Economic Sustainability of Small-Scale Aquaponic Systems for Food Self-Production
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Description and Experimental Setup of the Systems
2.2. Fish and Plant Species
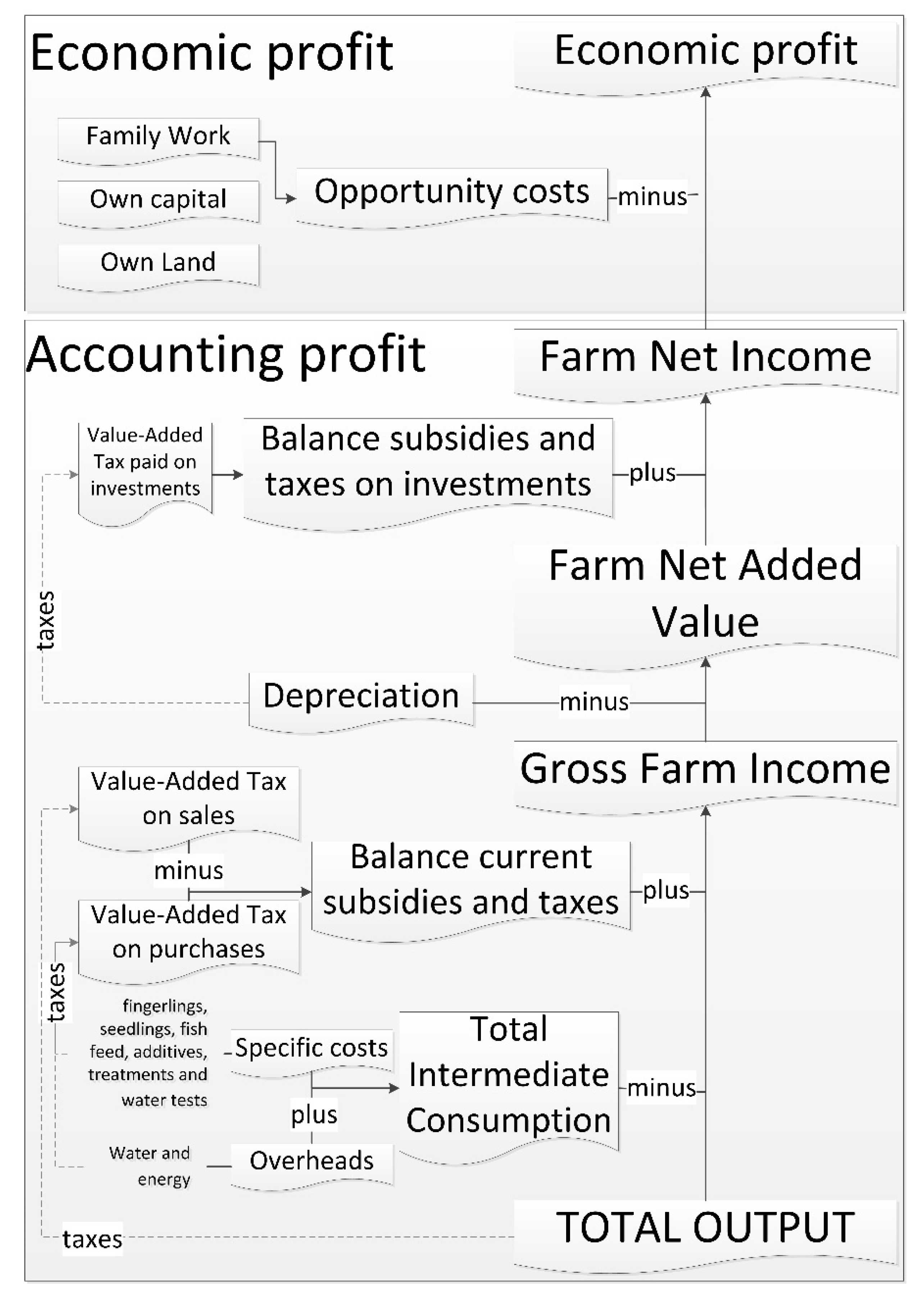
2.3. Cost-Benefit Analysis and Level of Commoditization
3. Results
| SAS | SAS1 | SAS2 | Average Values | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Produce | Total per Product (kg) | Total Market Value (€) | Total per Product (kg) | Total Market Value (€) | Total per Product (kg) | % of Total Production | Total Market Value (€) | % of Total Market Value |
| Lettuce | 68.72 | 70.09 | 64.54 | 65.83 | 66.63 | 32.1 | 67.96 | 10.8 |
| Watermelon | 4.90 | 4.31 | 1.65 | 1.45 | 3.28 | 1.6 | 2.88 | 0.5 |
| Chard | 9.33 | 19.78 | 7.31 | 15.50 | 8.32 | 4.0 | 17.64 | 2.8 |
| Raf tomato | 8.50 | 17.51 | 12.44 | 25.63 | 10.47 | 5.0 | 21.57 | 3.4 |
| Roma tomato | 14.16 | 26.20 | 12.48 | 23.09 | 13.32 | 6.4 | 24.64 | 3.9 |
| Eggplant | 3.34 | 6.01 | 10.16 | 18.29 | 6.75 | 3.3 | 12.15 | 1.9 |
| Cucumber | 18.52 | 26.48 | 20.34 | 29.09 | 19.43 | 9.4 | 27.78 | 4.4 |
| Basil | 1.78 | 71.20 | 1.61 | 64.40 | 1.70 | 0.8 | 67.80 | 10.7 |
| Onion | 0.06 | 0.07 | 0.06 | 0.07 | 0.06 | 0.0 | 0.07 | 0.0 |
| Italian frying pepper | 10.44 | 22.76 | 8.28 | 18.05 | 9.36 | 4.5 | 20.40 | 3.2 |
| Goat horn pepper | 2.02 | 4.24 | 1.51 | 3.17 | 1.77 | 0.9 | 3.71 | 0.6 |
| Lamuyo pepper | 4.66 | 11.09 | 3.86 | 9.19 | 4.26 | 2.1 | 10.14 | 1.6 |
| Broccoli | 2.92 | 6.92 | 1.77 | 4.19 | 2.35 | 1.1 | 5.56 | 0.9 |
| Strawberry | 0.75 | 2.64 | 0.79 | 2.78 | 0.77 | 0.4 | 2.71 | 0.4 |
| Cauliflower | 0.49 | 0.94 | 0.63 | 1.20 | 0.56 | 0.3 | 1.07 | 0.2 |
| Cabbage | 0.52 | 0.72 | 0.65 | 0.90 | 0.59 | 0.3 | 0.81 | 0.1 |
| Potato | 2.50 | 2.55 | 1.09 | 1.11 | 1.80 | 0.9 | 1.83 | 0.3 |
| Zucchini | 16.84 | 28.12 | 16.77 | 28.01 | 16.81 | 8.1 | 28.06 | 4.4 |
| Chinese cabbage | 1.73 | 3.39 | 1.79 | 3.51 | 1.76 | 0.8 | 3.45 | 0.5 |
| Stevia | 0.22 | 1.21 | 0.17 | 0.94 | 0.20 | 0.1 | 1.07 | 0.2 |
| Melon | 0.66 | 0.90 | 1.43 | 1.94 | 1.05 | 0.5 | 1.42 | 0.2 |
| Pumpkin | 4.63 | 7.41 | 5.44 | 8.70 | 5.04 | 2.4 | 8.06 | 1.3 |
| Total horticultural production | 177.66 | 334.55 | 174.77 | 327.04 | 176.22 | 84.9 | 330.79 | 52.3 |
| Tilapia | 33.50 | 321.60 | 29.28 | 281.09 | 31.39 | 15.1 | 301.34 | 47.7 |
| SAS1 | SAS2 | |
|---|---|---|
| Total investment | 2266.27 € | 2252.13 € |
| Total output livestock. Fish production | 292.36 € | 273.95 € |
