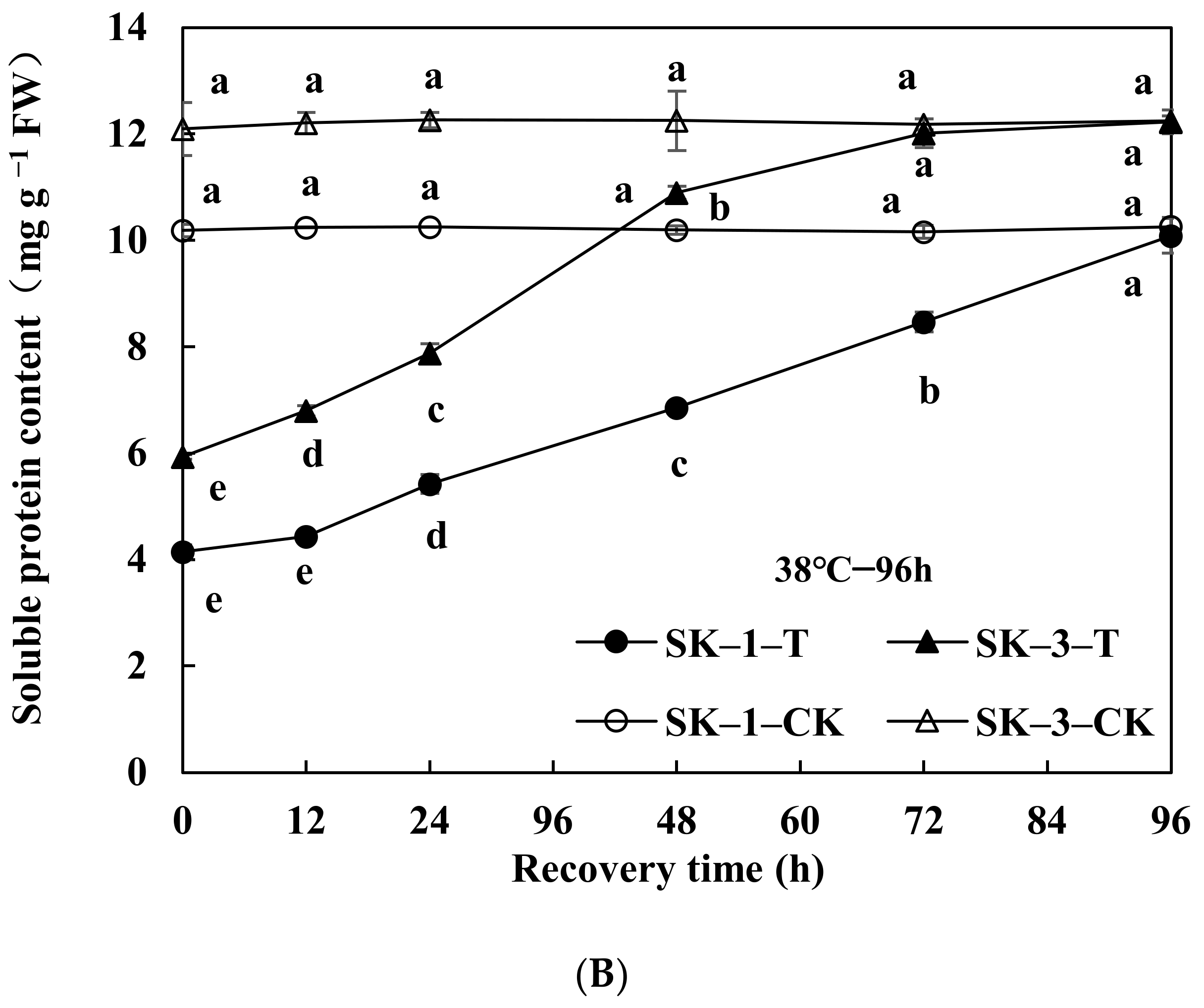
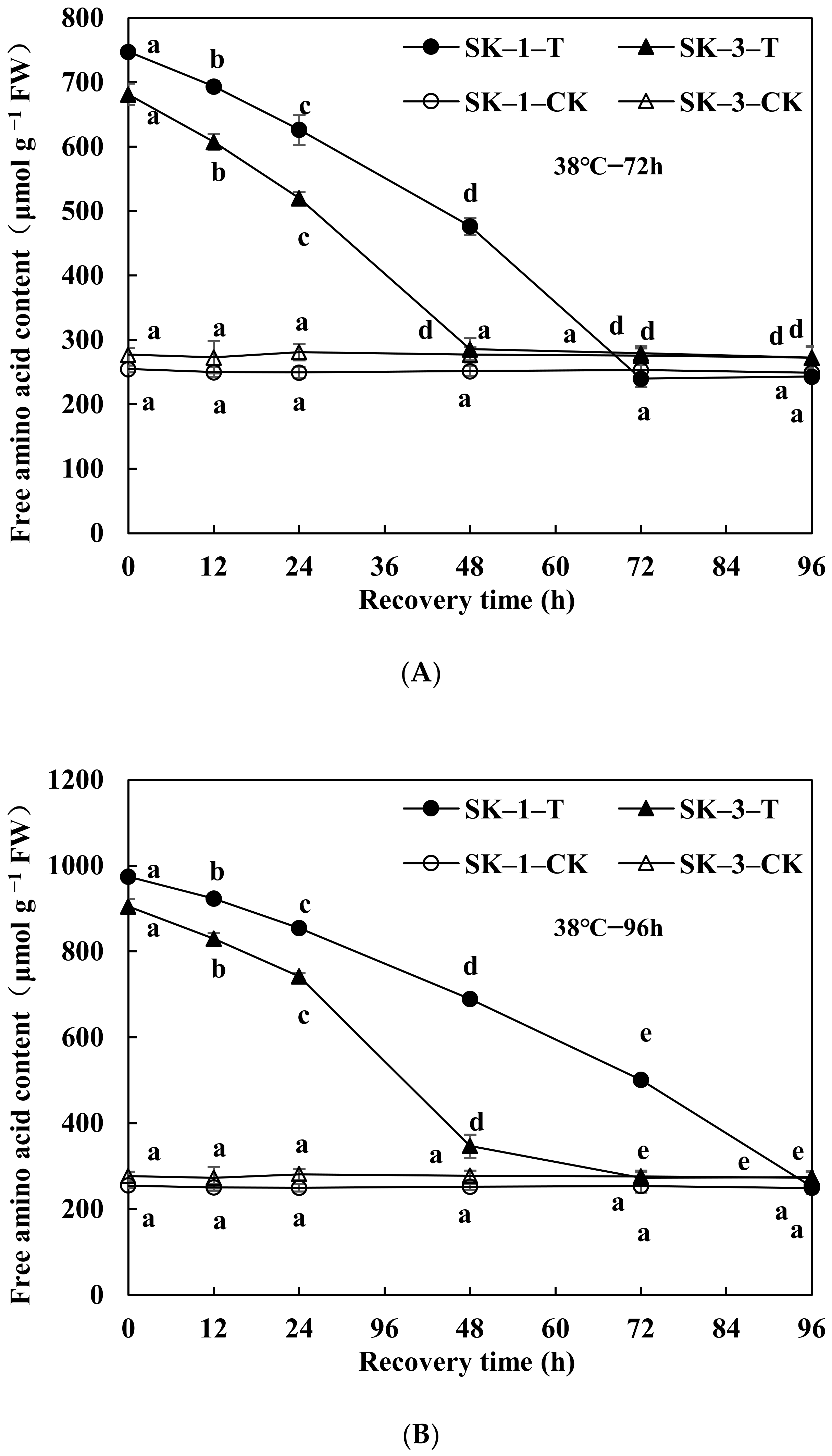
3.2.1. Changes in Soluble Protein and Free Amino Acid Contents
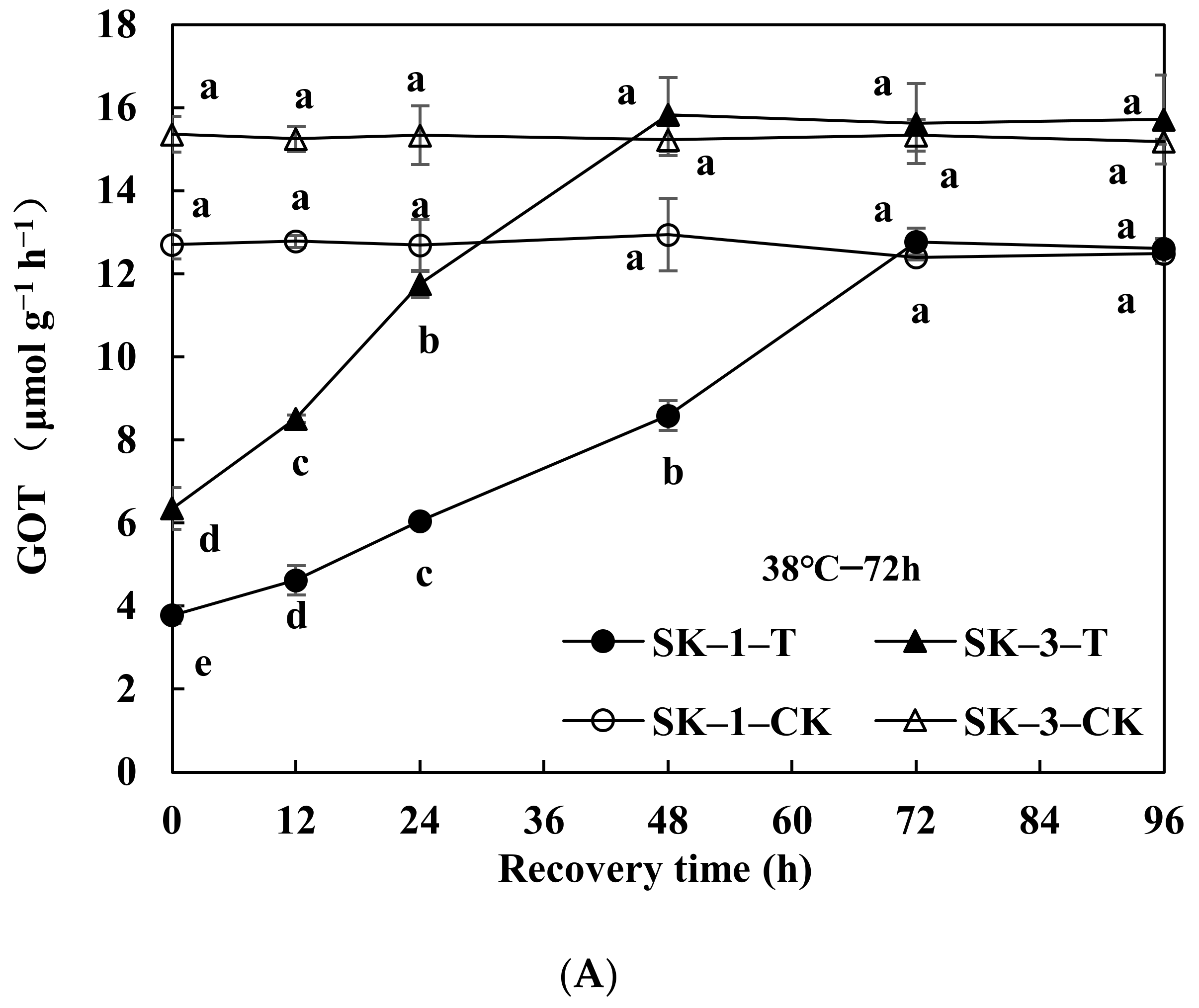
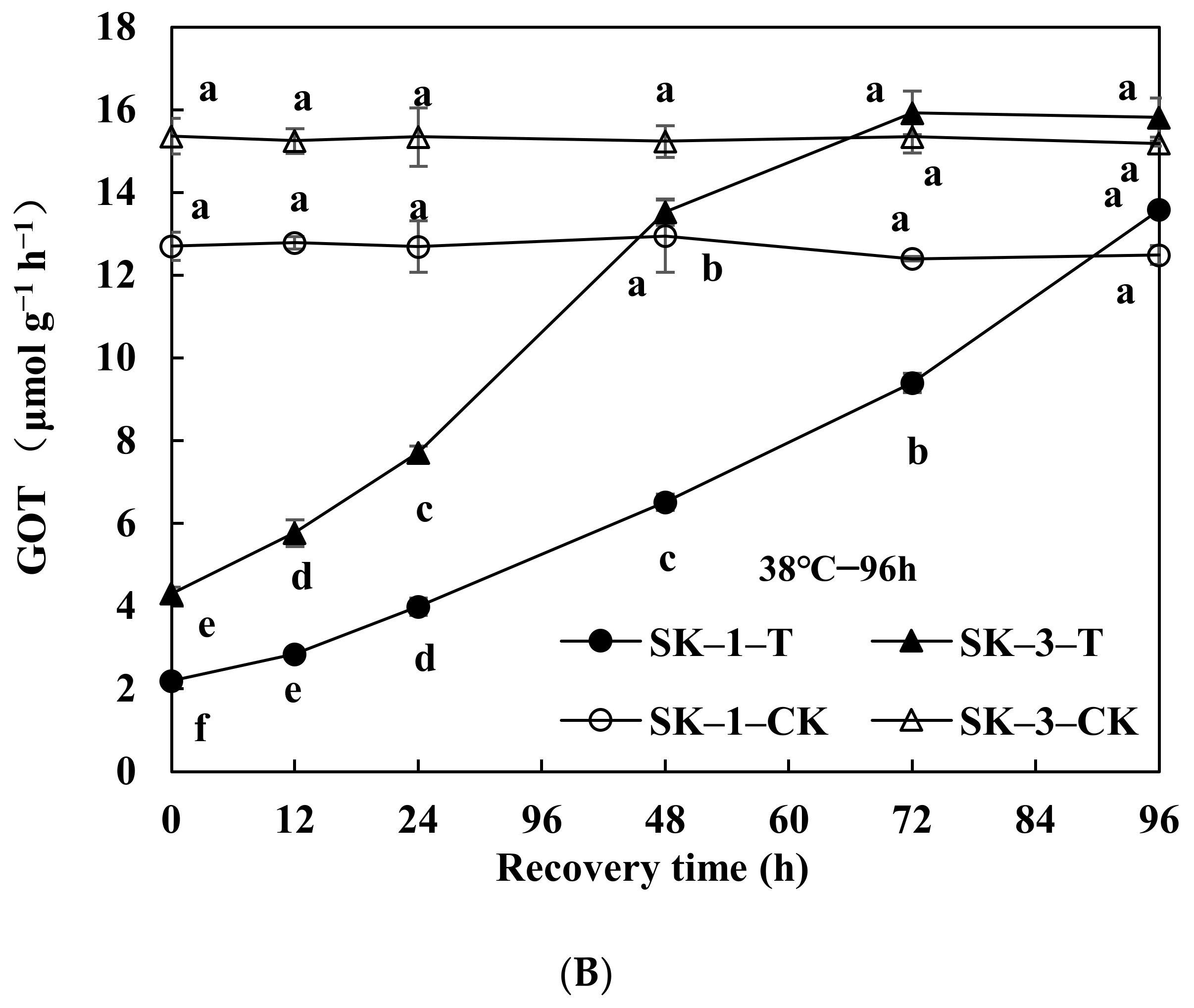
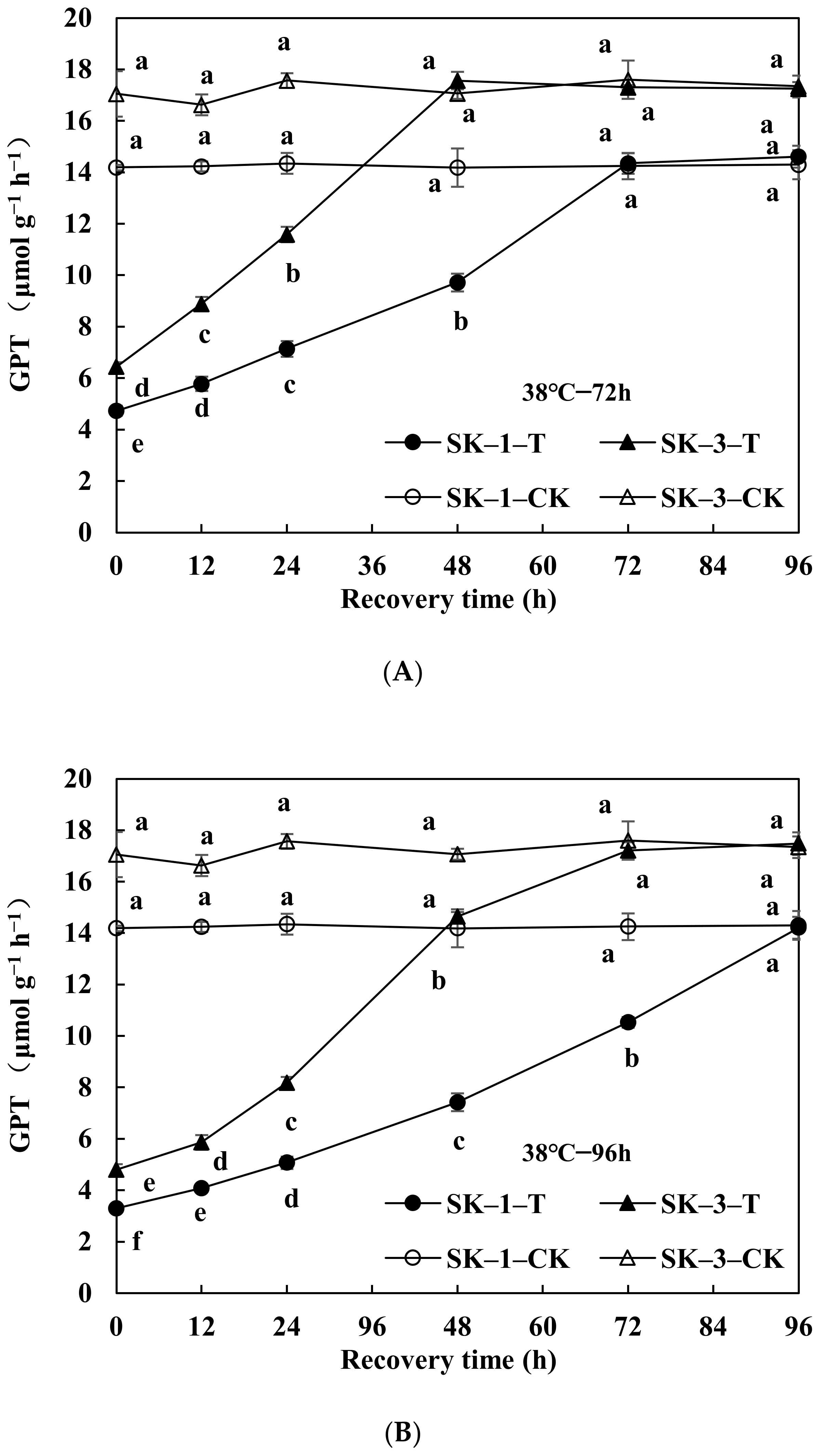
3.2.2. Changes of GOT and GPT Activities
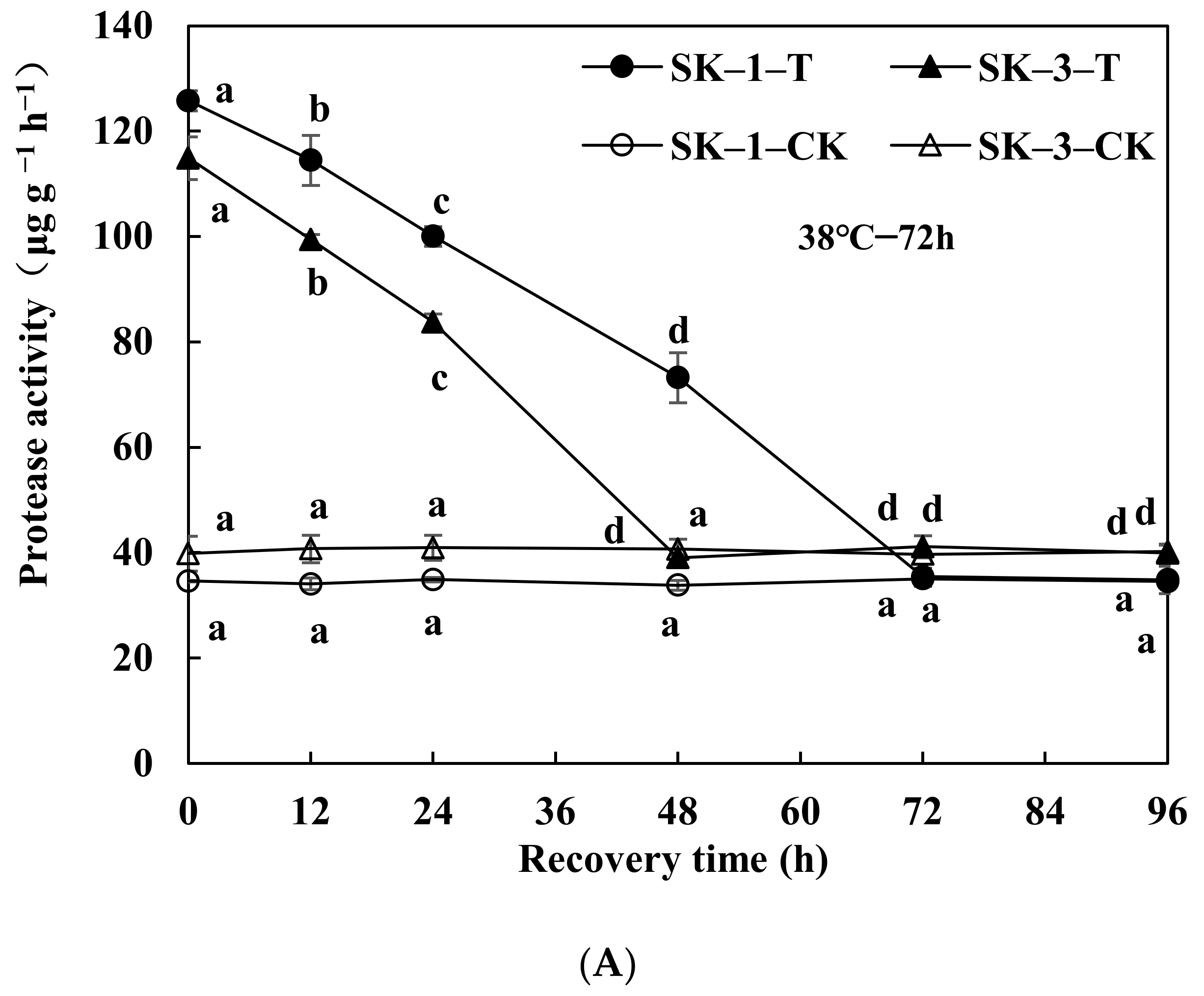
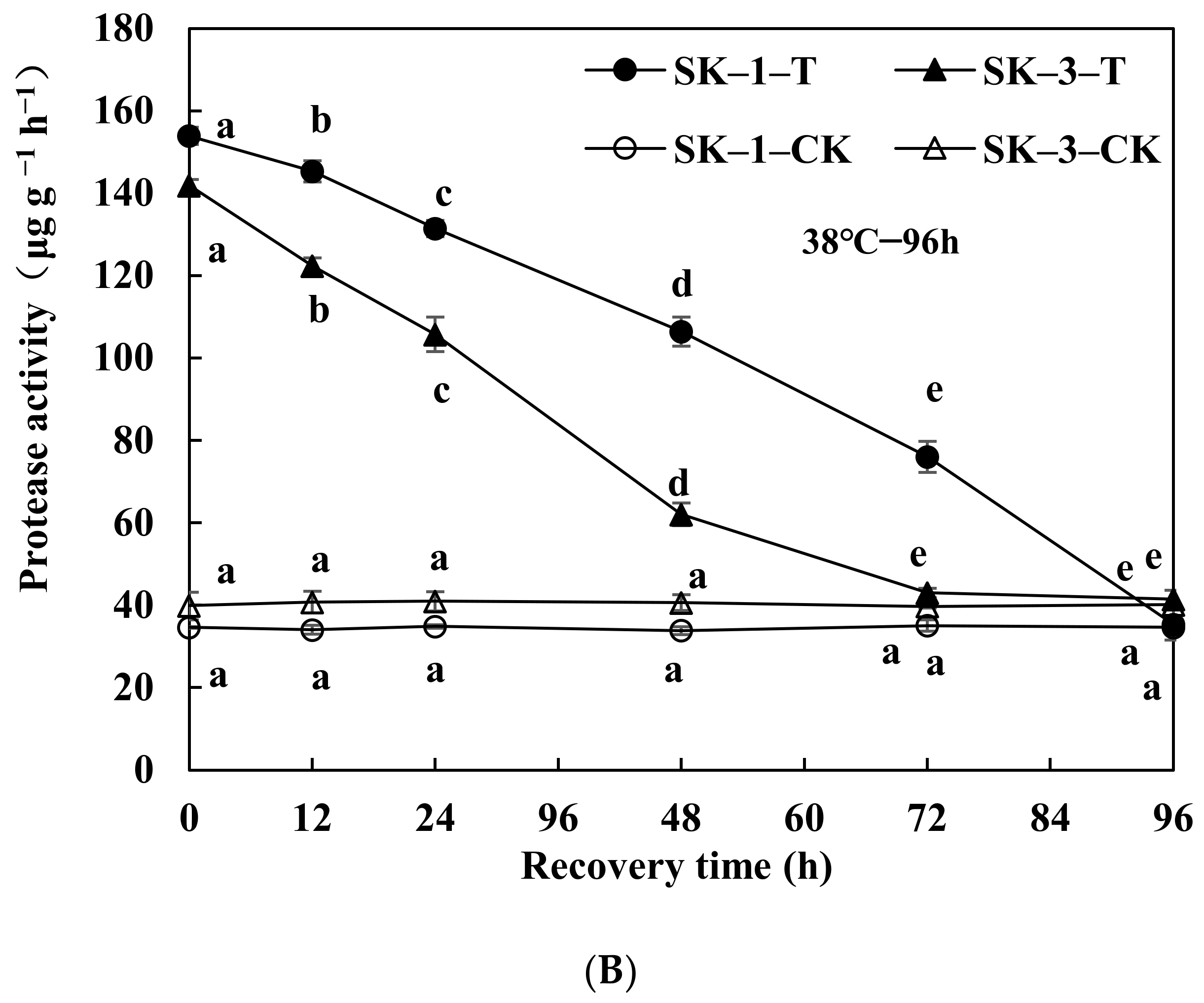
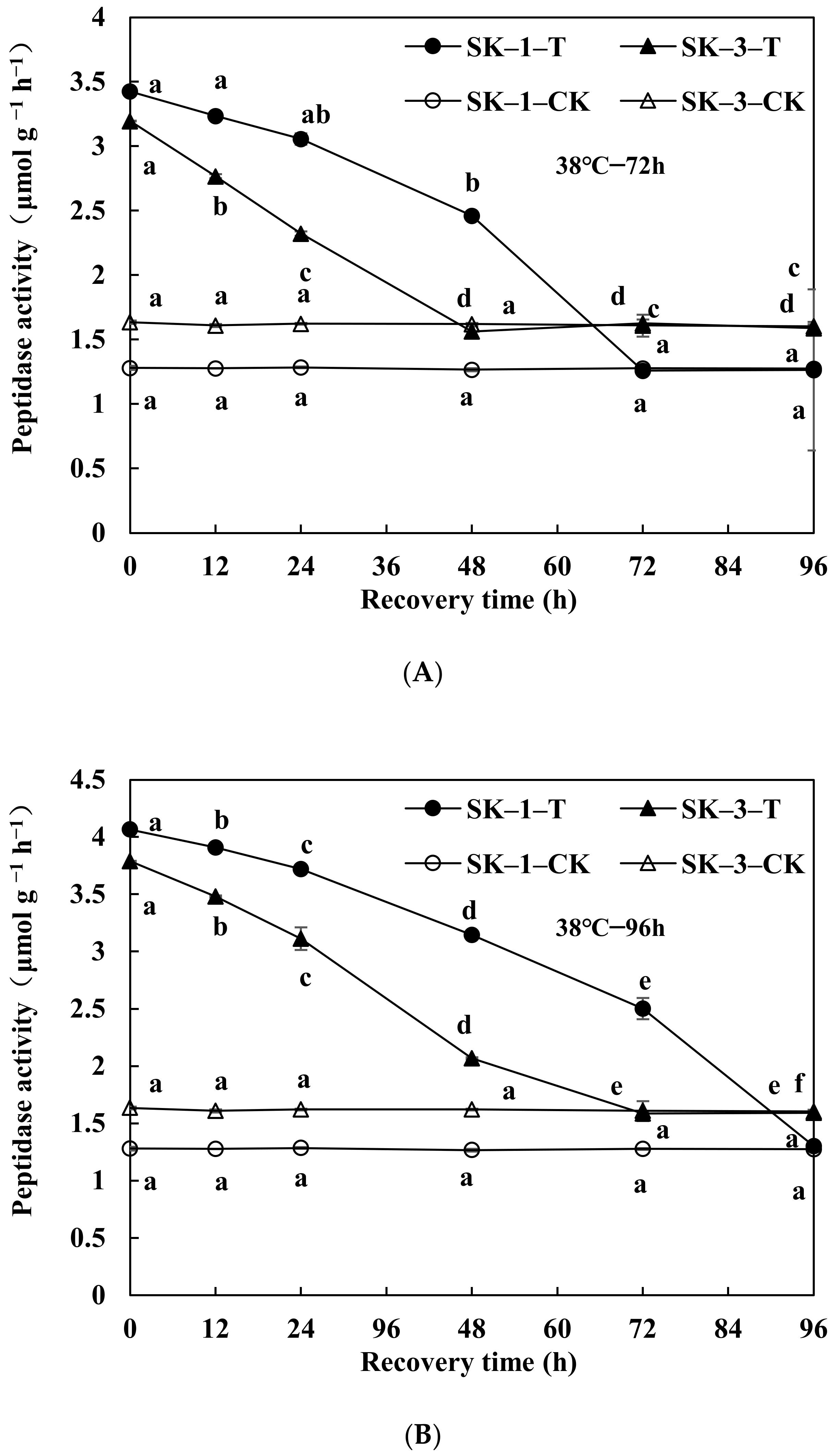
3.2.3. Changes of Protease Activity and Peptidase Activity
4. Discussion
4.1. High-Temperature Stress Duration Affecting the Recovery of Bt Protein Expression in Cotton Squares after Stress Termination
4.2. The Recovery of Cry1Ac Endotoxin Expression in Cotton Squares Related to Nitrogen Metabolism
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Huang, J.K.; Mi, J.W.; Lin, H.; Wang, Z.J.; Chen, R.J.; Hu, R.F.; Scott, R.; Carl, P. Adecade of Bt cotton in Chinese field: Assessing direct effect and indirect externalities of Bt cotton adoption in China. Sci. China Life Sci. 2010, 53, 981–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clive, J. The development state for commercial Biotechnology and transgenic crops. China Biotechnol. 2012, 32, 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Jenkins, J.N.; McCarty, J.C.J.; Wofford, T. Bt cotton—A new era in cotton production. Am. Proc. Beltwide Cotton Conf. 1995, 1, 171–173. [Google Scholar]
