The Sensitivity of Field Populations of Metopolophium dirhodum (Walker) (Hemiptera: Aphididae) to Seven Insecticides in Northern China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Insect Populations and Insecticides
2.2. Bioassays
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Susceptibility Baseline of M. dirhodum to Seven Insecticides
3.2. Monitoring Sensitivity to Seven Insecticides in Northern China
3.3. Insecticide Resistance at Five Locations in 2018–2019
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Simon, J.C.; Peccoud, J. Rapid evolution of aphid pests in agricultural environments. Curr. Opin. Insect. Sci. 2018, 26, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, G. On the ecological genetics of Metopolophium dirhodum (Walker) (Hemiptera, Aphididae). Zeits. Ange. Entomol. 1985, 100, 451–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saska, P.; Skuhrovec, J.; Tylová, E.; Platková, H.; Tuan, S.-J.; Hsu, Y.-T.; Vítámvás, P. Leaf structural traits rather than drought resistance determine aphid performance on spring wheat. J. Pest. Sci. 2021, 94, 423–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Honek, A.; Martinkova, Z.; Saska, P.; Dixon, A.F.G. Aphids (Homoptera: Aphididae) on winter wheat: Predicting maximum abundance of Metopolophium dirhodum. J. Econ. Entomol. 2018, 111, 1751–1759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, X.; Gong, P.; Wang, B.; Wang, C.; Li, M.; Zhang, Y.; Li, X.; Gao, H.; Ju, J.; Zhu, X. Selection and validation of experimental condition-specific reference genes for qRT-PCR in Metopolophium dirhodum (Walker) (Hemiptera: Aphididae). Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 21951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapin, J.W.; Thomas, J.S.; Gray, S.M.; Smith, D.M.; Halbert, S.E. Seasonal abundance of aphids (Homoptera: Aphididae) in wheat and their role as barley yellow dwarf virus vectors in the South Carolina coastal plain. J. Econ. Entomol. 2001, 94, 410–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sepúlveda, D.A.; Zepeda-Paulo, F.; Ramírez, C.C.; Lavandero, B.; Figueroa, C.C. Diversity, frequency, and geographic distribution of facultative bacterial endosymbionts in introduced aphid pests. Insect. Sci. 2017, 24, 511–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clement, S.L.; Elberson, L.R.; Youssef, N.; Evans, F.L.Y.A. Cereal aphid and natural enemy populations in cereal production systems in Eastern Washington. J. Kans. Entomol. Soc. 2004, 77, 165–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Havlíková, H. Character and extent of damage to winter wheat cultivars caused by cereal aphids. J. Rostl. Vyroba. 1997, 43, 113–116. [Google Scholar]
- Gong, P.; Chen, D.; Wang, C.; Li, M.; Li, X.; Zhang, Y.; Li, X.; Zhu, X. Susceptibility of four species of aphids in wheat to seven insecticides and its relationship to detoxifying enzymes. Front. Physiol. 2021, 11, 623612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, S.; Gong, S. Effect of temperature on growth of laboratory population of Metopolophium dirhodum. Acta. Entomol. Sin. 1985, 01, 36–44. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.; Xia, Y.; Ni, H.; Ding, H.; Cao, Y. Study on population dynamics among field population of Metopolophium dirhodum. J. Plant. Prot. 1994, 21, 7–13. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Li, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, X.; Cheng, D. Impact of seed coating with imidacloprid on laboratory populations of Metopolophium dirhodum (Walker) (Homoptera: Aphididae). Plant. Prot. 2019, 45, 25–29. [Google Scholar]
