Soil Enzyme Activities Affect SOC and TN in Aggregate Fractions in Sodic-Alkali Soils, Northeast of China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sites and Soil Sampling
2.2. Aggregate Separation
2.3. Soil Analysis
2.4. Enzyme Assays
2.4.1. AMY Assay
2.4.2. INV Assay
2.4.3. GLU Assay
2.4.4. CAT Assay
2.4.5. NAG Assay
2.4.6. URE Assay
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
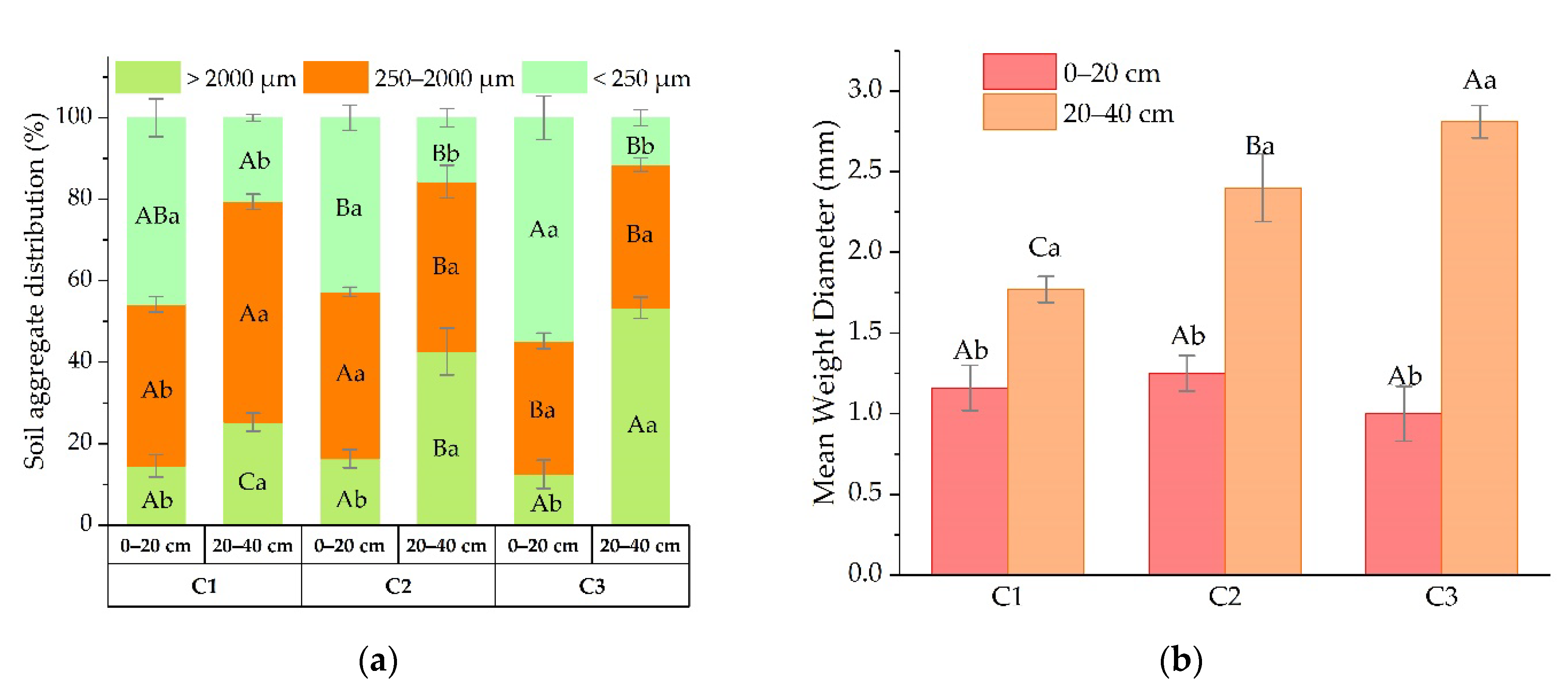
3.1. Soil Aggregate Distribution
3.2. SOC, TN, MBC, and MBN Content in Aggregates
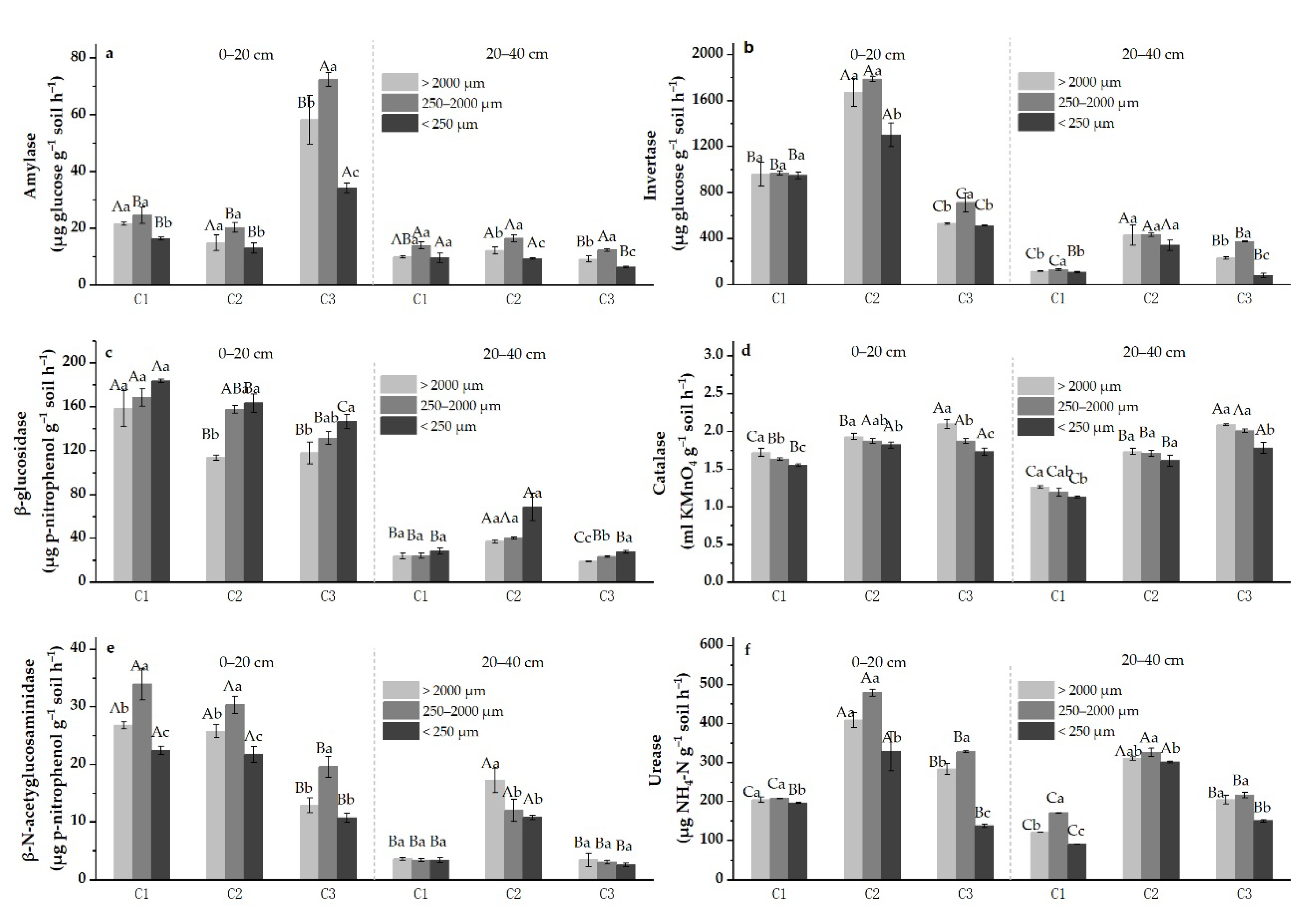
3.3. Soil Enzyme Activities in Aggregates
