Inter-Specific Hybridization in Cotton (Gossypium hirsutum) for Crop Improvement
Abstract
1. Introduction
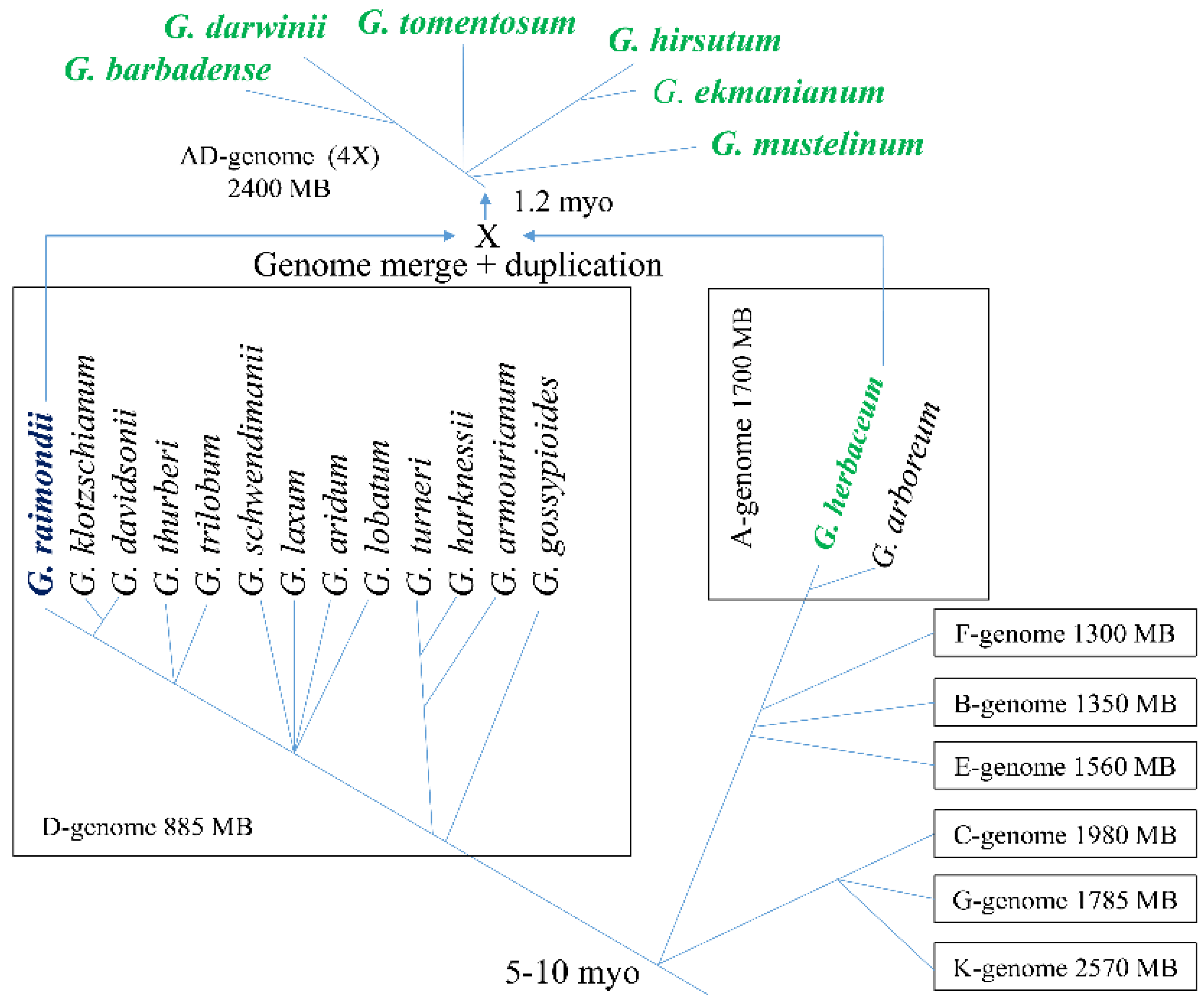
2. Taxonomy of Gossypium and Origin of Gossypium hirsutum
3. Domestication of Upland Cotton
4. Cotton Improvement
5. Development of Spinnable Fiber and Polyploidization
6. Gene Introgression and Inter-Specific Hybridization
7. Introgressive Breeding
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mensah, R. Travel: International Cotton Advisory Committee (ICAC) 77th Plenary Meeting, Present; New South Wales Department of Primary Industries: Orange, Australia, 2019.
- Townsend, T. World natural fibre production and employment. In Handbook of Natural Fibres; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; pp. 15–36. [Google Scholar]
- Baffes, J. Cotton: Market Setting, Trade Policies, and Issues; World Bank: Washington, DC, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhardwaj, S.; Devkar, V.; Kumar, A.; Alisha, A.; Sharma, S.; Deshmukh, R.K.; Patil, G.B. Advances and Applicability of Genotyping Technologies in Cotton Improvement. In Genotyping by Sequencing for Crop Improvement; John Wiley & Sons Ltd.: Chichester, UK, 2022; pp. 250–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wendel, J.F.; Cronn, R.C. Polyploidy and the evolutionary history of cotton. Adv. Agron. 2003, 78, 78004–78008. [Google Scholar]
- Wendel, J.F.; Grover, C.E. Taxonomy and evolution of the cotton genus, Gossypium. Cotton 2015, 57, 25–44. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, Y.; Chen, J.; Fang, L.; Zhang, Z.; Ma, W.; Niu, Y.; Ju, L.; Deng, J.; Zhao, T.; Lian, J. Gossypium barbadense and Gossypium hirsutum genomes provide insights into the origin and evolution of allotetraploid cotton. Nat. Genet. 2019, 51, 739–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, G.; Grover, C.E.; Yuan, D.; Dong, Y.; Miller, E.; Conover, J.L.; Wendel, J.F. Evolution and diversity of the cotton genome. In Cotton Precision Breeding; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2021; pp. 25–78. [Google Scholar]
- Paterson, A.H. Molecular genetic map of cotton. In DNA-Based Markers in Plants; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2001; pp. 239–253. [Google Scholar]
- Barroso, P.A.V.; Hoffmann, L.V.; da Costa, N.D.L. Challenges and Opportunities for in situ Maintenance of the Native Brazilian Cotton Gossypium mustelinum Miers. Front. Ecol. Evol. 2021, 9, 323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grover, C.; Zhu, X.; Grupp, K.; Jareczek, J.; Gallagher, J.; Szadkowski, E.; Seijo, J.G.; Wendel, J. Molecular confirmation of species status for the allopolyploid cotton species, Gossypium ekmanianum Wittmack. Genet. Resour. Crop Evol. 2015, 62, 103–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krapovickas, A.; SEIJO, G.; Seijo, J.G. Gossypium ekmanianum (Malvaceae), algodon silvestre de la Republica Dominicana. Bonplandia 2008, 17, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallagher, J.P.; Grover, C.E.; Rex, K.; Moran, M.; Wendel, J.F. A new species of cotton from Wake Atoll, Gossypium stephensii (Malvaceae). Syst. Bot. 2017, 42, 115–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senchina, D.S.; Alvarez, I.; Cronn, R.C.; Liu, B.; Rong, J.; Noyes, R.D.; Paterson, A.H.; Wing, R.A.; Wilkins, T.A.; Wendel, J.F. Rate variation among nuclear genes and the age of polyploidy in Gossypium. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2003, 20, 633–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reinisch, A.J.; Dong, J.M.; Brubaker, C.L.; Stelly, D.M.; Wendel, J.F.; Paterson, A.H. A detailed RFLP map of cotton, Gossypium hirsutum × Gossypium barbadense: Chromosome organization and evolution in a disomic polyploid genome. Genetics 1994, 138, 829–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hendrix, B.; Stewart, J.M. Estimation of the nuclear DNA content of gossypium species. Ann. Bot. 2005, 95, 789–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geever, R.F.; Katterman, F.R.; Endrizzi, J.E. DNA hybridization analyses of a Gossypium allotetmploid and two closely related diploid species. TAG Theor. Appl. Genet. Theor. Und Angew. Genet. 1989, 77, 553–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rong, J.; Feltus, F.A.; Waghmare, V.N.; Pierce, G.J.; Chee, P.W.; Draye, X.; Saranga, Y.; Wright, R.J.; Wilkins, T.A.; May, O.L.; et al. Meta-analysis of polyploid cotton QTL shows unequal contributions of subgenomes to a complex network of genes and gene clusters implicated in lint fiber development. Genetics 2007, 176, 2577–2588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Zhang, D.; Wang, X.; Tan, X.; Guo, H.; Paterson, A.H. A whole-genome DNA marker map for cotton based on the D-genome sequence of Gossypium raimondii L. G3 2013, 3, 1759–1767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, C.W. (Ed.) Cotton: Origin, History, Technology and Production; J. Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Desai, A.; Chee, P.W.; Rong, J.; May, O.L.; Paterson, A.H. Chromosome structural changes in diploid and tetraploid A genomes of Gossypium. Genome 2006, 49, 336–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hurt, R.D. A Companion to American Agricultural History; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Fryxell, P.A. The Natural History of the Cotton Tribe (Malvaceae, Tribe Gossypieae); Texas A & M University Press: College Station, TX, USA, 1979. [Google Scholar]
