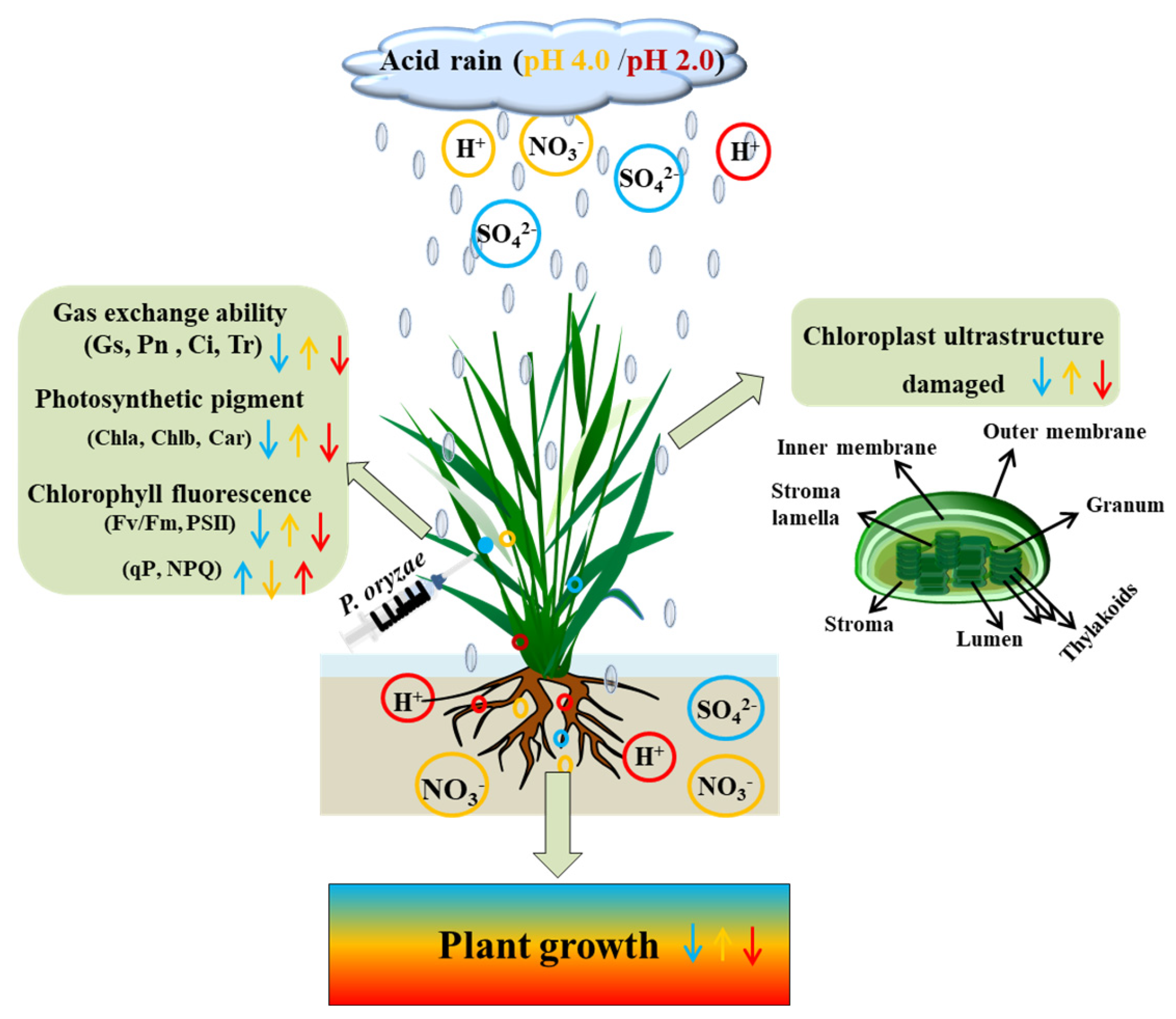
Dual Role of Acid Rain and Pyricularia oryzae on Growth, Photosynthesis and Chloroplast Ultrastructure in Rice Seedlings
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Materials and P. oryzae Culture
2.2. Preparation of SAR Treatments
2.3. Determination of Rice Growth Indexes
2.4. Chlorophyll Determination
2.5. Evaluation of Chlorophyll Photosynthetic Parameters and Fluorescence
2.6. Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM)
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Combined Effects of SAR and P. oryzae on Growth Indices of Rice Seedlings
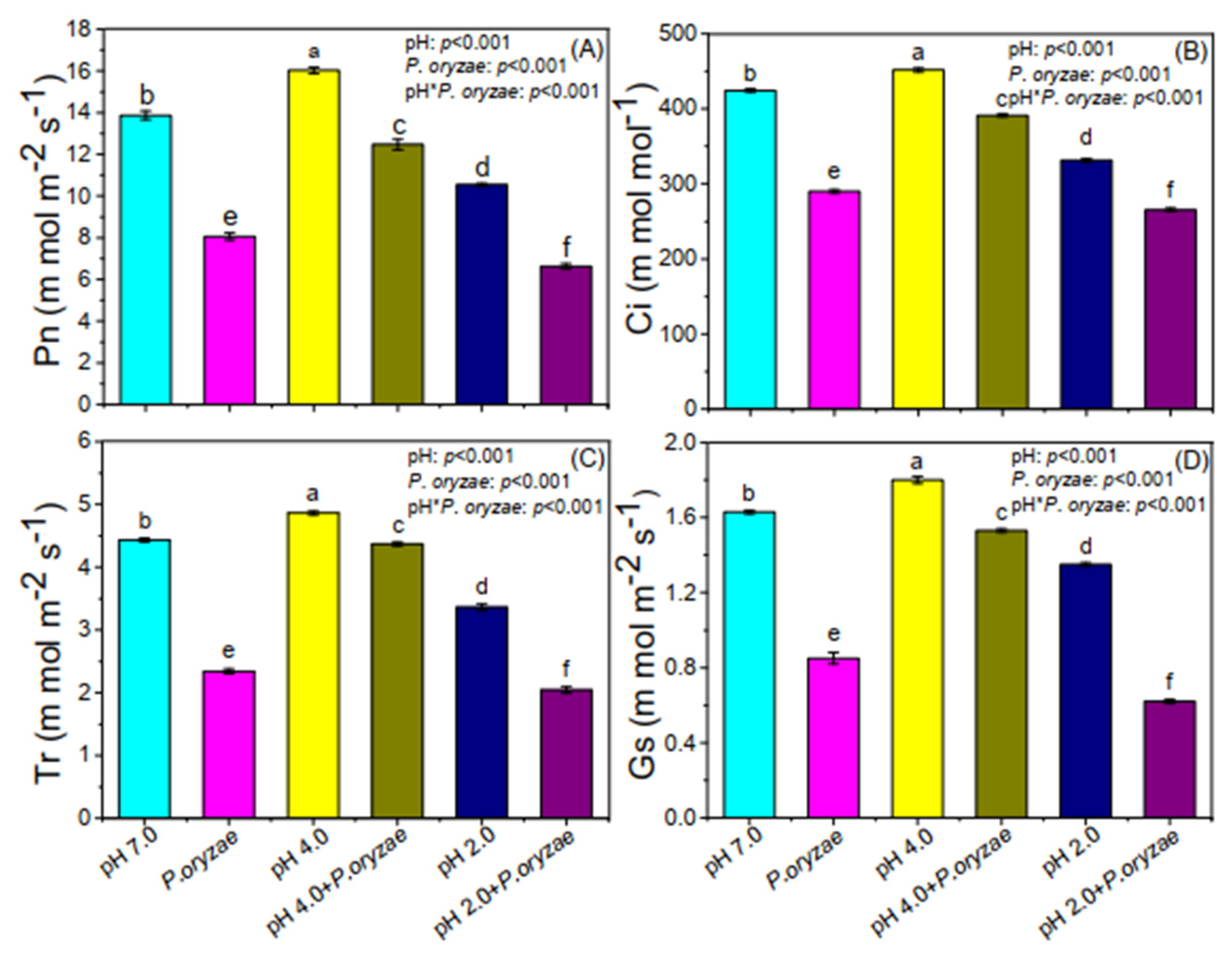
3.2. Combined Effects of SAR and P. oryzae on Photosynthetic Parameters of Rice Seedlings
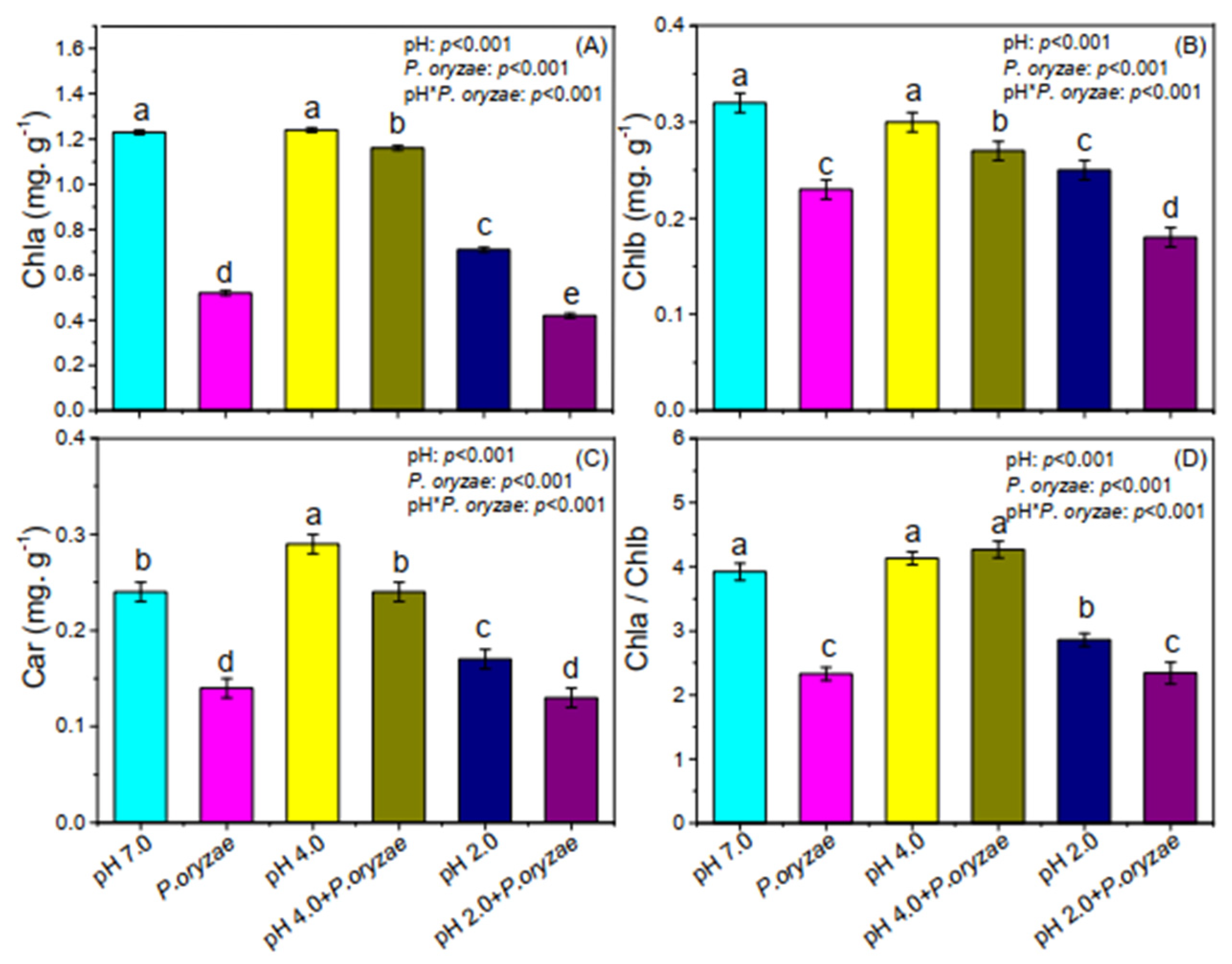
3.3. Combined Effects of SAR and P. oryzae on Photosynthetic Pigment Content of Rice Seedlings
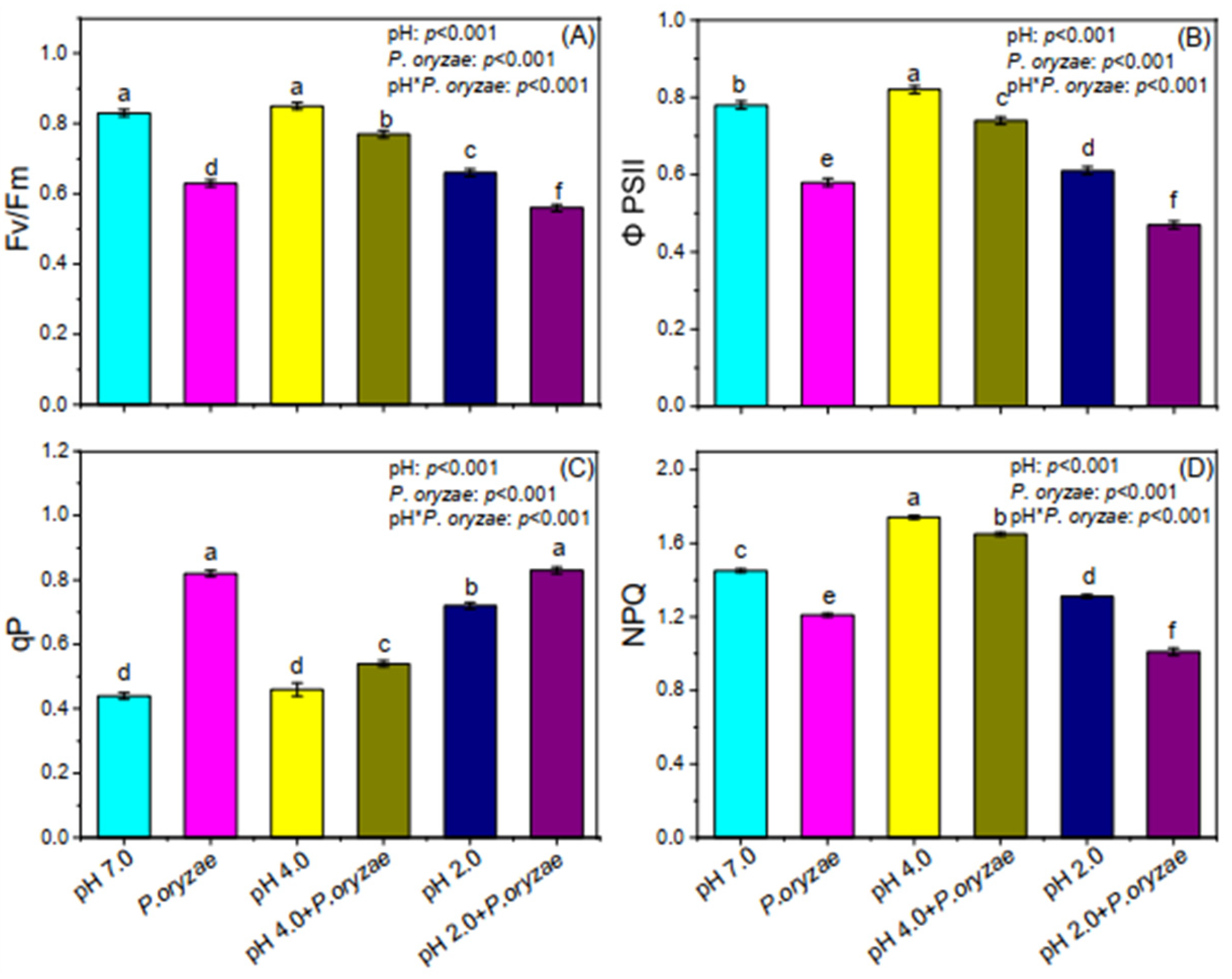
3.4. Combined Effects of SAR and P. oryzae on Chlorophyll Fluorescence of Rice Seedlings
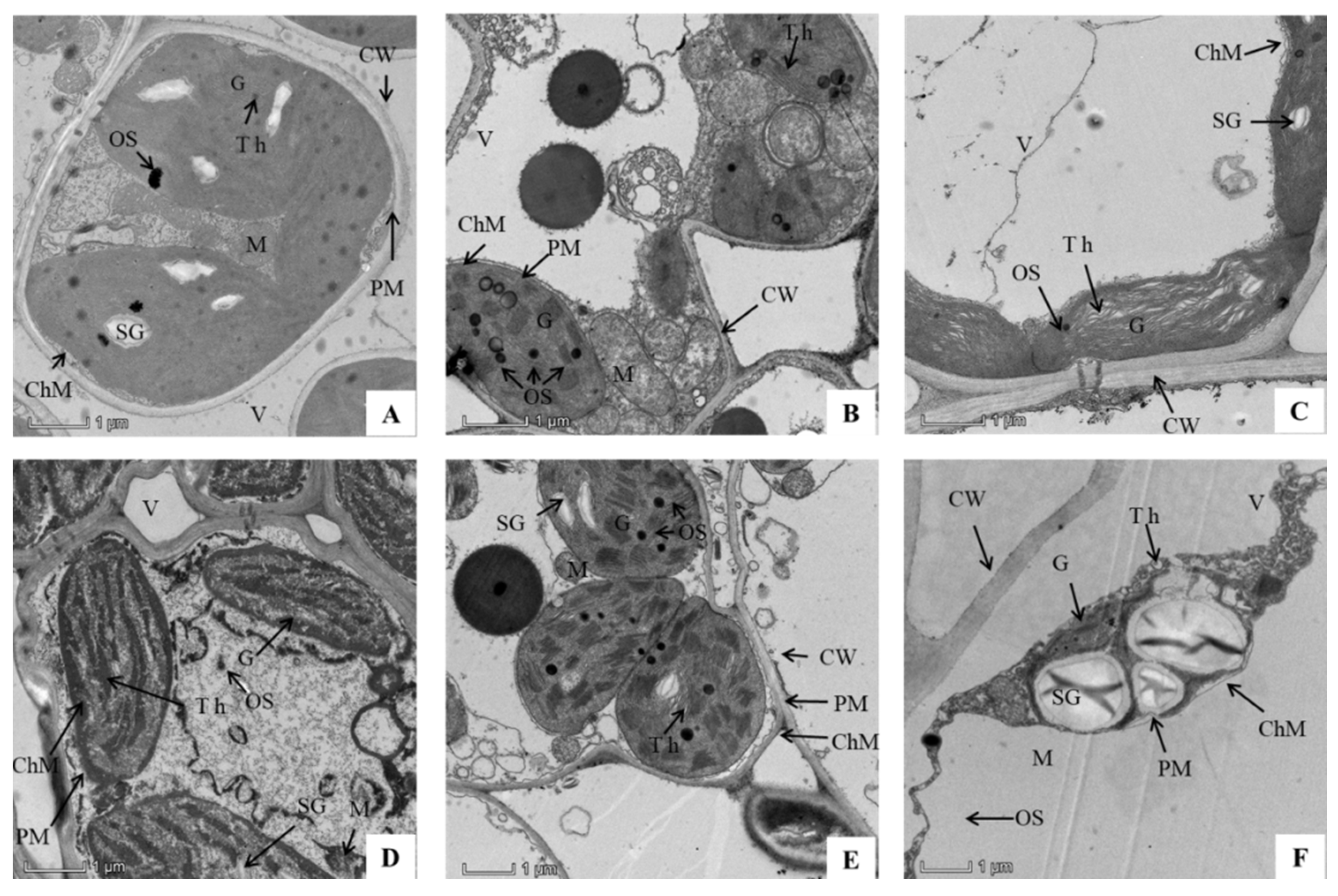
3.5. Combined Effects of SAR and P. oryzae on Chloroplast Ultrastructure
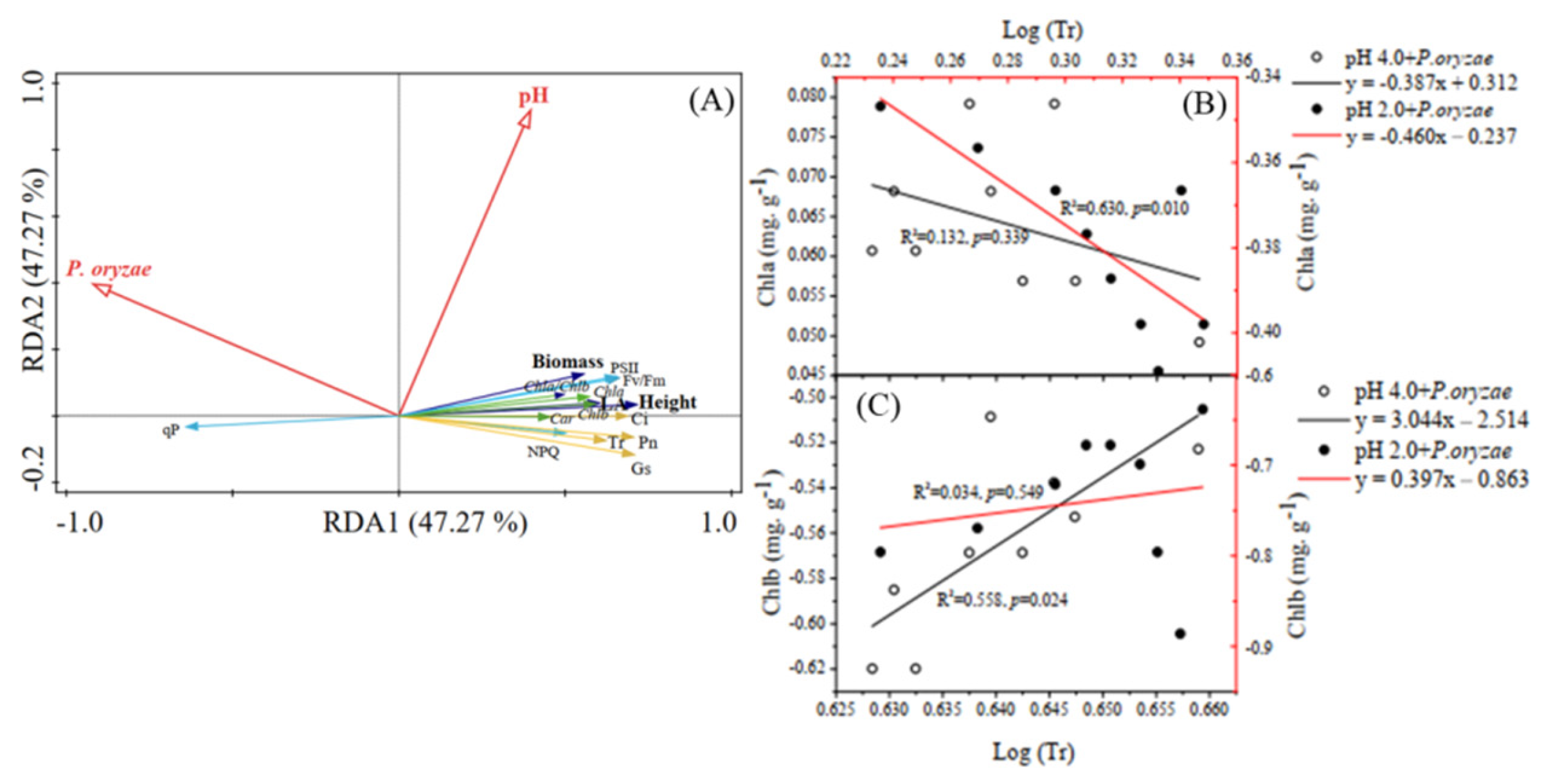
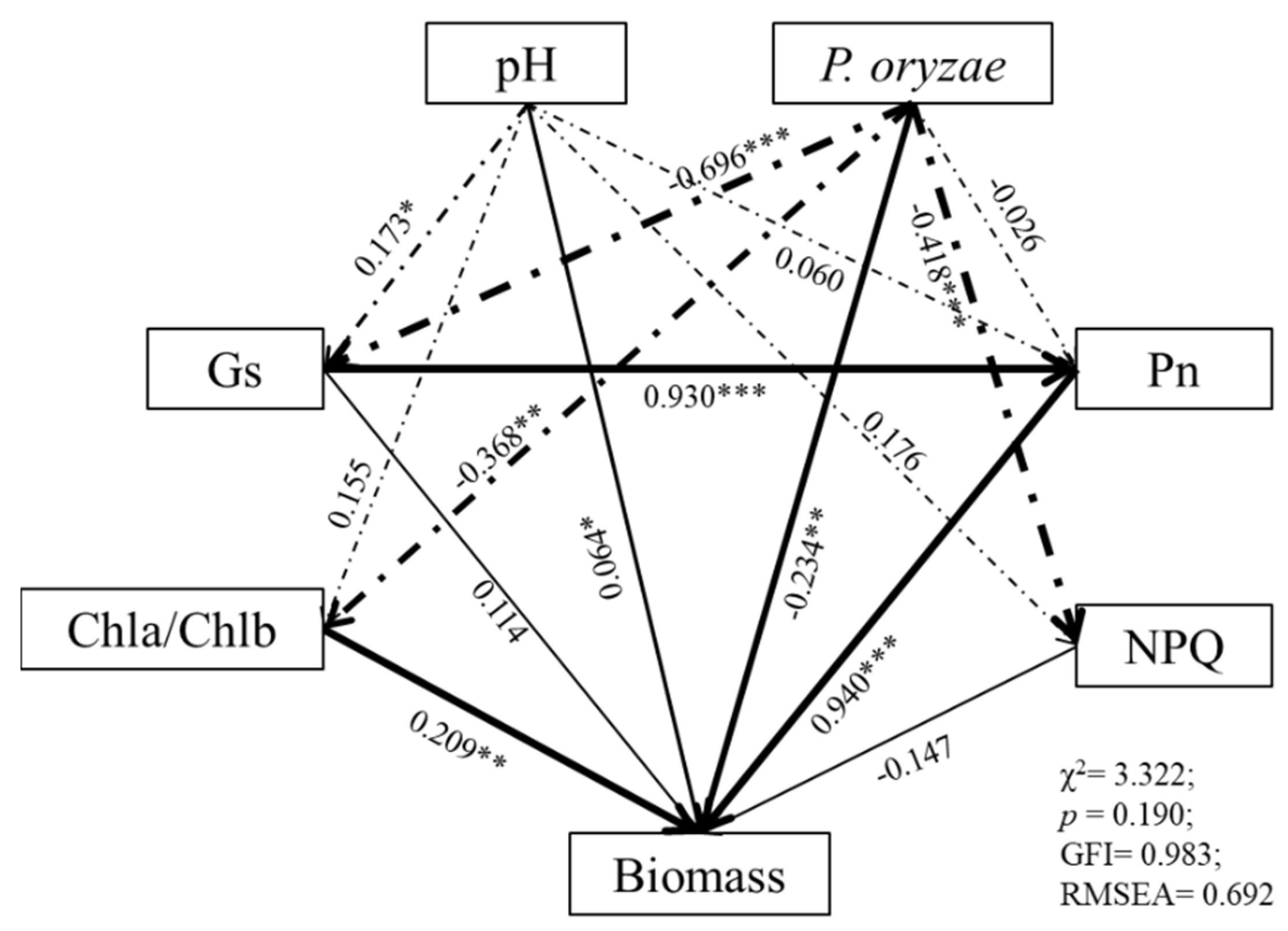
3.6. Linking Rice Seedling Growth Indices with Photosynthetic Pigments, Photosynthetic Parameters, and Chlorophyll Fluorescence
3.7. SEM Results
4. Discussion
4.1. Negative Effect of P. oryzae on the Photosynthesis in Rice Leaves
4.2. Antagonistic Effect of Medium Acidity SAR on P. oryzae—Induced Influence
4.3. Synergistic Effect of High Acidity SAR and P. oryzae—Induced Influence
4.4. Correlations between Tr and Content of Chla and Chlb of Rice Seedlings
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mentlak, T.A.; Kombrink, A.; Shinya, T.; Ryder, L.S.; Otomo, I.; Saitoh, H.; Terauchi, R.; Nishizawa, Y.; Shibuya, N.; Thomma, B.P.H.J.; et al. Effector-mediated suppression of chitin-triggered immunity by Magnaporthe oryzae is necessary for rice blast disease. Plant Cell 2012, 1, 322–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Marroquin-Guzman, M.; Hartline, D.; Wright, J.D.; Elowsky, C.; Bourret, T.J.; Wilson, R.A. The Magnaporthe oryzae nitrooxidative stress response suppresses rice innate immunity during blast disease. Nat. Microbiol. 