Influence of Metal-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus Strain K1 on the Alleviation of Chromium Stress in Wheat
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Soil Preparation
2.2. Segregation of Cr-Resistant Bacteria
2.3. Bacterial Identification
2.4. Bacterial Inoculum Preparation
2.5. Seed Coating and Pot Experiment
2.6. Treatments
2.7. Plant Harvesting
2.8. Determination of Chlorophyll Contents and Gas Exchange Parameters
2.9. Determination of Reactive Oxygen Species and Antioxidant Enzyme Activities
2.10. Estimation of Cr Contents in Plants
2.11. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Growth Characteristics of Isolate K1
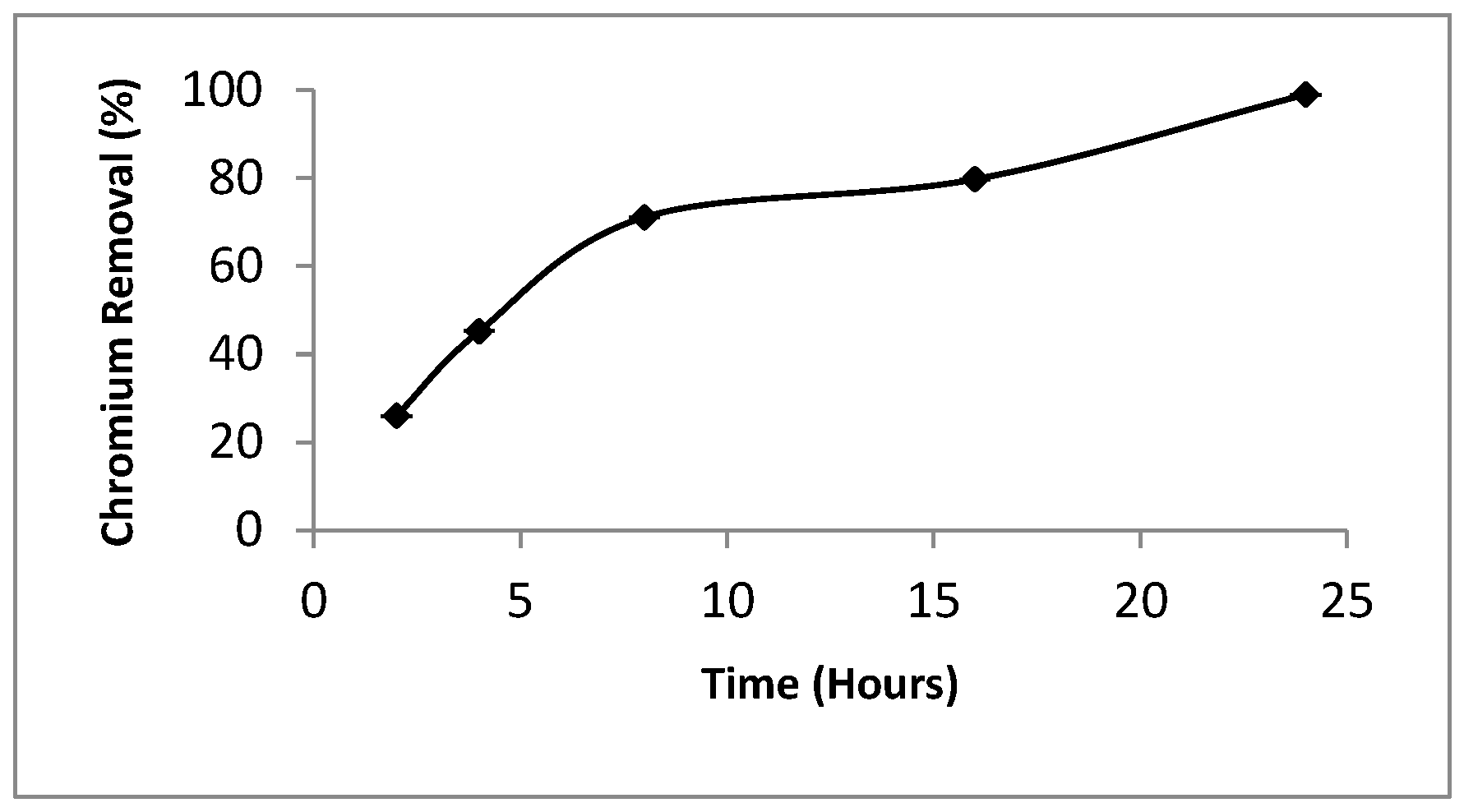
3.2. Effect of S. aureus K1 Contact Time on Chromium (Cr6+) Reduction
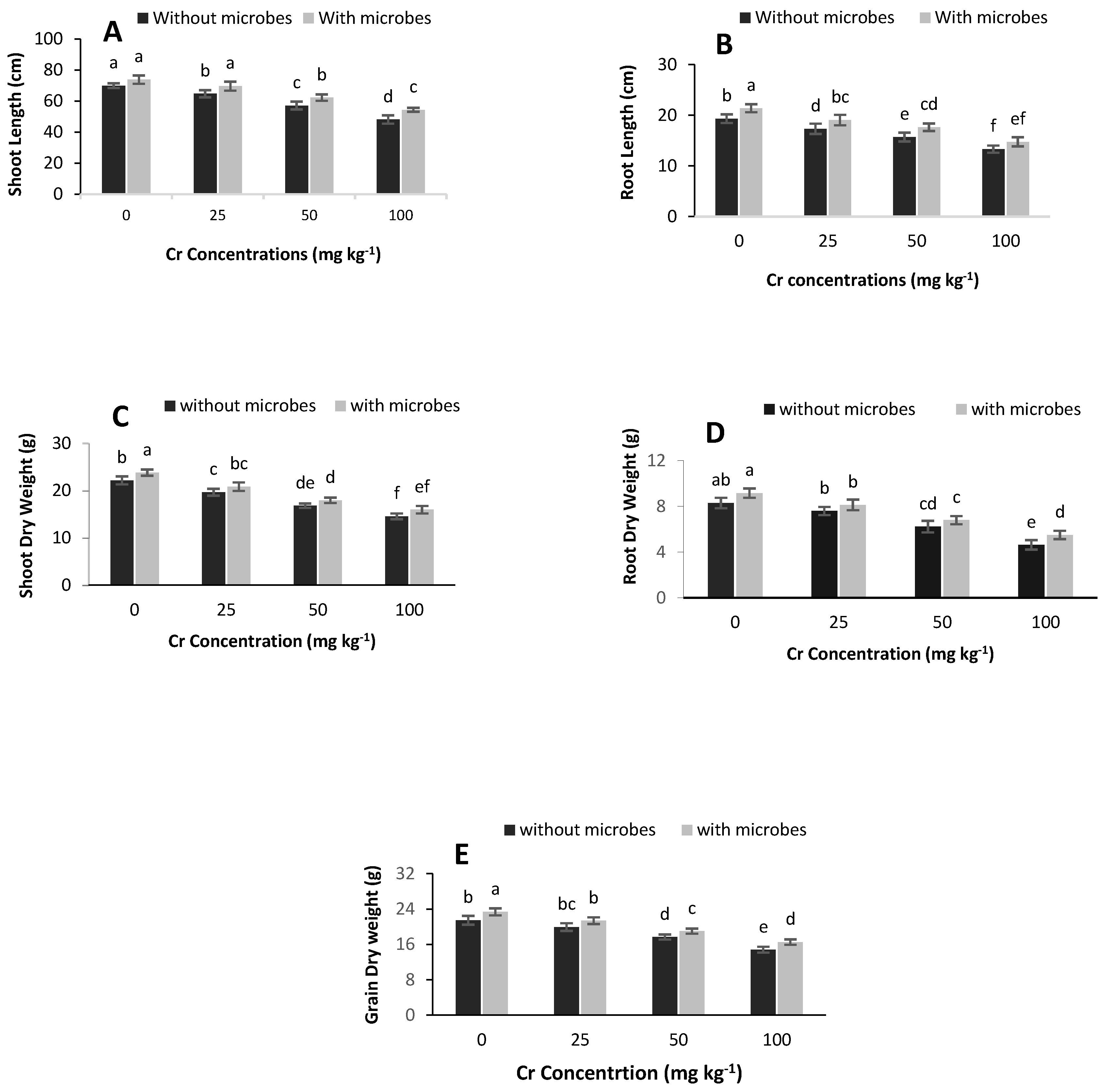
3.3. Effect of S. aureus K1 on Plant Growth Promotion
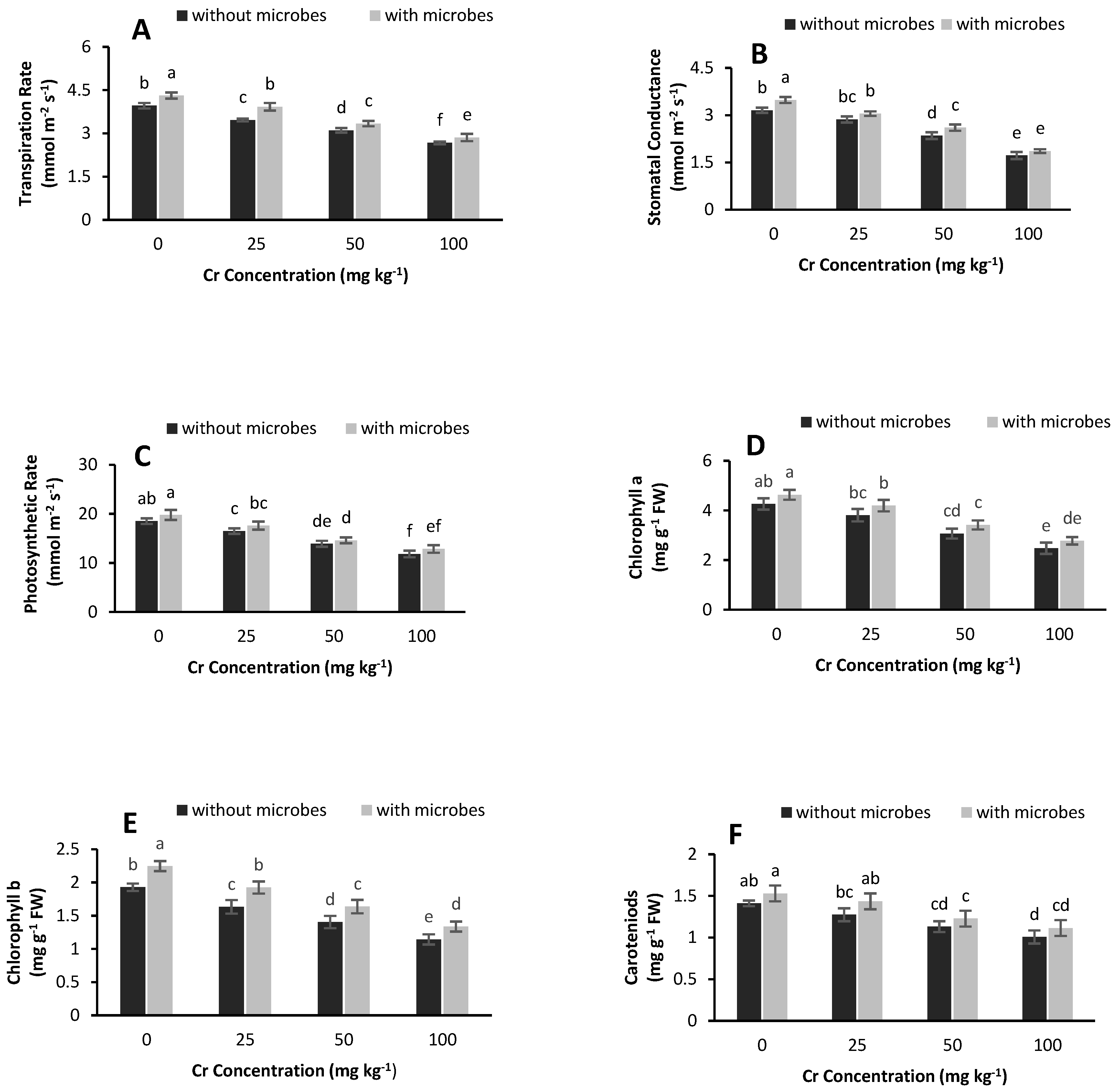
3.4. IRGA Parameters and Chlorophyll Contents
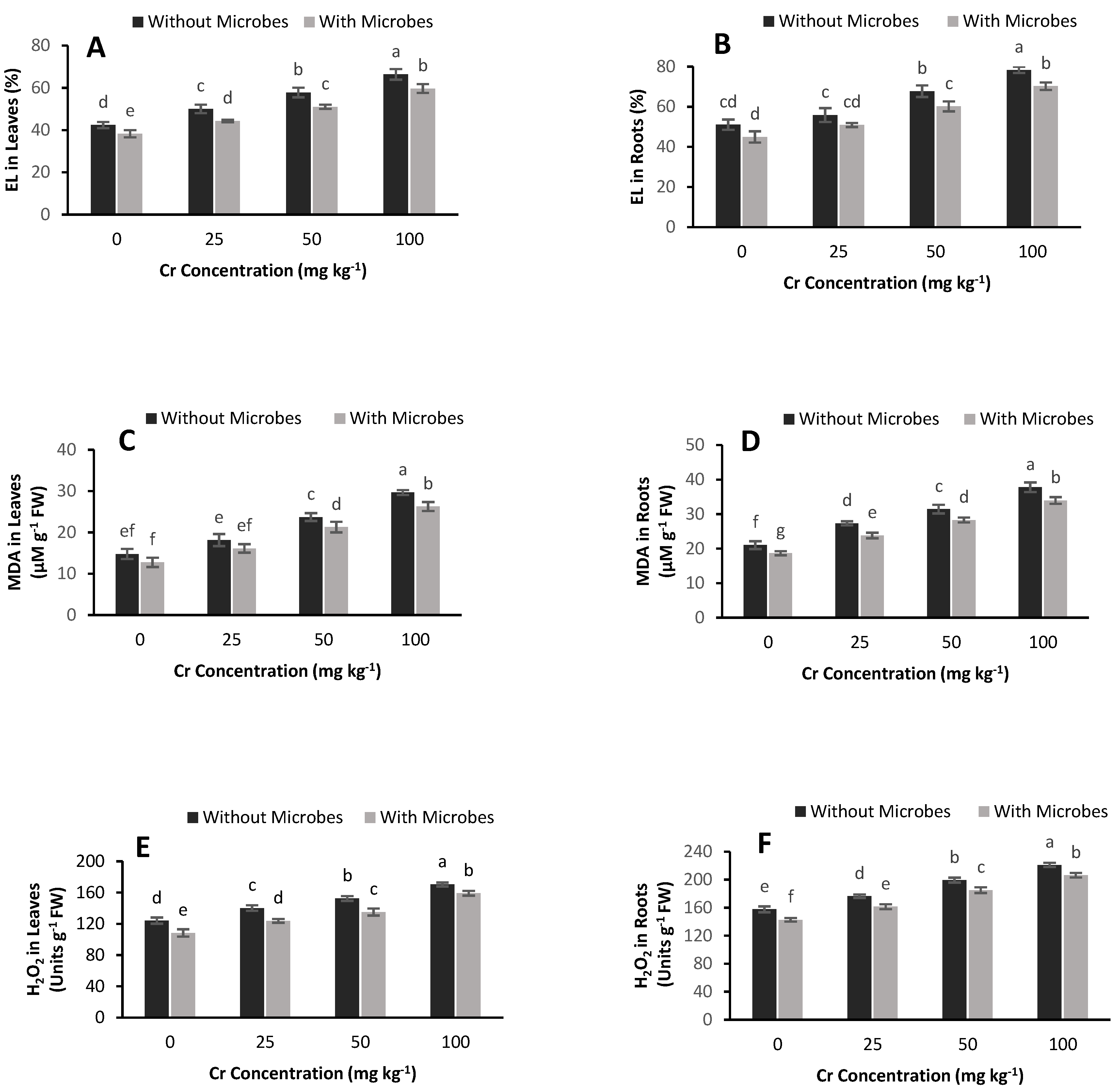
3.5. Estimation of EL, MDA and H2O2
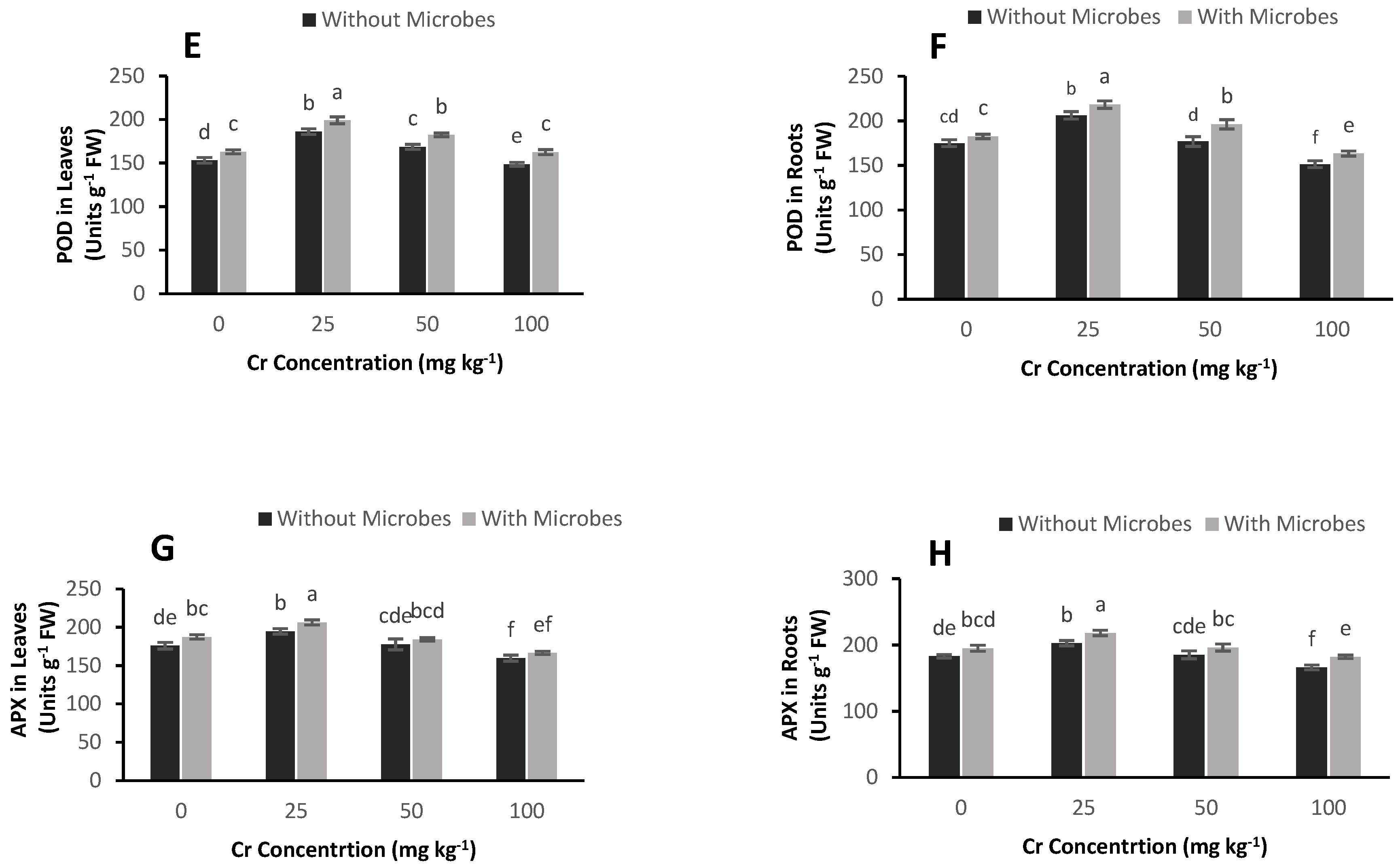
3.6. Effect of S. aureus on Antioxidant Enzyme Activities
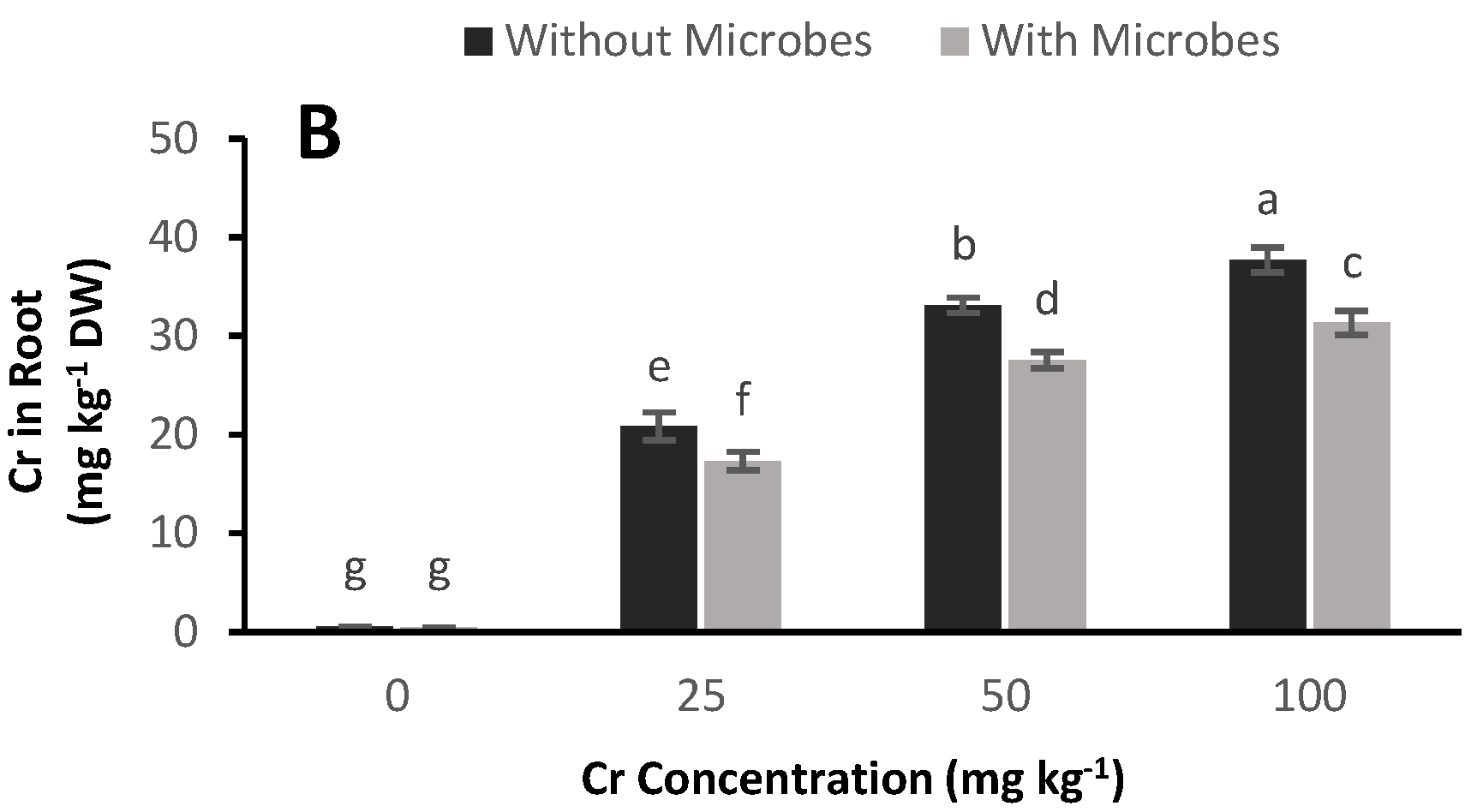
3.7. Cr Accumulation in Plants
4. Discussion
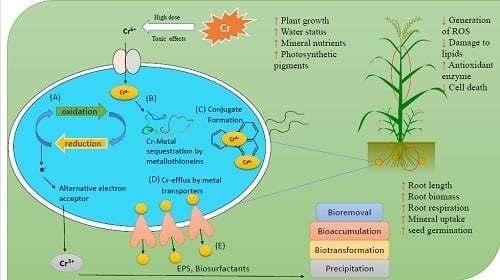
4.1. Detoxification of Metals by S. aureus K1
4.2. Effect of S. aureus on Plant Growth Promotion under Cr Metal Stress
4.3. Chlorophyll Contents
4.4. ROS Species and Antioxidant Enzyme Production
4.5. Reduction of Cr Concentration in Plants by Bacterial Inoculation
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Singh, H.P.; Mahajan, P.; Kaur, S.; Batish, D.R.; Kohli, R.K. Chromium toxicity and tolerance in plants. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2013, 11, 229–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunjam, M. Studies on selected heavy metals on seed germination and plant growth in pea plant (Pisum sativum) grown in solid medium. J. Pharmacogn. Phytochem. 2015, 3, 85–87. [Google Scholar]
- Habiba, U.; Ali, S.; Farid, M.; Shakoor, M.B.; Rizwan, M.; Ibrahim, M.; Abbasi, G.H.; Hayat, T.; Ali, B. EDTA enhanced plant growth, antioxidant defense system, and phytoextraction of copper by Brassica napus L. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2014, 22, 1534–1544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adrees, M.; Ali, S.; Iqbal, M.; Bharwana, S.A.; Siddiqi, Z.; Farid, M.; Ali, Q.; Saeed, R.; Rizwan, M. Mannitol alleviates chromium toxicity in wheat plants in relation to growth, yield, stimulation of anti-oxidative enzymes, oxidative stress and Cr uptake in sand and soil media. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2015, 122, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mathur, S.; Kalaji, H.M.; Kalaji, H.M. Investigation of deleterious effects of chromium phytotoxicity and photosynthesis in wheat plant. Photosynthetica 2016, 54, 185–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamran, M.A.; Mufti, R.; Mubariz, N.; Syed, J.H.; Bano, A.; Javed, M.T.; Munis, M.F.H.; Tan, Z.; Chaudhary, H.J. The potential of the flora from different regions of Pakistan in phytoremediation: A review. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2013, 21, 801–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daud, M.K.; Mei, L.; Variath, M.T.; Ali, S.; Li, C.; Rafiq, M.T.; Zhu, S.J. Chromium (VI) Uptake and Tolerance Potential in Cotton Cultivars: Effect on Their Root Physiology, Ultramorphology, and Oxidative Metabolism. BioMed Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afshan, S.; Ali, S.; Bharwana, S.A.; Rizwan, M.; Farid, M.; Abbas, F.; Ibrahim, M.; Mehmood, M.A.; Abbasi, G.H. Citric acid enhances the phytoextraction of chromium, plant growth, and photosynthesis by alleviating the oxidative damages in Brassica napus L. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 22, 11679–11689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagajyoti, P.C.; Lee, K.D.; Sreekanth, T.V.M. Heavy metals, occurrence and toxicity for plants: A review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2010, 8, 199–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanker, A. Chromium toxicity in plants. Environ. Int. 2005, 31, 739–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamran, M.A.; Eqani, S.A.M.A.S.; Bibi, S.; Xu, R.-K.; Monis, M.F.H.; Katsoyiannis, A.; Bokhari, H.; Chaudhary, H.J. Bioaccumulation of nickel by E. sativa and role of plant growth promoting rhizobacteria (PGPRs) under nickel stress. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2016, 126, 256–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dotaniya, M.L.; Das, H.; Meena, V.D. Assessment of chromium efficacy on germination, root elongation, and coleoptile growth of wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) at different growth periods. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2014, 186, 2957–2963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lenka, S. Impacts of fertilizers use on environmental quality. In Proceedings of the National Seminar on Environmental Concern for Fertilizer Use in Future, Bidhan Chandra Krishi Viswavidyalaya, Kalyani, India, 26 February 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Saha, J.; Selladurai, R.; Coumar, M.V.; Dotaniya, M.L.; Kundu, S.; Patra, A.K. Industrial Activities in India and Their Impact on Agroecosystem; Springer Science and Business Media LLC: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2017; Volume 10, pp. 229–249. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, M.Y. Effect of microbial inoculation on wheat growth and phytostabilization of chromium contaminated soil. Pak. J. Bot. 2013, 45, 27–34. [Google Scholar]
- Rizwan, M.; Ali, S.; Abbas, T.; Zia-Ur-Rehman, M.; Hannan, F.; Keller, C.; Al-Wabel, M.I.; Ok, Y.S. Cadmium minimization in wheat: A critical review. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2016, 130, 43–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shewry, P.R.; Hey, S.J. The contribution of wheat to human diet and health. Food Energy Secur. 2015, 4, 178–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awan, N.; Fatima, A.; Farhan, M.; Awan, N. Comparative Analysis of Chromium and Cadmium in Various Parts of Wheat and Maize. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2019, 28, 1561–1566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlin, D.J.; Naujokas, M.F.; Bradham, K.D.; Cowden, J.; Heacock, M.; Henry, H.F.; Lee, J.S.; Thomas, D.J.; Thompson, C.; Tokar, E.J.; et al. Arsenic and Environmental Health: State of the Science and Future Research Opportunities. Environ. Health Perspect. 2016, 124, 890–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, Q.; Yousaf, B.; Liu, G.; Zia-Ur-Rehman, M.; Ali, M.U.; Munir, M.A.M.; Hussain, S.A. Evaluating the health risks of potentially toxic elements through wheat consumption in multi-industrial metropolis of Faisalabad, Pakistan. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 26646–26657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lytle, C.M.; Lytle, F.W.; Yang, N.; Qian, J.-H.; Hansen, D.; Zayed, A.; Terry, N. Reduction of Cr(VI) to Cr(III) by Wetland Plants: Potential for In Situ Heavy Metal Detoxification. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1998, 32, 3087–3093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, J.; Singh, R.; Arora, N.K. Alleviation of Heavy Metal Stress in Plants and Remediation of Soil by Rhizosphere Microorganisms. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 1706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashraf, S.; Ali, Q.; Zahir, Z.A.; Ashraf, S.; Asghar, H.N. Phytoremediation: Environmentally sustainable way for reclamation of heavy metal polluted soils. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 174, 714–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, Z.; Glick, B.R. The Role of Plant Growth-Promoting Bacteria in Metal Phytoremediation; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; pp. 97–132. [Google Scholar]
- Ryan, R.P.; Monchy, S.; Cardinale, M.; Taghavi, S.; Crossman, L.; Avison, M.B.; Berg, G.; Van Der Lelie, D.; Dow, J.M. The versatility and adaptation of bacteria from the genus Stenotrophomonas. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2009, 7, 514–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taj, Z.Z.; Rajkumar, M. Perspectives of Plant Growth-Promoting Actinomycetes in Heavy Metal Phytoremediation; Springer Science and Business Media LLC: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016; pp. 213–231. [Google Scholar]
- Mishra, S.; Bharagava, R.N. Toxic and genotoxic effects of hexavalent chromium in environment and its bioremediation strategies. J. Environ. Sci. Health Part C 2015, 34, 1–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wirtanen, G.; Salo, S. Biofilm risks. In Handbook of Hygiene Control in the Food Industry; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016; pp. 55–79. [Google Scholar]
- Ahemad, M. Enhancing phytoremediation of chromium-stressed soils through plant-growth-promoting bacteria. J. Genet. Eng. Biotechnol. 2015, 13, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, Y.X.; Yan, J.L.; He, H.D.; Yang, D.J.; Xiao, L.; Zhong, T.; Yuan, M.; De Cai, X.; Bin Li, S. Characterization of Bacteria in the Rhizosphere Soils ofPolygonum Pubescensand Their Potential in Promoting Growth and Cd, Pb, Zn Uptake byBrassica napus. Int. J. Phytoremediation 2013, 16, 321–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukhtar, S. Potential of sunflower (Helianthus annuus L.) for phytoremediation of nickel (Ni) and lead (Pb) contaminated water. Pak. J. Bot. 2010, 42, 4017–4026. [Google Scholar]
