Influence of Microbial Inoculation of Igneous Rock Phosphate-Amended Cow and Pig Manures on Vermidegradation and Nutrient Release
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Source of Materials
2.2. Treatments, Experimental Design, and Experimental Establishment
- 1)
- Cow manure (CM) with no E. fetida or P. fluorescence (Control)
- 2)
- Pig manure (PG) with no E. fetida or P. fluorescence (Control)
- 3)
- CM with E. fetida alone
- 4)
- PG with E. fetida alone
- 5)
- CM with P. fluorescence alone
- 6)
- PG with P. fluorescence alone
- 7)
- CM with E. fetida plus P. fluorescence
- 8)
- PG with E. fetida plus P. fluorescence
2.3. Chemical Properties
2.3.1. Total C and N Determination
2.3.2. Humic and Fulvic Acids
2.3.3. Inorganic Extractable Nitrogen (Ammonium, Nitrate, and Nitrite)
2.3.4. Olsen Extractable P
2.4. Crop Phytotoxicity
2.5. Earthworm Biomass
2.6. pH and Electrical Conductivity (EC)
2.7. Data Analysis
3. Results
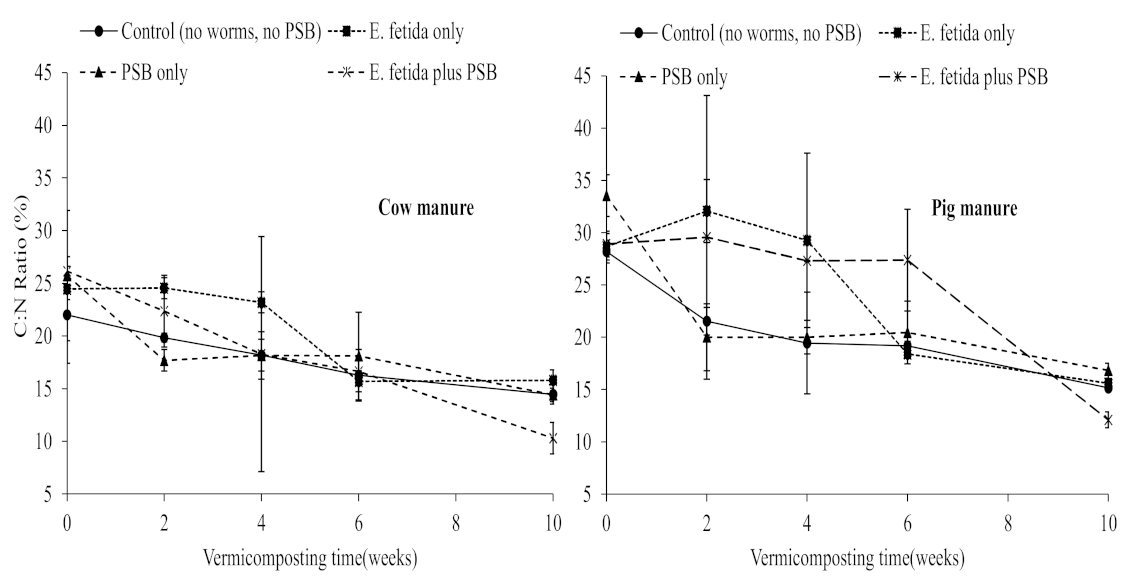
3.1. Effects of E. fetida and P. fluorescence Presence on Vermidegradation Efficiency
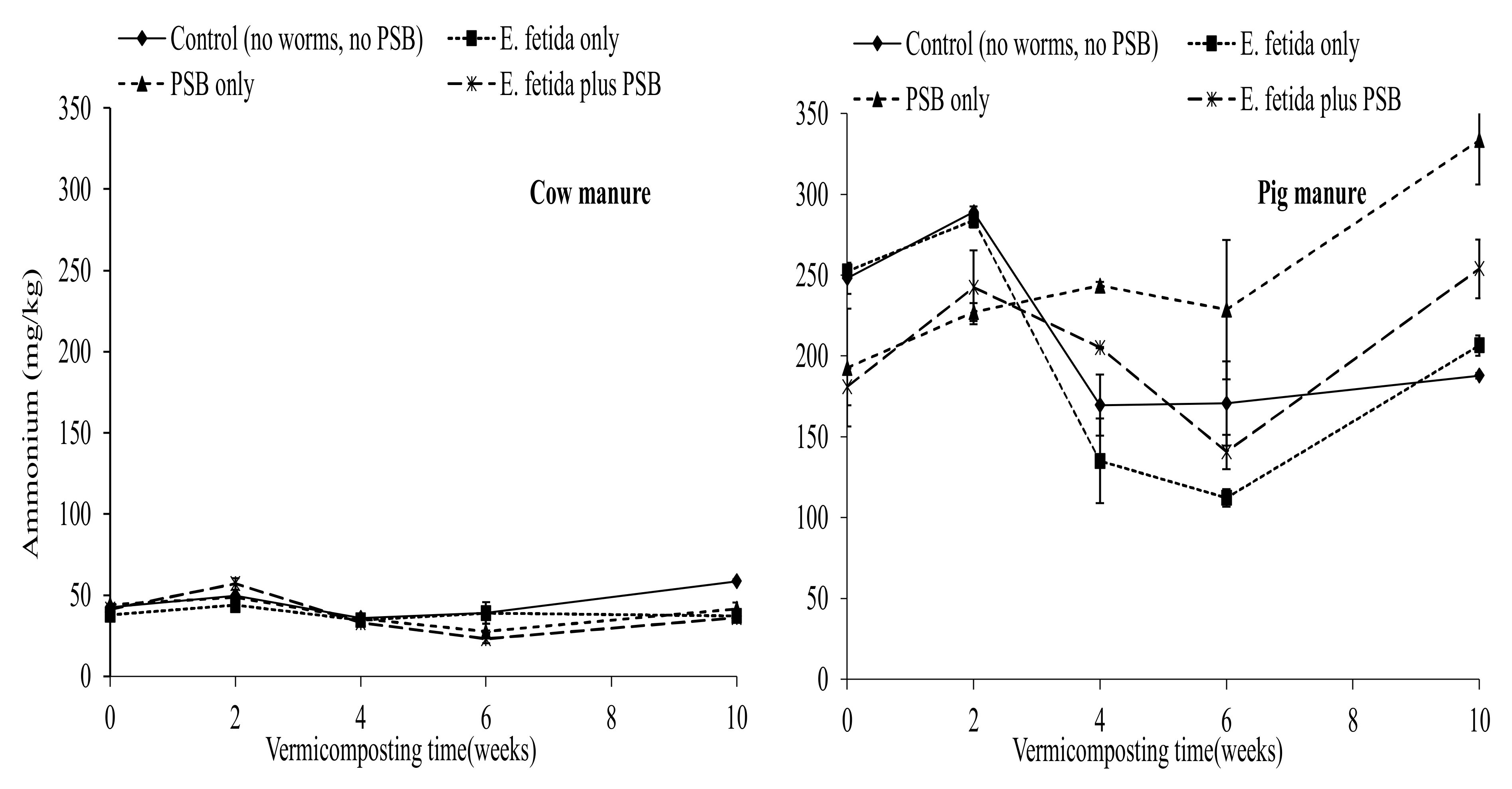
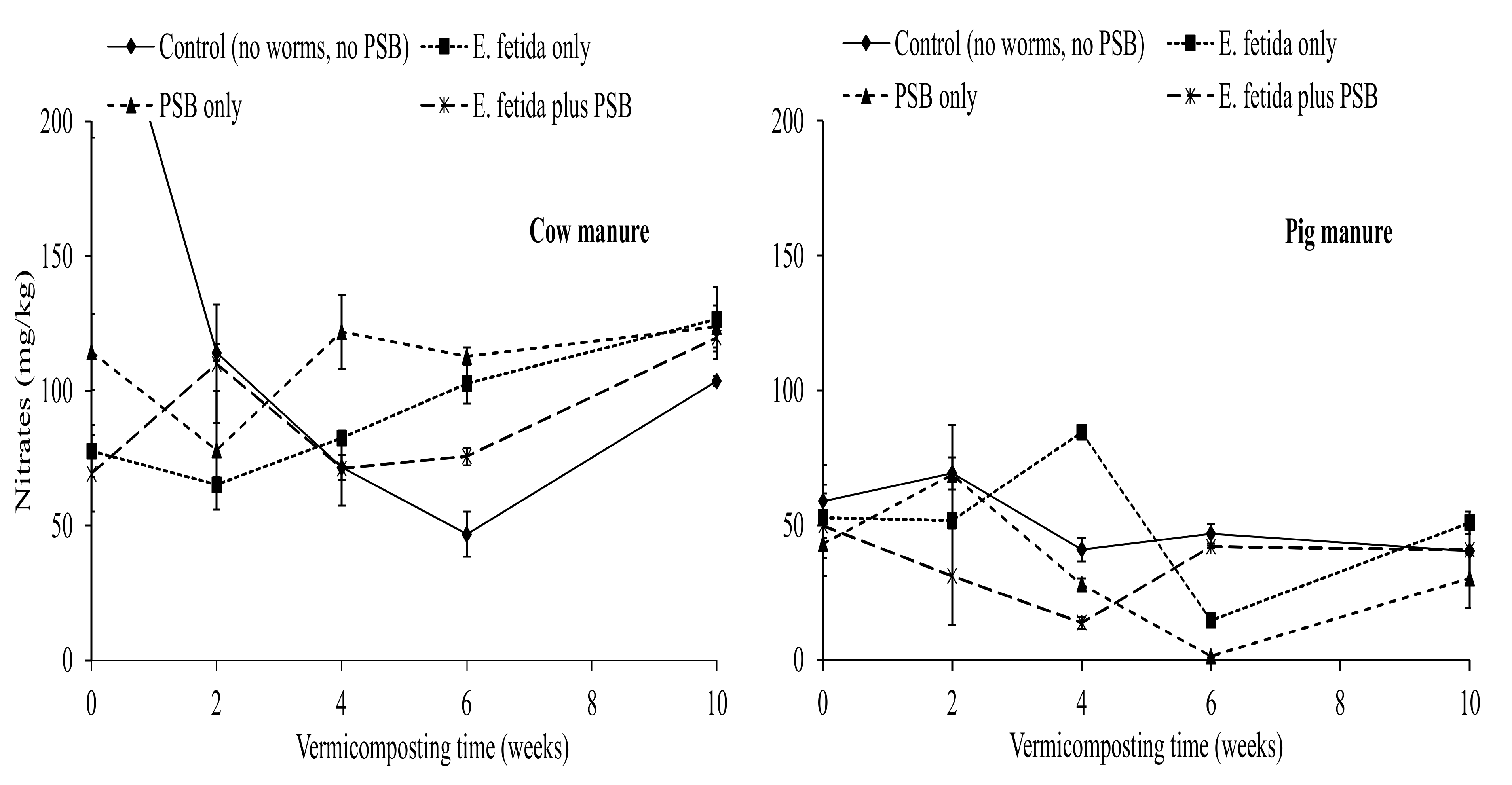
3.2. Effects of E. fetida and P. fluorescence Presence on Inorganic Nitrogen Content
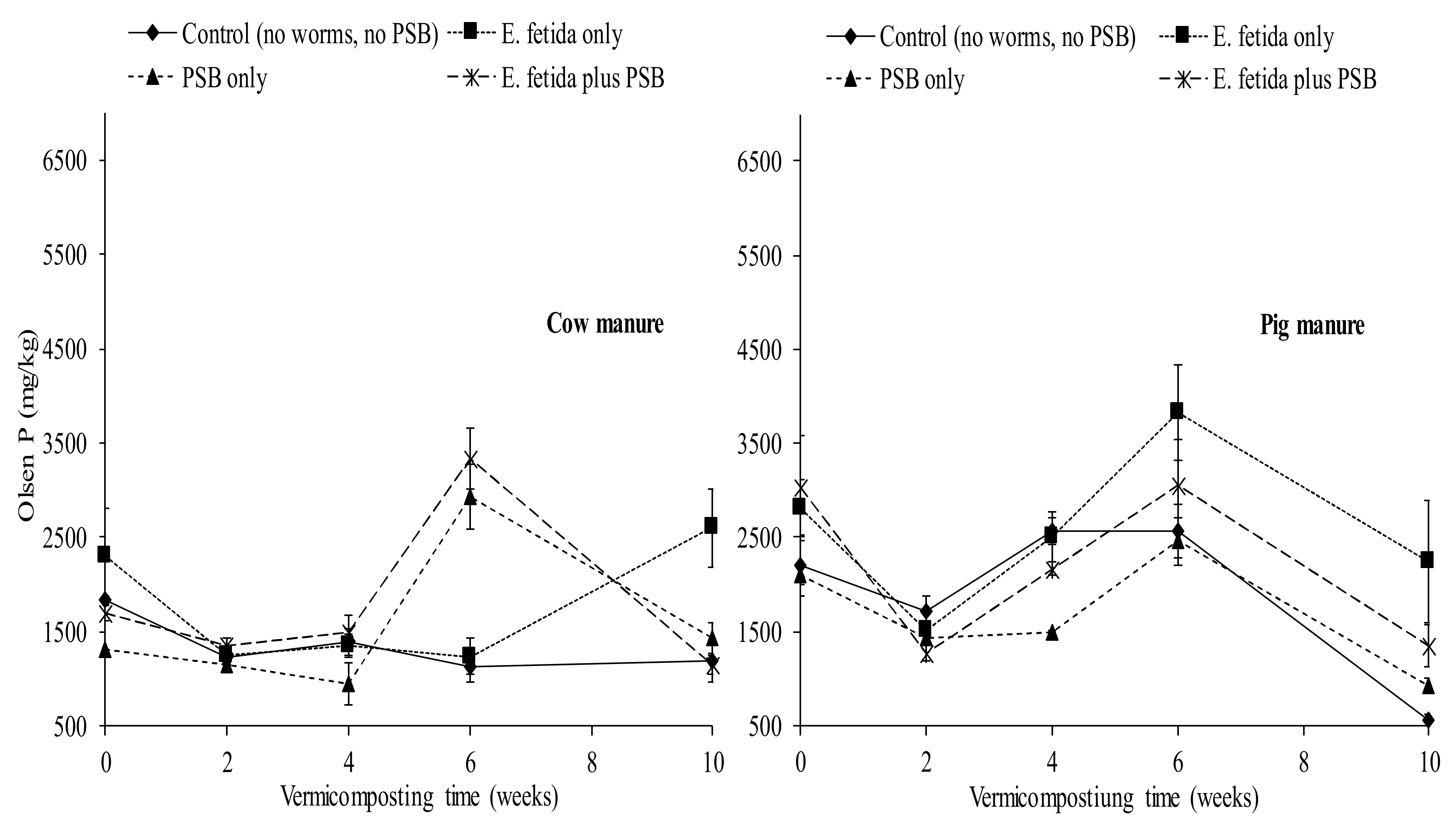
3.3. Effects of E. fetida and P. fluorescence Presence on Olsen Extractable P
3.4. Phytotoxicity Test
3.5. The Effects of Manure Type and P. fluorescence Presence on E. fetida Biomass
3.6. The Effect of E. fetida and P. fluorescence Inoculation on Changes in pH and EC
4. Discussion
4.1. The Effect of P. fluorescence Inoculation on the E. fetida Biomass
4.2. Effects of E. fetida and P. fluorescence on Changes in pH and EC During RP-enriched Vermicomposting
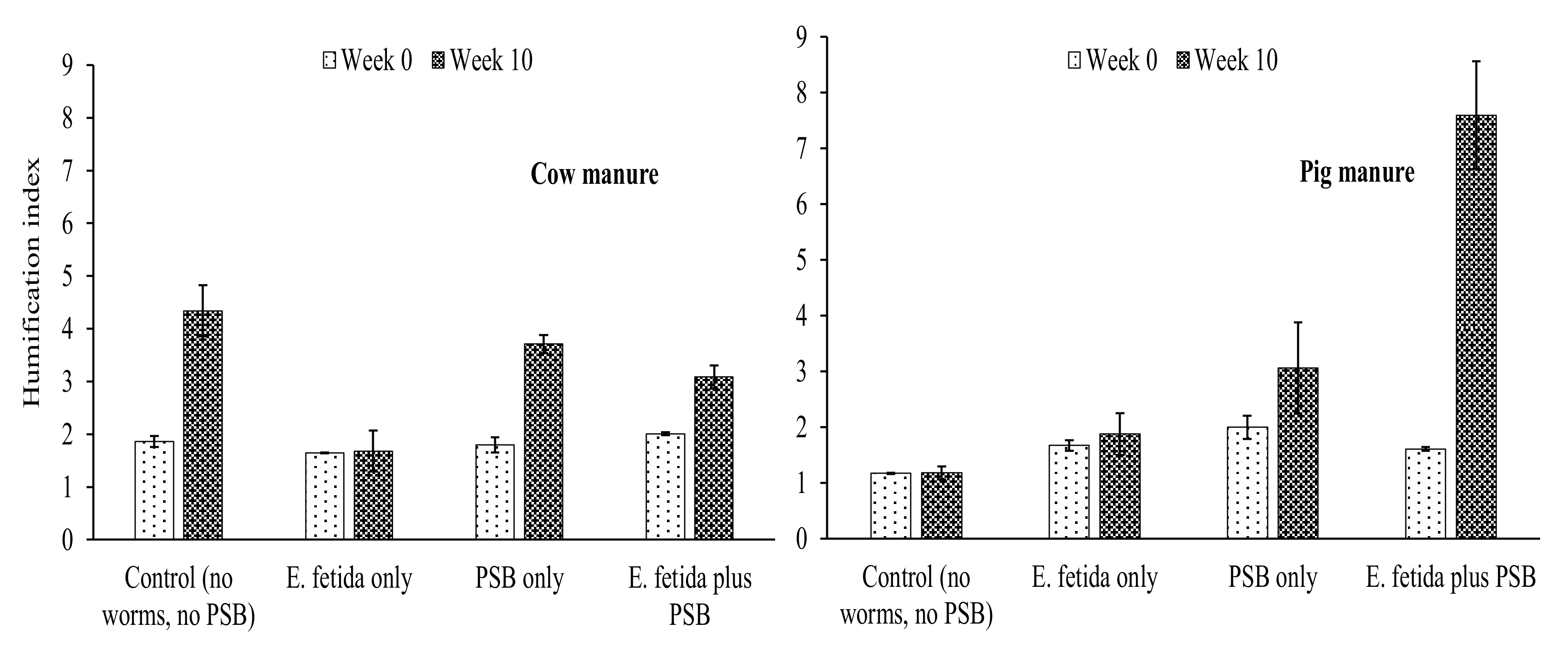
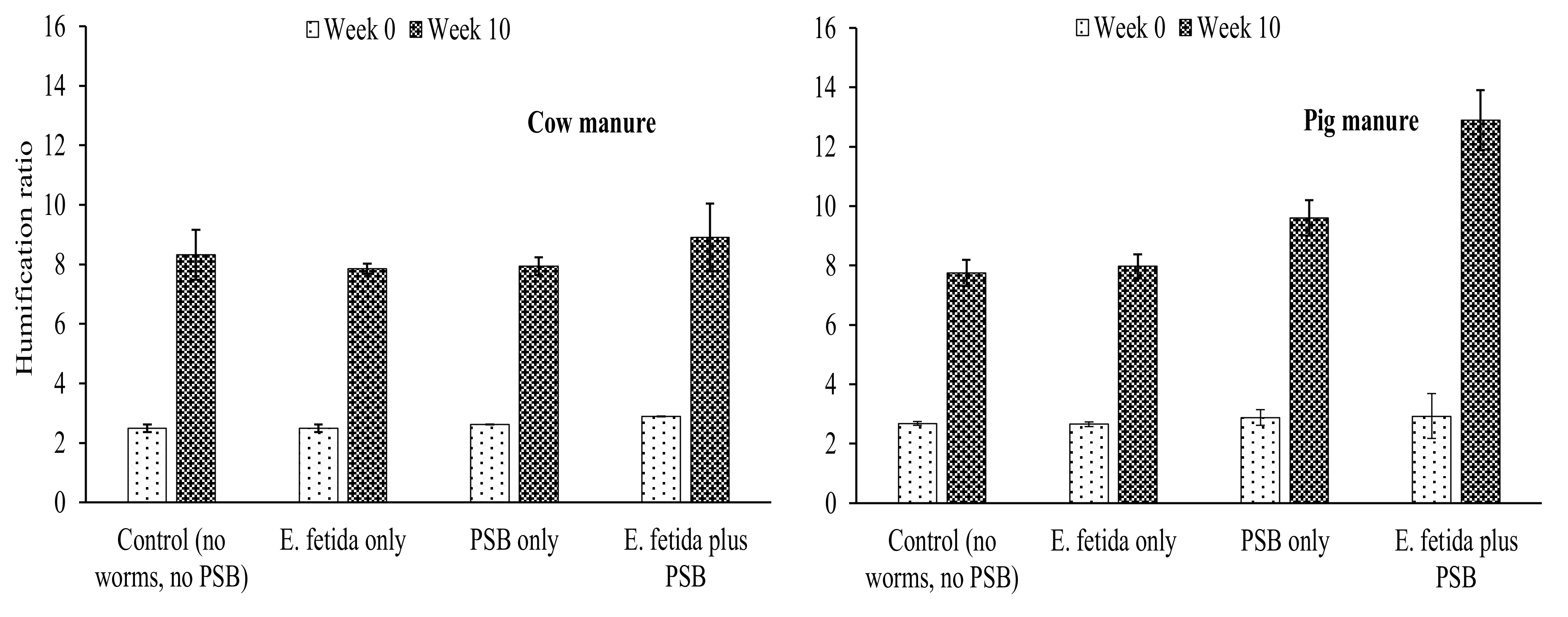
4.3. Effects of E. fetida and P. fluorescence on Humification Parameters During RP-enriched Vermicomposting
HI and HR
4.4. Effects of E. fetida and P. fluorescence on the Ammonium and Nitrates During RP-Enriched Vermicomposting
4.5. Effects of E. fetida and P. fluorescence on the Olsen Extractable P During RP-enriched Vermicomposting
4.6. Effects of E. fetida and P. fluorescence on the Phytotoxicity of Vermicomposting Cow and Pig Manures Mixtures Enriched with RP
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hoornweg, D.; Bhada-Tata, P. What a Waste: A Global Review of Solid Waste Management; World Bank: Washington, DC, USA, 2012; Volume 15, p. 116. [Google Scholar]