| Total output crops. Plant production | 321.68 € | 318.07 € |
| Total output | 614.05 € | 592.01 € |
| Specific cost. Fingerlings, seedlings, fish feed, additives, treatments and water tests | 201.63 € | 201.59 € |
| Overheads. Water and energy | 92.64 € | 119.24 € |
| Intermediate consumption | 294.27 € | 320.84 € |
| Depreciation | 139.92 € | 144.06 € |
| Total inputs | 434.19 € | 464.9 € |
| Value added tax balance excluding on investments | 1.24 € | −5.52 € |
| Output/Input | 1.41 | 1.27 |
| Gross farm income | 321.02 € | 265.65 € |
| Farm net income | 151.72 € | 91.34 € |
| Annual work unit | 0.049 | 0.059 |
| Farm Net Added Value | ||
| 181.10 € | 121.59 € | |
| Economic Profit | ||
| −376.23 € | −527.47 € | |
| Costs Analysis | ||
| Variable costs (Specific costs) | 201.63 € | 201.59 € |
| Fixed costs (Value of labor, overheads and depreciation) | 668.13 € | 789.73 € |
| Total costs | 869.76 € | 991.32 € |
| Fish production | 33.25 kg | 29.28 kg |
| Plant production | 177.66 kg | 174.77 kg |
| Total production | 210.91 kg | 204.05 kg |
| Average cost per unit | 4.12 € kg−1 | 4.86 € kg−1 |
| Family Farm Income/FWU | ||
| 3090.41 € | 1539.50 € | |
| Degree of Commoditization | ||
| 44.8% | 43.1% | |
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A. Aquaponic Systems’ Description and System Operations
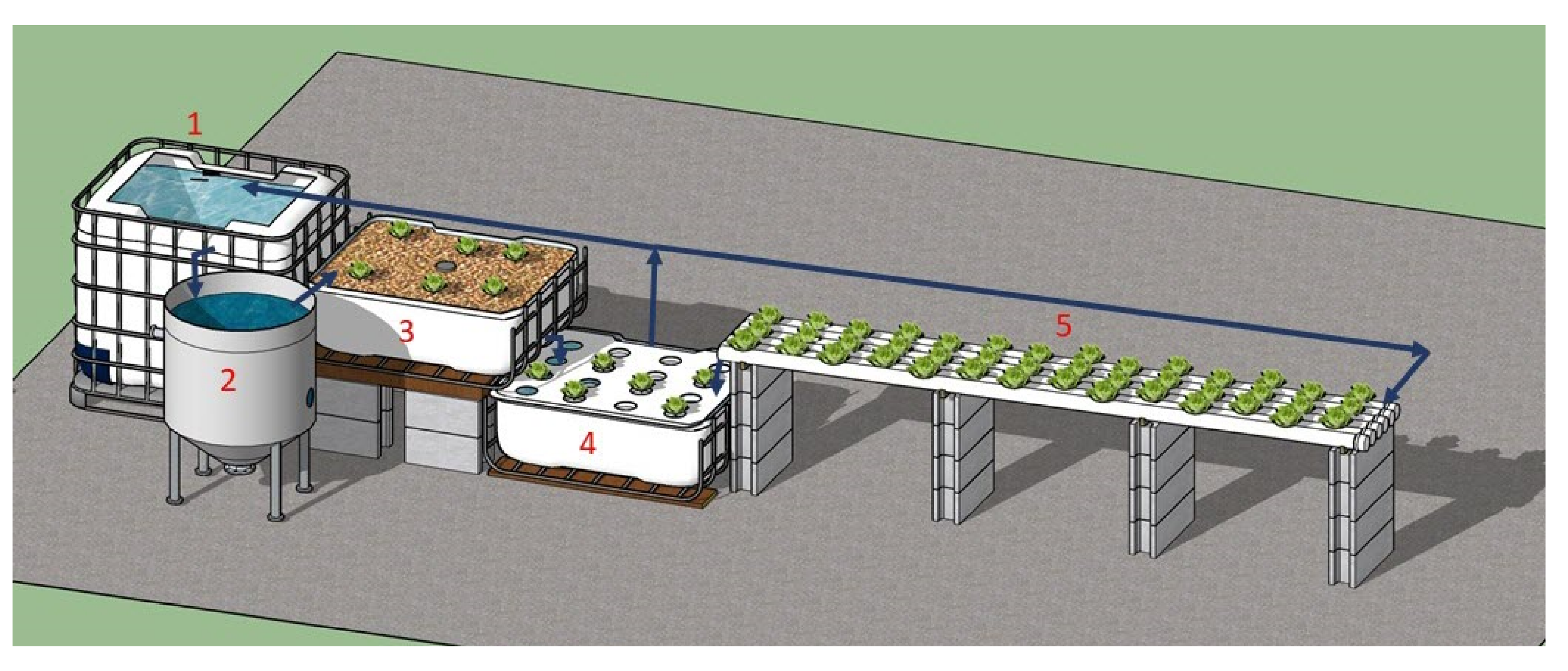
Appendix B. Economic Data
| Year | 2018 | 2019 | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | May | June | July | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Jan | Feb | Mar | April | Mean± SD |
| Lettuce | 0.97 | 0.97 | 0.99 | 1.01 | 1.04 | 1.05 | 1.05 | 1.03 | 1.09 | 1.06 | 0.97 | 1.02 ± 0.04 | |
| Water melon | 0.88 | 0.88 | |||||||||||
| Chard | 2.08 | 2.12 | 2.17 | 2.21 | 2.15 | 2.07 | 2.05 | 2.12 ± 0.06 | |||||
| Raf tomato | 2.03 | 2.03 | 2.11 | 2.06 ± 0.05 | |||||||||
| Roma tomato | 1.85 | 1.85 | 1.85 | 1.85 | |||||||||
| Eggplant | 1.58 | 1.58 | 1.93 | 1.94 | 1.95 | 1.80 ± 0.20 | |||||||
| Cucumber | 1.49 | 1.39 | 1.36 | 1.46 | 1.43 ± 0.06 | ||||||||
| Basil | 40 | 40 | 40 | 40 | 40 | 40 | 40 | 40.00 | |||||
| Onion | 1.17 | 1.17 | |||||||||||
| Italian frying pepper | 2.54 | 2.14 | 2.13 | 2.03 | 2.05 | 2.17 | 2.18 ± 0.19 | ||||||
| Goat horn pepper | 2.14 | 2.13 | 2.03 | 2.05 | 2.17 | 2.10 ± 0.06 | |||||||
| Lamuyo pepper | 2.4 | 2.39 | 2.35 | 2.39 | 2.38 ± 0.02 | ||||||||
| Broccoli | 2.45 | 2.4 | 2.27 | 2.37 ± 0.09 | |||||||||
| Strawberry | 3.87 | 3.6 | 3.45 | 3.15 | 3.52 ± 0.30 | ||||||||
| Cauliflower | 1.91 | 1.91 | |||||||||||
