Nitrogen Fate and Efficiency of Fertilizer Application under a Rapeseed–Wheat–Rice Rotation System in Southwest China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Site Information
2.2. Experiment Design
2.3. Plant and Soil Sampling and Measurements
2.4. Calculations and Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. The Effects of N Application Rate on Previous Crop Yield
3.2. Effects of N Application Rate in the Previous Season and N Management in Rice Season, on Rice Yield, Biomass, and Harvest Index
3.3. Effects of N Application Rate in the Previous Season and N Management in Rice Season, on N Accumulation and N-Use Efficiency (NUE) in Rice
3.4. Fate of 15N-Labeled Urea in the Previous Season Crop
3.5. Residual N Uptake and Use Regulated by N Management in Rice Season
4. Discussion
4.1. The Fate of 15N Fertilizer of the Previous Crop in Rapeseed/Wheat and Rice Crop Rotation
4.2. Crop Yield Influenced by N Rates and N Management in Rapeseed/Wheat and Rice Rotation System
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mohammed, Y.A.; Kelly, J.; Chim, B.K.; Rutto, E.; Waldschmidt, K.; Mullock, J.; Torres, G.; Desta, K.G.; Raun, W. Nitrogen fertilizer management for improved grain quality and yield in winter wheat in Oklahoma. J. Plant Nutr. 2013, 36, 749–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, S.B.; Buresh, R.J.; Huang, J.L.; Zhong, X.H.; Zou, Y.B.; Yang, J.C. Improving nitrogen fertilization in rice by site-specifc Nmanagement. A review. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2010, 30, 649–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, C.; Jia, X.P.; Huang, J.K.; Powlson, D. Reducing excessive nitrogen use in Chinese wheat production through knowledge training: What are the implications for the public extension system? Agroecol. Sustain. Food Syst. 2015, 39, 189–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fowler, D.; Pyle, J.A.; Raven, J.A.; Sutton, M.A. The global nitrogen cycle in the twenty-first century: Introduction. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 2013, 368, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evanoski-Cole, A.R.; Gebhart, K.A.; Sive, B.C.; Zhou, Y.; Capps, S.L.; Day, D.E. Composition and sources of winter haze in the Bakken oil and gas extractionregion. Atmos. Environ. 2017, 156, 77–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.H.; Liu, X.J.; Zhang, Y.; Shen, J.L.; Han, W.X.; Zhang, W.F. Significant acidification in major Chinese croplands. Science 2010, 327, 1008–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ministry of Agriculture of the People’s Republic of China. The Action Plan for Zero-Growth Fertilizer Use by 2020. 2015. Available online: http://jiuban.moa.gov.cn/zwllm/tzgg/tz/201503/t20150318_4444765.htm (accessed on 18 March 2018).
- Shang, Q.Y.; Gao, C.M.; Yang, X.X.; Wu, P.P.; Ling, N.; Shen, Q.R.; Guo, S.W. Ammonia volatilization in Chinese double ricecropping systems: A 3-year field measurement in long-term fertilizer experiments. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2014, 50, 715–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.T.; Wang, Z.M.; Liang, S.B. Quantitative study on the fate of residual soil nitrate in winter wheat based on a 15N-labeling method. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0171014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouraima, A.K.; He, B.; Tian, T. Runoff, nitrogen (N) and phosphorus (P) losses from purple slope cropland soil under rating fertilization in Three Gorges Region. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 4541–4550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Chen, Y.; Zhao, G.H.; Cheng, W.D.; Cuo, S.W.; Zhang, H.L. Do high nitrogen use efficiency rice cultivars reduce nitrogen losses from paddy fields? Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2015, 209, 26–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Y.H.; Shi, X.J.; Li, S.L.; Sun, X.F.; He, X.H. Nitrogen use efciency as affected by phosphorus and potassium in long-term rice and wheat experiments. J. Integr. Agric. 2014, 13, 588–596. Available online: http://www.docin.com/p-1373331377.html (accessed on 18 December 2013). [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Li, Y.; Liu, F.; Li, Y.Y.; Song, L.F.; Li, H.; Meng, C.; Wu, J.S. Linking rice agriculture to nutrient chemical composition, concentration and mass flux in catchment streams in subtropical central China. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2014, 184, 9–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Zou, X.; Song, L.; Chen, L.; Li, S.Y. Effects of nitrogen fertilizer reduction and application of nitrogen fertilizer as base fertilizer on rapeseed yield and nitrogen absorption. Agric. Sci. Technol. 2013, 14, 116–121. Available online: http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTotal-HNNT201301029.htm (accessed on 24 December 2012).
