Identifying Within-Field Spatial and Temporal Crop Water Stress to Conserve Irrigation Resources with Variable-Rate Irrigation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
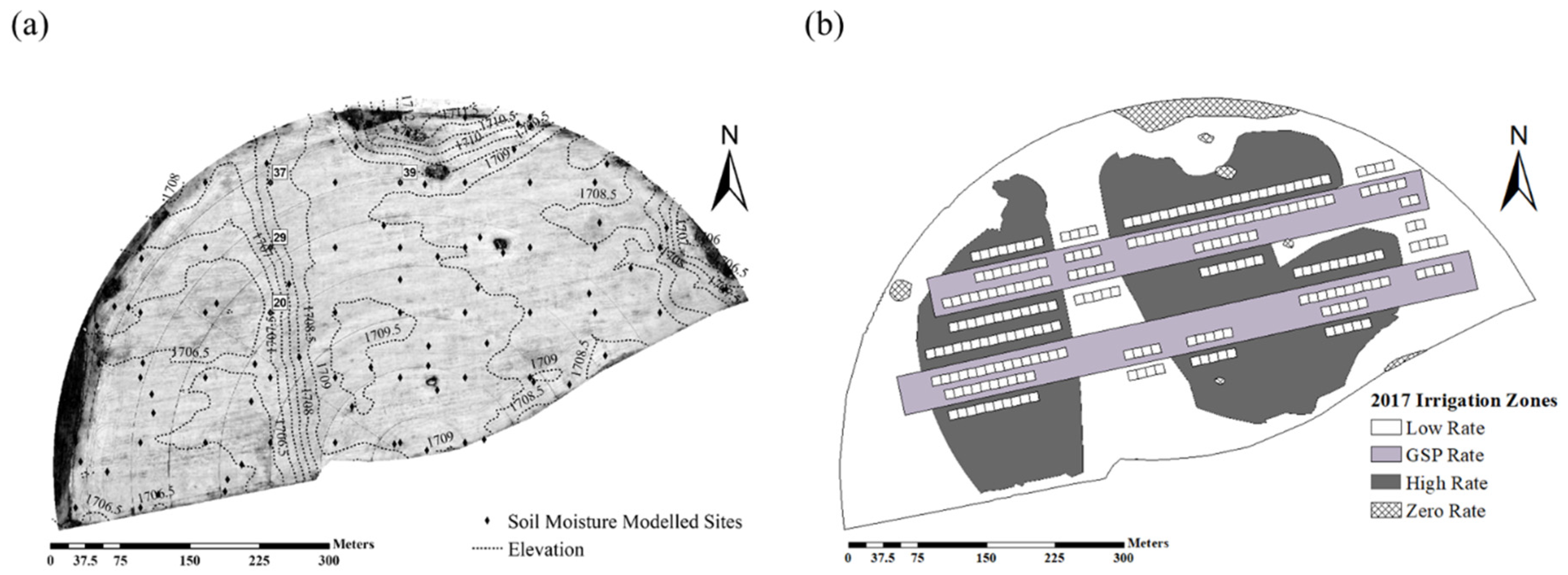
2.1. Site Description, Field Observations, and Management Practices
2.2. Modelling Water Dynamics and Crop Stress
2.3. Statistical Analysis
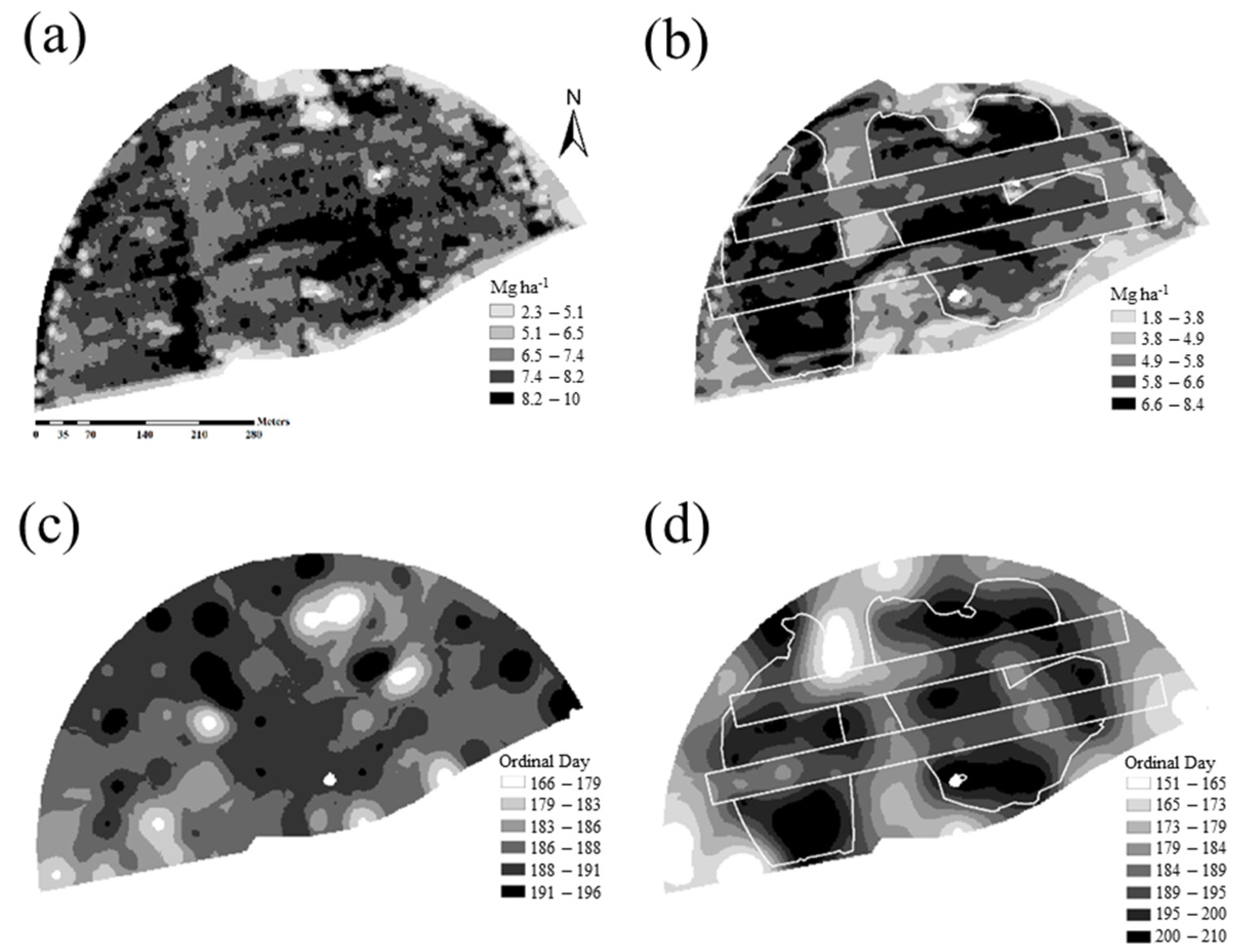
3. Results and Discussion
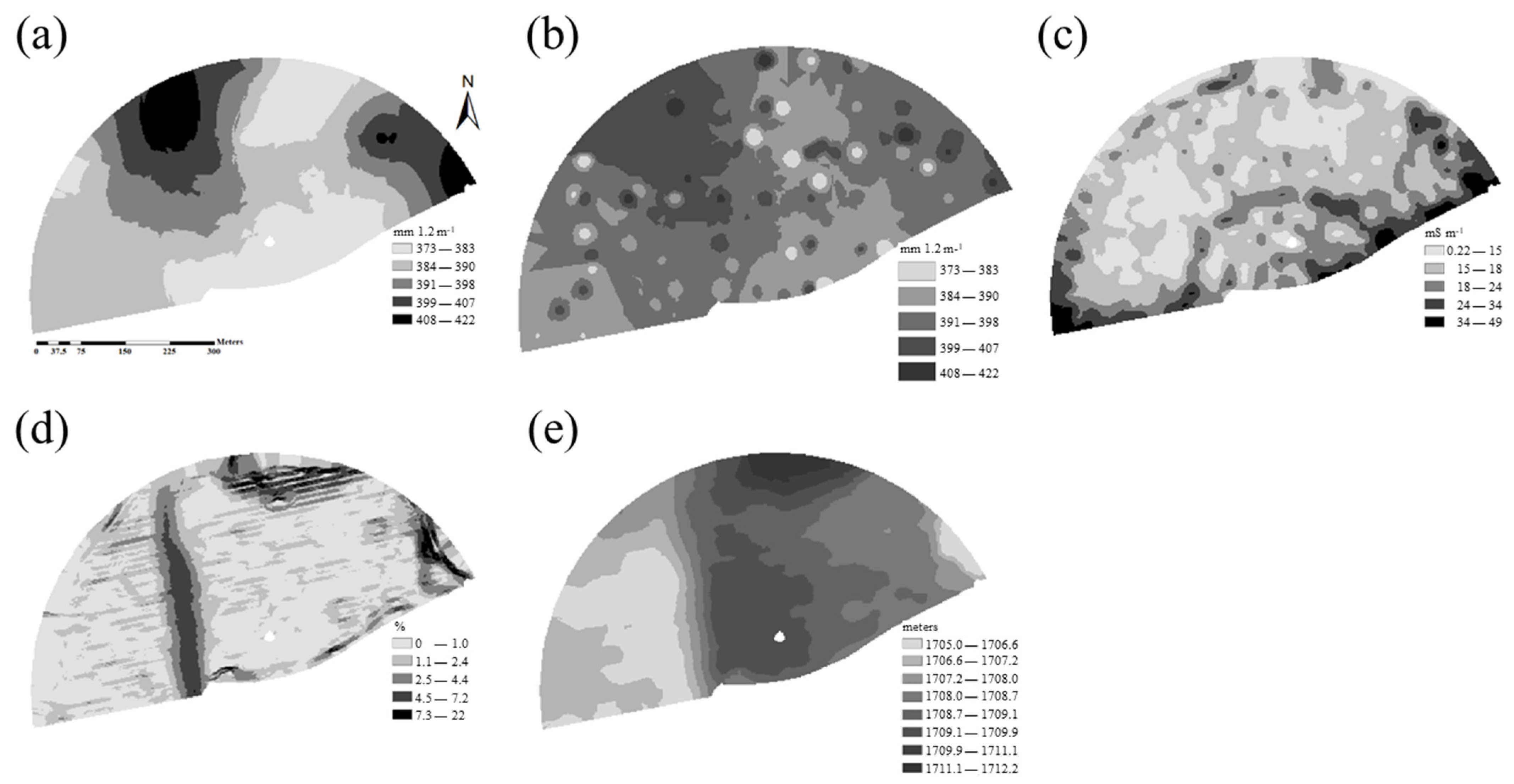
3.1. Spatial Variation of Soil Properties and Topographic Features
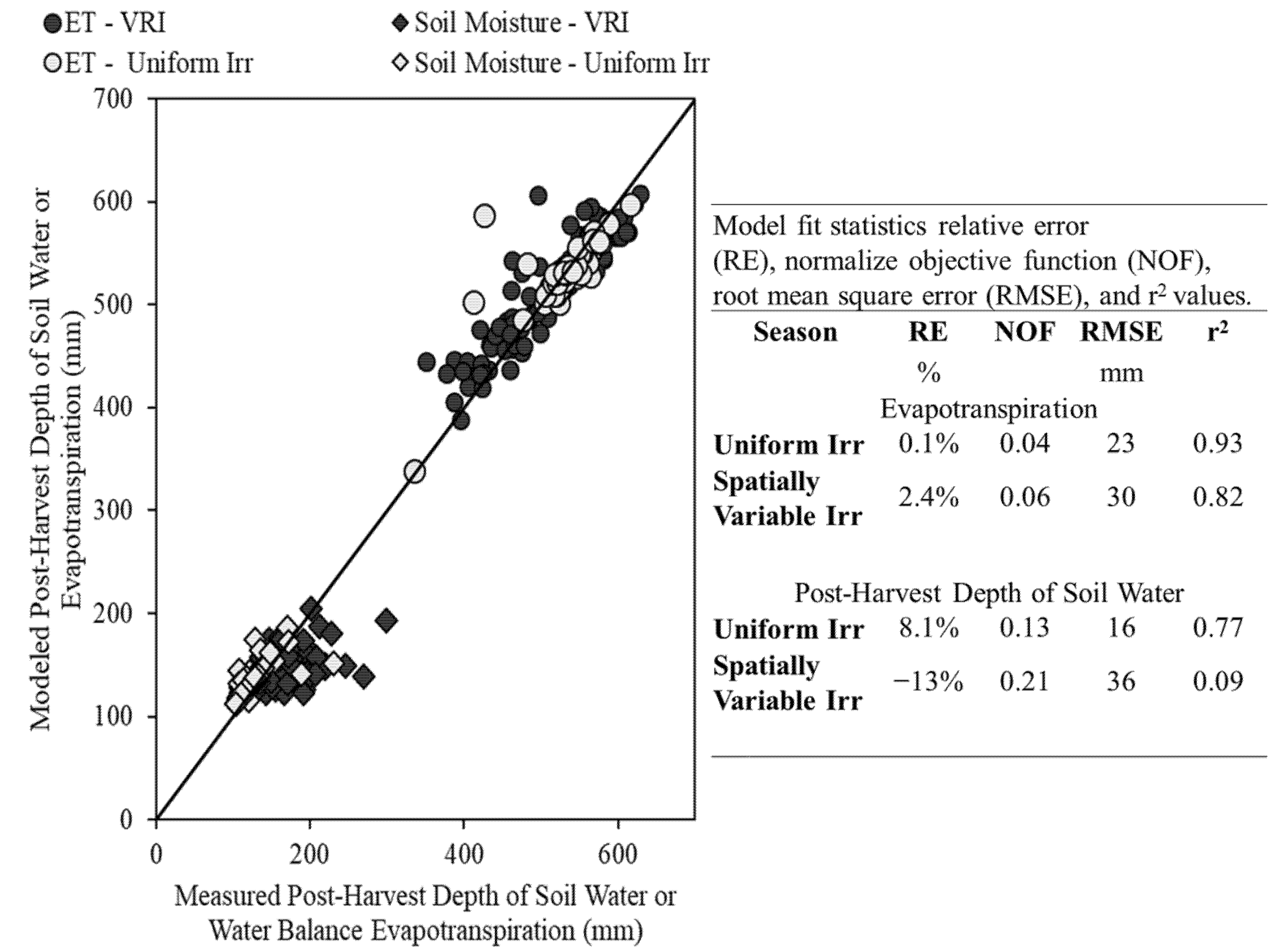
3.2. Model Validation
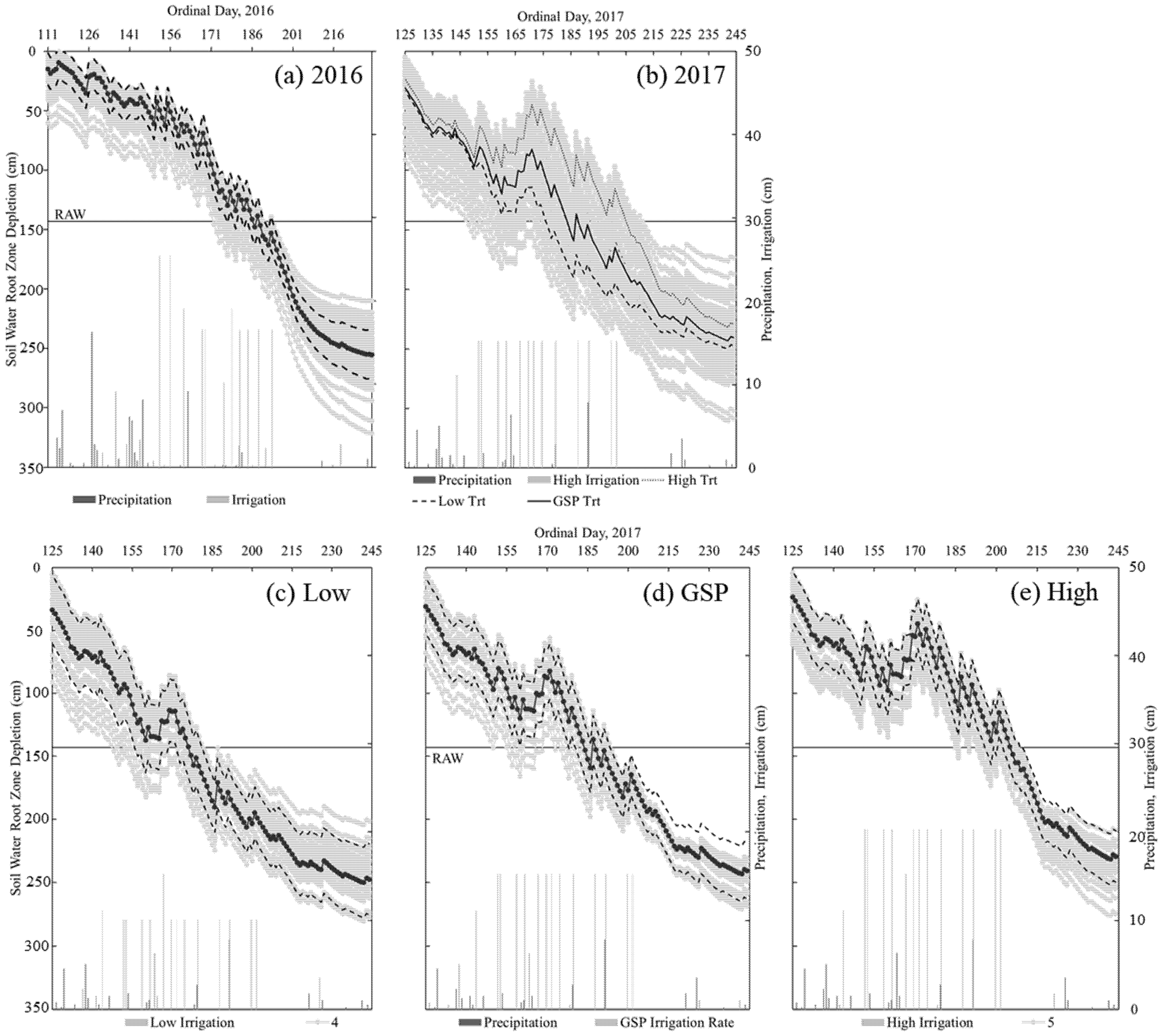
3.3. Uniform Irrigation Season (2016)
3.4. Spatially Variable Irrigation (2017)
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Evans, R.G.; LaRue, J.; Stone, K.C.; King, B.A. Adoption of site-specific variable rate sprinkler irrigation systems. Irrig. Sci. 2013, 31, 871–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abdullah, K.B. Use of water and land for food security and environmental sustainability. Irrig. Drain. 