The Potential for Improving Rice Yield and Nitrogen Use Efficiency in Smallholder Farmers: A Case Study of Jiangsu, China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Site Description and Data Collection
2.2. Database Description
2.2.1. Scenario Analysis
2.2.2. Potential Yield
2.2.3. Yield Gaps Analysis
2.2.4. Nitrogen Use Efficiency
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Measures of Yield and Nitrogen Status Amongst Surveyed Farmers
3.2. Assessing Yield Gaps and Nitrogen Use Efficiency Gaps
3.3. Closing Yield Gaps and Increasing NUE
4. Discussion
4.1. Yield Gaps and Nitrogen Use Efficiency Gaps
4.2. Narrowing Gaps of Yield and NUE
4.3. Analysis of Limiting Factors
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- FAO, Statistics Database. Available online: http://faostat.fao.org (accessed on 10 February 2020).
- Peng, S.; Tang, Q.; Zou, Y. Current status and challenges of rice production in China. Plant Prod. Sci. 2009, 12, 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J. China’s success in increasing per capita food production. J. Exp. Bot. 2011, 62, 3707–3711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lobell, D.B.; Cassman, K.G.; Field, C.B. Crop yield gaps: Their importance, magnitudes, and causes. Annu. Rev. Environ. Resour. 2009, 34, 179–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godfray, H.C.J.; Beddington, J.R.; Crute, I.R.; Haddad, L.; Lawrence, D.; Muir, J.F.; Pretty, J.; Robinson, S.; Thomas, S.M.; Toulmin, C. Food security: The challenge of feeding 9 billion people. Science 2010, 327, 812–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Tao, F.; Zhou, G. Potential yields, yield gaps, and optimal agronomic management practices for rice production systems in different regions of China. Agric. syst. 2019, 171, 100–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Cui, Z.; Fan, M.; Vitousek, P.; Zhao, M.; Ma, W.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, W.; Yan, X.; Yang, J. Producing more grain with lower environmental costs. Nature 2014, 514, 486–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keating, B.A.; Carberry, P.S.; Bindraban, P.S.; Asseng, S.; Meinke, H.; Dixon, J. Eco-efficient agriculture: Concepts, challenges, and opportunities. Crop Sci. 2010, 50, S-109–S-119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guilpart, N.; Grassini, P.; Sadras, V.O.; Timsina, J.; Cassman, K.G. Estimating yield gaps at the cropping system level. Field Crop. Res. 2017, 206, 21–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mills, G.; Sharps, K.; Simpson, D.; Pleijel, H.; Frei, M.; Burkey, K.; Emberson, L.; Uddling, J.; Broberg, M.; Feng, Z.; et al. Closing the global ozone yield gap: Quantification and cobenefits for multistress tolerance. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2018, 24, 4869–4893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- West, P.C.; Gerber, J.S.; Engstrom, P.M.; Mueller, N.D.; Brauman, K.A.; Carlson, K.M.; Cassidy, E.S.; Johnston, M.; MacDonald, G.K.; Ray, D.K. Leverage points for improving global food security and the environment. Science 2014, 345, 325–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- George, T. Why crop yields in developing countries have not kept pace with advances in agronomy. Glob. Food Secur. Agric. Policy 2014, 3, 49–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pampolino, M.F.; Manguiat, I.J.; Ramanathan, S.; Gines, H.C.; Tan, P.S.; Chi, T.T.N.; Rajendran, R.; Buresh, R.J. Environmental impact and economic benefits of site-specific nutrient management (SSNM) in irrigated rice systems. Agric. Syst. 2007, 93, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Dou, Z.; He, P.; Ju, X.; Powlson, D.; Chadwick, D.; Norse, D.; Lu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, L.; et al. New technologies reduce greenhouse gas emissions from nitrogenous fertilizer in China. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 8375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robertson, M.J.; Lyle, G.; Bowden, J.W. Within-field variability of wheat yield and economic implications for spatially variable nutrient management. Field Crop. Res. 2008, 105, 211–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Liu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Shen, J.; Han, W.; Zhang, W.; Christie, P.; Goulding, K.W.T.; Vitousek, P.; Zhang, F. Significant acidification in major Chinese croplands. Science 2010, 327, 1008–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayer, J.; Cassman, K.G. Agricultural innovation to protect the environment. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 8345–8348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, M.; Shen, J.; Yuan, L.; Jiang, R.; Chen, X.; Davies, W.J.; Zhang, F. Improving crop productivity and resource use efficiency to ensure food security and environmental quality in China. J. Exp. Bot. 2012, 63, 13–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, N.; Wei, W.; Qiao, L.; Zhang, F.; Christie, P.; Jiang, R.; Dobermann, A.; Goulding, K.W.T.; Fan, J.; Fan, M. Agronomic and environmental causes of yield and nitrogen use efficiency gaps in Chinese rice farming systems. Eur. J. Agron. 2018, 93, 40–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cassman, K.G.; Dobermann, A.; Walters, D.T.; Yang, H. Meeting cereal demand while protecting natural resources and improving environmental quality. Annu. Rev. Environ. Resour. 2003, 28, 315–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Davidson, E.A.; Mauzerall, D.L.; Searchinger, T.D.; Dumas, P.; Shen, Y. Managing nitrogen for sustainable development. Nature 2015, 528, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mueller, N.D.; Gerber, J.S.; Johnston, M.; Ray, D.K.; Ramankutty, N.; Foley, J.A. Closing yield gaps through nutrient and water management. Nature 2012, 490, 254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- An, N.; Fan, M.; Zhang, F.; Christie, P.; Yang, J.; Huang, J.; Guo, S.; Shi, X.; Tang, Q.; Peng, J. Exploiting co-benefits of increased rice production and peduced greenhouse gas emission through optimized crop and soil management. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0140023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Affholder, F.; Poeydebat, C.; Corbeels, M.; Scopel, E.; Tittonell, P. The yield gap of major food crops in family agriculture in the tropics: Assessment and analysis through field surveys and modelling. Field Crop. Res. 2013, 143, 106–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Cao, G.; Li, X.; Zhang, H.; Wang, C.; Liu, Q.; Chen, X.; Cui, Z.; Shen, J.; Jiang, R.; et al. Closing yield gaps in China by empowering smallholder farmers. Nature 2016, 537, 671–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, W.; Xu, X.; He, P.; Ullah, S.; Zhang, J.; Cui, Z.; Zhou, W. Improving yield and nitrogen use efficiency through alternative fertilization options for rice in China: A meta-analysis. Field Crop. Res. 2018, 227, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linquist, B.A.; Liu, L.; Kessel, C.V.; Groenigen, K.J.V. Enhanced efficiency nitrogen fertilizers for rice systems: Meta-analysis of yield and nitrogen uptake. Field Crop. Res. 2013, 154, 246–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, S.; Buresh, R.J.; Huang, J.; Zhong, X.; Zou, Y.; Yang, J.; Wang, G.; Liu, Y.; Hu, R.; Tang, Q. Improving nitrogen fertilization in rice by site-specific N management. A review. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2010, 30, 649–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; He, P.; Zhao, S.; Qiu, S.; Johnston, A.M.; Zhou, W. Quantification of yield gap and nutrient use efficiency of irrigated rice in China. Field Crop. Res. 2016, 186, 58–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nhamo, N.; Rodenburg, J.; Zenna, N.; Makombe, G.; Luzi-Kihupi, A. Narrowing the rice yield gap in East and Southern Africa: Using and adapting existing technologies. Agric. Syst. 2014, 131, 45–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobermann, A.; Witt, C.; Dawe, D.; Abdulrachman, S.; Gines, H.C.; Nagarajan, R.; Satawathananont, S.; Son, T.T.; Tan, P.S.; Wang, G.H. Site-specific nutrient management for intensive rice cropping systems in Asia. Field Crop. Res. 2002, 74, 37–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lassaletta, L.; Billen, G.; Garnier, J.; Bouwman, L.; Velazquez, E.; Mueller, N.D.; Gerber, J.S. Nitrogen use in the global food system: Past trends and future trajectories of agronomic performance, pollution, trade, and dietary demand. Environ. Res. Lett. 2016, 11, 095007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NBSC, National Bureau of Statistics of China. China Statistical Yearbook 2015; Statistical Press: Beijing, China, 2015.
