Influence of Wheat Straw Return on Yield and Grain Quality in Different Direct-Seeding Rice Production Systems
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Site and Weather Conditions
2.2. Experimental Design and Treatments
2.3. Crop Cultivation
2.4. Sampling and Measurements
2.4.1. Tillering Dynamics, Biomass, and Yield
2.4.2. Grain Quality
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
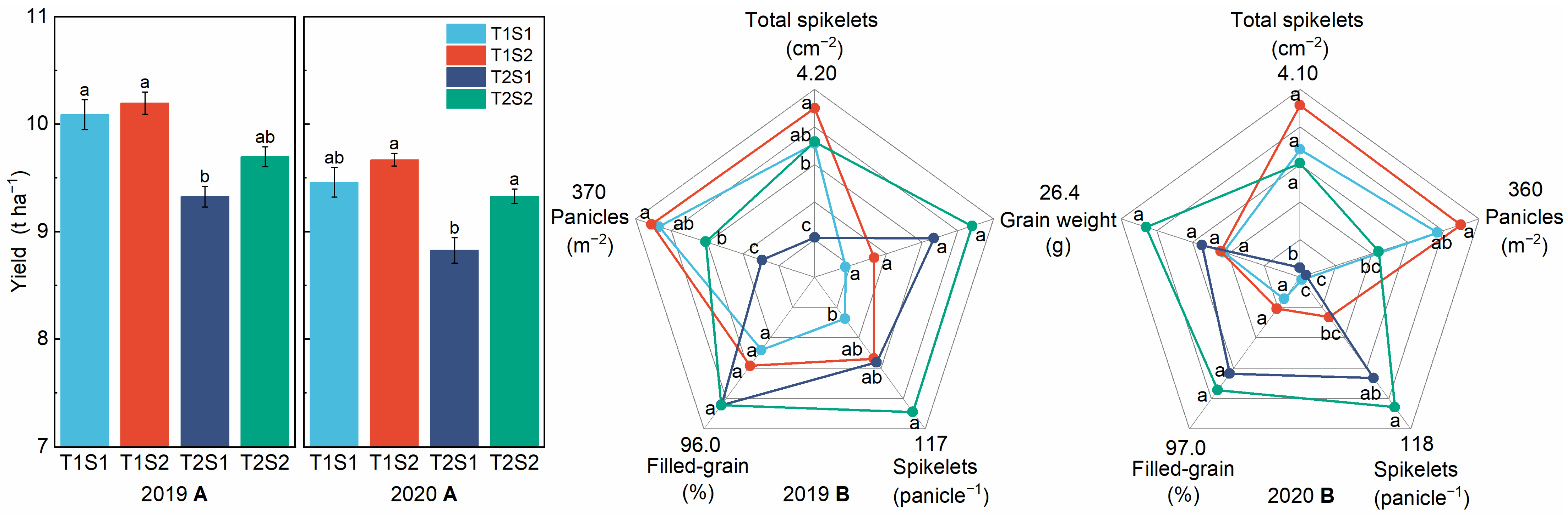
3.1. Grain Yield and Yield Components
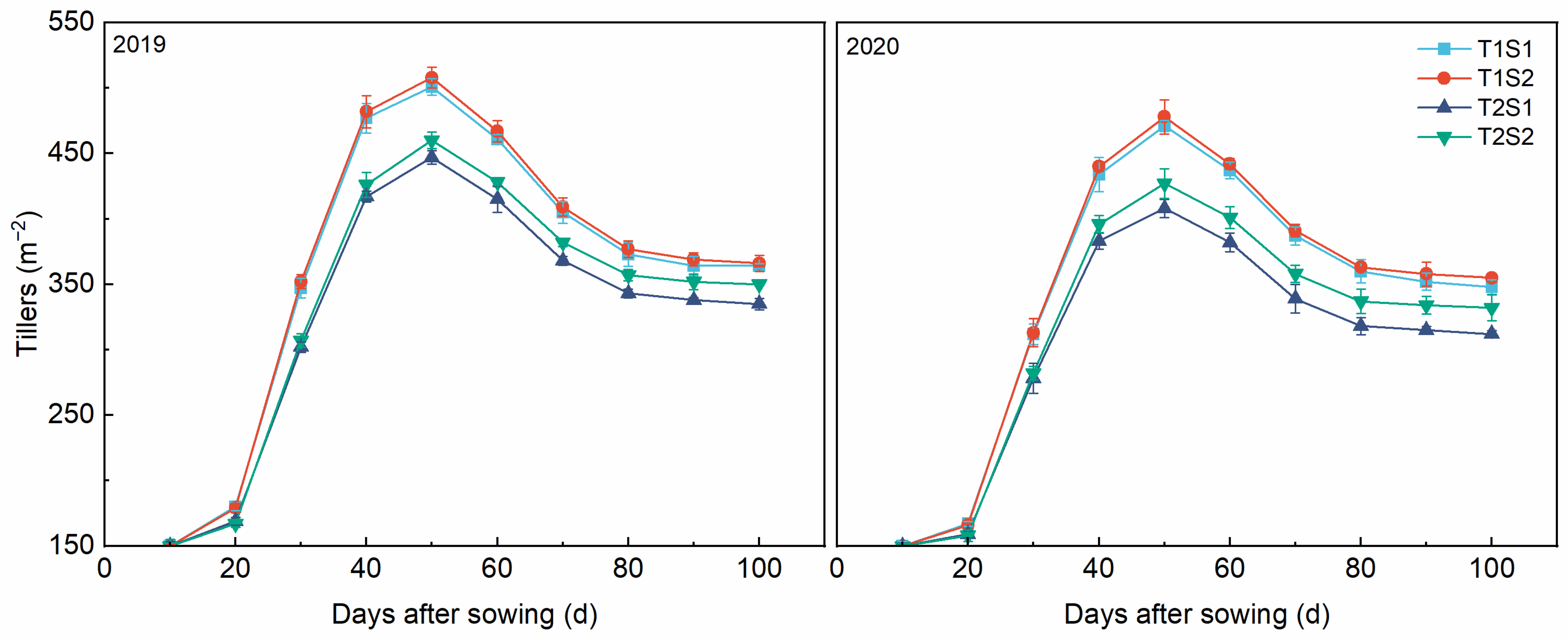
3.2. Tillering Dynamics
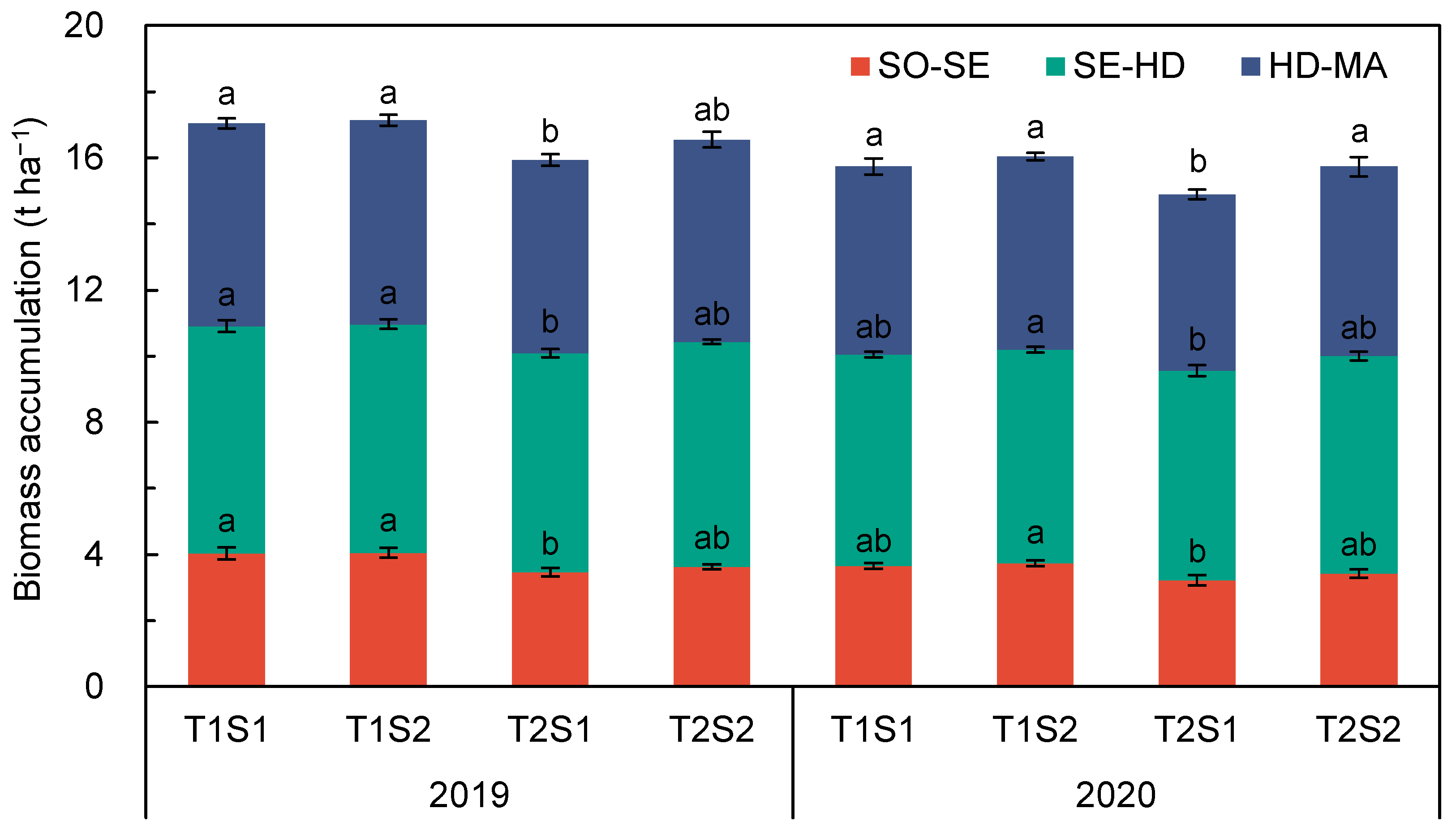
3.3. Biomass Accumulation
3.4. Amylose and Protein Content
3.5. Appearance Quality
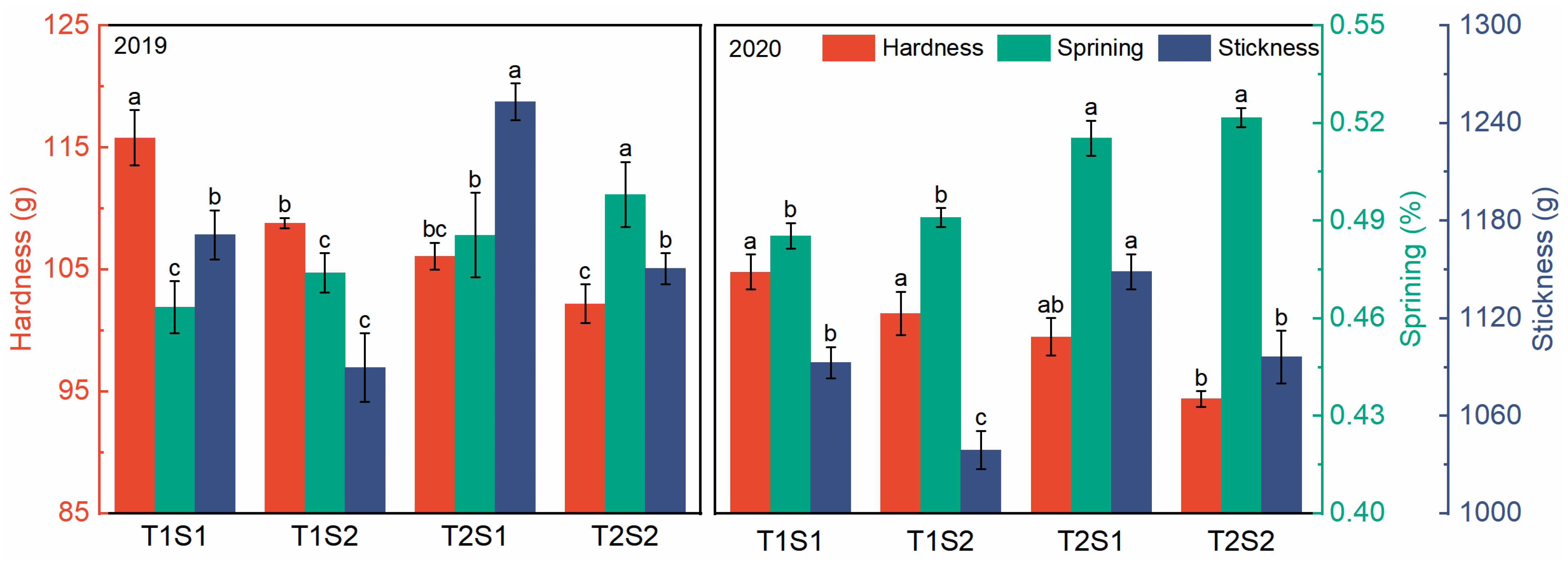
3.6. Cooking Quality
3.7. RVA Parameters
3.8. Correlation Analysis
4. Discussion
4.1. Grain Yield
4.2. Grain Quality
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tong, C.; Gao, H.Y.; Luo, S.J.; Liu, L.; Bao, J.S. Impact of Postharvest Operations on Rice Grain Quality: A Review. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2019, 18, 626–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xu, L.; Li, X.X.; Wang, X.Y.; Xiong, D.L.; Wang, F. Comparing the Grain Yields of Direct-Seeded and Transplanted Rice: A Meta-Analysis. Agronomy 2019, 9, 767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Devkota, K.P.; Sudhir, Y.; Khanda, C.M.; Beebout, S.J.; Mohapatra, B.K.; Singleton, G.R.; Puskur, R. Assessing alternative crop establishment methods with a sustainability lens in rice production systems of Eastern India. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 244, 118835–118849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishfaq, M.; Akbar, N.; Zulfiqar, U.; Hussain, S.; Murtza, K.; Batool, Z.; Ashraf, U.; Alyemeni, M.N.; Ahmad, P. Influence of Nitrogen Management Regimes on Milling Recovery and Grain Quality of Aromatic Rice in Different Rice Production Systems. Agronomy 2020, 10, 1841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.Q.; Peng, S.B.; Liu, H.Y.; Tao, Y.; Huang, J.L.; Cui, K.H.; Nie, L.X. The possibility of replacing puddled transplanted flooded rice with dry seeded rice in central China: A review. Field Crops Res. 2017, 214, 310–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weerakoon, W.M.W.; Mutunayake, M.M.P.; Bandara, C.; Rao, A.N.; Bhandari, D.C.; Ladha, J.K. Direct-seeded