A Polyvinyl Alcohol-Polyaniline Based Electro-Conductive Hydrogel for Controlled Stimuli-Actuable Release of Indomethacin
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Optimization of Electro-Conductive Hydrogel
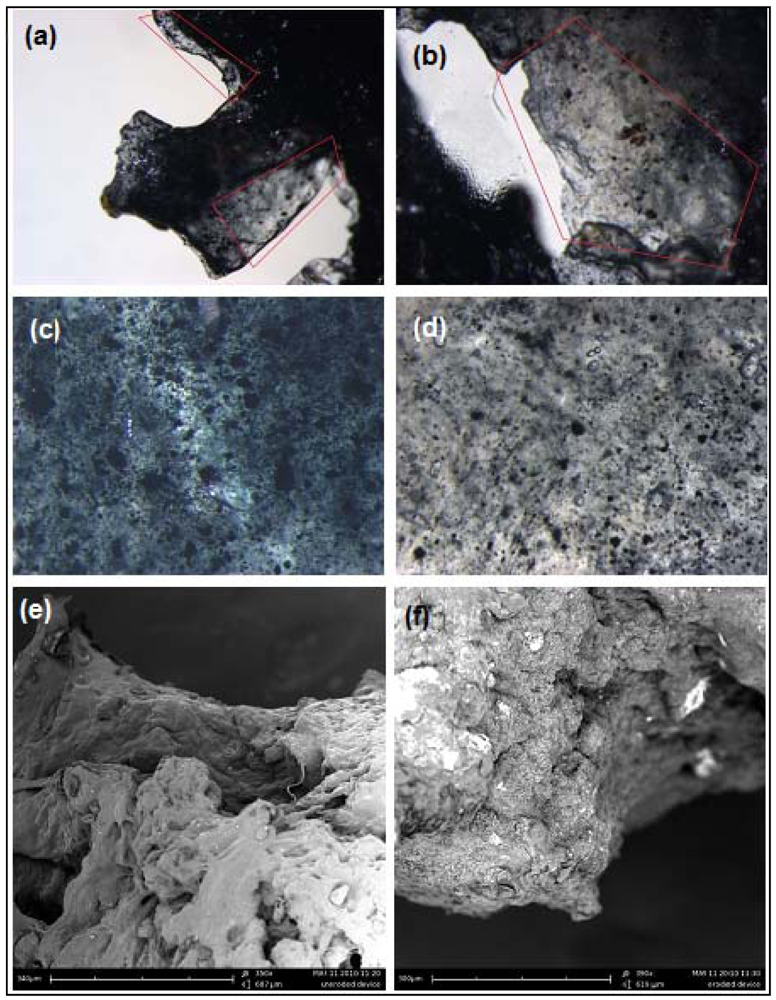
2.2. Assessment of the Surface Morphology of the ECH
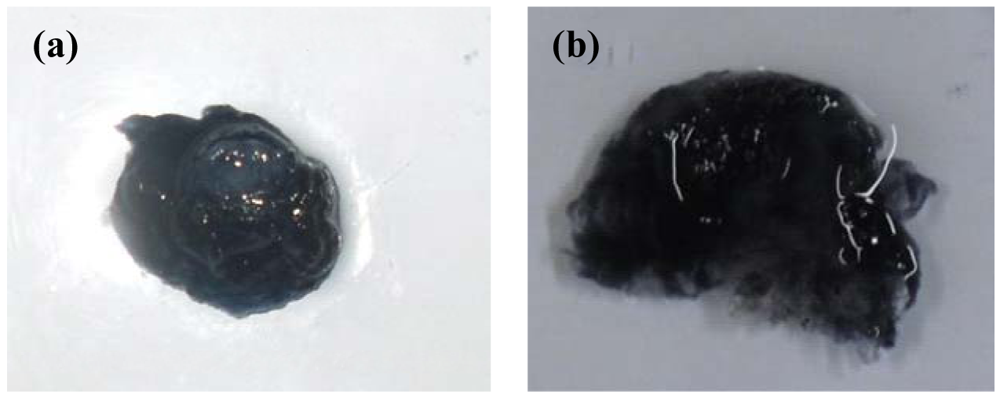
2.3. Effect of Crosslinking on the Rate of Erosion of the ECH
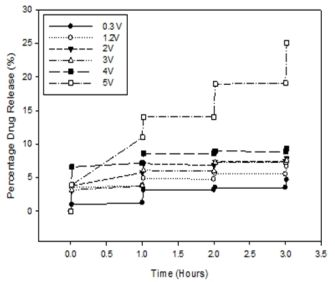
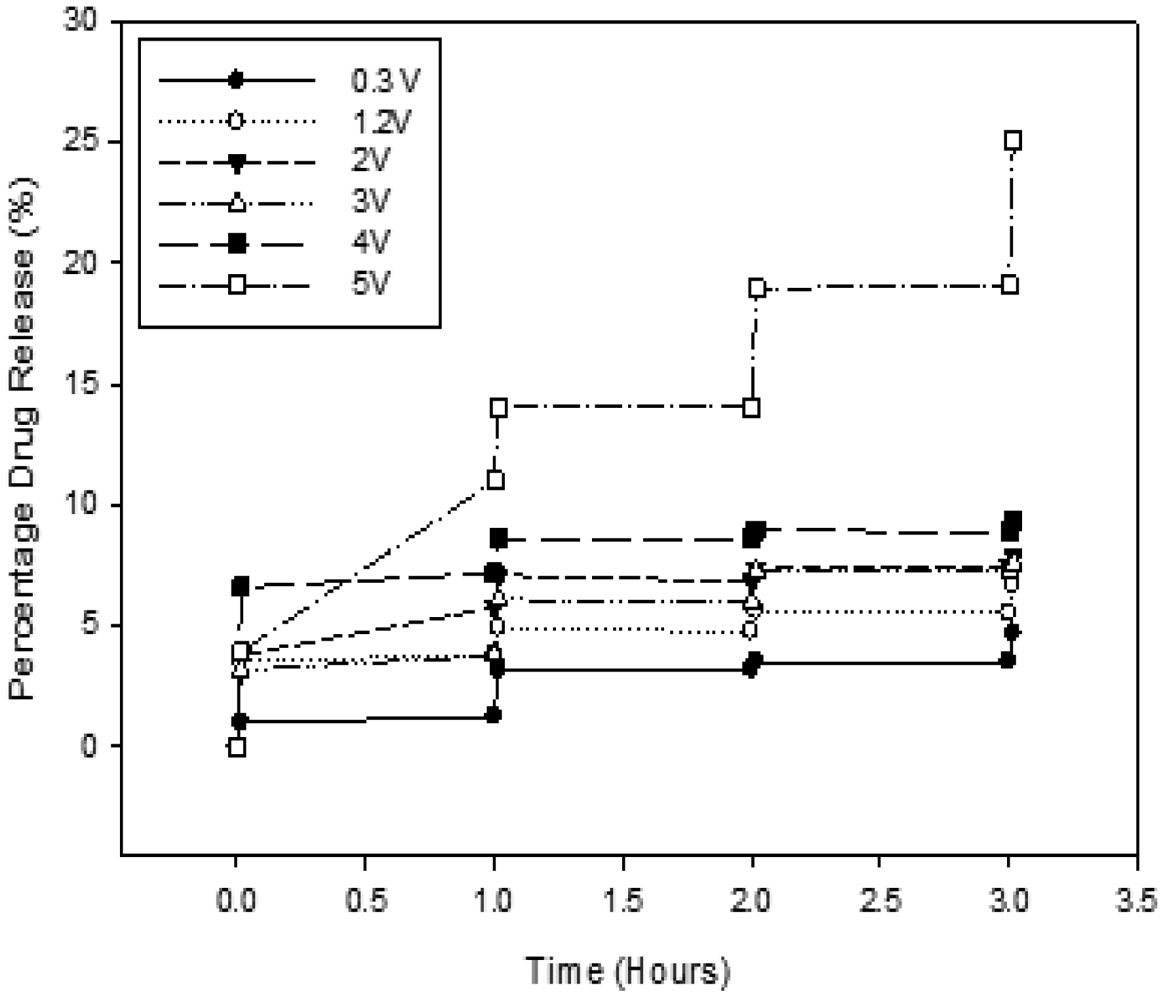
2.4. Voltage Optimization Based on the Drug Release Profile from the ECH
2.5. The Rate of Erosion as a Mechanism for Drug Release from the ECH
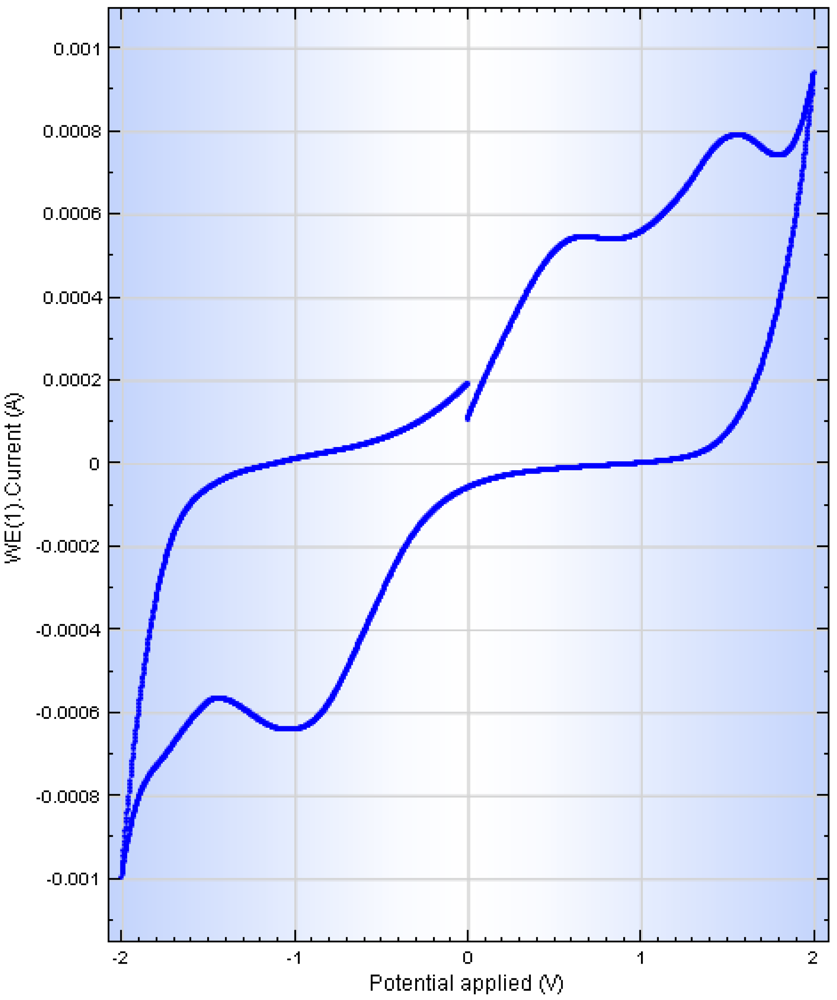
2.6. Cyclic Voltammetry Studies on the Electro-Conductive Hydrogel
2.7. Conductivity Measurement of the ECH
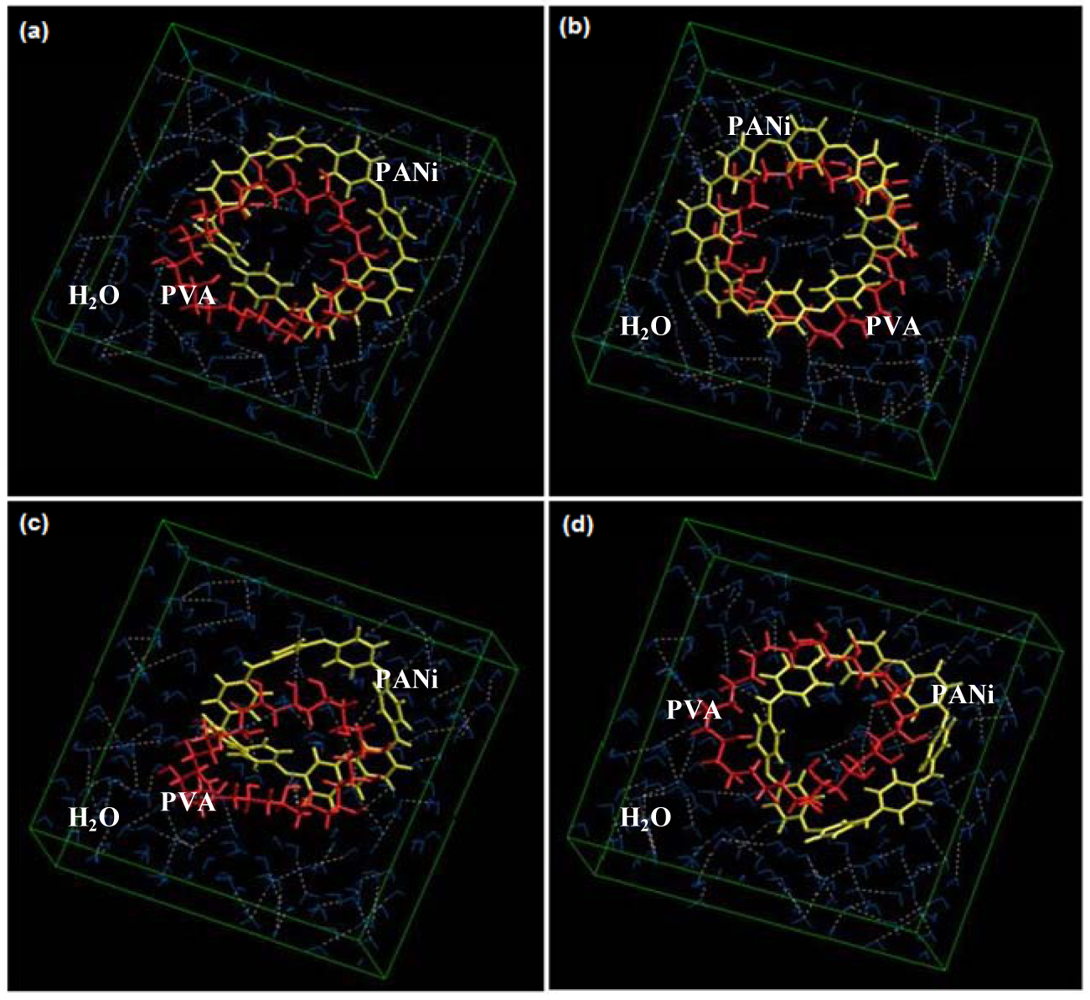
2.8. Molecular Mechanics Simulations of the ECH under the Influence of an External Electric Field
3. Experimental Section
3.1. Materials
3.2. Preparation of the Electro-Conductive Hydrogel
3.3. Optimization Studies Employing a Box-Behnken Experimental Design Template
3.4. Determination of the Surface Morphology of the Electro-Conductive Hydrogel
3.5. Assessment of the Drug Release from the Electro-Conductive Hydrogel
3.6. Determination of the Drug Entrapment Efficiency
3.7. Determination of the Erosion Rate
3.8. The influence of Varying Concentration of Polyaniline on the Electro-Conductive Hydrogel
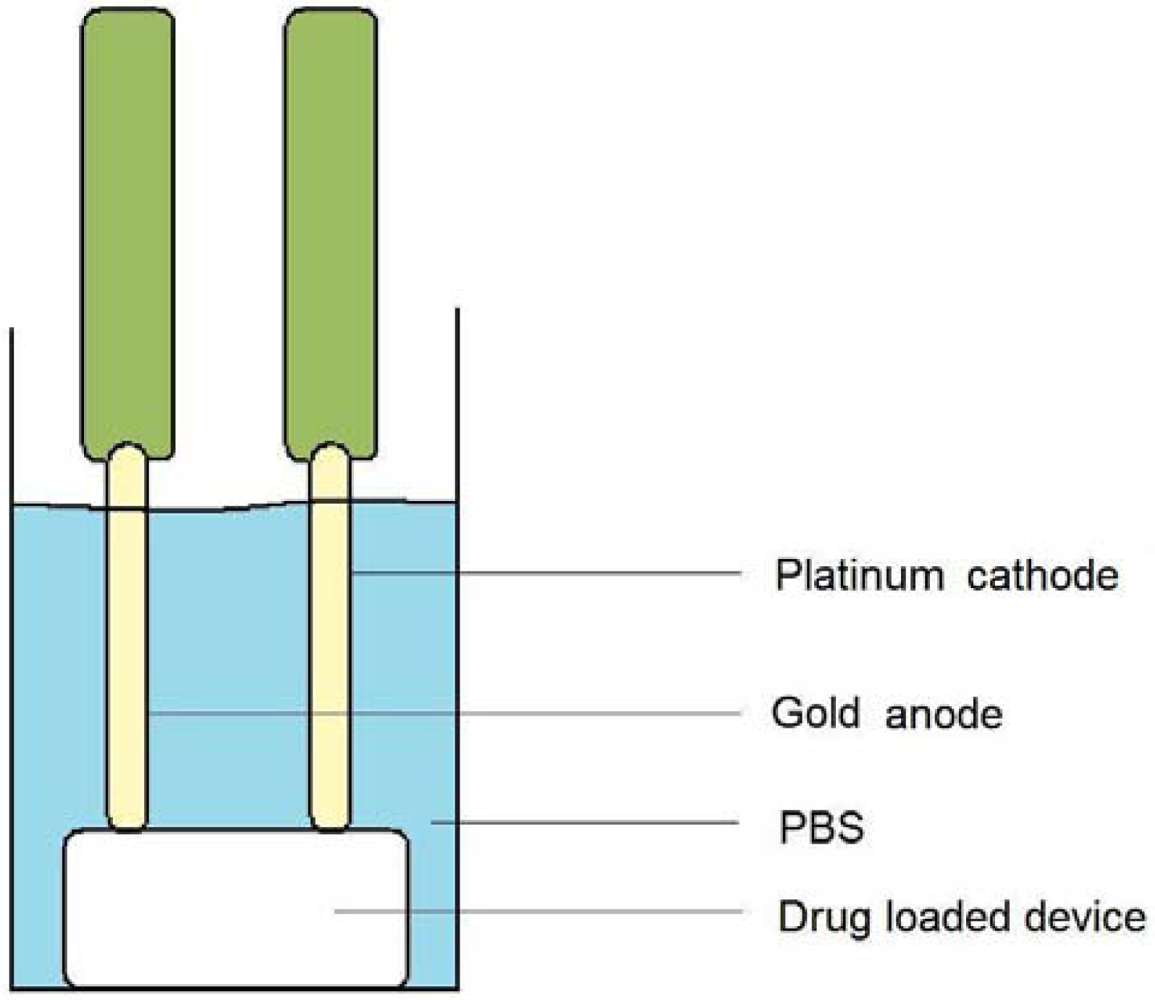
3.9. Cyclic Voltammetry Studies on the Electro-Conductive Hydrogel
3.10. Molecular Mechanics Simulations
4. Conclusions





| Batch | Independent variables | Dependent variables | Levels, Actual (Coded) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PANi (%w/w) | PVA (g) | DAA (g) | Drug Release (%) | DEE (%) | Erosion (%w/w) | Low (−1) | Medium (0) | High(1) | |
| 1 | −1 | 1 | 0 | 1.9 | 89.44 | 5.5 | |||
| 2 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 12.0 | 37.89 | 17.32 | |||
| 3 | −1 | 0 | 1 | 18.0 | 43.18 | 10.43 | |||
| 4a | 0 | 0 | 0 | 24.0 | 36.62 | 14.16 | |||
| 5 | 0 | 1 | −1 | 16.0 | 39.74 | 8.97 | |||
| 6 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 11.0 | 59.22 | 7.36 | |||
| 7 | −1 | 0 | −1 | 5.9 | 73.67 | 5.67 | |||
| 8a | 0 | 0 | 0 | 57.0 | 23.87 | 4.28 | |||