- Ju, X.T.; Xing, G.X.; Chen, X.P.; Zhang, S.L.; Zhang, L.J.; Liu, X.J. Reducing environmental risk by improving N management in intensive Chinese agricultural systems. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 3041–3046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.J.; Sun, Y.Y.; Xu, H.; Li, Y.; Yan, F.J.; Jiang, M.J.; Ma, J. Effects of water-nitrogen management patterns on nitrogen utilization characteristics and yield in rice cultivars with different nitrogen use efficiencies. Acta Agron. Sin. 2014, 40, 1639–1649, (in Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.Y.; Xu, C.M.; Yan, J.X.; Zhang, X.G.; Chen, S.; Wang, L.; Zhang, X.F. 15N tracer-based analysis of genotypic differences in the uptake and partitioning of N applied at different growth stages in transplanted rice. Field Crop Res. 2017, 211, 27–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.F.; Li, X.K.; Hou, W.F.; Ren, T.; Cong, R.H.; Du, C.W.; Xing, L.H.; Wang, S.H.; Lu, J.W. Studying the fate and recovery efficiency of controlled release urea in paddy soil using 15N tracer technique. Sci. Agric. Sin. 2018, 51, 3961–3971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norman, R.; Roberts, T.; Slaton, N. Nitrogen uptake efficiency of a hybrid compared with a conventional, pure-line rice cultivar. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2013, 77, 1235–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.S.; Yin, B. Effects of integrated high-efficiency practice versus conventional practice on rice yield and N fate. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2015, 202, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, S.G.; Huang, S.Q.; Zhai, J. Effects of N management on yield and N uptake of rice in central China. J. Integr. Agric. 2012, 11, 1993–2000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Xie, Y.X.; Xiong, Z.Q.; Yan, X.Y.; Xing, G.X.; Zhu, Z.L. Nitrogen fate and environmental consequence in paddy soil under rice-wheat rotation in the Taihu lake region, China. Plant Soil 2009, 319, 225–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Yang, Z.; Zhang, H. The fate of fertilizer-derived nitrogen in a rice field in the Qingtongxia irrigation area. Acta Sci Circumst. 2010, 30, 1707–1714, (in Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikolenko, O.; Jurado, A.; Borges, A. VIsotopic composition of nitrogen species in groundwater under agricultural areas: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 621, 1415–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbasi, M.K.; Khizar, A. Microbial biomass carbon and nitrogen transformations in a loam soil amended with organic–inorganic N sources and their effect on growth and N-uptake in maize. Ecol. Eng. 2012, 39, 123–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.Z. Fate and management of fertilizer nitrogen in agro-ecosystems. In Nitrogen in Soils of China; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, X.; Li, Y.; Huang, P. Effects of planting patterns and nitrogen application rates on yield, water and nitrogen use efficiencies of winter rapeseed rape (Brassica napus L.). Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2018, 34, 113–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Yang, J.P.; Xv, W.; Wang, H.; Sun, J.H. Influence of nitrogen rates with split application on N use efficiency and its eco-economic suitable amount analysis in rice. J. Zhejiang Univ. Agric. Life Sci. 2009, 35, 71–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.; Shen, Q.R.; Yin, B.; Wan, X.J. Fertilizer-N uptake and distribution in rice plants using 15N tracer technique. J. Nucl. Agric. Sci. 2009, 23, 487–491, (in Chinese with English Abstract). Available online: http://en.cnki.com.cn/article_en/cjfdtotal-hnxb200903028.htm (accessed on 27 March 2009).