rice culture in Sri Lanka: Lessons from farmers. Field Crops Res. 2011, 121, 53–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Zhan, X.W.; Yu, T.T.; Nie, L.X.; Huang, J.L.; Cui, K.H.; Wang, F.; Li, Y.; Peng, S.B. Yield performance of direct-seeded, double-season rice using varieties with short growth durations in central China. Field Crops Res. 2018, 227, 49–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, V.; Ladha, J.K. Direct Seeding of Rice: Recent Developments and Future Research Needs. Adv. Agron. 2011, 111, 297–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sidhu, H.S.; Singh, M.; Singh, Y.; Blackwell, J.; Lohan, S.K.; Humphreys, E.; Jat, M.L.; Singh, V.; Singh, S. Development and evaluation of the Turbo Happy Seeder for sowing wheat into heavy rice residues in NW India. Field Crops Res. 2015, 184, 201–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Shen, J.L.; Tang, H.; Inubushi, K.; Guggenberger, G.; Li, Y.; Wu, J.S. Greenhouse gas emissions in response to straw incorporation, water management and their interaction in a paddy field in subtropical central China. Arch. Agron. Soil Sci. 2017, 63, 171–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Li, Q.K.; Lin, Z.H.; Zhang, Z.; Tian, H.; Ashraf, U.; Alhaj Hamoud, Y.; Duan, M.Y.; Tang, X.R.; Pan, S.G. Effects of nitrogen deep placement coupled with straw incorporation on grain quality and root traits from paddy fields. Crop Sci. 2021, 61, 3675–3686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, X.; Zheng, Z.; Sha, Z.M.; Cao, H.L.; Yuan, Q.X.; Yu, H.B.; Li, Q. Biorefining waste into nanobiotechnologies can revolutionize sustainable agriculture. Trends Biotechnol. 2022, 40, 1503–1518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Dai, M.W.; Dai, S.L.; Dong, X.J. Current status and environment impact of direct straw return in China’s cropland—A review. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 159, 293–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, H.J.; Zhao, W.Q.; Li, T.; Cheng, X.Y.; Liu, Q. Balancing straw returning and chemical fertilizers in China: Role of straw nutrient resources. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2018, 81, 2695–2702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.H.; Luo, Y.L.; Chen, J.; Jin, M.; Wang, Z.L.; Li, Y.F. Effects of Main Food Yield Under Straw Return in China: A Meta-Analysis. Sci. Agric. Sin. 2020, 53, 4415–4429, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Zeng, Y.J.; Wu, J.F.; Shi, Q.H.; Pan, X.H. Effect of crop residue retention on rice yield in China: A meta-analysis. Field Crops Res. 2013, 154, 188–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, F.J.; Sun, Y.J.; Xu, H.; Yin, Y.Z.; Wang, H.Y.; Wang, C.Y.; Guo, C.C.; Yang, Z.Y.; Sun, Y.Y.; Ma, J. Effects of wheat straw mulch application and nitrogen management on rice root growth, dry matter accumulation and rice quality in soils of different fertility. Paddy Water Environ. 2018, 16, 507–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, L.; Zhang, X.; Yang, J.; Yang, C.L.; Cao, X.C.; Wu, L.H. Effects of different cultivation methods and straw incorporation on grain yield and nutrition quality of rice. Acta Agron. Sin. 2013, 39, 350–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.H.; Wang, Z.M.; Luo, X.W.; Zang, Y.; Yang, W.W.; Xing, H.; Wang, B.L.; Dai, Y.Z. Review of precision rice hill-drop drilling technology and machine for paddy. Int. J. Agric. Biol. Eng. 2018, 11, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.Z.; Nie, L.X.; Buresh, R.J.; Huang, J.L.; Cui, K.H.; Xu, B.; Gong, W.H.; Peng, S.B. Agronomic performance of late-season rice under different tillage, straw, and nitrogen management. Field Crops Res. 2010, 115, 79–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, W.X.; Li, J.G.; Liu, J.; Lv, j.; Liang, C.B.; Shi, H.R.; Li, M.S. Effects of total straw returning on grain yield and quality under different soil background. China Rice 2021, 27, 73–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahra, N.; Hafeez, M.B.; Nawaz, A.; Farooq, M. Rice production systems and grain quality. J. Cereal Sci. 2022, 105, 103463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, J.Y.; Li, S.P.; Cheng, S.; Liu, Q.Y.; Zhou, L.; Tao, Y.; Xing, Z.P.; Hu, Y.J.; Guo, B.W.; Wei, H.Y.; et al. Increasing appropriate seedling density for higher yield in dry direct-seeded rice sown by multifunctional seeder after wheat-straw returning. J. Integr. Agric. 2021, 12, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CRDC (China Rice Data Center). Super Hybrid Rice Cultivars Approved by the Ministry of Agriculture of China. 2022. Available online: http://www.ricedata.cn/variety/superice.htm (accessed on 11 November 2022).