| Cabbage | 1.43 | 1.35 | 1.39 ± 0.06 | ||||||||||
| Potato | 1.02 | 1.02 | |||||||||||
| Zucchini | 1.63 | 1.71 | 1.67 ± 0.06 | ||||||||||
| Chinese cabbage | 1.96 | 1.93 | 1.98 | 1.96 ± 0.03 | |||||||||
| Stevia | 5.5 | 5.5 | 5.5 | 5.5 | 5.50 | ||||||||
| Melon | 1.29 | 1.43 | 1.36 ± 0.10 | ||||||||||
| Pumpkin | 1.6 | 1.6 | 1.60 | ||||||||||
| Item | Total Cost (€) | Annual Cost (Depreciation) (€ year−1) |
|---|---|---|
| Greenhouse | 580.321 | 58.03 |
| Shade mesh | 25 | 5 |
| Electrical installation | 45 | 2.25 |
| Fish tank and related equipment | 182.75 | 19.85 |
| Tank for water refill | 54 | 5.40 |
| Clarifier | 166 | 10.32 |
| Biofilter and expanded clay growing bed | 86 | 8.93 |
| NFT system | 69 | 7.5 |
| Sump & pump | 137 | 19.02 |
| Accessories | 57.90 | 17.07 |
| Solar panel and related equipment (only for SAS1) | 247.55 | 15.93 |
| Vermicompost facility (only for SAS2) | 181.91 | 8.62 |
| Vermicompost accessories (only for SAS2) | 51.50 | 12.33 |
| Total cost for SAS1 | 1650.52 | 169.30 |
| Total cost for SAS2 | 1636.38 | 174.32 |
| Year | 2018 | 2019 | Annual Cost | % over Total | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | March | April | May | June | July | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Jan | Feb | Mar | April | ||
| Energy costs (electricity) | 3.17 | 3.52 | 4.37 | 4.92 | 6.07 | 5.98 | 6.07 | 6.23 | 6.83 | 9.16 | 15.80 | 7.36 | 6.81 | 5.27 | 91.57 | 27.33 |
| Fish (fingerlings) | 86.68 | 86.68 | 25.86 | |||||||||||||
| Plants (seedlings) | 0.95 | 0.85 | 1.25 | 2.15 | 0.60 | 3.15 | 2.05 | 2.65 | 0.60 | 2.60 | 0.30 | 3.25 | 0.00 | 20.40 | 6.09 | |
| Fish feed | 1.39 | 4.44 | 6.53 | 9.91 | 11.02 | 7.50 | 6.82 | 2.45 | 2.40 | 1.09 | 1.13 | 3.41 | 2.64 | 60.72 | 18.12 | |
| Water | 1.52 | 1.00 | 1.80 | 3.00 | 3.44 | 2.13 | 1.06 | 0.52 | 0.80 | 0.15 | 0.95 | 1.17 | 1.12 | 18.66 | 5.57 | |
| Additives for plants | 0.06 | 0.31 | 0.33 | 0.06 | 0.07 | 0.39 | 0.13 | 0.12 | 0.23 | 0.35 | 0.45 | 0.24 | 0.25 | 2.97 | 0.89 | |
| Treatments for plants | 0.34 | 0.34 | 0.43 | 0.74 | 1.14 | 3.34 | 0.55 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 6.95 | 2.07 | |||||
| Water tests | 0.40 | 2.03 | 3.67 | 3.74 | 4.48 | 8.56 | 4.82 | 4.88 | 3.32 | 2.75 | 2.05 | 1.80 | 2.57 | 2.12 | 47.18 | 14.08 |
| Monthly running costs | 5.08 | 94.62 | 14.64 | 18.57 | 26.01 | 30.02 | 24.49 | 21.90 | 17.04 | 19.27 | 22.58 | 11.98 | 17.49 | 11.42 | 335.11 | |