- Xie, Z.J.; He, Y.Q.; Tu, S.X.; Xu, C.X.; Liu, G.R.; Wang, H.M.; Cao, W.D.; Liu, H. Chinese milk vetch improves plant growth, development and 15 N recovery in the rice-based rotation system of South China. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 3577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.C.; Zeng, X.Z.; Feng, W.Q.; Qin, Y.S.; Wang, C.Q.; Tu, S.H. Effects of long-term straw mulch and fertilization on crop yields and soil physical and chemical properties under rice-rapeseed rotation. J. Plant Nutr. Fertil. 2014, 6, 1450–1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, J. Study on Response of Winter Rapeseed to NPKB Fertilization and Abundance & Difficiency Indicates of Soil Nutrients. Ph.D. Thesis, Huazhong Agricultural University, Wuhan, China, 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, C.; Peng, J.W.; Song, H.X. Effects of combined application of organic fertilizers on nutrient absorption, grain yield and quality of winter rape. China Soil Fertil. 2012, 4, 70–74. [Google Scholar]
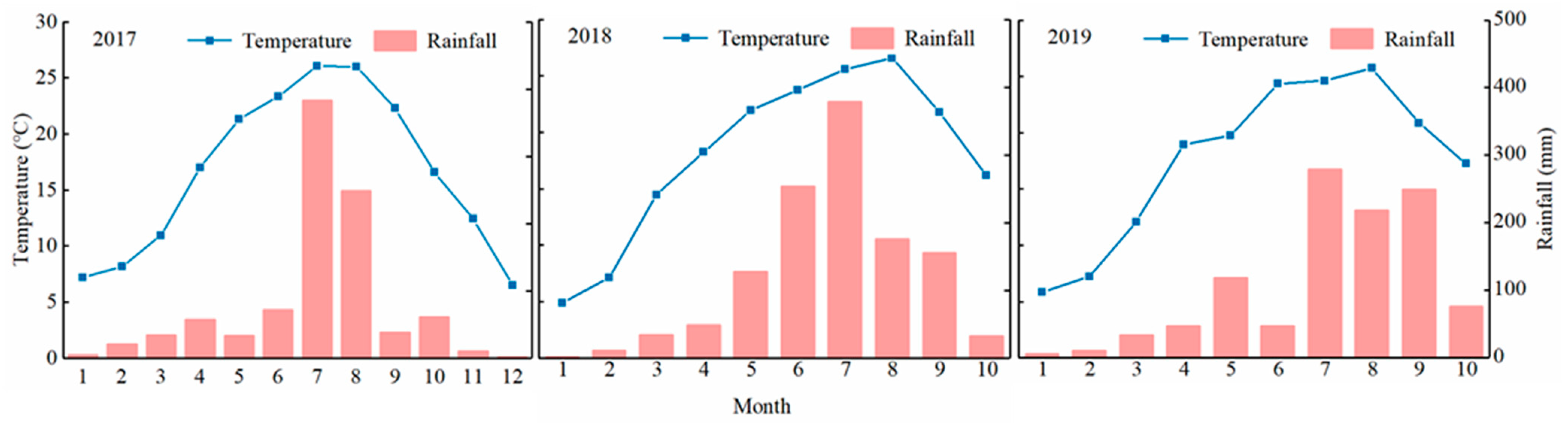
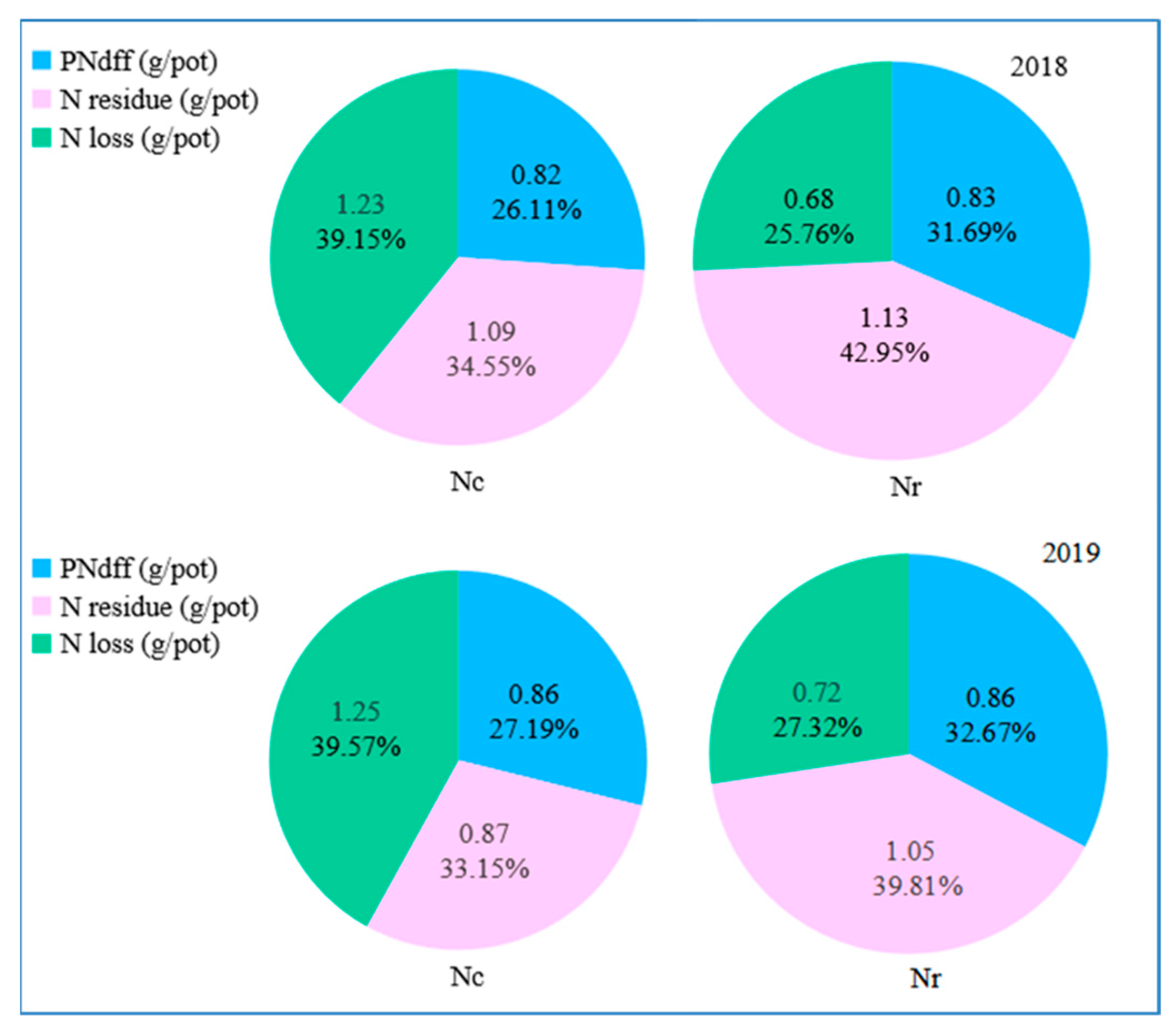
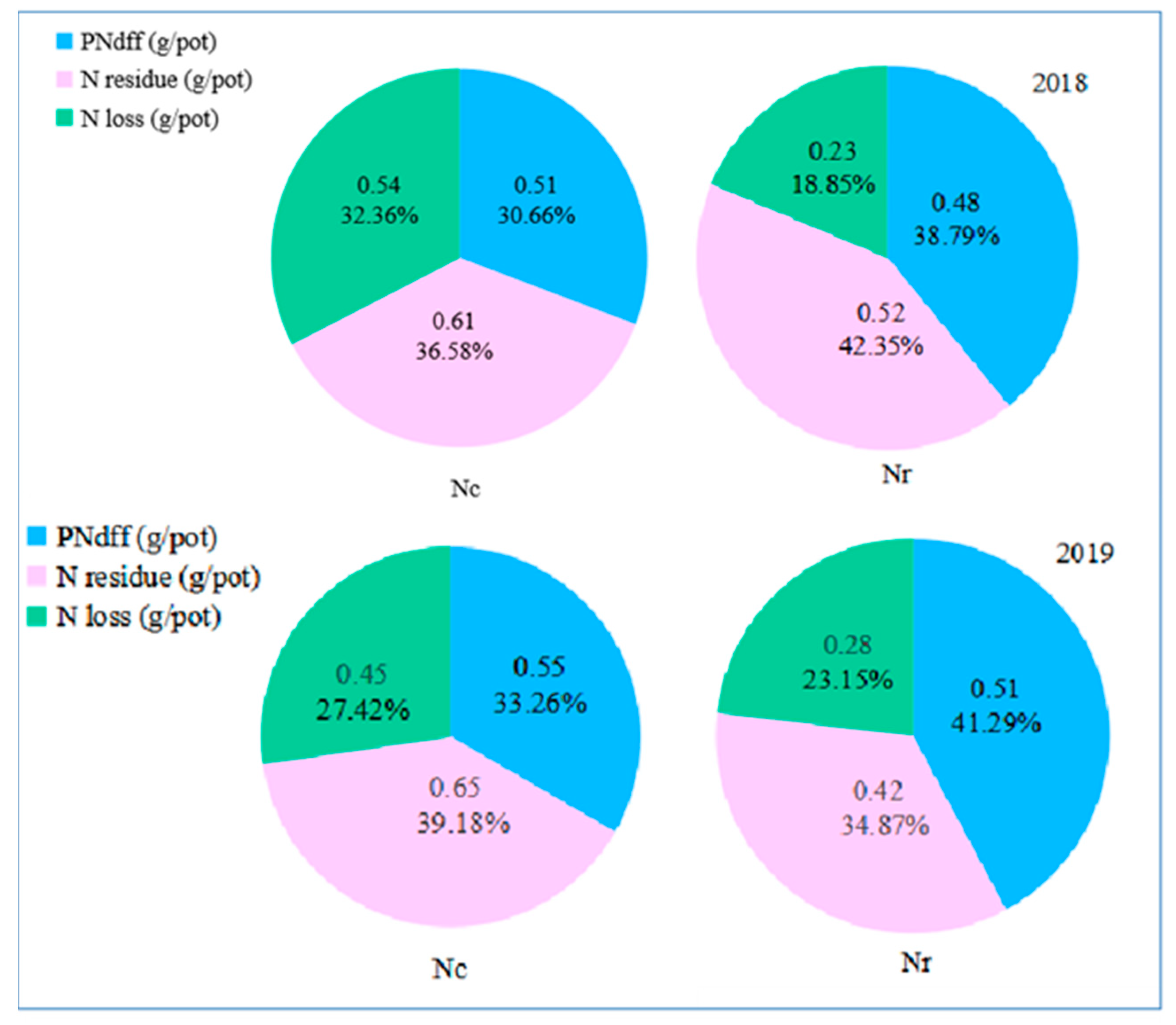
| Year | Total N (g kg−1) | Organic Matter (g kg−1) | Available Nutrient (mg·kg−1) | pH | Bulk Density (g cm−3) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | P | K | |||||
| 2017 | 1.52 | 24.21 | 114.93 | 23.89 | 52.61 | 6.19 | 1.31 |
| 2019 | 1.57 | 26.89 | 117.73 | 21.32 | 55.76 | 6.21 | 1.34 |
| ANOVA | GY | HI | RNDff | NRR | NLR | NUE |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Year | 5.09 ns | 0.73 ns | 1.63 ns | 1.71 ns | 1.01 ns | 0.76 ns |