2017, 2, 17054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Domiciano, G.P.; Cacique, I.S.; Chagas, F.C.; Filippi, M.C.; DaMatta, F.M.; Do, V.F.; Rodrigues, F.A. Alterations in gas exchange and oxidative metabolism in rice leaves infected by Pyricularia oryzae are attenuated by silicon. Phytopathology 2015, 6, 738–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, X.; He, Y.; Xie, C.; Zu, Y.; Zhan, F.; Mei, X.; Xia, Y.; Li, Y. Effects of UV-B radiation on the infectivity of Magnaporthe oryzae and rice disease-resistant physiology in yuanyang terraces. Photochem. Photobiol. Sci. 2018, 1, 8–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, D.; Cai, K.; Chen, J.; Luo, S.; Zeng, R.; Yang, J.; Zhu, X. Silicon enhances photochemical efficiency and adjusts mineral nutrient absorption in Magnaporthe oryzae infected rice plants. Acta Physiol. Plant. 2010, 33, 675–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, A.A.; Guimarães, L.M.D.S.; Chaves, A.R.D.M.; DaMatta, F.M.; Alfenas, A.C. Leaf gas exchange and chlorophyll a fluorescence of Eucalyptus urophylla in response to Puccinia psidii infection. Acta Physiol. Plant. 2011, 33, 1831–1839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Resende, R.S.; Rodrigues, F.Á.; Cavatte, P.C.; Martins, S.; Moreira, W.R.; Chaves, A.; Damatta, F.M. Leaf gas exchange and oxidative stress in sorghum plants supplied with silicon and infected by Colletotrichum sublineolum. Phytopathology 2012, 9, 892–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fisher, M.C.; Henk, D.A.; Briggs, C.J.; Brownstein, J.S.; Madoff, L.C.; Mccraw, S.L.; Gurr, S.J. Emerging fungal threats to animal, plant and ecosystem health. Nature 2012, 7393, 186–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, H.; Liu, W.; Zhang, J.; Qin, Z. Effects of simulated acid rain on soil fauna community composition and their ecological niches. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 220, 460–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zhang, B.; Zhao, W.; Wang, L.; Xie, D.; Huo, W.