- Mupambwa, H.A.; Mnkeni, P.N.S. Optimizing the vermicomposting of organic wastes amended with inorganic materials for production of nutrient-rich organic fertilizers: A review. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 10577–10595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gómez-Brandón, M.; Juárez, M.F.D.; Domínguez, J.; Insam, H. Animal manures: Recycling and management technologies. In Biomass Now-Cultivation and Utilization; InTech: Rijeka, Croatia, 2013; pp. 237–272. [Google Scholar]
- Lukashe, N.S.; Mupambwa, H.A.; Green, E.; Mnkeni, P.N.S. Inoculation of fly ash amended vermicompost with phosphate solubilizing bacteria (Pseudomonas fluorescens) and its influence on vermi-degradation, nutrient release and biological activity. Waste Manag. 2019, 83, 14–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mupondi, L.T.; Mnkeni, P.N.S.; Muchaonyerwa, P.; Mupambwa, H.A. Vermicomposting manure-paper mixture with igneous rock phosphate enhances biodegradation, phosphorus bioavailability and reduces heavy metal concentrations. Heliyon 2018, 4, e00749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ali, U.; Sajid, N.; Khalid, A.; Riaz, L.; Rabbani, M.M.; Syed, J.H.; Malik, R.N. A review on vermicomposting of organic wastes. Environ. Prog. Sustain. Energy 2015, 34, 1050–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Gupta, R.K.; Kumar, S.; Kumar, S. Nutrient variations in vermicompost prepared from different types of straw wastes. Forage Res. 2017, 42, 267–270. [Google Scholar]
- Baversiha, N.; Parvanak, K.; Nasrabadi, M. Reduction of adverse environmental impacts caused by urban sewage: Application of green soil fertilizers. Ukr. J. Ecol. 2018, 8, 437–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novo, D.L.; Pereira, R.M.; Costa, V.C.; Hartwig, C.A.; Mesko, M.F. A novel and eco-friendly analytical method for phosphorus and sulfur determination in animal feed. Food Chem. 2018, 246, 422–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meyer, J.; Rein, P.; Turner, P.; Mathias, K.; McGregor, C. Good Management Practices for the Cane Sugar Industry (Final); Produced for the International Finance Corporation (IFC): Johannesburg, South Africa, 2011; pp. 200–206. [Google Scholar]
- Wendling, L.A.; Blomberg, P.; Sarlin, T.; Priha, O.; Arnold, M. Phosphorus sorption and recovery using mineral-based materials: Sorption mechanisms and potential phytoavailability. Appl. Geochem. 2013, 37, 157–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, T.; Biswas, D.R.; Datta, S.C.; Sarkar, A. Phosphorus release from rock phosphate as influenced by organic acid loaded nanoclay polymer composites in an alfisol. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. India Sect. B Biol. Sci. 2018, 88, 121–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unuofin, F.O.; Mnkeni, P.N.S. Optimization of Eisenia fetida stocking density for the bioconversion of rock phosphate enriched cow dung–waste paper mixtures. Waste Manag. 