Simple Tuning Rules for Feedforward Compensators Applied to Greenhouse Daytime Temperature Control Using Natural Ventilation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
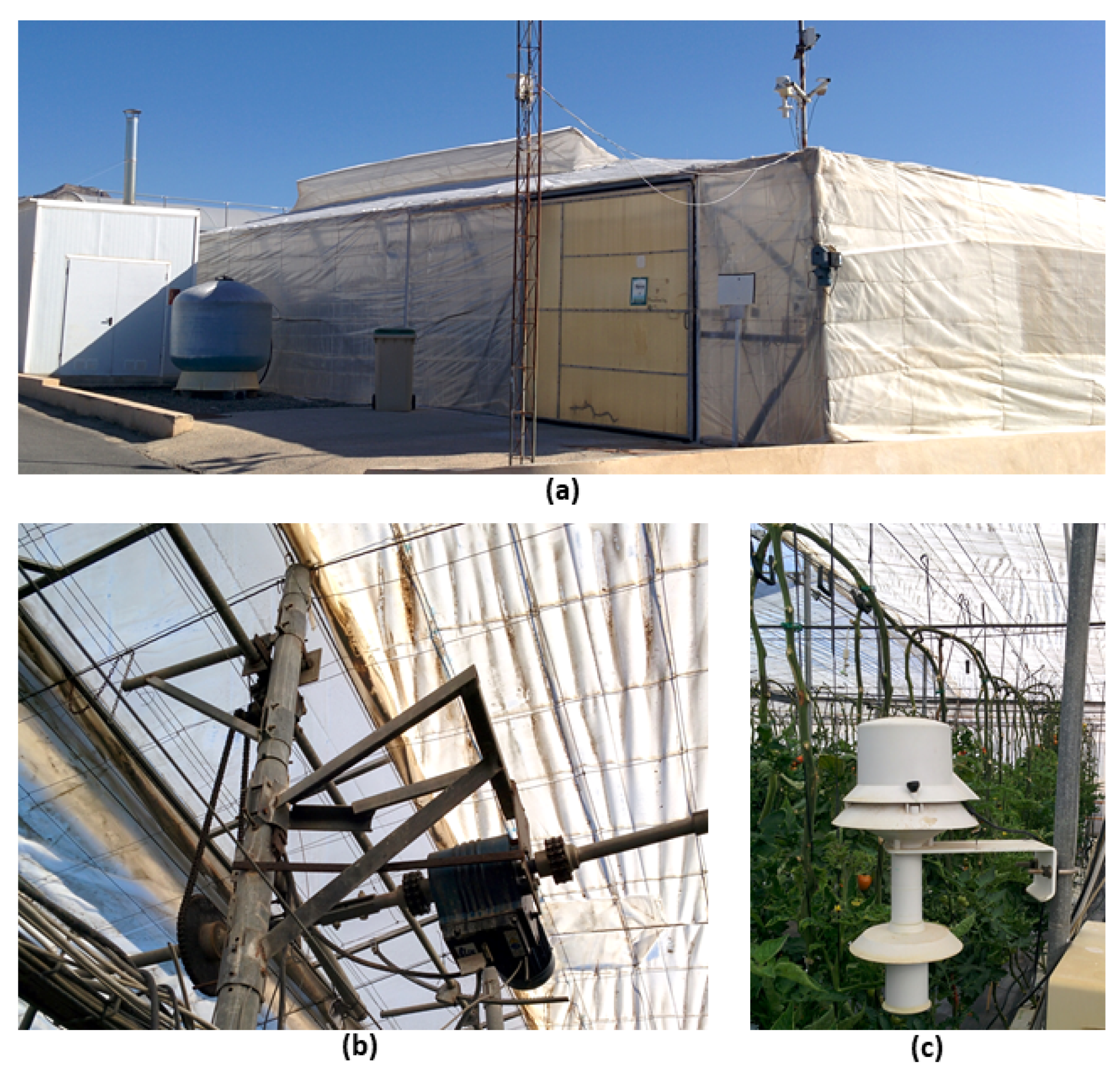
2.1. Experimental Greenhouse
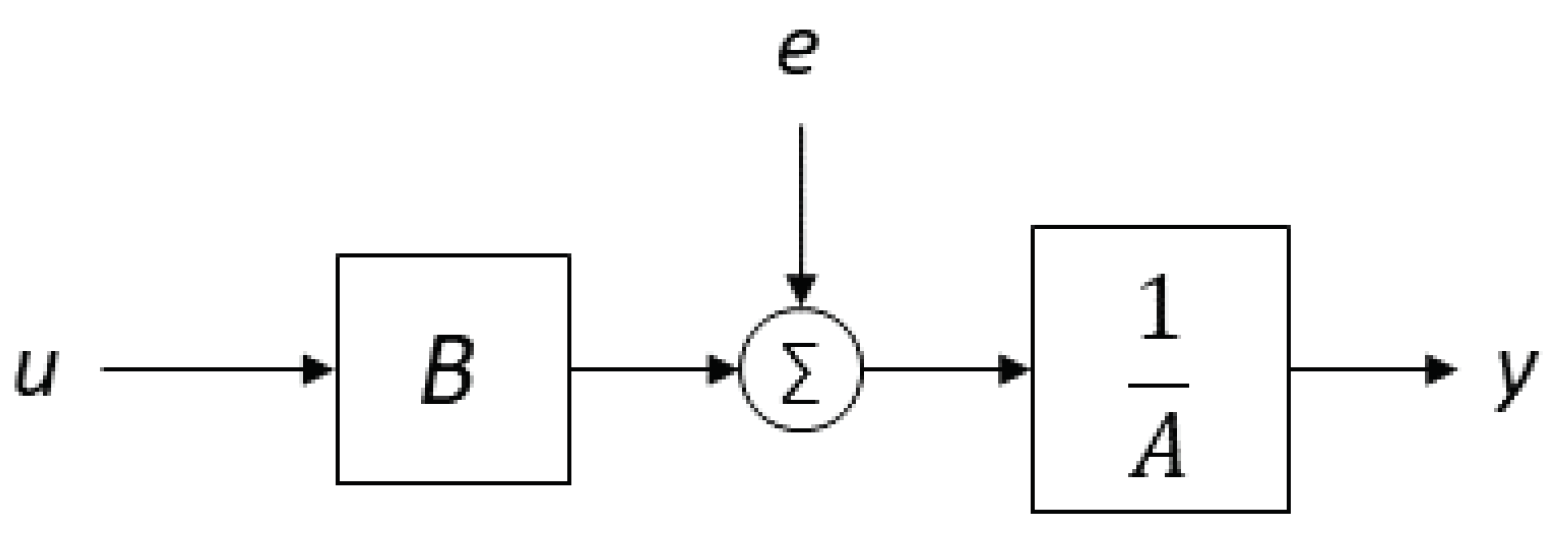
2.2. System Identification Methodology