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, J. Comparative effects of sulfuric and nitric acid rain on litter decomposition and soil microbial community in subtropical plantation of Yangtze River Delta region. Ence Total Environ. 2017, 601–602, 669–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imran, M.A.; Hussain, S.; Hussain, M.; Meo, A.A. Effect of simulated acid rain (SAR) on some morphochemical aspects of mash (Vigna mungo L.). Pak. J. Bot. 2014, 46, 245–250. [Google Scholar]
- Ramlall, C.; Varghese, B.; Ramdhani, S.; Pammenter, N.W.; Bhatt, A.; Berjak, P. Effects of simulated acid rain on germination, seedling growth and oxidative metabolism of recalcitrant-seeded Trichilia dregeana grown in its natural seed bank. Physiol. Plant. 2015, 153, 149–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Macaulay, B.M.; Enahoro, G.E. Effects of simulated acid rain on the morphology, phenology and dry biomass of a local variety of maize (Suwan-1) in Southwestern Nigeria. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2015, 10, 621–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, K.; Liang, C.; Wang, L.; Hu, G.; Zhou, Q. Combined effects of lanthanumion and acid rain on growth, photosynthesis and chloroplast ultrastructure in soybean seedlings. Chemosphere 2011, 84, 601–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Z.G.; Wang, L.H.; Chen, M.M.; Wang, L.; Liang, C.J.; Zhou, Q.; Huang, X.H. Interactive effects of cadmium and acid rain on photosynthetic light reaction in soybean seedlings. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2012, 79, 62–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Wang, W.; Zhou, Q.; Huang, X. Combined effects of lanthanum (III) chloride and acid rain on photosynthetic parameters in rice. Chemosphere 2014, 112, 355–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polishchuk, O.V.; Vodka, M.V.; Belyavskaya, N.A.; Khomochkin, A.P.; Zolotareva, E.K. The effect of acid rain on ultrastructure and functional parameters of photosynthetic apparatus in pea leaves. Cell Tissue Biol. 2016, 10, 250–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Korpelainen, H.; Dong, L.; Yi, L. Physiological responses of Elaeocarpus glabripetalus seedlings exposed to simulated acid rain and cadmium. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 15, 118–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.H.; Yi, L.T.; Yu, S.Q.; Yu, F.; Yin, X.M. Chlorophyll fluorescence characteristics and the growth response of Elaeocarpus glabripetalus to simulated acid rain. Photosynthetica 2015, 1, 23–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Yi, X.; Gao, X.; Wang, M.; Shao, C.; Lv, Z.; Chen, J.; Liu, Z.; Shen, C. Physiological and biochemical responses of tea seedlings (Camellia sinensis) to simulated acid rain conditions. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 192, 110315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, X.; Zhang, K.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, W. Ecophysiological responses of Jatropha curcas L. seedlings to simulated acid rain under different soil types. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 185, 109705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, X.; Zhu, J.; Liu, H.; Xu, X.; Liang, C. Response of antioxidative system in rice (Oryza sativa) leaves to simulated acid rain stress. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 148, 851–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Liang, C. Exogenous application of Ca2+ mitigates simulated acid rain stress on soybean productivity and quality by maintaining nutrient absorption. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 4975–4986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Xiang, H.; Zhong, J.; Ren, X.; Wei, H.; Zhang, J.; Xu, Q.; Zhao, B. Acid rainincreases impact of rice blast on crop health via inhibition of resistance enzymes. Plants 2020, 7, 881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, D.Y.; Xu, Y.G.; Peng, P.; Zhang, H.H.; Lan, J.B. Chemical composition and seasonal variation of acid deposition in Guangzhou, South China: Comparison with precipitation in other major Chinese cities. Environ. Pollut. 