2006, 55, 219–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, A.P.; Cook, E.R.; Smerdon, J.E.; Cook, B.I.; Abatzoglou, J.T.; Bolles, K.; Baek, S.H.; Badger, A.M.; Livneh, B. Large contribution from anthropogenic warming to an emerging North American megadrought. Science 2020, 368, 314–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daccache, A.; Knox, J.W.; Weatherhead, E.K.; Daneshkhah, A.; Hess, T.M. Implementing precision irrigation in a humid climate - Recent experiences and on-going challenges. Agric. Water Manag. 2015, 147, 135–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Longchamps, L.; Khosla, R.; Reich, R.; Gui, D.W. Spatial and Temporal Variability of Soil Water Content in Leveled Fields. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2015, 79, 1446–1454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sadler, E.J.; Evans, R.G.; Stone, K.C.; Camp, C.R. Opportunities for Conservation with Precision Irrigation. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2005, 60, 371–379. [Google Scholar]
- King, B.A.; Reeder, R.E.; Wall, R.W.; Stark, J.C. Comparison of Site-Specific and Conventional Uniform Irrigation Management for Potatoes. Appl. Eng. Agric. 2006, 22, 677–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hedley, C.B.; Yule, I.J. A method for spatial prediction of daily soil water status for precise irrigation scheduling. Agric. Water Manag. 2009, 96, 1737–1745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo, T.H.; Heeren, D.M.; Martin, D.L.; Mateos, L.; Luck, J.D.; Eisenhauer, D.E. Pumpage Reduction by Using Variable-Rate Irrigation to Mine Undepleted Soil Water. Trans. ASABE 2016, 59, 1285–1298. [Google Scholar]
- Evans, R.G.; King, B.A. Site-specific sprinkler irrigation in a water-limited future. Trans. ASABE 2012, 55, 493–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haghverdi, A.; Leib, B.G.; Washington-Allen, R.A.; Ayers, P.D.; Buschermohle, M.J. High-resolution prediction of soil available water content within the crop root zone. J. Hydrol. 2015, 530, 167–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hedley, C.B.; Yule, I.J. Soil water status mapping and two variable-rate irrigation scenarios. Precis. Agric. 