| Year × P | 2.55 ns | 0.66 ns | 2.44 ns | 0.43 ns | 1.67 ns | 2.83 ns |
| Year × N | 1.71 ns | 0.05 ns | 0.07 ns | 1.23 ns | 2.06 ns | 2.31 ns |
| Year × M | 0.95 ns | 0.74 ns | 0.26 ns | 1.49 ns | 2.33 ns | 2.71 ns |
| Treatment (kg·ha−1) | 2018 | 2019 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rapeseed (g·plot−1) | Wheat (g·plot−1) | Rapeseed (g·plot−1) | Wheat (g·plot−1) | |
| Nc | 45.44 a | 472.96 a | 62.10 a | 505.07 a |
| Nr | 43.89 b | 400.30 b | 47.75 b | 445.21 b |
| Average | 44.66 | 436.63 | 54.92 | 475.14 |
| F value | 11.03 * | 53.82 ** | 33.53 ** | 37.20 ** |
| Treatment | PN (plant−1) | SPN (NO.panicle−1) | SSR (%) | 1000-GW (g) | GY (g·plot−1) | HI (%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pr | Nc | M0 | 7.44 c | 148.42 k | 87.03 g | 30.58 h | 74.61 f | 45.74 i |
| M1 | 10.11 b | 169.87 d | 91.31 cd | 31.34 cde | 100.33 cd | 51.05 f | ||
| M2 | 10.49 ab | 164.77 h | 91.07 d | 31.17 efg | 102.68 abcd | 50.81 g | ||
| M3 | 10.40 ab | 175.47 b | 92.15 a | 32.16 a | 104.74 ab | 51.41 e | ||
| average | 9.61 | 164.63 | 90.39 | 31.31 | 95.59 | 49.75 | ||
| Nr | M0 | 7.63 c | 149.41 j | 86.15 h | 30.44 h | 69.11 g | 44.54 j | |
| M1 | 10.47 ab | 174.33 c | 89.14 f | 31.22 defg | 100.33 cd | 51.66 d | ||
| M2 | 10.19 b | 167.37 f | 90.05 e | 31.24 defg | 101.33 bcd | 52.84 b | ||
| M3 | 10.75 a | 175.56 b | 91.30 cd | 32.06 a | 106.41 a | 54.12 a | ||
| average | 9.76 | 166.67 | 89.16 | 31.24 | 94.30 | 50.79 | ||
| Pw | Nc | M0 | 7.65 c | 147.92 k | 85.64 i | 29.94 i | 71.04 fg | 44.70 j |
