Prospects for Integrating Augmentative and Conservation Biological Control of Leaffolders and Stemborers in Rice
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Augmentative Biological Control
3.1.1. Target Herbivore Species for Augmentative Biological Control
3.1.2. Trichogramma spp. Used in Augmentative Biocontrol
3.1.3. Release Methods during Augmentative Biocontrol
3.1.4. Parasitism Rates during Augmentative Biological Control
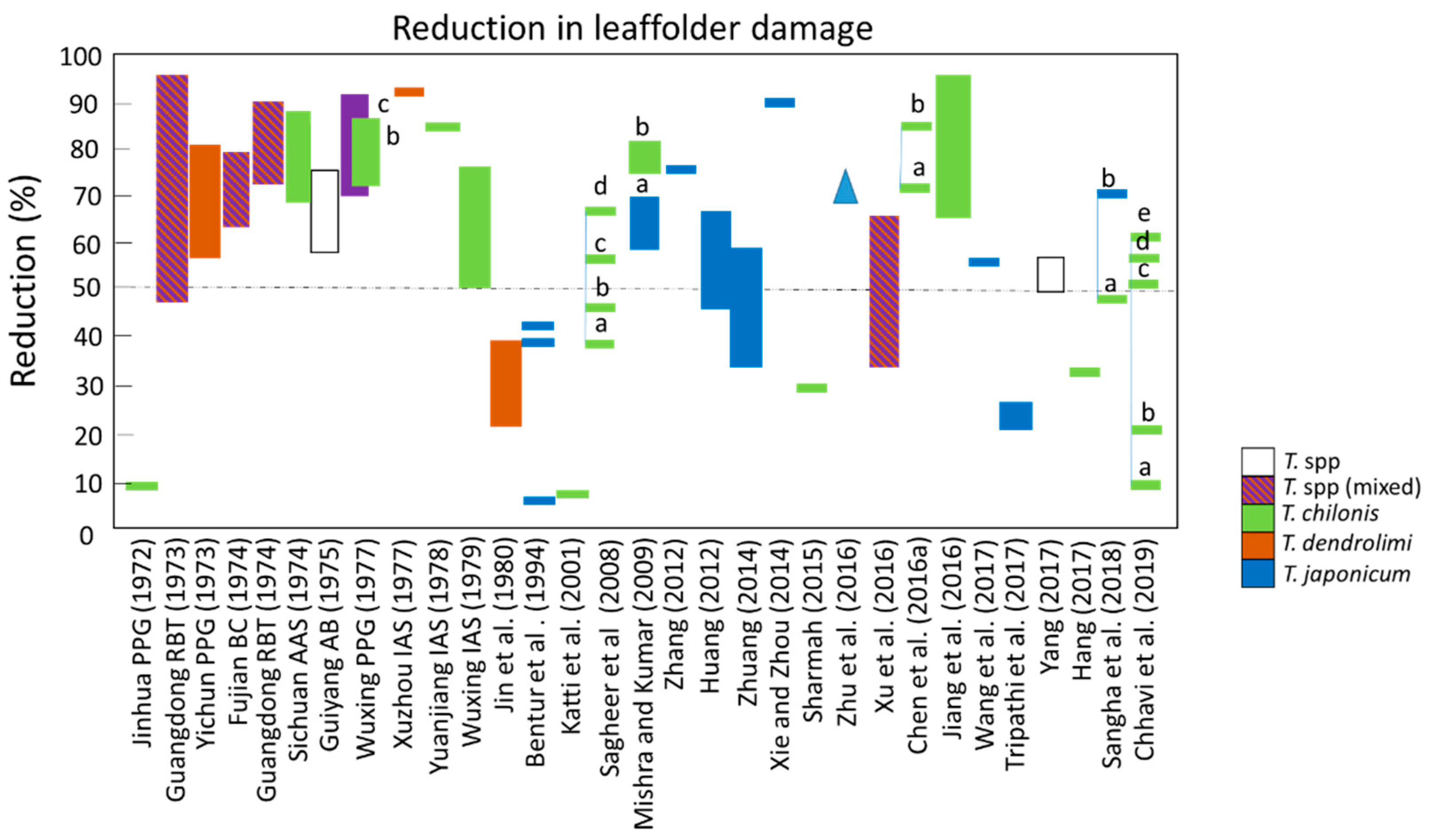
3.1.5. Damage Reductions Associated with Augmentative Biological Control
3.1.6. Comparisons between Augmentative Biocontrol and Chemical Controls
3.2. Conservation Biological Control
3.2.1. Impact of Surrounding Landscapes on Lepidoptera Pests and Trichogramma
3.2.2. Impact of Vegetation Strips on Lepidoptera Pests and Trichogramma
3.2.3. Effects of Rice Field Management on Lepidoptera Pests and Trichogramma
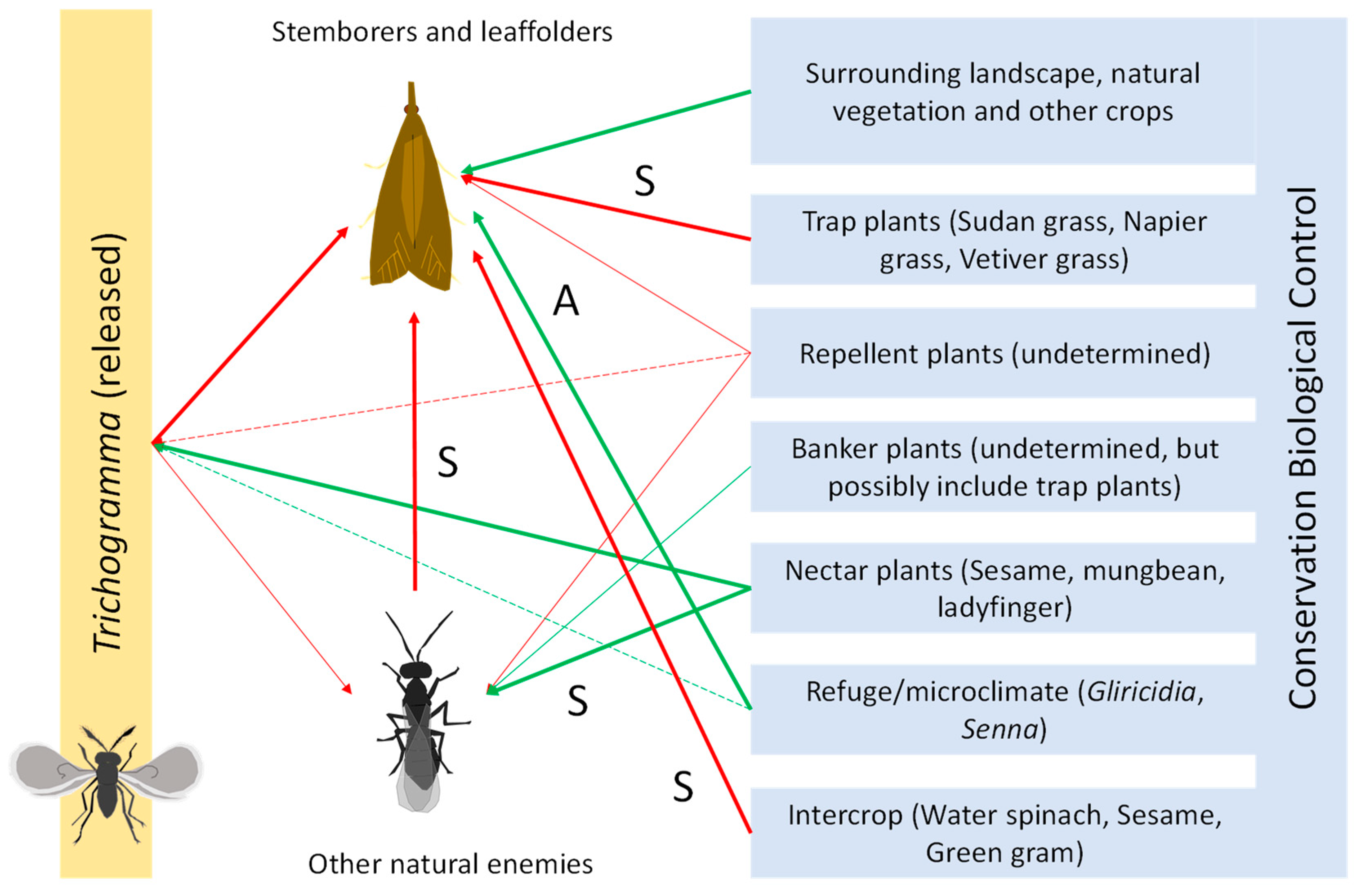
3.3. Possibilities for Combining Augmentative and Conservation Biological Control
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Muthayya, S.; Sugimoto, J.D.; Montgomery, S.; Maberly, G.F. An overview of global rice production, supply, trade, and consumption. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2014, 1324, 7–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godfray, H.C.J.; Beddington, J.R.; Crute, I.R.; Haddad, L.; Lawrence, D.; Muir, J.F.; Pretty, J.; Robinson, S.; Thomas, S.M.; Toulmin, C. Food security: The challenge of feeding 9 billion people. Science 2010, 327, 812–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Horgan, F.G.; Crisol, E. Hybrid rice and insect herbivores in Asia. Entomol. Exp. Et Appl. 2013, 148, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laborte, A.G.; de Bie, K.; Smaling, E.M.A.; Moya, P.F.; Boling, A.A.; Van Ittersum, M.K. Rice yields and yield gaps in Southeast Asia: Past trends and future outlook. Eur. J. Agron. 2012, 36, 9–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, W. Changes in rice yields in China since 1980 associated with cultivar improvement, climate and crop management. Field Crops Res. 2012, 136, 65–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stuart, A.M.; Pame, A.R.P.; Silva, J.V.; Dikitanan, R.C.; Rutsaert, P.; Malabayabas, A.J.B.; Lampayan, R.M.; Radanielson, A.M.; Singleton, G.R. Yield gaps in rice-based farming systems: Insights from local studies and prospects for future analysis. Field Crops Res. 2016, 194, 43–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Horgan, F.G. Insect herbivores of rice: Their natural regulation and ecologically based management. In Rice Production Worldwide; Chauhan, B.S., Shivay, Y.S., Kumar, D., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 279–302. [Google Scholar]
- Matteson, P.C. Insect pest management in tropical Asian irrigated rice. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2000, 45, 549–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horgan, F.G.; Romena, A.M.; Bernal, C.C.; Almazan, M.L.P.; Ramal, A.F. Stem borers revisited: Host resistance, tolerance, and vulnerability determine levels of field damage from a complex of Asian rice stemborers. Crop Prot. 2021, 142, 105513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubia, E.; Shepard, B.; Yambao, E.; Ingram, K.; Arida, G.; Penning, D.V. Stem borer damage and grain yield of flooded rice. J. Plant Prot. Trop. 1989, 6, 205–211. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, X.; Chang, C.; Dai, S.-M. Responses of striped stem borer, Chilo suppressalis (Lepidoptera:Pyralidae), from Taiwan to a range of insecticides. Pest Manag. Sci. 2010, 66, 762–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.; Ge, L.; Liu, F.; Song, Q.; Stanley, D. Pesticide-induced planthopper population resurgence in rice cropping systems. Annu. Rev. Entomol 2020, 65, 409–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, D.; Lü, L.; He, Y.; Shi, Q.; Wang, G. Effects of insecticides on oviposition and host discrimination behavior in Trichogramma chilonis (Hymenoptera:Trichogrammatidae). J. Econ. Entomol. 2016, 109, 2380–2387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pingali, P.L.; Roger, P.A. Impact Of Pesticides On Farmer Health And The Rice Environment; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012; Volume 7. [Google Scholar]
- Jensen, H.K.; Konradsen, F.; Jørs, E.; Petersen, J.H.; Dalsgaard, A. Pesticide use and self-reported symptoms of acute pesticide poisoning among aquatic armers in Phnom Penh, Cambodia. J. Toxicol. 2011, 2011, 639814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Snelder, D.; Masipiqueña, M.; De Snoo, G. Risk assessment of pesticide usage by smallholder farmers in the Cagayan Valley (Philippines). Crop Prot. 2008, 27, 747–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sapbamrer, R.; Nata, S. Health symptoms related to pesticide exposure and agricultural tasks among rice farmers from northern Thailand. Environ. Health Prev. Med. 2014, 19, 12–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Luo, Y.F.; Fu, H.L.; Traore, S. Biodiversity conservation in rice paddies in China: Toward ecological sustainability. Sustainability 2014, 6, 6107–6124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chantarasa-ard, S.; Hirashima, Y.; Miura, T. Ecological studies on Anagrus incarnatus Haliday (Hymenoptera:Mymaridae), an egg parasitoid of the rice planthoppers: II. Spatial distribution of parasitism and host eggs in the paddy field. J. Fac. Agric. Kyushu Univ. 1984, 29, 67–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Litsinger, J.A.; Alviola, A.L.; Dela Cruz, C.G.; Canapi, B.L.; Batay-An, E.H.; Barrion, A.T. Rice white stemborer Scirpophaga innotata (Walker) in southern Mindanao, Philippines. II. Synchrony of planting and natural enemies. Int. J. Pest Manag. 2006, 52, 23–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horgan, F.G.; Ramal, A.F.; Villegas, J.M.; Jamoralin, A.; Bernal, C.C.; Perez, M.O.; Pasang, J.M.; Naredo, A.I.; Almazan, M.L.P. Effects of bund crops and insecticide treatments on arthropod diversity and herbivore regulation in tropical rice fields. J. Appl. Entomol. 2017, 141, 587–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Kraker, J.; van Huis, A.; Heong, K.L.; van Lenteren, J.C.; Rabbinge, R. Population dynamics of rice leaffolders (Lepidoptera:Pyralidae) and their natural enemies in irrigated rice in the Philippines. Bull. Entomol. Res. 1999, 89, 411–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kenmore, P.E.; Perez, C.; Dyck, V.; Gutierrez, A. Population regulation of the rice brown planthopper (Nilaparvata lugens Stål) within rice fields in the Philippines. J. Plant Prot. Trop. 1984, 1, 19–37. [Google Scholar]