- GB/T 17891–2017; The National Standard for Rice Quality Evaluation, the People’s Republic of China. NBQTC (National Bureau of Quality and Technology Control): Beijing, China, 2017.
- Yang, H.S.; Feng, J.X.; Weih, M.; Meng, Y.; Li, Y.F.; Zhai, S.L.; Zhang, W.Y. Yield reduction of direct-seeded rice under returned straw can be mitigated by appropriate water management improving soil phosphorus availability. Crop Pasture Sci. 2020, 71, 134–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, G.W.; Tan, G.L.; Wang, Z.Q.; Liu, L.J.; Yang, J.C. Effects of Wheat-Residue Application and Site-Specific Nitrogen Management on Grain Yield and Quality and Nitrogen Use Efficiency in Direct-Seeding Rice. Sci. Agric. Sin. 2009, 42, 2736–2746, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, K.; Xie, Y.Q.; Lin, Z.M.; Liu, Z.H.; Wang, S.H.; Ding, Y.F. Effect of nitrogen on rice seedling growth and nutrient uptake under wheat straw returning. J. Nanjing Agric. Univ. 2016, 39, 18–25, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Ni, T.; Xun, W.B.; Huang, X.L.; Huang, Q.W.; Ran, W.; Shen, B.; Zhang, R.F.; Shen, Q.R. Influence of straw incorporation with and without straw decomposer on soil bacterial community structure and function in a rice-wheat cropping system. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2017, 101, 4761–4773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.; Singh, P.; Choudhary, O.P. Neemisha Nitrogen and rice straw incorporation impact nitrogen use efficiency, soil nitrogen pools and enzyme activity in rice-wheat system in north-western India. Field Crops Res. 2021, 266, 108–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, J.Y.; Li, S.P.; Xing, Z.P.; Cheng, S.; Guo, B.W.; Hu, Y.J.; Wei, H.Y.; Gao, H.; Liao, P.; Wei, H.H.; et al. Differences in rice yield and biomass accumulation dynamics for different direct seeding methods after wheat straw return. Food Energy Secur. 2022, 11, e425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, S.; Li, S.P.; Tian, J.Y.; Xing, Z.P.; Hu, Y.J.; Guo, B.W.; Wei, H.Y.; Gao, H.; Zhang, H.C. Effects of one-time nitrogen basal application on the yield and quality of different direct-seeding rice crops by machine. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2020, 36, 1–10, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.F.; Liu, H.J.; Guo, Z.; Zhang, C.S.; Sheng, J.; Chen, L.G.; Luo, Y.Q.; Zheng, J.C. Direct-seeded rice increases nitrogen runoff losses in southeastern China. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2018, 251, 149–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.F.; Dong, M.H.; Gu, J.R.; Hui, F.; Qiao, Z.Y.; Yang, D.F.; Liu, T.F. Effects of returning wheat-residue to field and nitrogen management on grain weight and quality of superior and inferior grains in super rice. Chin. J. Rice Sci. 2012, 26, 715–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.C.; Xing, Z.P.; Weng, W.A.; Tian, J.Y.; Tao, Y.; Cheng, S.; Hu, Q.; Hu, Y.J.; Guo, B.W.; Wei, H.Y. Growth characteristics and key techniques for stable yield of growth constrained direct seeding rice. Sci. Agric. Sin. 2021, 54, 1322–1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, T.D.; Li, C.; Xing, X.; Pan, X.P.; Liu, C.H.; Tian, Y.J.; Wang, Z.Y.; Zhao, J.S.; Wang, J.P.; He, B. Straw return and organic fertilizers instead of chemical fertilizers on growth, yield and quality of rice. Earth Sci. Inf. 2022, 15, 1363–1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, J.Y.; Li, S.P.; Xing, Z.P.; Cheng, S.; Liu, Q.Y.; Zhou, L.; Liao, P.; Hu, Y.J.; Guo, B.W.; Wei, H.Y.; et al. Seedling establishment and yield performance of dry direct-seeded rice after wheat straw returning coupled with early nitrogen application. Agriculture 2022, 12, 565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, P.; Xu, J.; Wei, H.Y.; Liu, G.D.; Zhang, Z.Z.; Tian, J.Y.; Zhang, H.C. Recent Research Advances in the Development of Chalkiness and Transparency in Rice. Agriculture 2022, 12, 1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.Y.; Li, X.F.; Cheng, J.Q.; Ren, H.R.; Liang, J.; Zhang, H.C.; Huo, Z.Y. Effects of Total Straw Returning and Nitrogen Application Regime on Grain Yield and Quality in Mechanical Transplanting Japonica Rice with Good Taste Quality. Acta Agron. Sin. 2017, 43, 1802–1816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fageria, N.K.; Santos, A.B.; Filho, M.P.B.; Guimarães, C.M. Iron Toxicity in Lowland Rice. J. Plant Nutr. 2008, 31, 1676–1697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chun, A.; Song, J.; Kim, K.J.; Lee, H.J. Quality of head and chalky rice and deterioration of eating quality by chalky rice. J. Crop Sci. Biotechnol. 