| 9 | 0 | −1 | −1 | 12.0 | 82.02 | 15.91 | |||
| 10 | 1 | −1 | 0 | 7.7 | 82.43 | 23.39 | |||
| 11 | 0 | −1 | 1 | 15.8 | 41.95 | 8.77 | |||
| 12a | 0 | 0 | 0 | 24.4 | 36.07 | 24.36 | |||
| 13 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 42.0 | 34.25 | 9.05 | |||
| 14 | −1 | −1 | 0 | 41.0 | 25.07 | 15.31 | |||
| 15 | 1 | 0 | −1 | 34.0 | 26.63 | 10.16 | |||
| Independent variables | |||||||||
| PVA (g) | 0.50 | 0.65 | 0.80 | ||||||
| DAA (g) | 0.00 | 0.15 | 0.30 | ||||||
| PANi (%w/w) | 1.0 | 2.5 | 4.0 | ||||||
| Constraints set | Drug Release | DEE | Erosion rate |
|---|---|---|---|
| (%) | (%) | (%) | |
| Target | 1.7 | Maximized | Minimized |
| Yield | 1.9040 | 80.5381 | 6.3201 |
| d* | 0.99993 | 0.87179 | 0.93052 |
| Optimal = PANi (1.3418 %w/w), PVA (0.8g), DAA (0.0689g); D** = 0.93261 | |||
| Formulation | DAA | PVA | PANi | Erosion |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| g (%) | g (%) | mg (%) | % of original mass | |
| F1 | 0.0 (0.0) | 0.5 (96.15) | 20 (3.85) | 14 |
| F2 | 1.0 (65.79) | 0.5 (32.89) | 20 (1.32) | 4 |
| F3 | 0.5 (64.94) | 0.25 (32.47) | 20 (2.59) | 6 |
| F4 | 0.5 (32.89) | 1.0 (65.79) | 20 (1.32) | 7 |
| F5 | 0.25 (32.47) | 0.5 (64.94) | 20 (2.59) | 11 |
| PANi concentration | Erosion rate (% of original mass) |
|---|---|
| 1 %w/w | 4.23 |
| 3 %w/w | 10.43 |
| PANi concentration | Conductivity |
|---|---|
| (%w/w) | (μS) |
| 1 | 97.45 ± 7.00 |
| 2.5 | 108.20 ± 4.52 |
| 4 | 130.30 ± 11.99 |
| Structure | Energy(kcal/mol) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total | ΔEstimulation | Bond | Angle | vdW | |
| PVA-PANi-0.00 | −3,115.92 | - | 33.4948 | 56.3898 | 71.5598 |
| PVA-PANi-0.01 | −2,826.36 | +289.56 | 44.6791 | 82.9305 | 72.6148 |
| PVA-PANi-0.02 | −2,643.41 | +472.51 | 61.2286 | 129.845 | 76.1276 |
| PVA-PANi-0.03 | −2,213.01 | +902.91 | 86.1102 | 184.596 | 82.4647 |
| PVA-PANi-0.04 | −1,982.23 | +1,133.69 | 111.422 | 255.45 | 91.9177 |
| PVA-PANi-0.05 | −1,772.02 | +1,343.9 | 141.338 | 335.476 | 98.5723 |
Acknowledgments
References
- Li, H.; Luo, R.; Lam, K.Y. Modeling of ionic transport in electric-stimulus-responsive hydrogels. J. Membr. Sci. 2007, 289, 284–296. [Google Scholar]
