Evaluation of the DNDC Model to Estimate Soil Parameters, Crop Yield and Nitrous Oxide Emissions for Alternative Long-Term Multi-Cropping Systems in the North China Plain
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Site
2.2. Cropping Systems
2.3. Field Measurements and N2O Fluxes
2.4. Soil Temperature, WFPS (%) and Soil Mineral N (Exchangeable NH4+ and NO3−)
2.5. Model Description, Validation and Statistical Evaluation
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Evaluation of the DNDC Model to Estimate Soil Parameters
3.1.1. Soil Temperature
3.1.2. Soil Water Filled Pore Space (WFPS)
3.1.3. Soil Nitrogen (Exchangeable NH4+ and NO3−)
3.2. Evaluation of the DNDC Model to Estimate Crop Yield
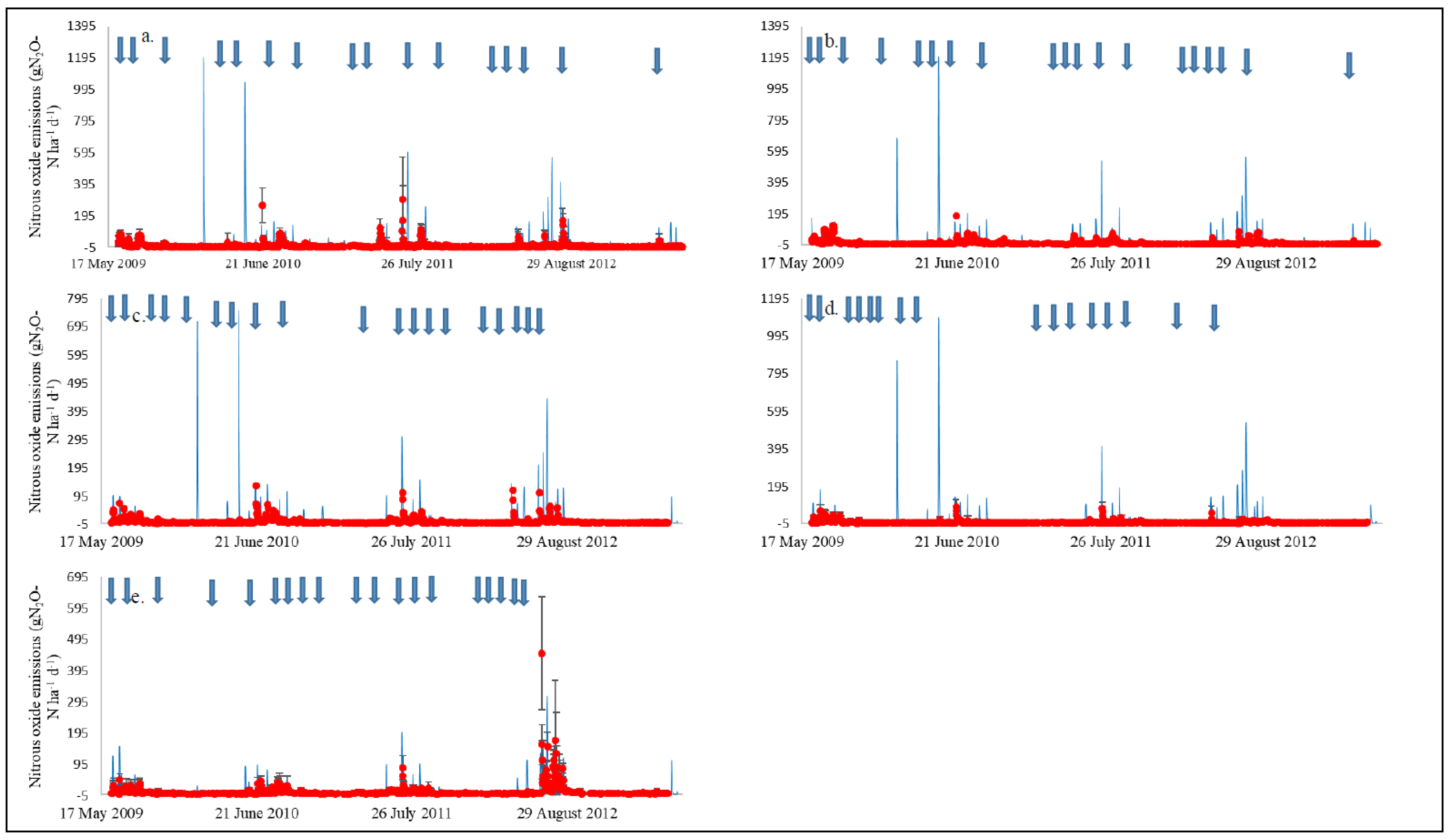
3.3. Evaluation of the DNDC Model to Estimate N2O Emissions
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- IPCC. Summary for Policymakers. In Climate Change 2021: The Physical Science Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Masson-Delmotte, V., Zhai, P., Pirani, A., Connors, S.L., Péan, C., Berger, S., Caud, N., Chen, Y., Goldfarb, L., Gomis, M.I., et al., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2021; in press. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, P.; Martino, D.; Cai, Z.; Gwary, D.; Janzen, H.; Kumar, P.; McCarl, B.; Ogle, S.; O’Mara, F.; Rice, C.; et al. Greenhouse gas mitigation in agriculture. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B 2008, 363, 789–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bouwman, A.F. Direct emissions of nitrous oxide from agricultural soils. Nutr. Cycl. Agroecosyst. 1996, 46, 53–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makarov, M.I.; Glaser, B.; Malysheva, T.I.; Bulatnikova, I.V.; Volkov, A.V. Nitrogen dynamics in alpine ecosystems of the northern Caucasus. Plant Soil 2003, 256, 389–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, S.L.; Knapp, A.K.; Briggs, J.M.; Blair, J.M.; Steinauer, E.M. Modulation of diversity by grazing and mowing in native tallgrass prairie. Science 1998, 280, 745–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patra, A.K.; Abbadie, L.; Clays-Josserand, A.; Degrange, V.; Grayston, S.J.; Guillaumaud, N.; Loiseau, P.; Louault, F.; Mahmood, S.; Nazaret, S.; et al. Effects of management regime and plant species on the enzyme activity and genetic structure of N-fixing, denitrifying and nitrifying bacterial communities in grassland soils. Environ. Microbiol. 