- Wendel, J.F.; Brubaker, C.; Alvarez, I.; Cronn, R.; Stewart, J.M. Evolution and natural history of the cotton genus. In Genetics and Genomics of Cotton; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009; pp. 3–22. [Google Scholar]
- Stephens, S. Evolution under domestication of the New World cottons (Gossypium spp.). Cienc. Cult. 1967, 19, 118–134. [Google Scholar]
- Applequist, W.L.; Cronn, R.; Wendel, J.F. Comparative development of fiber in wild and cultivated cotton. Evol. Dev. 2001, 3, 3–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hovav, R.; Udall, J.A.; Chaudhary, B.; Hovav, E.; Flagel, L.; Hu, G.; Wendel, J.F. The evolution of spinnable cotton fiber entailed prolonged development and a novel metabolism. PLoS Genet. 2008, 4, e25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waghmare, V.N. Cotton Breeding. In Fundamentals of Field Crop Breeding; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2022; pp. 609–676. [Google Scholar]
- Wendel, J.F.; Brubaker, C.L.; Percival, A.E. Genetic diversity in Gossypium hirsutum and the origin of upland cotton. Am. J. Bot. 1992, 79, 1291–1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ware, J.O. Origin, Rise and Development of American Upland Cotton Varieties and Their Status at Present; University of Arkansas College of Agriculture, Agricultural Experiment Station: Fayetteville, NC, USA, 1951. [Google Scholar]
- Lubbers, E.L.; Chee, P.W.; Saranga, Y.; Paterson, A.H. Recent advances and future prospective in molecular breeding of cotton for drought and salinity stress tolerance. In Advances in Molecular Breeding toward Drought and Salt Tolerant Crops; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2007; pp. 775–796. [Google Scholar]
- Ware, J.O. Plant breeding and the cotton industry. In U.S. Dept. of Agriculture Yearbook 1936; GPO: Washington, DC, USA, 1936; pp. 657–744. [Google Scholar]
- Kulkarni, V.N.; Khadi, B.M.; Maralappanavar, M.S.; Deshapande, L.A.; Narayanan, S. The worldwide gene pools of Gossypium arboreum L. and G. herbaceum L. and their improvement. In Genetics and Genomics of Cotton; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009; pp. 69–97. [Google Scholar]
- Zeng, L.; Wu, J.; Bourland, F.M.; Campbell, B.T.; Dever, J.K.; Hague, S.; Myers, G.O.; Raper, T.B.; Smith, W.; Zhang, J. Comparative study of transgenic and nontransgenic cotton. Crop Sci. 2021, 61, 2467–2477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowman, D.T. Attributes of public and private cotton breeding programs. J. Cotton Sci. 2000, 4, 130–136. [Google Scholar]
- Mauney, J.R. Anatomy and Morphology of Cultivated Cottons. In Cotton; Fang, D.D., Percy, R.G., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2015; pp. 77–96. [Google Scholar]
- Bourland, F.; Myers, G.O. Conventional cotton breeding. Cotton 2015, 57, 205–228. [Google Scholar]
- Mason, A.S. Polyploidy and Hybridization for Crop Improvement; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Worley, S.; Culp, T.; Harrell, D. The relative contributions of yield components to lint yield of upland cotton, Gossypium hirsutum L. Euphytica 1974, 23, 399–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Culp, T.; Harrell, D.; Kerr, T. Some genetic implications in the transfer of high fiber strength genes to upland cotton 1. Crop Sci. 1979, 19, 481–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, L.; Stetina, S.R.; Erpelding, J.E.; Bechere, E.; Turley, R.B.; Scheffler, J. History and current research in the USDA-ARS cotton breeding program at Stoneville, MS. J. Cotton Sci. 2018, 22, 24–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kearney, T. Lint index and lint percentage in cotton breeding. J. Hered. 1912, os-7, 25–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Culp, T.; Harrell, D. Influence of Lint Percentage, Boll Size, and Seed Size on Lint Yield of Upland Cotton with High Fiber Strength. Crop Sci. 1975, 15, 741–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, H.; Ge, Q.; Shang, H.; Yuan, Y. Inheritance, QTLs, and Candidate Genes of Lint Percentage in Upland Cotton. Front. Genet. 2022, 13, 855574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Gao, Y.; Chen, P.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, C.; Song, Z.; Huo, X.; Du, Z.; Gong, J.; Zhao, C. Genome-wide association study reveals novel quantitative trait loci and candidate genes of lint percentage in upland cotton based on the CottonSNP80K array. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2022, 135, 2279–2295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, N.; Wang, W.; Grover, C.E.; Jiang, K.; Pan, Z.; Guo, B.; Zhu, J.; Su, Y.; Wang, M.; Nie, H. Genomic and GWAS analyses demonstrate phylogenomic relationships of Gossypium barbadense in China and selection for fibre length, lint percentage and Fusarium wilt resistance. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2022, 20, 691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, R.; Jones, D.C.; Liu, F.; Zhang, B. From sequencing to genome editing for cotton improvement. Trends Biotechnol. 2021, 39, 221–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majeed, S.; Rana, I.A.; Mubarik, M.S.; Atif, R.M.; Yang, S.-H.; Chung, G.; Jia, Y.; Du, X.; Hinze, L.; Azhar, M.T. Heat stress in cotton: A review on predicted and unpredicted growth-yield anomalies and mitigating breeding strategies. Agronomy 2021, 11, 1825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Fu, Y.; Liu, Q.; Du, L.; Trotsenko, V. A review of genetic mechanisms of early maturity in cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.). Euphytica 2020, 216, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Negm, M. Cotton breeding. In Handbook of Natural Fibres; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; pp. 579–603. [Google Scholar]