- El-Sherbiny, I.M.; Abdel-Bary, E.M.; Harding, D.R.K. Preparation and in vitro evaluation of new pH-sensitive hydrogel beads for oral delivery of protein drugs. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2009, 115, 2828–2837. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, G.; Imanishi, Y.; Ito, Y. pH-sensitive thin hydrogel microfabricated by photolithography. Langmuir 1998, 14, 6610–6612. [Google Scholar]
- Santos, J.R.; Alves, N.M.; Mano, J.F. New thermo-responsive hydrogel based on poly(N-isopropylacrylamide)/Hyaluronic acid semi-interpenetrated networks: Swelling properties and drug release studies. J. Bioact. Compat. Polym. 2010, 25, 169–184. [Google Scholar]
- Hou, H.; Kim, W.; Grunlan, M.; Han, A. A thermal responsive hydrogel poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) micropatterning method using microfluidic technique. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2009, 19, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- McDonald, T.O.; Qu, H.; Saunders, B.R.; Ulijn, R.V. Branched peptide actuators for enzyme responsive hydrogel particles. Soft Matter 2009, 5, 1728–1734. [Google Scholar]
- Thornton, P.D.; Mart, R.J.; Ulijn, R.V. Enzyme-responsive polymer hydrogel particles for controlled release. Adv. Mater. 2006, 19, 1252–1256. [Google Scholar]
- Luiz, L.M.; de Torresi, S.I.C. Conducting polymer-hydrogel composites for electrochemical release devices: Synthesis and characterization of semi-interpenetrating polyaniline-polyacrylamide networks. Electrochem. Commun. 2005, 7, 717–723. [Google Scholar]
- Iseki, M.; Ikematsu, M.; Sugiyama, Y.; Tago, I.; Mizukami, A. A new type of current oscillation in polypyrrole membranes produced by electrochemical potential control. J. Electroanal. Chem. 1995, 386, 253–256. [Google Scholar]
- Geetha, S.; Rao, C.R.K.; Vijayan, M.; Trivedi, D.C. Biosensing and drug delivery by polypyrrole. Anal. Chim. Acta 2006, 568, 119–125. [Google Scholar]
- Posadas, D.; Florit, M.I. The redox switching of electroactive polymers. J. Phys. Chem. B 2004, 108, 15470–15476. [Google Scholar]
- Small, C.J.; Too, C.O.; Wallace, G.G. Responsive conducting polymer-hydrogel composite. Polym. Gels Netw. 1997, 5, 251–265. [Google Scholar]