2006, 8, 1005–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lal, R. Soil carbon sequestration impacts on global climate change and food security. Science 2004, 304, 1623–1627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Smith, P. Carbon sequestration in croplands: The potential in Europe and the global context. Eur. J. Agron. 2004, 20, 229–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdalla, M.; Osborne, B.; Lanigan, G.; Forristal, D.; Williams, M.; Smith., P.; Jones, M.B. Conservation tillage systems: A review of its consequences for greenhouse gas emissions. Soil Use Manag. 2013, 29, 199–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butterbach-Bahl, K.; Baggs, E.M.; Dannenmann, M.; Kiese, R.; Zechmeister-Boltenstern, S. Nitrous oxide emissions from soils: How well do we understand the processes and their controls? Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B 2013, 368, 20130122. [Google Scholar]
- Saikawa, E.; Prinn, R.G.; Dlugokencky, E.; Ishijima, K.; Dutton, G.S.; Hall, B.D.; Langenfelds, R.; Tohjima, Y.; Machida, T.; Manizza, M.; et al. Global and regional emissions estimates for N2O. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2014, 14, 4617–4641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- WMO. WMO Greenhouse Gas Bulletin (GHG Bulletin)—No. 14: The State of Greenhouse Gases in the Atmosphere Based on Global Observations through 2017; World Meteorological Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Brady, N.C.; Weil, R.R. The Nature and Properties of Soils, 12nd ed.; Prentice Hall: Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA, 1999; p. 881. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, K.A.; Conen, F. Impacts of land management on fluxes of trace greenhouse gases. Soil Use Manag. 2004, 20, 255–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oenema, O.; Wrage, N.; Velthof, G.L.; van Groenigen, J.W.; Dolfing, J.; Kuikman, P.J. Trends in global nitrous oxide emissions from animal production systems. Nutr. Cycl. Agroecosyst. 2005, 72, 51–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Signor, D.; Cerri, C.E.P. Nitrous oxide emissions in agricultural soils: A review. Pesqui. Agropecu. Trop. 2013, 43, 322–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norse, D.; SAIN. Improved Nutrient Management in Agriculture—A Neglected. Opportunity for China’s Low Carbon Growth Path, Policy Brief No. 1. Sustainable Innovation Network. 2011. Available online: http://www.eu-china.net/upload/pdf/materialien/11-02-11_PolicyBriefNo1updatedfinal.pdf (accessed on 2 September 2021).
- Powlson, D.; Norse, D.; Lu, Y. Agricultural Development in China—Environmental Impacts, Sustainability Issues and Policy Implications Assessed through China-UK Projects under SAIN (UK-China Sustainable Agriculture Innovation Network), 2008–2017; SAIN: Norwich, UK, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Laik, R.; Sharma, S.; Idris, M.; Singh, A.K.; Singh, S.S.; Bhatt, B.P.; Saharawat, Y.; Humphreys, E.; Ladha, J.K. Integration of conservation agriculture with best management practices for improving system performance of the rice-wheat rotation in the Eastern Indo-Gangetic Plains of India. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2014, 195, 68–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behnke, G.D.; Zuber, S.M.; Pittelkow, C.M.; Nafziger, E.D.; Villamil, M.B. Long-term crop rotation and tillage effects on soil greenhouse gas emissions and crop production in Illinois, USA. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2018, 261, 62–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lupwayi, N.Z.; Harker, K.N.; O’Donovan, J.T.; Turkington, T.K.; Blackshaw, R.E.; Hall, L.M.; Willenborg, C.J.; Gan, Y.; Lafond, G.P.; May, W.E.; et al. Relating soil microbial properties to yields of no-till canola on the Canadian prairies. Eur. J. Agron. 2015, 62, 110–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Hamel, C.; Gan, Y.; Vujanovic, V. Bacterial endophytes mediate positive feedback effects of early legume termination times on the yield of subsequent durum wheat crops. Can. J. Microbiol. 2012, 58, 1368–1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luce, M.S.; Grant, C.A.; Ziadi, N.; Zebarth, B.J.; O’Donovan, J.T.; Blackshaw, R.E.; Harker, K.N.; Johnson, E.N.; Gan, Y.; Lafond, G.P.; et al. Preceding crops and nitrogen fertilization influence soil nitrogen cycling in no-till canola and wheat cropping systems. Field Crops Res. 2016, 191, 20–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuber, S.M.; Behnke, G.D.; Nafziger, E.D.; Villamil, M.B. Crop rotation and tillage effects on soil physical and chemical properties in Illinois. Agron. J. 2015, 107, 971–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bainard, L.D.; Hamel, C.; Gan, Y. Edaphic properties override the influence of crops on the composition of the soil bacterial community in a semiarid agroecosystem. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2016, 105, 160–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trivedi, P.; Delgado-Baquerizo, M.; Anderson, I.C.; Singh, B.K. Response of soil properties and microbial communities to agriculture: Implications for primary productivity and soil health indicators. Front. Plant Sci. 2016, 7, 990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, L.; Cutforth, H.; Lal, R.; Chai, Q.; Zhao, C.; Gan, Y.; Siddique, K.H.M. Decoupling’ land productivity and greenhouse gas footprints: A review. Land Degrad. Dev. 2017, 29, 4348–4361. [Google Scholar]
- Linton, N.F.; Machado, P.V.F.; Deen, B.; Wagner-Riddle, C.; Dunfield, K.E. Long-term diverse rotation alters nitrogen cycling bacterial groups and nitrous oxide emissions after nitrogen fertilization. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2020, 149, 107917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conthe, M.; Wittorf, L.; Kuenen, J.G.; Kleerebezem, R.; van Loosdrecht, M.C.; Hallin, S. Life on N2O: Deciphering the ecophysiology of N2O respiring bacterial communities in a continuous culture. ISME J. 2018, 12, 1142–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mafa-Attoye, T.G.; Baskerville, M.A.; Ofosu, E.; Oelbermann, M.; Thevathasan, N.V.; Dunfield, K.E. Riparian land-use systems impact soil microbial communities and nitrous oxide emissions in an agro-ecosystem. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 724, 138148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Aber, J.; Stange, F.; Butterbach-Bahal, K.; Papen, H. A process—Model of N2O and NO emissions from forest soils: 1. Model Dev. J. Geophys. Res. 2000, 105, 4369–4384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Frolking, S.; Frolking, T.A. A model of nitrous oxide evolution from soil driven by rainfall events. 1. Model structure and sensitivity. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 1992, 97, 9759–9776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kesik, M.; Bruggemann, N.; Forkel, R.; Kiese, R.; Knoche, R.; Li, C.; Seufert, G.; Simpson, D.; Butterbach-Bahl, K. Future scenarios of N2O emissions from European forest soils. J. Geophys. Res. 2006, 111, G02018. [Google Scholar]
- Abdalla, M.; Wattenbach, M.; Smith, P.; Ambus, P.; Jones, M.; Williams, M. Application of the DNDC model to predict emissions of N2O from Irish agriculture. Geoderma 2009, 151, 327–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdalla, M.; Song, X.; Ju, X.; Topp, C.F.E.; Smith, P. Calibration and validation of the DNDC model to estimate nitrous oxide emissions and crop productivity for a summer maize-winter wheat double cropping system in Hebei, China. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 262, 114199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grant, R.F.; Lin, S.; Hernandez-Ramirez, G. Modelling nitrification inhibitor effects on N2O emissions after fall and spring-applied slurry by reducing nitrifier NH4+ oxidation rate. Biogeosciences 2020, 17, 2021–2039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gao BJu, X.T.; Su, F.; Meng, Q.F.; Oenema, O.; Christie, P.; Chen, X.P.; Zhang, F.S. Nitrous oxide and methane emissions from optimized and alternative cereal cropping systems on the North China Plain: A two-year field study. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 472, 112–124. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, B.; Ju, X.; Meng, Q.; Cui, Z.; Christie, P.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, F. The impact of alternative cropping systems on global warming potential, grain yield and groundwater use. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2015, 203, 46–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Q.F.; Sun, Q.P.; Chen, X.P.; Cui, Z.L.; Yue, S.C.; Zhang, F.C.; Römheld, V. Alternative cropping systems for sustainable water and nitrogen use in the North China Plain. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2012, 146, 93–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.H.; Mei, B.L.; Wang, Y.H.; Xie, B.H.; Wang, Y.S.; Docng, H.B.; Xu, H.; Chen, G.X.; Cai, Z.C.; Yue, J.; et al. Quantification of N2O fluxes from soil-plant systems may be biased by the applied gas chromatograph methodology. Plant Soil 2008, 311, 211–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Z.; Sawamoto, T.; Li, C.; Kang, G.; Boonjawat, J.; Mosier, A.; Wassmann, R.; Tsuruta, H. Field validation of the DNDC-model for greenhouse gas emissions in East Asian cropping systems. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycl. 2003, 7, 1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cui, F.; Zheng, X.; Liu, C.; Wang, K.; Zhou, Z.; Deng, J. Assessing biogeochemical effects and best management practice for a wheat-maize cropping system using the DNDC model. Biogeosciences 2014, 11, 91–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Uzoma, K.C.; Smith, W.; Grant, B.; Desjardins, R.L.; Gao, X.; Hanis, K.; Tenuta, M.; Goglio, P.; Li, C. Assessing the effects of agricultural management on nitrous oxide emissions using flux measurements and the DNDC model. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2015, 206, 71–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Yang, J.Y.; Drury, C.F.; Yang, X.M.; Reynolds, W.D.; Li, X.; Hu, C. Evaluation of the DNDC model for simulating soil temperature, moisture and respiration from monoculture and rotational corn, soybean and winter wheat in Canada. Ecol. Model. 2017, 360, 230–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdalla, M.; Kumar, S.; Jones, M.; Burke, J.; Williams, M. Testing DNDC model for simulating soil respiration and assessing the effects of climate change on the CO2 gas flux from Irish agriculture. Glob. Planet Chang. 2011, 78, 106–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wennman, P.; Katterer, T. Effects of moisture and temperature on carbon and nitrogen mineralisation in mine tailing mixed with sewage sludge. J. Environ. Qual. 2006, 35, 1135–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, L.I.; Qiu, J.J.; Wang, L.G.; Xu, M.Y.; Liu, Z.Q.; Wang, W. Estimates of N2O emissions and mitigation potential from a spring maize field based on DNDC model. J. Integr. Agric. 2012, 11, 2067–2078. [Google Scholar]
- Vargas, V.P.; Soares, J.R.; Oliveira, B.G.; Lourenço, K.S.; Martins, A.A.; Del Grosso, S.J.; Carmo, J.B.D.; Cantarella, H. Sugarcane Straw, Soil Temperature, and Nitrification Inhibitor Impact N2O Emissions from N Fertilizer. BioEnergy Res. 2019, 12, 801–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lassey, K.; Harvey, M. Nitrous oxide: The serious side of laughing gas. Water Atmos. 2007, 15, 10–11. [Google Scholar]
- Maag, M.; Vinther, F. Nitrous oxide emission by nitrification and denitrification in different soil types and at different soil moisture contents and temperatures. Appl. Soil Ecol. 1996, 4, 5–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, W.N.; Qi, Z.; Grant, B.B.; VanderZaag, A.; Desjardins, R. Comparing hydrological frameworks for simulating crop biomass, water and nitrogen dynamics in a tile drained soybean-corn system: Cascade vs computational approach. J. Hydrol. X 2019, 2, 100015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kröbel, R.; Sun, Q.P.; Ingwersen, J. Modelling water dynamics with DNDC and DAISY in a soil of the North China Plain: A comparative study. Environ. Model. Softw. 2010, 25, 583–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ussiri, D.; Lal, R. Soil Emission of N2O and Its Mitigation; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Song, X.; Ju, X.; Topp, C.F.E.; Rees, R.M. Oxygen regulates nitrous oxide production directly in agricultural soils. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 12539–12547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruser, R.; Flessa, H.; Russow, R.; Schmidt, G.; Buegger, F.; Munch, J. Emission of N2O, N2 and CO2 from soil fertilized with nitrate: Effect of compaction, soil moisture and rewetting. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2006, 38, 263–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdalla, M.; Hastings, A.; Helmy, M.; Prescher, A.; Osborne, B.; Lanigan, G.; Forristal, D.; Killi, D.; Maratha, P.; Williams, M.; et al. Assessing the combined use of reduced tillage and cover crops for mitigating greenhouse gas emissions from arable ecosystem. Geoderma 2014, 223–225, 9–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, F.; Song, J.; Giltrap, D.; Feng, D.; Yang, X.; Zhang, S. Crop yield and N2O emission affected by long-term organic manure substitution fertilizer under winter wheat-summer maize cropping system. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 732, 139321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- St Luce, M.; Lemke, R.; Gan, Y.; McConkey, B.; May, W.; Campbell, C.; Zentner, R.; Wang, H.; Kroebel, R.; Fernandez, M.; et al. Diversifying cropping systems enhances productivity, stability and nitrogen use efficiency. Agron. J. 2020, 112, 1517–1536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jarecki, M.; Grant, B.; Smith, W.; Deen, B.; Drury, C.; VanderZaag, A.; Qian, B.; Yang, J.; Wagner-Riddle, C. Long-term trends in corn yields and soil carbon under diversified crop rotations. J. Environ. Qual. 2018, 47, 635–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dobbie, K.E.; Smith, K.A. The effects of temperature, water filled pore space and land use on N2O emissions from an imperfectly drained gleysol. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2001, 52, 667–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Amon, B.; Schulz, K.; Mehdi, B. Factors That Influence Nitrous Oxide Emissions from Agricultural Soils as Well as Their Representation in Simulation Models: A Review. Agronomy 2021, 11, 770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parkin, T.B. Effect of sampling frequency on estimates of cumulative nitrous oxide emissions. J. Environ. Qual. 2008, 37, 1390–1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hastings, A.F.; Wattenbach, M.; Eugster, W.; Li, C.; Buchmann, N.; Smith, P. Uncertainty propagation in soil greenhouse gas emission models: An experiment using the DNDC model and at the Oensingen cropland site. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2010, 136, 97–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, M.J.; Jones, E.; Smith, J.; Smith, P.; Yeluripati, J.; Augustin, J.; Juszczak, R.; Olejnik, J.; Sommer, M. Simulation of soil nitrogen, nitrous oxide emissions and mitigation scenarios at 3 European cropland sites using the ECOSSE model. Nutr. Cycl. Agroecosyst. 2012, 92, 161–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdalla, M.; Jones, M.; Ambus, P.; Williams, M. Emissions of nitrous oxide from Irish arable soils: Effects of tillage and reduced N input. Nutr. Cycl. Agroecosyst. 2010, 86, 53–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Cao, L.; Sha, Z.; Deng, J.; Chu, C.; Zhou, D.; Wu, S.; Lv, W. Impacts of fertilization optimization on N loss from paddy fields: Observations and DNDC modeling case study in Shanghai, China. Soil Tillage Res. 2020, 199, 104587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Treatment/Parameter | Observed | Simulated | RD (%) | RMSE | nRMSE (%) | d |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chem. W/M | ||||||
| Average daily soil temperature (°C) | 17.71 | 19.96 | 13 | 3.38 | 19 | 0.95 |
| Average daily WFPS (%) | 52.02 | 29.55 | −43 | 26.44 | 51 | 0.33 |
| Average daily soil N (kg N ha−1) | 98.14 | 155.49 | 58 | 124.23 | >100 | 0.00 |
| N2O emissions | 7.85 | 8.32 | 5 | 54.48 | >100 | 0.16 |
| Opt. W/M | ||||||
| Average daily soil temperature (°C) | 17.57 | 19.95 | 14 | 3.73 | 21 | 0.94 |
| Average daily WFPS (%) | 53.91 | 29.01 | −46 | 27.43 | 51 | 0.35 |
| Average daily soil N (kg N ha−1) | 63.97 | 119.29 | 86 | 73.66 | >100 | −0.60 |
| N2O emissions | 7.37 | 7.87 | 6 | 50.23 | >100 | 0.08 |
| W/M-M | ||||||
| Average daily soil temperature (°C) | 17.69 | 19.91 | 13 | 3.83 | 22 | 0.94 |
| Average daily WFPS (%) | 51.59 | 29.29 | −43 | 25.26 | 49 | 0.35 |
| Average daily soil N (kg N ha−1) | 67.26 | 66.12 | −1 | 48.47 | 72 | 0.22 |
| N2O emissions | 5.46 | 5.25 | −3 | 35.70 | >100 | 0.14 |
| W/S-M | ||||||
| Average daily soil temperature (°C) | 17.72 | 19.92 | 12 | 3.94 | 22 | 0.94 |