| M1 | 10.45 ab | 169.10 e | 88.91 f | 31.06 fg | 100.18 d | 51.74 d | ||
| M2 | 10.51 ab | 178.32 a | 91.80 ab | 31.68 b | 105.44 a | 52.65 b | ||
| M3 | 10.49 ab | 165.64 g | 91.63 bc | 31.06 g | 103.41 abcd | 52.20 c | ||
| average | 9.78 | 165.25 | 89.50 | 30.94 | 95.02 | 50.32 | ||
| Nr | M0 | 7.60 c | 151.01 i | 86.12 h | 29.22 j | 68.81 g | 44.52 j | |
| M1 | 10.44 ab | 169.42 de | 88.99 f | 31.29 cdef | 95.56 e | 51.65 d | ||
| M2 | 10.35 ab | 168.70 e | 91.02 d | 31.41 cd | 104.04 abc | 51.80 d | ||
| M3 | 10.23 ab | 169.88 d | 91.91 ab | 31.49 bc | 100.63 cd | 50.38 h | ||
| average | 9.66 | 164.75 | 89.51 | 30.85 | 92.26 | 49.59 | ||
| F value | P | 0.95 ns | 50.67 * | 77.10 * | 119.30 ** | 5.09 ns | 208.49 ** | |
| N | 0.10 ns | 15.86 * | 117.2 ** | 5.06 ns | 19.70 * | 33.94 ** | ||
| M | 6.49 ns | 42.95 ** | 122.73 ** | 0.02 ns | 2.55 ns | 1156.98 ** | ||
| P × N | 199.39 ** | 2894.82 ** | 1218.18 ** | 556.03 ** | 789.56 ** | 10184.70 ** | ||
| P × M | 0.66 ns | 2003.61 ** | 41.44 ** | 46.09 ** | 3.28 * | 110.16 ** | ||
| N × M | 0.73 ns | 401.02 ** | 7.72 ** | 18.80 ** | 1.71 ns | 81.16 ** | ||
| P × N × M | 0.66 ns | 664.95 ** | 7.76 ** | 11.01 ** | 4.60 * | 340.68 ** | ||
| Treatment | FTNA (g·pot−1) | MTNA (g·pot−1) | NMPE (kg·kg−1) | NGPE (kg·kg−1) | NAE (kg·kg−1) | NPFP (kg·kg−1) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pr | Nc | M0 | 1.06 cd | 1.27 g | 127.44 ab | 58.74 a | - | - |
| M1 | 1.26 abc | 1.90 bcde | 103.38 d | 52.81 h | 15.43 j | 60.20 abc | ||
| M2 | 1.46 ab | 1.95 ab | 101.58 e | 52.65 i | 16.84 hi | 61.60 ab | ||
| M3 | 1.51 a | 1.99 a | 96.10 g | 52.63 h | 18.07 efg | 62.84 a | ||