- Gwathmey, C.O.; Bange, M.P.; Brodrick, R. Cotton crop maturity: A compendium of measures and predictors. Field Crops Res. 2016, 191, 41–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, X.; Zhang, L.; Du, M.; Evers, J.B.; van der Werf, W.; Tian, X.; Li, Z. Managing mepiquat chloride and plant density for optimal yield and quality of cotton. Field Crops Res. 2013, 149, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Constable, G.; Llewellyn, D.; Walford, S.A.; Clement, J.D. Cotton breeding for fiber quality improvement. In Industrial Crops; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015; pp. 191–232. [Google Scholar]
- Culp, T.; Harrell, D. Breeding methods for improving yield and fiber quality of upland cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.) 1. Crop Sci. 1973, 13, 686–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, X.; Sun, G.; Qu, Y.; Sarfraz, Z.; Jia, Y.; He, S.; Pan, Z.; Sun, J.; Iqbal, M.S.; Wang, Q. Genome-wide dissection of hybridization for fiber quality-and yield-related traits in upland cotton. Plant J. 2020, 104, 1285–1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chee, P.W.; Campbell, B.T. Bridging classical and molecular genetics of cotton fiber quality and development. In Genetics and Genomics of Cotton; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009; pp. 283–311. [Google Scholar]
- Campbell, B.T. Examining the relationship between agronomic performance and fiber quality in ten cotton breeding populations. Crop Sci. 2021, 61, 989–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, B.; Chee, P.; Lubbers, E.; Bowman, D.; Meredith, W., Jr.; Johnson, J.; Fraser, D.; Bridges, W.; Jones, D. Dissecting genotype× environment interactions and trait correlations present in the Pee Dee cotton germplasm collection following seventy years of plant breeding. Crop Sci. 2012, 52, 690–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meredith, W.R., Jr.; Bridge, R. Yield, Yield Component and Fiber Property Variation of Cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.) within and among Environments. Crop Sci. 1973, 13, 307–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meredith, W.R., Jr.; Bridge, R. Recurrent Selection for Lint Percent within a Cultivar of Cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.). Crop Sci. 1973, 13, 698–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandnani, R.; Zhang, Z.; Patel, J.D.; Adhikari, J.; Khanal, S.; He, D.; Brown, N.; Chee, P.W.; Paterson, A.H. Comparative genetic variation of fiber quality traits in reciprocal advanced backcross populations. Euphytica 2017, 213, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; He, S.; Dia, S.; Sun, G.; Liu, X.; Wang, X.; Pan, Z.; Jia, Y.; Wang, L.; Pang, B. Alien genomic introgressions enhanced fiber strength in upland cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.). Ind. Crops Prod. 2021, 159, 113028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konan, N.; Baudoin, J.-P.; Mergeai, G. Potential of ten wild diploid cotton species for the improvement of fiber fineness of upland cotton through interspecific hybridisation. J. Plant Breed. Crop Sci. 2020, 12, 97–105. [Google Scholar]
- Mergeai, G. Forty years of genetic improvement of cotton through interspecific hybridization at Gembloux Agricultural University: Achievement and prospects. In Proceedings of the World Cotton Research Conference, Cape Town, South Africa, 9–13 March 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Z.J.; Sreedasyam, A.; Ando, A.; Song, Q.; De Santiago, L.M.; Hulse-Kemp, A.M.; Ding, M.; Ye, W.; Kirkbride, R.C.; Jenkins, J. Genomic diversifications of five Gossypium allopolyploid species and their impact on cotton improvement. Nat. Genet. 2020, 52, 525–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, G.; Thakar, B. Cotton improvement through interspecific hybridization. Indian Cotton Grow. Rev. 1950, 4, 185–198. [Google Scholar]
- Thiyagu, K.; Nadarajan, N.; Rajarathinam, S.; Sudhakar, D.; Rajendran, K. Association and path analysis for seed cotton yield improvement in interspecific crosses of cotton (Gossypium spp.). Electron. J. Plant Breed. 2010, 1, 1001–1005. [Google Scholar]
- Choudki, V.; Sangannavar, P.; Savita, S.; Khadi, B.; Vamadevaiah, H.; Katageri, I. Genetic improvement of fibre traits in diploid cotton (G. herbaceum L.) through interspecific hybridization using G. barbadense tetraploid species. Electron. J. Plant Breed. 2012, 3, 686–691. [Google Scholar]
