Assessing the Attractiveness of Three Baits for Roof Rats in California Citrus Orchards
Abstract
1. Introduction
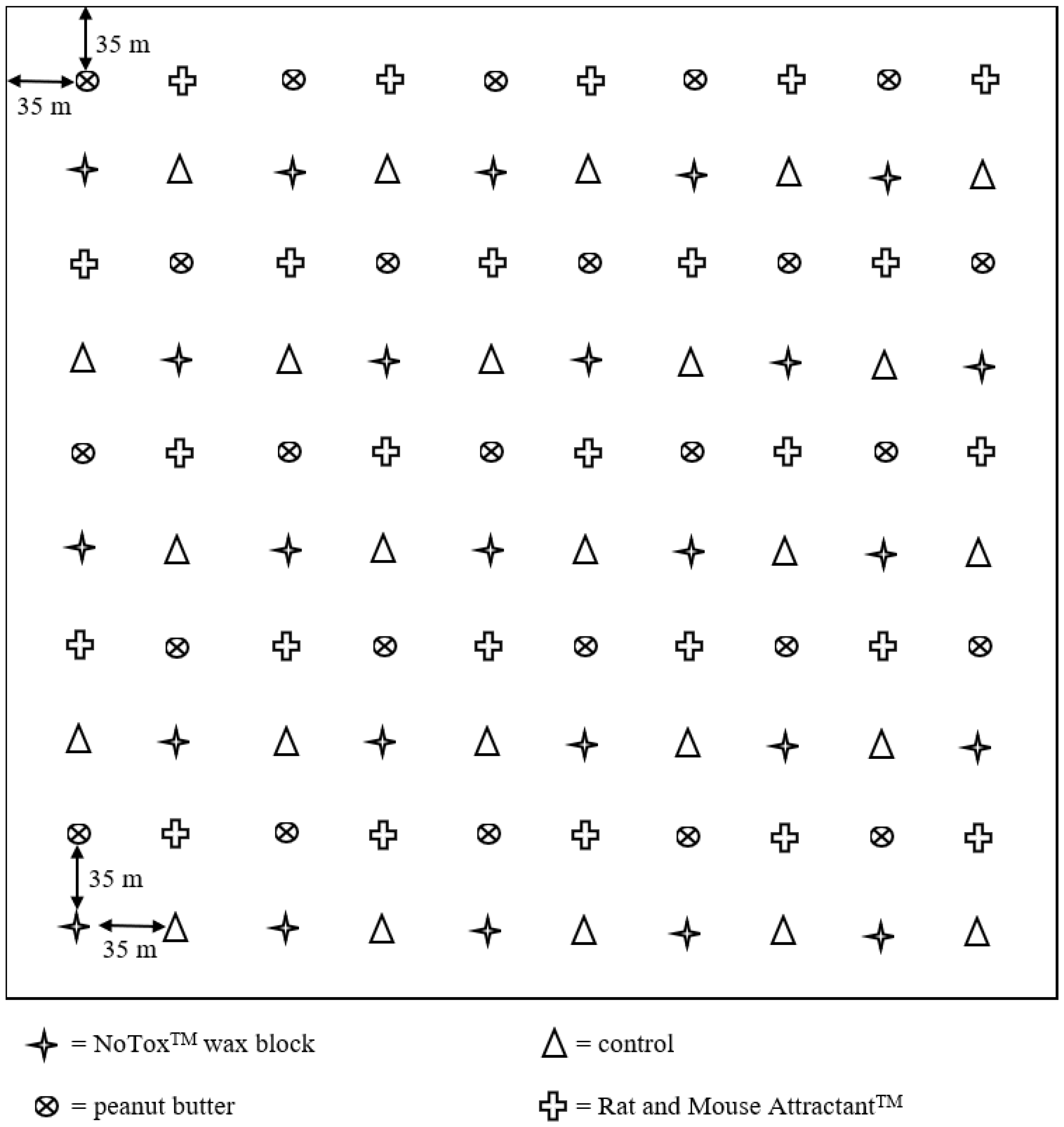
2. Materials and Methods
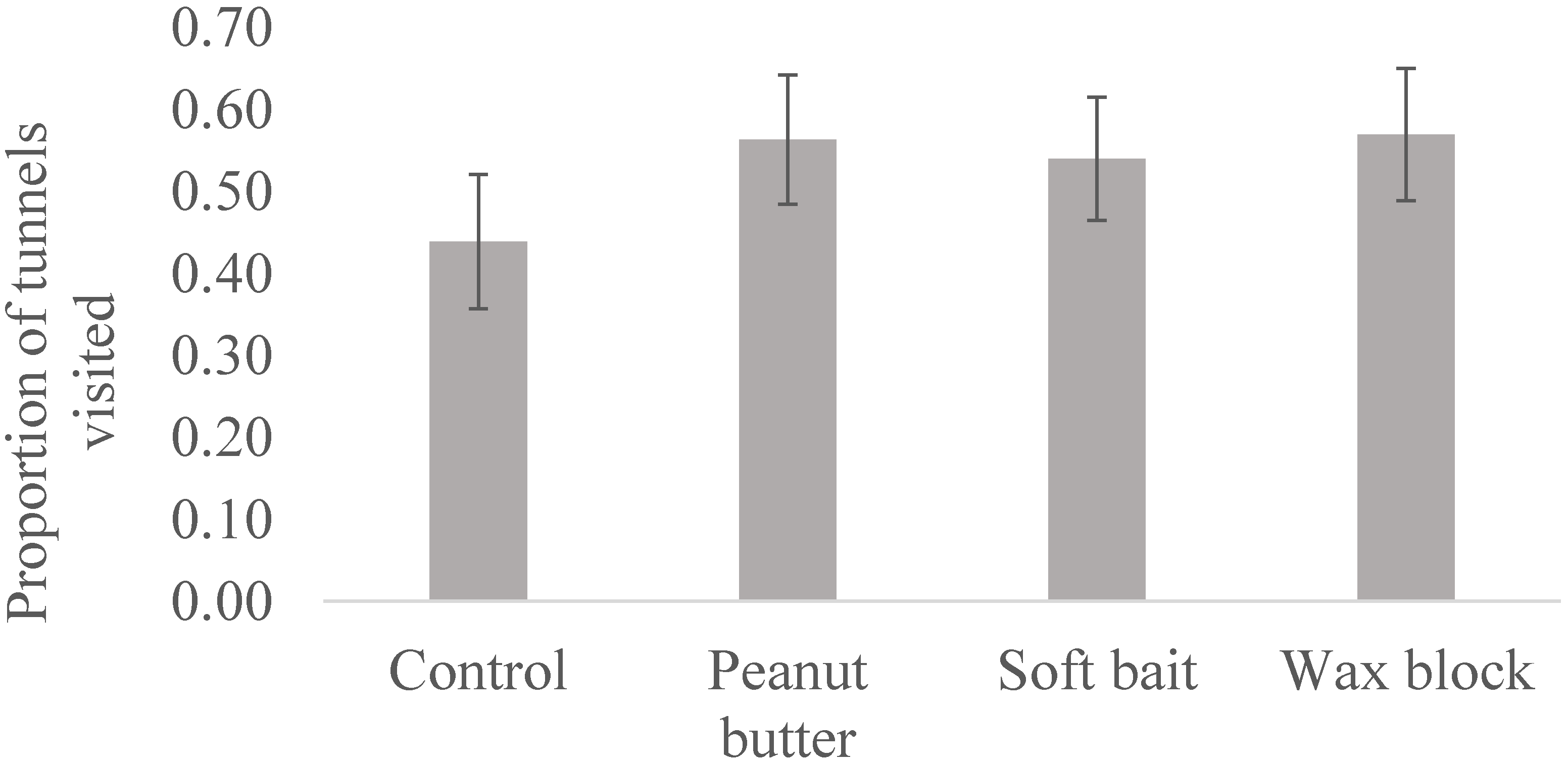
3. Results
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pimentel, D. Environmental and economic costs of vertebrate species invasions into the United States. In Managing Vertebrate Invasive Species, Proceedings of an International Symposium, Fort Collins, CO, USA, 7–9 August 2007; Witmer, G.W., Pitt, W.C., Fagerstone, K.A., Eds.; US Department of Agriculture, Animal and Plant Health Inspection Service, Wildlife Services, National Wildlife Research Center: Fort Collins, CO, USA, 2007; pp. 2–8. [Google Scholar]
- Marsh, R.E. Roof rats. In Prevention and Control of Wildlife Damage, 4th ed.; Hygnstrom, S., Timm, R., Larsen, G., Eds.; Cooperative Extension Division, University of Nebraska: Lincoln, NE, USA, 1994; pp. B-125–B-132. [Google Scholar]
- Witmer, G.; Burke, P.; Jojola, S. An evaluation of the effectiveness of potential Norway rat attractants. Proc. Vertebr. Pest. Conf. 2008, 23, 35–38. [Google Scholar]
- Meerburg, B.G.; Singleton, G.R.; Kijlstra, A. Rodent-borne diseases and their risks for public health. Crit. Rev. Microbiol. 2009, 35, 221–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buckle, A.P.; Smith, R.H. Rodent Pests and Their Control, 2nd ed.; CAB International: Wallingford, UK, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Worth, C.B. Field and laboratory observations on roof rats, Rattus rattus (Linnaeus), in Florida. J. Mammal. 1950, 31, 293–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tobin, M.E. Rodent damage in Hawaiian macadamia orchards. Proc. Vertebr. Pest. Conf. 1992, 15, 272–276. [Google Scholar]