- Miao, J.; Du, Z.; Wu, Y.; Gong, Z.; Jiang, Y.; Duan, Y.; Li, T.; Lei, C. Sub-lethal effects of four neonicotinoid seed treatments on the demography and feeding behaviour of the wheat aphid Sitobion avenae. Pestic. Manag. Sci. 2014, 70, 55–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, Y.; Wang, K.; Zhang, M.; Peng, X.; Piñero, J.C.; Chen, M. Regional susceptibilities of Rhopalosiphum padi (Hemiptera: Aphididae) to ten insecticides. Fla. Entomol. 2016, 99, 269–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mingeot, D.; Hautier, L.; Jansen, J.P. Structuration of multilocus genotypes associated with insecticide resistance of the peach potato aphid, Myzus persicae (Sulzer), in potato fields in southern Belgium. Pestic. Manag. Sci. 2021, 77, 482–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Margaritopoulos, J.T.; Kati, A.N.; Voudouris, C.C.; Skouras, P.J.; Tsitsipis, J.A. Long-term studies on the evolution of resistance of Myzus persicae (Hemiptera: Aphididae) to insecticides in Greece. Bull. Entomol. Res. 2021, 111, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mirza, F.K.; Yarahmadi, F.; Jalal-Abadi, A.L.; Meraaten, A.A. Enzymes mediating resistance to chlorpyriphos in Aphis fabae (Homoptera: Aphididae). Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 206, 111335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, Y.; Wen, S.; Chen, X.; Gao, X.; Zeng, X.; Liu, X.; Tian, F.; Shang, Q. UDP-glycosyltransferases contribute to spirotetramat resistance in Aphis gossypii Glover. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2020, 166, 104565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.P.; Lu, H.; Guo, K.; Yao, S.M.; Cui, F. Insecticide resistance status and detoxification enzymes of wheat aphids Sitobion avenae and Rhopalosiphum padi. Sci. China Life Sci. 2017, 60, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, P.; Li, X.; Gao, H.; Wang, C.; Li, M.; Zhang, Y.; Li, X.; Liu, E.; Zhu, X. Field evolved resistance to pyrethroids, neonicotinoids, organophosphates and macrolides in Rhopalosiphum padi (Linnaeus) and Sitobion avenae (Fabricius) from China. Chemosphere 2021, 269, 128747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, K.; Ren, Z.; Li, W.; Liu, C.; Xu, P.; He, S.; Li, J.; Wan, H. An insecticide resistance diagnostic kit for whitebacked planthopper Sogatella furcifera (Horvath). J. Pest. Sci. 2021, 94, 531–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flores, J.M.; Gámiz, V.; Gil-Lebrero, S.; Rodríguez, I.; Navas, F.J.; García-Valcárcel, A.I.; Cutillas, V.; Fernández-Alba, A.R.; Hernando, M.D. A three-year large scale study on the risk of honey bee colony exposure to blooming sunflowers grown from seeds treated with thiamethoxam and clothianidin neonicotinoids. Chemosphere 2021, 262, 127735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsvetkov, N.; Samson-Robert, O.; Sood, K.; Patel, H.S.; Malena, D.A.; Gajiwala, P.H.; Maciukiewicz, P.; Fournier, V.; Zayed, A. Chronic exposure to neonicotinoids reduces honey bee health near corn crops. Science 2017, 356, 1395–1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ludicke, J.C.; Nieh, J.C. Thiamethoxam impairs honey bee visual learning, alters decision times, and increases abnormal behaviors. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 193, 110367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Garrood, W.T.; Zimmer, C.T.; Gorman, K.J.; Nauen, R.; Bass, C.; Davies, T.G. Field-evolved resistance to imidacloprid and ethiprole in populations of brown planthopper Nilaparvata lugens collected from across South and East Asia. Pestic. Manag. Sci. 2016, 72, 140–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ding, Y.R.; Yan, Z.T.; Si, F.L.; Li, X.D.; Mao, Q.M.; Asghar, S.; Chen, B. Mitochondrial genes associated with pyrethroid resistance revealed by mitochondrial genome and transcriptome analyses in the malaria vector Anopheles sinensis (Diptera: Culicidae). Pestic. Manag. Sci. 2019, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stevenson, B.J.; Bibby, J.; Pignatelli, P.; Muangnoicharoen, S.; O′Neill, P.M.; Lian, L.-Y.; Müller, P.; Nikou, D.; Steven, A.; Hemingway, J.; et al. Cytochrome P450 6M2 from the malaria vector Anopheles gambiae metabolizes pyrethroids: Sequential metabolism of deltamethrin revealed. Insect. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2011, 41, 492–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chanda, J.; Saili, K.; Phiri, F.; Stevenson, J.C.; Mwenda, M.; Chishimba, S.; Mulube, C.; Mambwe, B.; Lungu, C.; Earle, D.; et al. Pyrethroid and Carbamate Resistance in Anopheles funestus Giles along Lake Kariba in Southern Zambia. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2020, 103, 90–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Tie, M.; Chen, A.; Ma, K.; Li, F.; Liang, P.; Liu, Y.; Song, D.; Gao, X. Pyrethroid resistance associated with M918L mutation and detoxifying metabolism in Aphis gossypii from Bt cotton growing regions of China. Pestic. Manag. Sci. 2017, 73, 2353–2359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, K.Y.; Gao, J.-R. Kinetic properties and variability of esterases in organophosphate-susceptible and-resistant greenbugs, Schizaphis graminum (Homoptera: Aphididae). J. Pestici. Biochem. 1998, 62, 135–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, P.; Gao, X.W.; Zheng, B.Z. Genetic basis of resistance and studies on cross-resistance in a population of diamondback moth, Plutella xylostella (Lepidoptera: Plutellidae). Pestic. Manag. Sci. 2003, 59, 1232–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Yao, M.; Wu, Y. Cross-resistance, inheritance and biochemical mechanisms of imidacloprid resistance in B-biotype Bemisia tabaci. Pestic. Manag. Sci. 2009, 65, 1189–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, Q.; Guo, Z.; Xie, W.; Zhou, X.; Wang, S. Transcriptome profiling and functional analysis suggest that the constitutive overexpression of four cytochrome P450s confers resistance to abamectin in Tetranychus urticae from China. Pestic. Manag. Sci. 2021, 77, 1204–1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhang, Y.; Xie, X.; Gao, X. Monitoring of wheat aphid resistance to insecticides in China. Barl Cere Sci. 2018, 35, 61. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, Z.; Zhang, S.; Song, S.; Zhu, Q.; Xie, C.; Ji, J.; Gao, X. Resistance of wheat aphids to six insecticides and assessment of their field efficacy. Acta Entomo Sin. 2016, 59, 1206–1212. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wei, J.; Guo, X.; Li, L.; Wang, K.; Chen, M. Insecticide resistance monitoring of Rhopalosiphum padi to seven insecticides from wheat fields of Guanzhong area in Shaanxi province. Plant. Prot. 2019, 45, 211–214. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Y.; Cao, Y.; Zhao, F.; Xing, K. Resistance risk of sitobion avenae to common insecticides in linfen wheat area. J. Shanxi Agric. Sci. 2019, 47, 1061–1064. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, W.; Tu, X.; Xu, J.; Tu, X.; Bu, A.; Hou, L. Preliminary report on field chemical control of wheat aphid in winter wheat area of Hotan region. Xinjiang Agric. Sci. 2007, 44, 148–149. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, K.; Hu, J. Occurrence and control of wheat aphid in Kashgar, Xinjiang. Plant. Prot. 1980, 05, 11–13. [Google Scholar]
- Hong, B.; Guan, X.; Chi, Y.; Shi, H.; Wen, Z. Bioassay of the sensitivity of wheat aphids to several insecticides in Ningxia. J. Agric. Sci. 2004, 03, 17–20. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, W.; Zhang, H.; Chen, A.; Yan, J.; Wei, Y.; Ma, K.; Pu, L.; Cao, S.; Shi, X. Resistance levels to five insecticides of wheat aphid field populations from some regions of Gansu and Qinghai province of China. Agrochemicals 2020, 59, 532–536. [Google Scholar]
- Abbott, W.S. A method of computing the effectiveness of an insecticide. J. Econ. Entomol. 1925, 18, 265–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chopa, C.S.; Descamps, L.R. Composition and biological activity of essential oils against Metopolophium dirhodum (Hemiptera: Aphididae) cereal crop pest. Pestic. Manag. Sci. 2012, 68, 1492–1500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L. Strategic measures to ban and replace the sustainable development of China’s pesticide industry. Pestic. Mark. News 2007, 1, 4–6. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, X.; Pan, Y.; Xin, X.; Zheng, C.; Gao, X.; Xi, J.; Shang, Q. Cross-resistance pattern and basis of resistance in a thiamethoxam-resistant strain of Aphis gossypii Glover. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2017, 138, 91–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, K.; Bai, J.; Zhao, J.; Su, S.; Liu, L.; Han, Z.; Chen, M. Super-kdr mutation M918L and multiple cytochrome P450s associated with the resistance of Rhopalosiphum padi to pyrethroid. Pestic. Manag. Sci. 2020, 76, 2809–2817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, F.; Parthasarathya, R.; Bai, H.; Woithe, K.; Kaussmann, M.; Naima, R.; Harrison, D.; Palli, S. A brain-specific cytochrome P450 responsible for the majority of deltamethrin resistance in the QTC279 strain of Tribolium castaneum. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 8557–8562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lu, K.; Song, Y.; Zeng, R. The role of cytochrome P450-mediated detoxification in insect adaptation to xenobiotics. Curr. Opin. Insect. Sci. 2021, 43, 103–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Liang, Q.M.; Zhou, W.W.; Jiang, Y.D.; Zhu, Q.Z.; Yu, H.; Zhang, C.X.; Gurr, G.M.; Zhu, Z.R. RNA interference of NADPH-cytochrome P450 reductase of the rice brown planthopper, Nilaparvata lugens, increases susceptibility to insecticides. Pestic. Manag. Sci. 2015, 71, 32–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
