Weed Control, Rice Safety, and Mechanism of the Novel Paddy Field Herbicide Glyamifop
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant and Chemical Materials
2.2. Sensitivity to Glyamifop
2.3. Rice Safety
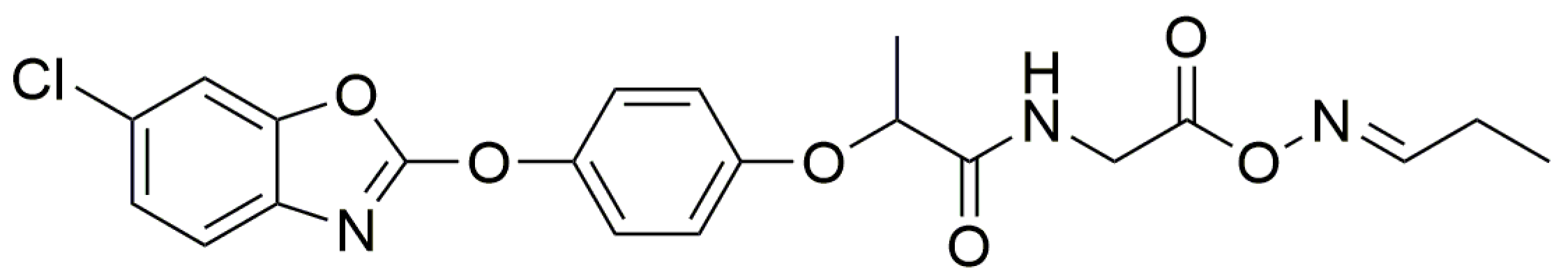
2.4. Glyamifop Mechanism of Action
2.5. Selective Mechanism of Glyamifop on Rice and Weeds
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Efficacy of Glyamifop on Sensitive- and Resistant Weeds in a Paddy Field
3.2. Rice Safety
3.2.1. Glyamifop Safety on Different Rice Types
3.2.2. Glyamifop Safety in Rice at Different Leaf Stages
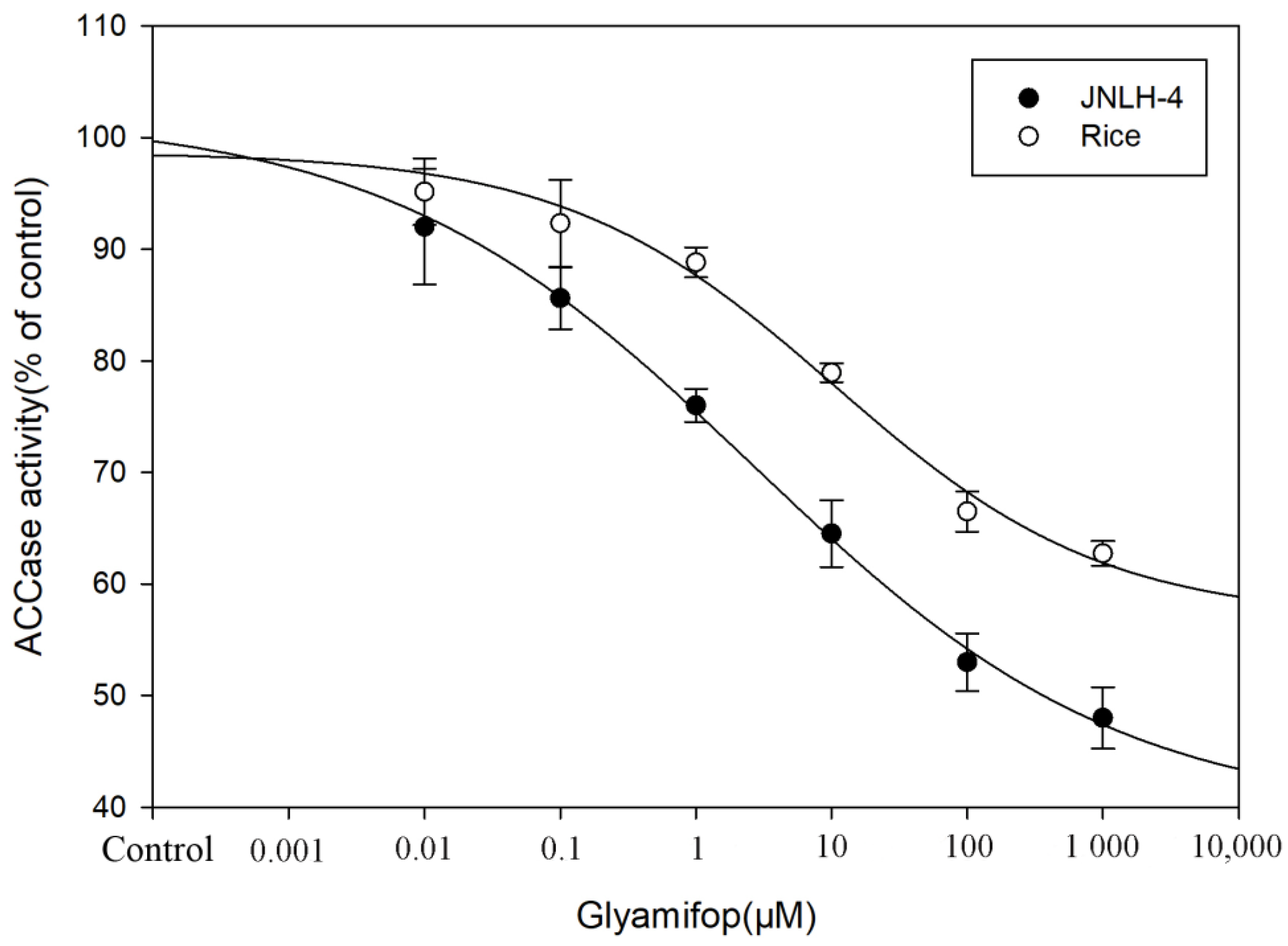
3.3. Glyamifop Mechanism of Action
3.4. Selective Mechanism of Glyamifop on Rice and Weeds
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Nie, L.; Peng, S. Rice Production in China. In Rice Production Worldwide; Chauhan, B.S., Jabran, K., Mahajan, G., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 33–52. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, T.; Yu, J.; Fang, J.; Dong, L. Rice safety and control of penoxsulam-resistant and -susceptible barnyardgrass (Echinochloa crus-galli) populations with soil-applied herbicides. Weed Technol. 2021, 35, 492–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Gao, H.; Pan, L.; Yao, Z.; Dong, L. Mechanism of resistance to cyhalofop-butyl in Chinese sprangletop (Leptochloa chinensis (L.) Nees). Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2017, 143, 306–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, J.; He, Z.; Liu, T.; Li, J.; Dong, L. A novel mutation Asp-2078-Glu in ACCase confers resistance to ACCase herbicides in barnyardgrass (Echinochloa crus-galli). Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2020, 168, 104634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.P. Development of chemical weed control and integrated weed management in China. Weed Biol. Manag. 2003, 3, 197–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, R.-Y.; Nan, J.-X.; Yan, Y.-C.; Chen, Q.; Ndikuryayo, F.; Wei, X.-F.; Yang, W.-C.; Lin, H.-Y.; Yang, G.-F. Structure-Guided Discovery of Silicon-Containing Subnanomolar Inhibitor of Hydroxyphenylpyruvate Dioxygenase as a Potential Herbicide. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2021, 69, 459–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Liu, H.; Wang, J.; Chen, W.; Bai, L.; Pan, L. Enhanced Metabolism Evolved High-Level Resistance to Fenoxaprop-P-Ethyl in Alopecurus japonicus. Agronomy 2022, 12, 2172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Fang, J.; Zongzhe, H.; Li, J.; Dong, L. Target site–based resistance to penoxsulam in late watergrass (Echinochloa phyllopogon) from China. Weed Sci. 2019, 67, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, T.; Yan, B.; Li, J.; Dong, L. Target-Site and Metabolic Resistance Mechanisms to Penoxsulam in Barnyardgrass (Echinochloa crus-galli (L.) P. Beauv). J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 67, 8085–8095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, J.; Liu, T.; Zhang, Y.; Li, J.; Dong, L. Target Site–Based Penoxsulam Resistance in Barnyardgrass (Echinochloa crus-galli) from China. Weed Sci. 2019, 67, 281–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Li, J.; Pan, X.; Liu, D.; Napier, R.; Dong, L. Quinclorac resistance induced by the suppression of the expression of 1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylic acid (ACC) synthase and ACC oxidase genes in Echinochloa crus-galli var. zelayensis. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2018, 146, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, X.; Chen, J.; Wang, X.; Gao, H.; Xiang, B.; Dong, L. Mefenacet resistance in multiple herbicide-resistant Echinochloa crus-galli L. populations. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2022, 182, 105038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Q.; Powles, S.B. Resistance to AHAS inhibitor herbicides current understanding. Pest Manag. Sci. 2014, 70, 1340–1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pallett, K.E. Can We Expect New Herbicides with Novel Modes of Action in the Foreseeable. Outlooks Pest Manag. 2016, 27, 39–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Wendeborn, S.; Godineau, E.; Mondière, R.; Smejkal, T.; Smits, H. 1.8 Chirality in Agrochemicals. In Comprehensive Chirality; Carreira, E.M., Yamamoto, H., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2012; pp. 120–166. [Google Scholar]
- Anonymous. China Pesticide Information Network. Available online: http://www.chinapesticide.gov.cn (accessed on 13 July 2022).