- Dongol, E.M.A.; Abdel Samad, M.A.; Ali, M.K.; Baghdadi, S.A.S. Estimation of damage caused by rodents on orange and mandarin orchards at Sohag governorate, Egypt. Arch. Agric. Sci. J. 2021, 4, 14–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witmer, G.W. Perspectives on existing and potential new alternatives to anticoagulant rodenticides and the implications for integrated pest management. In Anticoagulant Rodenticides and Wildlife; van den Brink, N.W., Elliott, J.E., Shore, R.F., Rattner, B.A., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 357–378. [Google Scholar]
- Whisson, D.A.; Engeman, R.M.; Collins, K. Developing relative abundance techniques (RATs) for monitoring rodent populations. Wildl. Res. 2005, 32, 239–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witmer, G.W.; Boyd, F.; Hillis-Starr, Z. The successful eradication of introduced roof rats (Rattus rattus) from Buck Island using diphacinone, followed by an irruption of house mice (Mus musculus). Wildl. Res. 2007, 34, 108–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldwin, R.A.; Quinn, N.; Davis, D.H.; Engeman, R.M. Effectiveness of rodenticides for managing invasive roof rats and native deer mice in orchards. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2014, 21, 5795–5802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shiels, A.B.; Bogardus, T.; Rohrer, J.; Kawelo, K. Effectiveness of Snap and A24-Automated traps and broadcast anticoagulant bait in suppressing commensal rodents in Hawaii. Hum. Wildl. Int. 2019, 13, 226–237. [Google Scholar]