- Richardson-Burns, S.; Hendricks, J.L.; Foster, B.; Povlich, L.K.; Kim, D.; Martin, D.C. Polymerization of the conducting polymer poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene) (PEDOT) around living neural cells. Biomaterials 2007, 28, 1539–1552. [Google Scholar]
- Kinlen, P.J.; Frushour, B.G.; Ding, Y.; Menon, V. Synthesis and characterization of organically soluble polyaniline and polyaniline block copolymer. Synth. Met. 1999, 101, 758–761. [Google Scholar]
- Kaneto, K.; Kaneko, M.; Min, Y.; MacDiarmid, A.G. “Artificial Muscle”: Electromechanical actuators using polyaniline films. Synth. Mater. 1995, 71, 2211–2212. [Google Scholar]
- Spinks, G.M.; Mottaghitalab, V.; Bahrami-Samani, M.; Whitten, P.G.; Wallace, G.G. Carbon-Nanotube-Reinforced Polyaniline Fibres for high-strength artificial muscle. Adv. Mater. 2006, 18, 637–640. [Google Scholar]
- Rodrigues, M.A.; De Peoli, M.-A. Electrochemical properties of chemically prepared poly(aniline). Synth. Met. 1991, 43, 2957–2962. [Google Scholar]
- Ćirić-Marjanović, G.; Dragičević, L.; Milojević, M.; Mojović, M.; Mentus, S.; Dojčinović, B.; Marjanović, B.; Stejskal, J. Synthesis and characterization of self-assembled polyaniline nanotubes/silica nanocomposites. J. Phys. Chem. 2009, 113, 7116–7127. [Google Scholar]
- Wallace, G.G.; Smyth, M.; Zhao, H. Conducting electroactive polymer-based biosensors. Trends Anal. Chem. 1999, 18, 245–251. [Google Scholar]
- Park, Y.H.; Park, C.R. Preparation of conducting polyacrylonitrile/polyaniline composite films by electrochemical synthesis and their electroactivity. Synth. Met. 2001, 118, 187–192. [Google Scholar]
- Jayanty, S.; Prasad, G.K.; Sreedhar, B.; Radhakrishnan, T.P. Polyelectrolyte templated polyaniline-film morphology and conductivity. Polymer 2003, 44, 7265–7270. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.H.; Dong, Y.Q.; Sengothi, K.; Tan, K.L.; Kang, E.T. In-vivo tissue response to polyaniline. Synth. Met. 1999, 102, 1313–1314. [Google Scholar]
- Kamalesh, S.; Tan, P.; Wang, J.; Lee, T.; Kang, E.; Wang, C. Biocompatibility of electroactive polymer in tissues. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 2000, 52, 467–478. [Google Scholar]
- Bidez, P.R.; Li, S.; MacDiarmid, A.G.; Venancio, E.C.; Wei, Y.; Lelkes, P.I. Polyaniline, an electroactive polymer, supports adhesion and proliferation of cardiac myoblasts. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 2006, 17, 199–212. [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt, C.E.; Venkatram, R.S.; Vacanti, J.; Langer, R. Stimulation of neurite outgrowth using an electrically conducting polymer. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 1997, 94, 8948–8953. [Google Scholar]
- Brahim, S.; Guiseppi-Elie, A. Electroconductive hydrogels: Electrical and electrochemical properties of polypyrrole-poly(HEMA) composite. Electroanalysis 2004, 17, 556–570. [Google Scholar]
- Davis, K.A.; Anseth, K.S. Controlled release from crosslinked degradable networks. Crit. Rev. Drug Carr. Sys. 2002, 19, 385–423. [Google Scholar]
- Chien-Chi, L.; Andrew, T.M. Hydrogels in controlled release formulation network design and mathematical modeling. Adv. Drug Delivery Rev. 2006, 58, 1379–1408. [Google Scholar]
- Bajpai, A.K.; Shukla, S.K.; Bhanu, S.; Kankane, S. Responsive polymers in controlled drug delivery. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2008, 33, 1088–1118. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, B.C.; Spinks, G.M.; Wallace, G.G.; John, R. Electroformation of conducting polymers in a hydrogel support matrix. Polymer 2000, 41, 1783–1790. [Google Scholar]
- Prabaharan, M.; Mano, J.F. Stimuli-responsive hydrogels based on polysaccharides incorporated with thermo-responsive polymers as novel biomaterial. Macromol. Biosci. 2006, 6, 991–1008. [Google Scholar]
- Collett, J.; Crawford, A.; Hatton, P.V.; Geoghegan, M.; Rimmer, S. Thermally responsive polymeric hydrogel brushes: Synthesis, physical properties and the use for the culture of chondrocytes. J. Roy. Soc. Interface 2007, 4, 117–126. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Yuan, K.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, J. Preparation and pH responsive behavior of poly(vinyl alcohol)-chitosan-poly(acrylic acid) full IPN hydrogels. J. Bioact. Compat. Polym. 2007, 22, 207–218. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, S.J.; Lee, Y.M.; Kim, I.Y.; Kim, S.I. Electrical/pH sensitive swelling behavior of polyelectrolyte hydrogels prepared with hyaluronic acid-poly(vinyl alcohol) interpenetrating polymer networks. React. Funct. Polym. 2003, 55, 291–298. [Google Scholar]
