Hydrophobic Fibers with Hydrophilic Domains for Enhanced Fog Water Harvesting
Abstract
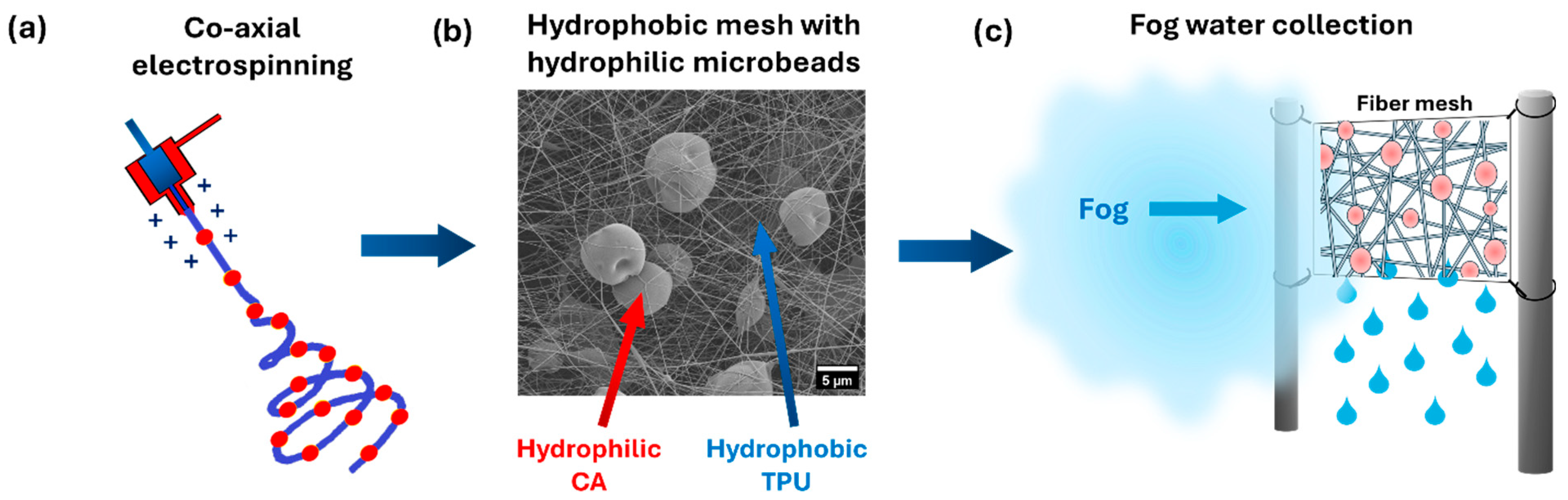
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Electrospinning
2.2. Materials Characterization
2.3. Wetting, Roughness and Fog Collection Experiment
3. Results and Discussion
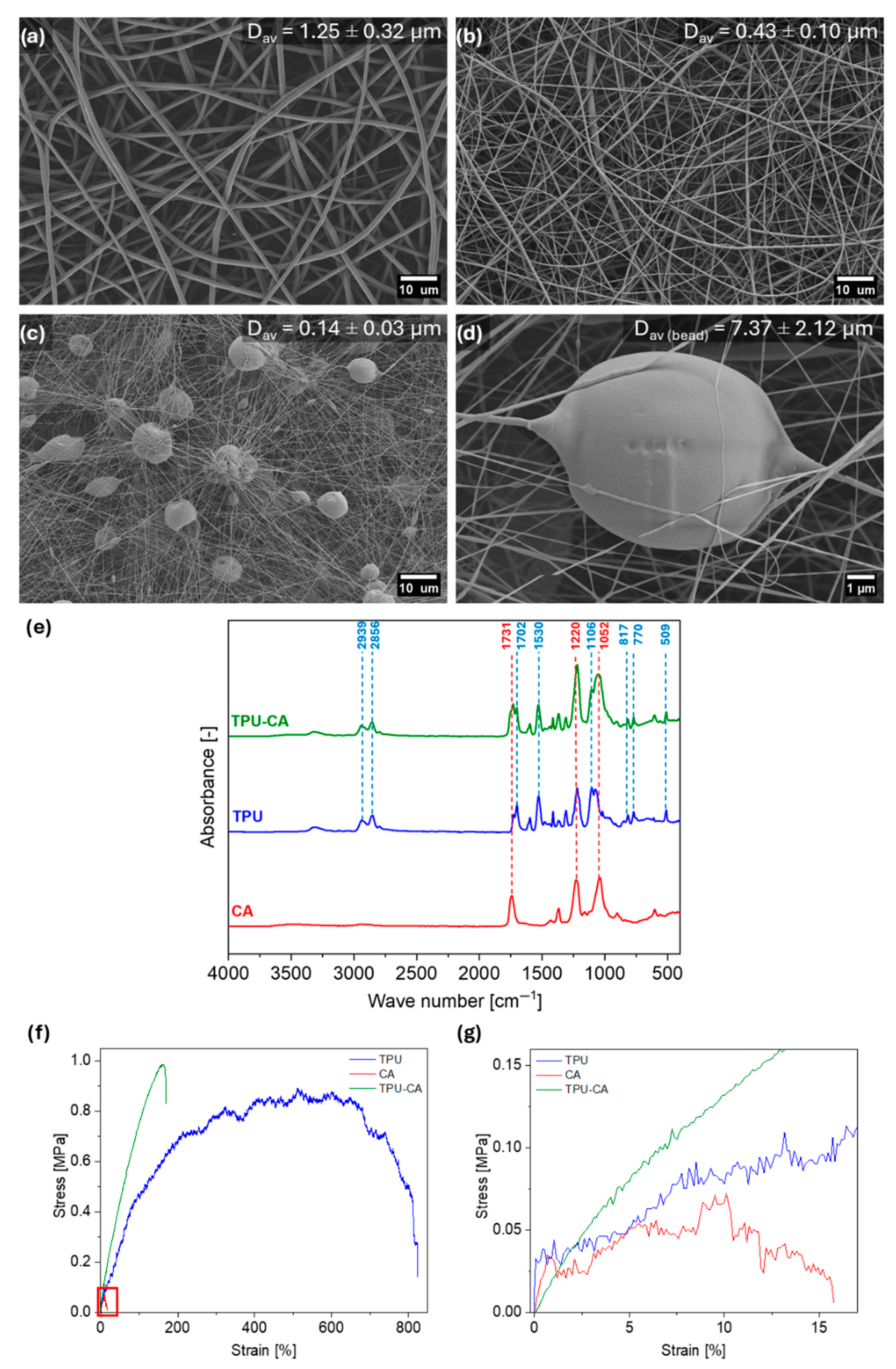
3.1. Material Characterization
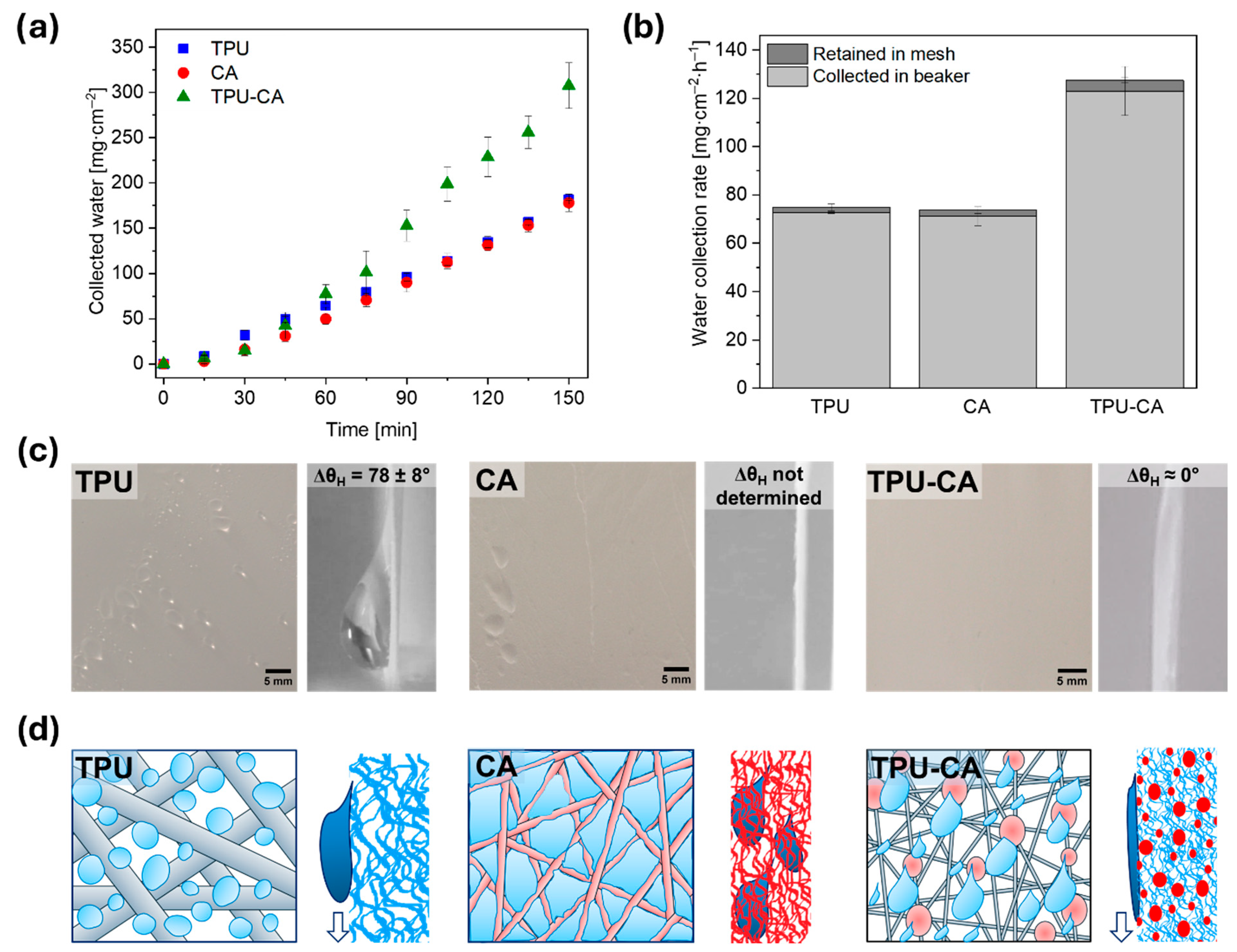
3.2. Wetting and FWC Experiments
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Schemenauer, R.S.; Cereceda, P. The Role of Wind in Rainwater Catchment and Fog Collection. Water Int. 1994, 19, 70–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarimi, H.; Powell, R.; Riffat, S. Review of Sustainable Methods for Atmospheric Water Harvesting. Int. J. Low Carbon Technol. 2020, 15, 253–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Yang, Z.; Li, Z.; Fu, H.; Chen, J. Comprehensive Review on Atmospheric Water Harvesting Technologies. J. Water Process. Eng. 2025, 69, 106836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivera, J.d.D.; Lopez-Garcia, D. Mechanical Characteristics of Raschel Mesh and Their Application to the Design of Large Fog Collectors. Atmos. Res. 2015, 151, 250–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmes, R.; Rivera, J.d.D.; de la Jara, E. Large Fog Collectors: New Strategies for Collection Efficiency and Structural Response to Wind Pressure. Atmos. Res. 2015, 151, 236–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azeem, M.; Guérin, A.; Dumais, T.; Caminos, L.; Goldstein, R.E.; Pesci, A.I.; De Dios Rivera, J.; Torres, M.J.; Wiener, J.; Campos, J.L.; et al. Optimal Design of Multilayer Fog Collectors. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 7736–7743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klemm, O.; Schemenauer, R.S.; Lummerich, A.; Cereceda, P.; Marzol, V.; Corell, D.; Van Heerden, J.; Reinhard, D.; Gherezghiher, T.; Olivier, J.; et al. Fog as a Fresh-Water Resource: Overview and Perspectives. Ambio 2012, 41, 221–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivera, J.d.D. Aerodynamic Collection Efficiency of Fog Water Collectors. Atmos. Res. 2011, 102, 335–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez, D.M.; Torregrosa, A.; Weiss-Penzias, P.S.; Zhang, B.J.; Sorensen, D.; Cohen, R.E.; McKinley, G.H.; Kleingartner, J.; Oliphant, A.; Bowman, M. Fog Water Collection Effectiveness: Mesh Intercomparisons. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2018, 18, 270–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, K.C.; Chhatre, S.S.; Srinivasan, S.; Cohen, R.E.; McKinley, G.H. Optimal Design of Permeable Fiber Network Structures for Fog Harvesting. Langmuir 2013, 29, 13269–13277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qadir, M.; Jiménez, G.C.; Farnum, R.L.; Dodson, L.L.; Smakhtin, V. Fog Water Collection: Challenges beyond Technology. Water 2018, 10, 372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korkmaz, S.; Kariper, İ.A. Fog Harvesting against Water Shortage. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2020, 18, 361–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fessehaye, M.; Abdul-Wahab, S.A.; Savage, M.J.; Kohler, T.; Gherezghiher, T.; Hurni, H. Fog-Water Collection for Community Use. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2014, 29, 52–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, C.; Guo, H.; Bai, H.; Xu, T.; Liu, M.; Yang, J.; Zhu, Y.; Zhao, W.; Zhang, J.; Cao, M.; et al. Beetle-Inspired Hierarchical Antibacterial Interface for Reliable Fog Harvesting. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 34330–34337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, B.; Sarkar, A.; Kietzig, A.M. Fog-Harvesting Inspired by the Stenocara Beetle-An Analysis of Drop Collection and Removal from Biomimetic Samples with Wetting Contrast. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2013, 284, 826–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhushan, B. Design of Water Harvesting Towers and Projections for Water Collection from Fog and Condensation. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 2020, 378, 20190440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.; Zhang, H.; Huang, J.; Li, S.; Zhang, S.; Cheng, Y.; Mao, J.; Dong, X.; Gao, S.; Wang, S.; et al. Namib Desert Beetle Inspired Special Patterned Fabric with Programmable and Gradient Wettability for Efficient Fog Harvesting. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2021, 61, 85–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comanns, P.; Esser, F.J.; Kappel, P.H.; Baumgartner, W.; Shaw, J.; Withers, P.C. Adsorption and Movement of Water by Skin of the Australian Thorny Devil (Agamidae: Moloch horridus). R. Soc. Open Sci. 2017, 4, 170591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joel, A.-C.; Buchberger, G.; Comanns, P. Moisture-Harvesting Reptiles: A Review. In Functional Surfaces in Biology III; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2017; pp. 93–106. [Google Scholar]
- Ju, J.; Bai, H.; Zheng, Y.; Zhao, T.; Fang, R.; Jiang, L. A Multi-Structural and Multi-Functional Integrated Fog Collection System in Cactus. Nat. Commun. 2012, 3, 1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, F.T.; Clement, R.M.; Gethin, D.T.; Kiernan, M.; Goral, T.; Griffiths, P.; Beynon, D.; Parker, A.R. Hierarchical Structures of Cactus Spines That Aid in the Directional Movement of Dew Droplets. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 2016, 374, 20160110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhushan, B.; Feng, W. Water Collection and Transport in Bioinspired Nested Triangular Patterns. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 2020, 378, 20190441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Y.; Wang, T.; Shi, W.; Sun, L.; Zheng, Y. Water Collection Abilities of Green Bristlegrass Bristle. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 40837–40840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurera, D.; Bhushan, B. Passive Water Harvesting by Desert Plants and Animals: Lessons from Nature. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 2020, 378, 20190444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhushan, B. Biomimetics: Lessons from Nature—An Overview. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 2009, 367, 1445–1486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, P.S.; Bhushan, B. Bioinspired Materials for Water Supply and Management: Water Collection, Water Purification and Separation of Water from Oil. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 2016, 374, 20160135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Zheng, Y. Bioinspired Micro-/Nanostructure Fibers with a Water Collecting Property. Nanoscale 2014, 6, 7703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ura, D.P.; Knapczyk-Korczak, J.; Szewczyk, P.K.; Sroczyk, E.A.; Busolo, T.; Marzec, M.M.; Bernasik, A.; Kar-Narayan, S.; Stachewicz, U. Surface Potential Driven Water Harvesting from Fog. ACS Nano 2021, 15, 8848–8859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agarwal, S.; Greiner, A.; Wendorff, J.H. Functional Materials by Electrospinning of Polymers. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2013, 38, 963–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, J.; Wu, T.; Dai, Y.; Xia, Y. Electrospinning and Electrospun Nanofibers: Methods, Materials, and Applications. Chem. Rev. 2019, 119, 5298–5415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ura, D.P.; Rosell-Llompart, J.; Zaszczyńska, A.; Vasilyev, G.; Gradys, A.; Szewczyk, P.K.; Knapczyk-Korczak, J.; Avrahami, R.; Šišková, A.O.; Arinstein, A.; et al. The Role of Electrical Polarity in Electrospinning and on the Mechanical and Structural Properties of As-Spun Fibers. Materials 2020, 13, 4169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ura, D.P.; Stachewicz, U. The Significance of Electrical Polarity in Electrospinning: A Nanoscale Approach for the Enhancement of the Polymer Fibers’ Properties. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2022, 307, 2100843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hohman, M.M.; Shin, M.; Rutledge, G.; Brenner, M.P. Electrospinning and Electrically Forced Jets. I. Stability Theory. Phys. Fluids 2001, 13, 2201–2220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szewczyk, P.K.; Stachewicz, U. The Impact of Relative Humidity on Electrospun Polymer Fibers: From Structural Changes to Fiber Morphology. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2020, 286, 102315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobs, V.; Anandjiwala, R.D.; Maaza, M. The Influence of Electrospinning Parameters on the Structural Morphology and Diameter of Electrospun Nanofibers. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2010, 115, 3130–3136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Y.; Yu, L.; Mou, J.; Wu, D.; Zhou, P.; Xu, M. Mechanical Properties and Application Analysis of Spider Silk Bionic Material. e-Polymers 2020, 20, 443–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garb, J.E.; Haney, R.A.; Schwager, E.E.; Gregorič, M.; Kuntner, M.; Agnarsson, I.; Blackledge, T.A. The