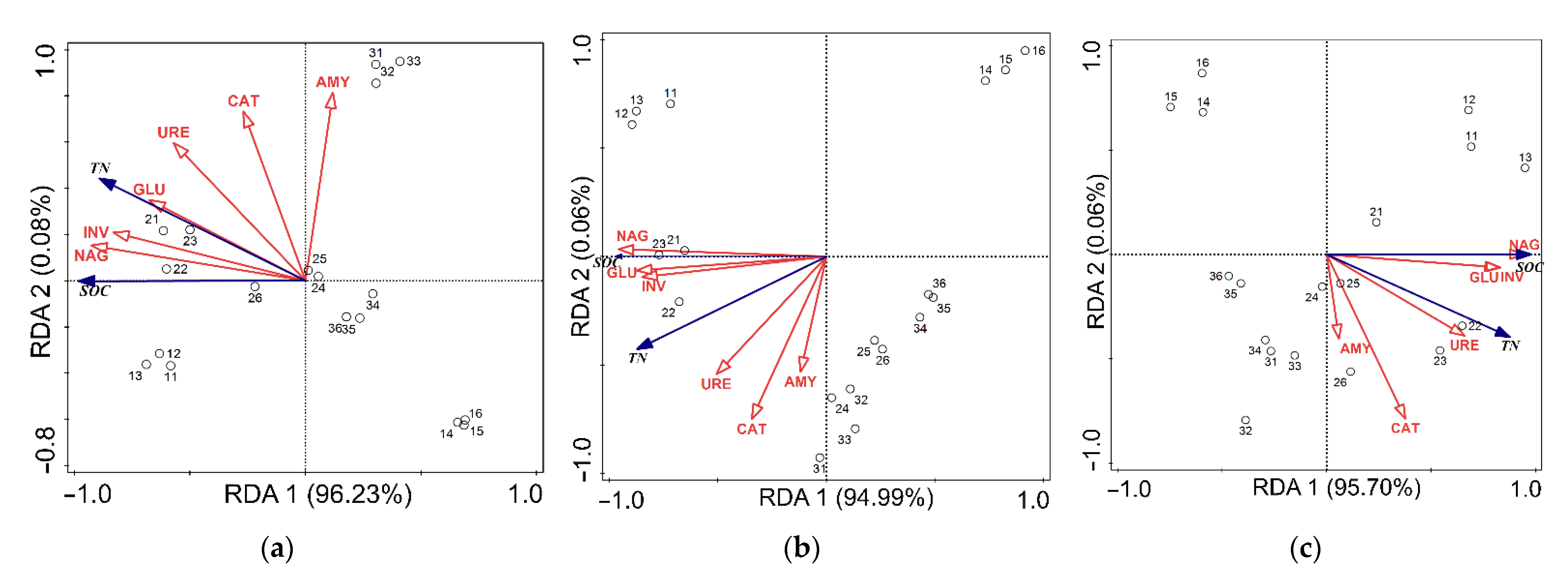
3.4. Redundancy Analysis between Soil Enzyme Activities and SOC, TN in Aggregates
4. Discussion
4.1. Soil Aggregate Distribution and Stability
4.2. SOC, TN, and Microbial Biomass in Soil Aggregates
4.3. C- and N-Cycling Enzymes in Soil Aggregates
5. Conclusions
- (1)
- SOC, TN, MBC, and MBN were heterogeneously distributed in soil aggregates. SOC, TN, and MBN in aggregates were in the order of meso-aggregates > macro-aggregates > micro-aggregates. MBC in aggregates was in the order of meso-aggregates > micro-aggregates > macro-aggregates.
