How Does Long-Term Organic Matter Treatment Affect the Biological Activity of a Centre European Forest Soil?
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
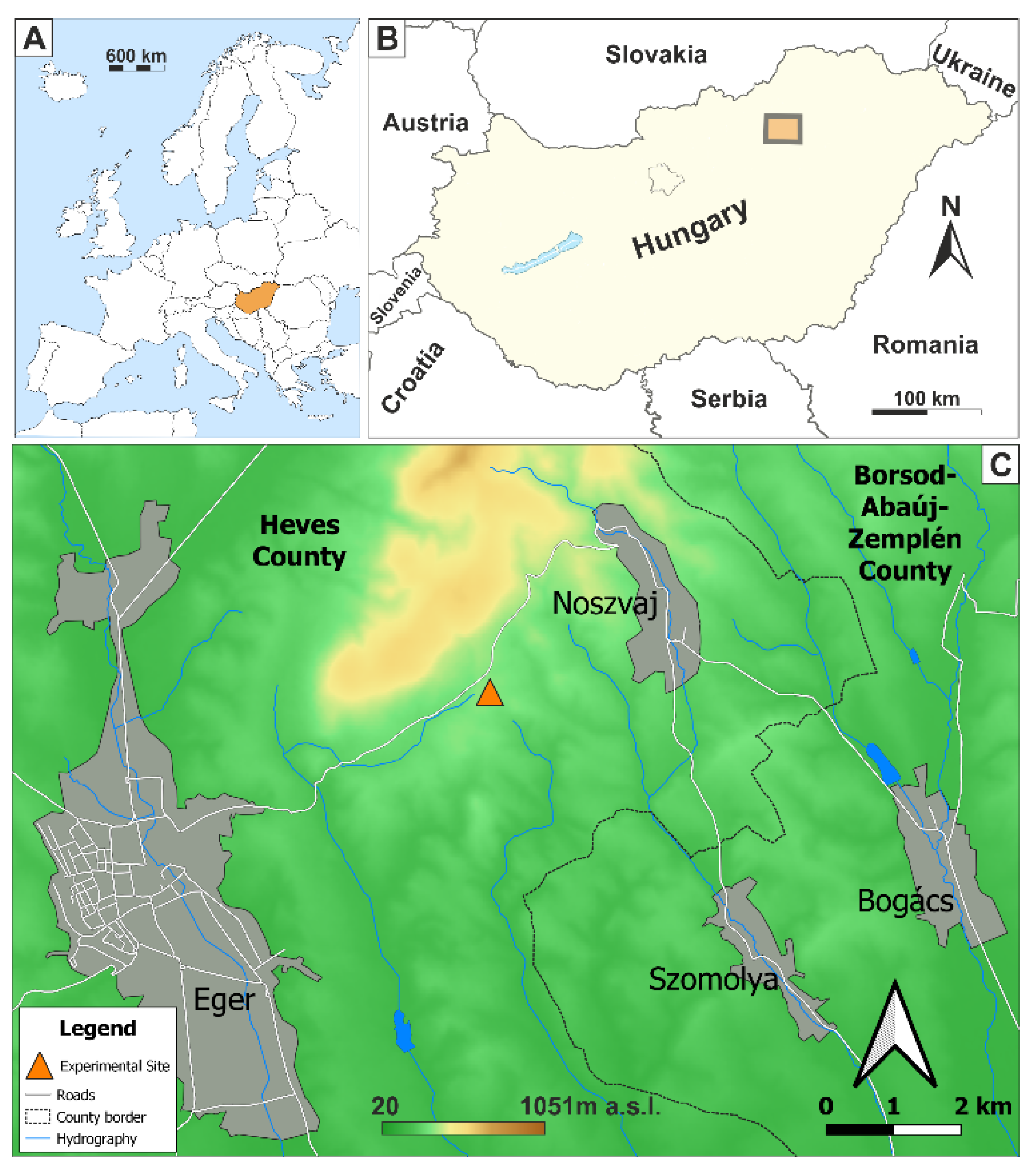
2.1. Research Area
2.2. Soil Sampling and Test Methods
2.3. Statistical Methods
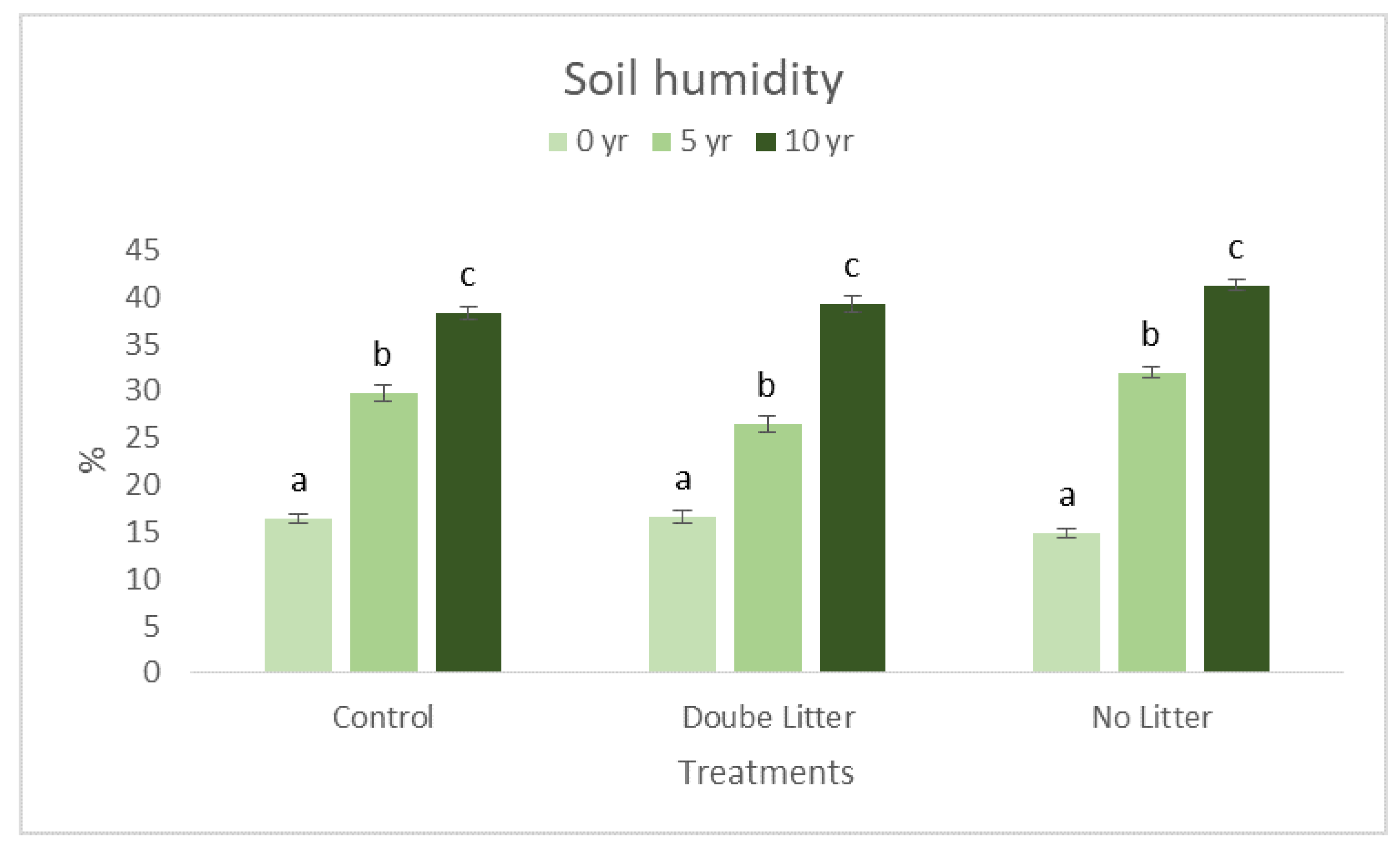
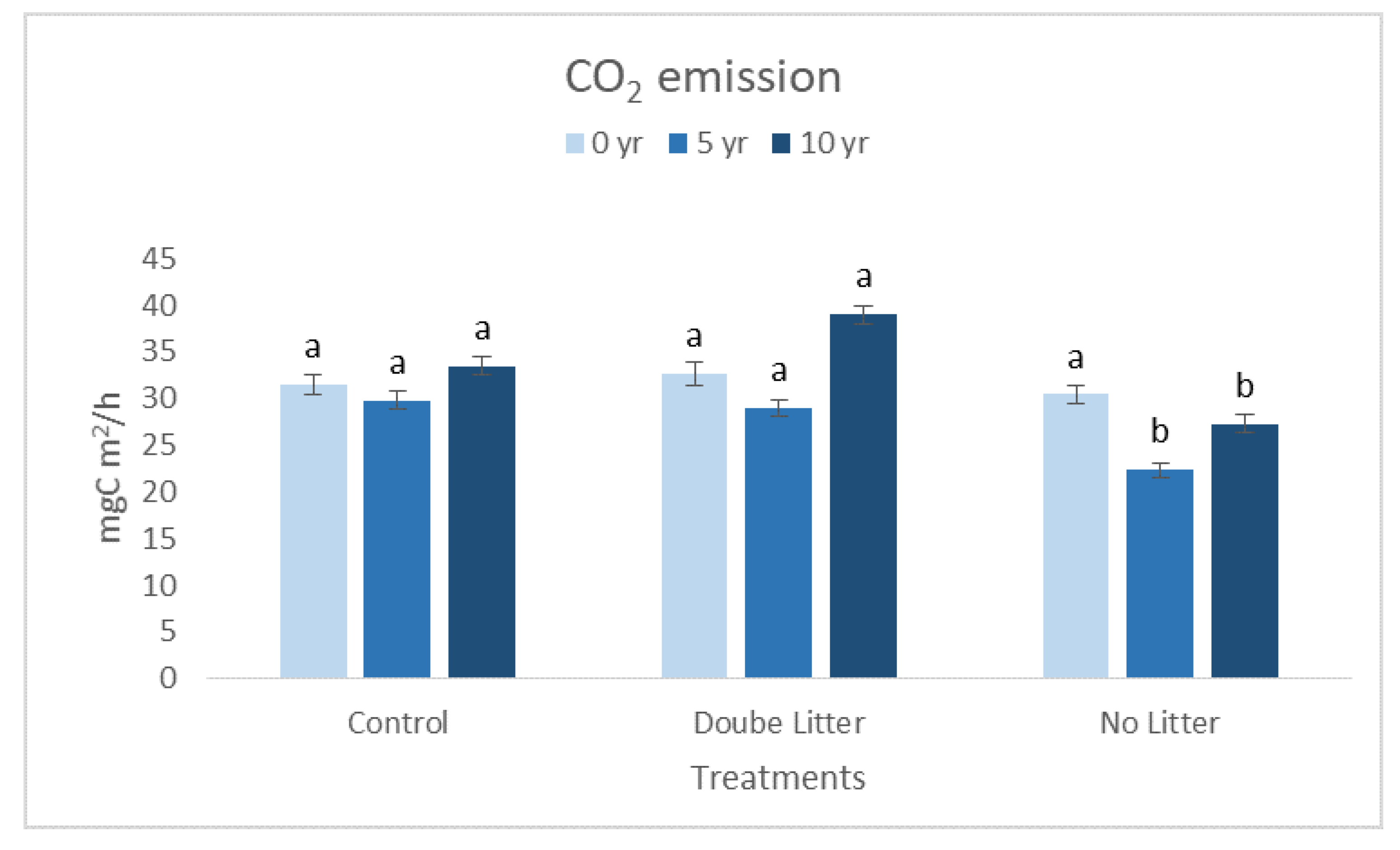
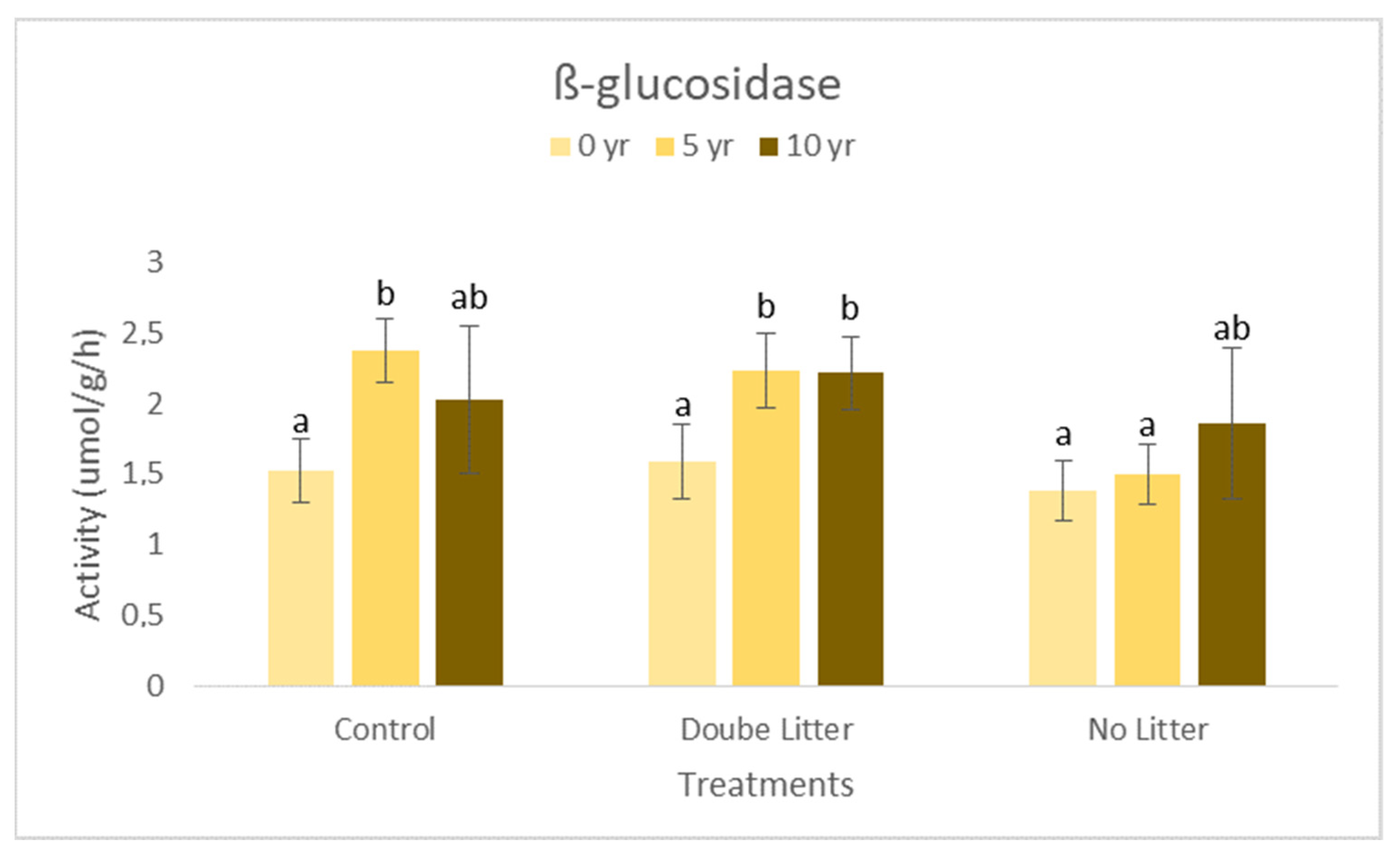
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fekete, I.; Lajtha, K.; Kotroczó, Z.; Várbíró, G.; Varga, C.; Tóth, J.A.; Demeter, I.; Veperdi, G.; Berki, I. Long term effects of climate change on carbon storage and tree species composition in a dry deciduous forest. Glob. Change Biol. 2017, 23, 3154–3168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Błońska, E.; Lasota, J.; Piaszczyk, W.; Wiecheć, M.; Klamerus-Iwan, A. The effect of landslide on soil organic carbon stock and biochemical properties of soil. J. Soils Sediments 2018, 18, 2727–2737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotroczó, Z.; Veres, Z.; Fekete, I.; Papp, M.; Tóth, J.A. Effects of Climate Change on Litter Production in a Quercetum petraeae-cerris Forest in Hungary. Acta Silv. Lignaria Hung. 2012, 8, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tóth, J.A.; Nagy, P.T.; Krakomperger, Z.; Veres, Z.; Kotroczó, Z.; Kincses, S.; Fekete, I.; Papp, M.; Mészáros, I.; Viktor, O. The Effects of Climate Change on Element Content and Soil pH (Síkfőkút DIRT Project, Northern Hungary). In The Carpathians: Integrating Nature and Society Towards Sustainability, Environmental Science and Engineering; Kozak, J., Ostapowicz, K., Bytnerowicz, A., Wyżga, B., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013; pp. 77–88. [Google Scholar]