| Year | 2018 | 2019 | Annual Cost | % over Total | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | March | April | May | June | July | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Jan | Feb | Mar | April | ||
| Energy costs (electricity) | 3.17 | 3.38 | 4.48 | 5.28 | 6.33 | 6.16 | 6.07 | 6.46 | 5.90 | 4.91 | 5.25 | 5.45 | 5.85 | 4.51 | 73.2 | 20.09 |
| Fish (fingerlings) | 81.96 | 43.79 | 22.50 | |||||||||||||
| Plants (seedlings) | 1.00 | 0.80 | 1.25 | 2.10 | 0.55 | 3.15 | 1.90 | 2.65 | 0.65 | 2.75 | 0.20 | 3.05 | 20.05 | 5.50 | ||
| Fish feed | 1.45 | 4.27 | 6.57 | 10.29 | 10.92 | 7.55 | 6.11 | 47.15 | 12.94 | |||||||
| Water | 1.48 | 1.00 | 1.80 | 3.10 | 3.53 | 2.19 | 1.04 | 1.33 | 2.11 | 2.62 | 2.05 | 2.94 | 2.76 | 27.95 | 7.67 | |
| Additives for plants | 0.06 | 0.31 | 0.37 | 0.06 | 0.07 | 0.39 | 0.13 | 3.37 | 7.46 | 13.11 | 8.36 | 12.50 | 12.55 | 58.74 | 16.12 | |
| Treatments for plants | 0.34 | 0.34 | 0.43 | 0.74 | 1.14 | 3.34 | 0.55 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 6.94 | 1.91 | |||||
| Water tests | 0.40 | 2.03 | 3.67 | 3.74 | 4.48 | 8.56 | 4.82 | 4.88 | 5.21 | 3.81 | 2.37 | 2.13 | 2.20 | 0.03 | 48.32 | 13.26 |
| Monthly running costs | 5.04 | 89.85 | 14.53 | 19.01 | 26.70 | 30.13 | 24.59 | 21.25 | 19.60 | 22.27 | 26.65 | 18.18 | 26.57 | 19.88 | 364.28 | |
References
- König, B.; Janker, J.; Reinhardt, T.; Villarroel, M.; Junge, R. Analysis of aquaponics as an emerging technological innovation system. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 180, 232–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rakocy, J.E.; Masser, M.P.; Losordo, T.M. Recirculating aquaculture tank production systems: Aquaponics-integrating fish and plant culture. SRAC Publ. South. Reg. Aquac. Cent. 2006, 454, 1–16. [Google Scholar]
- Calone, R.; Pennisi, G.; Morgenstern, R.; Sanyé-Mengual, E.; Lorleberg, W.; Dapprich, P.; Winkler, P.; Orsini, F.; Gianquinto, G. Improving water management in European catfish recirculating aquaculture systems through catfish-lettuce aquaponics. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 687, 759–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delaide, B.; Teerlinck, S.; Decombel, A.; Bleyaert, P. Effect of wastewater from a pikeperch (Sander lucioperca L.) recirculated aquaculture system on hydroponic tomato production and quality. Agric. Water Manag. 