- Engeman, R.M.; Baldwin, R.A.; Stetson, D.I. Guiding the management of an agricultural pest: Indexing abundance of California meadow voles in artichoke field. Crop. Prot. 2016, 88, 53–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sked, S.; Abbar, S.; Cooper, R.; Corrigan, R.; Pan, X.; Ranabhat, S.; Wang, C. Monitoring and controlling house mouse, Mus musculus domesticus, infestations in low-income multi- family dwellings. Animals 2021, 11, 648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, K.P.; Moller, H.; Innes, J.; Alterio, N. Calibration of tunnel tracking rates to estimate relative abundance of ship rats (Rattus rattus) and mice (Mus musculus) in a New Zealand forest. N. Z. J. Ecol. 1996, 20, 271–275. [Google Scholar]
- Jackson, M.; Hartley, S.; Linklater, W. Better food-based baits and lures for invasive rats Rattus spp. and the brushtail possum Trichosurus vulpecula: A bioassay on wild, free-ranging animals. J. Pest. Sci. 2016, 89, 479–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cochran, W.G. Some methods of strengthening the common χ2 tests. Biometrics 1954, 10, 417–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mantel, N.; Haenszel, W. Statistical aspects of the analysis of data from retrospective studies of disease. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 1959, 22, 719–748. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lai, G.P.; Mink, D.R.; Pasta, D.J. Beyond Breslow-Day: Homogeneity across R × C Tables. 2011. Available online: https://lexjansen.com/wuss/2011/analy/Papers_Lai_G_74949.pdf (accessed on 23 February 2021).