- Bottrell, D.G.; Schoenly, K.G. Resurrecting the ghost of green revolutions past: The brown planthopper as a recurring threat to high-yielding rice production in tropical Asia. J. Asia-Pac. Entomol. 2012, 15, 122–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horgan, F.G.; Peñalver-Cruz, A. Compatibility of insecticides with rice resistance to planthoppers as influenced by the timing and frequency of applications. Insects 2022, 13, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horgan, F.G.; Peñalver-Cruz, A.; Almazan, M.L.P. Rice resistance buffers against the induced enhancement of brown planthopper fitness by some insecticides. Crops 2021, 1, 166–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babendreier, D.; Hou, M.; Tang, R.; Zhang, F.; Vongsabouth, T.; Win, K.K.; Kang, M.; Peng, H.; Song, K.; Annamalai, S.; et al. Biological control of lepidopteran pests in rice: A multi-nation case study from Asia. J. Integr. Pest Manag. 2020, 11, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babendreier, D.; Wan, M.; Tang, R.; Gu, R.; Tambo, J.; Liu, Z.; Grossrieder, M.; Kansiime, M.; Wood, A.; Zhang, F.; et al. Impact assessment of biological control-based integrated pest management in rice and maize in the Greater Mekong Subregion. Insects 2019, 10, 226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zang, L.-S.; Wang, S.; Zhang, F.; Desneux, N. Biological control with Trichogramma in China: History, present status, and perspectives. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2021, 66, 463–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, M.P.; Bari, M.N.; Haque, S.S.; Kabir, M.M.M.; Afrin, S.; Nowrin, F.; Islam, M.S.; Landis, D.A. Establishing next-generation pest control services in rice fields: Eco-agriculture. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 10180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gurr, G.M.; Read, D.M.Y.; Catindig, J.L.A.; Cheng, J.A.; Liu, J.; Lan, L.P.; Heong, K.L. Parasitoids of the rice leaffolder Cnaphalocrocis medinalis and prospects for enhancing biological control with nectar plants. Agric. For. Entomol. 2012, 14, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horgan, F.G.; Ramal, A.F.; Bernal, C.C.; Villegas, J.M.; Stuart, A.M.; Almazan, M.L.P. Applying ecological engineering for sustainable and resilient rice production systems. Procedia Food Sci. 2016, 6, 7–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gurr, G.M.; Lu, Z.; Zheng, X.; Xu, H.; Zhu, P.; Chen, G.; Yao, X.; Cheng, J.; Zhu, Z.; Catindig, J.L.; et al. Multi-country evidence that crop diversification promotes ecological intensification of agriculture. Nat. Plants 2016, 2, 16014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horgan, F.G.; Vu, Q.; Mundaca, E.A.; Crisol-Martínez, E. Restoration of rice ecosystem services: ‘ecological engineering for pest management’ incentives and practices in the Mekong Delta Region of Vietnam. Agronomy 2022, 12, 1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, P.; Zheng, X.; Zhang, F.; Xu, H.; Yang, Y.; Chen, G.; Lu, Z.; Johnson, A.C.; Gurr, G.M. Quantifying the respective and additive effects of nectar plant crop borders and withholding insecticides on biological control of pests in subtropical rice. J. Pest Sci. 2018, 91, 575–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horgan, F.G. Integrating gene deployment and crop management for improved rice resistance to Asian planthoppers. Crop Prot. 2018, 110, 21–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peñalver-Cruz, A.; Horgan, F.G. Interactions between rice resistance to planthoppers and honeydew-related egg parasitism under varying levels of nitrogenous fertilizer. Insects 2022, 13, 251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, P.; Zheng, X.; Johnson, A.C.; Chen, G.; Xu, H.; Zhang, F.; Yao, X.; Heong, K.; Lu, Z.; Gurr, G.M. Ecological engineering for rice pest suppression in China. A review. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2022, 42, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherif, A.; Mansour, R.; Grissa-Lebdi, K. The egg parasitoids Trichogramma: From laboratory mass rearing to biological control of lepidopteran pests. Biocontrol Sci. Technol. 2021, 31, 661–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenberg, S.M.; Morrison, R.K.; Nordlund, D.A.; King, E.G. A review of the scientific literature and methods for production of factitious hosts for use in mass rearing of Trichogramma spp. (Hymenoptera:Trichogrammatidae) in the former Soviet Union, the United States, Western Europe and China. J. Entomol. Sci. 1998, 33, 15–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, M.; Yang, H.; Yang, S.; Lui, D. Review on control of rice leaf roller by Trichogramma and bacteria. South Agric. Bull. 1980, 28–32. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, S.M. Biological control with Trichogramma: Advances, successes, and potential of their use. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 1996, 41, 375–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Consoli, F.L.; Parra, J.R.; Zucchi, R.A. Egg Parasitoids in Agroecosystems with Emphasis on Trichogramma; Springer Science and Business Media: Cham, Switzerland, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.H.; Wu, C.X.; Cang, T.; Yang, L.Z.; Yu, W.H.; Zhao, X.P.; Wang, Q.; Cai, L.M. Toxicity risk of insecticides to the insect egg parasitoid Trichogramma evanescens Westwood (Hymenoptera:Trichogrammatidae). Pest Manag. Sci. 2014, 70, 398–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Lenteren, J.C.; Bolckmans, K.; Köhl, J.; Ravensberg, W.J.; Urbaneja, A. Biological control using invertebrates and microorganisms: Plenty of new opportunities. BioControl 2018, 63, 39–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Z.-Y.; He, K.-L.; Zhao, J.-Z.; Zhao, D.-R. Integrated pest management in China. In Integrated Pest Management in the Global Arena; Maredia, M., Dakouo, D., Mota-Sanchez, D., Eds.; CABI Publishing: Wallingford, UK, 2003; pp. 197–208. [Google Scholar]
- Nickel, J.L. Biological control of rice stem borers: A feasibility study. Int. Rice Res. Inst. Tech. Bull. 1964, 2, 112. [Google Scholar]