2019, 226, 105814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palm, H.W.; Knaus, U.; Appelbaum, S.; Goddek, S.; Strauch, S.M.; Vermeulen, T.; Jijakli, M.H.; Kotzen, B. Towards commercial aquaponics: A review of systems, designs, scales and nomenclature. Aquac. Int. 2018, 26, 813–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Love, D.C.; Fry, J.P.; Li, X.; Hill, E.S.; Genello, L.; Semmens, K.; Thompson, R.E. Commercial aquaponics production and profitability: Findings from an international survey. Aquaculture 2015, 435, 67–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maucieri, C.; Forchino, A.A.; Nicoletto, C.; Junge, R.; Pastres, R.; Sambo, P.; Borin, M. Life cycle assessment of a micro aquaponic system for educational purposes built using recovered material. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 172, 3119–3127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maucieri, C.; Nicoletto, C.; Zanin, G.; Birolo, M.; Trocino, A.; Sambo, P.; Borin, M.; Xiccato, G. Effect of stocking density of fish on water quality and growth performance of European Carp and leafy vegetables in a low-tech aquaponic system. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0217561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Somerville, C.; Cohen, M.; Pantanella, E.; Stankus, A.; Lovatelli, A. Small-Scale Aquaponic Food Production: Integrated Fish and Plant Farming; FAO Fisheries and Aquaculture Technical Paper 589; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations: Rome, Italy, 2014; ISBN 9789251085332. [Google Scholar]
- Menon, R. Small Scale Aquaponic System. Int. J. Agric. Food Sci. Technol. 2013, 4, 2249–3050. [Google Scholar]
- Maucieri, C.; Nicoletto, C.; Schmautz, Z.; Sambo, P.; Komives, T.; Borin, M.; Junge-Berberovic, R. Vegetable Intercropping in a Small-Scale Aquaponic System. Agronomy 2017, 7, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Urrestarazu, L.; Lobillo-Eguíbar, J.; Fernández-Cañero, R.; Fernández-Cabanás, V.M. Suitability and optimization of FAO’s small-scale aquaponics systems for joint production of lettuce (Lactuca sativa) and fish (Carassius auratus). Aquac. Eng. 2019, 85, 129–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dos Santos, M.J.P.L. Smart cities and urban areas—Aquaponics as innovative urban agriculture. Urban For. Urban Green. 2016, 20, 402–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Junge-Berberovic, R.; König, B.; Villarroel, M.; Komives, T.; Jijakli, M.H. Strategic Points in Aquaponics. Water 2017, 9, 182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Csortan, G.; Ward, J.D.; Koth, B. Aquaponics in Urban Agriculture: Social Acceptance and Urban Food Planning. Horticulturae 2017, 3, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Konig, B.; Junge, R.; Bittsanszky, A.; Villarroel, M.; Komives, T. On the sustainability of aquaponics. Ecocycles 2016, 2, 26–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Greenfeld, A.; Becker, N.; McIlwain, J.; Fotedar, R.; Bornman, J.F. Economically viable aquaponics? Identifying the gap between potential and current uncertainties. Rev. Aquac. 2018, 11, 848–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ako, H.; Baker, A. Small-Scale Lettuce Production with Hydroponics or Aquaponics. Sustain. Agric. 2009, SA-2, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Goda, A.M.A.-S.; Essa, M.A.; Hassaan, M.S.; Sharawy, Z. Bio Economic Features for Aquaponic Systems in Egypt. Turkish J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2015, 15, 525–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sunny, A.R.; Islam, M.M.; Rahman, M.; Miah, M.Y.; Mostafiz, M.; Islam, N.; Hossain, M.Z.; Chowdhury, M.A.; Islam, M.A.; Keus, H.J. Cost effective aquaponics for food security and income of farming households in coastal Bangladesh. Egypt. J. Aquat. Res. 2019, 45, 89–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quagrainie, K.K.; Flores, R.M.V.; Kim, H.-J.; McClain, V. Economic analysis of aquaponics and hydroponics production in the U.S. Midwest. J. Appl. Aquac. 2017, 30, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, K.; Rosentrater, K. Life cycle assessment (LCA) and Techno-economic analysis (TEA) of tilapia-basil aquaponics. In Proceedings of the 2015 ASABE International Meeting, New Orleans, LA, USA, 26–29 July 2015; Volume 3, pp. 2248–2277. [Google Scholar]
- Somerville, C. Rooftop aquaponics for family nutrition in the Gaza strip, Palestine. In Rooftop Urban Agriculture; Orsini, F., Dubbeling, M., de Zeeuw, H., Gianquinto, G., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2017; pp. 344–354. [Google Scholar]
- Ellis, F. Livelihoods and Diversity in Developing Countries; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2000; ISBN 0198296967. [Google Scholar]
- Schneider, S.; Niederle, P.A. Resistance strategies and diversification of rural livelihoods: The construction of autonomy among Brazilian family farmers. J. Peasant. Stud. 2010, 37, 379–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Der Ploeg, J.D. The peasantries of the twenty-first century: The commoditisation debate revisited. J. Peasant. Stud. 2010, 37, 1–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milliken, S.; Stander, H. Aquaponics and Social Enterprise. In Aquaponics Food Production Systems; Springer Science and Business Media LLC.: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2019; pp. 607–619. [Google Scholar]
- INE. Indicadores Urbanos. Available online: https://www.ine.es/prensa/ua_2019.pdf (accessed on 27 August 2019).
- Dasgan, H.; Cetinturk, T.; Altuntas, O. The effects of biofertilisers on soilless organically grown greenhouse tomato. Acta Hortic. 2017, 555–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FADN. Farm Accounting Data Network An A to Z of Methodology. Available online: https://ec.europa.eu/agriculture/rica/pdf/site_en.pdf (accessed on 4 March 2020).
- Ministerio de Agricultura, Pesca y Alimentación. Análisis Comparativo de Costes Ligados al Modelo Europeo de Producción; Ministerio de Agricultura, Pesca y Alimentación: Madrid, España, 2019.
- Agri benchmark. Glossary of Terms Used in Agri Benchmark. Available online: http://www.agribenchmark.org/fileadmin/Dateiablage/B-Beef-and-Sheep/Misc/Other-Articles-Papers/BSR15-glossary.pdf (accessed on 10 December 2019).
- dos Santos, M.J.P.L.; Diz, H. Towards sustainability in European agricultural firms. Adv. Intell. Syst. Comput. 2019, 783, 161–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedmann, H. Household production and the national economy: Concepts for the analysis of Agrarian formations. J. Peasant. Stud. 1980, 7, 158–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Ploeg, J.D. Peasants and the Art of Farming; Practical Action Publishing: Warwickshire, UK, 2013; ISBN 978-1552665657. [Google Scholar]
- Dudin, M.N.; Lyasnikov, N.V.; Reshetov, K.Y.; Smirnova, O.O.; Vysotskaya, N.V. Economic Profit as Indicator of Food Retailing Enterprises’ Performance. Eur. Res. Stud. J. 2018, XXI, 468–479. [Google Scholar]
- Tynchenko, V.S.; Fedorova, N.V.; Kukartsev, V.V.; Boyko, A.A.; Stupina, A.A.; Danilchenko, Y.V. Methods of developing a competitive strategy of the agricultural enterprise. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2019, 315, 022105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asciuto, A.; Schimmenti, E.; Cottone, C.; Borsellino, V. A financial feasibility study of an aquaponic system in a Mediterranean urban context. Urban For. Urban Green. 2019, 38, 397–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EUROSTAT. Electricity Price Statistics—Statistics Explained. Available online: https://ec.europa.eu/eurostat/statistics-explained/index.php/Electricity_price_statistics (accessed on 9 September 2020).