2009, 12, 239–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, S.; Wang, A.; Wang, Y.; Xu, X.; Luo, D.; Shen, Q.; Wu, J. Effect of cooking on aroma profiles of Chinese foxtail millet (Setaria italica) and correlation with sensory quality. Food Chem. 2019, 289, 680–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prom-u-thai, C.; Rerkasem, B. Rice quality improvement. A review. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2020, 40, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.D.; Zhang, C.; Gao, H.; Zhang, H.C.; Wei, H.Y. Water migration, texture and oral processing properties of semi-waxy rice during retrogradation. J. Food Sci. 2021, 86, 5100–5106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, D.W.; Zhang, L.P.; Chen, M.X.; Fang, C.Y.; Yu, Y.H.; Zheng, X.L.; Shao, Y.F. Characteristics of High-Quality Rice Varieties and Taste Sensory Evaluation Values in China. Sci. Agric. Sin. 2022, 55, 1271–1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Year | Treatment | Amylose Content (%) | Protein Content (%) | Protein Component Content (mg g−1) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Albumin Content (mg g−1) | Globulin Content (mg g−1) | Gliadin Content (mg g−1) | Glutenin Content (mg g−1) | ||||
| 2019 | T1S1 | 10.3 b 1 | 9.00 a | 4.40 a | 6.07 a | 10.0 a | 58.7 a |
| T1S2 | 10.9 a | 8.79 a | 4.29 a | 5.90 ab | 9.61 b | 55.7 ab | |
| T2S1 | 9.79 c | 8.42 b | 4.23 a | 5.88 ab | 9.38 b | 52.5 bc | |
| T2S2 | 10.3 b | 8.26 b | 4.16 a | 5.75 b | 8.92 c | 50.4 c | |
| 2020 | T1S1 | 10.9 bc | 8.39 a | 4.20 a | 5.85 a | 9.02 a | 52.1 a |
| T1S2 | 11.5 a | 8.16 ab | 4.14 ab | 5.67 a | 8.60 ab | 50.2 ab | |
| T2S1 | 10.4 c | 7.82 bc | 4.12 ab | 5.64 a | 8.30 bc | 47.0 bc | |
| T2S2 | 10.9 b | 7.66 c | 4.01 b | 5.58 a | 8.02 c | 45.2 c | |
| Year | Treatment | Appearance Value | Hardness Value | Viscosity Value | Balance Value | Taste Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2019 | T1S1 | 6.67 ab 1 | 6.91 a | 7.02 b | 6.56 b | 69.8 b |
| T1S2 | 6.53 b | 6.76 ab | 6.70 c | 6.06 c | 65.8 c | |