- Iyatomi, K. Parasitism of eggs of Chilo suppressalis by Trichogramma japonicum. In Proceedings of the Tenth International Congress Entomology, Montreal, QC, Canada, 17–25 August 1956; pp. 897–899. [Google Scholar]
- Afifah, L.; Bayfurqon, F.M.; Siriyah, S.L. Control of rice stem borer Scirpophaga sp. using Trichogramma sp. J. Pengabdi. Kpd. Masy. 2019, 5, 99–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabudlong, B.M.; Estoy, G.F., Jr. Field validation of egg parasitoid, Trichogramma japonicum Ashmead, against white rice stemborer, Scirpophaga innotata Walker, in Agusan del Norte [Philippines]. Philipp. Entomol. 2014, 28, 210. [Google Scholar]
- Perex, M.; Cadapan, E. The efficacy of Trichogramma species as biological control agents against some rice insect pests. Philipp. Entomol. 1986, 6, 463–470. [Google Scholar]
- Oskoo, H. Effects of rearing conditions on efficacy of Trichogramma maidis against rice stem borer (Chilo suppressalis) and green rice semilooper (Naranga aenescens) in Mazandaran, Iran. In Proceedings of the 11th Plant Protection Congress of Iran, Rasht, Iran, 28 August–2 September 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Polaszek, A.; Rabbi, M.F.; Islam, Z.; Buckley, Y.M. Trichogramma zahiri (Hymenoptera: Trichogrammatidae) an egg parasitoid of the rice hispa Dicladispa armigera (Coleoptera: Chrysomelidae) in Bangladesh. Bull. Entomol. Res. 2007, 92, 529–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bari, M.N.; Jahan, M.; Islam, K.S.; Ali, M.P. Host egg age and supplementary diet influence the parasitism activity of Trichogramma zahiri (Hymenoptera: Trichogrammatidae). J. Econ. Entomol. 2016, 109, 1102–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horgan, F.G.; Romena, A.M.; Bernal, C.C.; Almazan, M.L.P.; Ramal, A.F. Differences between the strength of preference–performance coupling in two rice stemborers (Lepidoptera: Pyralidae, Crambidae) promotes coexistence at field-plot scales. Environ. Entomol. 2021, 50, 929–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandi, V.; Babu, P.C.S.; Kailasam, C. Prediction of damage and yield loss caused by rice leaffolder at different crop periods in a susceptible rice cultivar (IR 50). J. Appl. Entomol. 1998, 122, 595–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Litsinger, J.A.; Bandong, J.P.; Canapi, B.L.; Dela Cruz, C.G.; Pantua, P.C.; Alviola, A.L.; Batay-An, E.H. Evaluation of action thresholds for chronic rice insect pests in the Philippines. III. Leaffolders. Int. J. Pest Manag. 2006, 52, 181–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripathi, P.P.; Anup, C.; Asha, S. Suppression of dead-heart and folded leaf symptoms in paddy by Trichogramma japonicum Ashmead in Seppa area of Arunachal Pradesh, India. Environ. Ecol. 2017, 35, 1297–1299. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, S.; Shera, P.; Sangha, K. Impact of bio-intensive integrated pest management practices on insect pests and grain yield in basmati rice. J. Biol. Control 2018, 32, 137–141. [Google Scholar]
- Sangha, K.S.; Shera, P.S.; Sharma, S.; Kaur, R. On-farm impact of egg parasitoid, Trichogramma spp. against lepidopteran pests in organic basmati rice. J. Biol. Control 2018, 32, 116–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jinhua Plant Protection Group. Briefing on experiments using Trichogramma for control of rice leaf roller. Technol. Brief. 1972, 9–11. [Google Scholar]
- Wuxing Plant Protection Group. Several technical issues on Trichogramma release for rice leaf roller. Technol. Today 1977, 26–31. [Google Scholar]
- Wuxing Institute of Agricultural Sciences. Control of rice leaf roller with Trichogramma during 1977. Nat. Enemies Insects 1979, 51–55. [Google Scholar]
- Jinhua Institute of Agricultural Sciences. Discussion on release technology of Trichogramma confusum Viggiani for control of rice leaf roller. Entomol. Knowl. 1979, 11–13. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, L.; Zhao, L.; Liu, G.; Zhang, X.; Li, J.; Xu, Y.; Chen, Y. Effects of species and release density of Trichogramma on control effects to rice leaf roller. China Plant Prot. 2016, 8, 37–40. [Google Scholar]
- Guangdong Rice Biocontrol Team. Using of Trichogramma for control of rice leaf roller. Chin. Sci. Bull. 1973, 232. [Google Scholar]
- Guangdong Rice Biocontrol Team. Utilization of Trichogramma for control of rice leaf roller. Acta Entomol. Sin. 1974, 269–280. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, M. Discrimination of Trichogramma japonicum and other species of Trichogramma for hosts and competition among them. Nat. Enemies Insects 1985, 7, 192–200. [Google Scholar]
- Yichun Plant Protection Group. Field trials on control of rice leaf roller with Trichogramma. Jiangxi Agric. Technol. 1973, 9–19. [Google Scholar]
- Fujian Biocontrol Group. Experiments on pest control with Trichogramma. Fujian Agric. Technol. 1974, 27–33. [Google Scholar]
- Zhuang, J. Effects of Trichogramma on rice leaf roller. Gubei Plant Prot. 2014, 21–22. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, R. Controlling rice leaf roller by artificial release Trichogramma. Fujian Sci. Technol. Rice Wheat 2012, 30, 53–54. [Google Scholar]
- Sichuan Academy of Agricultural Sciences. Briefing on control of rice leaf roller with Trichogramma chilonis. Sichuan Agric. Technol. 1974, 31–36. [Google Scholar]
- Guiyang Agricultural Bureau. Effects on control of rice stem borer with Trichogramma. Entomol. Knowl. 1975, 14–16. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, S.; Zhou, W. Effects of Trichogramma japonicum on rice leaf roller. Agric. Techonol. 2014, 106. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, G.; Wen, J.; Li, W.; Fang, B.; Liu, Y.; Xia, C.; Liu, G. Evaluation of control effect of Trichogramma japonicum against Cnaphalocrocis medinalis and Chilo suppressalis. Acta Agric. Jiangxi 2012, 24, 37–40. [Google Scholar]
- Xuzhou Institute of Agricultural Sciences. Experiments on application of Trichogramma for controlling rice leaf roller. Entomol. Knowl. 1977, 5. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, L. Effects of sex pheromone and Trichogramma for rice borer. Shanghai Agric. Technol. 2017, 4, 130–131. [Google Scholar]
- Yuanjiang Institute of Agricultural Sciences. Experiments on control of rice leaf roller with Trichogramma Yunnan. Agric. Technol. 1972, 2, 18–20.