2014, 34, 2000–2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.W.; Nor Azwady, A.A.; Zulkifli, H.S.; Muskhazli, M.; Suraini, A.A.; Teng, S.K. Ehancement of plant nutrient contents in rice straw vermicompost through the addition of rock phosphate. Acta Biol. Malays. 2012, 1, 41–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adhami, E.; Hosseini, S.; Owliaie, H. Forms of phosphorus of vermicompost produced from leaf compost and sheep dung enriched with rock phosphate. Int. J. Recycl. Org. 2014, 3, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Busato, J.G.; Lima, L.S.; Aguiar, N.O.; Canellas, L.P.; Olivares, F.L. Changes in labile phosphorus forms during maturation of vermicompost enriched with phosphorus-solubilizing and diazotrophic bacteria. Bioresour. Technol. 2012, 110, 390–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Krishnaraj, P.U.; Dahale, S. Mineral phosphate solubilization: Concepts and prospects in sustainable agriculture. Proc. Indian Natl. Sci. Acad. 2014, 80, 389–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mupondi, L.T. Improving Sanitization and Fertiliser Value of Dairy Manure and Waste Paper Mixtures Enriched with Rock Phosphate through Combined Thermophilic Composting and Vermicomposting. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Fort Hare, Alice, South Africa, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Mupambwa, H.A.; Mnkeni, P.N.S. Optimization of fly ash incorporation into cow dung–waste paper mixture for enhanced vermidegradation and nutrient release. J. Environ. Qual. 2015, 44, 972–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, D.; Battacharya, P.; Gosh, B.C.; Banik, P. Bioconversion and biodynamics of Eisenia foetida in different organic wastes through microbially enriched vermiconversion technologies. Ecol. Eng. 2016, 86, 154–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LECO. Truspec CN Carbon/Nitrogen Determinator Instructors Manual; LECO Corporation: St Joseph, MI, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Sánchez-Monedero, M.A.; Roig, A.; Martínez-Pardo, C.; Cegarra, J.; Paredes, C. A microanalysis method for determining total organic carbon in extracts of humic substances. Relationships between total organic carbon and oxidable carbon. Bioresour. Technol. 1996, 57, 291–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maynard, D.G.; Kalra, Y.P.; Crumbaugh, J.A. Nitrate and exchangeable ammonium nitrogen. In Soil Sampling and Methods of Analysis, 2nd ed.; Carter, M.R., Gregorich, E.G., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2006; pp. 71–80. [Google Scholar]