- Paterson, A.H.; Wendel, J.F.; Gundlach, H.; Guo, H.; Jenkins, J.; Jin, D.; Llewellyn, D.; Showmaker, K.C.; Shu, S.; Udall, J. Repeated polyploidization of Gossypium genomes and the evolution of spinnable cotton fibres. Nature 2012, 492, 423–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, C.; Wright, R.J.; El-Zik, K.M.; Paterson, A.H. Polyploid formation created unique avenues for response to selection in Gossypium (cotton). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 4419–4424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lynch, M.; Conery, J.S. The evolutionary fate and consequences of duplicate genes. Science 2000, 290, 1151–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.P.; Si, Y.; Hanson, R.E.; Crane, C.F.; Price, H.J.; Stelly, D.M.; Wendel, J.F.; Paterson, A.H. Dispersed repetitive DNA has spread to new genomes since polyploid formation in cotton. Genome Res. 1998, 8, 479–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanson, R.E.; Zhao, X.p.; Islam-Faridi, M.N.; Paterson, A.H.; Zwick, M.S.; Crane, C.F.; McKnight, T.D.; Stelly, D.M.; Price, H.J. Evolution of interspersed repetitive elements in Gossypium (Malvaceae). Am. J. Bot. 1998, 85, 1364–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Small, R.L.; Ryburn, J.A.; Wendel, J.F. Low levels of nucleotide diversity at homoeologous Adh loci in allotetraploid cotton (Gossypium, L.). Mol. Biol. Evol. 1999, 16, 491–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Rong, J.; Waghmare, V.N.; Chee, P.W.; May, O.L.; Wright, R.J.; Gannaway, J.R.; Paterson, A.H. QTL alleles for improved fiber quality from a wild Hawaiian cotton, Gossypium tomentosum. TAG Theor. Appl. Genet. Theor. Und Angew. Genet. 2011, 123, 1075–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Wang, X.; Gundlach, H.; Mayer, K.F.X.; Peterson, D.G.; Scheffler, B.E.; Chee, P.W.; Paterson, A.H. Extensive and biased intergenomic nonreciprocal DNA exchanges shaped a nascent polyploid genome, Gossypium (cotton). Genetics 2014, 197, 1153–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutchinson, J. Intra-specific differentiation in Gossypium hirsutum. Heredity 1951, 5, 161–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyagi, P.; Gore, M.A.; Bowman, D.T.; Campbell, B.T.; Udall, J.A.; Kuraparthy, V. Genetic diversity and population structure in the US Upland cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.). TAG Theor. Appl. Genet. Theor. Und Angew. Genet. 2014, 127, 283–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, D.D.; Hinze, L.L.; Percy, R.G.; Li, P.; Deng, D.; Thyssen, G. A microsatellite-based genome-wide analysis of genetic diversity and linkage disequilibrium in Upland cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.) cultivars from major cotton-growing countries. Euphytica 2013, 191, 391–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aslam, S.; Khan, S.H.; Ahmed, A.; Dandekar, A.M. The tale of cotton plant: From wild type to domestication, leading to its improvement by genetic transformation. Am. J. Mol. Biol. 2020, 10, 91–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lubbers, E.L.; Chee, P.W. The worldwide gene pool of G. hirsutum and its improvement. In Genetics and Genomics of Cotton; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009; pp. 23–52. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Y.; Wang, H.; Chen, W.; Li, Y.; Gong, H.; Sang, X.; Huo, F.; Zeng, F. Genetic diversity and population structure of elite cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.) germplasm revealed by SSR markers. Plant Syst. Evol. 2015, 301, 327–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowman, D.T.; Gutiérrez, O.A. Sources of fiber strength in the US upland cotton crop from 1980 to 2000. J. Cotton Sci. 2003, 7, 164–169. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Fang, H.; Zhou, H.; Hughs, S.; Jones, D.C. Inheritance and transfer of thrips resistance from Pima cotton to Upland cotton. J. Cotton Sci 2013, 17, 163–169. [Google Scholar]
- Islam, M.S.; Fang, D.D.; Jenkins, J.N.; Guo, J.; McCarty, J.C.; Jones, D.C. Evaluation of genomic selection methods for predicting fiber quality traits in Upland cotton. Mol. Genet. Genom. MGG 2020, 295, 67–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saha, S.; Raska, D.A.; Stelly, D.M. Upland Cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.) × Hawaiian Cotton (G. tomentosum Nutt. Ex. Seem.) F1 hybrid hypoaneuploid chromosome substitution series. J. Cotton Sci. 2006, 10, 263–272. [Google Scholar]
- Muthuraj, M.; Mahalingam, L.; Premalatha, N.; Senguttuvan, K.; Kumar, M. F1 Interspecific hybridity confirmation in cotton through morphological, cytological and molecular analysis. Electron. J. Plant Breed. 2019, 10, 862–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newaskar, G.S.; Chimote, V.P.; Mehetre, S.S.; Jadhav, A.S. Interspecific hybridization in G. ossypium L.: Characterization of progenies with different ploidy-confirmed multigenomic backgrounds. Plant Breed. 2013, 132, 211–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Draye, X.; Chee, P.; Jiang, C.-X.; Decanini, L.; Delmonte, T.A.; Bredhauer, R.; Smith, C.W.; Paterson, A.H. Molecular dissection of interspecific variation between Gossypium hirsutum and G. barbadense (cotton) by a backcross-self approach: II. Fiber fineness. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2005, 111, 764–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Wu, M.; Yu, J.; Li, X.; Pei, W. Breeding potential of introgression lines developed from interspecific crossing between upland cotton (Gossypium hirsutum) and Gossypium barbadense: Heterosis, combining ability and genetic effects. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0143646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hulse-Kemp, A.M.; Lemm, J.; Plieske, J.; Ashrafi, H.; Buyyarapu, R.; Fang, D.D.; Frelichowski, J.; Giband, M.; Hague, S.; Hinze, L.L. Development of a 63K SNP array for cotton and high-density mapping of intraspecific and interspecific populations of Gossypium spp. G3 Genes Genomes Genet. 