2009, 157, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lichtenthaler, H.; Lichtenthaler, H.K.; Lichtenthaler, H.K.; Lichtenthaler, H.K.; Lichtenthaler, H.K. Chlorophylls and carotenoids: Pigment photosynthetic biomembranes. Methods Enzymol. 1987, 1, 350–382. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, T.; Yang, W.; Xie, Y.; Shi, D.; Ma, Y.; Sun, X. Effects of exogenous nitric oxide on the photosynthetic characteristics of bamboo (Indocalamus barbatus McClure) seedlings under acid rain stress. Plant Growth Regul. 2017, 82, 69–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helliot, B.; Swennen, R.; Poumay, Y.; Frison, E.; Lepoivre, P.; Panis, B. Ultrastructural changes associated with cryopreservation of banana (Musa spp.) highly proliferating meristems. Plant Cell Rep. 2003, 21, 690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scholes, J.D.; Rolfe, S.A. Photosynthesis in localised regions of oat leaves infected with crown rust (Puccinia coronata): Quantitative imaging of chlorophyll fluorescence. Planta 1996, 199, 573–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dallagnol, L.J.; Rodrigues, F.A.; DaMatta, F.M.; Mielli, M.; Pereira, S.C. Deficiency in silicon uptake affects cytological, physiological, and biochemical events in the rice—Bipolaris oryzae interaction. Phytopathology 2011, 101, 92–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Haruki, K.; Mimi, H.S.; Koh, I.; Ichiro, T.; Wataru, Y. Improved stomatal opening enhances photosynthetic rate and biomass production in fluctuating light. J. Exp. Bot. 2020, 71, 2339–2350. [Google Scholar]
- Rios, J.A.; Rodrigues, F.D.; Debona, D.; Silva, L.C. Photosynthetic gas exchange in leaves of wheat plants supplied with silicon and infected with Pyricularia oryzae. Acta Physiol. Plant. 2014, 36, 371–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smirnoff, N. Antioxidant systems and plant responses to the environment. In Environment and Plant Metabolism: Flexibility and Acclimation; Sminorff, N., Ed.; Bios Scientific Publishers: Oxford, UK, 1995; pp. 217–243. [Google Scholar]