| Average daily WFPS (%) | 49.42 | 29.01 | −41 | 23.34 | 47 | 0.44 |
| Average daily soil N (kg N ha−1) | 53.72 | 89.46 | 66 | 68.77 | >100 | −0.13 |
| N2O emissions | 3.96 | 6.18 | 56 | 42.02 | >100 | 0.13 |
| M | ||||||
| Average daily soil temperature (°C) | 18.10 | 19.85 | 10 | 4.36 | 24 | 0.92 |
| Average daily WFPS (%) | 50.24 | 29.01 | −42 | 23.79 | 47 | 0.41 |
| Average daily soil N (kg N ha−1) | 57.46 | 41.59 | −27 | 50.08 | 87 | 0.27 |
| N2O emissions | 6.18 | 4.51 | −26 | 33.42 | >100 | 0.38 |
| Cropping System | Grown Crop | Season/Year | Observed Yield (t ha−1) | Simulated Yield (t ha−1) | RD (%) | Observed Cumulative N2O(kg N2O-N ha−1) | Simulated Cumulative N2O(kg N2O-N ha−1) | RD (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chem. W/M | Summer maize | 2009 | 7.2 | 8.4 | 17 | 7.9 | 8.3 | 6 |
| Winter wheat | 2009–2010 | 4.4 | 2.9 | −34 | ||||
| Summer maize | 2010 | 6.9 | 5.7 | −17 | ||||
| Winter wheat | 2010–2011 | 4.1 | 2.8 | −32 | ||||
| Summer maize | 2011 | 6.7 | 6.4 | −4 | ||||
| Winter wheat | 2011–2012 | 5.9 | 5.0 | −15 | ||||
| Summer maize | 2012 | 8.9 | 9.5 | 7 | ||||
| Winter wheat | 2012–2013 | 3.9 | 5.4 | 38 | ||||
| Opt. W/M | Summer maize | 2009 | 7.1 | 8.4 | 18 | 7.4 | 7.9 | 7 |
| Winter wheat | 2009–2010 | 6.0 | 3.2 | −47 | ||||
| Summer maize | 2010 | 7.4 | 6.1 | −18 | ||||
| Winter wheat | 2010–2011 | 5.8 | 5.3 | −9 | ||||
| Summer maize | 2011 | 7.5 | 7.9 | 5 | ||||
| Winter wheat | 2011–2012 | 6.5 | 4.6 | −29 | ||||
| Summer maize | 2012 | 10.2 | 9.4 | −8 | ||||
| Winter wheat | 2012–2013 | 6.7 | 5.6 | −16 | ||||
| W/M-M | Spring maize | 2009 | 7.1 | 9.6 | 35 | 5.5 | 5.4 | −1 |
| Winter wheat | 2009–2010 | 6.8 | 2.9 | −57 | ||||
| Summer maize | 2010 | 7.5 | 8.6 | 15 | ||||
| Spring maize | 2011 | 9.1 | 7.7 | −15 | ||||
| Winter wheat | 2011–2012 | 6.7 | 4.5 | −33 | ||||
| Summer maize | 2012 | 10.4 | 9.6 | −8 | ||||
| W/S-M | Spring maize | 2009 | 7.3 | 9.6 | 32 | 4.0 | 6.2 | 56 |
| Winter wheat | 2009–2010 | 6.8 | 2.9 | −57 | ||||
| Summer soybean | 2010 | 3.1 | 2.2 | −29 | ||||
| Spring maize | 2011 | 9.8 | 9.0 | −8 | ||||
| Winter wheat | 2011–2012 | 6.7 | 4.3 | −36 | ||||
| Summer soybean | 2012 | 3.3 | 3.1 | −6 | ||||
| M | Spring maize | 2009 | 7.2 | 9.7 | 35 | 6.2 | 4.5 | −27 |
| Spring maize | 2010 | 6.6 | 9.6 | 45 | ||||
| Spring maize | 2011 | 8.9 | 9.6 | 8 | ||||
| Spring maize | 2012 | 10.6 | 9.6 | −9 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Abdalla, M.; Song, X.; Ju, X.; Smith, P. Evaluation of the DNDC Model to Estimate Soil Parameters, Crop Yield and Nitrous Oxide Emissions for Alternative Long-Term Multi-Cropping Systems in the North China Plain. Agronomy 2022, 12, 109. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12010109
Abdalla M, Song X, Ju X, Smith P. Evaluation of the DNDC Model to Estimate Soil Parameters, Crop Yield and Nitrous Oxide Emissions for Alternative Long-Term Multi-Cropping Systems in the North China Plain. Agronomy. 2022; 12(1):109. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12010109
Chicago/Turabian StyleAbdalla, Mohamed, Xiaotong Song, Xiaotang Ju, and Pete Smith. 2022. "Evaluation of the DNDC Model to Estimate Soil Parameters, Crop Yield and Nitrous Oxide Emissions for Alternative Long-Term Multi-Cropping Systems in the North China Plain" Agronomy 12, no. 1: 109. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12010109
APA StyleAbdalla, M., Song, X., Ju, X., & Smith, P. (2022). Evaluation of the DNDC Model to Estimate Soil Parameters, Crop Yield and Nitrous Oxide Emissions for Alternative Long-Term Multi-Cropping Systems in the North China Plain. Agronomy, 12(1), 109. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12010109