- Shen, X.C.; Wang, K.Z.; Meng, G. The inoculative release of Trichogramma dendrolimi for controlling corn borer and rice leafroller. Colloq. De L’inra 1988, 43, 575–580. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, B.; Zhang, W.; Yang, W.; Jiang, Q.; Huang, C.; Zhou, G.; Huang, X. Experiment on release of Trichogramma for control of rice leaf roller in organic rice fields. Guangxi Plant Prot. 2016, 29, 5–7. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.; Lin, C.; Xie, Y.; Qin, B.; Wang, H. Experiment on rice leaf folder control by releasing Trichogramma chilonis J. Guangxi Agric. 2016, 31, 15–17. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, Q.; Zhang, W.; Peng, H.; Chen, B.; Huang, C.; Huang, X.; Zhou, G. Study on release technology for Trichogramma chilonis against rice leaf roller. Guangxi Plant Prot. 2016, 29, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, X.; Ouyang, C.; He, J.; Fang, T. Briefing on demonstration of Trichogramma release for control of rice leaf roller. China Agric. Inform. 2016, 8, 110–111. [Google Scholar]
- Hang, D. Study on control effects of different release strategy for Trichogramma on rice stem borer and leaf roller. Anhui Agric. Sci. Bull. 2017, 23, 64–66. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, R.; Xiao, W.; Shao, C.; Wei, Q.; Qin, A.; Yang, R. Research on application of manually released Trichogramma for control of rice leaf roller. China Plant Prot. 2017, 37, 46–48. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, C.C.; Chiu, S.C. Studies on the field releases of Trichogramma chilonis and the factors affecting its activity. J. Agric. Res. China 1986, 35, 99–106. [Google Scholar]
- Bentur, J.S.; Kalode, M.B.; Rajendran, B.; Patel, V.S. Field evaluation of the egg parasitoid, Trichogramma japonicum Ash. (Hym., Trichogrammatidae) against the rice leaf folder, Cnaphalocrocis medinalis (Guen.) (Lep., Pyralidae) in India. J. Appl. Entomol. 1994, 117, 257–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katti, G.; Pasalu, I.C.; Varma, N.R.G.; Krishnaiah, K. Integration of pheromone mass trapping and biological control for management of yellow stem borer and leaf folder in rice. Indian J. Entomol. 2001, 63, 325–328. [Google Scholar]
- Sehrawat, S.; Lal, R.; Dahiya, K. Efficacy of different insecticides and Trichogramma chilonis Ishii in managing rice leaffolder, Cnaphalocrocis medinalis Guenee. Pestic. Res. J. 2002, 14, 153–157. [Google Scholar]
- Garg, D.K.; Kumar, P.; Singh, R.N.; Pathak, M. Role of parasitoid Trichogramma japonicum and other natural enemies in the management of yellow stem borer and leaf folder in basmati rice. Indian J. Entomol. 2002, 64, 117–123. [Google Scholar]
- Mishra, D.; Kamlesh, K. Field efficacy of bio-agent Trichogramma spp. against stem borer and leaf folder in rice crop under mid-western plain zone of UP. Environ. Ecol. 2009, 27, 1885–1887. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, S.; Prasad, C.S.; Nath, L.; Tiwari, G.N. Eco-friendly management of Scirpophaga incertulas (Walk.) and Cnaphalocrocis medinalis (Guen.) in Basmati rice. Ann. Plant Prot. Sci. 2008, 16, 11–16. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, S.; Khan, M. Bio-efficacy of Trichogramma spp. against yellow stem borer and leaf folder in rice ecosystem. Ann. Plant Prot. Sci. 2005, 13, 97–99. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, S.; Maurya, R.P.; Khan, M.A. Impact of biointensive pest management strategies on yellow stem borer and leaf folder in rice and their effect on the economics of production. J. Entomol. Res. 2007, 31, 11–13. [Google Scholar]
- Bade, B.; Pokharkar, D.; Ghorpade, S. Evaluation of trichogrammatids for the management of stem borer and leaf folder infesting paddy. J.-Maharashtra Agric. Univ. 2006, 31, 308. [Google Scholar]
- Usha Rani, P.; Indu Kumari, S.; Sriramakrishna, T.; Ratna Sudhakar, T. Kairomones extracted from rice yellow stem borer and their influence on egg parasitization by Trichogramma japonicum Ashmead. J. Chem. Ecol. 2007, 33, 59–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nalini, R.; Vasanthi, A.; Saritha, K.; Shanthi, M.; Yesuraja, I.; Baskaran, R. Evaluation of rice IPDM in farmers field at Madurai. Ann. Plant Prot. Sci. 2013, 21, 199–200. [Google Scholar]
- Karthikeyan, K.; Jacob, S.; Purushothaman, S. Field evaluation of egg parasitoids, Trichogramma japonicum Ashmead and Trichogramma chilonis Ishii, against rice yellow stem borer and leaf folder. J. Biol. Control 2007, 21, 261–265. [Google Scholar]
- Karthikeyan, K.; Sosamma, J.; Pathummal, J.; Purushothaman, S.M. Evaluation of different integrated pest management modules for the management of major pests of rice (Oryza sativa). Indian J. Agric. Sci. 2010, 80, 59–62. [Google Scholar]
- Kaur, R.; Brar, K.S.; Jagmohan, S.; Maninder, S. Large-scale evaluation of bio-intensive management for leaf folder and stem borer on basmati rice. J. Biol. Contr. 2007, 21, 255–259. [Google Scholar]
- Jena, B.C.; Gupta, S.; Das, S.K. Effectiveness of integrated pest management modules in suppression of major insect pests in rice. J. Plant Prot. Environ. 2012, 9, 57–59. [Google Scholar]
- Sharmah, D. Eco-friendly management of rice leaf folder (Cnaphalocrocis medinalis) Guenee (Pyralidae:Lepidoptera) in South Tripura, India. Int. J. Phys. Appl. Sci. 2015, 2, 17–23. [Google Scholar]
- Chhavi, P.K.S.; Srivastava, A. Field efficacy of Trichogramma chilonis against rice leaf folder, Cnaphalocrocis medinalis in Kangra Valley of Himachal Pradesh. J. Entomol. Zool. Stud. 2019, 7, 600–603. [Google Scholar]
- Sagheer, M.; Ashfaq, M.; Rana, S. Integration of some biopesticides and Trichogramma chilonis for the sustainable management of rice leaf folder, Cnaphalocrocis medinalis (Guenee) (Lepidoptera:Pyralidae). Pak. J. Agric. Sci. 2008, 45, 69–74. [Google Scholar]
- Pham, B.Q.; Nguyen, V.V.; Nguyen, V.S. Utilization of Trichogramma Japonicum for control of the rice leaf folder (Cnaphalocorosis medinalis) at Van Quan Cooperative, Me Linh District, Vinh Phu Province. In Proceedings of the Trichogramma and Other Egg Parasitoids 4th International Symposium, Cairo, Egypt, 4–7 October 1995; Ed. INRA: Paris, France, 1995; Volume 73, pp. 127–129. [Google Scholar]
- Hattori, I.; Siwi, S.S. Rice stemborers in Indonesia. Jpn. Agric. Res. Q. 1986, 20, 25–30. [Google Scholar]
- Ragini, J.; Thangaraju, D.; David, P. Relative abundance of rice stem borer species in Tamil Nadu. Madras Agric. J. 2000, 87, 228–234. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, G.-H.; Luo, Z.-X.; Zhang, Z.-L.; Sun, Y.; Lu, M.-H.; Shu, Z.-L.; Tian, Z.-H.; Hoffmann, A.A.; Fang, J.-C. The response to flooding of two overwintering rice stem borers likely accounts for their changing impacts. J. Pest Sci. 2021, 94, 451–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iyatomi, K. Studies on the utilization of Trichogramma japonicum, an egg parasitoid of rice stem borer. Tech. Bull. Shizuoka Agric. Exp. Sta. 1943, 2, 1–107. [Google Scholar]
- Shibuya, M. Studies on the utilization of Trichogramma japonicum, an egg-parasite of rice stem borer. In Commemoration Issue of the 50th Anniversary of the Foundation of Shizuoka Agricultural Experiment Station; Shizouka Agricultural Experiment Station: Shizouka, Japan, 1950; pp. 12–33. [Google Scholar]
- Hang, D.; Jiao, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Yang, X.; Xia, B.; Sun, W. Control of first generation Chilo suppressalis by releasing Trichogramma confusum Viggiani in rice field. J. Agric. Catastrophol. 2011, 1, 28–30. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, C.; Wang, J.; Du, G.; Wang, B.; Lin, H.; Li, G. Demonstration on Trichogramma release against rice stem borer. Anhui Agric. Sci. Bull. 2016, 22, 70. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, B.; Li, X.; Gao, D.; Zhang, F. Research on Trichogramma chilonis for control of rice stem borer. Plant Prot. 2001, 27, 45–46. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, R.; Zheng, H.; Shi, Z.; Huang, Y.; Fan, L.; Ma, J. Trichogramma as a vector of pest control microbes against rice stem borer. J. Jilin Agric. Sci. 2007, 32, 39–40. [Google Scholar]
- Ko, K.; Liu, Y.; Hou, M.; Babendreier, D.; Zhang, F.; Song, K. Evaluation for potential Trichogramma (Hymenoptera: Trichogrammatidae) strains for control of the striped stem borer (Lepidoptera: Crambidae) in the Greater Mekong Subregion. J. Econ. Entomol. 2014, 107, 955–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si, Z.; Chen, J.; Song, X.; Gong, X.; Zhao, Y.; Zhai, H. Control effect of Trichogramma japonicum on Chilo suppressalis in rice. China Rice 2014, 20, 98–100. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, D. Application tests on controlling rice-stem borer by artificial releasing of Trichogramma in 2015. North Rice 2016, 46, 36–37. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, L.; Wang, L.; Zhao, S.; Dong, Y.; Yang, H.; Tan, K.; Hu, J. Control effect with different kinds of Trichogramma against Chilo suppressalis in Qiqihar Area. Heilongjiang Agric. Sci. 2016, 11, 67–68. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y. Effects of Trichogramma chilonis on rice stem borer. Shanghai Agric. Technol. 2015, 3, 130. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, X.; Lu, Y.; Zhong, L.; Huang, X.; Chen, H.; Yao, X.; Lv, Z. Practice on green technology for striped stem borer control in Zhejiang rice fields. China Plant Prot. 2017, 37, 42–45. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, D.; Ma, X. Evaluation of Trichogramma on rice stem borer. Jiangsu Agric. Sci. 2015, 43, 113–115. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, M.; Zhao, J.; Gu, Z. Effects of Trichogramma on rice stem borers in Mangshi Dehong. Yunnan Agric. Sci. Technol. 2015, 5, 54–55. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, R.; Babendreier, D.; Zhang, F.; Kang, M.; Song, K.; Hou, M.-L. Assessment of Trichogramma japonicum and T. chilonis as potential biological control agents of yellow stem borer in rice. Insects 2017, 8, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kumar, A.; Lal, M.N.; Prasad, C.S. Effect of treatments on yield and economics of paddy cultivation against yellow stem borer, Scirpophaga incertulas (Walker). Ann. Plant Prot. Sci. 2011, 19, 37–40. [Google Scholar]
- Pandey, S.; Choubey, M. Management of yellow stem borer, Scirpophaga incertulas in rice. Agric. Sci. Dig. 2012, 32, 7–12. [Google Scholar]
- Visalakshmi, V.; Rao, P.M.; Satyanarayna, N. Evaluation of pest management modules in kharif rice. J. Crop Weed 2013, 9, 165–167. [Google Scholar]
- Shirke, M.S.; Bade, B.A. Efficacy of Trichogramma japonicum against paddy stem borer. J. Maharashtra Agric. Univers. 1997, 22, 338–339. [Google Scholar]
- Beevi, S.P.; Lyla, K.R.; Karthikeyan, K. Biological Control of Lepidopteran Pests. In Proceedings of the Symposium of Biological Control of Lepidopteran Pests, Bangalore, India, 17–18 July 2002; Tandon, P.L., Ballal, C.R., Jalali, S.K., Rabindra, R.J., Eds.; 2003; pp. 329–332. [Google Scholar]
- Kaur, R.; Brar, K. Evaluation of different doses of Trichogramma species for the management of leaf folder and stem borer on Basmati rice. J. Biol. Control 2008, 22, 131–135. [Google Scholar]
- Lyla, K.; Beevi, S.P.; Babu, M.P.; Jalali, S. Biological control of rice pests in ‘kole’ lands of Kerala. J. Biol. Control 2010, 24, 268–270. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, D.; Singh, A.K.; Kumar, A. On-farm evaluation of integrated management of rice yellow stem borer (Scirpophaga incertulas Walk.) in rice-wheat cropping system under low land condition. J. AgriSearch 2014, 1, 40–44. [Google Scholar]
- Mahal, M.; Kajal, V.; Kaur, R.; Singh, R. Integration of chemical and biocontrol approaches for the management of leaffolder, Cnaphalocrocis medinalis Guenee and stem borer, Scirpophaga incertulas Walker on basmati rice. J. Biol. Control 2006, 20, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Aggarwal, N.; Sharma, S.; Jalali, S. On-farm impact of biocontrol technology against rice stem borer, Scircophaga incertulas (Walker) and rice leaf folder Cnaphalocrocis medinalis (Guenee) in aromatic rice. Entomol. Gen. 2016, 36, 137–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shenhmar, M.; Varma, G.C. Field evaluation of Trichogramma japonicum Ashmed against rice stem borer Scirpophaga incertulas Walker. J. Biol. Control 1995, 9, 7633. [Google Scholar]
- Basana, G.G.; Pandi, G.G.P.; Ullah, F.; Patil, N.B.; Sahu, M.; Adak, T.; Pokhare, S.; Yadav, M.K.; Mahendiran, A.; Mittapelly, P.; et al. Performance of Trichogramma japonicum under field conditions as a function of the factitious host species used for mass rearing. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0256246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borah, R.K. Parasitization efficacy of Trichogramma japonicum on rice stem borer in Assam. Ann. Agric. Res. 1994, 15, 124–125. [Google Scholar]
- Upamanya, G.; Dutta, P.; Sarma, R.; Sarmah, A.; Kalita, N.; Sarma, H. Biological management of rice stem borer in the farmer’s field of Assam. Insect Environ. 2013, 19, 73–76. [Google Scholar]
- Mohanraj, P.; Veenakumari, K.; Mandal, A. Biocontrol of the yellow stem borer using Trichogramma—A parasitoid native to the Andamans. Rice Biotechnol. 1995, 23, 9–10. [Google Scholar]
- Shikari, D. Studies on Bio-Intensive Management of Rice Yellow Stem Borer (Scirpophaga incertulas Walk.) and Rice Leaf Folder (Cnaphalocrocis medinalis Guen.) in Rain Fed Rice Growing Areas of West Bengal. Ph.D. Thesis, Bidhan Chandra Agricultural University, West Bengal, India, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Syarief, M.; Erdiyansyah, I. Augmentation Model of Trichogramma japonicum for Yellow Rice Stem Borer (Schirpophaga incertulas Waker) Control on Organic Rice Cultivation. In Proceedings of the 1st international conference on food and agriculture, Bali, Indonesia, 20–21 October 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Astrodjojo, S.; Sudjud, S.; DAS, S.S. Effectiveness test of parasitization by parasitoid Tricogramma japonicum in controlling white rice stem borer (Scirphopaga innotata). Int. J. Food Agric. Nat. Resour. 2021, 2, 25–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metwally, M.M.; Serag El-Dien, F.S. Parasitism and biology of the egg parasitoid, Trichogramma evanescens Westw. in relation to various host insects at Kafr El-Sheike Region J. Plant Prot. Pathol. 2009, 34, 3905–3911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Habashy, M.M.; El-Shafey, R.A.S.; Anis, G.B.; Hammoud, S.A.A. Yield potential of novel rice genotypes and effect of Trichogramma release and blas resistance on rice productivity. J. Plant Prot. Pathol. 2015, 6, 1381–1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shawer, M.B.; El-Agamy, F.M.; Hendawy, A.S.; Refaei, E.A. Effect of Trichogramma evanescens West. Release in rice stem borer control. J. Plant Prot. Pathol. 2013, 4, 261–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hendawy, A.S.; Sherif, M.R.; El-Sayed, A.A.; Omar, A.M.; Taha, A.S. Role of the egg parasitoid, Trichogramma evanescens West., release and silica applications in controlling of the stem borer, Chilo agamemnon Bles. (Lepidoptera: Crambidae), in rice fields in Egypt. Egypt. J. Biol. Pest Control 2018, 28, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Habashy, M.M. Appropriate dates of Trichogramma evanescens (West.) release to control rice stem borer, and effect of sprayed chemicals on parasitoid survival. J. Plant Prot. Pathol. 2009, 34, 2269–2278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majidi-Shilsar, F. Evaluation releasing of parasitoid wasp Trichogramma brassicae with other methods for the control of rice striped stem borer (Chilo suppressalis) in field conditions. Plant Pests Res. 2017, 7, 67–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimian, Z.; Majidi, F.; Asadi, H. Investigation on determining the best time of releasing Trichogramma maidis to control Chilo suppressalis in rice fields in Guilan. In Proceedings of the 12th Iranian Plant Protection Congress, Karadj, Iran, 2–7 September 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Rahimoon, M.Y.; Lanjar, A.G.; Bukero, A.; Chang, B.H.; Hajano, J.-U.D.; McNeill, M.R.; Rajput, A.; Lanjar, Z. Trichogramma chilonis, an effective egg parasitoid for control of white stem borer Scirpophaga innotata (Walker), (Lepidoptera:Pyralidae) in rice. Abasyn J. Life Sci. 2021, 4, 51–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maung, K.L.; Latt, Z.K.; Htun, P.W.; Myint, M.; Khai, A.A. Rice stem borer distributions and their native parasitoids rearing on the host eggs, Corcyra cephalonica in Mandalay region, Myanmar. Asian J. Res. 2020, 4–6, 13–21. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.-X.; Zheng, L.; Shen, Z. Using internally transcribed spacer 2 sequences to re-examine the taxonomic status of several cryptic species of Trichogramma (Hymenoptera: Trichogrammatidae). Eur. J. Entomol. 2004, 101, 347–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Singh, P.; Prasad, G. Seasonal parasitism of Trichogramma japonicum in South Andamans. Insect Environ. 2002, 8, 139–140. [Google Scholar]