- Mofunanya, A.; Soonen, L. Physiological and morphological responses of Amaranthus hybridus L. (green) to simulated nitric and sulphuric acid rain. Br. J. Appl. Sci. Technol. 2017, 21, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sun, J.; Gu, J.; Zeng, J.; Han, S.; Song, A.; Chen, F.; Fang, W.; Jiang, J.; Chen, S. Changes in leaf morphology, antioxidant activity and photosynthesis capacity in two different drought-tolerant cultivars of chrysanthemum during and after water stress. Entia Hortic. 2013, 161, 249–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velikova, V.; Tsonev, T.; Yordanov, I. Light and CO2 responses of photosynthesis and chlorophyll fluorescence characteristics in bean plants after simulated acid rain. Physiol. Plant. 1999, 107, 77–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.; Kumar, V.; Shahzad, B.; Ramakrishnan, M.; Singh Sidhu, G.P.; Bali, A.S.; Handa, N.; Kapoor, D.; Yadav, P.; Khanna, K.; et al. Photosynthetic response of plants under different abiotic stresses: A review. J. Plant Growth Regul. 2020, 39, 509–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.Y.; Qin, C.; Begum, N.; Ashraf, M.; Zhang, L.X. Acetylcholine ameliorates the adverse effects of cadmium stress through mediating growth, photosynthetic activity and subcellular distribution of cadmium in tobacco (Nicotiana benthamiana). Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 198, 110671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, P.; Zuo, Z.; Wu, X.; Gao, Y.; Gao, R.; Zhang, R. Effects of cycloheximide on photosynthetic abilities, reflectance spectra and fluorescence emission spectra in Phyllostachys edulis. Trees 2016, 30, 719–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, P.; Jaleel, C.A.; Salem, M.A.; Nabi, G.; Sharma, S. Roles of enzymatic and nonenzymatic antioxidants in plants during abiotic stress. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 2010, 30, 161–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Li, D.; Zhang, J.; Saleem, M.; Zhang, Y.; Ma, R.; He, Y.; Yang, J.; Xiang, H.; Wei, H. Effect of simulated acid rain on soil CO2, CH4 and N2O emissions and microbial communities in an agricultural soil. Geoderma 2020, 366, 114222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Hu, H.; Li, Y.; Wang, L.; Zhou, Q.; Huang, X. Effects and mechanism of acid rain on plant chloroplast ATP synthase. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 18296–18306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, C.; Zhang, B. Effect of exogenous calcium on growth, nutrients uptake and plasma membrane H+-ATPase and Ca2+-ATPase activities in soybean (Glycine max) seedlings under simulated acid rain stress. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 165, 261–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Fu, Z.; Zhang, B.; Zhai, L.; Meng, M.; Lin, J.; Zhuang, J.; Wang, G.G.; Zhang, J. Effects of sulfuric, nitric, and mixed acid rain on Chinese fir sapling growth in Southern China. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 160, 154–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, H.; Wang, L.; Zhou, Q.; Huang, X. Combined effects of simulated acid rain and lanthanum chloride on chloroplast structure and functional elements in rice. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 8902–8916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinto, S.; Souza, A.E.; Oliva, M.A.; Pereira, E.G. Oxidative damage and photosynthetic impairment in tropical rice cultivars upon exposure to excess iron. Sci. Agric. 2016, 73, 217–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, C.; Zhao, W.; Sasaki, S.; Tamiaki, H.; Wang, X. A chlorophyll derivative-based bio-solar energy conversion and storage device. Electrochim. Acta 2020, 347, 136283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sena, L.A.; Navdeep, S. Chandel, Physiological roles of mitochondrial reactive oxygen specie. Mol. Cell 2012, 48, 158–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Richman, D.E.; Majumdar, A.; García-Moreno, E.B. pH dependence of conformational fluctuations of the protein backbone. Proteins: Struct. Funct. Bioinform. 2014, 82, 3132–3143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, R.R.; Emblow, M.S.M.; Hetherington, A.M.; Foster, G.D. Plant virus infections control stomatal development. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 34507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Du, E.Z.; Dong, D.; Zeng, X.T.; Sun, Z.Z.; Jiang, X.F.; Vries, W.D. Direct effect of acid rain on leaf chlorophyll content of terrestrial plants in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 605, 764–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Acid Rain (pH)/Pyricularia oryzae | Height (cm) | Leaf Area (cm2) | Biomass (g/plant) |
|---|---|---|---|
| pH 7.0 (control) | 63.98 ± 0.41 a | 18.56 ± 0.12 b | 2.13 ± 0.03 b |
| pH 4.0 | 64.31 ± 0.38 a | 19.50 ± 0.15 a | 2.27 ± 0.01 a |
| pH 2.0 | 53.94 ± 0.53 c | 11.71 ± 0.11 d | 1.53 ± 0.01 d |
| P. oryzae | 49.89 ± 0.47 d | 9.01 ± 0.12 e | 1.44 ± 0.02 e |
| pH 4.0 + P. oryzae | 58.96 ± 0.85 b | 17.72 ± 0.17 c | 2.05 ± 0.02 c |
| pH 2.0 + P. oryzae | 47.39 ± 0.63 e | 47.39 ± 0.63 e | 1.36 ± 0.02 f |
| pH | *** | *** | *** |
| P. oryzae | *** | *** | *** |
| pH × P. oryzae | *** | *** | *** |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, H.; Xu, Q.; Li, C.; Zhang, J.; Wang, Q.; Xiang, H.; Liu, Y.; Wei, H.; Qin, Z. Dual Role of Acid Rain and Pyricularia oryzae on Growth, Photosynthesis and Chloroplast Ultrastructure in Rice Seedlings. Agronomy 2022, 12, 567. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12030567
Li H, Xu Q, Li C, Zhang J, Wang Q, Xiang H, Liu Y, Wei H, Qin Z. Dual Role of Acid Rain and Pyricularia oryzae on Growth, Photosynthesis and Chloroplast Ultrastructure in Rice Seedlings. Agronomy. 2022; 12(3):567. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12030567
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Hongru, Qiuyuan Xu, Chao Li, Jiaen Zhang, Qi Wang, Huimin Xiang, Yiliang Liu, Hui Wei, and Zhong Qin. 2022. "Dual Role of Acid Rain and Pyricularia oryzae on Growth, Photosynthesis and Chloroplast Ultrastructure in Rice Seedlings" Agronomy 12, no. 3: 567. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12030567
APA StyleLi, H., Xu, Q., Li, C., Zhang, J., Wang, Q., Xiang, H., Liu, Y., Wei, H., & Qin, Z. (2022). Dual Role of Acid Rain and Pyricularia oryzae on Growth, Photosynthesis and Chloroplast Ultrastructure in Rice Seedlings. Agronomy, 12(3), 567. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12030567






