Triethyl Citrate (TEC) as a Dispersing Aid in Polylactic Acid/Chitin Nanocomposites Prepared via Liquid-Assisted Extrusion
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of Chitin Nanocrystals and Suspensions for Liquid Feeding
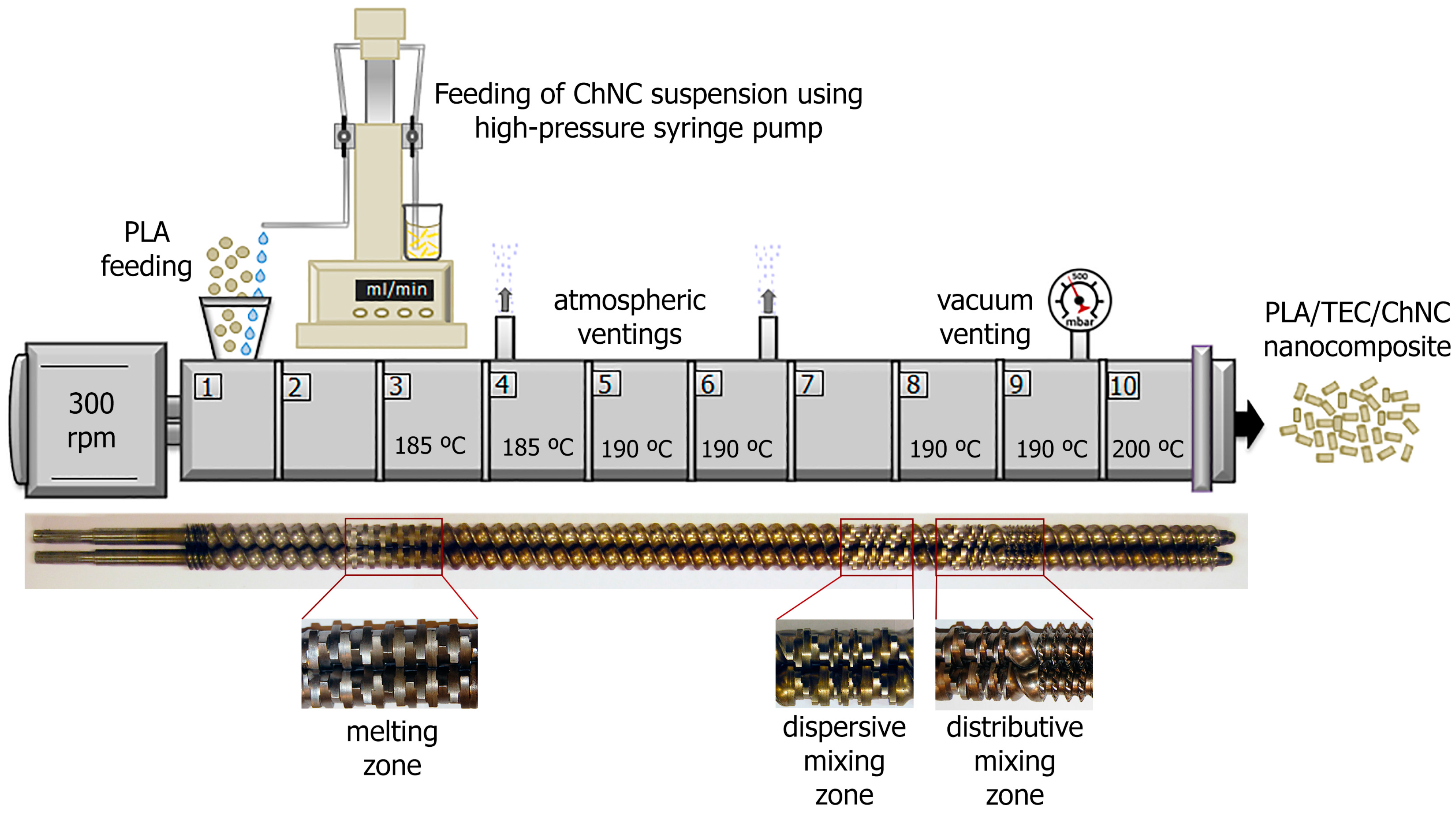
2.3. Extrusion of Nanocomposites
2.4. Characterization
2.4.1. Weight
2.4.2. Melt Flow
2.4.3. Transparency
2.4.4. Dispersion and Morphology
2.4.5. Chemical Characterization
2.4.6. Thermal Properties and Crystallinity
2.4.7. Thermo-Mechanical Properties
2.4.8. Mechanical Testing
3. Results and Discussion
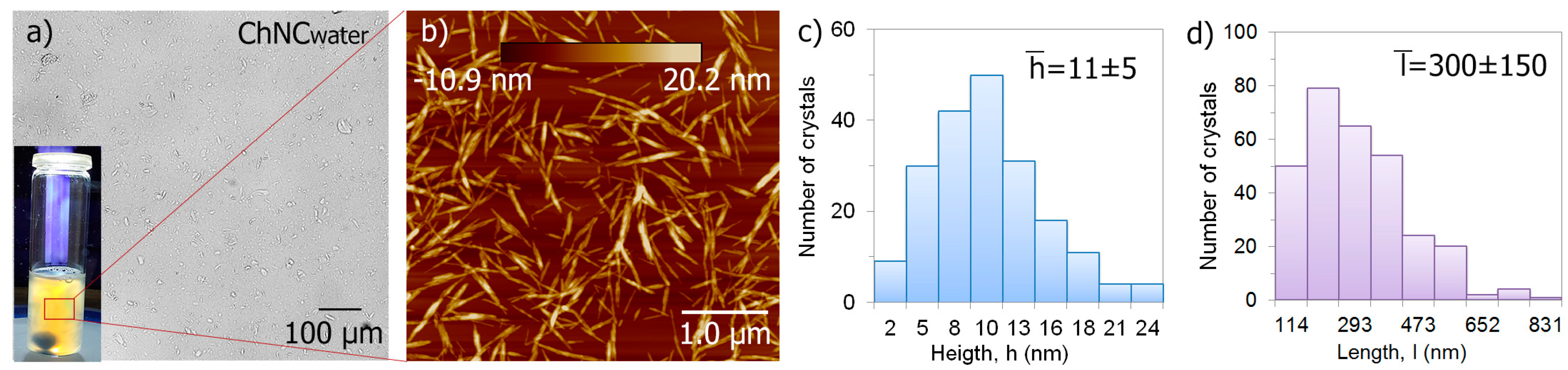
3.1. Suspensions for Liquid Feeding
3.2. Molecular Weight
3.3. Melt Flow
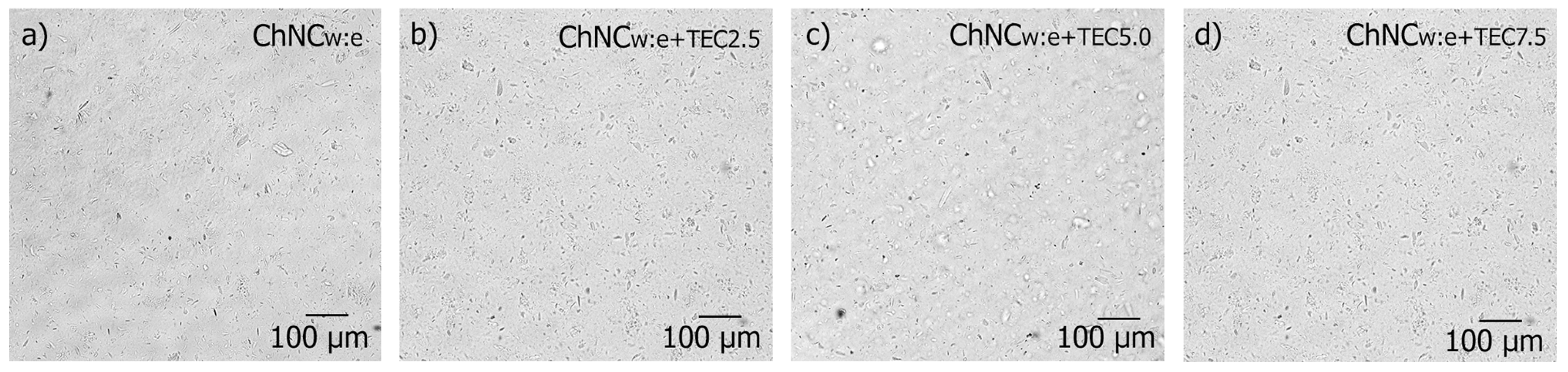
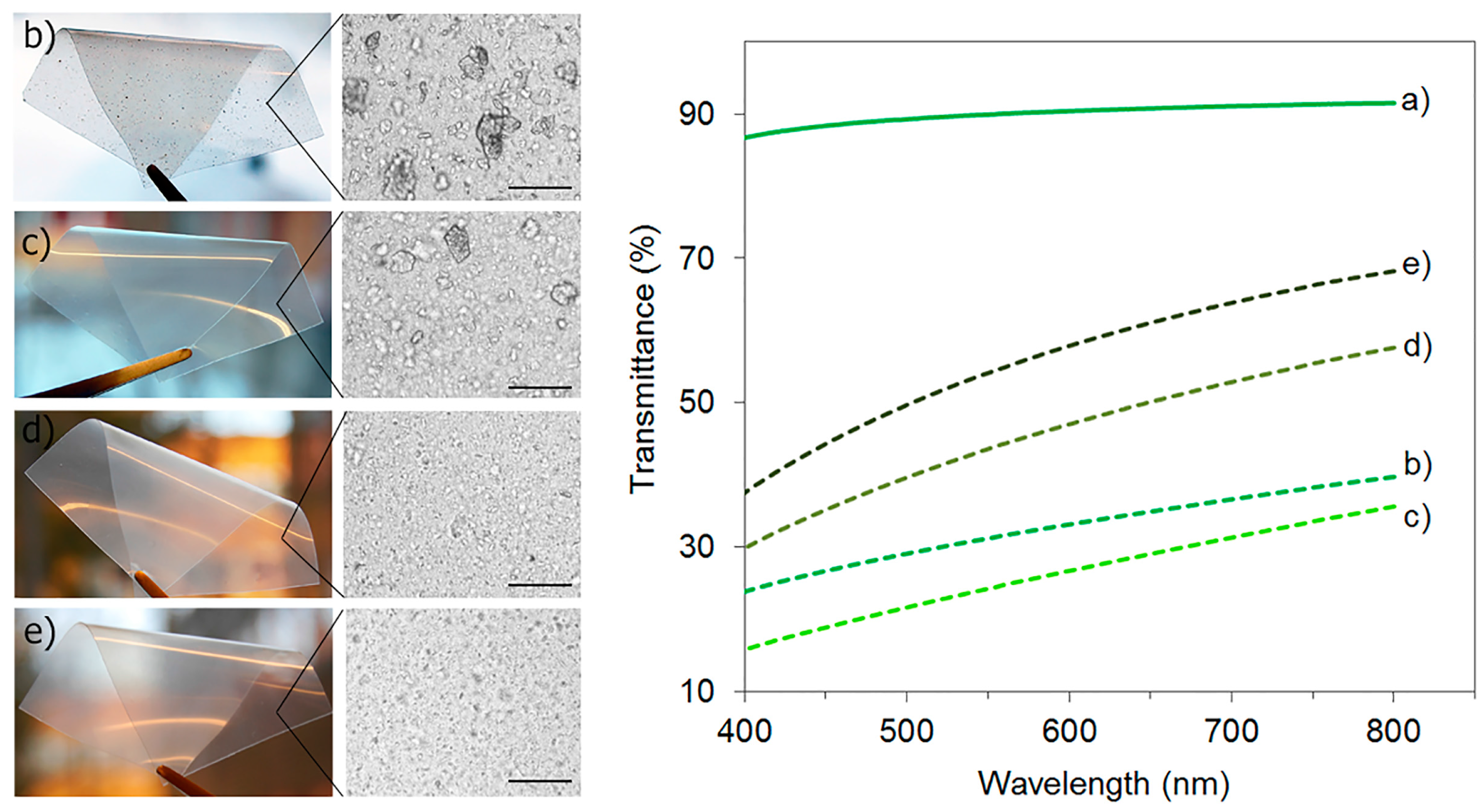
3.4. Transparency and Visual Appearance
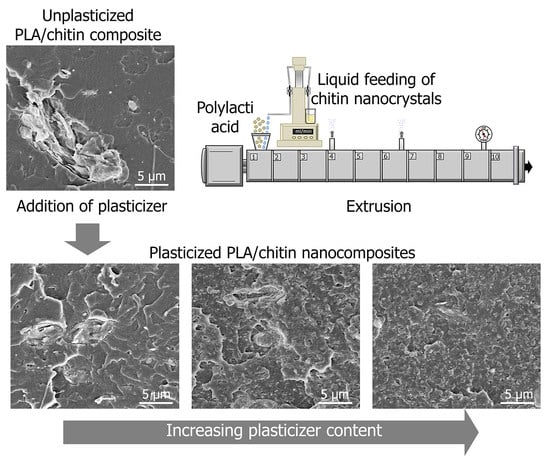
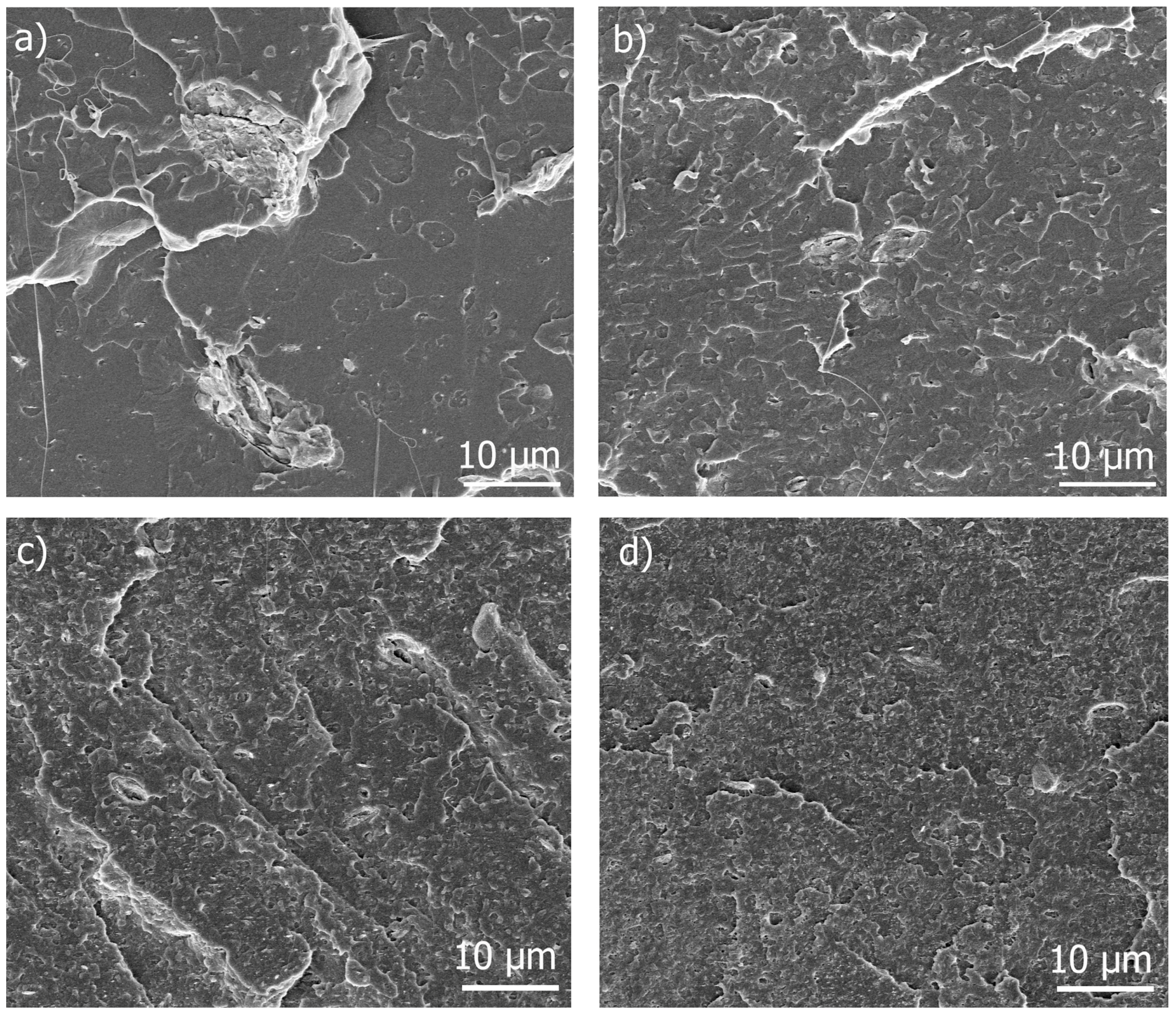
3.5. Morphology of Nanocomposites and ChNC Dispersion
3.6. Chemical Charaterization
3.7. Thermal Properties and Crystallinity
3.8. Thermo-Mechanical Properties
3.9. Mechanical Properties
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lim, L.-T.; Auras, R.; Rubino, M. Processing technologies for poly(lactic acid). Prog. Polym. Sci. 2008, 33, 820–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mochizuki, M. Chapter 29. Textile applications. In Poly(Lactic Acid): Synthesis, Structures, Properties, Processing, and Applications; Auras, R., Lim, L.-T., Selke, S.E.M., Tsuji, H., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2010; pp. 469–476. ISBN 978-0-470-29366-9. [Google Scholar]
- Soulestin, J.; Prashantha, K.; Lacrampe, M.; Krawczak, P. Chapter 4. Bioplastics based nanocomposites for packing applications. In Handbook Bioplastics Biocomposites Engineering Applications; Pilla, S., Ed.; John Wiley & Sons and Scrivener Publishing LLC: Hoboken, NJ, USA; Beverly, MA, USA, 2011; Part II; pp. 77–120. ISBN 978-0-470-62607-8. [Google Scholar]