- Pray, C.E.; Huang, J.K.; Hu, R.F.; Rozelle, S. Five years of Bt cotton in China the benefits continue. Plant J. 2002, 31, 423–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gould, F. Evolutionary biology and genetically engineered crops. Bioscience 1988, 38, 26–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gasser, C.S.; Fraley, R.T. Genetically engineering plants for crop improvement. Science 1989, 244, 1293–1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhao, J.Z.; Zhou, C.H.; Lu, M.G.; Fan, X.L.; Rong, L.J.; Meng, X.Q. Monitoring and management of Helicoverpa armigera resistance to transgenic Bt cotton in Northern China. Res. Pest Manag. 2000, 1, 28–31. [Google Scholar]
- Adamczyk, J.J.; Meredith, W.R. Genetic basis for the variability of Cry1Ac expression among commercial transgenic Bacillus thuringiensis (Bt) cotton cultivars in the United States. J. Cotton Sci. 2004, 8, 17–23. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, P.; Lin, K.J.; Zhang, Y.J.; Wu, K.M.; Guo, Y.Y. Seasonal expression of Bacillius thuingiensis insecticidal protein and control to cotton bollworm in different varieties of transgenic cotton. Cotton Sci. 2010, 22, 393–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glenn, D.S. Field versus farm in Warangal: Bt cotton, higher yields, and larger questions. World