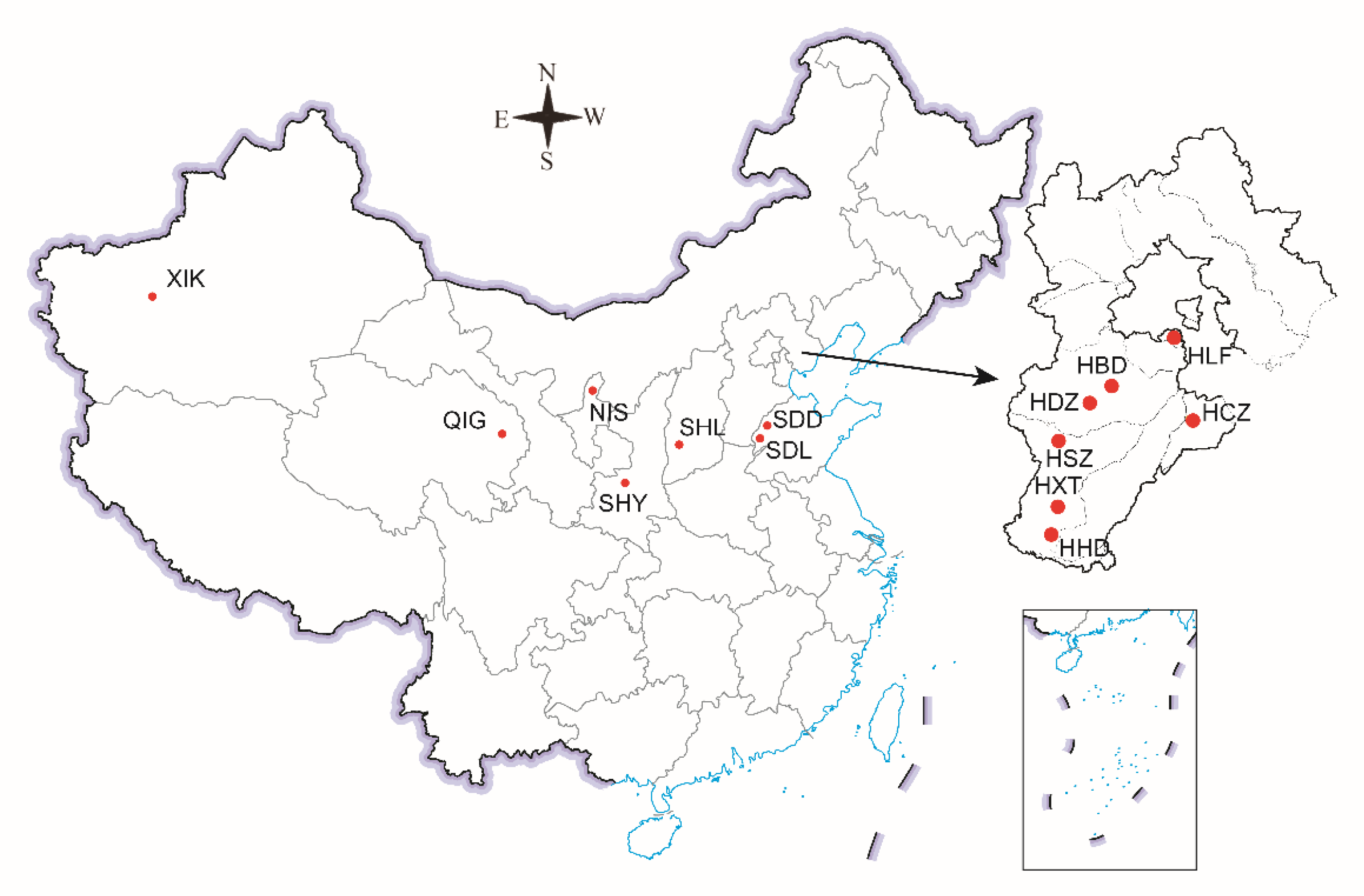


| No. | Collecting Locality | Code | Collection Date | Longitude and Latitude | HIS a | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Dingzhou, Hebei | HDZ | 17 May 2017 | 38°31′09″ N, 115°04′09″ E | unknown | - |
| 2 | Shijiazhuang, Hebei | HSZ | 17 May 2017 | 37°54′59″ N, 114°45′19″ E | unknown | - |
| 3 | Xingtai, Hebei | HXT | 18 May 2017 | 37°05′04″ N, 114°36′21″ E | unknown | - |
| 4 | Handan, Hebei | HHD | 18 May 2017 | 36°32′31″ N, 114°33′32″ E | unknown | - |
| 5 | Cangzhou, Hebei | HCZ | 26 April 2017 | 38°03′14″ N, 116°40′25″ E | neonicotinoids | [35] |
| 6 | Langfang, Hebei | HLF | 30 April 2017 | 39°30′29″ N, 116°36′09″ E | neonicotinoids | [13] |
| 7 | Baoding, Hebei | HBD | 29 April 2017 | 39°12′56″ N, 115°47′54″ E | unknown | - |
| 8 | Dezhou, Shandong | SDD | 18 May 2017 | 36°57′45″ N, 115°58′01″ E | neonicotinoids pyrethroids organophosphates | [36] |
| 9 | Liaocheng, Shandong | SDL | 18 May 2017 | 36°28′18″ N, 115°39′23″ E | ||
| 10 | Yangling, Shaanxi | SHY | 3 May 2018 | 34°15′33″ N, 108°02′33″ E | neonicotinoids pyrethroids organophosphates macrolides | [37] |
| 13 May 2019 | 34°15′33″ N, 108°02′33″ E | |||||
| 11 | Linfen, Shanxi | SHL | 14 May 2018 | 36°06′38″ N, 111°30′04″ E | neonicotinoids pyrethroids organophosphates | [38] |
| 14 May 2019 | 36°06′38″ N, 111°30′04″ E | |||||
| 12 | Kashi, Xinjiang | XIK | 7 June 2018 | 38°11′25″ N, 77°11′12″ E | neonicotinoids organophosphates | [39,40] |
| 28 May 2019 | 38°11′25″ N, 77°11′12″ E | |||||
| 13 | Shizuishan, Ningxia | NIS | 12 June 2018 | 39°05′57″ N, 106°44′51″ E | pyrethroids organophosphates | [41] |
| 16 June 2019 | 39°05′57″ N, 106°44′51″ E | |||||
| 14 | Guide, Qinghai | QIG | 14 June 2018 | 36°02′15″ N, 101°27′13″ E | neonicotinoids pyrethroids organophosphates | [42] |
| 18 June 2019 | 36°02′15″ N, 101°27′13″ E |
| Insecticides | Population | N a | LC50 (95%CI; mg/L) b | Slope ± SE | p-Value | Correlation Coefficient |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Thiamethoxam | HBD-2017 | 1849 | 4.27 (2.27–8.03) | 4.64 ± 0.10 | 0.0001 | 0.9810 |
| Imidacloprid | SDD-2017 | 1817 | 3.93 (2.55–6.05) | 4.71 ± 0.05 | 0.0001 | 0.9940 |
| Beta-cypermethrin | NIS-2019 | 713 | 0.52 (0.48–0.56) | 0.58 ± 0.05 | 0.0001 | 0.9999 |
| Omethoate | SHL-2019 | 460 | 18.63 (8.44–41.03) | 0.75 ± 0.12 | 0.0087 | 0.9625 |
| Bifenthrin | QIG-2019 | 543 | 9.47 (5.68–15.80) | 0.57 ± 0.05 | 0.0017 | 0.9874 |
| Chlorpyrifos | SHY-2019 | 702 | 0.44 (0.31–4066) | 2.33 ± 0.37 | 0.0083 | 0.9637 |
| Abamectin | HHD-2019 | 2109 | 1.60 (0.97–2.63) | 4.80 ± 0.12 | 0.0014 | 0.9697 |
| Population | Thiamethoxam | Imidacloprid | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N a | LC50 (95% CI; mg/L) b | Slope ± SE | p-Value | Correlation Coefficient | RLR c | N | LC50 (95% CI; mg/L) | Slope ± SE | p-Value | Correlation Coefficient | RLR c | |
| SDD-2017 | 1857 | 13.42 (7.42–24.95) | 4.23 ± 0.13 | 0.0009 | 0.9753 | 3.14 | 1817 | 3.93 (2.55–6.05) | 4.71 ± 0.05 | 0.0001 | 0.9940 | 1.00 |