- Kokotos, G.; Martin, V.; Constantinou-Kokotou, V.; Gibbons, W.A. Synthesis of medicinally useful lipidca-amino acids, 2 amino alcohols and diamines. Amino Acids 1996, 11, 329–343. [Google Scholar]
- Kotha, S.; Singh, K. N-alkylation of diethyl acetamidomalonate: synthesis of constrained amino acid derivatives by ring-closing metathesis. Tetrahedron Lett. 2004, 45, 9607–9610. [Google Scholar]
- Pawed, S.M.; Deshmukh, K. Characterization of poly vinyl alcohol/gelatin blend hydrogel films for biomedical applications. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2008, 109, 3431–3437. [Google Scholar]
- Henderson, K.J.; Zhou, T.C.; Otim, K.J.; Shull, K.R. Ionically crosslinked tri-block copolymer hydrogels with high strength. Macromolecules 2010, 43, 6193–6201. [Google Scholar]
- Sui, K.; Gao, S.; Wu, W.; Xia, Y. Injectable supermolecular hybrid hydrogels formed by MWNT-grafted-poly ethylene glycol and a-cyclodextrin. J. Polym. Sci. A Polym. Chem. 2010, 48, 3145–3151. [Google Scholar]
- Kulkarni, R.V.; Sa, B. Electroresponsive polyacrylamide-grafted-xanthan hydrogels for drug delivery. J. Bioact. Compat. Polym. 2009, 24, 368–384. [Google Scholar]
- Prashantha, K.V. IPNs based on polyol modified castor oil polyurethane and poly(HEMA): Synthesis, chemical, mechanical and thermal properties. Bull. Mater. Sci. 2001, 24, 535–538. [Google Scholar]
- Lü, S.; Liu, M.; Ni, B.; Gao, C. A novel pH- and thermo-sensitive PVP/CMC semi-IPN hydrogel: Swelling, phase behavior, and drug release study. J. Polym. Sci. B Polym. Phys. 2010, 48, 1749–1756. [Google Scholar]
- You, J.; Auguste, D.T. Conductive, physiologically responsive hydrogels. Langmuir 2010, 26, 4607–4612. [Google Scholar]
- Gűrsoy, A.; Eroğlu, L.; Ulutin, S.; Tasyűrek, M.; Fessi, H.; Puisieux, P.; Devissaguet, J. Evaluation of indomethacin nanocapsules for their physical stability and inhibitory activity on inflammation and platelet aggregation. Int. J. Pharm. 1989, 52, 101–108. [Google Scholar]
- Chao, D.; Ma, X.; Lu, X.; Cui, L.; Mao, H.; Zhang, W.; Wei, Y. Design, synthesis and characterization of novel electroactive polyamide with amine-capped aniline pentamer in the main chain via oxidative coupling polymerization. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2007, 104, 1603–1608. [Google Scholar]