2015, 5, 1187–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinze, L.L.; Hulse-Kemp, A.M.; Wilson, I.W.; Zhu, Q.-H.; Llewellyn, D.J.; Taylor, J.M.; Spriggs, A.; Fang, D.D.; Ulloa, M.; Burke, J.J. Diversity analysis of cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.) germplasm using the CottonSNP63K Array. BMC Plant Biol. 2017, 17, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, D.; Li, X.; Wang, Z.; You, C.; Nie, X.; Sun, J.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, D.; Lin, Z. Genetic dissection of an allotetraploid interspecific CSSLs guides interspecific genetics and breeding in cotton. BMC Genom. 2020, 21, 431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Desalegn, Z.; Ratanadilok, N.; Kaveeta, R. Correlation and heritability for yield and fiber quality parameters of Ethiopian cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.) estimated from 15 (diallel) crosses. Agric. Nat. Resour. 2009, 43, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Ulloa, M. Heritability and correlations of agronomic and fiber traits in an okra-leaf upland cotton population. Crop Sci. 2006, 46, 1508–1514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulloa, M.; De Santiago, L.M.; Hulse-Kemp, A.M.; Stelly, D.M.; Burke, J.J. Enhancing Upland cotton for drought resilience, productivity, and fiber quality: Comparative evaluation and genetic dissection. Mol. Genet. Genom. 2020, 295, 155–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shim, J.; Mangat, P.K.; Angeles-Shim, R. Natural variation in wild Gossypium species as a tool to broaden the genetic base of cultivated cotton. J. Plant Sci. Curr. Res 2018, 2, 9. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, X.; Zhan, R.; He, Y.; Song, S.; Wang, L.; Ge, Y.; Chen, D. Morphological description of a novel synthetic allotetraploid (A1A1G3G3) of Gossypium herbaceum L. and G. nelsonii Fryx. suitable for disease-resistant breeding applications. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0242620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, G.; Huang, J.-Q.; Chen, X.-Y.; Zhu, Y.-X. Recent advances and future perspectives in cotton research. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2021, 72, 437–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meredith, W., Jr. Use of insect resistant germplasm in reducing the cost of production in the 1980s. In Proceedings of the Beltwide Cotton Conference, St. Louis, MO, USA, 6 January 1980; pp. 4–8. [Google Scholar]
- Levin, D.A. Somatic Cell Hybridization: Application in Plant Systematics. Taxon 1975, 24, 261–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, C.X.; Chee, P.W.; Draye, X.; Morrell, P.L.; Smith, C.W.; Paterson, A.H. Multilocus interactions restrict gene introgression in interspecific populations of polyploid Gossypium (cotton). Evol. Int. J. Org. Evol. 2000, 54, 798–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, H.; Ware, J. Cotton; Mc Graw, Hill, Book Company Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1958. [Google Scholar]
- Brubaker, C.L.; Wendel, J.F. Reevaluating the origin of domesticated cotton (Gossypium hirsutum; Malvaceae) using nuclear restriction fragment length polymorphisms (RFLPs). Am. J. Bot. 1994, 81, 1309–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Percy, R.G. The worldwide gene pool of Gossypium barbadense L. and its improvement. In Genetics and Genomics of Cotton; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009; pp. 53–68. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, G.L.; Dong, J.M.; Paterson, A.H. The distribution of Gossypium hirsutum chromatin in G. barbadense germ plasm: Molecular analysis of introgressive plant breeding. TAG Theor. Appl. Genet. Theor. Und Angew. Genet. 1995, 91, 1153–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Chen, J.; Zhang, W.; Hu, Y.; Chang, L.; Fang, L.; Wang, Q.; Lv, F.; Wu, H.; Si, Z.; et al. Sequence-based ultra-dense genetic and physical maps reveal structural variations of allopolyploid cotton genomes. Genome Biol. 2015, 16, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Z.; Zhu, X.; Chen, H.; Zhang, T. Fine mapping of clustered quantitative trait loci for fiber quality on chromosome 7 using a Gossypium barbadense introgressed line. Mol. Breed. 2015, 35, 215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.; Singh, R.; Lubbers, E.L.; Shen, X.; Paterson, A.H.; Campbell, B.T.; Jones, D.C.; Chee, P.W. Mapping and validation of fiber strength quantitative trait loci on chromosome 24 in upland cotton. Crop Sci. 2012, 52, 1115–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paterson, A.H.; Boman, R.K.; Brown, S.M.; Chee, P.W.; Gannaway, J.R.; Gingle, A.R.; May, O.L.; Smith, C.W. Reducing the genetic vulnerability of cotton. Crop Sci 2004, 44, 1900–1901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanksley, S.D.; Nelson, J.C. Advanced backcross QTL analysis: A method for the simultaneous discovery and transfer of valuable QTLs from unadapted germplasm into elite breeding lines. TAG Theor. Appl. Genet. Theor. Und Angew. Genet. 1996, 92, 191–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baohua, W.; Peng, W.C. Application of advanced backcross QTL analysis in crop improvement. J. Plant Breed. Crop Sci. 2010, 2, 221–232. [Google Scholar]
