Allelopathic Activity of Annona reticulata L. Leaf Extracts and Identification of Three Allelopathic Compounds for the Development of Natural Herbicides
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Collection of A. reticulata Samples
2.2. Extraction of A. reticulata Leaves for a Growth Bioassay
2.3. Steps in the Isolation and Purification of the Allelopathic Compounds
2.4. Bioassay of the Identified Compounds
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Evaluation of the Phytotoxic Action of the A. reticulata Extracts
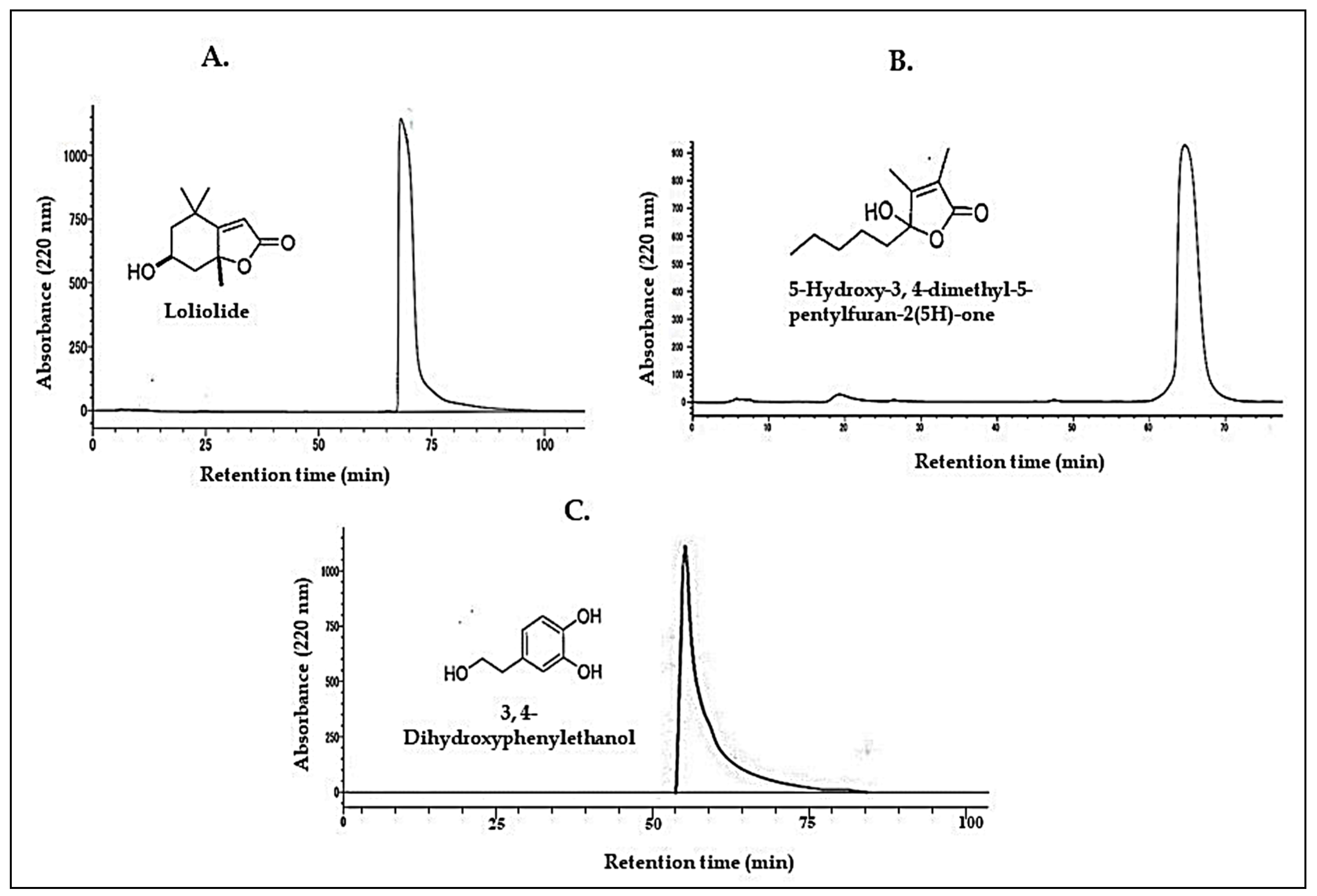
3.2. Characterization of the Active Compounds
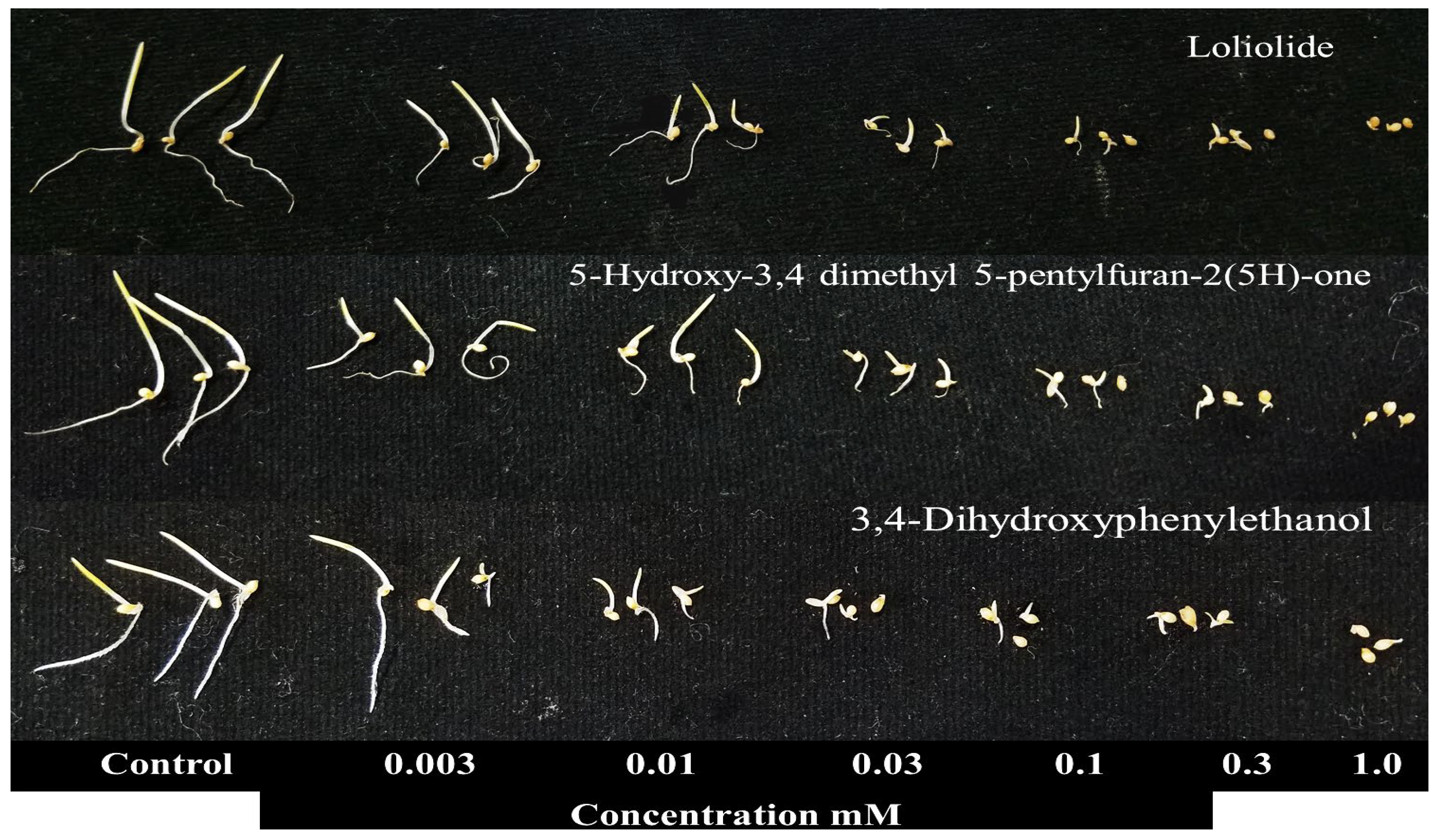
3.3. The Bioactivity of the Three Compounds Identified from the A. reticulata Extracts
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kumar, S.; Bhowmick, M.K.; Ray, P. Weeds as alternate and alternative hosts of crop pests. Indian J. Weed Sci. 2021, 53, 14–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heap, I. The International Herbicide-Resistant Weed Database. Available online: www.weedscience.org (accessed on 4 June 2022).