- Raich, J.W.; Schlesinger, W.H. The global carbon dioxid flux in soil respiration and its relationship to vegetation and climate. Tellus B 1992, 44, 81–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlesinger, W.H. Carbon balance in terrestrial detritus. Ann. Rev. Ecol. Syst. 1977, 8, 51–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raich, J.W.; Nadelhoffer, K.J. Belowground carbon allocation in forest ecosystems: Global trends. Ecology 1989, 70, 1346–1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDowell, W.H.; Likens, G.E. Origin, composition, and flux of dissolved organic carbon in the Hubbard Brook valley. Ecol. Monogr. 1988, 58, 177–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qualls, R.G.; Haines, B.L.; Swank, W.T. Fluxes of dissolved organic nutrients and humic substances in a deciduous forest. Ecology 1991, 72, 254–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ringer, M.; Jakab, G.; Sipos, P.; Szabó, M.; Perényi, K.; Szalai, Z. Vertical differentiation of pedogenic iron forms–a key of hydromorphic soil profile development. Hung. Geogr. Bull. 2021, 70, 369–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotroczó, Z.; Veres, Z.; Biró, B.; Tóth, J.A.; Fekete, I. Influence of temperature and organic matter content on soil respiration in a deciduous oak forest. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2014, 3, 303–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zágoni, M. Üvegházhatás és globális felmelegedés. Ezredforduló, Stratégiai tanulmányok a Magyar Tudományos Akadémián II. In História; Ferenc, G., Ed.; Hungarian Academy of Sciences: Budapest, Hungary, 2006; pp. 12–15. (In Hungarian) [Google Scholar]
- Wild, A. Plant Nutrients in Soil: Phosphate. Russell’s Soil conditions and Plant Growth, 11th ed.; Longman Group UK Limited: Harlow, Essex, UK, 1988; pp. 695–742. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, Z.; Wang, E.; Sun, O.J. Soil carbon change and its responses to agricultural practices in Australian agro-ecosystems: A review and synthesis. Geoderma 2010, 155, 211–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldock, J.A. Nitrogen and Soil Organic Matter Decline—What Is Needed to Fix It; GRDC Updates: Bendigo, Australia, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Fekete, I.; Kotroczó, Z.; Varga, C.; Hargitai, R.; Townsend, K.; Csányi, G.; Várbiró, G. Variability of organic matter inputs affects soil moisture and soil biological parameters in a European detritus manipulation experiment. Ecosystems 2012, 15, 792–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fekete, I.; Varga, C.; Biró, B.; Tóth, J.A.; Várbíró, G.; Lajtha, K.; Szabó, G.; Kotroczó, Z. The effects of litter production and litter depth on soil microclimate in a central european deciduous forest. Plant Soil 2016, 398, 291–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tóth, J.A.; Lajtha, K.; Kotroczó, Z.; Krakomperger, Z.; Caldwel, B.; Bowden, R.D.; Papp, M. The effect of climate change on soil organic matter decomposition. Acta Silv. Lignaria Hung. 2007, 3, 75–85. [Google Scholar]
- Jenkinson, D.S.; Adams, D.E.; Wild, A. Model estimates of CO2 emissions from soil in response to global warming. Nature 1991, 351, 304–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirschbaum, M.U.F. The temperature dependence of soil organic matter decomposition, and the effect of global warming on soil organic C storage. Soil Biol. Biochem. 1995, 27, 753–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaye, J.P.; Hart, S.C. Restoration and canopy-type effects soil respiration in a Ponderosa Pine—Bunchgrass ecosystem. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1998, 62, 1062–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cox, P.M.; Betts, R.A.; Jones, C.D.; Spall, S.A.; Totterdell, I.J. Acceleration of global warming due to carbon-cycle feedbacks in a coupled climate model. Nature 2000, 408, 750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varga, C.; Fekete, I.; Kotroczó, Z.; Krakomperger, Z.; Vincze, G. The Effect of litter on soil organic matter (SOM) turnover in Síkfőkút site. Cereal Res. Commun. 2008, 36, 547–550. [Google Scholar]
- Sulzman, E.W.; Brant, J.B.; Bowden, R.D.; Lajtha, K. Contribution of aboveground litter, belowground litter, and rhizosphere respiration to total soil CO2 efflux in an old growth coniferous forest. Biogeochemistry 2005, 73, 231–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, M.; Kjøller, A.; Struwe, S. Microbial enzyme activities in leaf litter, humus and mineral soil layers of European forests. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2004, 36, 1527–1537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freeman, C.; Ostle, N.; Kang, H. An enzymic ‘latch’ on a global carbon store—A shortage of oxygen locks up carbon in peatlands by restraining a single enzyme. Nature 2001, 409, 149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boerner, R.E.J.; Brinkman, J.A.; Smith, A. Seasonal variations in enzyme activity and organic carbon in soil of burned and unburned hardwood forest. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2005, 37, 1419–1426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dick, R.P. Soil enzyme activities as indicators of soil quality. In Defining Soil Quality for a Sustainable Environment; Doran, J.W., Coleman, D.C., Bezdicek, D.F., Stewart, B.A., Eds.; Soil Science Society America: Madison, WI, USA, 1994; pp. 107–124. [Google Scholar]
- Gregorich, E.G.; Carter, M.R.; Angers, D.A.; Monreal, C.M.; Ellert, B.H. Towards a minimum data set to assess soil organic matter quality in agricultural soils. Can. J. Soil Sci. 1994, 74, 367–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kocsis, T.; Kotroczó, Z.; Juhos, K.; Ferschl, B.; Rozmann, V.; Brückner, A.; Biró, B. Opposite tendency between yield and taste of organic tomato by increasing biochar doses in a slightly humous arenosol. Agron. Res. 2022, 20, 200–214. [Google Scholar]
- Chróst, R.J.; Velimirov, B. Measurement of enzyme kinetics in water samples: Effect of freezing and soluble stabilizer. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1991, 70, 93–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misik, T.; Kotroczó, Z.; Kárász, I.; Tóthmérész, B. Long-term oak seedling dynamics and regeneration ability in a deciduous forest in Hungary. Balt. For. 2017, 23, 595–602. [Google Scholar]
