Identification of Wheat Cultivars for Low Nitrogen Tolerance Using Multivariable Screening Approaches
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Materials and Field Experiments
2.2. Phenotypic Evaluation of Yield, Yield Components, and Physiological Traits
2.3. Evaluation of Various Yield Based Selection Indices
- Percentage reduction of grain yield (PRGY) = (Yield under high N − Yield under low N)/Yield under high N × 100 [24].
- Tolerance index (TOL) = (Yp − Ys) [25].
- Stress susceptible index (SSI) = (1 − Ys/Yp)/SI [19].Where Stress intensity (SI) was calculated as 1 − (Xs/Xp) and SSI value < 1 is more resistant to stress condition
- Geometric mean productivity (GMP) = (Ys × Yp)0.5 [26].
- Yield Stability Index (YSI) = Ys/Yp [20].Where Yp and Ys are the grain yield of a cultivar under high N and low N conditions, respectively. The Xp and Xs represents mean grain yield of all cultivars under high N and low N conditions, respectively.
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Analysis of Variance and Genotype × Year Interaction
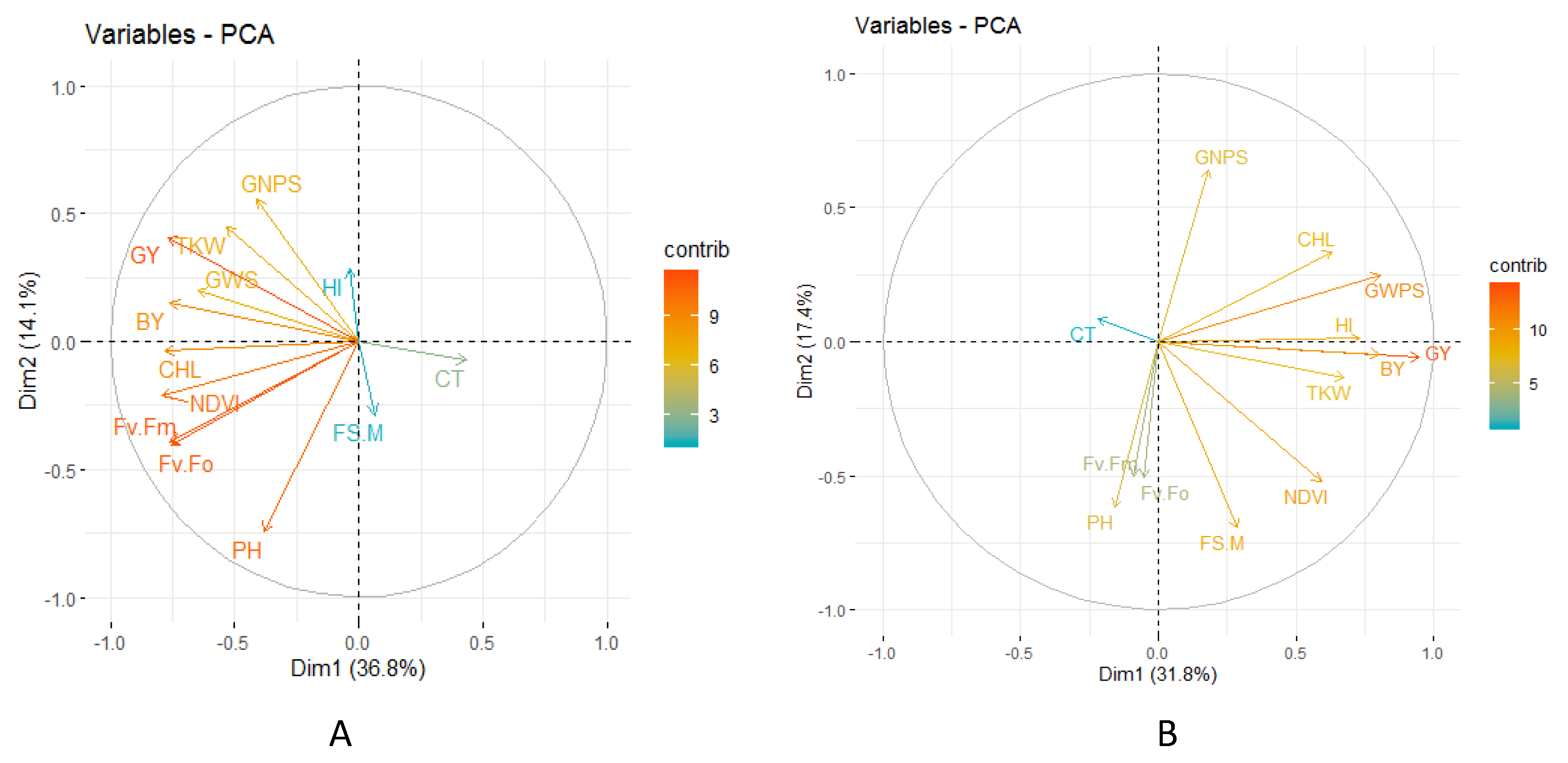
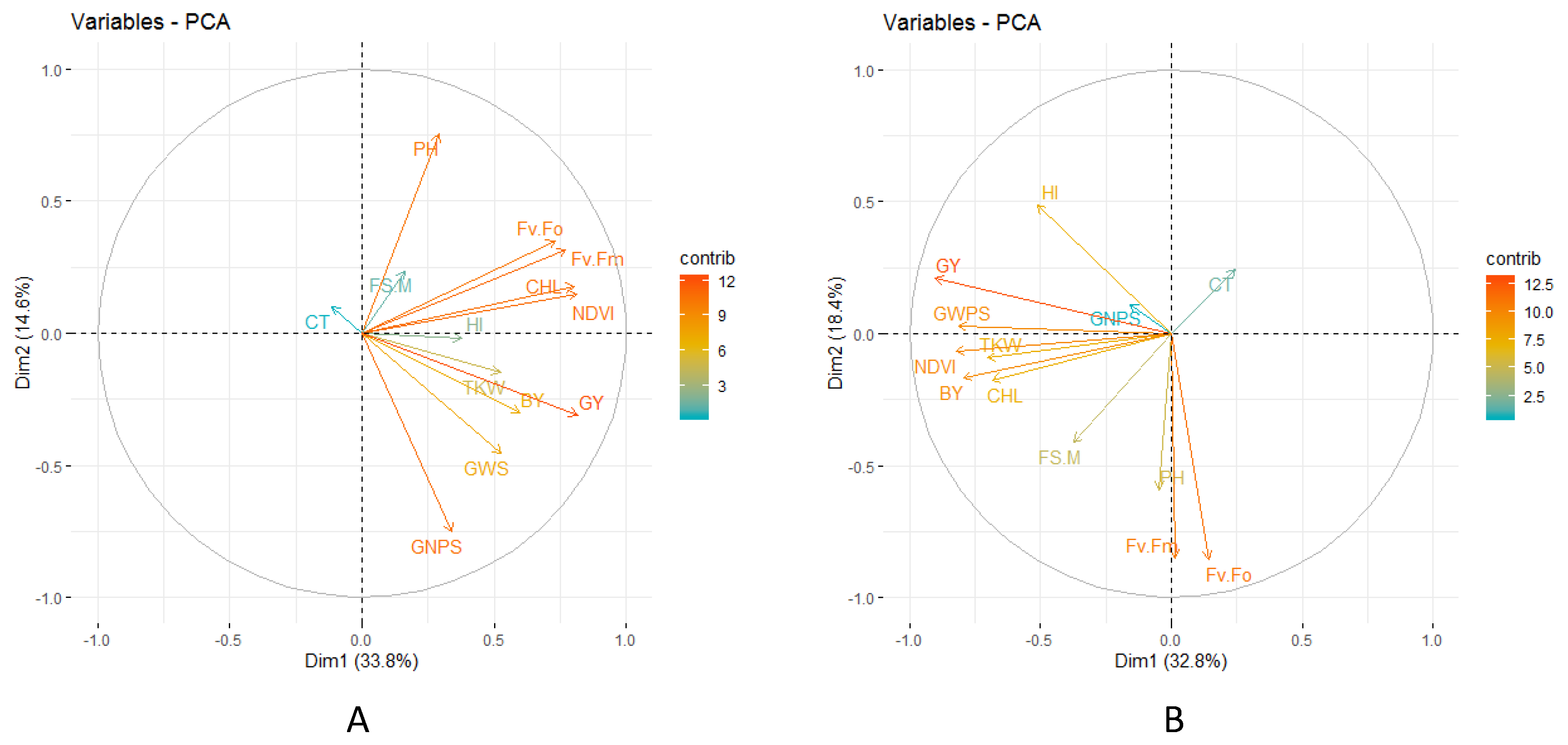
3.2. Phenotypic Variability
3.3. Yield Performance under High N and Low N Conditions
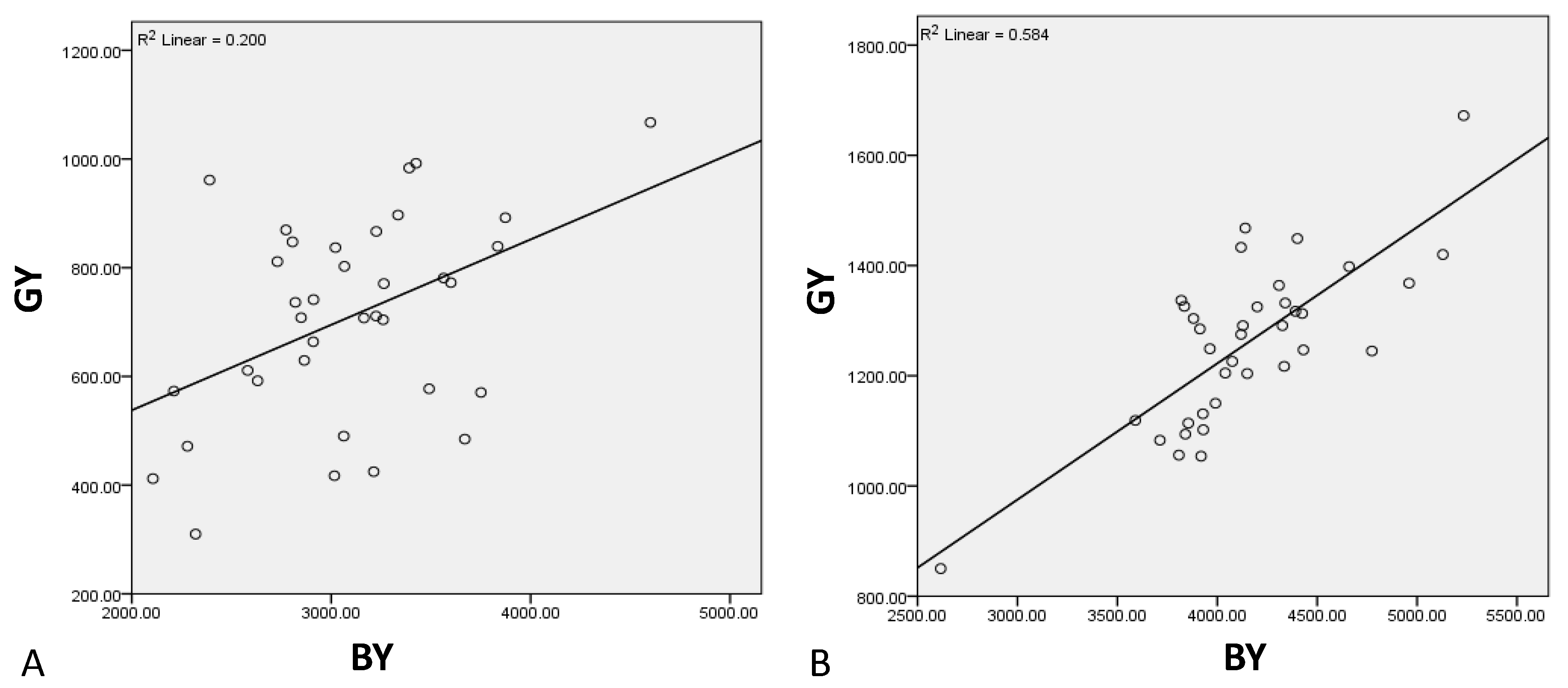
3.4. Correlation Studies
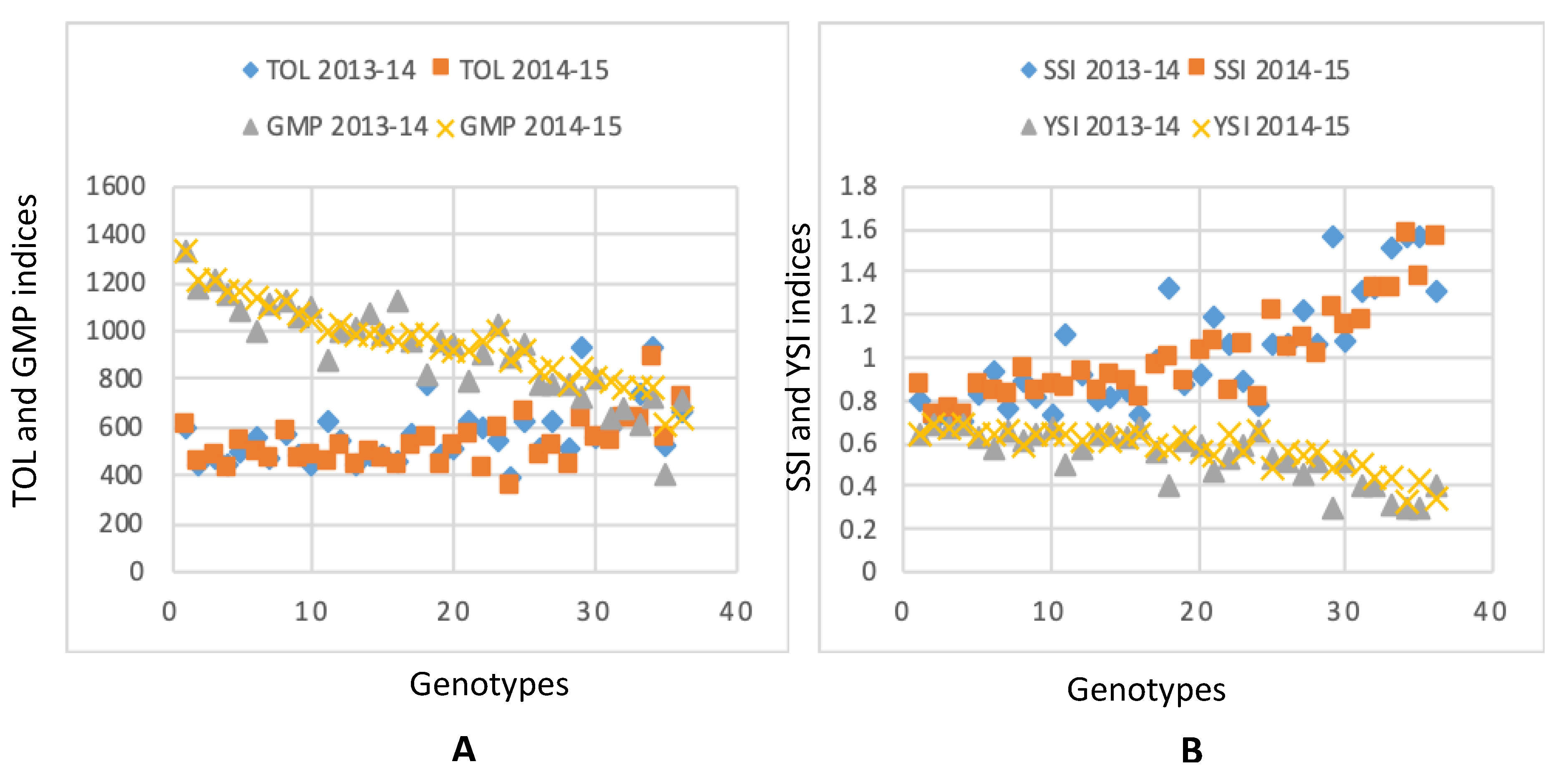
3.5. Phenotypic Variation in Yield Based Selection Indices
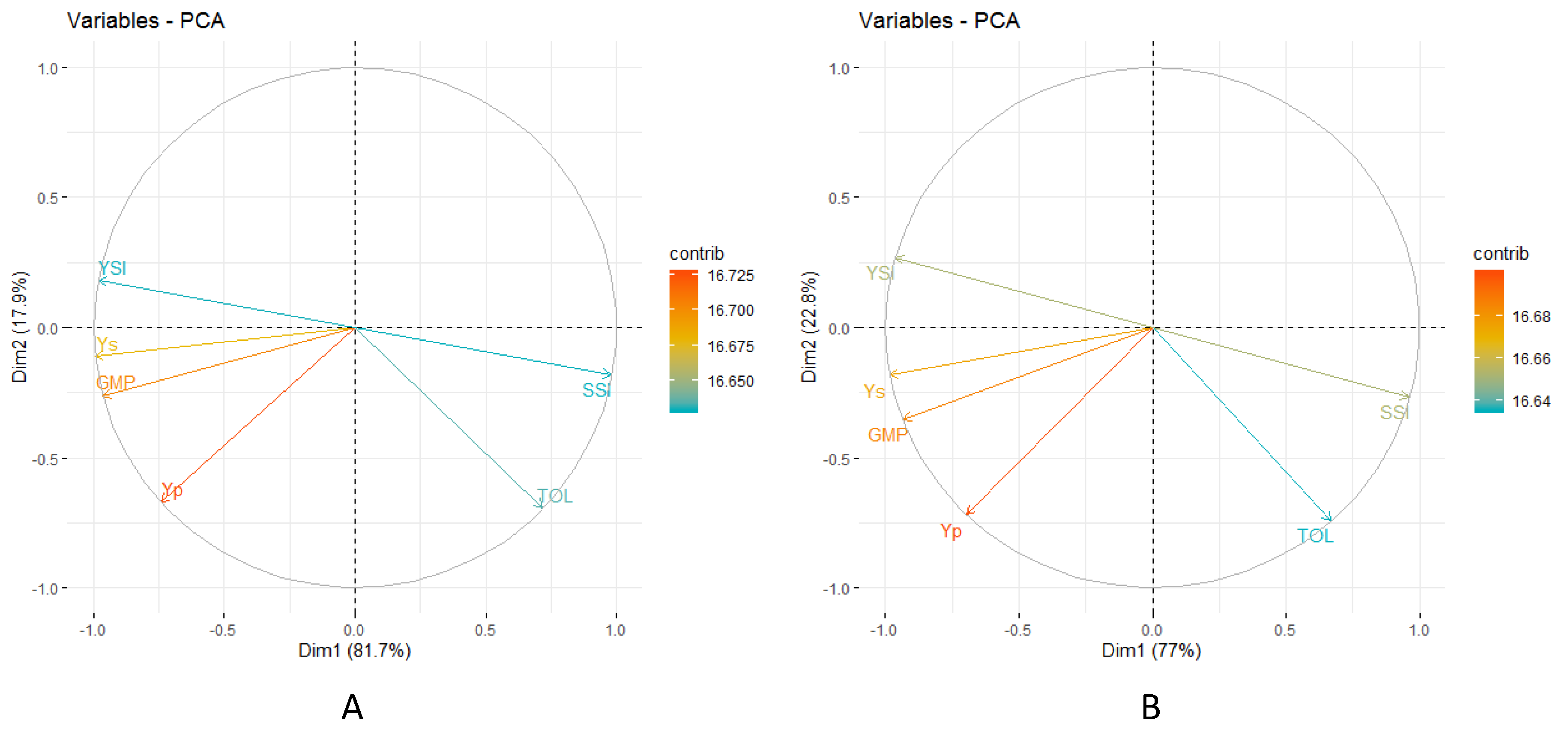
3.6. Correlation Studies for Selection Indices
3.7. Consistency of the Stress Tolerance Indices
3.8. Identification of Promising Cultivarsbased on Selection Indices
4. Discussion
4.1. Phenotypic Variation
4.2. Correlation Studies
4.3. Correlation Studies of Selection Indices
4.4. Consistency of the Tolerance Indices
4.5. Selection of Promising Cultivars Based on Selection Indices
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- FAO. FOASTAT, Food and Agriculture Data. 2016. Available online: http://www.fao.org/faostat (accessed on 20 November 2018).