- Harsimran, K.G.; Harsh, G. Pesticides: Environmental Impacts and Management Strategies, Pesticides—Toxic Aspects; IntechOpen Limited: London, UK, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Rice, E.L. Allelopathy, 2nd ed.; Academic Press: Orlando, FL, USA, 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Duke, S.O. Phytotchemical phytotoxins and hormesis—A commentary. Dose-Response 2010, 9, 76–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bari, I.N.; Kato-Noguchi, H. Phytotoxic effects of Cerbera manghas L. leaf extracts on seedling elongation of four monocot and four dicot test species. Acta Agrobot. 2017, 70, 1720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dayan, F.E.; Duke, S.O. Natural compounds as next-generation herbicides. Plant Physiol. 2014, 166, 1090–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Lu, L.Y.; Hu, L.Y.; Cao, W.; Sun, K.; Sun, Q.B.; Siddikee, A.; Shi, R.H.; Dai, C.C. Evidence for the involvement of auxin, ethylene and ROS signaling during primary root inhibition of Arabidopsis by the allelochemical benzoic acid. Plant Cell Physiol. 2018, 59, 1889–1904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, Z.; Li, P.; Xiao, Y.; Cao, L.; Yao, L. Phytotoxic effects of allelochemical acacetin on seed germination and seedling growth of selected vegetables and its potential physiological mechanism. Agronomy 2022, 12, 1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacob, J.; Sarada, S. Role of phenolics in allelopathic interactions. Allelopathy J. 2012, 29, 215–230. [Google Scholar]
- Duke, S.O.; Dayan, F.E.; Rimando, R.M.; Schrader, K.K.; Aliotta, G.; Oliva, A.; Romagni, J.G. Chemicals from nature for weed management. Weed Sci. 2002, 50, 138–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngbolua, K.N.; Inkoto, C.L.; Bongo, G.N.; Mokel, L.E.; Lufuluabo, L.G.; Ashande, C.M.; Tshibangu, D.S.T.; Tshilanda, D.D.; Mpiana, P.T. Phytochemistry and bioactivity of Annona reticulata L. (Annonaceae): A Mini-review. S. Asian Res. J. Nat. Prod. 2018, 1, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, J.; Kumar, S.V.; Kadam, V. Antiulcer activity of Annona reticulata leaves extract in rats. Int. J. Pharm. Sci. 2012, 4, 412–414. [Google Scholar]
- Kirtikar, K.R.; Basu, B.D. Indian Medicinal Plants; International Book Distributors: Deharadun, India, 1987; pp. 68–69. [Google Scholar]
- Shin, S.-H.; Choi, G.-H.; Choi, D.; Kwon, K.; Im, G.J.; Park, J.-U.; Choi, B.-R.; Kim, T.-W.; Kim, J.-H. Insecticidal activity of the crude extract and its fractions of Custard apple (Annona reticulata L.). J. Appl. Biol. Chem. 2010, 53, 21–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanachpakorn, Y.; Vanachpakorn, P.; Kulvijitra, R.; Ding, W. Toxicity and repellency of ethanol extracts of Annona recticulata L. seed and leaf against Callosobruchus maculatus (F) (Coleoptera: Bruchidae). In Proceedings of the 11th International Working Conference on Stored Product Protection, Chiang Mai, Thailand, 24–28 November 2014; pp. 1080–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suresh, H.M.; Shivakumar, B.; Shivakumar, S.I. Phytochemical potential of Annona reticulata roots for antiproliferative activity on human cancer cell lines. Adv. Life Sci. 2012, 2, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chavan, S.S.; Shamkuwar, P.B.; Damale, M.G.; Pawar, D.P. A comprehensive review on Annona reticulata. Int. J. Pharm. Sci. Res. 2014, 5, 45–50. [Google Scholar]