- Zar, J.H. Biostatistical Analysis, 4th ed.; Prentice-Hall: Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Witmer, G.W.; Snow, N.P.; Moulton, R.S. Time allocation to resources by three species of rats (Rattus spp.) in a radial arm maze. Wildl. Res. 2020, 47, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takács, S.; Musso, A.E.; Gries, R.; Rozenberg, E.; Borden, J.H.; Brodie, B.; Gries, G. New food baits for trapping house mice, black rats and brown rats. Appl. Anim. Behav. Sci. 2018, 200, 130–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, M.D.; Brown, J.A.; Henderson, R.J. Feasibility of using wax blocks to measure rat and possum abundance in native forest. Proc. N. Z. Plant Prot. Conf. 1999, 52, 125–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burke, C.B.; Quinn, N.M.; Stapp, P. Use of rodenticide bait stations by commensal rodents at the urban-wildland interface: Insights for management to reduce nontarget exposure. Pest. Manag. Sci. 2021, 77, 3126–3134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paull, D.J.; Claridge, A.W.; Barry, S.C. There’s no accounting for taste: Bait attractants and infrared digital cameras for dectecting small to medium ground-dwelling mammals. Wildl. Res. 2011, 38, 188–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, M.D.; Keyzers, R.A.; Linklater, W.L. Single compounds elicit complex behavioural responses in wild, free-ranging rats. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 12588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baldwin, R.A.; Meinerz, R. Developing an effective strategy for indexing roof rat abundance in citrus orchards. Crop. Prot. 2022, 151, 105837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puan, C.L.; Goldizen, A.W.; Zakaria, M.; Hafidzi, M.N.; Baxter, G.S. Absence of differential predation on rats by Malaysian barn owls in oil palm plantations. J. Raptor Res. 2011, 45, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engeman, R.; Whisson, D. Using a general indexing paradigm to monitor rodent populations. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2006, 58, 2–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wales, K.N.; Meinerz, R.; Baldwin, R.A. Assessing the Attractiveness of Three Baits for Roof Rats in California Citrus Orchards. Agronomy 2021, 11, 2417. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy11122417
Wales KN, Meinerz R, Baldwin RA. Assessing the Attractiveness of Three Baits for Roof Rats in California Citrus Orchards. Agronomy. 2021; 11(12):2417. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy11122417
Chicago/Turabian StyleWales, Kallista N., Ryan Meinerz, and Roger A. Baldwin. 2021. "Assessing the Attractiveness of Three Baits for Roof Rats in California Citrus Orchards" Agronomy 11, no. 12: 2417. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy11122417
APA StyleWales, K. N., Meinerz, R., & Baldwin, R. A. (2021). Assessing the Attractiveness of Three Baits for Roof Rats in California Citrus Orchards. Agronomy, 11(12), 2417. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy11122417