Transcriptome of Darwin’s Bark Spider Silk Glands Predicts Proteins Contributing to Dragline Silk Toughness. Commun. Biol. 2019, 2, 275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Hien, K.T.T.; Mizutani, G.; Rutt, H.N. Second-Order Nonlinear Optical Microscopy of Spider Silk. Appl. Phys. B 2017, 123, 188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Greco, G.; Maniglio, D.; Mazzolai, B.; Migliaresi, C.; Pugno, N.; Motta, A. Spider (Linothele megatheloides) and Silkworm (Bombyx mori) Silks: Comparative Physical and Biological Evaluation. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2020, 107, 110197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, H.; Tian, X.; Zheng, Y.; Ju, J.; Zhao, Y.; Jiang, L. Direction Controlled Driving of Tiny Water Drops on Bioinspired Artificial Spider Silks. Adv. Mater. 2010, 22, 5521–5525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Y.; Bai, H.; Huang, Z.; Tian, X.; Nie, F.Q.; Zhao, Y.; Zhai, J.; Jiang, L. Directional Water Collection on Wetted Spider Silk. Nature 2010, 463, 640–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knapczyk-Korczak, J.; Szewczyk, P.K.; Ura, D.P.; Berent, K.; Stachewicz, U. Hydrophilic Nanofibers in Fog Collectors for Increased Water Harvesting Efficiency. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 22335–22342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knapczyk-Korczak, J.; Szewczyk, P.K.; Ura, D.P.; Bailey, R.J.; Bilotti, E.; Stachewicz, U. Improving Water Harvesting Efficiency of Fog Collectors with Electrospun Random and Aligned Polyvinylidene Fluoride (PVDF) Fibers. Sustain. Mater. Technol. 2020, 25, e00191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knapczyk-Korczak, J.; Zhu, J.; Ura, D.P.; Szewczyk, P.K.; Gruszczyński, A.; Benker, L.; Agarwal, S.; Stachewicz, U. Enhanced Water Harvesting System and Mechanical Performance from Janus Fibers with Polystyrene and Cellulose Acetate. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 180–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knapczyk-Korczak, J.; Szewczyk, P.K.; Stachewicz, U. The Importance of Nanofiber Hydrophobicity for Effective Fog Water Collection. RSC Adv. 2021, 11, 10866–10873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knapczyk-Korczak, J.; