Response of Winter Wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) to Fertilizers with Nitrogen-Transformation Inhibitors and Timing of Their Application under Field Conditions
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Site and Field Treatments
2.2. Yield and Grain Quality Measurement
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. The Grain Yield
3.2. Qualitative Parameters of Wheat
4. Discussions
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Raun, W.R.; Johnson, G.V. Improving nitrogen use efficiency for cereal production. Agron. J. 1999, 91, 357–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, D.; Suter, H.; Islam, A.; Edis, R.; Freney, J.; Walker, C. Prospects of improving efficiency of fertiliser nitrogen in Australian agriculture: A review of enhanced efficiency fertilisers. Soil Res. 2008, 46, 289–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, Y.A.; Kelly, J.; Chim, B.K.; Rutto, E.; Waldschmidt, K.; Mullock, J.; Torres, G.; Desta, K.G.; Raun, W. Nitrogen fertilizer management for improved grain quality and yield in winter wheat in Oklahoma. J. Plant Nutr. 2013, 36, 749–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subbarao, G.V.; Ito, O.; Sahrawat, K.L.; Berry, W.L.; Nakahara, K.; Ishikawa, T.; Watanabe, T.; Suenaga, K.; Rondon, M.; Rao, I.M. Scope and strategies for regulation of nitrification in agricultural systems—Challenges and opportunities. Crit. Rev. Plant Sci. 2006, 25, 303–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wiesler, F. Comparative assessment of the efficacy of various nitrogen fertilizers. J. Crop Prod. 1998, 1, 81–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engel, R.; Jones, C.; Wallander, R. Ammonia volatilization from urea and mitigation by NBPT following surface application to cold soils. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2011, 75, 2348–2357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cameron, K.C.; Di, H.J.; Moir, J.L. Nitrogen losses from the soil/plant system: A review. Ann. Appl. Biol 2013, 162, 145–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilbeam, D.J. Nitrogen. In Handbook of Plant Nutrition, 2nd ed.; Barker, A.V., Pilbeam, D.J., Eds.; CRC Press Taylor and Francis Group: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2015; pp. 17–63. [Google Scholar]
- Cantarella, H.; Otto, R.; Soares, J.R.; de Brito Silva, A.G. Agronomic efficiency of NBPT as a urease inhibitor: A review. J. Adv. Res. 2018, 13, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schlesinger, W.H.; Hartley, A.E. A global budget for atmospheric NH3. Biogeochemistry 1992, 15, 191–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, R.; Webb, J. A review of the effect of N fertilizer type on gaseous emissions. Adv. Agron. 2001, 73, 65–108. [Google Scholar]
- Bowles, T.M.; Atallah, S.S.; Campbell, E.E.; Gaudin, A.C.M.; Wieder, W.R.; Grandy, A.S. Addressing agricultural nitrogen losses in a changing climate. Nat. Sustain. 2018, 1, 399–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reyer, C.P.O.; Leuzinger, S.; Rammig, A.; Wolf, A.; Bartholomeus, R.P.; Bonfante, A.; Lorenzi, F.D.; Dury, M.; Gloning, P.; Jaoudé, R.A.; et al. Plant’s perspective of extremes: Terrestrial plant responses to changing climatic variability. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2013, 19, 75–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erisman, J.; Bleeker, A.; Galloway, J.; Sutton, M. Reduced nitrogen in ecology and the environment. Environ. Pollut. 2007, 150, 140–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gaudin, R. The kinetics of ammonia disappearance from deep-placed urea supergranules (USG) in transplanted rice: The effects of split USG application and PK fertilizer. Paddy Water Environ. 2012, 10, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher, R.A.; Howe, G.N.; Ibrahim, Z. Irrigated spring wheat and timing and amount of nitrogen fertilizer. I. Grain yield and protein content. Field Crop. Res. 1993, 33, 37–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sowers, K.E.; Miller, B.C.; Pan, W.L. Optimizing yield and grain protein in soft white winter wheat with split nitrogen applications. Agron. J. 1994, 86, 1020–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, C.; Erley, G.S.A.; Rossmann, A.; Schuster, R.; Koehler, P.; Mühling, K.H. Split Nitrogen Application Improves Wheat Baking Quality by Influencing Protein Composition Rather Than Concentration. Front. Plant Sci. 2016, 7, 738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Manunza, B.; Deiana, S.; Pintore, M.; Gessa, C. The binding mechanism of urea, hydroxamic acid and N-(N-butyl)-phosphoric triamide to the urease active site. A comparative molecular dynamics study. Soil Biol. Biochem. 1999, 31, 789–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, D.; Edis, R.; Chen, D.; Freney, J.; Denmead, O.; Christie, R. Determination and mitigation of ammonia loss from urea applied to winter wheat with N-(n-butyl) thiophosphorictriamide. Agr. Ecosyst Environ. 