- Sherif, M.R.; Hendawy, A.S.; El-Habashy, M.M. Utilization of Trichogramma evanescens (Ashmead) for controlling rice stem borer, Chilo agamemnon Bles. in rice fields in Egypt. Egypt. J. Biol. Pest Control 2008, 18, 11–16. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, F.; Babendreier, D.; Wang, Z.Y.; Il, K.S.; Zheng, L.; Pyon, Y.C.; Bai, S.X.; Song, K.; Ri, J.O.; Grossrieder, M.; et al. Mass releases of Trichogramma ostriniae increase maize production in DPR Korea. J. Appl. Entomol. 2010, 134, 481–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wyckhuys, K.A.G.; Lu, Y.; Morales, H.; Vazquez, L.L.; Legaspi, J.C.; Eliopoulos, P.A.; Hernandez, L.M. Current status and potential of conservation biological control for agriculture in the developing world. Biol. Control 2013, 65, 152–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jonsson, M.; Wratten, S.D.; Landis, D.A.; Gurr, G.M. Recent advances in conservation biological control of arthropods by arthropods. Biol. Control 2008, 45, 172–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Betz, L.; Tscharntke, T. Enhancing spider families and spider webs in Indian rice fields for conservation biological control, considering local and landscape management. J. Insect Conserv. 2017, 21, 495–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sann, C.; Theodorou, P.; Heong, K.L.; Villareal, S.; Settele, J.; Vidal, S.; Westphal, C. Hopper parasitoids do not significantly benefit from non-crop habitats in rice production landscapes. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2018, 254, 224–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horgan, F.G. Integrated pest management for sustainable rice cultivation: A holistic approach. In Achieving Sustainable Cultivation of Rice; Sasaki, T., Ed.; Burleigh-Dodds Science Publishing: Cambridge, UK, 2017; pp. 309–342. [Google Scholar]
- Westphal, C.; Vidal, S.; Horgan, F.G.; Gurr, G.M.; Escalada, M.; Van Chien, H.; Tscharntke, T.; Heong, K.L.; Settele, J. Promoting multiple ecosystem services with flower strips and participatory approaches in rice production landscapes. Basic Appl. Ecol. 2015, 16, 681–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horgan, F.G.; Kudavidanage, E.P. Translating research into wildlife conservation actions through multi-sector collaboration in tropical Asia. In Closing the Knowledge-Implementation Gap in Conservation Science: Interdisciplinary Evidence Transfer across Sectors and Spatiotemporal Scales; Ferreira, C.C., Klütsch, C.F.C., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; pp. 371–411. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, P.Y.; Wang, G.W.; Zheng, X.S.; Tian, J.C.; Lu, Z.X.; Heong, K.L.; Xu, H.X.; Chen, G.H.; Yang, Y.J.; Gurr, G.M. Selective enhancement of parasitoids of rice Lepidoptera pests by sesame (Sesamum indicum) flowers. Biocontrol 2015, 60, 157–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, P.Y.; Gurr, G.M.; Lu, Z.X.; Heong, K.; Chen, G.H.; Zheng, X.S.; Xu, H.X.; Yang, Y.J. Laboratory screening supports the selection of sesame (Sesamum indicum) to enhance Anagrus spp. parasitoids (Hymenoptera: Mymaridae) of rice planthoppers. Biol. Control 2013, 64, 83–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horgan, F.G.; Martinez, E.C.; Stuart, A.M.; Bernal, C.C.; Martin, E.D.; Almazan, M.L.P.; Ramal, A.F. Effects of vegetation strips, fertilizer levels and varietal resistance on the integrated management of arthropod biodiversity in a tropical rice ecosystem. Insects 2019, 10, 328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhu, P.Y.; Lu, Z.X.; Heong, K.; Chen, G.H.; Zheng, X.S.; Xu, H.X.; Yang, Y.J.; Nicol, H.I.; Gurr, G.M. Selection of nectar plants for use in ecological engineering to promote biological control of rice pests by the predatory bug, Cyrtorhinus lividipennis, (Heteroptera: Miridae). PLoS ONE 2014, 9, 0108669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sattler, C.; Schrader, J.; Flor, R.J.; Keo, M.; Chhun, S.; Choun, S.; Hadi, B.A.R.; Settele, J. Reducing pesticides and increasing crop diversification offer ecological and economic benefits for farmers-A case study in Cambodian rice fields. Insects 2021, 12, 267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balogbog, K.J. Indigenous knowledge system of the upland rice farmers in Sarangani Province and General Santos City, Philippines. Available online: https://papers.ssrn.com/sol3/papers.cfm?abstract_id=3683315 (accessed on 15 July 2022).
- Chouichom, S.; Yamao, M. Organic rice farming in northeastern Thailand: An assessment of farmers’ practices. Philipp. Sci. 2012, 49, 44–67. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, X.-s.; Xu, H.-x.; Chen, G.-h.; Lü, Z.-x. Potential function of Sudan grass and vetiver grass as trap crops for suppressing population of stripped stem borer, Chilo suppressalis in rice. Chin. J. Biol. Control 2009, 25, 299. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, Y.H.; Zheng, X.S.; Lu, Z.X. Application of vetiver grass Vetiveria zizanioides: Poaceae (L.) as a trap plant for rice stem borer Chilo suppressalis: Crambidae (Walker) in the paddy fields. J. Integr. Agric. 2019, 18, 797–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Khan, Z.R.; Midega, C.A.O.; Hutter, N.J.; Wilkins, R.M.; Wadhams, L.J. Assessment of the potential of Napier grass (Pennisetum purpureum) varieties as trap plants for management of Chilo partellus. Entomol. Exp. Et Appl. 2006, 119, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van den Berg, J. Vetiver grass (Vetiveria zizanioides (L.) Nash) as trap plant for Chilo partellus (Swinhoe) (Lepidoptera:Pyralidae) and Busseola fusca (Fuller) (Lepidoptera:Noctuidae). Ann. De La Soc. Entomol. De Fr. 2006, 42, 449–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.-h.; Liu, K.; Zheng, X.-s.; Lü, Z.-x. Electrophysiological responses of the rice striped stem borer Chilo suppressalis to volatiles of the trap plant vetiver grass (Vetiveria zizanioides L.). J. Integr. Agric. 2017, 16, 2525–2533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, H.-X.; Zheng, X.-S.; Yang, Y.-J.; Tian, J.-C.; Lu, Y.-H.; Tan, K.-H.; Heong, K.-L.; Lu, Z.-X. Methyl eugenol bioactivities as a new potential botanical insecticide against major insect pests and their natural enemies on rice (Oryza sativa). Crop Prot. 2015, 72, 144–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Himawan, T.; Rachmawati, R.; Rifandani, E.P. The effectiveness of lemongrass oil against brown planthopper Nilaparvata lugens Stål. (Hemiptera: Delphacidae) on rice plant. J. Trop. Plant Prot. 2021, 2, 14–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singla, N.; Kaur, R. Potential of citronella oil as rodent repellent measured as aversion to food. Appl. Biol. Res. 2014, 16, 191–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicolas, A.R.; Cabarogias, A.S. Indigenous knowledge and sustainable pest management in rice farming communities of southeastern Luzon, Philippines. Int. J. Adv. Sci. Eng. Inf. Technol. 2015, 5, 440–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Carpenter, D. An investigation into the transition from technological to ecological rice farming among resource poor farmers from the Philippine island of Bohol. Agric. Hum. Values 2003, 20, 165–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polthanee, A.; Yamazaki, K. Effect of marigold (Tagetes patula L.) on parasitic nematodes of rice in northeast Thailand. Kaen Kaset 1996, 24, 105–107. [Google Scholar]
- Mao, G.-F.; Mo, X.-C.; Fouad, H.; Abbas, G.; Mo, J.-C. Attraction behaviour of Anagrus nilaparvatae to remote lemongrass (Cymbopogon distans) oil and its volatile compounds. Nat. Prod. Res. 2018, 32, 514–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iamba, K.; Teksep, C.; Roméo, N.G.; Münir, A. Biological role of marigold (Tagetes erecta L.) in habitat manipulation and sustenance of natural enemy populations in upland rice. Arthropods 2021, 10, 66–81. [Google Scholar]