| average | 1.32 | 1.77 | 107.07 | 54.21 | 16.78 | 61.54 | ||
| Nr | M0 | 1.02 de | 1.21 g | 128.23 a | 57.12 b | - | - | |
| M1 | 1.18 bcd | 1.81 f | 107.35 c | 55.43 d | 18.76 def | 60.19 abc | ||
| M2 | 1.28 abc | 1.86 ef | 100.41 ef | 55.07 e | 19.33 cd | 60.79 abc | ||
| M3 | 1.36 abc | 1.85 def | 99.81 f | 57.51 bc | 22.38 a | 63.84 a | ||
| average | 1.21 | 1.68 | 108.92 | 56.28 | 20.16 | 61.61 | ||
| Pw | Nc | M0 | 0.99 de | 1.26 g | 126.13 b | 56.38 c | - | - |
| M1 | 1.29 abc | 1.92 abcd | 100.84 ef | 52.18 hi | 17.48 gh | 60.10 abc | ||
| M2 | 0.93 e | 1.93 abc | 103.72 d | 53.58 g | 20.64 b | 63.26 a | ||
| M3 | 1.49 ab | 1.95 ab | 94.02 h | 54.07 fg | 19.42 cd | 62.05 ab | ||
| average | 1.17 | 1.76 | 106.15 | 54.05 | 19.18 | 61.8 | ||
| Nr | M0 | 1.11 cd | 1.22 g | 126.69 ab | 56.4 c | - | - | |
| M1 | 1.27 abc | 1.91 bcde | 99.31 f | 50.82 j | 16.05 ij | 57.33 c | ||
| M2 | 1.17 bcd | 1.88 cde | 103.63 d | 54.47 g | 19.97 bc | 60.42 abc | ||
| M3 | 1.28 abc | 1.92 bcd | 95.64 gh | 52.41 h | 19.09 cde | 60.37 abc | ||
| average | 1.20 | 1.73 | 106.28 | 53.52 | 18.37 | 59.37 | ||
| F value | P | 2.31 ns | 13.90 * | 37.32 * | 153.23 ** | 1.38 ns | 2.81 ns | |
| N | 0.76 ns | 31.60 ** | 11.24 * | 44380.44 ** | 4.31 ns | 7.65 * | ||
| M | 10.70 ** | 855.91 ** | 6492.95 ** | 583.35 ** | 55.37 ** | 4.33 * | ||
| P × N | 2.71 ns | 7.80 * | 8.26 * | 21103.99 ** | 43.19 ** | 88.28 ** | ||
| P × M | 3.64 * | 1.44 ns | 99.43 ** | 68.40 ** | 158.64 ** | 39.66 ** | ||
| N × M | 1.24 ns | 0.49 ns | 16.25 ** | 59.60 ** | 196.50 ** | 51.93 ** | ||