- Prasad, G.J.; Amruta, S.W. Annona reticulata Linn. (Bullock’s heart): Plant profile, phytochemistry and pharmacological properties. J. Trad. Compl. Med. 2015, 5, 144–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, G.J.; Amruta, S.W.; Ashish, D.K.; Priti, S.T.; Mohan, G.K. Assessment of Annona reticulata Linn. leaves fractions for in vitro antioxidative effect and antimicrobial potential against standard human pathogenic strains. Alexandria J. Med. 2015, 52, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nirmal, S.A.; Gaikwad, S.B.; Dhasade, V.V.; Dhikale, R.S.; Kotkar, P.V.; Dighe, S.S. Anthelmintic activity of Annona reticulate leaves. Res. J. Pharm. Biol. Chem Sci. 2010, 1, 115–118. [Google Scholar]
- Rahman, M.; Rahman, S.; Ahmed, R.; Khatun, F.; Nasrin, D.; Ahsan, S.; Rahmatullah, M. Antihyperglycemic studies with methanol extract of Annona reticulata L. (Annonaceae) and Carissa carandas L. (Apocynaceae) leaves in swiss albino mice. Adv. Nat. Appl. Sci. 2011, 5, 218–222. [Google Scholar]
- Chavan, M.J.; Kolhe, D.R.; Wakte, P.S.; Shinde, D.B. Analgesic and anti-inflammatory activities of kaur-16-en-19-olic acid from Annona reticulata L. bark. Phytother. Res. 2011, 26, 273–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Padmanabhan, P.; Paliyath, G. Annonaceous Fruits. In Encyclopedia of Food and Health; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016; pp. 169–173. (accessed on 22 September 2015). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orwa, C.; Mutua, A.; Kindt, R.; Jamnadass, R.; Simons, A. Agroforestry Database: A Tree Reference and Selection Guide; Version 4.0; World Agroforestry Centre: Nairobi, Kenya, 2009; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Pier. Pacific Islands Ecosystems at Risk; HEAR, University of Hawaii: Honolulu, HI, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Morton, J.F. Custard apple. In Fruits of Warm Climates; Creative Resources Systems: Miami, FL, USA, 1987; pp. 80–83. Available online: https://www.hort.purdue.edu/newcrop/morton/custard_apple.html (accessed on 27 April 2022).
- Randall, R.P. A Global Compendium of Weeds; Department of Agriculture and Food Western Australia: Perth, Australia, 2012; p. 1124. Available online: http://www.cabi.org/isc/FullTextPDF/2013/20133109119.pdf (accessed on 1 June 2002).
- Bais, H.P.; Weir, T.L.; Perry, L.G.; Gilroy, S.; Vivanco, J.M. The role of root exudates in rhizosphere interactions with plants and other organisms. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2006, 57, 233–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mbagwu, F.N. The allelopathic effects of crude water extracts of Annona muricata on common weeds. Int. J. Appl. Nat. Sci. 2006, 2, 341–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumoto, S.; Varela, R.M.; Palma, M.; Molinillo, J.M.G.; Lima, I.S.; Barroso, C.G.; Macías, F.A. Bio-guided optimization of the ultrasound-assisted extraction of compounds from Annona glabra L. leaves using the etiolated wheat coleoptile bioassay. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2014, 21, 1578–1584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Islam, A.K.; Ohno, O.; Suenaga, K.; Kato-Noguchi, H. Two novel phytotoxic substances from Leucas aspera. J. Plant Physiol. 2014, 171, 877–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- IBM Corp. IBM SPSS Statistics for Windows; Version 16.0; IBM Corp: Armonk, NY, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, M.R.; Lee, S.K.; Kim, C.S.; Kim, K.S.; Moon, D.