- De La Lastra, A.C.; Motilva, V.; Martin, M.J.; Nieto, A.; Barranco, M.D.; Cabeza, J.; Herrerias, J.M. Protective effect of melatonin on indomethacin-induced gastric injury in rat. J. Pineal Res. 1999, 26, 101–107. [Google Scholar]
- Couppé, C.; Hansen, P.; Kongsgaard, M.; Kovanen, V.; Suetta, C.; Aagaard, P.; Kjær, M.; Magnusson, S.P. Mechanical properties and collagen cross-linking of the patellar tendon in old and young men. J. Appl. Physiol. 2009, 107, 880–886. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Emerson, D.; Ghiorse, W.C. Role of disulfide bonds in maintaining the structural integrity of the sheath of Leptothrix discophora SP-6. J. Bacteriol. 1993, 175, 7819–7827. [Google Scholar]
- Badenhorst, D.; Maseko, M.; Tsotetsi, O.J.; Naidoo, A.; Brooksbank, R.; Norton, G.R.; Woodiwiss, A.J. Cross-linking influences the impact of quantitative changes in myocardial collagen on cardiac stiffness and remodeling in hypertension in rats. Cardiovasc. Res. 2002, 57, 632–641. [Google Scholar]
- Rokhade, A.P.; Patil, S.A.; Aminabhavi, T.M. Synthesis and characterization of semi-interpenetrating polymer network microsphere of acrylamide grafted dextran and chitosan for controlled release of acyclovir. Carbohydr. Polym. 2007, 67, 605–613. [Google Scholar]
- Chao, D.; Lu, X.; Chen, J.; Liu, X.; Zhang, W.; Wei, Y. Synthesis and characterization of electroactive polyamide with amine-capped aniline pentamer and ferrocene in the main chain by oxidative coupling polymerization. Polymer 2006, 47, 2643–2648. [Google Scholar]
- De, S.K.; Aluru, N.R. A chemo-electro-mechanical mathematical model for simulation of pH sensitive hydrogels. Mech. Mater. 2004, 36, 395–410. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Zhao, J.; Liu, H.; Wang, H.; Liu, R.; Liu, J. Application of poly(3-methylthiophene) modified glassy carbon electrode as riboflavin sensor. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2010, 5, 295–301. [Google Scholar]
- Hegde, R.N.; Kumara Swamy, B.E.; Sherigara, B.S.; Nandibewoor, S.T. Electro-oxidation of atenolol at a glassy carbon electrode. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2008, 3, 302–314. [Google Scholar]