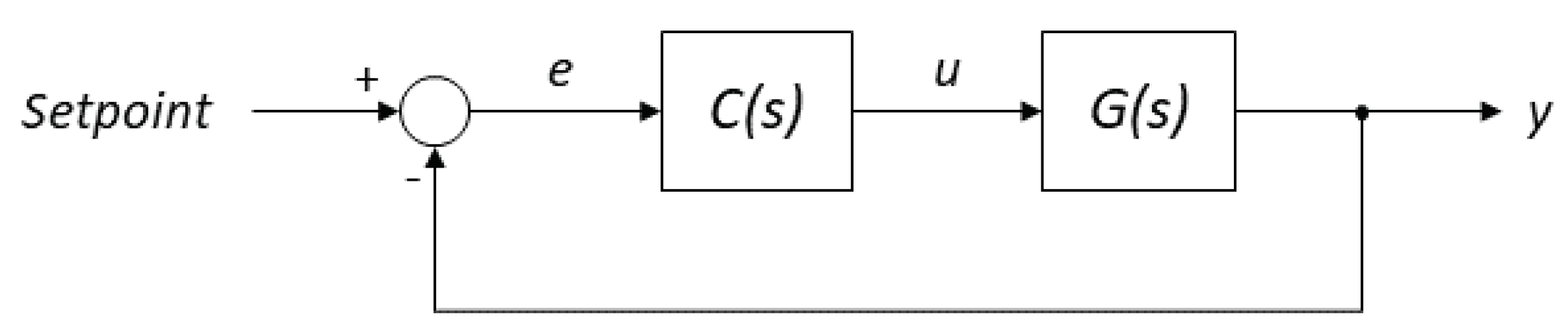
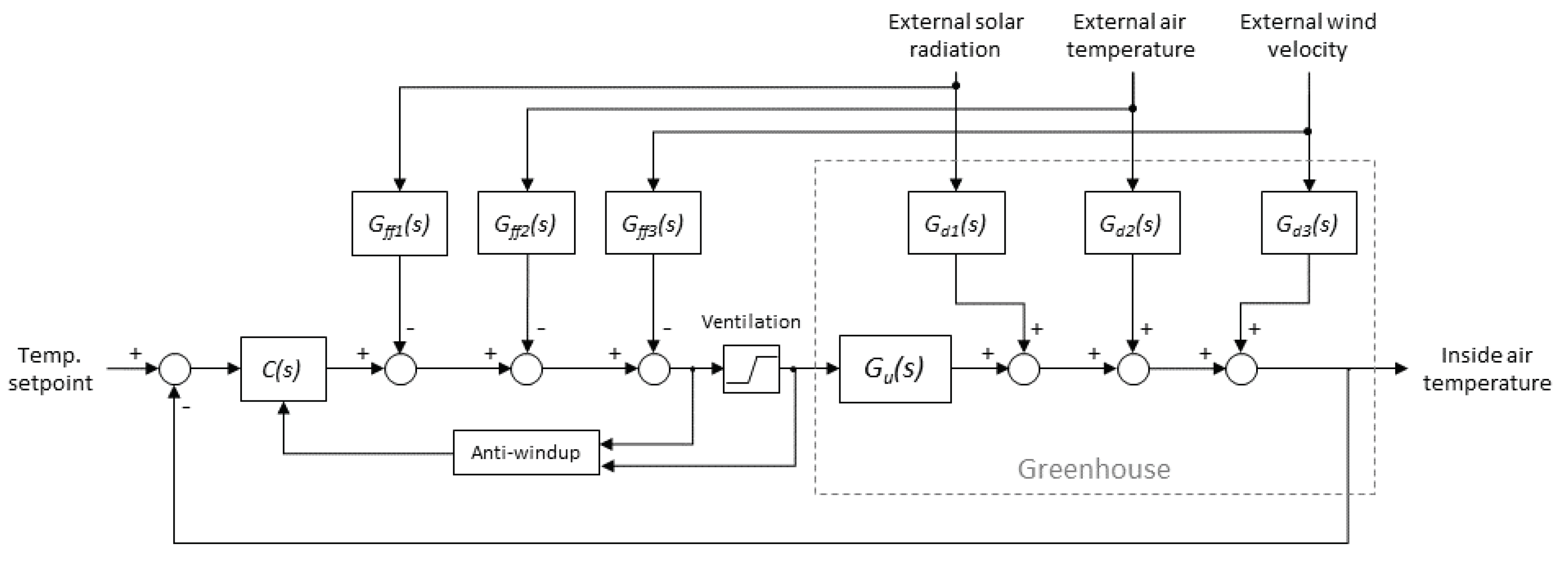
2.3. Automatic Control Strategies
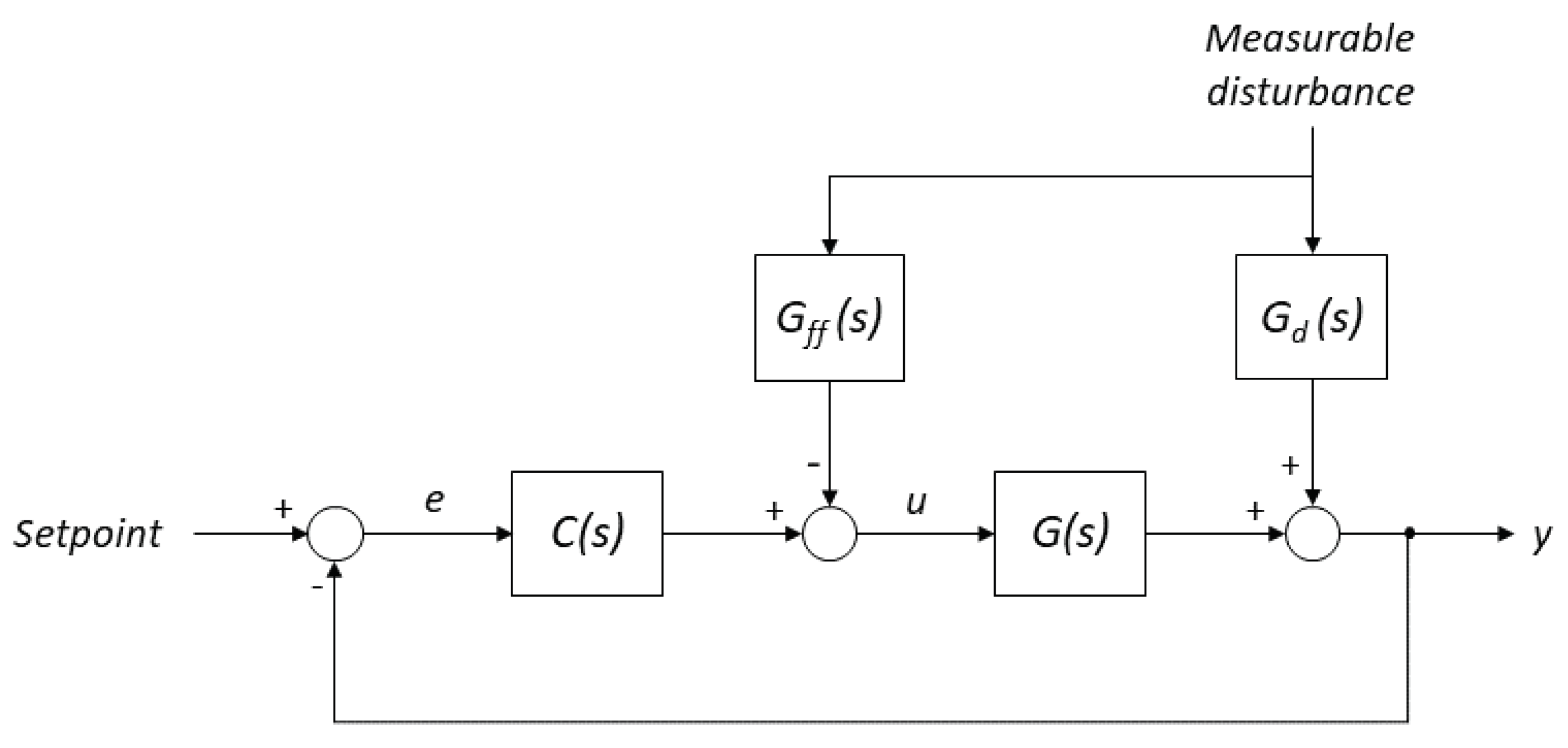
- The greenhouse micro-climate is strongly affected by disturbances, both measurable and non-measurable. Thus, the designed controller should consider the effect of the outside weather conditions.