| HDZ-2017 | 2302 | 35.60 (25.80–49.10) | 3.76 ± 0.10 | 0.0001 | 0.9926 | 8.34 | 1303 | 16.97 (12.38–23.27) | 4.20 ± 0.06 | 0.0001 | 0.9960 | 4.32 |
| HSZ-2017 | 843 | 75.25 (58.19–97.31) | 3.31 ± 0.13 | 0.0006 | 0.9934 | 17.62 | 2212 | 8.51 (5.31–13.63) | 4.38 ± 0.09 | 0.0009 | 0.9919 | 2.17 |
| HXT-2017 | 1951 | 8.71 (6.58–11.54) | 4.21 ± 0.08 | 0.0001 | 0.9939 | 2.04 | 1578 | 8.07 2.63–24.75) | 4.46 ± 0.20 | 0.0177 | 0.9543 | 2.05 |
| HHD-2017 | 1746 | 49.56 (7.22–16.59) | 3.99 ± 0.14 | 0.0001 | 0.9780 | 11.61 | 1742 | 16.72 (11.55–24.21) | 4.02 ± 0.08 | 0.0004 | 0.9951 | 4.25 |
| HCZ-2017 | 1968 | 11.39 (7.04–18.43) | 4.38 ± 0.10 | 0.0001 | 0.9839 | 2.67 | 1562 | 6.86 (4.00–11.78) | 4.46 ± 0.08 | 0.0001 | 0.9907 | 1.75 |
| HBD-2017 | 1849 | 4.27 (2.27–8.03) | 4.64 ± 0.10 | 0.0001 | 0.9810 | 1.00 | 2692 | 7.72 (3.97–14.93) | 4.41 ± 0.12 | 0.0004 | 0.9840 | 1.96 |
| HLF-2017 | 1486 | 51.81 (55.28–80.00) | 4.04 ± 0.03 | 0.0001 | 0.9716 | 12.13 | 1430 | 7.55 (3.99–14.30) | 4.45 ± 0.13 | 0.0001 | 0.9677 | 1.92 |
| SDL-2017 | 1726 | 48.10 (31.28–73.95) | 3.54 ± 0.14 | 0.0005 | 0.9826 | 11.26 | 1236 | 59.24 (35.46–98.98) | 3.63 ± 0.23 | 0.0008 | 0.9561 | 15.07 |
| QIG-2018 | 2426 | 82.33 (29.86–227.01) | 0.48 ± 0.12 | 0.0293 | 0.9151 | 19.28 | 925 | 13.09 (9.37–18.29) | 4.03 ± 0.11 | 0.0005 | 0.9943 | 3.33 |
| NIS-2018 | 550 | 572.29 (281.45–1163.67) | 0.78 ± 0.10 | 0.0045 | 0.9759 | 134.03 | 654 | 56.63 (14.41–222.55) | 3.79 ± 0.49 | 0.0594 | 0.8634 | 14.41 |
| SHY-2018 | 766 | 441.11 (150.42–1293.56) | 0.53 ± 0.11 | 0.0173 | 0.9404 | 103.30 | 511 | 21.87 (11.14–42.95) | 4.39 ± 0.11 | 0.0070 | 0.9674 | 5.56 |
| SHL-2018 | 2289 | 39.32 (25.96–59.56) | 0.62 ± 0.06 | 0.0020 | 0.9860 | 9.22 | 1145 | 43.05 (38.63–47.97) | 4.02 ± 0.03 | 0.0005 | 0.9995 | 10.95 |
| XIK-2018 | 560 | 130.48 (100.43–169.51) | 0.86 ± 0.06 | 0.0006 | 0.9939 | 30.56 | 913 | 9.51 (3.71–24.40) | 4.43 ± 0.20 | 0.0085 | 0.9630 | 2.42 |
| QIG-2019 | 780 | 62.29 (44.18–87.82) | 0.77 ± 0.06 | 0.0010 | 0.9913 | 14.59 | 686 | 13.96 (5.07–38.44) | 0.99 ± 0.20 | 0.0150 | 0.9459 | 3.54 |
| NIS-2019 | 689 | 199.72 (120.76–330.31) | 0.88 ± 0.09 | 0.0019 | 0.9864 | 46.77 | 515 | 12.23 (8.24–18.15) | 0.59 ± 0.06 | 0.0111 | 0.9889 | 3.11 |
| SHY-2019 | 546 | 24.58 (10.99–55.00) | 0.40 ± 0.07 | 0.0116 | 0.9545 | 5.76 | 603 | 12.29 (9.41–16.05) | 0.80 ± 0.05 | 0.0004 | 0.9951 | 3.13 |
| SHL-2019 | 660 | 126.19 (56.44–282.15) | 0.68 ± 0.10 | 0.0065 | 0.9691 | 29.55 | 556 | 225.16 (114.66–442.15) | 1.02 ± 0.24 | 0.1494 | 0.9726 | 57.29 |
| XIK-2019 | 571 | 149.86 (62.38–360.01) | 1.24 ± 0.22 | 0.0110 | 0.9561 | 35.10 | 605 | 5.89 (2.42–14.33) | 0.23 ± 0.04 | 0.0229 | 0.9771 | 1.50 |
| Population | Beta-Cypermethrin | Omethoate | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N a | LC50 (95% CI; mg/L) b | Slope ± SE | p-Value | Correlation Coefficient | RLR c | N | LC50 (95% CI; mg/L) | Slope ± SE | p-Value | Correlation Coefficient | RLR | |
| SDD-2017 | 1532 | 3.96 (1.88–8.33) | 4.55 ± 0.14 | 0.0017 | 0.9664 | 7.62 | 2129 | 73.22 (45.68–117.34) | 2.58 ± 0.23 | 0.0025 | 0.9835 | 3.93 |
| HDZ-2017 | 1272 | 1.25 (0.64–2.46) | 4.91 ± 0.14 | 0.0008 | 0.9764 | 2.40 | 3266 | 68.44 (47.45–98.71) | 2.03 ± 0.38 | 0.0026 | 0.9831 | 3.67 |
| HSZ-2017 | 1875 | 2.92 (15.30–45.69) | 4.21 ± 0.12 | 0.0002 | 0.9971 | 5.62 | 1228 | 54.49 (82.35–1159.44) | 3.21 ± 0.31 | 0.0001 | 0.9840 | 2.92 |