- Manjunatha, J.G.; Kumara Swamy, B.E.; Mamatha, G.P.; Chandra, U.; Niranjana, E.; Sherigara, B.S. Cyclic voltammetry studies of dopamine at lamotrigine and TX-100 modified carbon paste electrode. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2009, 4, 187–196. [Google Scholar]
- Raoof, J.; Ojani, R.; Nematollahi, D.; Kiani, A. Digital simulation of the cyclic voltammetry study of the catechols electrooxidation in the presence of some nitrogen and carbon nucleophiles. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2009, 4, 810–819. [Google Scholar]
- Zeng, Y.N.; Zheng, N.; Osborne, P.G.; Li, Y.Z.; Chang, W.B.; Wang, Z.M. Preparation and cyclic voltammetry characterization of Cu-dipyridyl imprinted polymer. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2002, 13, 317–320. [Google Scholar]
- Le, W.; Liu, Y.; Hi, G. Preparation of manganese dioxide modified glassy carbon electrode by a novel film plating/cyclic voltammetry method for H2O2. J. Chil. Chem. Soc. 2009, 54, 366–371. [Google Scholar]
© 2011 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Tsai, T.-S.; Pillay, V.; Choonara, Y.E.; Du Toit, L.C.; Modi, G.; Naidoo, D.; Kumar, P. A Polyvinyl Alcohol-Polyaniline Based Electro-Conductive Hydrogel for Controlled Stimuli-Actuable Release of Indomethacin. Polymers 2011, 3, 150-172. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym3010150
Tsai T-S, Pillay V, Choonara YE, Du Toit LC, Modi G, Naidoo D, Kumar P. A Polyvinyl Alcohol-Polyaniline Based Electro-Conductive Hydrogel for Controlled Stimuli-Actuable Release of Indomethacin. Polymers. 2011; 3(1):150-172. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym3010150
Chicago/Turabian StyleTsai, Tong-Sheng, Viness Pillay, Yahya E. Choonara, Lisa C. Du Toit, Girish Modi, Dinesh Naidoo, and Pradeep Kumar. 2011. "A Polyvinyl Alcohol-Polyaniline Based Electro-Conductive Hydrogel for Controlled Stimuli-Actuable Release of Indomethacin" Polymers 3, no. 1: 150-172. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym3010150
APA StyleTsai, T.-S., Pillay, V., Choonara, Y. E., Du Toit, L. C., Modi, G., Naidoo, D., & Kumar, P. (2011). A Polyvinyl Alcohol-Polyaniline Based Electro-Conductive Hydrogel for Controlled Stimuli-Actuable Release of Indomethacin. Polymers, 3(1), 150-172. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym3010150