- Soltanpour, P.N. Use of ammonium bicarbonate DTPA soil test to evaluate elemental availability and toxicity 1. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 1985, 16, 323–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moodie, C.D.; Smith, H.W.; McCreery, R.A. Laboratory Manual for Soil Fertility. Soil Sci. 1951, 71, 400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucious, S. Heavy metal tolerance and antibiotic sensitivity of bacterial strains isolated from tannery effluent. Asian J. Exp. Biol. Sci. 2013, 4, 597–606. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Krumholz, L.R.; Yu, Z.; Chen, Y.; Liu, P.; Li, X. A Novel Subspecies of Staphylococcus aureus from Sediments of Lanzhou Reach of the Yellow River Aerobically Reduces Hexavalent Chromium. J. Bioremediation Biodegrad. 2013, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, S.; Pryer, K.M.; Miao, V.P.W.; Palmer, J.D. Investigating deep phylogenetic relationships among cyanobacteria and plastids by small subunit rRNA sequence analysis. J. Eukaryot. Microbiol. 1999, 46, 327–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moyersoen, B.; E Beever, R.; Martin, F. Genetic diversity of Pisolithus in New Zealand indicates multiple long-distance dispersal from Australia. New Phytol. 2003, 160, 569–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamura, K.; Peterson, D.; Stecher, G.; Nei, M.; Kumar, S.; Peterson, N. MEGA5: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis Using Maximum Likelihood, Evolutionary Distance, and Maximum Parsimony Methods. Mol. Boil. Evol. 2011, 28, 2731–2739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hadi, F.; Bano, A. Effect of diazotrophs (Rhizobium and Azatebactor) on growth of maize (Zea mays L.) and accumulation of lead (Pb) in different plant parts. Pak. J. Bot. 2010, 42, 4363–4370. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, S.; Cheung, K.; Luo, Y.; Wong, M.H. Effects of inoculation of plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria on metal uptake by Brassica juncea. Environ. Pollut. 2006, 140, 124–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lichtenthaler, H.K. Chlorophylls and carotenoids: Pigments of photosynthetic biomembranes. In Methods in Enzymology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1987; pp. 350–382. [Google Scholar]