- Labrecque, L.V.; Kumar, R.A.; Davé, V.; Gross, R.A.; McCarthy, S.P. Citrate esters as plasticizers for poly(lactic acid). J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1997, 66, 1507–1513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walha, F.; Lamnawar, K.; Maazouz, A.; Jaziri, M. Rheological, morphological and mechanical studies of sustainably sourced polymer blends based on poly(lactic acid) and polyamide 11. Polymers 2016, 8, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoclet, G.; Sclavons, M.; Lecouvet, B.; Devaux, J.; Van Velthem, P.; Boborodea, A.; Bourbigot, S.; Sallem-Idrissi, N. Elaboration of poly(lactic acid)/halloysite nanocomposites by means of water assisted extrusion: Structure, mechanical properties and fire performance. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 57553–57563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chieng, B.; Ibrahim, N.; Yunus, W.; Hussein, M.; Then, Y.; Loo, Y. Effects of graphene nanoplatelets and reduced graphene oxide on poly(lactic acid) and plasticized poly(lactic acid): A comparative study. Polymers 2014, 6, 2232–2246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrera, N.; Mathew, A.P.; Oksman, K. Plasticized polylactic acid/cellulose nanocomposites prepared using melt-extrusion and liquid feeding: Mechanical, thermal and optical properties. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2015, 106, 149–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrera, N.; Salaberria, A.M.; Mathew, A.P.; Oksman, K. Plasticized polylactic acid nanocomposite films with cellulose and chitin nanocrystals prepared using extrusion and compression molding with two cooling rates: Effects on mechanical, thermal and optical properties. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2015, 83, 89–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trifol, J.; Plackett, D.; Sillard, C.; Szabo, P.; Bras, J.; Daugaard, A.E. Hybrid poly(lactic acid)/nanocellulose/nanoclay composites with synergistically enhanced barrier properties and improved thermomechanical resistance. Polym. Int. 2016, 65, 988–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Salaberria, A.M.; Diaz, R.H.; Labidi, J.; Fernandes, S.C.M. Preparing valuable renewable nanocomposite films based exclusively on oceanic biomass—Chitin nanofillers and chitosan. React. Funct. Polym. 2015, 89, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nair, K.G.; Dufresne, A. Crab Shell Chitin Whisker Reinforced Natural Rubber Nanocomposites. 2. Mechanical Behavior. Biomacromolecules 2003, 4, 666–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.; Lin, H.; Meredith, J.C. Poly(ethylene oxide) bionanocomposites reinforced with chitin nanofiber networks. Polymer 2016, 84, 267–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salaberria, A.M.; Labidi, J.; Fernandes, S.C.M. Chitin nanocrystals and nanofibers as nano-sized fillers into thermoplastic starch-based biocomposites processed by melt-mixing. Chem. Eng. J. 2014, 256, 356–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.C.Y.; Sun, Y.-C.; Guan, Q.; Naguib, H. Effects of chitin nanowhiskers on the thermal, barrier, mechanical, and rheological properties of polypropylene nanocomposites. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 72086–72095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Torres, F.G.; Vilaseca, F.; Peijs, T. Influence of the processing conditions on the mechanical properties of chitin whisker reinforced poly(caprolactone) nanocomposites. J. Biobased Mater. Bioenergy 2007, 1, 341–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrera, N.; Roch, H.; Salaberria, A.M.; Pino-Orellana, M.A.; Labidi, J.; Fernandes, S.C.M.; Radic, D.; Leiva, A.; Oksman, K. Functionalized blown films of plasticized polylactic acid/chitin nanocomposite: Preparation and characterization. Mater. Des. 2016, 92, 846–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Gao, Y.; Zhao, J.; Sun, J.; Li, D. Homogeneous dispersion of chitin nanofibers in polylactic acid with different pretreatment methods. Cellulose 2017, 24, 1705–1715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nair, K.G.; Dufresne, A.; Gandini, A.; Belgacem, M.N. Crab shell chitin whiskers reinforced natural rubber nanocomposites. 3. Effect of chemical modification of chitin whiskers. Biomacromolecules 2003, 4, 1835–1842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salaberria, A.M.; Diaz, R.H.; Andrés, M.A.; Fernandes, S.C.M.; Labidi, J. The antifungal activity functionalized chitin nanocrystals in poly (lactid acid) films. Materials 2017, 10, 546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, Y.; Saito, T.; Isogai, A. Chitin nanocrystals prepared by TEMPO-mediated oxidation of α-Chitin. Biomacromolecules 2008, 9, 192–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Liu, H.; Luo, B.; Wen, W.; He, L.; Liu, M.; Zhou, C. Nanocomposites of poly(l-lactide) and surface-modified chitin whiskers with improved mechanical properties and cytocompatibility. Eur. Polym. J. 2016, 81, 266–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oksman, K.; Mathew, A.P.; Bondeson, D.; Kvien, I. Manufacturing process of cellulose whiskers/polylactic acid nanocomposites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2006, 66, 2776–2784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Zhang, X.; Ma, X.; Fang, J. Influence of carbon black on the properties of plasticized poly(lactic acid) composites. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2008, 93, 1044–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, P.; Gao, Y.; Wu, G.F.; Zhang, L.P. Nanocomposites of poly(lactic acid) reinforced with cellulose nanofibrils. BioResources 2010, 5, 1811–1823. [Google Scholar]
- Yeniova Erpek, C.E.; Ozkoc, G.; Yilmazer, U. Effects of halloysite nanotubes on the performance of plasticized poly(lactic acid)-based composites. Polym. Compos. 2016, 37, 3134–3148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chieng, B.; Ibrahim, N.; Yunus, W.; Hussein, M. Poly(lactic acid)/poly(ethylene glycol) polymer nanocomposites: effects of graphene nanoplatelets. Polymers 2013, 6, 93–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathew, A.P.; Oksman, K.; Sain, M. The effect of morphology and chemical characteristics of cellulose reinforcements on the crystallinity of polylactic acid. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2006, 101, 300–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasanthakumari, R.; Pennings, A.J. Crystallization kinetics of poly(l-lactic acid). Polymer 1983, 24, 175–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hideto, T. Chapter 21. Hydrolytic degradation. In Poly(Lactic Acid): Synthesis, Structures, Properties, Processing, and Applications; Auras, R., Lim, L.-T., Selke, S.E., Tsuji, H., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2010; pp. 1–487. ISBN 978-0-470-29366-9. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Q.; Xanthos, M. Nanosize and microsize clay effects on the kinetics of the thermal degradation of polylactides. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2009, 94, 327–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizvi, R.; Cochrane, B.; Naguib, H.; Lee, P.C. Fabrication and characterization of melt-blended polylactide-chitin composites and their foams. J. Cell. Plast. 2011, 47, 283–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray, S.S.T. Chapter 19. Nanocomposites. In Poly(Lactic Acid): Synthesis, Structures, Properties, Processing, and Applications; Auras, R., Lim, L.-T., Selke, S.E., Tsuji, H., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2010; pp. 311–321. ISBN 978-0-470-29366-9. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; Huneault, M.A. Effect of nucleation and plasticization on the crystallization of poly(lactic acid). Polymer 2007, 48, 6855–6866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oksman, K.; Mathew, A.P. Chapter 5. Melt compounding process of cellulose nanocomposites. In Handbook of Green Materials—2. Bionanocomposites: Processing, Characterization and Properties—Materials and Energy; Oksman, K., Mathew, A.P., Bismarck, A., Rojas, O., Sain, M., Eds.; World Scientific Publishing: Singapore, 2014; Volume 5, pp. 53–68. ISBN 978-981-4566-45-2. [Google Scholar]
- Hishammuddin, N.; Zakaria, Z. Mechanical strength properties of chitin/polylactic acid biocomposite film. eProc. Chem. 2016, 1, 31–35. [Google Scholar]
- Rinaudo, M. Chitin and chitosan: Properties and applications. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2006, 31, 603–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathew, A.P.; Laborie, M.-P.G.; Oksman, K. Cross-linked chitosan/chitin crystal nanocomposites with improved permeation selectivity and pH stability. Biomacromolecules 2009, 10, 1627–1632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yew, G.H.; Yusof, A.M.M.; Ishak, Z.A.M.; Ishiaku, U.S. Water absorption and enzymatic degradation of poly(lactic acid)/rice starch composites. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2005, 90, 488–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosdi, N.; Zakaria, Z. Biodegradability properties of chitin/polylactic acid composite films. eProc. Chem. 2016, 1, 48–52. [Google Scholar]
- Ljungberg, N.; Wesslén, B. The effects of plasticizers on the dynamic mechanical and thermal properties of poly(lactic acid). J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2002, 86, 1227–1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Materials | Feeding Rate (kg/h) | Composition of Materials (wt %) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PLA | Suspension | PLA | TEC | ChNC | |
| PLA | 2.00 | 1.56 1 | 100 | - | - |
| PLA-ChNC | 1.94 | 1.56 2 | 97.0 | - | 3 |
| PLA-TEC2.5 | 1.95 | 1.55 3 | 97.5 | 2.5 | - |
| PLA-TEC2.5-ChNC | 1.89 | 1.61 4 | 94.5 | 2.5 | 3 |
| PLA-TEC5.0 | 1.90 | 1.60 3 | 95.0 | 5.0 | - |
| PLA-TEC5.0-ChNC | 1.84 | 1.66 4 | 92.0 | 5.0 | 3 |
| PLA-TEC7.5 | 1.85 | 1.65 3 | 92.5 | 7.5 | - |
| PLA-TEC7.5-ChNC | 1.79 | 1.71 4 | 89.5 | 7.5 | 3 |
| Materials | Molecular Weight (kg/mol) | Melt Flow Index (g/10 min) |
|---|---|---|
| PLA 1 | 199 | - |
| PLA 2 | 186 | - |
| PLA 3 | 199 | 3.1 |
| PLA-ChNC | 181 | 3.5 |
| PLA-TEC2.5 | - | 3.2 |
| PLA-TEC2.5-ChNC | - | 2.7 |
| PLA-TEC5.0 | 196 | 4.3 |
| PLA-TEC5.0-ChNC | 193 | 3.8 |
| PLA-TEC7.5 | - | 4.9 |
| PLA-TEC7.5-ChNC | - | 3.7 |
| Materials | Young’s Modulus (GPa) | Tensile Strength (MPa) | Ultimate Strength (MPa) | Elongation at Break (%) | Work of Fracture (MJ/m3) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PLA 1 | 1.86 ± 0.10 | 60.6 ± 0.6 | 52.0 ± 4.8 | 7.9 ± 0.4 | 3.5 ± 0.3 |
| PLA 2 | 1.87 a ± 0.05 | 59.2 a ± 2.1 | 55.2 a ± 3.3 | 5.8 a ± 0.4 | 2.3 a ± 0.2 |
| PLA-ChNC | 1.91 a ± 0.08 | 52.7 b ± 0.7 | 50.2 a ± 1.7 | 4.5 b ± 0.3 | 1.6 b ± 0.2 |