- Okalebo, J.R.; Gathua, K.W.; Woomer, P.L. Laboratory Methods of Soil and Plant Analysis: A Working Manual; TSBF-KARI-UNESCO: Nairobi, Kenya, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Schoenau, J.J.; O’Halloran, I.P. Sodium bicarbonate-extractable phosphorus. In Soil Sampling and Methods of Analysis; Taylor Francis Group: Abingdon, UK, 2008; Volume 2. [Google Scholar]
- Kuo, S. Methods of Soil Analysis. Part 3: Chemical methods; Soil Science Society of America: Madison, WI, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Ravindran, B.; Contreras-Ramos, S.M.; Wong, J.W.C.; Selvam, A.; Sekaran, G. Nutrient and enzymatic changes of hydrolysed tannery solid waste treated with epigeic earthworm Eudrilus eugeniae and phytotoxicity assessment on selected commercial crops. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2014, 21, 641–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenhouse, S.W.; Geisser, S. On methods in the analysis of profile data. Psychometrika 1959, 24, 95–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garg, V.K.; Suthar, S.; Yadav, A. Management offood industry waste employing vermicomposting technology. Bioresour. Technol. 2012, 126, 437–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suthar, S.; Mutiyar, P.K.; Singh, S. Vermicomposting of milk processing industry sludge spiked with plant wastes. Bioresour. Technol. 2012, 116, 214–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernal, M.P.; Alburquerque, J.A.; Moral, R. Composting of animal manures and chemical criteria for compost maturity assessment. A review. Bioresour. Technol. 2009, 100, 5444–5453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Lima Rodrigues, A.S.; Mesak, C.; Silva, M.L.G.; Silva, G.S.; Leandro, W.M.; Malafaia, G. Organic waste vermicomposting through the addition of rock dust inoculated with domestic sewage wastewater. J. Environ. Manag. 2017, 196, 651–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Unuofin, F.O.; Siswana, M.; Cishe, E.N. Enhancing rock phosphate integration rate for fast bio-transformation of cow-dung waste-paper mixtures to organic fertilizer. SpringerPlus 2016, 5, 1986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Panhwar, Q.A.; Jusop, S.; Naher, U.A.; Othman, R.; Razi, M.I. Application of potential phosphate-solubilizing bacteria and organic acids on phosphate solubilization from phosphate rock in aerobic rice. Sci. World J. 2013, 2013, 272409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Singh, J.; Vig, A.P. Earthworm as ecological engineers to change the physico-chemical properties of soil: Soil vs. vermicast. Ecol. Eng. 2016, 90, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Gomez, A.; Bernal, M.P.; Roig, A. Organic matter fractions involved in degradation and humification processes during composting. Compost Sci. Util. 2005, 13, 127e135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Zhang, Y.; Shen, M.; Zeng, G.; Zhou, M.; Li, M. Effect of vermicomposting on concentration and speciation of heavy metals in sewage sludge with additive materials. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 218, 867–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, K.; Garg, V.K. Comparative analysis of vermicompost quality produced from rice straw and paper waste employing earthworm Eisenia fetida (Sav.). Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 250, 708–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Negi, R.; Suthar, S. Degradation of paper mill wastewater sludge and cow dung by brown-rot fungi Oligoporus placenta and earthworm (Eisenia fetida) during vermicomposting. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 201, 842–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, L.; Gong, X.; Sun, X.; Li, S.; Yu, X. Comparison of chemical and microbiological changes during the aerobic composting and vermicomposting of green waste. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0207494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yadav, A.; Garg, V.K. Biotransformation of bakery industry sludge into valuable product using vermicomposting. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 274, 512–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lazcano, C.; Gómez-Brandón, M.; Domínguez, J. Comparison of the effectiveness of composting and vermicomposting for the biological stabilization of cattle manure. Chemosphere 2008, 72, 1013–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Lu, Z.; Yang, J.; Xing, M.; Yu, F.; Guo, M. Effect of earthworms on the performance and microbial communities of excess sludge treatment process in vermifilter. Bioresour. Technol. 2012, 117, 214–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vig, A.P.; Singh, J.; Wani, S.H.; Dhaliwal, S.S. Vermicomposting of tannery sludge mixed with cattle dung into valuable manure using earthworm Eisenia fetida (Savigny). Bioresour. Technol. 2011, 102, 7941–7945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hait, S.; Tare, V. Vermistabilization of primary sewage sludge. Bioresour. Technol. 