- Dionisio-Sese, M.L.; Tobita, S. Antioxidant responses of rice seedlings to salinity stress. Plant Sci. 1998, 135, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plumb-Dhindsa, P.; Dhindsa, R.S.; Thorpe, T.A. Leaf Senescence: Correlated with Increased Levels of Membrane Permeability and Lipid Peroxidation, and Decreased Levels of Superoxide Dismutase and Catalase. J. Exp. Bot. 1981, 32, 93–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Kirkham, M. Drought-Stress-Induced Changes in Activities of Superoxide Dismutase, Catalase, and Peroxidase in Wheat Species. Plant Cell Physiol. 1994, 35, 785–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jana, S.; Choudhuri, M.A. Glycolate metabolism of three submersed aquatic angiosperms: Effect of heavy metals. Aquat. Bot. 1981, 11, 67–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X. The measurement and mechanism of lipid peroxidation and SOD, POD and CAT activities in biological system. In Research Methodology of Crop Physiology; Agriculture Press: Beijing, China, 1992; pp. 208–211. [Google Scholar]
- Aebi, H. Catalase in vitro. Methods Enzym. 1984, 105, 121–126. [Google Scholar]
- Nakano, Y.; Asada, K. Hydrogen Peroxide is Scavenged by Ascorbate-specific Peroxidase in Spinach Chloroplasts. Plant Cell Physiol. 1981, 22, 867–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehman, M.Z.-U.; Rizwan, M.; Ghafoor, A.; Naeem, A.; Ali, S.; Sabir, M.; Qayyum, M.F. Effect of inorganic amendments for in situ stabilization of cadmium in contaminated soils and its phyto-availability to wheat and rice under rotation. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 22, 16897–16906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, Z.; Nisar, M.A.; Hussain, S.Z.; Arshad, M.N.; Rehman, A. Cadmium resistance mechanism in Escherichia coli P4 and its potential use to bioremediate environmental cadmium. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2015, 99, 10745–10757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oaikhena, E.E.; Makaije, D.B.; Denwe, S.D.; Namadi, M.M.; Haroun, A.A. Bioremediation Potentials of Heavy Metal Tolerant Bacteria Isolated from Petroleum Refinery Effluent. Am. J. Environ. Prot. 2016, 5, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mustapha, M.U.; Halimoon, N. Screening and Isolation of Heavy Metal Tolerant Bacteria in Industrial Effluent. Procedia Environ. Sci. 2015, 30, 33–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruins, M.R.; Kapil, S.; Oehme, F.W. Microbial Resistance to Metals in the Environment. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2000, 45, 198–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nies, D.H. Efflux-mediated heavy metal resistance in prokaryotes. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2003, 27, 313–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sørensen, S.J.; Bailey, M.; Hansen, L.H.; Kroer, N.; Wuertz, S. Studying plasmid horizontal transfer in situ: A critical review. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2005, 3, 700–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashif, M.; Ngaini, Z.; Harry, A.V.; Vekariya, R.L.; Ahmad, A.; Zuo, Z.; Alarifi, A. An experimental and DFT study on novel dyes incorporated with natural dyes on titanium dioxide (TiO2) towards solar cell application. Appl. Phys. A 2020, 126, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nies, D.H. Microbial heavy-metal resistance. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 1999, 51, 730–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, S.; Dash, H.R.; Chakraborty, J. Genetic basis and importance of metal resistant genes in bacteria for bioremediation of contaminated environments with toxic metal pollutants. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2016, 100, 2967–2984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roosa, S.; Wattiez, R.; Prygiel, E.; Lesven, L.; Billon, G.; Gillan, D.C. Bacterial metal resistance genes and metal bioavailability in contaminated sediments. Environ. Pollut. 2014, 189, 143–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chudobova, D.; Dostalova, S.; Ruttkay-Nedecký, B.; Guran, R.; Rodrigo, M.A.M.; Tmejová, K.; Krizkova, S.; Zitka, O.; Adam, V.; Kizek, R. The effect of metal ions on Staphylococcus aureus revealed by biochemical and mass spectrometric analyses. Microbiol. Res. 2015, 170, 147–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nies, D.H.; Silver, S.D. Ion efflux systems involved in bacterial metal resistances. J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 1995, 14, 186–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chatterjee, J.; Kumar, P.; Sharma, P.N.; Tewari, R.K. Chromium toxicity induces oxidative stress in turnip. Indian J. Plant Physiol. 2015, 20, 220–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, F.; Yasmeen, T.; Arif, M.S.; Riaz, M.; Shahzad, S.M.; Imran, Q.; Ali, I. Combined ability of chromium (Cr) tolerant plant growth promoting bacteria (PGPB) and salicylic acid (SA) in attenuation of chromium stress in maize plants. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2016, 108, 456–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, F.; Yasmeen, T.; Ali, Q.; Ali, S.; Arif, M.S.; Hussain, S.; Rizvi, H. Influence of Pseudomonas aeruginosa as PGPR on oxidative stress tolerance in wheat under Zn stress. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2014, 104, 285–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamhamdi, M.; El Galiou, O.; Bakrim, A.; Nóvoa-Muñoz, J.C.; Arias-Estévez, M.; Aarab, A.; Lafont, R. Effect of lead stress on mineral content and growth of wheat (Triticum aestivum) and spinach (Spinacia oleracea) seedlings. Saudi J. Boil. Sci. 2013, 20, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, H. Chromium as an Environmental Pollutant: Insights on Induced Plant Toxicity. J. Bot. 2012, 2012, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arif, M.S.; Yasmeen, T.; Shahzad, S.M.; Riaz, M.; Rizwan, M.; Iqbal, S.; Asif, M.; Soliman, M.H.; Ali, S. Lead toxicity induced phytotoxic effects on mung bean can be relegated by lead tolerant Bacillus subtilis (PbRB3). Chemosphere 2019, 234, 70–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sytar, O.; Kumar, A.; Latowski, D.; Kuczyńska, P.; Strzałka, K.; Prasad, M.N.V. Heavy metal-induced oxidative damage, defense reactions, and detoxification mechanisms in plants. Acta Physiol. Plant. 2012, 35, 985–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, F.; Yasmeen, T.; Ali, Q.; Mubin, M.; Ali, S.; Arif, M.S.; Hussain, S.; Riaz, M.; Abbas, F. Copper-resistant bacteria reduces oxidative stress and uptake of copper in lentil plants: Potential for bacterial bioremediation. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 23, 220–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.S.; Dietz, K.-J. The relationship between metal toxicity and cellular redox imbalance. Trends Plant Sci. 2009, 14, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Štolfa, I.; Pfeiffer, T.Z.; Špoljarić, D.; Teklić, T.; Lončarić, Z. Heavy Metal-Induced Oxidative Stress in Plants: Response of the Antioxidative System; Springer Science and Business Media LLC: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015; pp. 127–163. [Google Scholar]
- Fayiga, A.O.; Ma, L.Q.; Cao, X.; Rathinasabapathi, B. Effects of heavy metals on growth and arsenic accumulation in the arsenic hyperaccumulator Pteris vittata L. Environ. Pollut. 2004, 132, 289–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vital, S.A.; Fowler, R.W.; Virgen, A.; Gossett, D.R.; Banks, S.W.; Rodriguez, J. Opposing roles for superoxide and nitric oxide in the NaCl stress-induced upregulation of antioxidant enzyme activity in cotton callus tissue. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2008, 62, 60–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gururani, M.A.; Upadhyaya, C.P.; Baskar, V.; Venkatesh, J.; Nookaraju, A.; Park, S.W. Plant Growth-Promoting Rhizobacteria Enhance Abiotic Stress Tolerance in Solanum tuberosum Through Inducing Changes in the Expression of ROS-Scavenging Enzymes and Improved Photosynthetic Performance. J. Plant Growth Regul. 2012, 32, 245–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huffman, E.W.D.; Allaway, W.H. Chromium in plants. Distribution in tissues, organelles, and extracts and availability of bean leaf chromium to animals. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1973, 21, 982–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zayed, A.; Lytle, C.M.; Qian, J.-H.; Terry, N. Chromium accumulation, translocation and chemical speciation in vegetable crops. Planta 1998, 206, 293–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanker, A.; Djanaguiraman, M.; Sudhagar, R.; Chandrashekar, C.; Pathmanabhan, G. Differential antioxidative response of ascorbate glutathione pathway enzymes and metabolites to chromium speciation stress in green gram ((L.) R.Wilczek. cv CO 4) roots. Plant Sci. 2004, 166, 1035–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salunkhe, P.; Dhakephalkar, P.; Paknikar, K.M. Bioremediation of hexavalent chromium in soil microcosms. Biotechnol. Lett. 1998, 20, 749–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasnain, S.; Sabri, A.N. Growth stimulation of Triticum aestivum seedlings under Cr-stresses by non-rhizospheric pseudomonad strains. Environ. Pollut. 1997, 97, 265–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, S.; Shanker, K.; Srivastava, M.; Srivastava, S.; Shrivastav, R.; Dass, S.; Prakash, S. A study on the uptake of trivalent and hexavalent chromium by paddy (Oryza sativa): Possible chemical modifications in rhizosphere. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 1997, 62, 53–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheung, K.H.; Gu, J.-D. Reduction of chromate (CrO42−) by an enrichment consortium and an isolate of marine sulfate-reducing bacteria. Chemosphere 2003, 52, 1523–1529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, S.; Singh, D. Role of Genetically Modified Microorganisms in Heavy Metal Bioremediation. In Advances in Environmental Biotechnology; Springer Science and Business Media LLC: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2017; Volume 3, pp. 197–214. [Google Scholar]