- Hambrey, J.; Evans, S.; Pantanella, E. The Relevance of Aquaponics to the New Zealand aid Programme, Particularly in the Pacific; Ministry of Foreign Affairs and Trade (New Zealand): Wellington, New Zealand, 2013.
- Lennard, W. Aquaponic System Design Parameters: Fish to Plant Ratios (Feeding Rate Ratios). Aquaponics Solut. 2012, 3, 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Bailey, D.S.; Ferrarezi, R.S. Valuation of vegetable crops produced in the UVI Commercial Aquaponic System. Aquac. Rep. 2017, 7, 77–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryś-Jurek, R. Family farm income and their production and economic determinants according to the economic size in the EU countries in 2004–2015. In Economic Sciences for Agribusiness and Rural Economy, Proceedings of the 2018 International Scientific Conference, Warsaw, Poland, 7–8 June 2018; No 2; Gołębiewski, J., Ed.; Warsaw University of Life Sciences Press: Warsaw, Poland, 2018; pp. 21–28. [Google Scholar]
- Tokunaga, K.; Tamaru, C.; Ako, H.; Leung, P. Economics of Small-scale Commercial Aquaponics in Hawai‘i. J. World Aquac. Soc. 2015, 46, 20–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Commission. Energy Prices and Costs in Europe. Available online: https://ec.europa.eu/energy/sites/ener/files/epc_report_final_1.pdf (accessed on 5 March 2020).
- Nicoletto, C.; Maucieri, C.; Mathis, A.; Schmautz, Z.; Komives, T.; Sambo, P.; Junge-Berberovic, R. Extension of Aquaponic Water Use for NFT Baby-Leaf Production: Mizuna and Rocket Salad. Agronomy 2018, 8, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Upchurch, M.L. Implications of Economies of Scale to National Agricultural Adjustments. J. Farm Econ. 1961, 43, 1239–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Muyanga, M.; Jayne, T.S. Revisiting the Farm Size-Productivity Relationship Based on a Relatively Wide Range of Farm Sizes: Evidence from Kenya. Am. J. Agric. Econ. 2019, 101, 1140–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panzar, J.C.; Willig, R.D. Economies of Scope. Am. Econ. Rev. 1981, 71, 268. [Google Scholar]
- Shaik, S.; Addey, K.; Yeboah, O. Efficiency gains due to economies of scope and scale. In Proceedings of the 2017 Annual Meeting of Southern Agricultural Economics Association (SAEA), Mobile, Atlanta, 4–7 February 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Greenfeld, A.; Becker, N.; Bornman, J.F.; Dos Santos, M.J.; Angel, D. Consumer preferences for aquaponics: A comparative analysis of Australia and Israel. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 257, 109979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rödiger, M.; Hamm, U. How are organic food prices affecting consumer behaviour? A review. Food Qual. Prefer. 2015, 43, 10–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blidariu, F.; Grozea, A. Increasing the economical efficiency and sustainability of indoor fish farming by means of aquaponics. Anim. Sci. Biotechnol. 2011, 44, 1–8. [Google Scholar]

© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lobillo-Eguíbar, J.; Fernández-Cabanás, V.M.; Bermejo, L.A.; Pérez-Urrestarazu, L. Economic Sustainability of Small-Scale Aquaponic Systems for Food Self-Production. Agronomy 2020, 10, 1468. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy10101468
Lobillo-Eguíbar J, Fernández-Cabanás VM, Bermejo LA, Pérez-Urrestarazu L. Economic Sustainability of Small-Scale Aquaponic Systems for Food Self-Production. Agronomy. 2020; 10(10):1468. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy10101468
Chicago/Turabian StyleLobillo-Eguíbar, José, Víctor M. Fernández-Cabanás, Luis Alberto Bermejo, and Luis Pérez-Urrestarazu. 2020. "Economic Sustainability of Small-Scale Aquaponic Systems for Food Self-Production" Agronomy 10, no. 10: 1468. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy10101468
APA StyleLobillo-Eguíbar, J., Fernández-Cabanás, V. M., Bermejo, L. A., & Pérez-Urrestarazu, L. (2020). Economic Sustainability of Small-Scale Aquaponic Systems for Food Self-Production. Agronomy, 10(10), 1468. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy10101468