2011, 102, 2812–2820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malafaia, G.; da Costa Estrela, D.; Guimarães, A.T.B.; de Araújo, F.G.; Leandro, W.M.; de Lima Rodrigues, A.S. Vermicomposting of different types of tanning sludge (liming and primary) mixed with cattle dung. Ecol. Eng. 2015, 85, 301–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soobhany, N.; Mohee, R.; Garg, V.K. Experimental process monitoring and potential of Eudrilus eugeniae in the vermicomposting of organic solid waste in Mauritius. Ecol. Eng. 2015, 84, 149–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravindran, B.; Mupambwa, H.A.; Silwana, S.; Mnkeni, P.N. Assessment of nutrient quality, heavy metals and phytotoxic properties of chicken manure on selected commercial vegetable crops. Heliyon 2017, 3, e00493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helitha, A.M.; Manivannan, S. Enhancement of Humus Composition by Earthworms during Biotransformation of Coffee Pulp Amended with Sugar Industrial Wastes. Int. J. Zool. Appl. Biosci. 2018, 3, 82–88. [Google Scholar]
- Nigussie, A.; Kuyper, T.W.; Bruun, S.; de Neergaard, A. Vermicomposting as a technology for reducing nitrogen losses and greenhouse gas emissions from small-scale composting. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 139, 429–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, K.; Li, F.; Wei, Y.; Chen, X.; Fu, X. Changes of bacterial and fungal community compositions during vermicomposting of vegetable wastes by Eisenia foetida. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 150, 235–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Guardia, A.; Mallard, P.; Teglia, C.; Marin, A.; Le Pape, C.; Launay, M.; Benoist, J.C.; Petiot, C. Comparison of five organic wastes regarding their behaviour during composting: Part 2, nitrogen dynamic. Waste Manag. 2010, 30, 415–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Getachew, Z.; Adisu, T.; Abeble, L.; Anbessa, B. Vermicompost Potential of Common Earthworms (Eudrilus eugeniae) and Red Wiggler (Eisenia fetida) Worm on the Decomposition of Various Organic Wastes; Assosa, Ethiopia. Int. J. Plant Soil Sci. 2018, 24, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aalok, A.; Tripathi, A.K. Composting-Vermicomposting of different types of leaves using earthworm species Eisenia fetida. Dyn. Soil Dyn. Plant 2010, 4, 139–144. [Google Scholar]
- Schaik, A.V.; Prosser, J.; Graham, D.; Xue, J.; Booth, L. The Suitability of Using Vermicomposting for the Stabilization of Septic Tank Waste. J. Bioremediat. Biodegrad. 2016, 7, 368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dores-Silva, P.R.; Landgraf, M.D.; Rezende, M.O. Acompanhamento químico da vermicompostagem de lodo de esgoto doméstico. Química Nova 2011, 34, 956–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cesaro, A.; Belgiorno, V.; Guida, M. Compost from organic solid waste: Quality assessment and European regulations for its sustainable use. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2015, 94, 72–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Getahun, T.; Nigusie, A.; Entele, T.; Van Gerven, T.; Van der Bruggen, B. Effect of turning frequencies on composting biodegradable municipal solid waste quality. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2012, 65, 79–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jodice, R. Chemical and biological parameters for evaluating compost quality. In Proceedings of the International Symposium on Compost Production and Use, San Michele all’Adige, Italy, 20–23 June 1989; pp. 20–23. [Google Scholar]
- Zucconi, F.; Monaco, A.; Forte, M.; De Bertoldi, M. Phytotoxins during the stabilization of organic matter. In Composting of Agricultural and Other Wastes; Gasser, J.K.R., Ed.; Elsevier: London, UK, 1985; pp. 73–85. [Google Scholar]
- Olivera Viciedo, D.; de Mello Prado, R.; Lizcano Toledo, R.; Nascimento dos Santos, L.C.; Peña Calzada, K. Response of radish seedlings (Raphanus sativus L.) to different concentrations of ammoniacal nitrogen in absence and presence of silicon. Agronomía Colombiana 2017, 35, 198–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernal, D.Á.; Hernández, M.A.L.; Osben, H.R.B.; Ramos, S.M.C.; Mora, M. Vermicompost as an alternative of management for water hyacinth. Revista Internacional de Contaminación Ambiental 2016, 32, 425–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
| Chemical Property | Raw Material | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Cow Manure | Pig Manure | Wastepaper | |
| pH (H2O) | 8.53 ± 0.02 * | 6.52 ± 0.04 | 8.10 ± 0.10 |
| EC (µS/cm) | 4.00 ± 0.05 | 1.89 ± 2.83 | 1.80 ± 1.00 |
| Total C % | 22.84 ± 0.63 | 39.67 ± 1.37 | 37.96 ± 1.01 |
| Total N % | 2.05 ± 0.03 | 1.92 ± 0.04 | 0.04 ± 0.01 |
| C:N ratio | 11.14 ± 0.22 | 20.70 ± 0.94 | 998.94 ± 17.44 |
| Extractable NH4 (mg/kg) | 31.410 ± 0.90 | 341.07 ± 26.5 | nd 1 |
| Extractable NO3/NO2 (mg/kg) | 382.05 ± 63.71 | 97.03 ± 5.90 | nd |
| Olsen extractable P (mg/kg) | 1479.19 ± 162.52 | 2135.17 ± 59. | nd |
| Source of Variation | C/N Ratio | pH | EC (mS/cm) | HR (%) | HI (%) | NH4 (mg/kg) | NO3 (mg/kg) | Olsen P (mg/kg) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Between subjects | ||||||||
| Earthworm presence (E) | 0.0020 | ns | ns | 0.0003 | 0.0324 | ˂0.0001 | 0.0008 | ˂0.0001 |
| PSB presence (P) | Ns | ns | 0.0151 | ˂0.0001 | ˂0.0001 | 0.0131 | 0.0021 | 0.0202 |
| Manure type (M) | ˂0.0001 | ˂0.0001 | ˂0.0001 | ˂0.0001 | ns | ˂0.0001 | ˂0.0001 | ˂0.0001 |
| Within-subjects | ||||||||
| Time (T) | ˂0.0001 | ˂0.0001 | ˂0.0001 | ˂0.0001 | ˂0.0001 | ˂ 0.0001 | 0.0002 | ˂0.0001 |
| T × E | ˂0.0001 | ns | ns | 0.0483 | ns | 0.0003 | ˂0.0001 | 0.0058 |