- Guo, J.; Hu, X.; Gao, L.; Xie, K.; Ling, N.; Shen, Q.; Hu, S.; Guo, S. The rice production practices of high yield and high nitrogen use efficiency in Jiangsu, China. Sci Rep. 2017, 7, 2101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, Z.; Zhang, H.; Chen, X.; Zhang, C.; Ma, W.; Huang, C.; Zhang, W.; Mi, G.; Miao, Y.; Li, X.; et al. Pursuing sustainable productivity with millions of smallholder farmers. Nature 2018, 555, 363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, J.; Zhang, H.; Li, J.; Dai, Q.G.; Huo, Z.Y.; Xu, k.; Li, D.; Hua, Z.; Sha, A.; Zhou, Y.; et al. Progress in research on patterns and systematic theories of super-high-yielding cultivation in rice. Chin. J. Rice Sci. 2010, 24, 417–424. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, G.; Gao, J.; Zhao, M.; Dong, S.; Li, S.; Yang, Q.; Liu, Y.; Wang, L.; Xue, J.; Liu, J. Distribution, yield structure, and key cultural techniques of maize super-high yield plots in recent years. Acta Agron. Sinica 2013, 38, 80–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Cao, W.; Qian, H.; Xing, Z.; Zhang, H.; Dai, Q.; Huo, Z.; Xu, K.; Wei, H.; Guo, B. Effect of planting density of mechanically transplanted pot seedlings on yield, plant type and lodging resistance in rice with different panicle types. Acta Agron. Sinica 2015, 41, 743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tittonell, P.; Vanlauwe, B.; Corbeels, M.; Giller, K.E. Yield gaps, nutrient use efficiencies and response to fertilisers by maize across heterogeneous smallholder farms of western Kenya. Plant. Soil 2008, 313, 19–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, W.; Carberry, P.; Wang, G.; Lü, R.; Lü, H.; Xia, A. Quantifying the yield gap in wheat–maize cropping systems of the Hebei Plain, China. Field Crop. Res. 2011, 124, 180–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Q.; Hou, P.; Wu, L.; Chen, X.; Cui, Z.; Zhang, F. Understanding production potentials and yield gaps in intensive maize production in China. Field Crop. Res. 2013, 143, 91–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, J.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, H.; Li, Z.; Zhou, Q.; Yu, C.; Kong, X.; Liu, L.; Wang, Z.; Yang, J. Canopy light and nitrogen distributions are related to grain yield and nitrogen use efficiency in rice. Field Crop. Res. 2017, 206, 74–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Chen, X.; Cui, Z.; Meng, Q.; Zhao, M. Research advance in yield potential and yield gap of three major cereal crops. Chin. J. Eco-Agric. 2015, 23, 525–534. [Google Scholar]
- Cassman, K.G.; Dobermann, A.; Walters, D.T. Agroecosystems, nitrogen-use Efficiency, and nitrogen management. Ambio 2002, 31, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fageria, N.K.; Baligar, V.C. Enhancing nitrogen use efficiency in crop plants. Adv. Agron. 2005, 88, 97–185. [Google Scholar]
- Cassman, K.G.; Gines, G.C.; Dizon, M.A.; Samson, M.I.; Alcantara, J.M. Nitrogen-use efficiency in tropical lowland rice systems: Contributions from indigenous and applied nitrogen. Field Crop. Res. 1996, 47, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Noordwijk, M.; Brussaard, L. Minimizing the ecological footprint of food: Closing yield and efficiency gaps simultaneously? Curr. Opin. Environ. Sustain. 2014, 8, 62–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grassini, P.; Eskridge, K.M.; Cassman, K.G. Distinguishing between yield advances and yield plateaus in historical crop production trends. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 2918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, M.; Lu, S.; Jiang, R.; Liu, X.; Zhang, F. Triangular transplanting pattern and split nitrogen fertilizer application increase rice yield and nitrogen fertilizer recovery. Agron. J. 2009, 101, 1421–1425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, X.T.; Xing, G.X.; Chen, X.P.; Zhang, S.L.; Zhang, L.J.; Liu, X.J.; Cui, Z.L.; Yin, B.; Christie, P.; Zhu, Z.L. Reducing environmental risk by improving N management in intensive Chinese agricultural systems. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 3041–3046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, Y.; Stewart, B.A.; Zhang, F. Long-term experiments for sustainable nutrient management in China. A review. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2011, 31, 397–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobermann, A.; Fairhurst, T.H. Rice: Nutrient Disorders and Nutrient Management; Potash and Phosphate Institute: Singapore; IRRI: Manila, Philippines, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Dobermann, A.; Krauss, A.; Isherwood, K.; Heffer, P. Nutrient use efficiencymeasurement and management. In Fertilizer Best Management Practices. General Principles, Strategy for Their Adoption and Voluntary Initiatives vs. Regulations, IFA International Workshop on Fertilizer Best Management Practices, Brussels, Belgium, 7–9 March 2007; International Fertilizer Industry Association (IFA): Paris, France, 2007; pp. 1–28. [Google Scholar]
- Laborte, A.G.; de Bie, K.; Smaling, E.M.A.; Moya, P.F.; Boling, A.A.; Van Ittersum, M.K. Rice yields and yield gaps in Southeast Asia: Past trends and future outlook. Eur. J. Agron. 2012, 36, 9–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Ittersum, M.K.; Cassman, K.G.; Grassini, P.; Wolf, J.; Tittonell, P.; Hochman, Z. Yield gap analysis with local to global relevance—A review. Field Crops Res. 2013, 143, 4–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, M.; Lu, S.; Jiang, R.; Liu, X.; Zeng, X.; Goulding, K.W.T.; Zhang, F. Nitrogen input, 15N balance and mineral N dynamics in a rice–wheat rotation in southwest China. Nutr. Cycl. Agroecosyst. 2007, 79, 255–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, L.; Yu, Y.; Yang, L. Maintaining yields and reducing nitrogen loss in rice-wheat rotation system in Taihu Lake region with proper fertilizer management. Environ. Res. Lett. 2014, 9, 115010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, L.; Xia, Y.; Li, B.; Wang, J.; Wang, S.; Zhou, W.; Yan, X. Integrating agronomic practices to reduce greenhouse gas emissions while increasing the economic return in a rice-based cropping system. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2016, 231, 24–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Yao, Y.; Zhao, M.; Zhang, B.; Tian, Y.; Yin, B.; Zhu, Z. Integration of urea deep placement and organic addition for improving yield and soil properties and decreasing N loss in paddy field. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2017, 247, 236–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Zhang, M.; Li, Y.C.; Fan, X.; Geng, Y. Controlled release urea improved nitrogen use efficiency, activities of leaf enzymes, and rice yield. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2012, 76, 2307–2317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkinson, S.; Bacon, M.A.; Davies, W.J. Nitrate signalling to stomata and growing leaves: Interactions with soil drying, ABA, and xylem sap pH in maize. J. Exp. Bot. 2007, 58, 1705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, M.; Cui, Z.; Chen, X.; Jiang, R.; Zhang, F. Integrated nutrient management for improving crop yields and nutrient utilization efficiencies in China. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2008, 63, 126–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hati, K.M.; Mandal, K.G.; Misra, A.K.; Ghosh, P.K.; Bandyopadhyay, K.K. Effect of inorganic fertilizer and farmyard manure on soil physical properties, root distribution, and water-use efficiency of soybean in Vertisols of central India. Bioresour. Technol. 2006, 97, 2182–2188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azadi, H.; Schoonbeek, S.; Mahmoudi, H.; Derudder, B.; Maeyer, P.D.; Witlox, F. Organic agriculture and sustainable food production system: Main potentials. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2011, 144, 92–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, L.; Lam, S.K.; Yan, X.; Chen, D. How does recycling of livestock manure in agroecosystems affect crop productivity, reactive nitrogen losses and soil carbon balance? Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 7450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, L.; Shu, K.L.; Chen, D.; Wang, J.; Quan, T.; Yan, X. Can knowledge-based N management produce more staple grain with lower greenhouse gas emission and reactive nitrogen pollution? A meta-analysis. Global Change Biol. 2017, 23, 1917–1925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Chen, X.; Chen, Q. Guidelines for fertilization of major crops in China; China Agricultural Press: Beijing, China, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Zhen, L.; Zoebisch, M.A.; Chen, G.; Feng, Z. Sustainability of farmers’ soil fertility management practices: A case study in the North China Plain. J. Environ. Manag. 2006, 79, 409–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, X.; Gu, B.; Wu, Y.; Galloway, J.N. Reducing China’s fertilizer use by increasing farm size. Global Environ. Chang. 2016, 41, 26–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CSAC, The Office of China’s Second Agricultural Census. Compilation of China’s Second Agricultural Census; China Statistics Press: Beijing, China, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Foster, A.D.; Rosenzweig, M.R. Are there too many farms in the world? Labor-market transaction costs, machine capacities and optimal farm size. Soc. Sci. Electron. Publ. 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Y.; Xi, X.; Tang, X.; Luo, D.; Gu, B.; Lam, S.K.; Vitousek, P.M.; Chen, D. Policy distortions, farm size, and the overuse of agricultural chemicals in China. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, 7010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, R. Empirical study on the factors influencing rape framers’ adoption of new variety. Econom. Perspect. 2011, 8, 146–147. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, J.H.; Tang, L.Q.; Yu, X. Estimating the average treatment effect of adopting stress tolerant variety on rice yield in China. J. Integr. Agric. 2018, 17, 940–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Huang, Z.; Jia, X.; Hu, R.; Xiang, C. Long-term reduction of nitrogen fertilizer use through knowledge training in rice production in China. Agric. Syst. 2015, 135, 105–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Government of India. Literates and literacy Rate, Primary Census Data Highlights; Census of India: New Delhi, India, 2011; pp. 45–55.
- Government of Kerala. Agriculture and Allied Sectors, Economic Review, State Planning Board; Trivandrum, India, 2010.
- Wang, X.; Li, T.; Yang, X.; Zhang, T.; Liu, Z.; Guo, E.; Liu, Z.; Qu, H.; Chen, X.; Wang, L.; et al. Rice yield potential, gaps and constraints during the past three decades in a climate-changing Northeast China. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2018, 259, 173–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
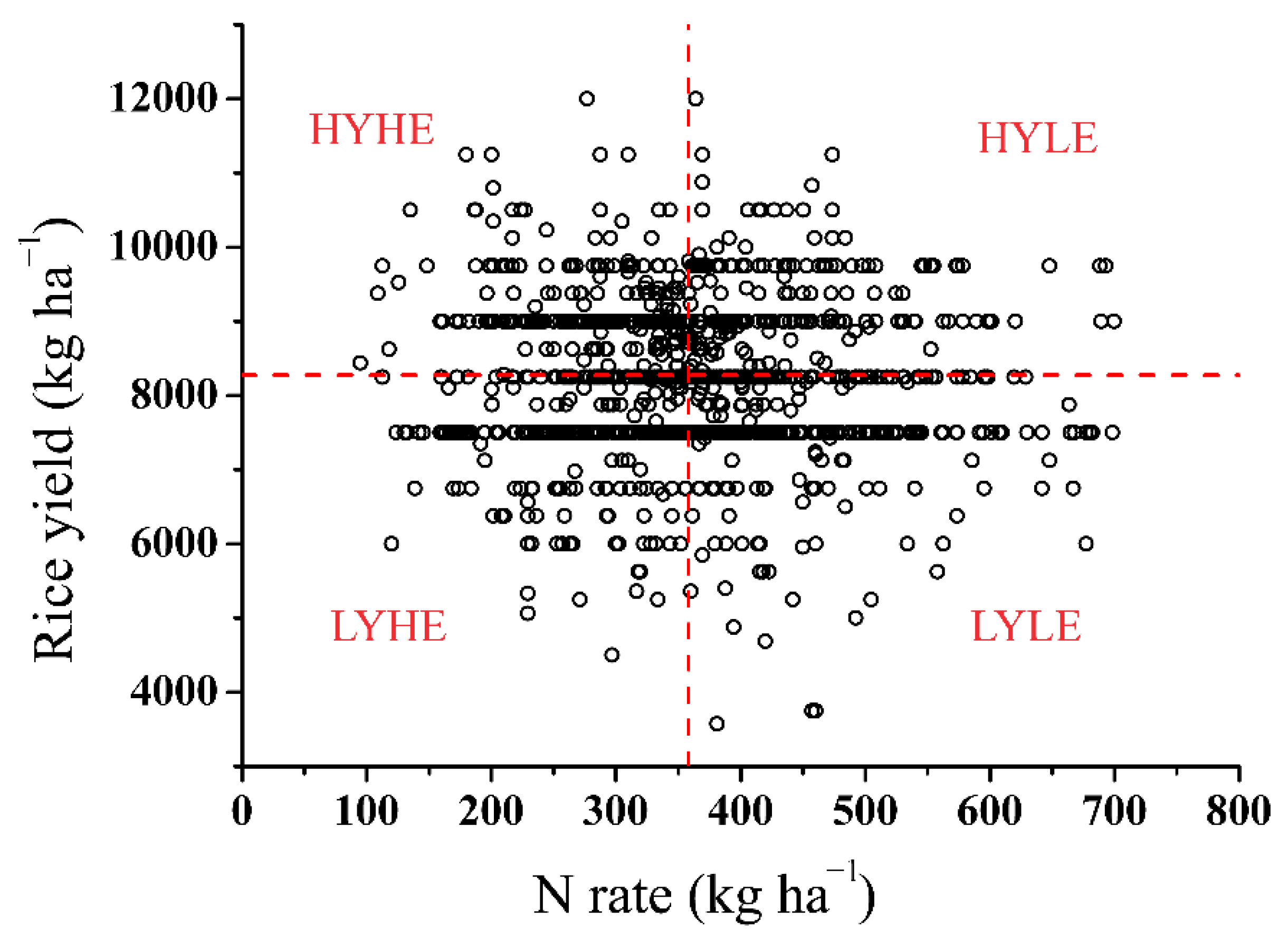


| Farmers’ Production Level a | N Range b (kg ha−1) | Yield Range c (kg ha−1) | Yield (kg ha−1) | N Rate (kg ha−1) | PFPN (kg kg−1) | Percentage of Farmers (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HYHE | <358 | >8273 | 9231a | 286c | 34.0a | 23.1 |
| LYHE | <358 | <8273 | 7537b | 289c | 27.2b | 30.6 |
| HYLE | >358 | >8273 | 9310a | 432b | 22.0c | 19.0 |
| LYLE | >358 | <8273 | 7568b | 446a | 17.4d | 27.3 |
| Farmers’ Production Level a | Jiangsu-Average | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HYHE | LYHE | HYLE | LYLE | |||
| Yields (kg ha−1) and PFPN (kg kg−1) | Average farmers’ yield (PFPN) | 9231 (34.0) | 7537 (27.2) | 9310 (22.0) | 7568 (17.4) | 8273 (23.1) |
| Best farmers’ yield (PFPN) | 10443 (34.6) | 10443 (34.6) | 10443 (34.6) | 10443 (34.6) | 10443 (34.6) | |
| Experimental yield (PFPN) | 12710 (47.1) | 12710 (47.1) | 12710 (47.1) | 12710 (47.1) | 12710 (47.1) | |
| Highest recorded yield (PFPN) | 14540 (48.5) | 14540 (48.5) | 14540 (48.5) | 14540 (48.5) | 14540 (48.5) | |
| Yield gap (kg ha−1) and PFPN gap (kg kg−1) | Gap F | 1212 (0.6) | 2906 (7.4) | 1133 (12.6) | 2875 (17.2) | 2170 (11.5) |
| Gap E | 3479 (13.1) | 5173 (19.9) | 3400 (25.1) | 5142 (29.7) | 4437 (24.0) | |
| Gap R | 5309 (14.5) | 7003 (23.1) | 5230 (26.5) | 6972 (31.1) | 6267 (25.4) | |
| Average yield or PFPN as % of | Best farmers’ yield (PFPN) | 88 (98) | 72 (79) | 89 (64) | 72 (50) | 79 (67) |
| Experimental yield (PFPN) | 73 (72) | 59 (58) | 73 (47) | 60 (37) | 65 (49) | |
| Highest recorded yield (PFPN) | 63 (70) | 52 (56) | 64 (45) | 52 (36) | 57 (48) | |
| Farmers’ Production Level a | N Rate (kg ha−1) | Yield (kg ha−1) | PFPN c (kg kg−1) | Sample Size (n) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FP | OPT | FP | OPT | FP | OPT | ||
| HYHE | 289.8 | 192.0 *** | 8961 | 9194 * | 31.1 | 52.5 *** | 114 |
| LYHE | 282.3 | 196.4 *** | 7455 | 8045 *** | 27.4 | 42.6 *** | 64 |
| HYLE, LYLE b | 370.8 | 256.5 ** | 9903 | 9279 | 26.9 | 36.9 *** | 8 |
| Total | 290.7 | 196.3 *** | 8484 | 8802 ** | 29.6 | 48.4 *** | 186 |
| Farmers’ Production Level a | Limiting Factors—Nutrient Applications | Limiting Factors—Farm and Farmer Characteristics | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N (kg ha−1) | P2O5 (kg ha−1) | K2O (kg ha−1) | Sample Size (n) | Area b (ha) | Age c (year) | Education Level d | Sample Size e (n) | |
| HYHE | 286c | 77.2a | 75.6a | 348 | 0.31ab | 49b | 3.3a | 95 |
| LYHE | 289c | 80.3a | 74.4a | 460 | 0.36a | 50b | 3.0b | 221 |
| HYLE | 432b | 81.1a | 75.4a | 286 | 0.30b | 48b | 3.4a | 72 |
| LYLE | 446a | 83.2a | 67.8b | 411 | 0.30b | 55a | 2.8b | 195 |
| Average | 358 | 80.6 | 73.0 | 1505 | 0.33 | 51 | 3.0 | 583 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xie, K.; Guo, J.; Ward, K.; Luo, G.; Shen, Q.; Guo, S. The Potential for Improving Rice Yield and Nitrogen Use Efficiency in Smallholder Farmers: A Case Study of Jiangsu, China. Agronomy 2020, 10, 419. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy10030419
Xie K, Guo J, Ward K, Luo G, Shen Q, Guo S. The Potential for Improving Rice Yield and Nitrogen Use Efficiency in Smallholder Farmers: A Case Study of Jiangsu, China. Agronomy. 2020; 10(3):419. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy10030419
Chicago/Turabian StyleXie, Kailiu, Junjie Guo, Katie Ward, Gongwen Luo, Qirong Shen, and Shiwei Guo. 2020. "The Potential for Improving Rice Yield and Nitrogen Use Efficiency in Smallholder Farmers: A Case Study of Jiangsu, China" Agronomy 10, no. 3: 419. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy10030419
APA StyleXie, K., Guo, J., Ward, K., Luo, G., Shen, Q., & Guo, S. (2020). The Potential for Improving Rice Yield and Nitrogen Use Efficiency in Smallholder Farmers: A Case Study of Jiangsu, China. Agronomy, 10(3), 419. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy10030419