| P × N × M | 1.24 ns | 0.62 ns | 17.82 ** | 79.91 ** | 170.30 ** | 64.34 ** | ||
| Treatment | 15N Accumulation of Rice Plant (mg 15N·pot−1) | 15N-Residue Ratio (%) | 15N Loss Ratio (%) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TS | HS | MS | |||||
| Pr | Nc | M0 | 13.48 de | 95.54 k | 97.57 lm | 11.84 hi | 68.78 b |
| M1 | 16.22 bc | 101.83 fgh | 102.13 ij | 14.21 bcdef | 63.78 g | ||
| M2 | 15.30 cd | 99.72 hij | 104.45 hij | 14.62 bcde | 63.32 h | ||
| M3 | 15.55 cd | 104.03 def | 108.95 def | 14.82 bcd | 62.36 i | ||
| average | 15.14 | 100.28 | 103.28 | 13.87 | 64.18 | ||
| Nr | M0 | 12.07 ef | 97.36 jk | 101.70 j | 12.13 ghi | 67.28 c | |
| M1 | 13.77 de | 108.02 abc | 108.56 efg | 13.02 efgh | 66.01 e | ||
| M2 | 15.41 cd | 103.55 ef | 107.57 efgh | 13.56 defg | 66.00 e | ||
| M3 | 15.22 cd | 105.58 cde | 111.98 bc | 12.93 fgh | 66.04 e | ||
| average | 14.11 | 103.62 | 107.45 | 12.91 | 66.71 | ||
| Pw | Nc | M0 | 15.27 cd | 100.59 ghi | 106.28 fgh | 18.94 a | 46.10 l |
| M1 | 16.60 bc | 105.75 cde | 110.51 cde | 19.18 a | 44.14 o | ||
| M2 | 17.08 ab | 100.17 ghi | 111.39 bc | 18.70 a | 45.24 m | ||
| M3 | 17.91 ab | 101.61 fgh | 111.84 bc | 18.69 a | 44.62 n | ||
| average | 17.71 | 105.53 | 111.75 | 18.12 | 45.02 | ||
| Nr | M0 | 9.27 h | 85.53 m | 89.24 n | 18.91 a | 44.89 mn | |
| M1 | 11.96 efg | 89.50 l | 94.62 m | 15.40 bc | 43.15 p | ||
| M2 | 9.81 gh | 91.28 l | 102.17 ij | 13.69 defg | 43.27 p | ||
| M3 | 10.62 fgh | 91.73 l | 105.37 ghi | 11.14 i | 42.18 q | ||
| average | 10.41 | 89.51 | 97.85 | 14.78 | 43.37 | ||
| F value | P | 23.19 ** | 252.29 ** | 13.83 * | 142.53 ** | 4740.04 ** | |