2010, 137, 261–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trenkel, M.E. Slow- and Controlled-Release and Stabilized Fertilizers: An Option for Enhancing Nutrient Efficiency in Agriculture, 2nd ed.; IFA: Paris, France, 2010; p. 160. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, L.; Li, D.; Wu, Z.; Xue, Y.; Xiao, F.; Zhang, L.; Song, Y.; Li, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Zhang, J.; et al. Effects of Nitrification Inhibitors on Soil Nitrification and Ammonia Volatilization in Three Soils with Different pH. Agronomy 2021, 11, 1674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruser, R.; Schulz, R. The effect of nitrification inhibitors on the nitrous oxide (N2O) release from agricultural soils—A review. J. Plant Nutr. Soil Sci. 2015, 178, 171–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braker, G.; Conrad, R. Diversity, Structure, and Size of N2O-Producing Microbial Communities in Soils—What Matters for Their Functioning? Adv Appl Microbiol. 2011, 75, 33–70. [Google Scholar]
- IPCC. Climate Change 2014: Mitigation of Climate Change. Contribution of Working Group III to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Slangen, J.H.G.; Kerkhoff, P. Nitrification inhibitors in agriculture and horticulture: A literature review. Fertil. Res. 1984, 5, 1–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, R.; Power, J.F. Nitrification inhibitors for agriculture, health, and the environment. Adv. Agron. 1995, 54, 233–281. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, S.N.; Verma, A. The potential of nitrification inhibitors to manage the pollution effect of nitrogen fertilizers in agricultural and other soils: A review. Env. Pr. 2007, 9, 266–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.G.; Saggar, S.; Roudier, P. The effect of nitrification inhibitors on soil ammonia emissions in nitrogen managed soils: A meta-analysis. Nutr. Cycl. Agroecosyst. 2012, 93, 51–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rose, T.J.; Wood, R.H.; Rose, M.T.; Van Zwieten, L. A re-evaluation of the agronomic effectiveness of the nitrification inhibitors DCD and DMPP and the urease inhibitor NBPT. Agric. Ecosyst. Env. 2018, 252, 69–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevens, W.B.; Hoeft, R.G.; Mulvaney, R.L. Fate of nitrogen-15 in a long-term nitrogen rate study. Agron. J. 2005, 97, 1046–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onken, A.B.; Matheson, R.L.; Nesmith, D.M. Fertilizer nitrogen and residual nitrate-nitrogen effects on irrigated corn yield. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1985, 49, 134–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jokela, W.E.; Randall, G.W. Corn yield and residual soil nitrate as affected by time and rate of nitrogen application. Agron. J. 1989, 81, 720–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuzyakov, Y. Priming effects: Interactions between living and dead organic matter. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2010, 42, 1363–1371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nieder, R.; Benbi, D.K.; Scherer, H.W. Fixation and defixation of ammonium in soils: A review. Biol. Fertil Soils 2011, 47, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sugihara, S.; Funakawa, S.; Kilasara, M.; Kosaki, T. Dynamics of microbial biomass nitrogen in relation to plant nitrogen uptake during the crop growth period in a dry tropical cropland in Tanzania. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2010, 56, 105–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klikocka, H.; Cybulska, M.; Barczak, B.; Narolski, B.; Szostak, B.; Kobiałka, A.; Nowak, A.; Wójcik, E. The effect of sulphur and nitrogen fertilization on grain yield and technological quality of spring wheat. Plant Soil Environ. 2016, 62, 230–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dostálová, Y.; Hřivna, L.; Kotková, B.; Burešová, I.; Janečková, M.; Šottníková, V. Effect of nitrogen and sulphur fertilization on the quality of barley protein. Plant Soil Environ. 2015, 61, 399–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, F.J.; Salmon, S.E.; Withers, P.J.A.; Evans, E.J.; Monaghan, J.M.; Shewry, P.R.; McGrath, S.P. Responses of breadmaking quality to sulphur in three wheat varieties. J. Sci. Food Agric. 1999, 79, 1865–1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halford, N.G.; Curtis, T.Y.; Muttucumaru, N.; Postles, J.; Elmore, J.S.; Mottram, D.S. The acrylamide problem: A plant and agronomic science issue. J. Exp. Bot. 2012, 63, 2841–2851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schumacher, B.A. Methods for the Determination of Total Organic Carbon (TOC) in Soils and Sediments; United States Environmental Protection Agency, Environmental Sciences Division National, Exposure Research Laboratory: Las Vegas, NV, USA, 2002.
- Zbíral, J.; Malý, S.; Váňa, M. Soil Analysis, 3rd ed.; Central Institute for Supervising and Testing in Agriculture: Brno, Czech Republic, 2011; pp. 18–52. (In Czech) [Google Scholar]
- Selgen. Available online: https://selgen.cz/psenice-ozima/julie/ (accessed on 25 September 2021).