- Switoniak, M.; Charzynski, P.; Novak, T.J.; Zalewska, K.; Bednarek, R. Forested hilly landscape of Büukkalja Foothill (Hungary). In Soil Sequences Atlas; Nicholaus Copernicus University Press: Torun, Poland, 2014; pp. 169–181. [Google Scholar]
- Juhos, K.; Madarász, B.; Kotroczó, Z.; Béni, Á.; Makádi, M.; Fekete, I. Carbon sequestration of forest soils is reflected by changes in physicochemical soil indicators—A comprehensive discussion of a long-term experiment on a detritus manipulation. Geoderma 2021, 385, 114918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lajtha, K.; Bowden, R.D.; Crow, S.; Fekete, I.; Kotroczó, Z.; Plante, A.; Simpson, M.J.; Nadelhoffer, K. The detrital input and removal treatment (DIRT) network: Insights into soil carbon stabilization. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 640–641, 1112–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotroczó, Z.; Juhos, K.; Biró, B.; Kocsis, T.; Pabar, S.A.; Fekete, I. Results of an international tea litter decomposition experiment at different litter treatments of soils in a decidouos forest. Talajvédelem. (In Hungarian). 2020, 117–132. [Google Scholar]
- Sinsabaugh, R.L.; Klug, M.J.; Collins, H.P.; Yeager, P.E.; Petersen, S.O. Characterizing Soil Microbial Communities. In Standard Soil Methods for Long Term Ecological Research; Robertson, G.P., Bledsoe, C.S., Coleman, D.C., Sollins, P., Eds.; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 1999; pp. 318–348. [Google Scholar]