| N | 172.97 ** | 148.16 ** | 31.59 ** | 17.02 ** | 1669.33 ** | ||
| M | 23.43 ** | 75.82 ** | 145.65 ** | 5.34 ** | 798.51 ** | ||
| P × N | 78.07 ** | 636.83 ** | 335.89 ** | 42.49 ** | 529.82 ** | ||
| P × M | 0.19 ns | 4.51 ** | 3.70 ** | 20.27 ** | 166.87 ** | ||
| N × M | 0.11 ns | 2.52 ns | 1.47 ns | 7.27 ** | 99.08 ** | ||
| P × N × M | 5.11 ** | 1.82 ns | 2.67 * | 1.47 ns | 18.61 ** | ||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ma, P.; Lan, Y.; Lyu, T.; Li, F.; Yang, Z.; Sun, Y.; Ma, J. Nitrogen Fate and Efficiency of Fertilizer Application under a Rapeseed–Wheat–Rice Rotation System in Southwest China. Agronomy 2021, 11, 258. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy11020258
Ma P, Lan Y, Lyu T, Li F, Yang Z, Sun Y, Ma J. Nitrogen Fate and Efficiency of Fertilizer Application under a Rapeseed–Wheat–Rice Rotation System in Southwest China. Agronomy. 2021; 11(2):258. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy11020258
Chicago/Turabian StyleMa, Peng, Yan Lan, Tengfei Lyu, Feijie Li, Zhiyuan Yang, Yongjian Sun, and Jun Ma. 2021. "Nitrogen Fate and Efficiency of Fertilizer Application under a Rapeseed–Wheat–Rice Rotation System in Southwest China" Agronomy 11, no. 2: 258. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy11020258
APA StyleMa, P., Lan, Y., Lyu, T., Li, F., Yang, Z., Sun, Y., & Ma, J. (2021). Nitrogen Fate and Efficiency of Fertilizer Application under a Rapeseed–Wheat–Rice Rotation System in Southwest China. Agronomy, 11(2), 258. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy11020258