- Dominik, C.; Seppelt, R.; Horgan, F.G.; Marquez, L.; Settele, J.; Václavík, T. Regional-scale effects override the influence of fine-scale landscape heterogeneity on rice arthropod communities. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2017, 246, 269–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Settele, J.; Heong, K.L.; Kühn, I.; Klotz, S.; Spangenberg, J.H.; Arida, G.; Beaurepaire, A.; Beck, S.; Bergmeier, E.; Burkhard, B.; et al. Rice ecosystem services in South-east Asia. Paddy Water Environ. 2018, 16, 211–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chandre Gowda, M.J.; Jayaramaiah, K.M. Comparative evaluation of rice production systems for their sustainability. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 1998, 69, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horgan, F.G.; Kudavidanage, E.P.; Weragodaarachchi, A.; Ramp, D. Traditional ‘maavee’ rice production in Sri Lanka: Environmental, economic and social pressures revealed through stakeholder interviews. Paddy Water Environ. 2018, 16, 225–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dominik, C.; Seppelt, R.; Horgan, F.G.; Settele, J.; Václavík, T. Landscape heterogeneity filters functional traits of rice arthropods in tropical agroecosystems. Ecol. Appl. 2022, 32, e2560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, Y.; de Kraker, J.; Bianchi, F.J.J.A.; Xiao, H.; Huang, J.; Deng, X.; Hou, L.; van der Werf, W. Do diverse landscapes provide for effective natural pest control in subtropical rice? J. Appl. Ecol. 2020, 57, 170–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kemp, J.; López-Baucells, A.; Rocha, R.; Wangensteen, O.S.; Andriatafika, Z.; Nair, A.; Cabeza, M. Bats as potential suppressors of multiple agricultural pests: A case study from Madagascar. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2019, 269, 88–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srilopan, S.; Bumrungsri, S.; Jantarit, S. The wrinkle-lipped free-tailed bat (Chaerephon plicatus Buchannan, 1800) feeds mainly on brown planthoppers in rice fields of central Thailand. Acta Chiropterologica 2018, 20, 207–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flaquer, C.; Torre, I.; Ruiz-Jarillo, R. The value of bat-boxes in the conservation of Pipistrellus pygmaeus in wetland rice paddies. Biol. Conserv. 2006, 128, 223–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baba, Y.G.; Kusumoto, Y.; Tanaka, K. Effects of agricultural practices and fine-scale landscape factors on spiders and a pest insect in Japanese rice paddy ecosystems. BioControl 2018, 63, 265–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dominik, C.; Seppelt, R.; Horgan, F.G.; Settele, J.; Václavík, T. Landscape composition, configuration, and trophic interactions shape arthropod communities in rice agroecosystems. J. Appl. Ecol. 2018, 55, 2461–2472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horgan, F.G.; Ramal, A.F.; Villegas, J.M.; Almazan, M.L.P.; Bernal, C.C.; Jamoralin, A.; Pasang, J.M.; Orboc, G.; Agreda, V.; Arroyo, C. Ecological engineering with high diversity vegetation patches enhances bird activity and ecosystem services in Philippine rice fields. Reg. Environ. Chang. 2017, 17, 1355–1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vu, Q.; Ramal, A.F.; Villegas, J.M.; Jamoralin, A.; Bernal, C.C.; Pasang, J.M.; Almazan, M.L.P.; Ramp, D.; Settele, J.; Horgan, F.G. Enhancing the parasitism of insect herbivores through diversification of habitat in Philippine rice fields. Paddy Water Environ. 2018, 16, 379–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maclean, R.; Litsinger, J.; Moody, K.; Watson, A. The impact of alley cropping Gliricidia sepium and Cassia spectabilis on upland rice and maize production. Agrofor. Syst. 1992, 20, 213–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandrasekar, K.; Muthukrishnan, N.; Soundararajan, R. Ecological engineering cropping methods for enhancing predator, Cyrtorhinus lividipennis (Reuter) and suppression of planthopper, Nilaparvata lugens (Stål) in rice-effect of intercropping system. J. Pharmacogn. Phytochem. 2017, 6, 2387–2391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandrasekar, K.; Muthukrishnan, N.; Soundararajan, R.; Robin, S.; Prabhakaran, N. Ecological engineering cropping method for enhancing predator Coccinella septempunctata and suppression of Planthopper, Nilaparvata lugens (Stål) in rice. Adv. Life Sci. 2016, 5, 1288–1294. [Google Scholar]
- Yele, Y.; Chander, S.; Suroshe, S.S.; Nebapure, S.M.; Arya, P.S.; Prabhulinga, T. Effect of ecological engineering on incidence of key rice pests. Indian J. Entomol. 2021, 84, 503–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanmugam, P.; Sangeetha, M.; Ayyadurai, P.; Prasad, Y. Demonstration of ecological engineering based pest management in rice Oryza sativa L. through farmers participatory approach. Agric. Sci. Dig. 2022, 42, 290–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amzah, B.; Jajuli, R.; Jaafar, N.A.I.; Jamil, S.Z.; Hamid, S.; Zulkfili, N.I.; Ismail, N.; Kadir, A.A.; Ariff, E.E.E.; Baki, R. Application of ecological engineering to increase arthropod’s diversity in rice ecosystem. Malays. Appl. Biol 2018, 47, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Ibrahim, E.; Mugiasih, A. Diversity of pests and natural enemies in rice field agroecosystem with ecological engineering and without ecological engineering. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2020, 484, 012108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinulingga, N.G.H.; Trisyono, Y.A.; Martono, E.; Hadi, B. Benefits of flowering plants as refuge to improve the ecosystem services by egg parasitoids of the rice brown planthopper. J. Perlindungan Tanam. Indones. 2019, 23, 68–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanker, C.; Chintagunta, L.; Muthusamy, S.; Vailla, S.; Srinivasan, A.; Katti, G. Flora surrounding rice fields as a source of alternative prey for coccinellids feeding on the pests of rice. Eur. J. Entomol. 2018, 115, 364–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nalini, R.; Porpavai, S. Enhancing floral and habitat diversity for augmenting natural enemies in rice ecosystem of Thanjavur, Tamil Nadu, India. Oryza 2019, 56, 285–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simões-Pires, P.; Jahnke, S.; Redaelli, L. Influence of the vegetation management of the leeves in irrigated rice organic in diversity of Hymenoptera parasitoids. Braz. J. Biol. 2016, 76, 774–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Acosta, L.G.; Jahnke, S.M.; Redaelli, L.R.; Pires, P.R.S. Insect diversity in organic rice fields under two management systems of levees vegetation. Braz. J. Biol. 2017, 77, 731–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- MacLean, R.; Litsinger, J.; Moody, K.; Watson, A.; Libetario, E. Impact of Gliricidia sepium and Cassia spectabilis hedgerows on weeds and insect pests of upland rice. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2003, 94, 275–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Punzal, B.; Arida, G.S.; Marquez, L.V.; Settele, J. Management of rice pests by ecological engineering in farmers’ field in Nueva Ecija, Philippines. Philipp. Entomol. 2017, 31, 162–163. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, K.; Yang, T.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, J.-e.; Luo, M.; Fu, L.; Zhao, B. Effects of intercropping rice and water spinach on net yields and pest control: An experiment in southern China. Int. J. Agric. Sustain. 2016, 14, 448–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, C.; Qu, J.; He, L.; Yang, R.; Chen, Q.; Luo, S.; Cai, K. Improvement of yield, pest control and Si nutrition of rice by rice-water spinach intercropping. Field Crops Res. 2017, 208, 34–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, C.; Wang, L.; Liu, R.; Pan, T.; Cai, Y.; Tian, J.; Luo, S.; Cai, K. Plant-mediated rhizospheric interactions in rice and water spinach intercropping enhance Si uptake by rice. Plant Soil 2021, 477, 183–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakur, R.B. Performance of intercrops in direct-seeded rain-fed rice (Oryza sativa) under deep-water ecosystem of north Bijar. Indian J. Agric. Sci. 1993, 63, 257–260. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, X.; Lu, Y.; Zhu, P.; Zhang, F.; Tian, J.; Xu, H.; Chen, G.; Nansen, C.; Lu, Z. Use of banker plant system for sustainable management of the most important insect pest in rice fields in China. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 45581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nwilene, F.E.; Togola, A.; Agunbiade, T.A.; Ogah, E.O.; Ukwungwu, M.N.; Hamadoun, A.; Kamara, S.I.; Dakouo, D. Parasitoid biodiversity conservation for sustainable management of the African rice gall midge, Orseolia oryzivora (Diptera: Cecidomyiidae) in lowland rice. Biocontrol Sci. Technol. 2008, 18, 1075–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Zheng, X.; Lü, Z. The potential of vetiver grass as a biological control for the rice stem borers Chilo suppressalis and Sesamia inferens. Chin. J. Appl. Entomol. 2018, 55, 1111–1117. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, Y.; Liang, Q.; Zheng, X. Effects of trap plant vetiver grass (Vetiveria zizanioides) on nutritional and digestive enzyme activities of pink stem borer (Sesamia inferens) larvae. Chin. J. Biol. Control 2017, 33, 719–724. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, Y.H.; Gao, G.C.; Zheng, X.S. The lethal mechanism of trap plant Vetiveria zizanioides against the larvae of Chilo suppressalis. Sci. Agric. Sin. 2017, 50, 486–495. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, H.-x.; Yang, Y.-j.; Lu, Y.-h.; Zheng, X.-s.; Tian, J.-c.; Lai, F.-x.; Fu, Q.; Lu, Z.-x. Sustainable management of rice insect pests by non-chemical-insecticide technologies in China. Rice Sci. 2017, 24, 61–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajesh, K.M.; Sinu, P.A.; Nasser, M. Eleocharis dulcis (Burm.f) as a promising trap plant for the biocontrol of rice white stem borer, Scirpophaga innotata (Walker). Biol. Control 2021, 160, 104676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Xu, H.; Hu, Z.; Yang, G.; Yu, X.; Chen, Q.; Zheng, L.; Yan, Z. Eleocharis dulcis corm: Phytochemicals, health benefits, processing and food products. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2022, 102, 19–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Kraker, J.; Rabbinge, R.; van Huis, A.; van Lenteren, J.C.; Heong, K.L. Impact of nitrogenous-fertilization on the population dynamics and natural control of rice leaffolders (Lep.: Pyralidae). Int. J. Pest Manag. 2000, 46, 225–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Shen, Y.; Li, B.; Meng, L. The effect of biochar amendment to soils on Cnaphalocrocis medinalis Guenee (Lepidoptera: Pyralidae) on rice. Crop Prot. 2019, 124, 104842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.-q.; Wen, J.-h.; Peng, Z.-p.; Zhang, D.-y.; Hou, M.-l. Effects of silicon amendment on the occurrence of rice insect pests and diseases in a field test. J. Integr. Agric. 2018, 17, 2172–2181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeer, M.; Suman, K.; Maheswari, T.U.; Voleti, S.R.; Padmakumari, A.P. Rice husk ash and imidazole application enhances silicon availability to rice plants and reduces yellow stem borer damage. Field Crops Res. 2018, 224, 60–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeer, M.; Telugu, U.M.; Voleti, S.R.; Padmakumari, A.P. Soil application of silicon reduces yellow stem borer, Scirpophaga incertulas (Walker) damage in rice. J. Appl. Entomol. 2017, 141, 189–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Yu, Y.; Baerson, S.R.; Song, Y.; Liang, G.; Ding, C.; Niu, J.; Pan, Z.; Zeng, R. Interactions between nitrogen and silicon in rice and their effects on resistance toward the brown planthopper Nilaparvata lugens. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, J.; Zhu, J.; Zhang, P.; Han, L.; Reynolds, O.L.; Zeng, R.; Wu, J.; Shao, Y.; You, M.; Gurr, G.M. Silicon supplementation alters the composition of herbivore induced plant volatiles and enhances attraction of parasitoids to infested rice plants. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rahaman, M.M.; Stout, M.J. Comparative Efficacies of Next-Generation Insecticides Against Yellow Stem Borer and Their Effects on Natural Enemies in Rice Ecosystem. Rice Sci. 2019, 26, 157–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chintalapati, P.; Katti, G.; Puskur, R.R.; Nagella Venkata, K. Neonicotinoid-induced resurgence of rice leaffolder, Cnaphalocrocis medinalis (Guénee). Pest Manag. Sci. 2016, 72, 155–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Kushwaha, K.S.; Sharma, P.D.; Singh, S. Resurgence of rice leaf folder Cnaphalocrocis medinalis Guenee due to application of phorate granules. Haryana J. Agron. 1995, 57, 366–372. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, A.-H.; Wu, J.-C.; Yu, Y.-S.; Liu, J.-L.; Yue, J.-F.; Wang, M.-Y. Selective insecticide-induced stimulation on fecundity and biochemical changes in Tryporyza incertulas (Lepidoptera: Pyralidae). J. Econ. Entomol. 2005, 98, 1144–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, K.; Liu, Y.; Hou, M.; Babendreier, D.; Zhang, F.; Song, K. Toxicity of insecticides targeting rice planthoppers to adult and immature stages of Trichogramma chilonis (Hymenoptera: Trichogrammatidae). J. Econ. Entomol. 2015, 108, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rakes, M.; Pasini, R.A.; Morais, M.C.; Araújo, M.B.; de Bastos Pazini, J.; Seidel, E.J.; Bernardi, D.; Grützmacher, A.D. Pesticide selectivity to the parasitoid Trichogramma pretiosum: A pattern 10-year database and its implications for integrated pest management. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 208, 111504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray, A.; Gadratagi, B.-G.; Rana, D.K.; Ullah, F.; Adak, T.; Govindharaj, G.-P.-P.; Patil, N.B.; Mahendiran, A.; Desneux, N.; Rath, P.C. Multigenerational insecticide hormesis enhances fitness traits in a key egg parasitoid, Trichogramma chilonis Ishii. Agronomy 2022, 12, 1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, L.-C.; Jin, L.-H.; Lu, Y.-H.; Xu, H.-X.; Zang, L.-S.; Tian, J.-C.; Lu, Z.-X. Resistance of lepidopteran egg parasitoids, Trichogramma japonicum and Trichogramma chilonis, to insecticides used for control of rice planthoppers. J. Econ. Entomol. 2022, 115, 446–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, P.; Li, M.-J.; Bai, Q.-R.; Ali, A.; Desneux, N.; Dai, H.-J.; Zang, L.-S. Performance of Trichogramma japonicum as a vector of Beauveria bassiana for parasitizing eggs of rice striped stem borer, Chilo suppressalis. Entomol. Gen. 2021, 41, 147–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Y.; Sui, L.; Yang, Z.; Mao, G.; Xu, W.-J.; Zhao, Y.; Li, L.; Li, Q.-Y.; Zhang, Z.-K. Synergistic control against Asian corn borer (ACB) by Trichogramma vectored Beauveria bassiana infection on survival larvae escaped from parasitism. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2020, 547, 012021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Fang, H.; Liu, X.; Michaud, J.P.; Xu, H.; Zhao, Z.; Zhang, S.; Li, Z. Laboratory evaluation of the compatibility of Beauveria bassiana with the egg parasitoid Trichogramma dendrolimi (Hymenoptera: Trichogrammatidae) for joint application against the oriental fruit moth Grapholita molesta (Lepidoptera: Tortricidae). Pest Manag. Sci. 2022, 78, 3608–3619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morisset, O.; Cabrera, P.; Todorova, S.; Cormier, D.; Chouinard, G.; Lucas, É. Compatibility of the egg parasitoid Trichogramma minutum (Hymenoptera: Trichogrammatidae) and the granulovirus (CpGV) used in combination against the codling moth Cydia pomonella (Lepidoptera: Tortricidae). Phytoprotection 2021, 101, 6–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.-Y.; Yang, F.; Lu, M.-H.; Luo, S.-Y.; Zhai, B.-P.; Lim, K.-S.; McInerney, C.E.; Hu, G. Determining the migration duration of rice leaf folder (Cnaphalocrocis medinalis (Guenée)) moths using a trajectory analytical approach. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 39853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.D. Preliminary study on the hymenopterous parasites of rice stem borers with description of two previously unrecorded species form Korea. Korean J. Appl. Entomol. 1978, 17, 65–69. [Google Scholar]
- Romeis, J.; Babendreier, D.; Wackers, F.L.; Shanower, T.G. Habitat and plant specificity of Trichogramma egg parasitoids—Underlying mechanisms and implications. Basic Appl. Ecol. 2005, 6, 215–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Kraker, J.; Van Huis, A.; Van Lenteren, J.C.; Heong, K.L.; Rabbinge, R. Egg mortality of rice leaffolders Cnaphalocrocis medinalis and Marasmia patnalis in irrigated rice fields. Biocontrol 1999, 44, 449–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Babendreier, D.; Tang, R.; Horgan, F.G. Prospects for Integrating Augmentative and Conservation Biological Control of Leaffolders and Stemborers in Rice. Agronomy 2022, 12, 2958. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12122958
Babendreier D, Tang R, Horgan FG. Prospects for Integrating Augmentative and Conservation Biological Control of Leaffolders and Stemborers in Rice. Agronomy. 2022; 12(12):2958. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12122958
Chicago/Turabian StyleBabendreier, Dirk, Rui Tang, and Finbarr G. Horgan. 2022. "Prospects for Integrating Augmentative and Conservation Biological Control of Leaffolders and Stemborers in Rice" Agronomy 12, no. 12: 2958. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12122958
APA StyleBabendreier, D., Tang, R., & Horgan, F. G. (2022). Prospects for Integrating Augmentative and Conservation Biological Control of Leaffolders and Stemborers in Rice. Agronomy, 12(12), 2958. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12122958