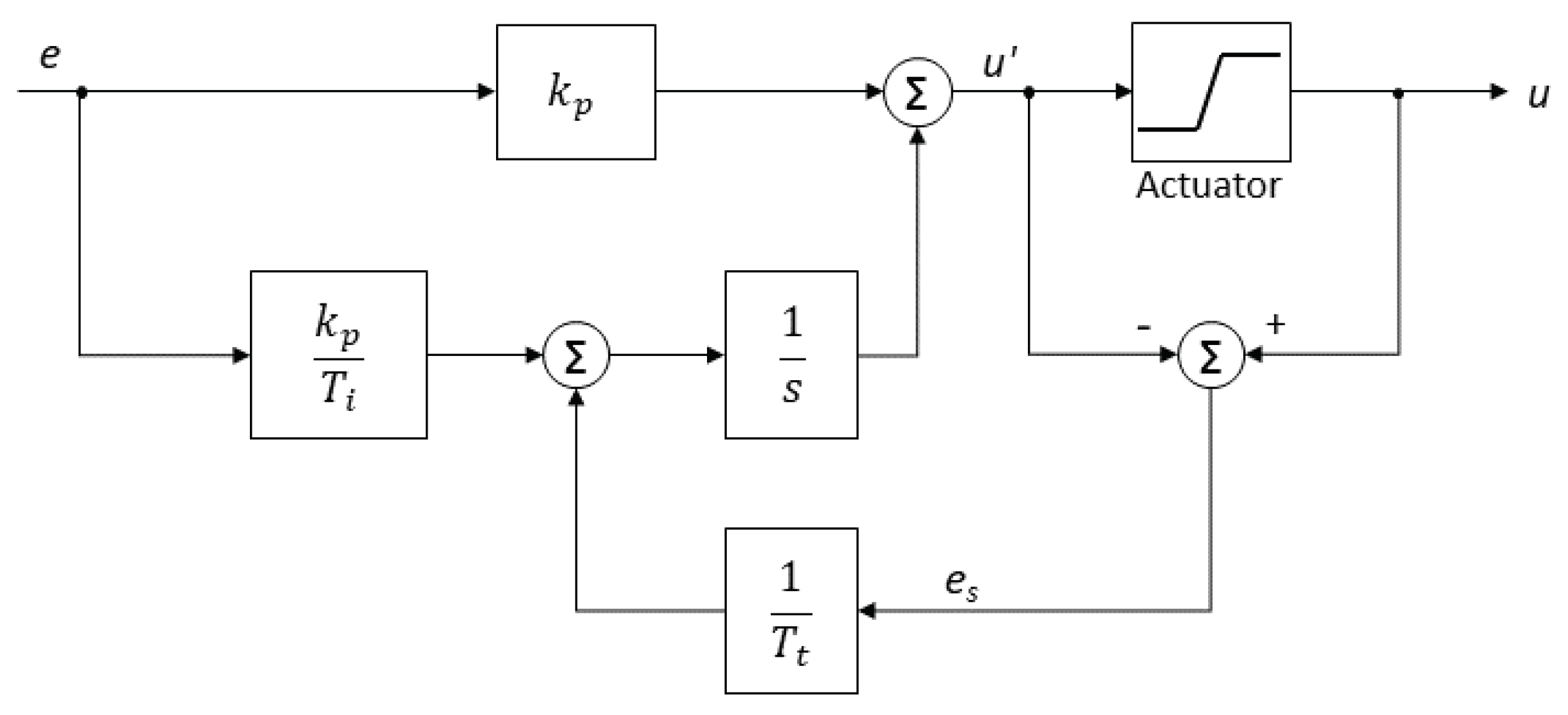
- The motors of the natural ventilation system present two limitations: (i) actuator saturation, due to a limited opening range from 0% to 100%; and (ii) resolution, since the windows opening is performed in steps of 10%.
2.3.1. PID Control
2.3.2. Feedforward Control
- Set:
- Calculate as:
- Calculate the compensator gain, , considering the PI controller parameters ( and ):
2.4. Software
3. Results
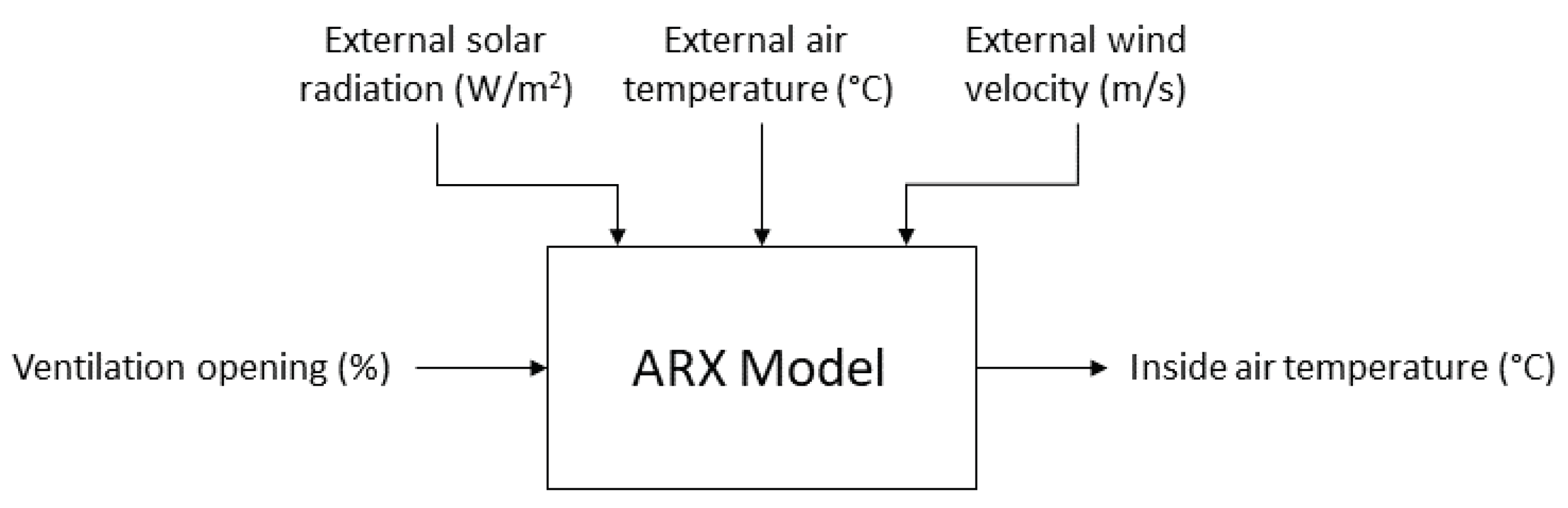
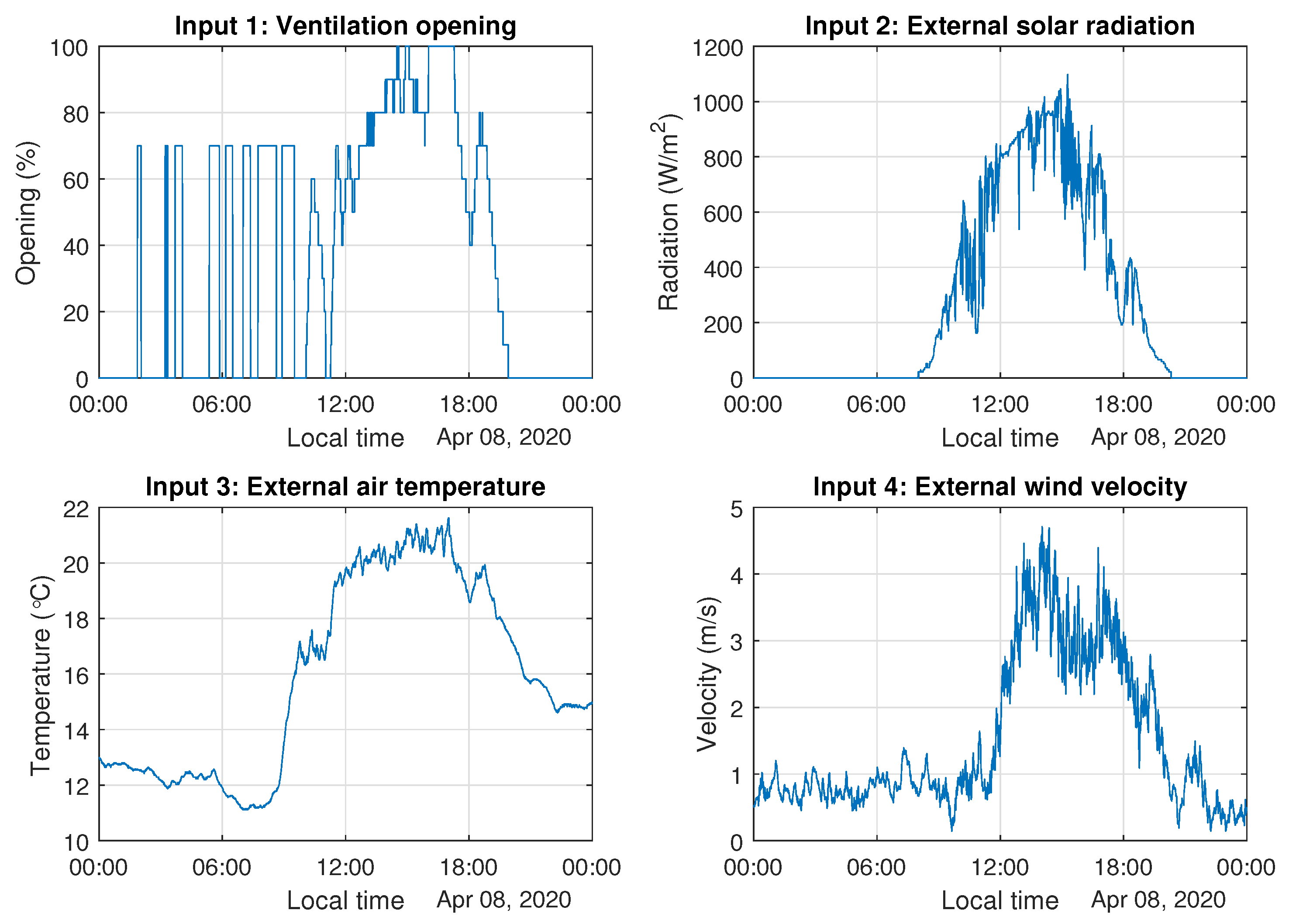
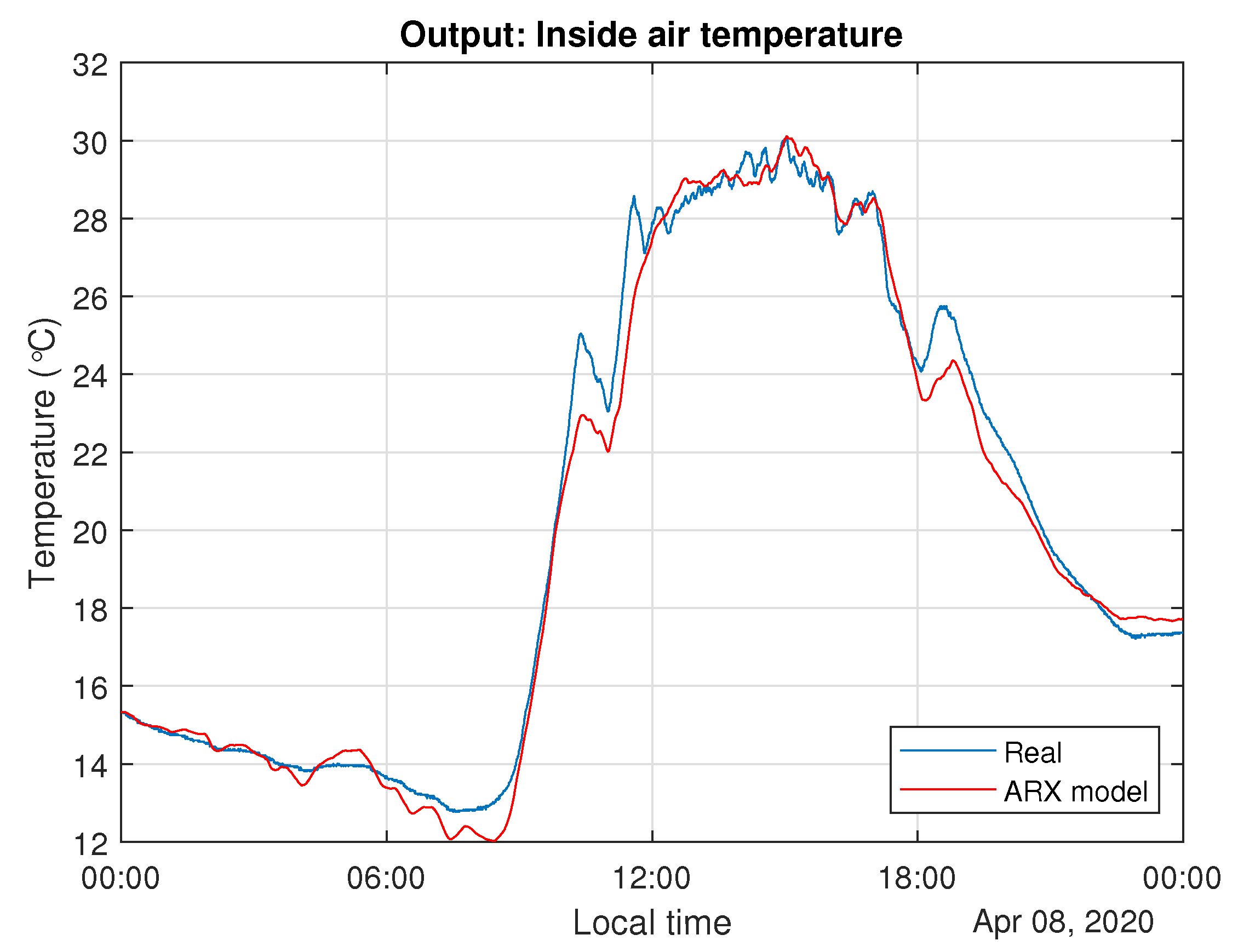
3.1. ARX Model
3.2. Low-Order Models
3.3. Design and Simulation of Control Strategies
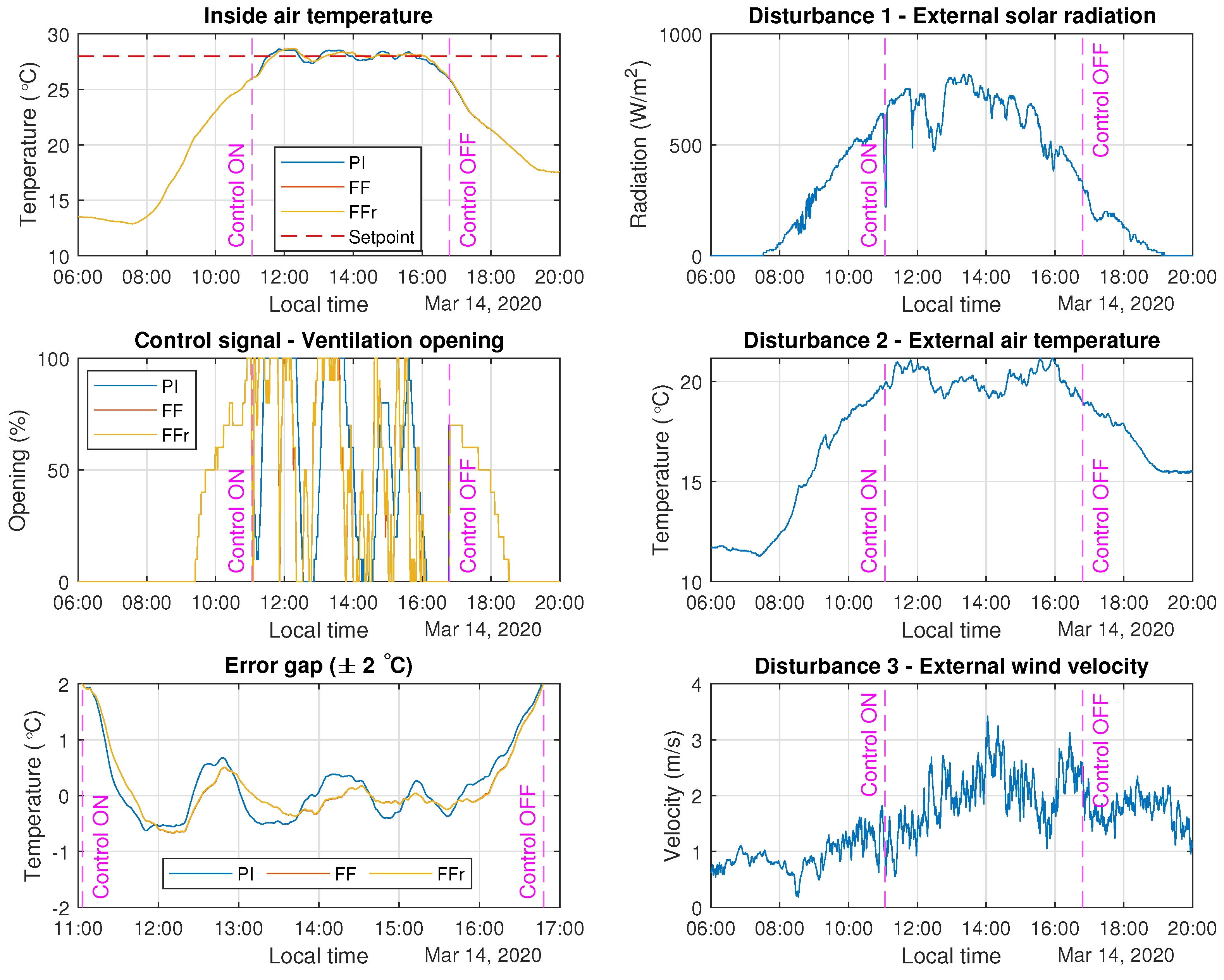
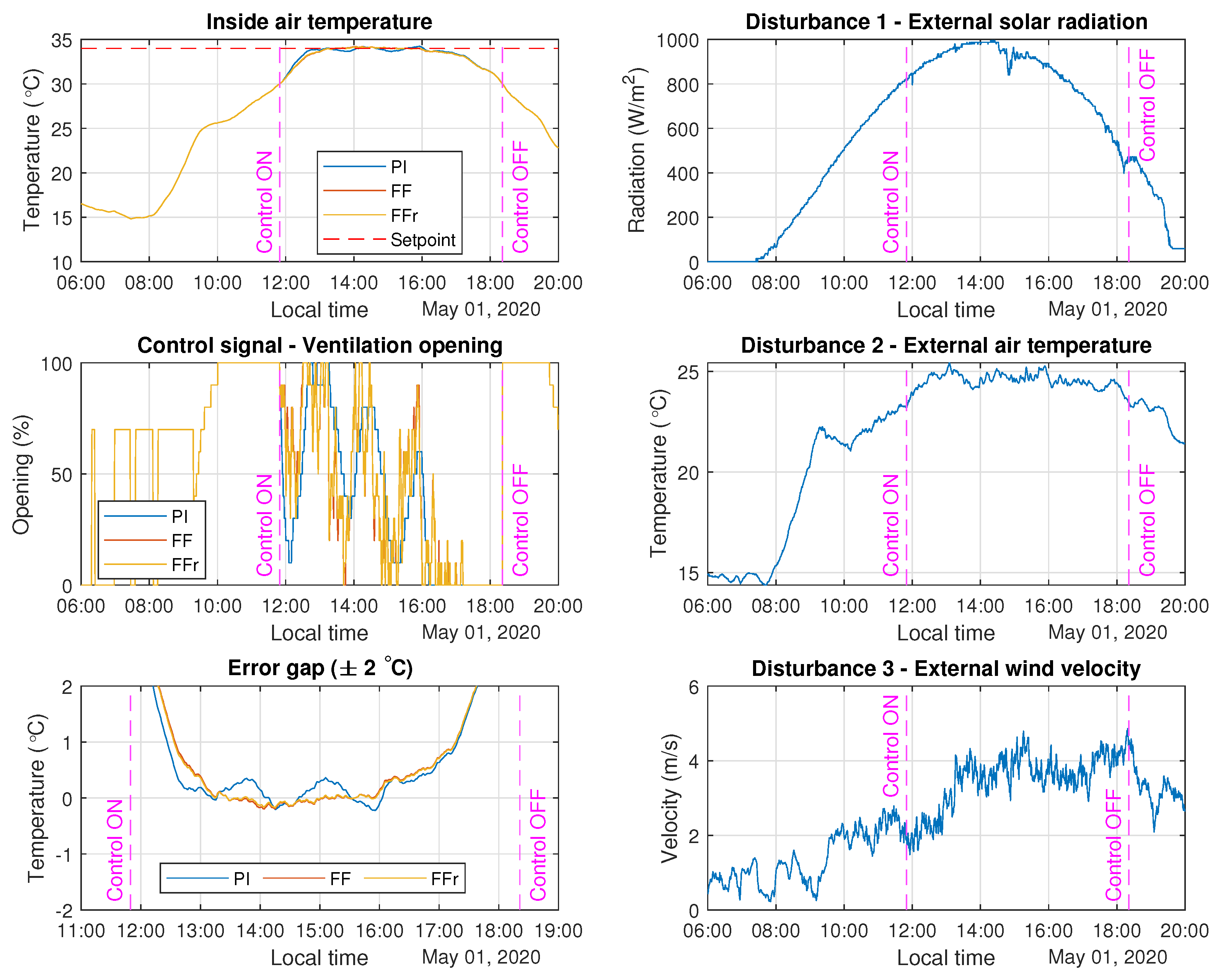
3.4. Real Tests with Feedforward Control
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ARX | Auto-Regressive with eXogenous input |
| FF | FeedForward |
| FOPDT | First-Order-Plus-Dead-Time |
| IAE | Integral Absolute Error |
| MISO | Multiple-Input and Single-Output |
| MPC | Model Predictive Control |
| PI | Proportional-Integral |
| PID | Proportional-Integral-Derivative |
| QFT | Quantitative Feedback Theory |
| SCADA | Supervisory Control And Data Acquisition |
| SISO | Single-Input and Single-Output |
References
- Rodríguez, F.; Berenguel, M.; Guzmán, J.L.; Ramírez-Arias, A. Modeling and Control of Greenhouse Crop Growth; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Davis, P. A technique of adaptive control of the temperature in a greenhouse using ventilator adjustments. J. Agric. Eng. Res. 1984, 29, 241–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunha, J.B.; Couto, C.; Ruano, A. Real-time parameter estimation of dynamic temperature models for greenhouse environmental control. Control Eng. Pract. 