- Hall, A.J.; Richards, R.A. Prognosis for genetic improvement of yield potential and water-limited yield of major grain crops. Field Crops Res. 2013, 143, 18–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodge, A.; Robinson, D.; Fitter, A. Are microorganisms more effective than plants at competing for nitrogen? Trends Plant Sci. 2000, 5, 304–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guarda, G.; Padovan, S.; Delogu, G. Grain yield, nitrogen use efficiency and baking quality of old and modern Italian bread-wheat cultivars grown at different nitrogen levels. Eur. J. Agron. 2004, 2, 181–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foulkes, M.; Hawkesford, M.; Barraclough, P.; Holdsworth, M.; Kerr, S.; Kightley, S.; Shewry, P. Identifying traits to improve the nitrogen economy of wheat: Recent advances and future pros pects. Field Crops Res. 2009, 114, 329–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swain, E.Y.; Leonidas, R.; Caroline, H.O.; Hall, G.; Chapman, R.; Almadni, M.; Elizabeth, A.S.; Kidd, J.; Carlo, L.; Julia, M. Optimizing nitrogen use efficiency in wheat and potatoes: Interactions between genotypes and agronomic practices. Euphytica 2014, 199, 119–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reynolds, M.; Foulkes, J.; Furbank, R.; Griffiths, S.; King, J.; Murchie, E.; Parry, M.; Slafer, G. Achieving yield gains in wheat. Plant Cell Environ. 2012, 35, 1799–1823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aisawi, K.; Reynolds, M.; Singh, R.; Foulkes, M. The physiological basis of the genetic progress in yield potential of CIMMYT spring wheat cultivars from 1966 to 2009. Crop Sci. 2015, 55, 1749–1764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moll, R.H.; Kamprath, E.J.; Jackson, W.A. Analysis and interpretation of factors which contribute to efficiency of nitrogen-utilization. Agron, J. 1982, 74, 562–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muurinen, S.; Slafer, G.A.; Peltonen-Sainio, P. Breeding effects on nitrogen use efficiency of spring cereals under northern conditions. Crop Sci. 2006, 46, 561–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barraclough, P.B.; Howarth, J.R.; Jones, J.; Lopez-Bellido, R.; Parmar, S.; Shepherd, C.E.; Hawkesford, M.J. Nitrogen efficiency of wheat: Genotypic and environmental variation and prospects for improvement. Eur. J. Agron. 2010, 33, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaju, O.; Allard, V.; Martre, P.; Snape, J.W.; Heumez, E.; LeGouis, J.; Moreau, D.; Bogard, M.; Griffiths, S.; Orford, S.; et al. Identification of traits to improve the nitrogen-use efficiency of wheat genotypes. Field Crops Res. 2011, 123, 139–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaju, O.; Allar, V.; Martre, P.; LeGouis, J.; Moreau, D.; Bogard, M.; Hubbart, S.; Foulkes, M.J. Nitrogen partitioning and remobilization in relation to leaf senescence, grain yield and grain nitrogen concentration in wheat cultivars. Field Crops Res. 2014, 155, 213–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brancourt-Hulmel, M.; Doussinault, G.; Lecomte, C.; Berard, P.; Le-Buanec, B.; Trottet, M. Genetic improvement of agronomic traits of winter wheat cultivars released in France from 1946 to 1992. Crop Sci. 2003, 43, 37–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cormier, F.; Faure, S.; Dubreuil, P.; Heumez, E.; Beauchene, K.; Lafarge, S.; Praud, S.; LeGouis, J. A multi-environmental study of recent breeding progress on nitrogen use efficiency in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Theor. Appl Genet. 2013, 126, 3035–3048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brancourt-Hulmel, M.; Heumez, E.; Pluchard, P.; Beghin, D.; Depatureaux, C.; Giraud, A.; Le, G.J. Indirect versus direct selection of winter wheat for low-input or high-input levels. Crop Sci. 2005, 45, 1427–1431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Przystalski, M.; Osman, A.M.; Thiemt, E.M.; Rolland, B.; Ericson, L.; Ostergard, H.; Levy, L.; Wolfe, M.S.; Buchse, A.; Piepho, H.P.; et al. Comparing the performance of cereal varieties in organic and non-organic cropping systems in different European countries. Euphytica 2008, 16, 417–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Annicchiarico, P.; Chiapparino, E.; Perenzin, M. Response of common wheat varieties to organic and