| HXT-2017 | 2844 | 2.85 (1.83–4.42) | 4.6 ± 0.10 | 0.0001 | 0.9818 | 5.48 | 2842 | 119.91 (96.03–149.72) | 1.45 ± 0.23 | 0.0008 | 0.9922 | 6.44 |
| HHD-2017 | 1733 | 5.84 (3.26–10.47) | 4.43 ± 0.13 | 0.0003 | 0.9704 | 11.23 | 1618 | 133.40 (89.28–199.32) | 1.09 ± 0.76 | 0.0103 | 0.9575 | 7.16 |
| HCZ-2017 | 1781 | 4.42 (2.56–7.63) | 4.47 ± 0.12 | 0.0007 | 0.9788 | 8.50 | 2076 | 88.43 (77.17–101.34) | 2.17 ± 0.13 | 0.0002 | 0.9974 | 4.75 |
| HBD-2017 | 1824 | 5.20 (2.15–12.63) | 4.41 ± 0.20 | 0.0075 | 0.9661 | 10.00 | 2781 | 79.11 (64.85–96.51) | 2.09 ± 0.24 | 0.0001 | 0.9905 | 4.25 |
| HLF-2017 | 1954 | 31.18 (18.33–53.03) | 4.08 ± 0.13 | 0.0002 | 0.9731 | 59.96 | 3001 | 117.61 (95.96–144.14) | 2.02 ± 0.19 | 0.0001 | 0.9941 | 6.31 |
| SDL-2017 | 1355 | 29.40 (19.49–44.33) | 3.64 ± 0.16 | 0.0006 | 0.9792 | 56.54 | 1290 | 74.97 (59.80–93.98) | 0.78 ± 0.26 | 0.0012 | 0.9898 | 4.02 |
| QIG-2018 | 1071 | 5.05(2.21–11.52) | 0.42 ± 0.06 | 0.0071 | 0.9673 | 9.71 | 809 | 19.90 (16.31–24.29) | 0.99 ± 0.04 | 0.0002 | 0.9971 | 1.07 |
| NIS-2018 | 475 | 63.14 (39.15–101.80) | 0.93 ± 0.09 | 0.0021 | 0.9856 | 121.42 | 309 | 169.53 (39.13–734.52) | 0.66 ± 0.17 | 0.0285 | 0.9168 | 9.10 |
| SHY-2018 | 702 | 8.81 (0.97–80.43) | 0.53 ± 0.21 | 0.0849 | 0.8259 | 16.94 | 666 | 177.05 (63.99–489.87) | 1.29 ± 0.49 | 0.2323 | 0.9342 | 9.50 |
| SHL-2018 | 1644 | 23.90 (16.10–35.50) | 0.85 ± 0.08 | 0.0015 | 0.9884 | 45.96 | 1791 | 348.86 (67.74–489.87) | 0.49 ± 0.12 | 0.0252 | 0.9342 | 18.73 |
| XIK-2018 | 620 | 22.55 (15.16–33.57) | 0.76 ± 0.08 | 0.0109 | 0.9891 | 43.37 | 499 | 82.63 (30.19–226.18) | 1.07 ± 0.21 | 0.0154 | 0.9450 | 4.44 |
| QIG-2019 | 496 | 4.79 (1.75–13.11) | 0.68 ± 0.15 | 0.0439 | 0.9561 | 9.21 | 724 | 100.70 (44.77–226.52) | 1.07 ± 0.19 | 0.0104 | 0.9576 | 5.41 |
| NIS-2019 | 713 | 0.52 (0.48–0.56) | 0.58 ± 0.05 | 0.0001 | 0.9999 | 1.00 | 520 | 220.23 (167.30–289.92) | 1.68 ± 0.18 | 0.0674 | 0.9944 | 11.82 |
| SHY-2019 | ND d | 723 | 43.80 (30.85–62.17) | 1.55 ± 0.14 | 0.0085 | 0.9915 | 2.35 | |||||
| SHL-2019 | 714 | 1.96 (0.59–6.55) | 0.53 ± 0.09 | 0.0115 | 0.9546 | 3.77 | 460 | 18.63 (8.44–41.03) | 0.75 ± 0.12 | 0.0087 | 0.9625 | 1.00 |
| XIK-2019 | 487 | 50.31 (29.09–86.98) | 0.85 ± 0.13 | 0.0232 | 0.9768 | 96.75 | 439 | 78.06 (35.90–169.75) | 1.18 ± 0.26 | 0.0438 | 0.9562 | 4.19 |
| Population | Bifenthrin | Chlorpyrifos | ||||||||||
| N a | LC50 (95% CI; mg/L) b | Slope ± SE | p-Value | Correlation Coefficient | RLR c | N | LC50 (95% CI; mg/L) | Slope ± SE | p-Value | Correlation Coefficient | RLR | |
| QIG-2019 | 543 | 9.47 (5.68–15.80) | 0.57 ± 0.05 | 0.0017 | 0.9874 | 1.00 | 702 | 0.49 (0.30–0.82) | 4.72 ± 1.12 | 0.0247 | 0.9244 | 1.11 |
| NIS-2019 | 571 | 10.09 (8.50–11.99) | 0.65 ± 0.02 | 0.0001 | 0.9981 | 1.14 | 704 | 0.80 (0.66–0.96) | 3.91 ± 0.45 | 0.0130 | 0.9870 | 1.82 |
| SHY-2019 | ND d | 702 | 0.44 (0.31–0.63) | 2.33 ± 0.37 | 0.0083 | 0.9637 | 1.00 | |||||
| SHL-2019 | 606 | 12.78 (5.84–27.98) | 0.69 ± 0.12 | 0.0102 | 0.9582 | 1.21 | 712 | 1.32 (1.21–1.44) | 3.09 ± 0.14 | 0.0002 | 0.9970 | 3.09 |
| XIK-2019 | 409 | 57.01 (25.86–125.69) | 0.81 ± 0.21 | 0.0302 | 0.9134 | 6.02 | 784 | 3.34 (1.40–7.97) | 1.61 ± 0.33 | 0.0396 | 0.9604 | 7.59 |