1997, 5, 1473–1481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Setiawan, A.; Albright, L.D.; Phelan, R.M. Simulation of greenhouse air temperature control using PI and PDF algorithms. IFAC Proc. Vol. 1998, 31, 111–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.; Xu, L.; Wei, R.; Zhu, B. Multi-objective control optimization for greenhouse environment using evolutionary algorithms. Sensors 2011, 11, 5792–5807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arvanitis, K.; Paraskevopoulos, P.; Vernardos, A. Multirate adaptive temperature control of greenhouses. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2000, 26, 303–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berenguel, M.; Yebra, L.; Rodríguez, F. Adaptive control strategies for greenhouse temperature control. In Proceedings of the 2003 European Control Conference (ECC), Cambridge, UK, 1–4 September 2003; pp. 2747–2752. [Google Scholar]
- Rodríguez, F.; Guzmán, J.; Berenguel, M.; Arahal, M. Adaptive hierarchical control of greenhouse crop production. Int. J. Adapt. Control. Signal Process. 2008, 22, 180–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senent, J.S.; Martinez, M.A.; Blasco, X.; Sanchis, J. MIMO predictive control of temperature and humidity inside a greenhouse using simulated annealing (SA) as optimizer of a multicriteria index. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Industrial, Engineering and Other Applications of Applied Intelligent Systems, Castellón, Spain, 1–4 June 1998; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1998; pp. 271–279. [Google Scholar]
- Blasco, X.; Martínez, M.; Herrero, J.M.; Ramos, C.; Sanchis, J. Model-based predictive control of greenhouse climate for reducing energy and water consumption. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2007, 55, 49–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gruber, J.; Guzmán, J.; Rodríguez, F.; Bordons, C.; Berenguel, M.; Sánchez, J. Nonlinear MPC based on a Volterra series model for greenhouse temperature control using natural ventilation. Control Eng. Pract. 2011, 19, 354–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ioslovich, I.; Gutman, P.O.; Seginer, I. A non-linear optimal greenhouse control problem with heating and ventilation. Optim. Control. Appl. Methods 1996, 17, 157–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linker, R.; Gutman, P.; Seginer, I. Robust controllers for simultaneous control of temperature and CO2 concentration in greenhouses. Control Eng. Pract. 1999, 7, 851–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoyo, A.; Moreno, J.C.; Guzman, J.L.; Rodríguez, F. Robust QFT-Based Feedback Linearization Controller of the Greenhouse Diurnal Temperature Using Natural Ventilation. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 64148–64161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fourati, F.; Chtourou, M. A greenhouse control with feed-forward and recurrent neural networks. Simul. Model. Pract. Theory 2007, 15, 1016–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, Y.; Ning, D.; Lai, Z.; Cheng, Q.; Mu, L. Neural networks based on PID control for greenhouse temperature. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2011, 27, 307–311. [Google Scholar]
- Pawlowski, A.; Guzman, J.L.; Rodríguez, F.; Berenguel, M.; Sánchez, J.; Dormido, S. Simulation of greenhouse climate monitoring and control with wireless sensor network and event-based control. Sensors 2009, 9, 232–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawlowski, A.; Guzmán, J.; Normey-Rico, J.; Berenguel, M. Improving feedforward disturbance compensation capabilities in Generalized Predictive Control. J. Process Control 2012, 22, 527–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajaoarisoa, L.H.; M’Sirdi, N.K.; Balmat, J.F. A case study of a hybrid controller design of a class of hybrid system application to a greenhouse micro-climate control. In Proceedings of the CCCA12, Marseilles, France, 6–8 December 2012; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Lafont, F.; Balmat, J.F. Optimized fuzzy control of a greenhouse. Fuzzy Sets Syst. 2002, 128, 47–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riahi, J.; Vergura, S.; Mezghani, D.; Mami, A. Intelligent Control of the Microclimate of an Agricultural Greenhouse Powered by a Supporting PV System. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez, F.; Berenguel, M.; Arahal, M. Feedforward controllers for greenhouse climate control based on physical models. In Proceedings of the 2001 European Control Conference (ECC), Porto, Portugal, 4–7 September 2001; pp. 2158–2163. [Google Scholar]