- Chee, P.W.; Draye, X.; Jiang, C.-X.; Decanini, L.; Delmonte, T.A.; Bredhauer, R.; Smith, C.W.; Paterson, A.H. Molecular dissection of phenotypic variation between Gossypium hirsutum and Gossypium barbadense (cotton) by a backcross-self approach: III. Fiber length. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2005, 111, 772–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chee, P.; Draye, X.; Jiang, C.-X.; Decanini, L.; Delmonte, T.A.; Bredhauer, R.; Smith, C.W.; Paterson, A.H. Molecular dissection of interspecific variation between Gossypium hirsutum and Gossypium barbadense (cotton) by a backcross-self approach: I. Fiber elongation. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2005, 111, 757–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, X.; Guo, W.; Zhu, X.; Yuan, Y.; Yu, J.Z.; Kohel, R.J.; Zhang, T. Molecular mapping of QTLs for fiber qualities in three diverse lines in Upland cotton using SSR markers. Mol. Breed. 2005, 15, 169–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Yuan, Y.; Yu, J.; Guo, W.; Kohel, R.J. Molecular tagging of a major QTL for fiber strength in Upland cotton and its marker-assisted selection. TAG Theor. Appl. Genet. Theor. Und Angew. Genet. 2003, 106, 262–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chandnani, R.; Kim, C.; Guo, H.; Shehzad, T.; Wallace, J.G.; He, D.; Zhang, Z.; Patel, J.D.; Adhikari, J.; Khanal, S. Genetic analysis of gossypium fiber quality traits in reciprocal advanced backcross populations. Plant Genome 2018, 11, 170057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chandnani, R.; Wang, B.; Draye, X.; Rainville, L.K.; Auckland, S.; Zhuang, Z.; Lubbers, E.L.; May, O.L.; Chee, P.W.; Paterson, A.H. Segregation distortion and genome-wide digenic interactions affect transmission of introgressed chromatin from wild cotton species. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2017, 130, 2219–2230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, B.; Draye, X.; Zhuang, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, M.; Lubbers, E.L.; Jones, D.; May, O.L.; Paterson, A.H.; Chee, P.W. QTL analysis of cotton fiber length in advanced backcross populations derived from a cross between Gossypium hirsutum and G. mustelinum. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2017, 130, 1297–1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Zhuang, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Draye, X.; Shuang, L.-S.; Shehzad, T.; Lubbers, E.L.; Jones, D.; May, O.L.; Paterson, A.H. Advanced backcross QTL analysis of fiber strength and fineness in a cross between Gossypium hirsutum and G. mustelinum. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 1848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Wang, W.; Khanal, S.; Han, J.; Zhang, M.; Chen, Y.; Li, Z.; Wang, K.; Paterson, A.H.; Yu, J. Transcriptome analysis reveals genes potentially related to high fiber strength in a Gossypium hirsutum line IL9 with Gossypium mustelinum introgression. Genome 2021, 64, 985–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zhang, R.; Shen, C.; Li, X.; Zhu, D.; Lin, Z. Transcriptome and QTL analyses reveal candidate genes for fiber quality in Upland cotton. Crop J. 2020, 8, 98–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Q.; Xiao, X.; Gong, J.; Li, P.; Zhao, Y.; Feng, J.; Peng, R.; Shi, Y.; Yuan, Y. Identification of candidate cotton genes associated with fiber length through quantitative trait loci mapping and RNA-sequencing using a chromosome segment substitution line. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 796722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Zhang, J.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, C.; Gong, J.; Song, Z.; Zhou, J.; Wang, J.; Zhao, C.; Jiao, M. Identification of candidate genes for key fibre-related QTL s and derivation of favourable alleles in Gossypium hirsutum recombinant inbred lines with G. barbadense introgressions. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2020, 18, 707–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, X.; Cao, Z.; Singh, R.; Lubbers, E.L.; Xu, P.; Smith, C.W.; Paterson, A.H.; Chee, P.W. Efficacy of qFL-chr1, a quantitative trait locus for fiber length in cotton (Gossypium spp.). Crop Sci. 2011, 51, 2005–2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanco-Montenegro, I.; De Ritis, R.; Chiappini, M. Imaging and modelling the subsurface structure of volcanic calderas with high-resolution aeromagnetic data at Vulcano (Aeolian Islands, Italy). Bull. Volcanol. 2007, 69, 643–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knight, R. The Genetics Of Blackarm Resistance Ix The Gene B6M From Gossypium Arboreum. J. Genet. 1953, 51, 270–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knight, R. The genetics of blackarm resistance XII. Transference of resistance from Gossypium herbaceum to G. barbadense. J. Genet. 1963, 58, 328–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Bourland, F.; Wheeler, T.; Wallace, T. Bacterial blight resistance in cotton: Genetic basis and molecular mapping. Euphytica 2020, 216, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delannoy, E.; Lyon, B.; Marmey, P.; Jalloul, A. Resistance of cotton towards Xanthomonas campestris pv. malvacearum. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 2005, 43, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Roberts, P. A Fusarium wilt resistance gene in Gossypium barbadense and its effect on root-knot nematode-wilt disease complex. Phytopathology 2006, 96, 727–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Idowu, J.; Flynn, R.; Wedegaertner, T. Progress in breeding for glandless cotton in New Mexico. In Proceedings of the Beltwide Cotton Conference, San Antonio, TX, USA, 3–5 January 2018; pp. 566–572. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J. Fighting Fusarium wilt through breeding in cotton: A successful story in China. In Proceedings of the Beltwide Cotton Conference, San Antonio, TX, USA, 3–5 January 2018; pp. 877–879. [Google Scholar]