- Nie, Z.-J.; Hang, B.-J.; Cai, S.; Xie, X.-T.; He, J.; Li, S.-P. Degradation of Cyhalofop-butyl (CyB) by Pseudomonas azotoformans Strain QDZ-1 and Cloning of a Novel Gene Encoding CyB-Hydrolyzing Esterase. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2011, 59, 6040–6046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.J.; Chang, H.S.; Ryu, J.W.; Ko, Y.K.; Kim, D.W.; Cho, K.Y.; Park, C.H.; Kwon, Y.; Chung, B.J. Metamifop: A new post-emergence grass killing herbicide for use in rice. In Proceedings of the International Congress on Crop Science and Technology, SECC, Glasgow, UK, 10–12 November 2003; pp. 81–86. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, T.J.; Chang, H.S.; Kim, J.S.; Hwang, I.T.; Hong, K.S.; Kim, D.W.; Cho, K.Y.; Myung, E.J.; Chung, B.J. Metamifop: Mechanism of herbicidal activity and selectivity in rice and barnyardgrass. In Proceedings of the International Congress on Crop Science and Technology, SECC, Glasgow, UK, 10–12 November 2003; pp. 833–838. [Google Scholar]
- Cox, M.C.; Askew, S.D. Metamifop Rates, Application Timings, and Broadleaf Herbicide Admixtures Affect Smooth Crabgrass Control in Turf. Weed Technol. 2014, 28, 617–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Rao, L.; Li, W.; Zhou, W.; Li, B.; Tang, L. Detection of Glyamifop residues in rice and its environment by the QuEChERS method combined with HPLC–MS. Microchem. J. 2020, 158, 105157. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, G.; Wang, Q.; Yao, Z.; Zhu, L.; Dong, L. Penoxsulam-resistant barnyardgrass (Echinochloa crus-galli) in rice fields in China. Weed Biol. Manag. 2016, 16, 16–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Pan, L.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, T.; Dong, L.; Li, J. Resistance to quinclorac caused by the enhanced ability to detoxify cyanide and its molecular mechanism in Echinochloa crus-galli var. zelayensis. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2017, 143, 231–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, G.L.; Du, C.; Liu, X.; Peng, Y.; Li, S. Evaluation of herbicidal activity of pyraclonil and its safety to rice and following crops. Plant Prot. 2017, 43, 218–223. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Shukla, A.; Leach, G.E.; Devine, M.D. High-level resistance to sethoxydim conferred by an alteration in the target enzyme, acetyl-CoA carboxylase, in Setaria faberi and Setaria viridis. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 1997, 35, 803–807. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, C.; Dong, L.; Li, J.; Moss, S.R. Identification of Japanese Foxtail (Alopecurus Japonicus) Resistant to Haloxyfop Using Three Different Assay Techniques. Weed Sci. 2007, 55, 537–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Q.; Cairns, A.; Powles, S. Glyphosate, paraquat and ACCase multiple herbicide resistance evolved in a Lolium rigidum biotype. Planta 2007, 225, 499–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, D.W.; Lin, H.Y.; Cao, R.J.; Yang, S.G.; Chen, Q.; Hao, G.F.; Yang, W.C.; Yang, G.F. Synthesis and herbicidal evaluation of triketone-containing quinazoline-2,4-diones. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2014, 62, 11786–11796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Liu, W.; Zhao, K.; Yu, H.; Zhang, J.; Wang, J. Evaluation of weed control efficacy and crop safety of the new HPPD-inhibiting herbicide-QYR301. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 7910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, F.; Bai, S.; Wang, H.; Liu, W.; Wang, J. Greenhouse and field evaluation of a novel HPPD-inhibiting herbicide, QYM201, for weed control in wheat. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Liu, W.; Jin, T.; Peng, X.; Zhang, L.; Wang, J. Bipyrazone: A new HPPD-inhibiting herbicide in wheat. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 5521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, F.; Ma, P.; Zhang, Y.-Y.; Li, P.; Yang, F.; Fu, Y. Herbicidal Activity and Molecular Docking Study of Novel ACCase Inhibitors. Front. Plant Sci. 2018, 9, 1850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Li, X.; Sun, Y.; He, J.; Zhang, W.; Lou, Y.; Zhang, F. Herbicidal activity of quintrione and its safety to rice. Jiangsu J. Agric. Sci. 2016, 32, 67–72. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]

| Weed Seed | Collection Site | Time | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Province | County | Village | ||
| Echinochloa crus-galli var. mitis | Jiangsu | Gulou | Yinzhuang | September 2019 |
| E. crus-galli | Jiangsu | Huaiyin | Lizhuang | November 2017 |
| E. glabrescens | Jiangsu | Jiangdu | Xiannv | October 2019 |
| E. crusgalli var. zelayensis | Jiangsu | Luhe | Xiaoying | September 2019 |
| E. caudata | Jiangsu | Wujin | Dongliutang | October 2019 |
| E. phyllopogon | Jiangsu | Gaoyou | Guzhuang | October 2019 |
| Leptochloa chinensis | Jiangsu | Luhe | Xiaoying | October 2019 |
| Setaria viridis | Jiangsu | Xuanwu | Xiaolingwei | October 2019 |
| Eragrostis japonica | Jiangsu | Huaiyin | Jiegou | October 2019 |
| Digitaria sanguinalis | Jiangsu | Jiangdu | Qili | September 2019 |
| Panicum bisulcatum | Anhui | Wuwei | Sanxi | November 2019 |
| Eclipta prostrata | Jiangsu | Jiangdu | Qili | November 2017 |
| Cyperus iria | Jiangsu | Ganyu | Songzhuang | September 2019 |
| Trial Weeds | Collection Site | Resistance to Herbicide | Reported | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Province | County | Village | |||
| Echinochloa phyllopogon (HSQX-R) | Heilongjiang | Qingxian | Qingyuanzhen | Penoxsulam | [8] |
| E. glabrescens (JHHZ-R) | Jiangsu | Hongze | Hepingnongchang | Penoxsulam | [22] |
| E. crusgalli var. zelayensis (JNNX-R) | Jiangsu | Xuanwu | Xiaolingwei | Quinclorac | [23] |
| Leptochloa chinensis (JHQP-R) | Jiangsu | Huaiyin | Lizhuang | Cyhalofop-butyl | [3] |
| E. crus-galli (AXYZ-R) | Anhui | Xuanzhou | Xingyang | Penoxsulam | [9] |
| Weed Species | Weeds | Dose (g a.i. ha−1) | GR50 (SE) g a.i. ha−1 | GR90 (SE) g a.i. ha−1 | r2 (Coefficient) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Inhibition Rate of Fresh Weight (%) | ||||||||||
| 6.25 | 12.5 | 25 | 50 | 100 | 200 | |||||
| Gramineae | Echinochloa crus-galli var. mitis | 23.98 | 47.31 | 73.72 | 92.06 | 99.98 | 100.00 | 12.91 (1.31) | 41.95 (3.97) | 0.9974 |
| E. crus-galli | 11.96 | 24.87 | 61.71 | 91.45 | 98.76 | 100.00 | 18.14 (7.5) | 49.28 (7.94) | 0.9939 | |
| E. glabrescens | 44.18 | 71.76 | 89.03 | 98.57 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 7.40 (1.09) | 23.62 (2.43) | 0.9964 | |
| E. crusgalli var. zelayensis | 14.49 | 25.98 | 48.13 | 82.27 | 94.33 | 100.00 | 21.44 (3.58) | 78.37 (20.70) | 0.9907 | |
| E. caudata | 20.47 | 42.76 | 57.69 | 82.39 | 96.48 | 100.00 | 16.45 (2.96) | 66.18 (13.81) | 0.9918 | |
| E. phyllopogon | 11.73 | 18.95 | 34.07 | 53.98 | 82.26 | 91.45 | 36.01 (6.11) | 189.64 (39.39) | 0.9910 | |
| Leptochloa chinensis | 46.89 | 73.33 | 96.55 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 7.03 (1.88) | 17.93 (7.15) | 0.9888 | |