| T × P | 0.0241 | ns | ns | 0.0002 | ˂0.0001 | ˂0.0001 | 0.0011 | ˂0.0001 |
| T × M | Ns | ns | 0.0064 | 0.0092 | ns | ˂0.0001 | 0.0024 | ˂0.0001 |
| T × E × P | ˂0.0001 | ns | 0.0004 | 0.0190 | ˂0.0001 | 0.0228 | 0.0002 | 0.0009 |
| T × E × M | 0.0105 | ns | 0.0176 | ns | ˂0.0001 | 0.0007 | ˂0.0001 | ns |
| T × P × M | 0.0051 | ns | ˂0.0001 | 0.0003 | ˂0.0001 | ˂0.0001 | 0.0004 | ˂0.0001 |
| T × E × P × M | 0.0072 | ns | 0.0387 | ns | 0.0038 | 0.0084 | ˂0.0001 | ns |
| Spinach | Radish | Tomato | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Treatments | Percentage | ||||||||
| RSG | RRE | GI | RSG | RRE | GI | RSG | RRE | GI | |
| CM: no worms, no PSB (Control) | 100 a | 78.2 c | 78.2 abc | 112 a | 48.7 c | 55.2 b | 52.4 bc | 129 a | 67.4 a |
| PG: no worms, no PSB (Control) | 43.3 d | 89 bc | 38.5 f | 96.3 a | 67.1 bc | 64.7 bc | 73.2 ab | 103 b | 75.9 a |
| CM: E. fetida only | 58.3 c | 129 a | 75 bcd | 100.4 a | 82.3 ab | 83.1 ab | 49 c | 131.3 a | 64 a |
| PG: E. fetida only | 58.3 | 83.4 bc | 48.3 ef | 105 a | 54 c | 56.4 bc | 57 bc | 103.3 b | 59 a |
| CM: PSB only | 86.7 b | 110 ab | 94.5 a | 104 a | 103 a | 106.5 a | 48 c | 105.2 b | 50.2 a |
| PG: PSB only | 65 c | 90 bc | 58.3 de | 100.5 a | 108 a | 112 a | 61.3 bc | 143.1 a | 77 a |
| CM: E. fetida plus PSB | 65 c | 127 a | 83 ab | 96 a | 54 c | 53.3 bc | 65.5 bc | 97.3 b | 64 a |
| PG: E. fetida plus PSB | 65 c | 89.2 bc | 60 cde | 108.3 a | 44 c | 49 c | 88 a | 71.4 c | 62 a |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ajibade, S.; Mupambwa, H.A.; Manyevere, A.; Mnkeni, P.N.S. Influence of Microbial Inoculation of Igneous Rock Phosphate-Amended Cow and Pig Manures on Vermidegradation and Nutrient Release. Agronomy 2020, 10, 1587. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy10101587
Ajibade S, Mupambwa HA, Manyevere A, Mnkeni PNS. Influence of Microbial Inoculation of Igneous Rock Phosphate-Amended Cow and Pig Manures on Vermidegradation and Nutrient Release. Agronomy. 2020; 10(10):1587. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy10101587
Chicago/Turabian StyleAjibade, Sinazo, Hupenyu Allan Mupambwa, Alen Manyevere, and Pearson Nyari Stephano Mnkeni. 2020. "Influence of Microbial Inoculation of Igneous Rock Phosphate-Amended Cow and Pig Manures on Vermidegradation and Nutrient Release" Agronomy 10, no. 10: 1587. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy10101587
APA StyleAjibade, S., Mupambwa, H. A., Manyevere, A., & Mnkeni, P. N. S. (2020). Influence of Microbial Inoculation of Igneous Rock Phosphate-Amended Cow and Pig Manures on Vermidegradation and Nutrient Release. Agronomy, 10(10), 1587. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy10101587