- Ulloa, M.; Hutmacher, R.B.; Roberts, P.A.; Wright, S.D.; Nichols, R.L.; Michael Davis, R. Inheritance and QTL mapping of Fusarium wilt race 4 resistance in cotton. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2013, 126, 1405–1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaidi, S.S.e.A.; Naqvi, R.Z.; Asif, M.; Strickler, S.; Shakir, S.; Shafiq, M.; Khan, A.M.; Amin, I.; Mishra, B.; Mukhtar, M.S. Molecular insight into cotton leaf curl geminivirus disease resistance in cultivated cotton (Gossypium hirsutum). Plant Biotechnol. J. 2020, 18, 691–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vij, S.; Pathak, D.; Rathore, P.; Kumar, H.; Sekhon, P.; Bhatia, D.; Chhuneja, P.; Singh, K. Molecular mapping of CLCuD resistance introgressed from synthetic cotton polyploid in upland cotton. J. Genet. 2022, 101, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazeer, W.; Ahmad, S.; Mahmood, K.; Tipu, A.; Mahmood, A.; Zhou, B. Introgression of genes for cotton leaf curl virus resistance and increased fiber strength from Gossypium stocksii into upland cotton (G. hirsutum). Genet. Mol. Res. 2014, 13, 1133–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, S.; Mahmood, K.; Hanif, M.; Nazeer, W.; Malik, W.; Qayyum, A.; Hanif, K.; Mahmood, A.; Islam, N. Introgression of cotton leaf curl virus-resistant genes from Asiatic cotton (Gossypium arboreum) into upland cotton (G. hirsutum). Genet. Mol. Res. 2011, 10, 2404–2414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, J.K.; Khan, Z. Breeding Cotton for Cotton Leaf Curl Disease Resistance. In Cotton Breeding and Biotechnology; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2022; pp. 171–197. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, Y.; Cai, X.; Wang, Q.; Wang, P.; Zhang, Y.; Cai, C.; Xu, Y.; Wang, K.; Zhou, Z.; Wang, C. Genome sequencing of the Australian wild diploid species Gossypium australe highlights disease resistance and delayed gland morphogenesis. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2020, 18, 814–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolek, Y.; Bell, A.; El-Zik, K.; Thaxton, P.; Magill, C. Reaction of cotton cultivars and an F2 population to stem inoculation with isolates Verticillium dahliae. J. Phytopathol. 2005, 153, 269–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelraheem, A.; Elassbli, H.; Zhu, Y.; Kuraparthy, V.; Hinze, L.; Stelly, D.; Wedegaertner, T.; Zhang, J. A genome-wide association study uncovers consistent quantitative trait loci for resistance to Verticillium wilt and Fusarium wilt race 4 in the US Upland cotton. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2020, 133, 563–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Q.; Magwanga, R.O.; Cai, X.; Lu, P.; Nyangasi Kirungu, J.; Zhou, Z.; Wang, X.; Wang, X.; Xu, Y.; Hou, Y. RNA-sequencing, physiological and RNAi analyses provide insights into the response mechanism of the ABC-mediated resistance to Verticillium dahliae infection in cotton. Genes 2019, 10, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grover, C.E.; Pan, M.; Yuan, D.; Arick, M.A.; Hu, G.; Brase, L.; Stelly, D.M.; Lu, Z.; Schmitz, R.J.; Peterson, D.G. The Gossypium longicalyx genome as a resource for cotton breeding and evolution. G3 Genes Genomes Genet. 2020, 10, 1457–1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutiérrez, O.A.; Jenkins, J.N.; McCarty, J.C.; Wubben, M.J.; Hayes, R.W.; Callahan, F.E. SSR markers closely associated with genes for resistance to root-knot nematode on chromosomes 11 and 14 of Upland cotton. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2010, 121, 1323–1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turcotte, E.; Harold, W.; O’Bannon, J.; Feaster, C. Evaluation of cotton root knot nematode resistance of a strain of G. barbadense. var. darwinni. In Proceedings of the 15th Cotton Improvement Conference, Dallas, TX, USA, 8–9 January 1963; National Cotton Council of America: Memphis, TN, USA, 1963; pp. 36–44. [Google Scholar]
- He, Y.; Kumar, P.; Shen, X.; Davis, R.F.; Van Becelaere, G.; May, O.L.; Nichols, R.L.; Chee, P.W. Re-evaluation of the inheritance for root-knot nematode resistance in the Upland cotton germplasm line M-120 RNR revealed two epistatic QTLs conferring resistance. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2014, 127, 1343–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romano, G.B.; Sacks, E.J.; Stetina, S.R.; Robinson, A.; Fang, D.D.; Gutierrez, O.A.; Scheffler, J.A. Identification and genomic location of a reniform nematode (Rotylenchulus reniformis) resistance locus (Ren ari) introgressed from Gossypium aridum into upland cotton (G. hirsutum). Theor. Appl. Genet. 2009, 120, 139–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sacks, E.J.; Robinson, A.F. Introgression of resistance to reniform nematode (Rotylenchulus reniformis) into upland cotton (Gossypium hirsutum) from Gossypium arboreum and a G. hirsutum/Gossypium aridum bridging line. Field Crops Res. 2009, 112, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, D.D.; Xiao, J.; Canci, P.C.; Cantrell, R.G. A new SNP haplotype associated with blue disease resistance gene in cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.). Theor. Appl. Genet. 2010, 120, 943–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Sun, J.; Liu, J.; Wu, Z. Genetic analysis of cotton resistance to spider mites. J. Huazhong Agric. Univ. 1992, 11, 127–133. [Google Scholar]