- Ali, B.; Wang, B.; Ali, S.; Ghani, M.A.; Hayat, M.T.; Yang, C.; Xu, L.; Zhou, W. 5-Aminolevulinic Acid Ameliorates the Growth, Photosynthetic Gas Exchange Capacity, and Ultrastructural Changes Under Cadmium Stress in Brassica napus L. J. Plant Growth Regul. 2013, 32, 604–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Soil Properties | Unit | Values |
|---|---|---|
| Texture Properties | Sandy Clay Loam | |
| pH | - | 7.71 |
| Sand | % | 63.7 |
| Clay | % | 21.9 |
| Silt | % | 14.4 |
| Electrical Conductivity (EC) | dSm−1 | 4.77 |
| Soluble Ion Values | ||
| Cl− | mmolcL−1 | 7.15 |
| Ca2+ + Mg2+ | mmolcL−1 | 14.92 |
| CO32− | mmolcL−1 | 0.85 |
| OM | % | 0.90 |
| CEC | cmolckg−1 | 13.2 |
| HCO3− | mmolcL−1 | 3.84 |
| Metal Concentration | ||
| Available Cr6+ | mg·kg−1 | 0.04 |
| Available Zn2+ | mg·kg−1 | 0.72 |
| Available Cu2+ | mg·kg−1 | 0.23 |
| Sr. No. | Characteristic | Staphylococcus aureus K1 |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Morphology | Convex, round |
| 2 | Color | Yellowish, golden |
| 3 | Gram-reaction | +ve |
| 4 | Catalase | +ve |
| 5 | Coagulase plasma reaction | −ve |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zeng, F.; Zahoor, M.; Waseem, M.; Anayat, A.; Rizwan, M.; Ahmad, A.; Yasmeen, T.; Ali, S.; El-Sheikh, M.A.; Alyemeni, M.N.; et al. Influence of Metal-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus Strain K1 on the Alleviation of Chromium Stress in Wheat. Agronomy 2020, 10, 1354. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy10091354
Zeng F, Zahoor M, Waseem M, Anayat A, Rizwan M, Ahmad A, Yasmeen T, Ali S, El-Sheikh MA, Alyemeni MN, et al. Influence of Metal-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus Strain K1 on the Alleviation of Chromium Stress in Wheat. Agronomy. 2020; 10(9):1354. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy10091354
Chicago/Turabian StyleZeng, Fanrong, Munazza Zahoor, Muhammad Waseem, Alia Anayat, Muhammad Rizwan, Awais Ahmad, Tahira Yasmeen, Shafaqat Ali, Mohamed A. El-Sheikh, Mohammed Nasser Alyemeni, and et al. 2020. "Influence of Metal-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus Strain K1 on the Alleviation of Chromium Stress in Wheat" Agronomy 10, no. 9: 1354. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy10091354
APA StyleZeng, F., Zahoor, M., Waseem, M., Anayat, A., Rizwan, M., Ahmad, A., Yasmeen, T., Ali, S., El-Sheikh, M. A., Alyemeni, M. N., & Wijaya, L. (2020). Influence of Metal-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus Strain K1 on the Alleviation of Chromium Stress in Wheat. Agronomy, 10(9), 1354. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy10091354