- Lancashire, P.D.; Bleiholder, H.; Boom, T.V.D.; Langelüddeke, P.; Stauss, R.; Weber, E.; Witzenberger, A. A uniform decimal code for growth stages of crops and weeds. Ann. Appl. Biol. 1991, 119, 561–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Saona, L.E.; Fry, F.S.; Calvey, E.M. Use of Fourier Transform Near-Infrared Reflectance Spectroscopy for Rapid Quantification of Castor Bean Meal in a Selection of Flour-Based Products. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2000, 48, 5169–5177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azizian, H.; Kramer, J.K.G.; Winsborough, S. Factors influencing the fatty acid determination in fats and oils using Fourier transform near-infrared spectroscopy. Eur. J. Lipid Sci. Technol. 2007, 109, 960–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- StatSoft, Inc. STATISTICA (Data Analysis Software System), Version 12. 2013. Available online: www.statsoft.com (accessed on 5 November 2021).
- Arregui, L.M.; Quemada, M. Strategies to improve nitrogen use efficiency in winter cereal crops under rainfed conditions. Agron. J. 2008, 100, 277–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrasco, I.; Villar, J.M. Field evaluation of DMPP as a nitrification inhibitor in the area irrigated by the Canal d’Urgell (Northeast Spain). J. Plant Nutr. 2001, 92, 764–765. [Google Scholar]
- Polychronaki, E.; Douma, C.; Giourga, C.; Loumou, A. Assessing nitrogen fertilization strategies in winter wheat and cotton crops in northern Greece. Pedosphere 2002, 22, 689–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villar, J.M.; Guillaumes, E. Use of nitrification inhibitor DMPP to improve nitrogen recovery in irrigated wheat on a calcareous soil. Span. J. Agric. Res. 2010, 8, 1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pasda, G.; Hähndel, R.; Zerulla, W. Effect of fertilizers with the new nitrification inhibitor DMPP (3,4-Dimethylpyrazole phosphate) on yield and quality of agricultural and horticultural crops. Biol. Fertil. Soils. 2002, 34, 85–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barth, G.; von Tucher, S.; Schmidhalter, U. Influence of soil parameters on the effect of 3,4-dimethylpyrazole-phosphate as a nitrification inhibitor. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2001, 34, 98–102. [Google Scholar]
- Weiske, A.; Benckiser, G.; Herbert, T.; Ottow, J.C.G. Influence of the nitrification inhibitor 3,4-dimethylpyrazole phosphate (DMPP) in comparison to dicyandiamide (DCD) on nitrous oxide emissions, carbon dioxide fluxes and methane oxidation during 3 years or repeated application in field experiments. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2001, 34, 109–117. [Google Scholar]
- Di, H.J.; Cameron, K.C.; Podolyan, A.; Robinson, A. Effect of soil moisture status and a nitrification inhibitor, dicyandiamide, on ammonia oxidizer and denitrifier growth and nitrous oxide emissions in a grassland soil. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2014, 73, 59–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chien, S.H.; Prochnow, L.I.; Cantarella, H. Chapter 8 Recent Developments of Fertilizer Production and Use to Improve Nutrient Efficiency and Minimize Environmental Impacts. Adv. Agron. 2009, 102, 267–322. [Google Scholar]
- Johansson, E.; Prieto-Linde, M.L.; Svensson, G. Influence of nitrogen application rate and timing on grain protein composition and gluten strength in Swedish wheat cultivars. J. Plant Nutr. Soil Sci. 2004, 167, 345–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimolka, J. Pšenice, Pěstování, Hodnocení a Užití Zrna; Profi Press: Prague, Czech Republic, 2005; p. 181. (In Czech) [Google Scholar]
- Hoel, B.O. Effects of sulphur application on grain yield and quality, and assessment of sulphur status in winter wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Acta Agric. Scand. B Soil Plant Sci. 2011, 61, 499–507. [Google Scholar]
- Abalos, D.; Jeffery, S.; Sanz-Cobena, A.; Guardia, G.; Vallejo, A. Meta-analysis of the effect of urease and nitrification inhibitors on crop productivity and nitrogen use efficiency. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2014, 189, 136–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Wang, K.; Zheng, X. Effects of nitrification inhibitors (DCD and DMPP) on nitrous oxide emission, crop yield and nitrogen uptake in a wheat-maize cropping system. Biogeosciences 2013, 10, 2427–2437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guardia, G.; Sanz-Cobena, A.; Sanchez-Martín, L.; Fuertes-Mendizábal, T.; González-Murua, C.; Álvarez, J.M.; Chadwick, D.; Vallejo, A. Urea-based fertilization strategies to reduce yield-scaled N oxides and enhance bread-making quality in a rainfed Mediterranean wheat crop. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2018, 265, 421–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peltonen, J.; Virtanen, A. Effect of nitrogen fertilizers differing in release characteristics on the quantity of storage proteins in wheat. Cereal Chem. 1994, 71, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Steinfurth, D.; Zörb, C.; Braukmann, F.; Mühling, K.H. Time dependent distribution of sulphur, sulphate and glutathione in wheat tissues and grain as affected by three sulphur fertilization levels and late S fertilization. J. Plant Physiol. 