2009, 10, 342–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Messick, R.M.; Heaton, M.J.; Hansen, N. Multivariate spatial mapping of soil water holding capacity with spatially varying cross-correlations. Ann. Appl. Stat. 2017, 11, 69–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Lara, A.; Khosla, R.; Longchamps, L. Characterizing Spatial Variability in Soil Water Content for Precision Irrigation Management. Agronomy 2018, 8, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jimenez, A.; Ortiz, B.V.; Bondesan, L.; Morata, G.; Damianidis, D. Artificial neural networks for irrigation management: A case study from southern Alabama, USA. In Precision Agriculture; Stafford, J.V., Ed.; Wageningen Academic Publishers: Wageningen, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 657–664. [Google Scholar]
- Hedley, C.B.; Yule, I.J.; Tuohy, M.P.; Vogeler, I. Key Performance indicators for simulated variable-rate irrigation of variable soil sin humid regions. Trans. ASABE 2009, 52, 1575–1584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vories, E.; O’Shaughnessy, S.; Andrade, M. Comparison of precision and conventional irrigation management of cotton. In Precision Agriculture; Stafford, J.V., Ed.; Wageningen Academic Publishers: Wageningen, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 695–702. [Google Scholar]
- Pugh, S.; Heaton, M.J.; Svedin, J.; Hansen, N. Spatiotemporal Lagged Models for Variable Rate Irrigation in Agriculture. J. Agric. Biol. Environ. Stat. 2019, 24, 634–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svedin, J.D. Characterizing the Spatial Variation of Crop Water Productivity for Variable-Rate Irrigation Management. M.S. Thesis 6878, Brigham Young University, Provo, UT, USA, June 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Kerry, R.; Oliver, M.A. Variograms of ancillary data to aid sampling for soil surveys. Precis. Agric. 2003, 4, 261–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, R.G.; Pereira, L.S.; Rae, D.; Smith, M. Crop Evapotranspiration: Guidelines for Computing Crop Water Requirements. In FAO Irrigation and Drainage Paper No. 56; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations: Rome, Italy, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Carroll, D.A.; Hansen, N.C.; Hopkins, B.G.; DeJonge, K.C. Leaf temperature of maize and Crop Water Stress Index with variable irrigation and nitrogen supply. Irrig. Sci. 2017, 35, 549–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miner, G.L.; Hansen, N.C.; Inman, D.; Sherrod, L.A.; Peterson, G.A. Constraints of no-till dryland agroecosystems as bioenergy production systems. Agron. J. 2013, 105, 364–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, D.L.; Stegman, E.C.; Freres, E. Irrigation scheduling principles. In Management of Farm Irrigation Systems; Hoffman, G.J., Howell, T.A., Solomon, K.H., Eds.; American Society of Agricultural Engineers: St. Joseph, MI, USA, 1990; pp. 155–206. [Google Scholar]
- Hebbali, A. olsrr: Tools for Building OLS Regression Models; R Package version 0.5.3. 2020. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=olsrr (accessed on 9 June 2021).