Dev. 2011, 39, 387–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, J.J.; Xia, J.Y. Studies on the resistance dynamics of the Bt transgenic cotton on cotton bollworm. Acta Gossipi Sin. 1999, 11, 141–146. [Google Scholar]
- Finnegan, E.J.; Mcelory, D. Transgenic inactivation: Plant fight back! Biotechnology 1994, 12, 883–888. [Google Scholar]
- Benedict, J.H.; Sachs, E.S.; Altman, D.W.; Deaton, W.R.; Kohel, R.J.; Ring, D.R.; Berberich, S.A. Field performance of cottons expressing transgenic Cry1Ac insecticidal proteins for resistance to Heliothis virescens and Helicoverpa zea (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae). J. Econ. Entomol. 1996, 89, 230–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stam, M.; Mol, J.M.; Kooter, J.M. The silence of gene in transgenic plant. Anal. Bot. 1997, 79, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Benedic, J.H.; Sachs, E.S.; Altman, D.W.; Ring, D.R.; Stone, T.B.; Sims, S.R. Impact of endotoxin-producing transgenic cotton on insect-plant interactions with Heliothis virescens and Helicoverpa zea (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae). Environ. Entomol. 1993, 22, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.H.; Ye, G.Y.; Luan, N.; Xiao, J.; Chen, Y.; Chen, D.H. Boll size affects the insecticidal protein content in Bacillius Thuringiensis (Bt) cotton. Field Crops Res. 2009, 110, 106–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Wen, Y.; Chen, Y.; Cothren, J.T.