| T2S1 | 7.03 a | 6.66 bc | 7.36 a | 7.03 a | 73.6 a | |
| T2S2 | 6.71 ab | 6.52 c | 6.98 bc | 6.53 b | 69.7 b | |
| 2020 | T1S1 | 6.59 b | 6.50 a | 6.80 b | 6.27 b | 66.9 b |
| T1S2 | 6.35 b | 6.38 a | 6.48 c | 5.96 b | 63.1 c | |
| T2S1 | 6.97 a | 6.26 ab | 7.20 a | 6.80 a | 70.5 a | |
| T2S2 | 6.66 ab | 6.04 b | 6.78 b | 6.40 ab | 66.5 b |
| Year | Treatment | Peak Viscosity (cP) | Trough Viscosity (cP) | Final Viscosity (cP) | Breakdown (cP) | Setback (cP) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2019 | T1S1 | 2195 c 1 | 1274 c | 1882 d | 921b c | −313 bc |
| T1S2 | 2243 bc | 1357 b | 1958 c | 886 c | −285 a | |
| T2S1 | 2327 ab | 1349 b | 2001 b | 978 a | −325 c | |
| T2S2 | 2362 a | 1432 a | 2061 a | 930 b | −301 ab | |
| 2020 | T1S1 | 2126 c | 1259 c | 1845 d | 867 b | −281 ab |
| T1S2 | 2195 b | 1346 b | 1931 c | 849 b | −264 a | |
| T2S1 | 2279 a | 1336 b | 1981 b | 943 a | −298 b | |
| T2S2 | 2302 a | 1430 a | 2023 a | 872 b | −279 a |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tian, J.; Xing, Z.; Li, S.; Cheng, S.; Guo, B.; Hu, Y.; Wei, H.; Gao, H.; Zhang, Z.; Fan, P.; et al. Influence of Wheat Straw Return on Yield and Grain Quality in Different Direct-Seeding Rice Production Systems. Agronomy 2022, 12, 3180. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12123180
Tian J, Xing Z, Li S, Cheng S, Guo B, Hu Y, Wei H, Gao H, Zhang Z, Fan P, et al. Influence of Wheat Straw Return on Yield and Grain Quality in Different Direct-Seeding Rice Production Systems. Agronomy. 2022; 12(12):3180. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12123180
Chicago/Turabian StyleTian, Jinyu, Zhipeng Xing, Shaoping Li, Shuang Cheng, Baowei Guo, Yajie Hu, Haiyan Wei, Hui Gao, Zhenzhen Zhang, Peng Fan, and et al. 2022. "Influence of Wheat Straw Return on Yield and Grain Quality in Different Direct-Seeding Rice Production Systems" Agronomy 12, no. 12: 3180. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12123180
APA StyleTian, J., Xing, Z., Li, S., Cheng, S., Guo, B., Hu, Y., Wei, H., Gao, H., Zhang, Z., Fan, P., & Zhang, H. (2022). Influence of Wheat Straw Return on Yield and Grain Quality in Different Direct-Seeding Rice Production Systems. Agronomy, 12(12), 3180. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12123180