conventional production systems across Italian locations and implications for selection. Field Crops Res. 2010, 116, 230–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, R.A.; Maurer, R. Drought resistance in spring wheat cultivars, 1. Grain yield responses. Aust. J. Agric. Res. 1978, 29, 897–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouslama, M.; Schapaugh, W.T. Stress tolerance in soybean. Part 1: Evaluation of three screening techniques for heat and drought tolerance. Crop Sci. 1984, 24, 933–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sio-Se Mardeh, A.; Ahmadi, A.; Poustini, K.; Mohammadi, V. Evaluation of drought resistance indices under various environmental conditions. Field Crops Res. 2006, 98, 222–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, G.; Singh, M.K.; Tyagi, B.S.; Singh, J.B.; Kumar, P. Germplasm characterization and selection indices in bread wheat for waterlogged soils in India. Indian J. Agric. Sci. 2017, 87, 1139–1148. [Google Scholar]
- Clarke, J.M.; Towenley-Smith, T.M.; McCaig, T.N.; Green, D.G. Growth analysis of spring wheat cultivars of varying drought resistance. Crop Sci. 1984, 24, 537–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choukan, R.; Taherkhani, T.; Ghannadha, M.R.; Khodarahmi, M. Evaluation of drought tolerance in grain maize inbred lines using drought tolerance indices. Iranian J. Crop Sci. 2006, 8, 79–89. [Google Scholar]
- Hossain, A.B.S.; Sears, A.G.; Cox, T.S.; Paulsen, G.M. Desiccation tolerance and its relationship to assimilate partitioning in winter wheat. Crop Sci. 1990, 30, 622–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez, G.C.J. Effective selection criteria for assessing plant stress tolerance. In Adaptation of Vegetables and Other Food Crops to Temperature Water Stress; Asian Vegetable Research and Development Center: Tainan, Taiwan, 1992; pp. 257–270. [Google Scholar]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Hitz, K.; Clark, J.A.; Sanford, D.A.V. Identifying nitrogen-use efficient soft red winter wheat lines in high and low nitrogen environments. Field Crops Res. 2017, 200, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarcevic, H.; Jukic, K.; Ikic, I.; Lovric, A. Estimation of quantitative genetic parameters for grain yield and quality in winter wheat under high and low nitrogen fertilization. Euphytica 2014, 199, 57–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, G.; Kulshreshtha, N.; Singh, B.N.; Setter, T.L.; Singh, M.K.; Saharan, M.S.; Tyagi, B.S.; Verma, A.; Sharma, I. Germplasm characterization, association and clustering for salinity and water logging tolerance in bread wheat (Triticum aestivum). Indian J. Agric. Sci. 2014, 84, 1102–1110. [Google Scholar]
- Richards, R.A. Defining selection criteria to improve yield under drought. Plant Growth Regul. 1996, 20, 157–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, A.K.; Mishra, B.; Chatrath, R.; Ortiz-Ferrara, G.; Singh, R.P. Wheat improvement in India: Present status, emerging challenges and future prospects. Euphytica 2007, 157, 431–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, J.M.; DePauw, R.M.; Townley-Smith, T.F. Evaluation of methods for quantification of drought tolerance in wheat. Crop Sci. 1992, 32, 728–7232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadi, R. Efficiency of yield-based drought tolerance indices to identify tolerant genotypes in durum wheat. Euphytica 2016, 211, 71–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, G.; Kumar, P.; Gupta, V.; Tyagi, B.S.; Singh, C.; Sharma, A.K.; Singh, G.P. Multivariate approach to identify and characterize bread wheat (Triticum aestivum) germplasm for waterlogging tolerance in India. Field Crops Res. 2018, 221, 81–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bansal, K.C.; Sinha, S.K. Assessment of drought resistance in 20 accessions of Triticum aestivum and related species total dry matter and grain yield stability. Euphytica 1991, 56, 7–14. [Google Scholar]
- Nagar, C.K.; Gayatri, B.A.; Sinha, S.K.; Venkatesh, K.; Mandal, P.K. Nitrogen stress induced changes in root system architecture (RSA) in diverse wheat (T. aestivum L.) genotypes at seedling stage. Wheat Barley Res. 2018, 10, 93–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Xu, Y.; Ma, B.; Nussinov, R. Structural and functional consequences of phosphate–arsenate substitutions in selected nucleotides: DNA, RNA, and ATP. J. Phys. Chem. 2012, 116, 4801–4811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pathak, R.R.; Ahmad, A.; Lochab, S.; Raghuram, N. Molecular physiology of plant nitrogen use efficiency and biotechnological options for its enhancement. Curr. Sci. 2008, 94, 1394–1403. [Google Scholar]
- Raghuram, N.; Sachdev, M.S.; Abrol, Y.P. Towards an integrative understanding of reactive nitrogen. Agric. Nitrogen Use Environ. Implic. 2007, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Mansour, E.; Merwad, A.M.A.; Yasin, M.A.T.; Abdul-Hamid, M.I.E.; El-Sobky, E.E.A.; Oraby, H.F. Nitrogen use efficiency in spring wheat: Genotypic variation and grain yield response under sandy soil conditions. J. Agric. Sci. 2017, 155, 1407–1423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Sr. No. | Variety | Pedigree | Year of Release | Production Condition |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | DPW 621-50 | KAUZ//ALTAR84/AOS/3/MILAN/KAUZ/4/HUITES | 2011 | TS, IR |
| 2 | MACS 3125 | RAJ 1555/CPAN6120 | 2003 | TS, RF |
| 3 | BH 1146* | EONTA PONTA GROSSA 1//FRETES/MARTIN | 1987 | - |
| 4 | GW 322 | PBW 173/GW 196 | 2002 | TS, IR |
| 5 | MACS 2496 | SERI”S” | 1991 | TS, IR |
| 6 | DBW 46* | PBW 343/INQ21 | 2011 | - |
| 7 | MACS 6222 | HD 2189*2//MACS 2496 | 2010 | TS, IR |
| 8 | K 0307 | K 8321/UP 2003 | 2007 | TS, IR |
| 9 | MACS 6478 | CS/TH.SC//3*PVN/3/MIRLO/BUC/4/MILAN/5/TILHI | 2014 | TS, IR |
| 10 | HD 2932 | KAUZ/STAR//HD 2643 | 2008 | TS, IR |
| 11 | Kharchia 65 | KHARCHIA LOCAL/EG 953 | 1970 | TS, IR |
| 12 | DBW 16 | RAJ 3765/WR 484//HUW 468 | 2006 | TS, IR |
| 13 | CBW 38 | CNDO/R143//ENTE/MEXI-2/3/Ae.SQUARROSA (TAUS)/4/WEAVER/5/2*PASTOR | 2008 | TS, IR |
| 14 | KRL 1-4 | KHARCHIA 65/WL 711 | 1990 | TS, IR |
| 15 | WH 1021 | NYOT 95/SONAK | 2007 | LS, IR |
| 16 | HI 8498 | CR ‘S’-GS’S’//A-9-30-1/RAJ 911 | 1999 | TS, IR |
| 17 | DBW 17 | CMH79A.95/3*CNO79//RAJ 3777 | 2007 | TS, IR |
| 18 | DBW 51 | SITE/MILAN | 2010 | LS, IR |
| 19 | PDW 314 | AJAIA 12/F3LOCAL(SEL.ETHIO.135.85)//PLATAI 13/3/SOMAT3/4/SOOTY/RASCON37 | 2010 | TS, IR |
| 20 | DBW 39 | ATTILA/HUI | 2010 | TS, IR |
| 21 | NW 1067 | TR 380-16-3-614/CHAT’S’ | 2004 | TS, IR |
| 22 | DBW 88 | KAUZ//ALTAR84/AOS/3/MILAN/KAUZ/4/HUITES | 2014 | TS, IR |
| 23 | KRL 210 | PBW65/2*PASTOR | 2010 | TS, IR |
| 24 | HW 2044 | HD 226*5/SUNSTAR*6/C-80-1 | 1999 | TS, IR |
| 25 | MACS 6273 | KAUZ*2/CHEN//BCN/MILAN | - | LS, IR |
| 26 | DBW 71 | PRINIA/UP 2425 | 2013 | LS, IR |
| 27 | KRL 213 | CNDO/R143//ENTE/MEXI-2/3AEGILOPS SQUARROSA(TAUS)/4/WEAVER/5/2*KAUZ | 2010 | TS, IR |
| 28 | NIAW 917 | GW 244/BOB WHITE | 2006 | TS, IR |
| 29 | NIAW 301 | SERI82/3/MRS/JUP//HOK’S’ | 2002 | TS IR |
| 30 | RAJ 4037 | DL 788-2/RAJ 3717 | 2004 | TS, IR |
| 31 | HD 2733 | ATTILA/3/TUI/CARC//CHEN/CHTO/4/ATILA | 2001 | TS, IR |
| 32 | RAJ 4238 | HW 2021/RAJ 3765 | 2012 | LS, IR |
| 33 | RAJ 4229 | HW 2048/RAJ 4000 | 2012 | TS, IR |
| 34 | DBW 14 | RAJ 3765/PBW 343 | 2002 | LS, IR |
| 35 | KRL 19 | PBW 255/KRL 1-4 | 2000 | TS, IR |
| 36 | HD 2967 | ALD/COC//USER/HD 2160M/HD2278 | 2011 | TS, IR |
| Source of Variation | df | Environment | Mean Sum of Square (MSS) | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PH (cm) | FS | TKW (g) | GNPS | GWPS | BY (g) | HI (%) | NDVI | CT | CHL (%) | FV/FM | FV/FO | GY (g) | |||
| Replication | 2 | High N | 1.61 | 2.56 | 6.00 * | 7.40 | 0.001 | 13,688.36 | 0.09 | 0.00 * | 0.07 | 53.40 ** | 0.00 | 0.07 * | 550.06 |
| Low N | 3.42 | 3.75 | 0.11 | 6.42 | 0.041 | 21,150.86 | 0.00 | 0.00 * | 0.13 | 29.74 ** | 0.00 ** | 0.13 | 1755.34 | ||
| Year | 1 | High N | 10.02 | 770.06 ** | 6.67 | 3.36 | 0.001 ** | 275,187.67 ** | 7.60 * | 0.03 * | 4.74 * | 1.28 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 2686.69 |
| Low N | 19.50 | 15.34 | 4.34 * | 158.34 * | 0.038 | 59,008.50 | 38.44 ** | 0.00 | 29.64 * | 3309.31 ** | 0.00 | 0.48 | 60,557.00 * | ||
| Genotypes | 35 | High N | 232.79 ** | 391.53 ** | 37.97 ** | 119.62 ** | 0.48 ** | 864,731.56 ** | 23.30 ** | 0.02 ** | 3.27 ** | 77.40 ** | 0.01 ** | 1.84 ** | 90,515.34 ** |
| Low N | 259.99 ** | 136.37 ** | 20.70 ** | 172.15 ** | 0.47 ** | 1,116,397.63 ** | 101.77 ** | 0.04 ** | 1.27 ** | 105.44 ** | 0.00 ** | 0.41 ** | 220,564.14 ** | ||