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Y.; Payne, W.A.; Chen., D.H. Effects of extreme air temperature and humidity on the insecticidal expression level of Bt cotton. J. Integr. Agric. 2012, 11, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Chen, Y.; Wen, Y.J.; Zhang, X.; Chen, D.H. The effects of the relative humidity on the insecticidal expression level of Bt cotton during bolling period under high temperature. Field Crops Res. 2012, 137, 141–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.H.; Ye, G.Y.; Yang, C.Q.; Chen, Y.; Wu, Y.K. The effect of high temperature on the insecticidal properties of Bt Cotton. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2005, 53, 333–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Eltayib, A.; Hua, M.M.; Heng, L.; Lv, C.H.; Chen, D.H. Effects of high temperature on Bt protein content and nitrogen metabolic physiology in boll wall of Bt cotton. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2015, 26, 3202–3206. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.M. Factors affecting the insect resistance of Bt transgenic cotton. Cotton Sci. 1999, 11, 336. [Google Scholar]
- Warren, G.W.; Carozzi, N.B.; Desai, N.; Koziel, M.G. Field evaluation of transgenic tobacco containing a Bt insecticial protein gene. J. Econ. Entomol. 1992, 85, 1651–1659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitt, G.P.; Mares, C.L.; Liewellyn, D.J. Field evaluation and potential ecological impact of transgenic cottons in Australia. Biocontrol Sci. Technol. 1994, 4, 535–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Wen, Y.J.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Y.H.; Chen, D.H. The recovery of Bt toxin content after temperature stress termination in transgenic cotton. Span. J. Agric. Res. 2013, 11, 438–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, M.Y.; Liu, Z.Y.; Li, L.N.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, X.; Chen, Y.; Chen, D.H. Effect of Urea Spray on Boll Shell Insecticidal Protein Content in Bt Cotton. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 623504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.Y.; Eltayib, H.M.A.A.; Wu, H.M.; Zhou, M.Y.; Zhang, X.; Chen, Y.; Chen, D.H. Bt insecticidal efficacy variation and agronomic regulation in Bt cotton. J. Cotton Res. 2019, 2, 219–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, M.Y. Insecticidal Protein Regulation and Physiological Mechanism of Reproductive Organ in Bt Cotton; Yangzhou University: Yangzhou, China, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, S.; Wu, J.Y.; He, X.L.; Huang, J.Q.; Zhou, B.L.; Zhang, R.X. Quantification