- Guzmán, J.L.; Hägglund, T. Simple tuning rules for feedforward compensators. J. Process Control 2011, 21, 92–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ljung, L. System Identification: Theory for the User, 2nd ed.; Prentice Hall PTR: Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Åström, K.J.; Hägglund, T.; Astrom, K.J. Advanced PID Control; ISA—The Instrumentation, Systems, and Automation Society: Research Triangle Park, NC, USA, 2006; Volume 461. [Google Scholar]
- Dahlin, E. Designing and tuning digital controllers. Instrum. Control Syst. 1968, 41, 77–83. [Google Scholar]
- Guzmán, J.L.; Hägglund, T.; Veronesi, M.; Visioli, A. Performance indices for feedforward control. J. Process Control 2015, 26, 26–34. [Google Scholar]
- Rodríguez, C.; Guzmán, J.L.; Berenguel, M.; Hägglund, T. Generalized feedforward tuning rules for non-realizable delay inversion. J. Process Control 2013, 23, 1241–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veronesi, M.; Guzmán, J.L.; Visioli, A.; Hägglund, T. Closed-loop tuning rules for feedforward compensator gains. IFAC-PapersOnLine 2017, 50, 7523–7528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

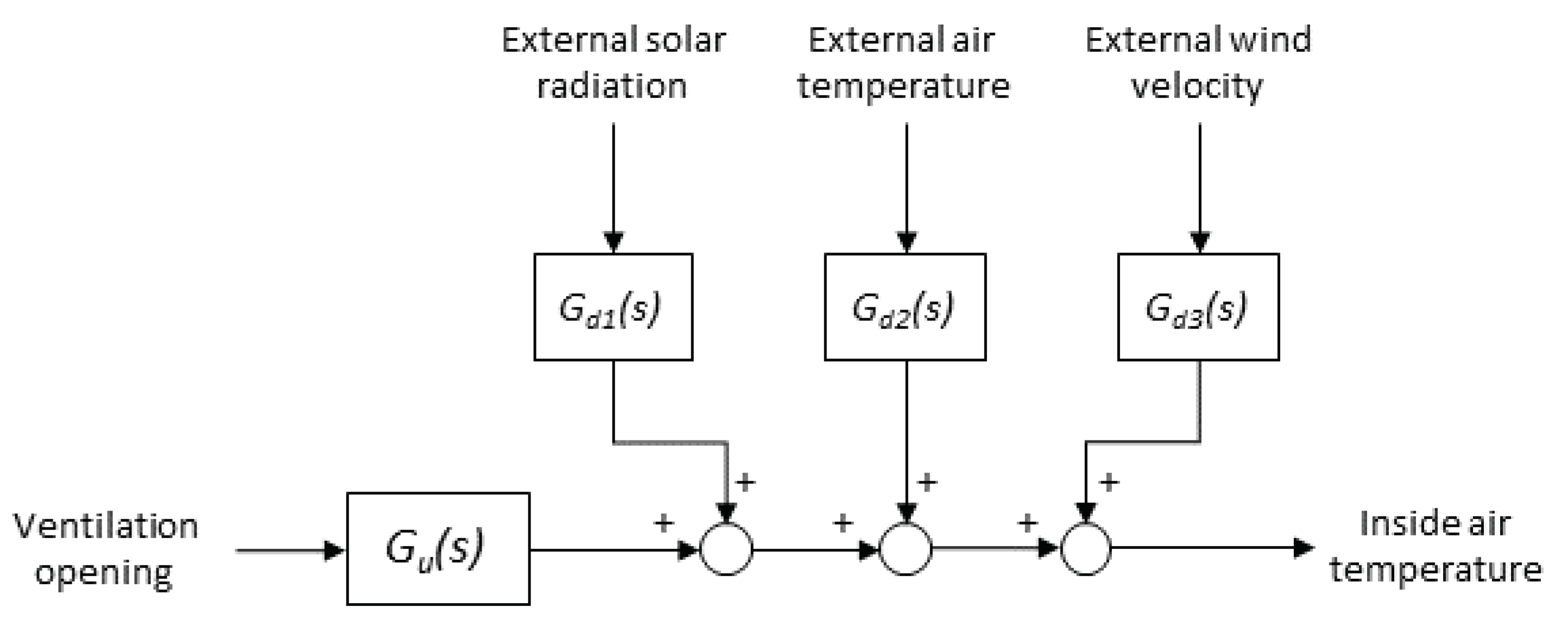
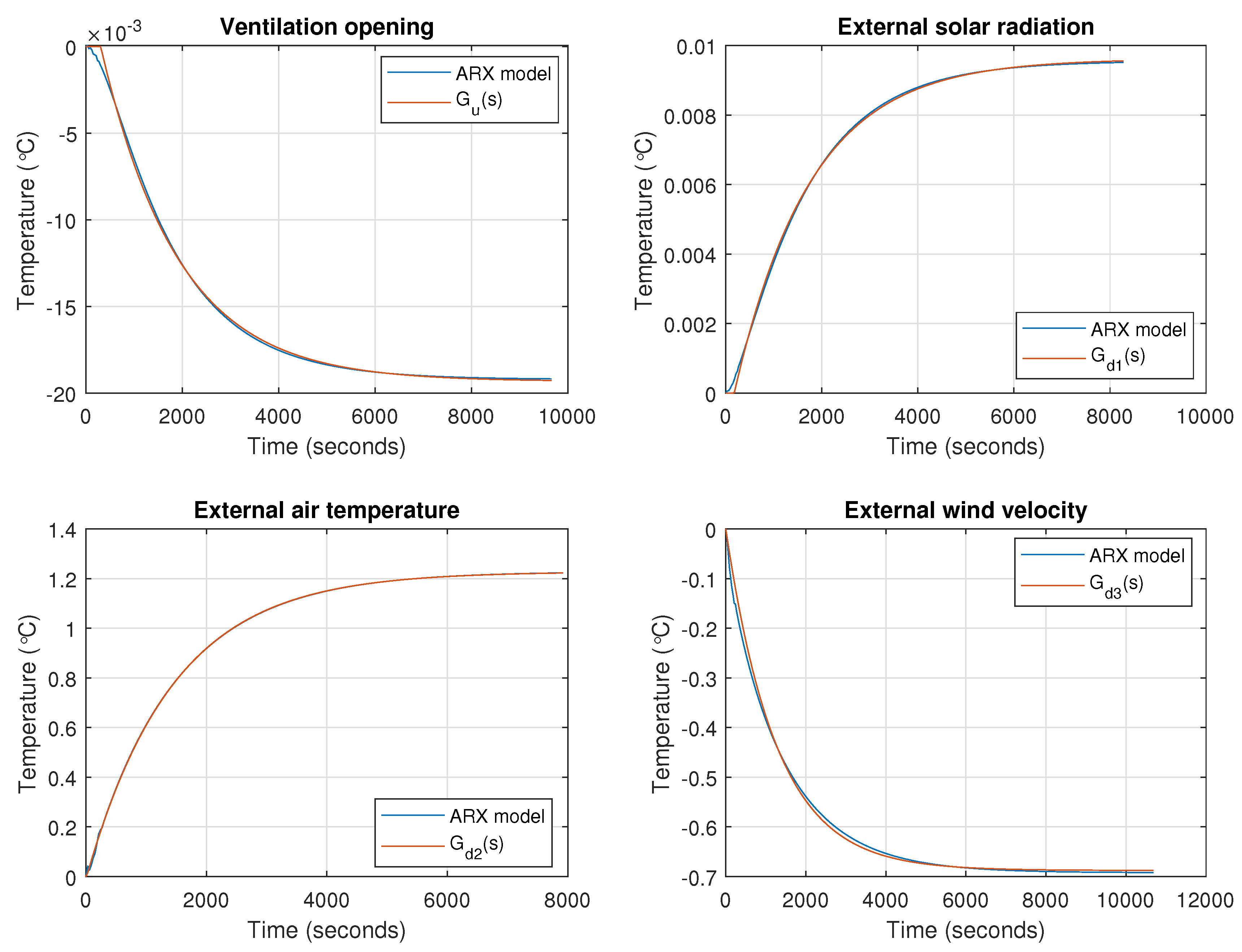
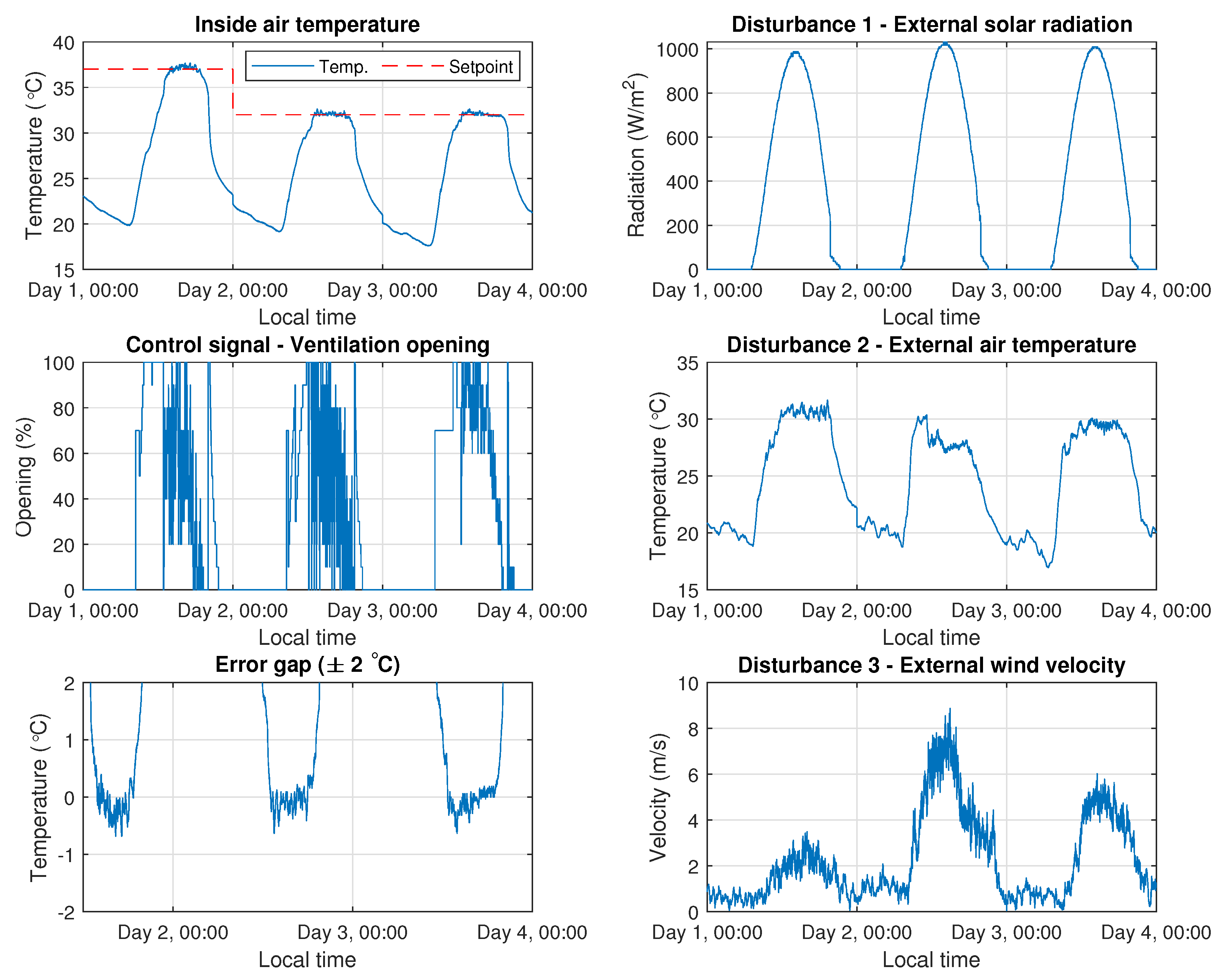
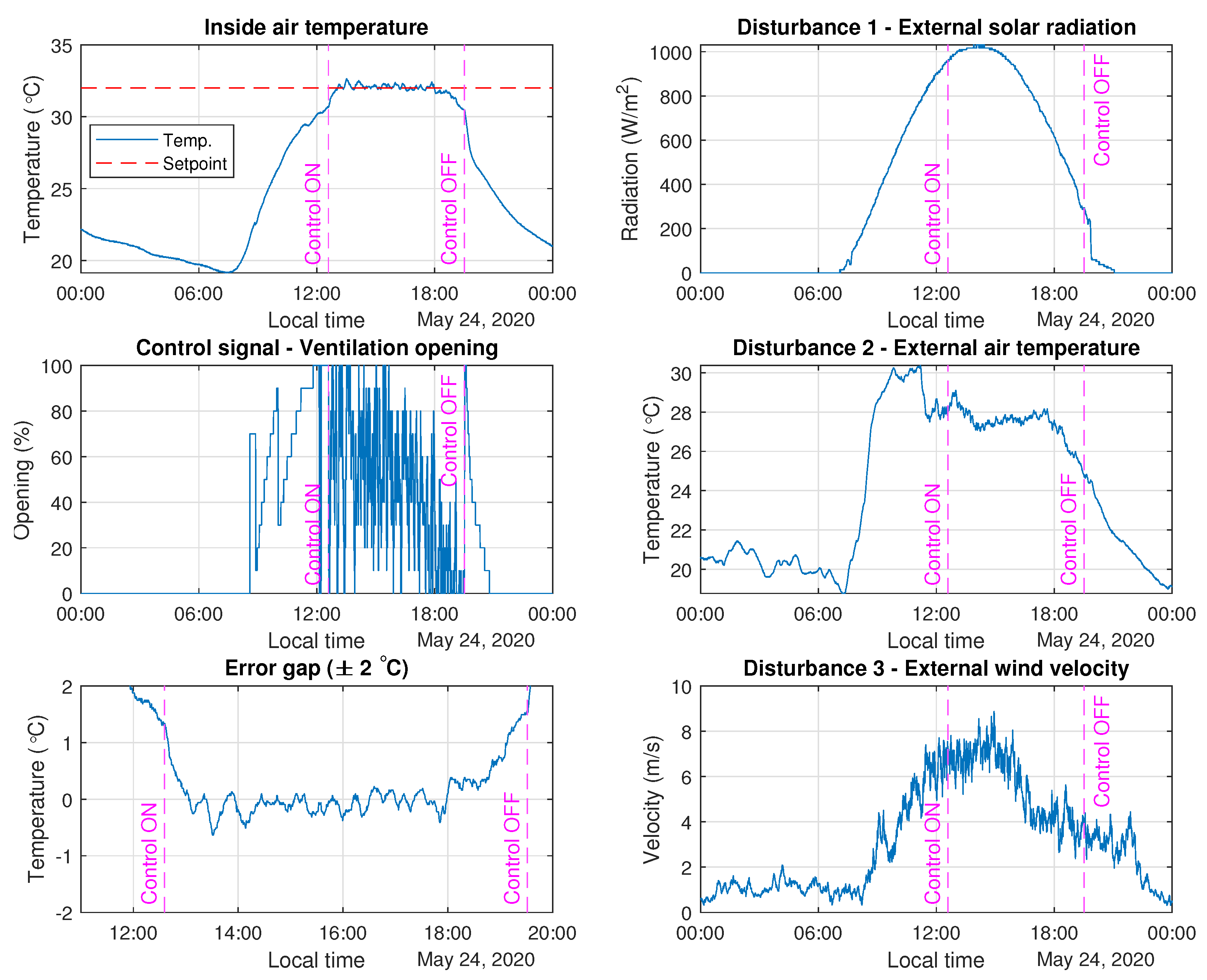
| Disturbance | Classical Approach | Simple Tuning Rules from Reference [23] |