- Raich, J.W.; Bowden, R.D.; Steudler, P.A. Comparison of two static chamber techniques for determining carbon dioxide eflux from forest soils. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1990, 54, 1754–1757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borowik, A.; Wyszkowska, J. Soil moisture as a factor affecting the microbiological and biochemical activity of soil. Plant Soil Environ. 2016, 62, 250–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tóth, J.A.; Nagy, P.T.; Krakomperger, Z.; Veres, Z.; Kotroczó, Z.; Kincses, S.; Fekete, I.; Papp, M.; Lajtha, K. Effect of litter fall on soil nutrient content and pH, and its consequences in view of climate change (Síkfőkút DIRT Project). Acta Silv. Lignaria Hung. 2011, 7, 75–86. [Google Scholar]
- Fujii, K.; Funakawa, S.; Kosaki, T. Soil acidification: Natural processes and human impact. Pedologist 2012, 55, 415–425. [Google Scholar]
- McElligott, K.M.; Seiler, J.R.; Strahm, B.D. The impact of water content on sources of heterotrophic soil respiration. Forests 2017, 8, 299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowden, R.D.; Newkirk, K.M.; Rullo, G. Carbon dioxide and methane fluxes by a forest soil under laboratory-controlled moisture and temperature conditions. Soil Biol. Biochem. 1998, 30, 1591–1597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yano, Y.; Lajtha, K.; Sollins, P.; Caldwell, B.A. Chemistry and dynamics of dissolved organic matter in a temperate coniferous forest on Andic soils: Effect of litter quality. Ecosystems 2005, 8, 286–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaefer, D.A.; Feng, W.; Zou, X. Plant carbon inputs and environmental factors strongly affect soil respiration in a subtropical forest of southwestern China. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2009, 41, 1000–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fekete, I.; Varga, C.; Kotroczó, Z.; Tóth, J.A.; Várbiró, G. The relation between various detritus inputs and soil enzyme activities in a Central European deciduous forest. Geoderma 2011, 167–168, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abs, E.; Ferrière, R. Modeling microbial dynamics and heterotrophic soil respiration: Effect of climate change. In Biogeochemical Cycles: Ecological Drivers and Environmental Impact; American Geophysical Union: Washington, DC, USA, 2020; pp. 103–129. [Google Scholar]