- Lo, T.H.; Heeren, D.M.; Mateos, L.; Luck, J.D.; Martin, D.L.; Miller, K.A.; Barker, J.B.; Shaver, T.M. Field Characterization of Field Capacity and Root Zone Available Water Capacity for Variable Rate Irrigation. Appl. Eng. Agric. 2017, 33, 559–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Shaughnessy, S.A.; Evett, S.R.; Colaizzi, P.D. Dynamic prescription maps for site-specific variable rate irrigation of cotton. Agric. Water Manag. 2015, 159, 123–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beeri, O.; Pelta, R.; Shilo, T.; Mey-tal, S.; Tanny, J. Accuracy of crop coefficient estimation methods based on satellite imagery. In Precision Agriculture; Stafford, J.V., Ed.; Wageningen Academic Publishers: Wageningen, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 437–444. [Google Scholar]
- Hopkins, B.G.; Hansen, N.C. Phosphorus management in high-yield systems. J. Environ. Qual. 2019, 48, 1265–1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Passioura, J. Increasing Crop Productivity when water is scarce-from breeding to field management. Agric. Water Manag. 2006, 80, 176–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
| P 1 | K | N | OM | CaCO3 | Clay | Silt | Sand | Textural Class | pH |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| mg kg−1 | % | ||||||||
| 30 | 234 | 0.13 | 1.7 | 2.8 | 34 | 58 | 8 | Silty Clay Loam | 7.6 |
| Season | Precipitation | Irrigation | ET | Onset of Crop Water Stress | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Average | First | Last | ||||
| mm | Ordinal Day | |||||
| 2016 | 95 | 198 | 520 | 188 | 175 | 196 |
| 2017 | 90 | 188 | 155 | 211 | ||
| 2017 Irrigation Treatments | ||||||
| Low | 158 | 437 | 174 | 155 | 187 | |
| GSP | 225 | 509 | 187 | 158 | 195 | |
| High | 291 | 573 | 203 | 186 | 211 | |
| Topographic Features | Dynamic Factors | Soil Properties | Model Parameters | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Predicted Variable | Slope | Elevation | Soil Water Content at Spring Green-up | Onset of Crop Water Stress | 2017 Irrigation Treatment | SWHC | ECa | Intercept | r2 | |
| % | m | mm 1.2 m−1 | day | Low | High | mm 1.2 m−1 | mS m−1 | |||
| Yield (Mg ha−1) | ||||||||||
| 2016 | −0.25 *** | −0.19 * | - | 0.03 | - | - | - | - | 322 | 0.21 |
| 2017 | −0.06 | −0.29 *** | - | 0.03 *** | - | - | - | - | 420 | 0.33 |
| Onset of Crop Water Stress (days) | ||||||||||
| 2016 | - | 0.87 * | 1.4 *** | - | - | - | - | −0.16 * | −1344 | 0.47 |
| 2017 | - | 1.17 * | 2.3 *** | - | −11.9 *** | 16.9 *** | −0.69 * | −0.26 * | −1887 | 0.85 |
| Yield Production | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2013 | 2014 | 2016 | 2017 | |
| Mg ha−1 | ||||
| Field Average | 6.2 | 4.1 | 7.5 | 5.8 |
| 2017 Irrigation Zones | ||||
| Low | 6.0 | 3.6 | 7.3 | 4.9 |
| GSP | 6.9 | 4.3 | 8.3 | 6 |
| High | 7.1 | 4.3 | 8.4 | 6.4 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Svedin, J.D.; Kerry, R.; Hansen, N.C.; Hopkins, B.G. Identifying Within-Field Spatial and Temporal Crop Water Stress to Conserve Irrigation Resources with Variable-Rate Irrigation. Agronomy 2021, 11, 1377. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy11071377
Svedin JD, Kerry R, Hansen NC, Hopkins BG. Identifying Within-Field Spatial and Temporal Crop Water Stress to Conserve Irrigation Resources with Variable-Rate Irrigation. Agronomy. 2021; 11(7):1377. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy11071377
Chicago/Turabian StyleSvedin, Jeffrey D., Ruth Kerry, Neil C. Hansen, and Bryan G. Hopkins. 2021. "Identifying Within-Field Spatial and Temporal Crop Water Stress to Conserve Irrigation Resources with Variable-Rate Irrigation" Agronomy 11, no. 7: 1377. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy11071377
APA StyleSvedin, J. D., Kerry, R., Hansen, N. C., & Hopkins, B. G. (2021). Identifying Within-Field Spatial and Temporal Crop Water Stress to Conserve Irrigation Resources with Variable-Rate Irrigation. Agronomy, 11(7), 1377. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy11071377