using ELISA of Bacillus thuringiensis insecticidal protein expressed in the tissue of transgenic insect-resistant cotton. J. Jiangsu Agri. Sci. 1997, 3, 154–156. [Google Scholar]
- Weiler, E.W.; Jourdan, P.S.; Conrad, W. Levels of indole-3-acetic acid and intact decapitated coleoptiples as determined by a specific and highly sensitive solid-phase enzyme immuno-assay. Planta 1981, 153, 561–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yemm, E.W.; Cocking, E.C. The determination of amino acid with ninhydrin. Analyst 1955, 80, 209–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradford, M.M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantification of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Ann. Biochem. 1976, 72, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tonhazy, N.E.; White, N.G.; Umbriet, W.W. Colorimetric assay of glutamic-pyruvic transaminase. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 1950, 28, 36–38. [Google Scholar]
- Vance, C.P.; Heichel, G.H.; Barnes, D.K.; Bryan, J.M.; Johnson, L.E. Nitrogen fixation, nodule development, and vegetative regrowth of alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.) following harvest. Plant Physiol. 1979, 64, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, J.; Huang, X.H. Advance and perspectives in crop heterosos. Sci. Sin. 2021, 51, 1396–1404. [Google Scholar]
- Tyagi, P.; Bowman, D.T.; Bourland, F.M.; Edmisten, E.K.; Campbell, B.T.; Fraser, D.E.; Wallace, T.; Kuraparthy, V. Components of hybrid vigor in upland cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.) and their relationship with environment. Euphytica 2014, 195, 117–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.Y.; Li, S.Y.; Zhu, J.B.; Chen, F.R.; Liu, F.Z.; Yu, C. Effects of alternating temperatures day and night on cotton bollworm mortality and insecticidal protein expression of two kinds of Bt cottons. Chin. Agric. Sci. Bull. 2015, 31, 103–108. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Han, Y.; Wang, J.; Hua, M.M.; Gu, C.; Li, G.S.; Zhang, X.; Chen, D.H. Effects of high temperature on Bt proteins expression and nitrogen metabolic physiology in square of Bt cotton at the peak squaring stage. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2014, 25, 2623–2628. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, D.H.; Yang, C.Q.; Chen, Y.; Nie, A.Q.; Wu, Y.K. The effects of the high temperature stress on the leaf Bt protein content and nitrogen metabolism of Bt cotton. Cotton Sci. 2003, 5, 288–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, Z.; Wang, G.