- Lloyd, J.; Taylor, J.A. On the temperature-dependence of soil respiration. Funct. Ecol. 1984, 8, 315–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidson, E.A.; Janssens, I.A. Temperature sensitivity of soil carbon decomposition and feedbacks to climate change. Nature 2006, 440, 165–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]

| Treatments | Description |
|---|---|
| Control (Co) | Normal litter inputs. Average litter amount typical of the forest site. |
| No Litter (NL) | Aboveground inputs are excluded from plots. Leaf litter was removed by a rake. This process was repeated continuously every year. |
| Double Litter (DL) | Aboveground leaf inputs are doubled by adding litter removed from No Litter plots. |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kotroczó, Z.; Kocsis, T.; Juhos, K.; Halász, J.; Fekete, I. How Does Long-Term Organic Matter Treatment Affect the Biological Activity of a Centre European Forest Soil? Agronomy 2022, 12, 2301. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12102301
Kotroczó Z, Kocsis T, Juhos K, Halász J, Fekete I. How Does Long-Term Organic Matter Treatment Affect the Biological Activity of a Centre European Forest Soil? Agronomy. 2022; 12(10):2301. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12102301
Chicago/Turabian StyleKotroczó, Zsolt, Tamás Kocsis, Katalin Juhos, Judit Halász, and István Fekete. 2022. "How Does Long-Term Organic Matter Treatment Affect the Biological Activity of a Centre European Forest Soil?" Agronomy 12, no. 10: 2301. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12102301
APA StyleKotroczó, Z., Kocsis, T., Juhos, K., Halász, J., & Fekete, I. (2022). How Does Long-Term Organic Matter Treatment Affect the Biological Activity of a Centre European Forest Soil? Agronomy, 12(10), 2301. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12102301