| Digitaria sanguinalis | 18.98 | 37.54 | 52.87 | 79.81 | 93.67 | 100.00 | 18.81 (2.69) | 84.30 (19.11) | 0.9934 | |
| Panicum bisulcatum | 31.94 | 58.23 | 65.34 | 77.99 | 90.26 | 94.45 | 11.78 (2.83) | 109.23 (48.14) | 0.9908 | |
| Eragrostis japonica | 17.36 | 25.00 | 42.29 | 64.33 | 99.65 | 100.00 | 41.70 (6.55) | 94.46 (22.11) | 0.9884 | |
| Setaria viridis | 34.82 | 49.84 | 68.22 | 89.14 | 97.44 | 100.00 | 11.48 (2.71) | 52.22 (12.05) | 0.9908 | |
| Broad-leaved and cyperaceae | Eclipta prostrata | 9.26 | 14.01 | 14.18 | 18.19 | 34.67 | 49.67 | 318.69 (65.23) | 10889.62 (101.21) | 0.9484 |
| Cyperus iria | 0.80 | 6.62 | 9.12 | 16.02 | 33.43 | 39.5 | 251.82 (78.09) | 2220.59 (96.07) | 0.9742 | |
| Population | Dose (g a.i. ha−1) | GR50 (SE) g a.i. ha−1 | GR90 (SE) g a.i. ha−1 | r2 (Coefficient) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Inhibition Rate of Fresh Weight (%) | |||||||||
| 6.25 | 12.5 | 25 | 50 | 100 | 200 | ||||
| Echinochloa crus-galli (AXYZ-R) | 6.42 | 11.24 | 26.54 | 45.72 | 89.02 | 100.00 | 56.07 (5.36) | 127.55 (15.23) | 0.9851 |
| E. crusgalli var. zelayensis (JNNX-R) | 4.28 | 10.36 | 26.72 | 52.17 | 91.48 | 100 | 37.66 (3.25) | 99.25 (10.67) | 0.9903 |
| E. glabrescens (JHHZ-R) | 13.92 | 16.85 | 27.46 | 48.62 | 95.26 | 100.00 | 50.43 (6.87) | 94.67 (12.97) | 0.9815 |
| E. phyllopogon (HSQX-R) | 5.72 | 12.38 | 13.15 | 41.63 | 72.41 | 82.61 | 57.05 (6.09) | 309.93 (50.48) | 0.9922 |
| Leptochloa chinensis (JHQP-R) | 21.48 | 36.09 | 57.39 | 87.51 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 16.78 (2.86) | 67.75 (7.71) | 0.9908 |
| Rice Type | Varieties | GR10 (SE) g a.i. ha−1 | r2 (Coefficient) | Selectivity Index (Z) a |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ssp. japonica | HuaiDao 5 | 500.04 (73.76) | 0.9976 | 5.93 |
| ssp. indica | Xiangliangyou 900 | 574.42 (67.01) | 0.9930 | 6.81 |
| ssp. glutinous | Zhennuo 29 | 413.94 (40.71) | 0.9896 | 4.91 |
| Application Period | Huai Dao 5 a | Digitaria sanguinalis | Selectivity Index (Z) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GR10 (SE) g a.i. ha−1 | r2 (Coefficient) | GR90 (SE) g a.i. ha−1 | r2 (Coefficient) | ||
| 1.5-leaf stage | 218.11 (23.08) | 0.9964 | 63.07 (16.74) | 0.9927 | 3.45 |
| 2.5-leaf stage | 394.16 (36.86) | 0.9976 | 76.13 (12.48) | 0.9702 | 5.18 |
| 3.5-leaf stage | 593.01 (71.58) | 0.9924 | 98.26 (14.71) | 0.9917 | 6.04 |
| 5.5-leaf stage | 1184.51 (102.08) | 0.9948 | 149.28 (29.04) | 0.9938 | 7.93 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gao, H.; Zheng, H.; Zhang, P.; Yu, J.; Li, J.; Dong, L. Weed Control, Rice Safety, and Mechanism of the Novel Paddy Field Herbicide Glyamifop. Agronomy 2022, 12, 3026. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12123026
Gao H, Zheng H, Zhang P, Yu J, Li J, Dong L. Weed Control, Rice Safety, and Mechanism of the Novel Paddy Field Herbicide Glyamifop. Agronomy. 2022; 12(12):3026. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12123026
Chicago/Turabian StyleGao, Haitao, Haowen Zheng, Pu Zhang, Jiaxing Yu, Jun Li, and Liyao Dong. 2022. "Weed Control, Rice Safety, and Mechanism of the Novel Paddy Field Herbicide Glyamifop" Agronomy 12, no. 12: 3026. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12123026
APA StyleGao, H., Zheng, H., Zhang, P., Yu, J., Li, J., & Dong, L. (2022). Weed Control, Rice Safety, and Mechanism of the Novel Paddy Field Herbicide Glyamifop. Agronomy, 12(12), 3026. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12123026