- Meyer, V.G. Interspecific cotton breeding. Econ. Bot. 1974, 28, 56–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, A.; Maitra, S.; Pramanick, B.; Bhutia, K.L.; Ahmad, Z.; Moulik, D.; Syed, M.A.; Shankar, T.; Adeel, M.; Hassan, M.M. Wild relatives of plants as sources for the development of abiotic stress tolerance in plants. In Plant Perspectives to Global Climate Changes; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2022; pp. 471–518. [Google Scholar]
- Stanton, M.; Stewart, J.M.; Tugwell, N. Evaluation of Gossypium arboreum L. germplasm for resistance to thrips. Genet. Resour. Crop Evol. 1992, 39, 89–95. [Google Scholar]
- Bowman, D.T.; McCarty, J.C., Jr. Thrips (Thysanoptera: Thripidae) tolerance in cotton: Sources and heritability. J. Entomol. Sci. 1997, 32, 460–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monga, D.; Sheo, R. Screening of germplasm lines against root rot of cotton (G. hirsutum). Adv. Plant Sci. 2000, 13, 603–607. [Google Scholar]
- Wilson, I.W.; Moncuquet, P.; Ellis, M.; White, R.G.; Zhu, Q.-H.; Stiller, W.; Llewellyn, D. Characterization and genetic mapping of black root rot resistance in Gossypium arboreum L. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 2642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodah, E.T. Root rot diseases in plants: A review of common causal agents and management strategies. Agric. Res. Technol. Open Access J. 2017, 5, 555661. [Google Scholar]
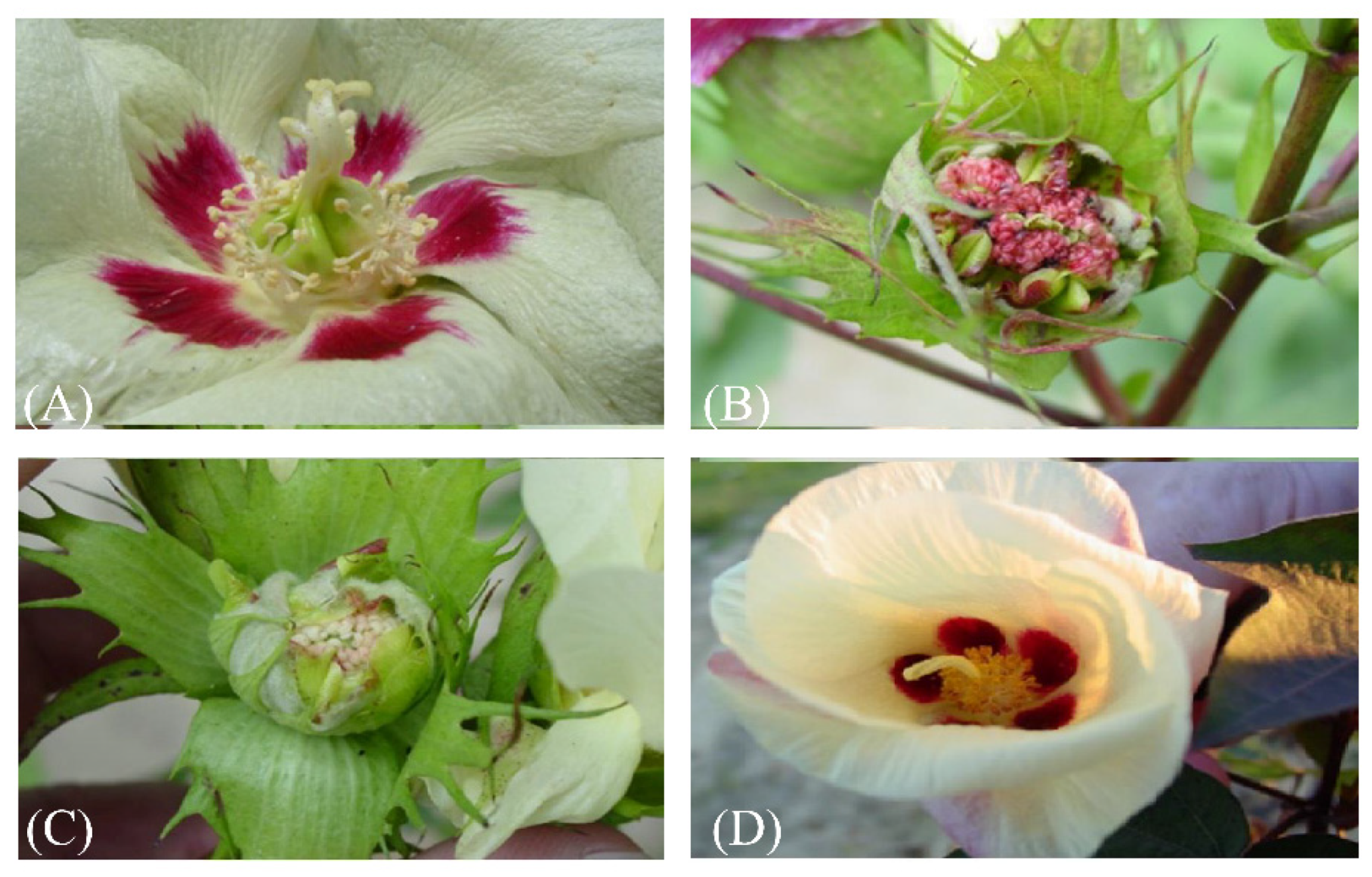

| Genome Group | Ploidy (No. of Species) | Species Name | Geographical Distribution |
|---|---|---|---|
| A | 2X (2) | G. herbaceum, G. arboreum, | Asia, Africa |
| B | 2X (3–4) | G. anomalum, G. capitis-viridis, G. triphyllum, G. trifurcatum | Cape Verde Island, Africa |
| C | 2X (2) | G. robinsonii, G. sturtianum | Australia |
| D | 2X (13–14) | G. armourianum, G. aridum, G. davidsonii, G. gossypioides, G. harknessii, G. klotzschianum, G. laxum, G. lobatum, (Gossypium sp. Nov), G. raimondii, G. schwendimanii, G. turneri, G. thurberi, G. trilobum | Mexico, Peru, Arizona, Galapagos Islands |
| E | 2X (5–9) | G. areysianum Deflers, (G. benadirense), (G. bricchettii), G. incanum, G. stocksii, G. somalense, G. trifurcatum, (G. trifurcatum), (G. vollesenii) | Southwest Asia, Northeast Africa, Arabian Peninsula |
| F | 2X (1) | G. longicalyx | East Africa |
| G | 2X (3) | G. australe, G. bickii, G. nelsonii | Australia |
| K | 2X (12) | G. anapoides, G. cunninghamii, G. costulatum, G. exiguum, G. enthyle, G. londonderriense, G. nobile, G. marchantii, G. populifolium, G. pilosum, G. pulchellum, G. rotundifolium. | Australia, Northern Territory, Cobourg Peninsula, Northwest Australia |
| AD | 4X (7) | G. barbadense, G. darwinii, G. ekmanianum, G. hirsutum, G. mustelinum, G. tomentosum, G. stephensii. | New World tropics and subtropics, including Hawaii, Galapagos Islands and the Wake Atoll |
| G. barbadense | G. tomentosum | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gh | Gb | Total | Gh | Gt | Total | |||
| Fiber length | 17 | 11 | 28 | [113] | 4 | 0 | 4 | [76] |
| Fiber strength | - | - | - | 4 | 0 | 4 | [76] | |
| Micronaire | 1 | 8 | 9 | [89] | 1 | 3 | 4 | [76] |
| Fiber elongation | 14 | 8 | 22 | [114] | 0 | 4 | 4 | [76] |
| Disease/Pest | Causal Agents | Source 1 | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bacterial Blight | Xanthomonas campestris pathovar malvacearum | Ga, Gb | [127,128,129,130] |
| Fusarium Wilt | Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. vasinfectum | Gb | [97,131,132,133,134] |
| Leaf curl virus | Begomoviruses | Gh | [135,136,137,138,139] |
| Verticulum wilt root knot | Verticillium dahliae | Gb, Ga, | [140,141,142,143] |
| Nematodes | Meloidogyne incognita, Rotylenchulus reniformis | Gh, Gd, Gb | [144,145,146,147,148,149] |
| Blue Viral Disease | Polerovirus | Gh | [150] |
| Spider mites | Tetranychus urticae | Gb | [151,152,153] |
| Suckig pest | Frankliniella occidentalis | Gb, Gm Gd, Gt | [27,84,154,155] |
| Root rot | Rhizoctonia bataticola | Gh | [156,157,158] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Anwar, M.; Iqbal, M.Z.; Abro, A.A.; Memon, S.; Bhutto, L.A.; Memon, S.A.; Peng, Y. Inter-Specific Hybridization in Cotton (Gossypium hirsutum) for Crop Improvement. Agronomy 2022, 12, 3158. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12123158
Anwar M, Iqbal MZ, Abro AA, Memon S, Bhutto LA, Memon SA, Peng Y. Inter-Specific Hybridization in Cotton (Gossypium hirsutum) for Crop Improvement. Agronomy. 2022; 12(12):3158. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12123158
Chicago/Turabian StyleAnwar, Muhammad, Muhammad Zafar Iqbal, Aamir Ali Abro, Shabana Memon, Liaquat Ali Bhutto, Shamim Ara Memon, and Yan Peng. 2022. "Inter-Specific Hybridization in Cotton (Gossypium hirsutum) for Crop Improvement" Agronomy 12, no. 12: 3158. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12123158
APA StyleAnwar, M., Iqbal, M. Z., Abro, A. A., Memon, S., Bhutto, L. A., Memon, S. A., & Peng, Y. (2022). Inter-Specific Hybridization in Cotton (Gossypium hirsutum) for Crop Improvement. Agronomy, 12(12), 3158. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12123158