-C. Phytochemical constituents of Carpesium macrocephalum FR- et SAV-. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2004, 27, 1029–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Tsujimori, M.; Hirai, H.; Kawagishi, H. Novel compounds from the mycelia and fruiting bodies of Climacodon septentrionalis. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2011, 75, 783–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pouységu, L.; Sylla, T.; Garnier, T.; Rojas, L.B.; Charris, J.; Deffieux, D.; Queneau, S. Hypervalent iodine-mediated oxygenative phenol dearomatization reactions. Tetrahedron 2010, 66, 5908–5917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, A.K.; Kato-Noguchi, H. Phytotoxic activity of Ocimum tenuiflorum extracts on germination and seedling growth of different plant species. Sci. World J. 2014, 2014, 676242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobayashi, K. Factors affecting phytotoxic activity of allelochemicals in soil. Weed Biol. Manag. 2004, 4, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sodaeizadeh, H.; Rafieiolhossaini, M.; Havlík, J.; Damme, P.V. Allelopathic activity of different plant parts of Peganum harmala L. and identification of their growth inhibitors substances. Plant Growth Regul. 2009, 59, 227–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rob, M.M.; Hossen, K.; Khatun, M.R.; Iwasaki, K.; Iwasaki, A.; Suenaga, K.; Kato-Noguchi, H. Identification and application of bioactive compounds from Garcinia xanthochymus Hook. for weed management. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 2264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krumsri, R.; Iwasaki, A.; Suenaga, K.; Kato-Noguchi, H. Assessment of allelopathic potential of Senna garrettiana leaves and identification of potent phytotoxic substances. Agronomy 2022, 12, 139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saboon, C.; Arshad, S.K.; Amjad, M.S.; Akhtar, M.S. Natural compounds extracted from medicinal plants and their applications. In Natural Bio-Active Compounds; Springer: Singapore, 2019; pp. 193–207. [Google Scholar]
- Bachheti, A.; Sharma, A.; Bachheti, R.K.; Husen, A.; Pandey, D.P. Plant allelochemicals and their various applications. In Co-Evolution of Secondary Metabolites; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 441–465. [Google Scholar]
- Dayan, F.E.; Romagni, J.G.; Duke, S.O. Investigating the mode of action of natural phytotoxins. J. Chem. Ecol. 2000, 26, 2079–2094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grabarczyk, M.; Wińska, K.; Mączka, W.; Potaniec, B.; Anioł, M. Loliolide-The most ubiquitous lactone. Acta Univ. Lodziensis. Folia Biol. Oecol. 2015, 11, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, C.H.; Xuan, T.D.; Khanh, T.D.; Tran, H.D.; Trung, N.T. Allelochemicals and signaling chemicals in plants. Molecules 2019, 24, 2737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ragasa, C.Y.; De Luna, R.D.; Hofilena, J.G. Antimicrobial terpenoids from Pterocarpus indicus. Nat. Prod. Res. 2005, 19, 305–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, W.; Liu, K.; Guan, Y.; Tan, G.T.; Van Hung, N.; Cuong, N.M.; Soejarto, D.D.; Pezzuto, J.M.; Fong, H.H.S.; Hongjie, Z. Bioactive compounds from Vitex leptobotrys. J. Nat. Prod. 2014, 77, 663–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.; Kang, M.; Lee, K.; Kang, S.; Lee, W.; Jeon, Y. Antioxidant activity