| PLA-TEC2.5 | 2.04 α ± 0.13 | 54.7 α ± 3.9 | 51.6 α ± 3.9 | 5.6 α ± 0.6 | 2.2 α ± 0.3 |
| PLA-TEC2.5-ChNC | 1.90 α ± 0.03 | 56.6 α ± 0.9 | 55.3 α ± 1.3 | 4.2 β ± 0.3 | 1.4 β ± 0.2 |
| PLA-TEC5.0 | 1.80 δ ± 0.04 | 49.4 δ ± 2.5 | 44.7 δ ± 2.0 | 6.5 δ ± 0.8 | 2.4 δ ± 0.3 |
| PLA-TEC5.0-ChNC | 1.94 γ ± 0.02 | 54.4 γ ± 1.7 | 52.3 γ ± 1.8 | 4.6 γ ± 0.1 | 1.6 γ ± 0.1 |
| PLA-TEC7.5 | 1.83 A ± 0.00 | 43.7 A ± 0.6 | 39.8 A ± 3.5 | 5.6 A ± 0.9 | 1.8 A ± 0.4 |
| PLA-TEC7.5-ChNC | 1.92 B ± 0.02 | 47.5 B ± 0.2 | 45.8 B ± 0.1 | 5.3 A ± 0.5 | 1.9 A ± 0.3 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Herrera, N.; Singh, A.A.; Salaberria, A.M.; Labidi, J.; Mathew, A.P.; Oksman, K. Triethyl Citrate (TEC) as a Dispersing Aid in Polylactic Acid/Chitin Nanocomposites Prepared via Liquid-Assisted Extrusion. Polymers 2017, 9, 406. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym9090406
Herrera N, Singh AA, Salaberria AM, Labidi J, Mathew AP, Oksman K. Triethyl Citrate (TEC) as a Dispersing Aid in Polylactic Acid/Chitin Nanocomposites Prepared via Liquid-Assisted Extrusion. Polymers. 2017; 9(9):406. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym9090406
Chicago/Turabian StyleHerrera, Natalia, Anshu Anjali Singh, Asier M. Salaberria, Jalel Labidi, Aji P. Mathew, and Kristiina Oksman. 2017. "Triethyl Citrate (TEC) as a Dispersing Aid in Polylactic Acid/Chitin Nanocomposites Prepared via Liquid-Assisted Extrusion" Polymers 9, no. 9: 406. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym9090406
APA StyleHerrera, N., Singh, A. A., Salaberria, A. M., Labidi, J., Mathew, A. P., & Oksman, K. (2017). Triethyl Citrate (TEC) as a Dispersing Aid in Polylactic Acid/Chitin Nanocomposites Prepared via Liquid-Assisted Extrusion. Polymers, 9(9), 406. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym9090406