2012, 169, 72–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, F.J.; Salmon, S.E.; Withers, P.J.; Monaghan, J.M.; Evans, E.J.; Shewry, P.R.; McGrath, S.P. Variation in the bread-making quality and rheological properties of wheat in relation to sulphur nutrition under field conditions. J. Cereal Sci. 1999, 30, 19–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erekul, O.; Götz, K.P.; Koca, Y.O. Effect of sulphur and nitrogen fertilization on bread-making quality of wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) varieties under Mediterranean climate conditions. J. Appl. Bot. Food Qual. 2012, 85, 17–22. [Google Scholar]
- Shahsavani, S.; Gholami, A. Effect of sulphur fertilization on breadmaking quality of three winter wheat varieties. Pak. J. Biol. Sci. 2008, 11, 2134–2138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Järvan, M.; Edesi, L.; Adamson, A. The effect of sulphur fertilization on yield, quality of protein and baking properties of winter wheat. J. Agric. Sci. 2009, 20, 8–15. [Google Scholar]
- Wieser, H.; Seilmeier, W. The influence of nitrogen fertilisation on quantities and proportions of different protein types in wheat flour. J. Sci. Food Agric. 1998, 76, 49–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blandino, M.; Vaccino, P.; Reyneri, A. Late-season nitrogen increases improver common and durum wheat quality. Agron. J. 2015, 107, 680–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kozlovský, O.; Balík, J.; Černý, J.; Kulhánek, M.; Kos, M.; Prášilová, M. Influence of nitrogen fertilizer injection (CULTAN) on yield, yield components formation and quality of winter wheat grain. Plant Soil Environ. 2018, 55, 536–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cahalan, E.; Ernfors, M.; Müller, C.; Devaney, D.; Laughlin, R.J.; Watson, C.J.; Hennessy, D.; Khalil, M.I.; McGeough, K.L.; Richards, K.G. 2014. The effect of the nitrification inhibitor dicyandiamide (DCD) on nitrous oxide and methane emissions after cattle slurry application to Irish grassland. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2014, 199, 339–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shepherd, M.; Wyatt, J.; Welten, B. Effect of soil type and rainfall on dicyandiamide concentrations in drainage from lysimeters. Soil Res. 2012, 50, 67–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGeough, K.L.; Watson, C.J.; Müller, C.; Laughlin, R.J.; Chadwick, D.R. Evidence that the efficacy of the nitrification inhibitor dicyandiamide (DCD) is affected by soil properties in UK soils. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2016, 94, 222–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wieser, H.; Gutser, R.; von Tucher, S. Influence of sulphur fertilisation on quantities and proportions of gluten protein types in wheat flour. J. Cereal Sci. 2004, 40, 239–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zörb, C.; Steinfurth, D.; Seling, S.; Langenkämper, G.; Koehler, P.; Wieser, H.; Lindhauer, M.G.; Mühling, K.H. Quantitative protein composition and baking quality of winter wheat as affected by late sulfur fertilization. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2009, 57, 3877–3885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martre, P.; Jamieson, P.D.; Semenov, M.A.; Zyskowski, R.F.; Porter, J.R.; Triboi, E. Modelling protein content and composition in relation to crop nitrogen dynamics for wheat. Eur. J. Agron. 2006, 25, 138–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moot, D.J.; Every, D. A comparison of bread baking, falling number, amylase essay and visual methods for assessment of pre-harvest sprouting in wheat. J. Cereal Sci. 1990, 11, 225–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koga, S.; Böcker, U.; Moldestad, A.; Tosi, P.; Shewry, P.R.; Mosleth, E.F.; Uhlen, A.K. Influence of temperature during grain filling on gluten viscoelastic properties and gluten protein composition. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2016, 96, 122–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schäfer, T.; Honermeier, B. Einfluss unterschiedlicher N- und SDüngung auf Kornertrag und Backqualitaet von Win-terweizen (Triticum aestivum L.). Mitt. Ges. Pflanzenbauwiss 2007, 19, 8–9. [Google Scholar]
- Volk, G.M. Efficiency of fertilizer urea as affected by method of application, soil moisture, and lime. Agron. J. 1966, 58, 249–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quemada, M.; Baranski, M.; Nobel-de Lange, M.N.J.; Vallejo, A.; Cooper, J.M. Meta-analysis of strategies to control nitrate leaching in irrigated agricultural systems and their effects on crop yield. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2013, 174, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abalos, D.; Sanz-Cobena, A.; Misselbrook, T.; Vallejo, A. Effectiveness of urease inhibition on the abatement of ammonia, nitrous oxide and nitric oxide emissions in a non-irrigated Mediterranean barley field. Chemosphere 2012, 89, 310–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Francisco, S.S.; Urrutia, O.; Martin, V.; Peristeropoulos, A.; Garcia-Mina, J.M. Efficiency of urease and nitrification inhibitors in reducing ammonia volatilization from diverse nitrogen fertilizers applied to different soil type sand wheat straw mulching. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2011, 91, 1569–1575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
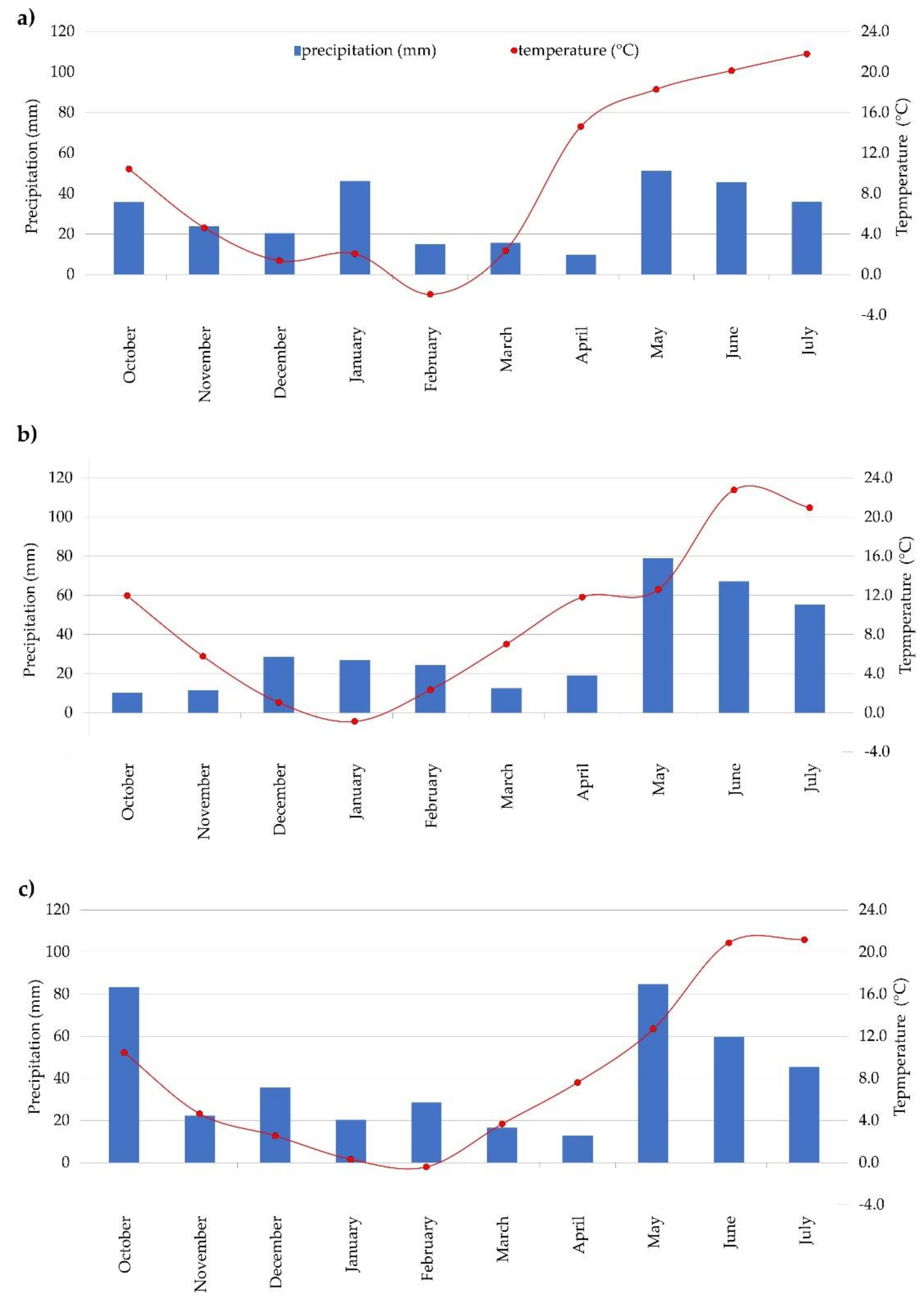
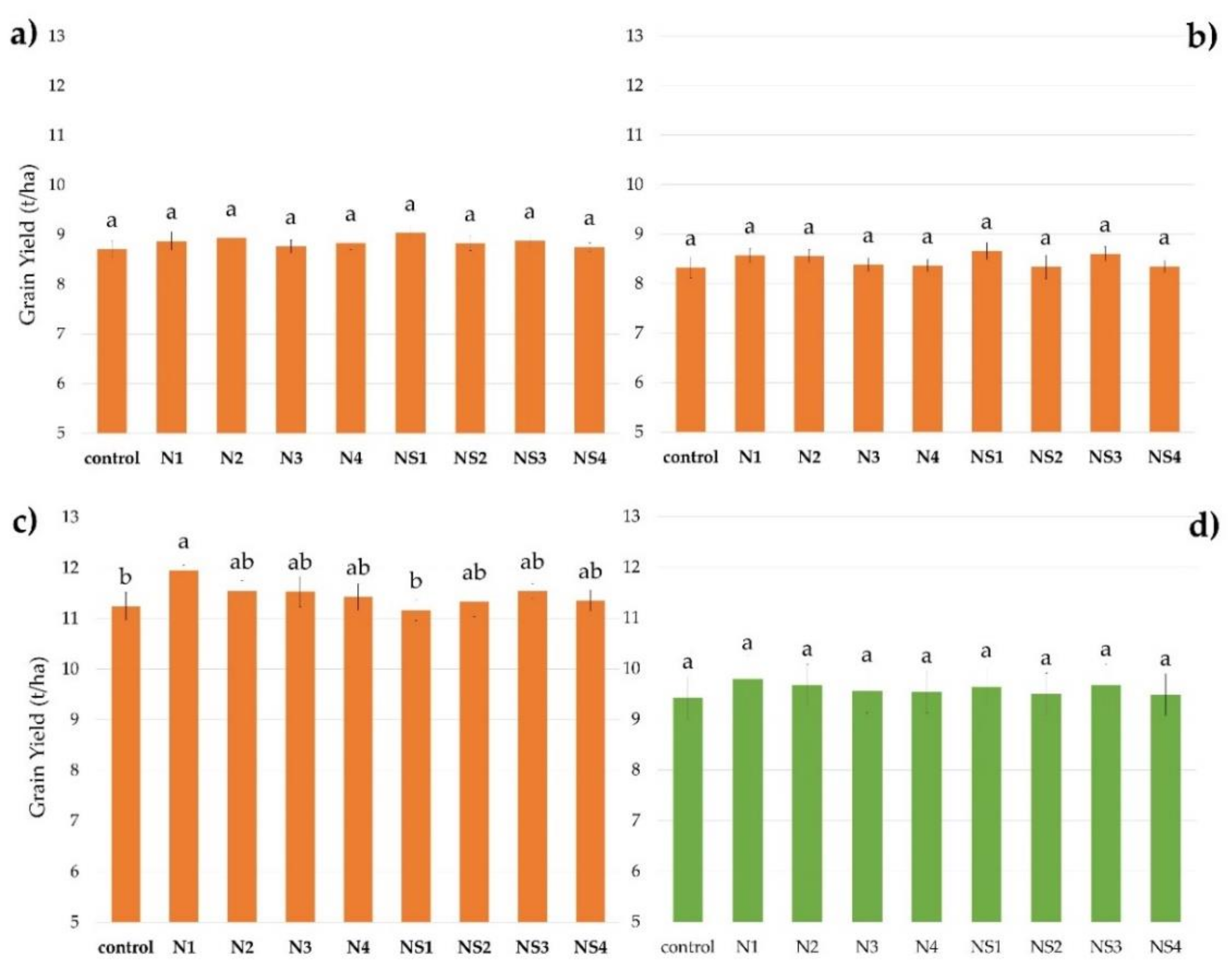