| Population | N a | LC50 (95%CI; mg/L) b | Slope ± SE | p-Value | Correlation Coefficient | RLR c |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HHD-2017 | 2109 | 1.60 (0.97–2.63) | 4.80 ± 0.12 | 0.0014 | 0.9697 | 1.00 |
| HDZ-2017 | 1399 | 41.42 (23.49–73.04) | 3.46 ± 0.19 | 0.0056 | 0.9719 | 25.89 |
| HSZ-2017 | 1722 | 11.35 (7.17–17.98) | 3.72 ± 0.18 | 0.0050 | 0.9741 | 7.09 |
| HXT-2017 | 1740 | 9.44 (6.13–14.55) | 4.18 ± 0.12 | 0.0001 | 0.9805 | 5.90 |
| SDD-2017 | 2189 | 8.46 (5.62–12.74) | 3.43 ± 0.24 | 0.0009 | 0.9752 | 5.29 |
| HCZ-2017 | 1918 | 3.82 (2.34–6.24) | 4.09 ± 0.19 | 0.0010 | 0.9735 | 2.39 |
| HBD-2017 | 2245 | 19.35 (13.91–26.90) | 3.91 ± 0.08 | 0.0005 | 0.9941 | 12.09 |
| HLF-2017 | 1258 | 18.22 (12.70–26.14) | 4.00 ± 0.00 | 0.0021 | 0.9852 | 11.39 |
| SDL-2017 | 1103 | 28.57 (20.78–39.29) | 2.39 ± 0.36 | 0.0014 | 0.9695 | 17.86 |
| QIG-2018 | 1488 | 36.19 (17.33–75.59) | 0.92 ± 0.15 | 0.0087 | 0.9624 | 22.62 |
| NIS-2018 | 771 | 9.52 (2.69–33.60) | 0.81 ± 0.21 | 0.0311 | 0.9116 | 5.95 |
| SHY-2018 | 621 | 21.01 (10.13–43.6) | 1.18 ± 0.19 | 0.0087 | 0.9623 | 13.13 |
| SHL-2018 | 1847 | 11.03 (4.36–27.89) | 0.67 ± 0.13 | 0.0145 | 0.9823 | 6.89 |
| XIK-2018 | 696 | 11.88 (9.24–15.29) | 1.07 ± 0.06 | 0.0003 | 0.9957 | 7.43 |
| QIG-2019 | 580 | 4.28 (2.57–7.12) | 0.97 ± 0.09 | 0.0016 | 0.9880 | 2.68 |
| NIS-2019 | 676 | 5.23 (4.48–6.09) | 1.78 ± 0.09 | 0.0024 | 0.9976 | 3.27 |
| SHY-2019 | 750 | 1.76 (0.88–3.49) | 0.81 ± 0.10 | 0.0035 | 0.9795 | 1.10 |
| SHL-2019 | 576 | 4.53 (3.52–5.84) | 1.49 ± 0.12 | 0.0060 | 0.9940 | 2.83 |
| XIK-2019 | 687 | 10.20 (7.23–14.40) | 1.04 ± 0.07 | 0.0008 | 0.9923 | 6.38 |
| Insecticides | Imidacloprid | Thiamethoxam | β-Cypermethrin | Abamectin |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Thiamethoxam | 0.165 | |||
| β-cypermethrin | 0.023 | 0.504 * | ||
| Abamectin | −0.119 | −0.041 | 0.024 | |
| Omethoate | −0.132 | 0.283 | 0.247 | −0.193 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gong, P.; Li, X.; Wang, C.; Zhu, S.; Li, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Li, X.; Li, G.; Liu, E.; Gao, H.; et al. The Sensitivity of Field Populations of Metopolophium dirhodum (Walker) (Hemiptera: Aphididae) to Seven Insecticides in Northern China. Agronomy 2021, 11, 1556. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy11081556
Gong P, Li X, Wang C, Zhu S, Li Q, Zhang Y, Li X, Li G, Liu E, Gao H, et al. The Sensitivity of Field Populations of Metopolophium dirhodum (Walker) (Hemiptera: Aphididae) to Seven Insecticides in Northern China. Agronomy. 2021; 11(8):1556. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy11081556
Chicago/Turabian StyleGong, Peipan, Xinan Li, Chao Wang, Saige Zhu, Qiuchi Li, Yunhui Zhang, Xiangrui Li, Guangkuo Li, Enliang Liu, Haifeng Gao, and et al. 2021. "The Sensitivity of Field Populations of Metopolophium dirhodum (Walker) (Hemiptera: Aphididae) to Seven Insecticides in Northern China" Agronomy 11, no. 8: 1556. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy11081556
APA StyleGong, P., Li, X., Wang, C., Zhu, S., Li, Q., Zhang, Y., Li, X., Li, G., Liu, E., Gao, H., Yang, X., & Zhu, X. (2021). The Sensitivity of Field Populations of Metopolophium dirhodum (Walker) (Hemiptera: Aphididae) to Seven Insecticides in Northern China. Agronomy, 11(8), 1556. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy11081556