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, C.; Li, H.; Wu, T.; Zhang, X.; Chen, D. Recovery Characteristics of Cry1Ac Endotoxin Expression and Related Physiological Mechanisms in Bt Transgenic Cotton Squares after High-Temperature Stress Termination. Agronomy 2022, 12, 668. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12030668
Liu Z, Wang G, Zhang Z, Zhang C, Li H, Wu T, Zhang X, Chen D. Recovery Characteristics of Cry1Ac Endotoxin Expression and Related Physiological Mechanisms in Bt Transgenic Cotton Squares after High-Temperature Stress Termination. Agronomy. 2022; 12(3):668. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12030668
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Zhenyu, Guixia Wang, Zhongning Zhang, Chenxia Zhang, Hanjia Li, Tianfan Wu, Xiang Zhang, and Dehua Chen. 2022. "Recovery Characteristics of Cry1Ac Endotoxin Expression and Related Physiological Mechanisms in Bt Transgenic Cotton Squares after High-Temperature Stress Termination" Agronomy 12, no. 3: 668. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12030668
APA StyleLiu, Z., Wang, G., Zhang, Z., Zhang, C., Li, H., Wu, T., Zhang, X., & Chen, D. (2022). Recovery Characteristics of Cry1Ac Endotoxin Expression and Related Physiological Mechanisms in Bt Transgenic Cotton Squares after High-Temperature Stress Termination. Agronomy, 12(3), 668. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12030668