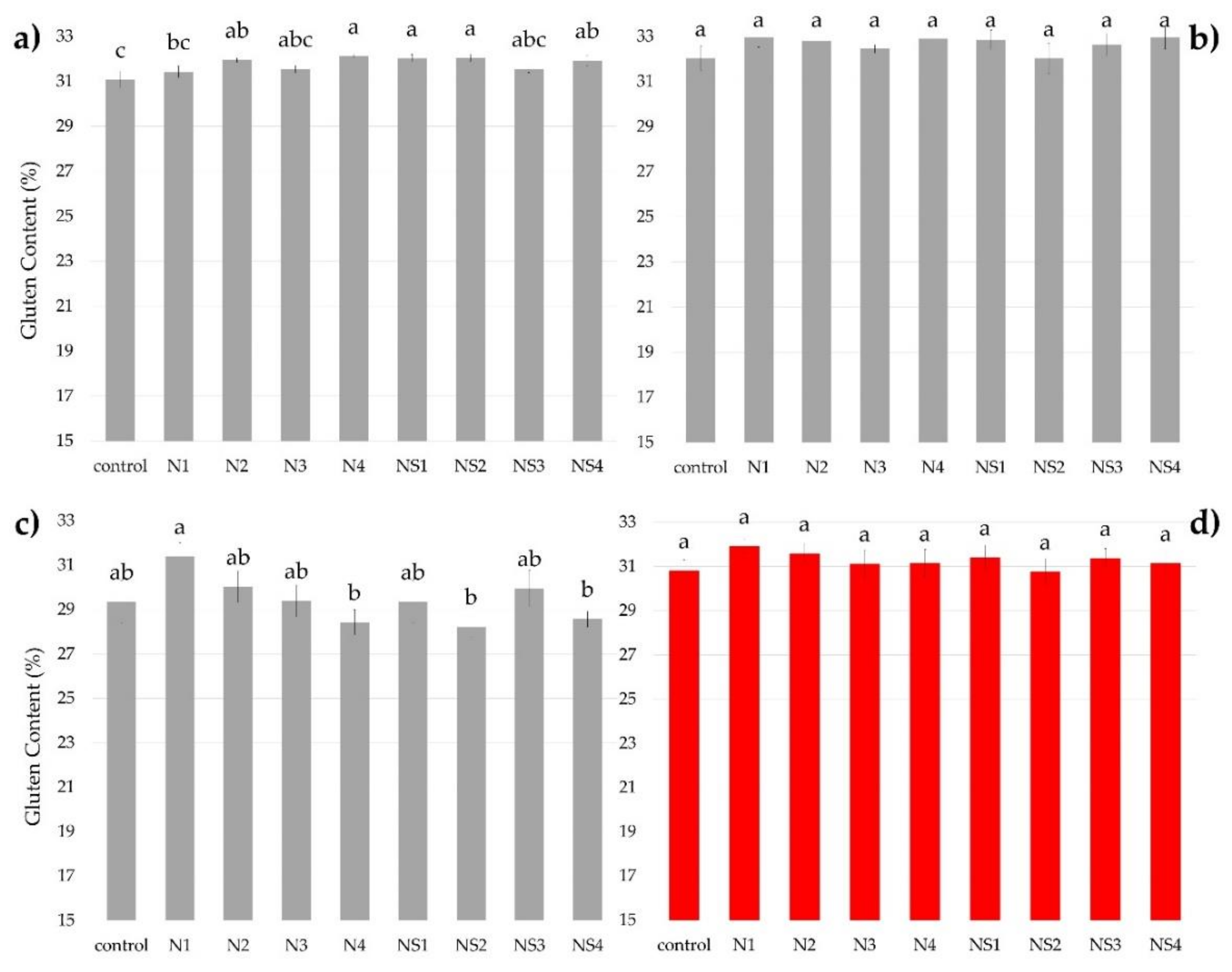
| Soil Parameter | Growing Season | Refs. | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2017/2018 | 2018/2019 | 2019/2020 | 2020/2021 | Average | ||
| Cox (%) | 1.32 | 1.43 | 1.33 | 1.36 | 1.36 | [41] |
| CEC (mmol/kg) | 219 | 257 | 208 | 234 | 230 | [42] |
| pH/CaCl2 | 6.8 | 6.6 | 6.4 | 5.9 | 6.4 | [42] |
| P (mg/kg) | 148 | 134 | 152 | 92 | 132 | [42] |
| K (mg/kg) | 276 | 247 | 283 | 184 | 248 | [42] |
| Ca (mg/kg) | 3644 | 3321 | 3641 | 3934 | 3635 | [42] |
| Mg (mg/kg) | 384 | 397 | 411 | 355 | 387 | [42] |
| SO42−(mg/kg) | 14.5 | 11.3 | 11.1 | 10.4 | 12 | [42] |
| NH4+ (mg/kg) | 1.84 | 2.69 | 1.49 | 9.73 | 4 | [42] |
| NO3− (mg/kg) | 3.86 | 14.00 | 4.62 | 14.30 | 9 | [42] |
| Treatments | Term (T) of Fertilization (Dose of N, S kg/ha) | Total Dose of N, S (kg/ha) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| T1 (BBCH 25) | T2 (BBCH 32) | T3 (BBCH 50) | ||
| control | CAN (55, 0) | CAN (65, 0) | UAN (40, 0) | 160, 0 |
| N1 | ALZON neo-N (160, 0) | 160, 0 | ||
| N2 | CAN (55, 0) | ALZON neo-N (105, 0) | 160, 0 | |
| N3 | UREAstabil (160, 0) | 160, 0 | ||
| N4 | CAN (55, 0) | UREAstabil (105, 0) | 160, 0 | |
| NS1 | CAN (55, 0) | ASN (105, 52) | 160, 52 | |
| NS2 | ASN (120, 60) | UAN (40, 0) | 160, 60 | |
| NS3 | ENSIN (160, 80) | 160, 80 | ||
| NS4 | ENSIN (120, 60) | UAN (40, 0) | 160, 60 | |
| Fertilizers | Nutrients Content (%) | Inhibitors | Producer | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | S | |||
| ALZON neo-N | 46 | 0 | nitrification (NI) and urease (UI) | (SKW Piesteritz, Wittenberg, Germany) |
| UREAstabil | 46 | 0 | urease (UI) | (AGRA GROUP a.s., Střelské Hoštice, the Czech Republic) |
| ENSIN | 26 | 13 | nitrification (NI) | (Duslo, a.s., Šaľa, the Slovak Republic) |
| UAN | 30 | 0 | none | (ADW AGRO, a.s., Okříšky, the Czech Republic) |
| CAN | 27 | 0 | none | (Duslo, a.s., Šaľa, the Slovak Republic) |
| ASN | 26 | 13 | none | (Duslo, a.s., Šaľa, the Slovak Republic) |
| Growing Season (GS) | Sowing | T1 (BBCH 25) | T2 (BBCH 32) | T3 (BBCH 50) | Harvest (BBCH 89) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GS1: 2017–2018 | 6 October 2017 | 5 March 2018 | 9 April 2018 | 2 May 2018 | 4 July 2018 |
| GS2: 2018–2019 | 9 October 2018 | 28 February 2019 | 29 April 2019 | 10 May 2019 | 11 July 2019 |
| GS3: 2020–2021 | 8 October 2020 | 3 March 2021 | 20 April 2021 | 29 May 2021 | 24 July 2021 |
| Treatments | GS1 | GS2 | GS3 | Average |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| control | 80.43 a ± 0.09 | 80.85 a ± 0.26 | 80.50 abc ± 0.11 | 80.59 ab ± 0.11 |
| N1 | 80.68 a ± 0.22 | 80.93 a ± 0.22 | 80.58 ab ± 0.23 | 80.73 ab ± 0.12 |