and cell protective effect of loliolide isolated from Sargassum ringgoldianum subsp. coreanum. Algae 2011, 26, 201–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okunade, A.L.; Wiemer, D.F. (−)-Loliolide, an ant-repellent compound from Xanthoxyllum setulosum. J. Nat. Prod. 1985, 48, 472–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.; Xie, H.; Gong, Y.; Wang, Q.; Yang, Y. Secondary metabolites from the seaweed Gracilaria lemaneiformis and their allelopathic effects on Skeletonema costatum. Biochem. Syst. Ecol. 2011, 39, 397–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaman, F.; Iwasaki, A.; Suenaga, K.; Kato-Noguchi, H. Two allelopathic substances from Paspalum commersonii Lam. Acta Agric. Scand. B Soil Plant Sci. 2018, 68, 342–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyaw, E.H.; Iwasaki, A.; Suenaga, K.; Kato-Noguchi, H. Allelopathy of the medicinal plant Dregea volubilis (lf) benth. ex hook. f. and its phytotoxic substances with allelopathic activity. Agronomy 2022, 12, 303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, X.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, S.; Zhou, Y. A new organic acid derivative from the fruits of Rosa roxburghii. Rec. Nat. Prod. 2022, 16, 264–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, W.; Ren, L.; Sun, J.; Zhang, D. Trimacoside A, a high molecular weight antioxidant phenylpropanoid glycoside from Tricyrtis maculate. Rec. Nat. Prod. 2021, 15, 194–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Liang, Y.; Liao, X.J.; Deng, Z.; Xu, S.H. Isolation of a new butenolide from the South China Sea gorgonian coral Subergorgia suberosa. Nat. Prod. Res. 2014, 28, 150–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.E.; Lee, T.H.; Ham, S.L.; Subedi, L.; Hong, S.M.; Kim, S.Y.; Choi, S.U.; Kim, C.S.; Lee, K.R. Anticancer and anti-neuroinflammatory constituents isolated from the roots of Wasabia japonica. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, S.; Bai, M.; Song, S. Chemical components from Crotalaria pallida Ait. and their antioxidant activities. Asian J. Tradit. Med. 2022, 17, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Husain, A.; Khan, S.A.; Iram, F.; Iqbal, M.A.; Asif, M. Insights into the chemistry and therapeutic potential of furanones: A versatile pharmacophore. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 171, 66–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon, M.H.; Paiva-Martins, F.; Almeida, M.J. Antioxidant activity of hydroxytyrosol acetate compared with that of other olive oil polyphenols. J. Agric. Food. Chem. 2001, 49, 2480–2485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De La Torre, R.; Covas, M.I.; Pujadas, M.A.; Fitó, M.; Farré, M. Is dopamine behind the health benefits of red wine? Eur. J. Nutr. 2006, 45, 307–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferguson, L.R. Role of plant polyphenols in genomic stability. Mutat. Res. 2001, 475, 89–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakihama, Y.; Cohen, M.F.; Grace, S.C.; Yamasaki, H. Plant phenolic antioxidant and prooxidant activities: Phenolics-induced oxidative damage mediated by metals in plants. Toxicology 2002, 177, 67–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldioli, M.; Servili, M.; Perretti, G.; Montedoro, G.F. Antioxidant activity of tocopherols and phenolic compounds of virgin olive oil. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 1996, 73, 1589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morelló, J.R.; Vuorela, S.; Romero, M.P.; Motilva, M.J.; Heinonen, M. Antioxidant activity of olive pulp and olive oil phenolic compounds of the arbequina cultivar. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2005, 53, 2002–2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, C.; Xu, L.; Sun, J.; Zhang, Z.; Fu, M.; Teng, H.; Yi, K. Allelochemical p-hydroxybenzoic acid inhibits root growth via regulating ROS accumulation in cucumber (Cucumis sativus L.). J. Integr. Agric. 2020, 19, 518–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jabran, K.; Mahajan, G.; Sardana, V.; Chauhan, B.S. Allelopathy for weed control in agricultural systems. Crop Prot. 2015, 72, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabaglio, V.; Gavazzi, C.; Schulz, M.; Marocco, A. Alternative weed control using the allelopathic effect of natural benzoxazinoids from rye mulch. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2008, 28, 397–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macías, F.A.; Molinillo, J.M.; Varela, R.M.; Galindo, J.C. Allelopathy—A natural alternative for weed control. Pest Manag. Sci. 2007, 63, 327–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khaliq, A.; Matloob, A.; Irshad, M.S.; Tanveer, A.; Zamir, M.S.I. Organic weed management in maize (Zea mays L.) through integration of allelopathic crop residues. Pak. J. Weed Sci. Res. 2010, 16, 409–420. [Google Scholar]
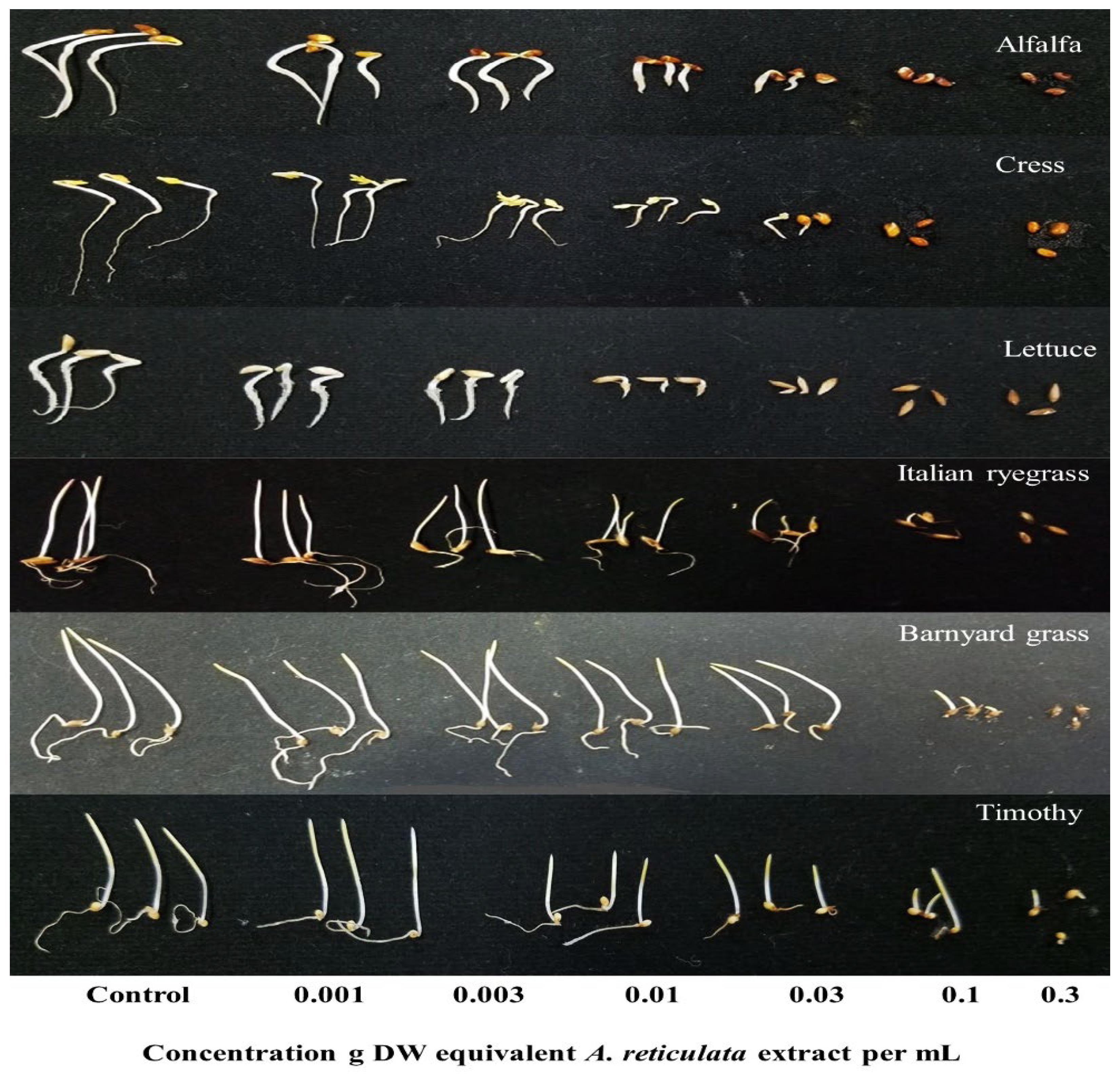




| Test Plant Species | I50 Value (g Dry Weight Equivalent Extract mL−1) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Shoot | Root | ||
| Alfalfa | 0.006 | 0.004 | |
| Dicots | Cress | 0.005 | 0.006 |
| Lettuce | 0.003 | 0.009 | |
| Italian ryegrass | 0.012 | 0.013 | |
| Monocots | Barnyard grass | 0.057 | 0.012 |
| Timothy | 0.021 | 0.003 | |
| Test Plants | I50 Value (mM) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Loliolide | 5-Hydroxy-3,4-dimethyl-5-pentylfuran-2(5H)-one | 3,4-Dihydroxyphenylethanol | ||
| Cress | Shoot | 0.060 | 0.120 | 0.080 |
| Root | 0.026 | 0.013 | 0.060 | |
| Timothy | Shoot | 0.015 | 0.030 | 0.028 |
| Root | 0.036 | 0.030 | 0.100 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Khatun, M.R.; Tojo, S.; Teruya, T.; Kato-Noguchi, H. Allelopathic Activity of Annona reticulata L. Leaf Extracts and Identification of Three Allelopathic Compounds for the Development of Natural Herbicides. Agronomy 2022, 12, 2883. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12112883
Khatun MR, Tojo S, Teruya T, Kato-Noguchi H. Allelopathic Activity of Annona reticulata L. Leaf Extracts and Identification of Three Allelopathic Compounds for the Development of Natural Herbicides. Agronomy. 2022; 12(11):2883. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12112883
Chicago/Turabian StyleKhatun, Mst. Rokeya, Shunya Tojo, Toshiaki Teruya, and Hisashi Kato-Noguchi. 2022. "Allelopathic Activity of Annona reticulata L. Leaf Extracts and Identification of Three Allelopathic Compounds for the Development of Natural Herbicides" Agronomy 12, no. 11: 2883. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12112883
APA StyleKhatun, M. R., Tojo, S., Teruya, T., & Kato-Noguchi, H. (2022). Allelopathic Activity of Annona reticulata L. Leaf Extracts and Identification of Three Allelopathic Compounds for the Development of Natural Herbicides. Agronomy, 12(11), 2883. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12112883