| Genotypes × Year | 35 | High N | 5.68 ** | 60.54 ** | 3.37 ** | 25.73 ** | 0.05 | 46,287.67 ** | 2.15 ** | 0.00 ** | 1.53 ** | 2.13 | 0.00 ** | 0.06 ** | 3978.23 |
| Low N | 8.97 ** | 6.16 | 2.52 * | 15.12 * | 0.03 | 50,134.57 ** | 5.33 ** | 0.01 ** | 0.19 | 45.69 ** | 0.00 * | 0.10 * | 8015.27 ** | ||
| Pooled error | 70 | High N | 2.82 | 21.10 | 2.04 | 6.18 | 0.04 | 21,365.51 | 0.97 | 0.00 | 0.09 | 2.71 | 0.00 | 0.01 | 3800.22 |
| Low N | 3.75 | 10.59 | 1.51 | 8.89 | 0.02 | 20,488.36 | 1.73 | 0.00 | 0.15 | 3.71 | 0.00 | 0.05 | 3424.94 | ||
| Year | Conditions | PH (cm) | FS | TKW (g) | GNPS | GWPS | BY (g) | HI (%) | NDVI | CT | CHL (%) | FV/FM | FV/FO | GY (g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2014 | High N | |||||||||||||
| Mean | 92.64 | 114.59 | 43.16 | 60.21 | 2.62 | 4103 | 30.67 | 0.756 | 22.45 | 45.58 | 0.778 | 3.807 | 1254 | |
| Minimum | 80.42 | 98.00 | 38.50 | 52.75 | 1.99 | 2215 | 26.28 | 0.605 | 21.13 | 31.05 | 0.615 | 2.200 | 749 | |
| Maximum | 118.33 | 145.00 | 55.50 | 75.50 | 3.50 | 5213 | 35.62 | 0.870 | 23.95 | 51.70 | 0.882 | 4.861 | 1682 | |
| Low N | ||||||||||||||
| Mean | 8401 | 78.94 | 39.29 | 55.00 | 2.32 | 3070 | 34.17 | 0.500 | 24.51 | 39.55 | 0.720 | 2.631 | 730 | |
| Minimum | 72.92 | 67.00 | 33.95 | 43.00 | 1.50 | 2063 | 23.03 | 0.313 | 23.15 | 33.73 | 0.650 | 1.890 | 370 | |
| Maximum | 115.00 | 92.50 | 45.32 | 66.50 | 3.15 | 4598 | 45.40 | 0.685 | 25.50 | 46.16 | 0.770 | 3.615 | 1066 | |
| RP | 9.21 | 31.37 | 9.11 | 8.65 | 11.80 | 25.68 | −11.42 | 34.60 | −9.23 | 13.66 | 7.45 | 30.96 | 45.70 | |
| 2015 | High N | |||||||||||||
| Mean | 93.24 | 109.87 | 43.59 | 59.95 | 2.63 | 4190 | 30.21 | 0.787 | 22.08 | 45.78 | 0.777 | 3.807 | 1263 | |
| Minimum | 84.00 | 91.50 | 35.50 | 44.50 | 2.02 | 3018 | 24.65 | 0.600 | 18.65 | 32.08 | 0.655 | 2.247 | 951 | |
| Maximum | 118.50 | 142.50 | 57.50 | 76.00 | 3.65 | 5330 | 35.31 | 0.885 | 24.60 | 50.15 | 0.892 | 4.825 | 1681 | |
| Low N | ||||||||||||||
| Mean | 83.25 | 78.27 | 39.62 | 52.92 | 2.29 | 3110 | 35.20 | 0.495 | 25.42 | 29.96 | 0.710 | 2.515 | 689 | |
| Minimum | 71.00 | 68.17 | 33.80 | 41.10 | 1.60 | 1925 | 24.58 | 0.330 | 24.10 | 17.67 | 0.640 | 1.871 | 220 | |
| Maximum | 115.00 | 91.50 | 44.50 | 70.50 | 3.00 | 4605 | 46.27 | 0.665 | 27.50 | 44.30 | 0.769 | 3.243 | 1069 | |
| RP | 10.80 | 28.87 | 9.16 | 11.82 | 13.02 | 26.20 | −16.53 | 37.68 | −15.13 | 35.43 | 8.58 | 33.73 | 42.76 | |
| Yp2014/Yp2015 | Ys2014/Ys2015 | TOL2014/TOL2015 | SSI2014/SSI2015 | GMP2014/GMP2015 | YSI2014/YSI2015 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.967 ** | 0.980 ** | 0.968 * | 0.979 ** | 0.983 ** | 0.979 ** |
| Statistics | High N (Yp) | Low N (Ys) | TOL | SSI | GMP | YSI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| W | 0.750 | 0.611 | 0.200 | 0.472 | 0.778 | 0.556 |
| 1-W | 0.250 | 0.389 | 0.800 | 0528 | 0.222 | 0.444 |
| Friedman’s χ2 test | 27.0 | 22.0 | 7.2 | 14.0 | 28.0 | 20.0 |
| p value | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.007 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tyagi, B.S.; Foulkes, J.; Singh, G.; Sareen, S.; Kumar, P.; Broadley, M.R.; Gupta, V.; Krishnappa, G.; Ojha, A.; Khokhar, J.S.; et al. Identification of Wheat Cultivars for Low Nitrogen Tolerance Using Multivariable Screening Approaches. Agronomy 2020, 10, 417. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy10030417
Tyagi BS, Foulkes J, Singh G, Sareen S, Kumar P, Broadley MR, Gupta V, Krishnappa G, Ojha A, Khokhar JS, et al. Identification of Wheat Cultivars for Low Nitrogen Tolerance Using Multivariable Screening Approaches. Agronomy. 2020; 10(3):417. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy10030417
Chicago/Turabian StyleTyagi, Bhudeva S., John Foulkes, Gyanendra Singh, Sindhu Sareen, Pradeep Kumar, Martin R. Broadley, Vikas Gupta, Gopalareddy Krishnappa, Ashish Ojha, Jaswant S. Khokhar, and et al. 2020. "Identification of Wheat Cultivars for Low Nitrogen Tolerance Using Multivariable Screening Approaches" Agronomy 10, no. 3: 417. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy10030417
APA StyleTyagi, B. S., Foulkes, J., Singh, G., Sareen, S., Kumar, P., Broadley, M. R., Gupta, V., Krishnappa, G., Ojha, A., Khokhar, J. S., King, I. P., & Singh, G. P. (2020). Identification of Wheat Cultivars for Low Nitrogen Tolerance Using Multivariable Screening Approaches. Agronomy, 10(3), 417. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy10030417