| N2 | 80.98 a ± 0.37 | 81.03 a ± 0.45 | 80.83 a ± 0.15 | 80.94 a ± 0.18 |
| N3 | 80.33 a ± 0.49 | 81.20 a ± 0.07 | 80.20 bc ± 0.07 | 80.58 ab ± 0.20 |
| N4 | 80.73 a ± 0.18 | 80.95 a ± 0.19 | 80.50 abc ± 0.22 | 80.73 ab ± 0.12 |
| NS1 | 80.88 a ± 0.11 | 81.13 a ± 0.16 | 80.30 bc ± 0.15 | 80.77 ab ± 0.13 |
| NS2 | 80.43 a ± 0.19 | 80.95 a ± 0.27 | 80.33 bc ± 0.21 | 80.57 ab ± 0.14 |
| NS3 | 80.45 a ± 0.17 | 81.05 a ± 0.31 | 80.08 c ± 0.10 | 80.53 b ± 0.16 |
| NS4 | 80.60 a ± 0.16 | 80.65 a ± 0.33 | 80.23 bc ± 0.17 | 80.59 b ± 0.13 |
| Treatments | GS1 | GS2 | GS3 | Average |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| control | 37.8 c ± 0.3 | 44.0 a ± 1.8 | 44.1 de ± 1.6 | 41.9 b ± 1.2 |
| N1 | 39.0 bc ± 0.6 | 47.0 a ± 1.2 | 51.3 a ± 0.6 | 45.8 a ± 1.6 |
| N2 | 40.8 a ± 0.3 | 46.5 a ± 1.7 | 50.0 ab ± 0.7 | 45.8 a ± 1.3 |
| N3 | 39.0 bc ± 0.4 | 45.8 a ± 1.0 | 47.3 bcd ± 1.3 | 44.0 ab ± 1.2 |
| N4 | 40.8 a ± 0.3 | 46.8 a ± 1.3 | 47.7 bc ± 1.3 | 45.1 ab ± 1.1 |
| NS1 | 40.5 a ± 0.5 | 46.5 a ± 1.3 | 48.1 abc ± 0.9 | 45.0 ab ± 1.1 |
| NS2 | 40.5 a ± 0.5 | 44.0 a ± 2.2 | 43.9 e ± 0.5 | 42.8 ab ± 0.9 |
| NS3 | 39.0 bc ± 0.4 | 45.8 a ± 1.7 | 49.0 ab ± 1.9 | 44.6 ab ± 1.5 |
| NS4 | 40.0 ab ± 0.7 | 47.0 a ± 1.8 | 45.0 cde ± 0.7 | 44.0 ab ± 1.0 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Školníková, M.; Škarpa, P.; Ryant, P.; Kozáková, Z.; Antošovský, J. Response of Winter Wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) to Fertilizers with Nitrogen-Transformation Inhibitors and Timing of Their Application under Field Conditions. Agronomy 2022, 12, 223. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12010223
Školníková M, Škarpa P, Ryant P, Kozáková Z, Antošovský J. Response of Winter Wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) to Fertilizers with Nitrogen-Transformation Inhibitors and Timing of Their Application under Field Conditions. Agronomy. 2022; 12(1):223. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12010223
Chicago/Turabian StyleŠkolníková, Marie, Petr Škarpa, Pavel Ryant, Zdenka Kozáková, and Jiří Antošovský. 2022. "Response of Winter Wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) to Fertilizers with Nitrogen-Transformation Inhibitors and Timing of Their Application under Field Conditions" Agronomy 12, no. 1: 223. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12010223
APA StyleŠkolníková, M., Škarpa, P., Ryant, P., Kozáková, Z., & Antošovský, J. (2022). Response of Winter Wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) to Fertilizers with Nitrogen-Transformation Inhibitors and Timing of Their Application under Field Conditions. Agronomy, 12(1), 223. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12010223