- (2)
- Soil activities of AMY, INV, CAT, NAG, and URE in macro- and meso-aggregates were more active than in micro-aggregates, while GLU activities increased with decreasing aggregate sizes in the studied sodic-alkali soils.
- (3)
- Soil enzyme activities affected SOC and TN, for NAG, INV, GLU, and URE were closely related to SOC and TN across aggregates in the current study.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhu, M.; Yang, S.; Ai, S.; Ai, X.; Jiang, X.; Chen, J.; Li, R.; Ai, Y. Artificial Soil Nutrient, Aggregate Stability and Soil Quality Index of Restored Cut Slopes along Altitude Gradient in Southwest China. Chemosphere 2020, 246, 125687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Yao, Y.; Qin, X.; Wei, X.; Jia, X.; Shao, M. Response of Carbon and Nitrogen to Afforestation from 0 to 5 m Depth on Two Semiarid Cropland Soils with Contrasting Inorganic Carbon Concentrations. Geoderma 2020, 357, 113940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Dorodnikov, M.; Splettstößer, T.; Kuzyakov, Y.; Pausch, J. Effects of Maize Roots on Aggregate Stability and Enzyme Activities in Soil. Geoderma 2017, 306, 50–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.; Wu, J.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, D.; Li, Q.; Long, C.; Yang, F.; Chen, Q.; Cheng, X. Stimulation of Nitrogen-Hydrolyzing Enzymes in Soil Aggregates Mitigates Nitrogen Constraint for Carbon Sequestration Following Afforestation in Subtropical China. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2018, 123, 136–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piazza, G.; Pellegrino, E.; Moscatelli, M.C.; Ercoli, L. Long-Term Conservation Tillage and Nitrogen Fertilization Effects on Soil Aggregate Distribution, Nutrient Stocks and Enzymatic Activities in Bulk Soil and Occluded Microaggregates. Soil Tillage Res. 2020, 196, 104482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Li, T.; Zheng, Z. Effects of Tea Plantation Age on Soil Aggregate-Associated C- and N-Cycling Enzyme Activities in the Hilly Areas of Western Sichuan, China. CATENA 2018, 171, 145–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, X.; Pu, L.; Wang, Q.; Zhu, M.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, M. Response of Soil Physicochemical Properties and Enzyme Activities to Long-Term Reclamation of Coastal Saline Soil, Eastern China. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 607–608, 1419–1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Sun, L.; Ling, N.; Zhu, C.; Chi, F.; Li, W.; Hao, X.; Zhang, W.; Bian, J.; Chen, L.; et al. Exploring Soil Factors Determining Composition and Structure of the Bacterial Communities in Saline-Alkali Soils of Songnen Plain. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 10, 2902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, V.N.L.; Greene, R.S.B.; Dalal, R.C.; Murphy, B.W. Soil Carbon Dynamics in Saline and Sodic Soils: A Review: Soil Carbon Dynamics in Saline and Sodic Soils. Soil Use Manag. 2010, 26, 2–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machado, R.; Serralheiro, R. Soil Salinity: Effect on Vegetable Crop Growth. Management Practices to Prevent and Mitigate Soil Salinization. Horticulturae 2017, 3, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paz, A.M.; Castanheira, N.; Farzamian, M.; Paz, M.C.; Gonçalves, M.C.; Monteiro Santos, F.A.; Triantafilis, J. Prediction of Soil Salinity and Sodicity Using Electromagnetic Conductivity Imaging. Geoderma 2020, 361, 114086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qadir, M.; Noble, A.D.; Schubert, S.; Thomas, R.J.; Arslan, A. Sodicity-Induced Land Degradation and Its Sustainable Management: Problems and Prospects. Land Degrad. Dev. 2006, 17, 661–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rengasamy, P. Soil Processes Affecting Crop Production in Salt-Affected Soils. Funct. Plant Biol. 2010, 37, 613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qadir, M.; Oster, J.D.; Schubert, S.; Noble, A.D.; Sahrawat, K.L. Phytoremediation of Sodic and Saline-Sodic Soils. In Advances in Agronomy; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2007; Volume 96, pp. 197–247. ISBN 978-0-12-374206-3. [Google Scholar]