|---|---|---|
| External solar radiation | ||
| External air temperature | ||
| External wind velocity |
| Control Strategy | IAE for 14 March 2020 | IAE for 1 May 2020 |
|---|---|---|
| PI controller | 168.98 | 55.88 |
| Classical FF | 115.12 | 18.67 |
| Simple tuning rules (FFr) | 114.91 | 15.27 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Montoya-Ríos, A.P.; García-Mañas, F.; Guzmán, J.L.; Rodríguez, F. Simple Tuning Rules for Feedforward Compensators Applied to Greenhouse Daytime Temperature Control Using Natural Ventilation. Agronomy 2020, 10, 1327. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy10091327
Montoya-Ríos AP, García-Mañas F, Guzmán JL, Rodríguez F. Simple Tuning Rules for Feedforward Compensators Applied to Greenhouse Daytime Temperature Control Using Natural Ventilation. Agronomy. 2020; 10(9):1327. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy10091327
Chicago/Turabian StyleMontoya-Ríos, Ana Paola, Francisco García-Mañas, José Luis Guzmán, and Francisco Rodríguez. 2020. "Simple Tuning Rules for Feedforward Compensators Applied to Greenhouse Daytime Temperature Control Using Natural Ventilation" Agronomy 10, no. 9: 1327. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy10091327
APA StyleMontoya-Ríos, A. P., García-Mañas, F., Guzmán, J. L., & Rodríguez, F. (2020). Simple Tuning Rules for Feedforward Compensators Applied to Greenhouse Daytime Temperature Control Using Natural Ventilation. Agronomy, 10(9), 1327. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy10091327