- Ananyeva, K.; Wang, W.; Smucker, A.J.M.; Rivers, M.L.; Kravchenko, A.N. Can Intra-Aggregate Pore Structures Affect the Aggregate’s Effectiveness in Protecting Carbon? Soil Biol. Biochem. 2013, 57, 868–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Qian, H.; Wang, X.; Chen, L.; Liu, M.; Li, H.; Sun, B. Nematodes and Microbial Community Affect the Sizes and Turnover Rates of Organic Carbon Pools in Soil Aggregates. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2018, 119, 22–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Six, J.; Elliott, E.T.; Paustian, K. Aggregate and Soil Organic Matter Dynamics under Conventional and No-Tillage Systems. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1999, 63, 1350–1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kushwaha, C.P.; Tripathi, S.K.; Singh, K.P. Soil Organic Matter and Water-Stable Aggregates under Different Tillage and Residue Conditions in a Tropical Dryland Agroecosystem. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2001, 16, 229–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Six, J.; Elliott, E.T.; Paustian, K. Soil Macroaggregate Turnover and Microaggregate Formation: A Mechanism for C Sequestration under No-Tillage Agriculture. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2000, 32, 2099–2103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, F.; Li, Y.; Cui, S.; Jagadamma, S.; Yang, G.; Zhang, Q. Soil Extracellular Enzyme Activities under Long-Term Fertilization Management in the Croplands of China: A Meta-Analysis. Nutr. Cycl. Agroecosyst. 2019, 114, 125–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sainju, U.M.; Terrill, T.H.; Gelaye, S.; Singh, B.P. Soil Aggregation and Carbon and Nitrogen Pools under Rhizoma Peanut and Perennial Weeds. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2003, 67, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bach, E.M.; Hofmockel, K.S. Soil Aggregate Isolation Method Affects Measures of Intra-Aggregate Extracellular Enzyme Activity. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2014, 69, 54–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinsabaugh, R.L.; Lauber, C.L.; Weintraub, M.N.; Ahmed, B.; Allison, S.D.; Crenshaw, C.; Contosta, A.R.; Cusack, D.; Frey, S.; Gallo, M.E.; et al. Stoichiometry of Soil Enzyme Activity at Global Scale: Stoichiometry of Soil Enzyme Activity. Ecol. Lett. 2008, 11, 1252–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Six, J.; Bossuyt, H.; Degryze, S.; Denef, K. A History of Research on the Link between (Micro)Aggregates, Soil Biota, and Soil Organic Matter Dynamics. Soil Tillage Res. 2004, 79, 7–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiesmeier, M.; Urbanski, L.; Hobley, E.; Lang, B.; von Lützow, M.; Marin-Spiotta, E.; van Wesemael, B.; Rabot, E.; Ließ, M.; Garcia-Franco, N.; et al. Soil Organic Carbon Storage as a Key Function of Soils—A Review of Drivers and Indicators at Various Scales. Geoderma 2019, 333, 149–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhtar, K.; Wang, W.; Ren, G.; Khan, A.; Feng, Y.; Yang, G. Changes in Soil Enzymes, Soil Properties, and Maize Crop Productivity under Wheat Straw Mulching in Guanzhong, China. Soil Tillage Res. 2018, 182, 94–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsalirou, E.; Deng, S.; Nofziger, D.L.; Gerakis, A. Long-Term Management Effects on Organic C and N Pools and Activities of C-Transforming Enzymes in Prairie Soils. Eur. J. Soil Biol. 2010, 46, 335–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, S.A.P.; Bettiol, W.; Cerri, C.C. Effect of Sewage Sludge on Microbial Biomass, Basal Respiration, Metabolic Quotient and Soil Enzymatic Activity. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2005, 30, 65–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Hu, W.; Tao, J.; Liu, Y.; Kong, Z.; Wu, L. Soil Bacterial Community Structure and Extracellular Enzyme Activities under Different Land Use Types in a Long-Term Reclaimed Wetland. J. Soils Sediments 2019, 19, 2543–2557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Nunan, N.; Dechesne, A.; Juarez, S.; Grundmann, G. The Spatial Distribution of Exoenzyme Activities across the Soil Micro-Landscape, as Measured in Micro- and Macro-Aggregates, and Ecosystem Processes. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2015, 91, 258–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jian, S.; Li, J.; Chen, J.; Wang, G.; Mayes, M.A.; Dzantor, K.E.; Hui, D.; Luo, Y. Soil Extracellular Enzyme Activities, Soil Carbon and Nitrogen Storage under Nitrogen Fertilization: A Meta-Analysis. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2016, 101, 32–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saiya-Cork, K.R.; Sinsabaugh, R.L.; Zak, D.R. The Effects of Long Term Nitrogen Deposition on Extracellular Enzyme Activity in an Acer Saccharum Forest Soil. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2002, 34, 1309–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, B.L.; Hopkins, D.W.; Haygarth, P.M.; Ostle, N. β-Glucosidase Activity in Pasture Soils. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2002, 6, 157–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guangming, L.; Xuechen, Z.; Xiuping, W.; Hongbo, S.; Jingsong, Y.; Xiangping, W. Soil Enzymes as Indicators of Saline Soil Fertility under Various Soil Amendments. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2017, 237, 274–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trivedi, P.; Delgado-Baquerizo, M.; Trivedi, C.; Hu, H.; Anderson, I.C.; Jeffries, T.C.; Zhou, J.; Singh, B.K. Microbial Regulation of the Soil Carbon Cycle: Evidence from Gene–Enzyme Relationships. ISME J. 2016, 10, 2593–2604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Yang, C.; Shen, Q.; Zhou, J.; Yang, L. Soil Enzymatic Activity and Growth of Rice and Barley as Influenced by Organic Manure in an Anthropogenic Soil. Geoderma 2003, 115, 149–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekenler, M. M., T. β-Glucosaminidase Activity of Soils: Effect of Cropping Systems and Its Relationship to Nitrogen Mineralization. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2002, 36, 367–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Wang, S.; Li, Y.; Zhang, N.; Zhao, B.; Zhuo, Y.; Chen, C. Influence of Flue Gas Desulfurization Gypsum Amendments on Heavy Metal Distribution in Reclaimed Sodic Soils. Environ. Eng. Sci. 2015, 32, 470–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Tang, J.; Li, Z.; Yang, W.; Yang, P.; Qu, Y. Corn and Rice Cultivation Affect Soil Organic and Inorganic Carbon Storage through Altering Soil Properties in Alkali Sodic Soils, Northeast of China. Sustainability 2020, 12, 1627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Wang, Z.; Song, K.; Zhang, B.; Hu, L.; Huang, N.; Zhang, S.; Luo, L.; Zhang, C.; Jiang, G. Land Use/Cover Changes and Environmental Consequences in Songnen Plain, Northeast China. Chin. Geogr. Sci. 2009, 19, 299–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.; Wang, J.; Li, Z.; Wang, S.; Qu, Y. Effects of Irrigation Regime and Nitrogen Fertilizer Management on CH4, N2O and CO2 Emissions from Saline–Alkaline Paddy Fields in Northeast China. Sustainability 2018, 10, 475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.; Liu, X.; Meng, Q.; Zeng, X.; Zhang, J.; Li, D.; Wang, J.; Du, W.; Ma, X. Additional Application of Aluminum Sulfate with Different Fertilizers Ameliorates Saline-Sodic Soil of Songnen Plain in Northeast China. J. Soils Sediments 2019, 19, 3521–3533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brookes, P.C.; Landman, A.; Pruden, G.; Jenkinson, D.S. Chloroform Fumigation and the Release of Soil Nitrogen: A Rapid Direct Extraction Method to Measure Microbial Biomass Nitrogen in Soil. Soil Biol. Biochem. 1985, 17, 837–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meruvu, H. Polyextremotolerant Amylase Produced from Novel Enterococcus with Potpourri of Applications. Int. J. Pept. Res. Ther. 2019, 25, 1669–1678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trasar-Cepeda, C.; Leirós, M.C.; Gil-Sotres, F. Hydrolytic Enzyme Activities in Agricultural and Forest Soils. Some Implications for Their Use as Indicators of Soil Quality. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2008, 40, 2146–2155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, C.; Kang, D.; Wu, J. ping; Zhao, F.; Yang, G.; Han, X.; Feng, Y.; Ren, G. Temporal Variation in Soil Enzyme Activities after Afforestation in the Loess Plateau, China. Geoderma 2016, 282, 103–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parham, J.A.; Deng, S.P. Detection, Quanti®cation and Characterization of b- Glucosaminidase Activity in Soil. Soil Biol. 2000, 32, 1183–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Fu, S.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, K.; Chen, H.Y.H. Intercropping Improves Soil Nutrient Availability, Soil Enzyme Activity and Tea Quantity and Quality. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2017, 119, 171–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siebers, N.; Abdelrahman, H.; Krause, L.; Amelung, W. Bias in Aggregate Geometry and Properties after Disintegration and Drying Procedures. Geoderma 2018, 313, 163–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Chen, J.; Zhu, L. Soil Aggregate Size Distribution and Stability of Farmland as Affected by Dry and Wet Sieving Methods. Zemdirb. -Agric. 2020, 107, 179–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okolo, C.C.; Gebresamuel, G.; Zenebe, A.; Haile, M.; Eze, P.N. Accumulation of Organic Carbon in Various Soil Aggregate Sizes under Different Land Use Systems in a Semi-Arid Environment. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2020, 297, 106924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tisdall, J.M.; Oades, J.M. Organic Matter and Water-Stable Aggregates in Soils. J. Soil Sci. 1982, 33, 141–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bronick, C.J.; Lal, R. Soil Structure and Management: A Review. Geoderma 2005, 124, 3–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunina, A.; Ryzhova, I.; Dorodnikov, M.; Kuzyakov, Y. Effect of Plant Communities on Aggregate Composition and Organic Matter Stabilisation in Young Soils. Plant Soil 2015, 387, 265–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Zhang, Y.; Jia, J.; Cui, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Y. Soil Aggregation and Aggregate-Associated Organic C and Total N as Affected by Revegetation Pattern at a Surface Mine on the Loess Plateau, China. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2019, 83, 388–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boix-Fayos, C.; Calvo-Cases, A.; Imeson, A.C.; Soriano-Soto, M.D. Influence of Soil Properties on the Aggregation of Some Mediterranean Soils and the Use of Aggregate Size and Stability as Land Degradation Indicators. CATENA 2001, 44, 47–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Fan, R.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, D.; McLaughlin, N.; Zhang, S.; Chen, X.; Jia, S.; Liang, A. Tillage-Induced Effects on SOC through Changes in Aggregate Stability and Soil Pore Structure. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 703, 134617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, M.; Xiang, Y.; Xue, Z.; An, S.; Darboux, F. Soil Aggregation and Intra-Aggregate Carbon Fractions in Relation to Vegetation Succession on the Loess Plateau, China. CATENA 2015, 124, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denef, K.; Six, J. Contributions of Incorporated Residue and Living Roots to Aggregate-Associated and Microbial Carbon in Two Soils with Different Clay Mineralogy. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2006, 57, 774–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mustafa, A.; Minggang, X.; Ali Shah, S.A.; Abrar, M.M.; Nan, S.; Baoren, W.; Zejiang, C.; Saeed, Q.; Naveed, M.; Mehmood, K.; et al. Soil Aggregation and Soil Aggregate Stability Regulate Organic Carbon and Nitrogen Storage in a Red Soil of Southern China. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 270, 110894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Wright, A.L.; Wang, J.; Li, Z. Long-Term Tillage Effects on the Distribution Patterns of Microbial Biomass and Activities within Soil Aggregates. CATENA 2011, 87, 276–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayoubi, S.; Mokhtari Karchegani, P.; Mosaddeghi, M.R.; Honarjoo, N. Soil Aggregation and Organic Carbon as Affected by Topography and Land Use Change in Western Iran. Soil Tillage Res. 2012, 121, 18–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, J.; Hu, R.; Feng, M.; Lin, S.; Malghani, S.; Ali, I.M. Microbial Biomass, and Dissolved Organic Carbon and Nitrogen Strongly Affect Soil Respiration in Different Land Uses: A Case Study at Three Gorges Reservoir Area, South China. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2010, 137, 294–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhople, P.; Djukic, I.; Keiblinger, K.; Zehetner, F.; Liu, D.; Bierbaumer, M.; Zechmeister-Boltenstern, S.; Joergensen, R.G.; Murugan, R. Variations in Soil and Microbial Biomass C, N and Fungal Biomass Ergosterol along Elevation and Depth Gradients in Alpine Ecosystems. Geoderma 2019, 345, 93–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kravchenko, A.; Chun, H.-C.; Mazer, M.; Wang, W.; Rose, J.B.; Smucker, A.; Rivers, M. Relationships between Intra-Aggregate Pore Structures and Distributions of Escherichia Coli within Soil Macro-Aggregates. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2013, 63, 134–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mangalassery, S.; Sjögersten, S.; Sparkes, D.L.; Sturrock, C.J.; Mooney, S.J. The Effect of Soil Aggregate Size on Pore Structure and Its Consequence on Emission of Greenhouse Gases. Soil Tillage Res. 2013, 132, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharyya, R.; Rabbi, S.M.F.; Zhang, Y.; Young, I.M.; Jones, A.R.; Dennis, P.G.; Menzies, N.W.; Kopittke, P.M.; Dalal, R.C. Soil Organic Carbon Is Significantly Associated with the Pore Geometry, Microbial Diversity and Enzyme Activity of the Macro-Aggregates under Different Land Uses. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 778, 146286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marx, M.-C.; Kandeler, E.; Wood, M.; Wermbter, N.; Jarvis, S.C. Exploring the Enzymatic Landscape: Distribution and Kinetics of Hydrolytic Enzymes in Soil Particle-Size Fractions. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2005, 37, 35–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Hayes, F.; Turner, R.; Chadwick, D.R.; Mills, G.; Jones, D.L. Effects of Four Years of Elevated Ozone on Microbial Biomass and Extracellular Enzyme Activities in a Semi-Natural Grassland. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 660, 260–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Hu, N.; Ge, T.; Kuzyakov, Y.; Wang, Z.-L.; Li, Z.; Tang, Z.; Chen, Y.; Wu, C.; Lou, Y. Soil Aggregation Regulates Distributions of Carbon, Microbial Community and Enzyme Activities after 23-Year Manure Amendment. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2017, 111, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, C.; Tian, D.; Zeng, H.; Li, Z.; Chen, H.Y.H.; Niu, S. Global Meta-Analysis on the Responses of Soil Extracellular Enzyme Activities to Warming. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 705, 135992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Soil Property | Soil Depth | C1 | C2 | C3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| BD (g cm−3) | 0–20 cm | 1.15 ± 0.02 1 | 1.17 ± 0.02 | 1.22 ± 0.05 |
| 20–40 cm | 1.30 ± 0.04 | 1.31 ± 0.03 | 1.31 ± 0.03 | |
| SP (%) | 0–20 cm | 56.45 ± 0.61 | 55.82 ± 0.72 | 53.79 ± 2.05 |
| 20–40 cm | 51.08 ± 1.57 | 50.72 ± 1.23 | 50.72 ± 1.23 | |
| Sand (%) | 0–20 cm | 67.04 ± 1.50 | 66.47 ± 1.35 | 73.76 ± 0.59 |
| 20–40 cm | 63.96 ± 1.52 | 53.40 ± 0.29 | 54.93 ± 0.55 | |
| Silt (%) | 0–20 cm | 28.57 ± 1.11 | 29.39 ± 1.15 | 22.89 ± 0.51 |
| 20–40 cm | 31.31 ± 1.41 | 39.41 ± 0.24 | 37.37 ± 0.53 | |
| Clay (%) | 0–20 cm | 4.39 ± 0.41 | 4.14 ± 0.21 | 3.35 ± 0.11 |
| 20–40 cm | 4.74 ± 0.14 | 7.19 ± 0.38 | 7.69 ± 0.13 | |
| Soil texture | Sand Loam | Sand Loam | Sand Loam | |
| Soil pH | 0–20 cm | 8.93 ± 0.02 | 9.54 ± 0.02 | 9.90 ± 0.05 |
| 20–40 cm | 8.98 ± 0.05 | 9.72 ± 0.03 | 10.14 ± 0.02 | |
| EC (ms cm−1) | 0–20 cm | 0.14 ± 0.02 | 0.18 ± 0.01 | 0.27 ± 0.01 |
| 20–40 cm | 0.15 ± 0.03 | 0.23 ± 0.02 | 0.32 ± 0.04 | |
| ESP (%) | 0–20 cm | 6.31 ± 2.29 | 15.17 ± 0.46 | 24.00 ± 1.85 |
| 20–40 cm | 6.49 ± 1.42 | 22.11 ± 2.97 | 38.98 ± 0.40 | |
| SOC (g kg−1) | 0–20 cm | 25.19 ± 0.33 | 22.87 ± 0.57 | 16.46 ± 0.68 |
| 20–40 cm | 14.19 ± 0.12 | 1.72 ± 1.06 | 14.64 ± 0.53 | |
| TN (g kg−1) | 0–20 cm | 1.68 ± 0.03 | 1.67 ± 0.14 | 1.24 ± 0.08 |
| 20–40 cm | 0.55 ± 0.04 | 1.38 ± 0.20 | 0.97 ± 0.08 | |
| SIC (g kg−1) | 0–20 cm | 1.29 ± 0.04 | 6.31 ± 0.07 | 12.18 ± 0.08 |
| 20–40 cm | 7.21 ± 0.01 | 13.74 ± 0.21 | 23.78 ± 0.47 |
| Site | Aggregates (μm) | SOC (g kg−1 soil) | TN (g kg−1 soil) | C:N | MBC (mg kg−1 soil) | MBN (mg kg−1 soil) | MBC:SOC (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0–20 cm | |||||||
| C1 | >2000 | 24.09 ± 2.54 Aa | 1.53 ± 0.03 Ab | 15.68 ± 1.36 Aa | 73.14 ± 15.79 Ab | 8.92 ± 1.66 Bb | 0.58 ± 0.10 Ab |
| 250–2000 | 28.28 ± 0.41 Aa | 1.66 ± 0.06 Aa | 17.09 ± 0.49 Aa | 276.51 ± 77.89 Aa | 13.54 ± 1.65 Aa | 0.81 ± 0.07 Aa | |
| <250 | 22.50 ± 0.46 Aa | 1.37 ± 0.05 Ac | 16.41 ± 0.99 Aa | 150.80 ± 25.49 Bab | 6.66 ± 0.36 Ab | 0.48 ±0.02 Bb | |
| C2 | >2000 | 23.02 ± 0.54 Aa | 1.66 ± 0.04 Ba | 13.87 ± 0.09 Aa | 88.91 ± 10.15 Aa | 11.39 ± 0.21 Aa | 0.69 ± 0.00 Aa |
| 250–2000 | 25.90 ± 1.51 Aa | 1.74 ± 0.05 Aa | 14.85 ± 0.49 Aa | 119.15 ± 23.78 Aa | 13.23 ± 0.90 Aa | 0.76 ± 0.03 Aa | |
| <250 | 18.73 ± 1.91 Ab | 1.34 ± 0.06 Ab | 13.90 ± 0.92 Ba | 110.76 ± 4.58 Ba | 8.56 ± 1.00 Ab | 0.63 ± 0.05 Aa | |
| C3 | >2000 | 12.01 ± 0.20 Bb | 1.27 ± 0.02 Cb | 9.42 ± 0.15 Ba | 102.59 ± 32.05 Ab | 4.34 ± 0.44 Ca | 0.34 ± 0.03 Ba |
| 250–2000 | 16.98 ± 2.40 Ba | 1.51 ± 0.02 Ba | 11.27 ± 1.48 Ba | 197.28 ± 35.30 Aa | 5.07 ± 0.68 Ba | 0.34 ± 0.04 Ba | |
| <250 | 11.37 ± 0.56 Bb | 1.06 ± 0.01 Bc | 10.75 ± 0.48 Ca | 148.72 ± 9.47 Aab | 3.12 ± 0.15 Bb | 0.30 ± 0.01 Ca | |
| 20–40 cm | |||||||
| C1 | >2000 | 7.88 ± 0.27 Ca | 0.48 ± 0.01 Ca | 16.50 ± 0.22 Aa | 35.24 ± 5.11 Bb | 2.77 ± 0.87 Bb | 0.58 ± 0.16 Ab |
| 250–2000 | 7.32 ± 0.15 Ca | 0.53 ± 0.02 Ba | 13.88 ± 0.18 Ab | 62.80 ± 10.49 Ba | 6.01 ± 0.76 Ba | 1.14 ± 0.11 Aa | |
| <250 | 7.31 ± 0.79 Ca | 0.46 ± 0.04 Cb | 16.05 ± 1.43 Aa | 24.29 ± 1.24 Bb | 0.64 ± 0.05 Cc | 0.14 ± 0.01 Bc | |
| C2 | >2000 | 17.05 ± 0.32 Aa | 1.25 ± 0.05 Aa | 13.62 ± 0.31 Ba | 35.47 ± 2.44 Ba | 5.44 ± 0.27 Ab | 0.43 ± 0.00 ABb |
| 250–2000 | 16.64 ± 0.10 Aa | 1.43 ± 0.09 Aa | 11.69 ± 0.69 Bb | 39.32 ± 1.55 Ba | 11.50 ± 0.06 Aa | 0.81 ± 0.05 Ba | |
| <250 | 14.91 ± 0.95 Ab | 1.21 ± 0.15 Aa | 12.430 ± 1.04 Bab | 32.71 ± 4.07 Ba | 3.02 ± 0.47 Ac | 0.25 ± 0.01 Ac | |
| C3 | >2000 | 13.38 ± 0.48 Ba | 0.98 ± 0.02 Bb | 13.65 ± 0.26 Ba | 118.49 ± 10.30 Aa | 3.10 ± 0.55 Ba | 0.32 ± 0.05 Ba |
| 250–2000 | 11.94 ± 0.20 Bb | 1.10 ± 0.01 Aa | 10.86 ± 0.13 Bb | 134.42 ± 19.83 Aa | 4.26 ± 0.51 Ba | 0.39 ± 0.04 Ca | |
| <250 | 10.37 ± 0.68 Bc | 0.89 ± 0.02 Bc | 11.66 ± 0.55 Bb | 106.56 ± 6.00 Aa | 1.79 ± 0.36 Bb | 0.20 ± 0.04 Ab | |
| Soil Aggregates (μm) | Soil Enzyme Activities | Explanation of SOC and TN (%) | p |
|---|---|---|---|
| >2000 | NAG | 82.7 | 0.002 |
| INV | 66.5 | 0.002 | |
| GLU | 43.9 | 0.006 | |
| URE | 31.3 | 0.016 | |
| 250–2000 | NAG | 87.0 | 0.002 |
| GLU | 72.6 | 0.002 | |
| INV | 68.4 | 0.002 | |
| URE | 24.3 | 0.040 | |
| <250 | NAG | 85.7 | 0.002 |
| GLU | 66.3 | 0.002 | |
| INV | 65.4 | 0.002 | |
| URE | 41.7 | 0.004 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, J.; Shu, K.; Wang, S.; Zhang, C.; Feng, Y.; Gao, M.; Li, Z.; Cai, H. Soil Enzyme Activities Affect SOC and TN in Aggregate Fractions in Sodic-Alkali Soils, Northeast of China. Agronomy 2022, 12, 2549. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12102549
Wang J, Shu K, Wang S, Zhang C, Feng Y, Gao M, Li Z, Cai H. Soil Enzyme Activities Affect SOC and TN in Aggregate Fractions in Sodic-Alkali Soils, Northeast of China. Agronomy. 2022; 12(10):2549. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12102549
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Jingjing, Kunliang Shu, Siyu Wang, Chang Zhang, Yanchun Feng, Ming Gao, Zhonghe Li, and Hongguang Cai. 2022. "Soil Enzyme Activities Affect SOC and TN in Aggregate Fractions in Sodic-Alkali Soils, Northeast of China" Agronomy 12, no. 10: 2549. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12102549
APA StyleWang, J., Shu, K., Wang, S., Zhang, C., Feng, Y., Gao, M., Li, Z., & Cai, H. (2022). Soil Enzyme Activities Affect SOC and TN in Aggregate Fractions in Sodic-Alkali Soils, Northeast of China. Agronomy, 12(10), 2549. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12102549





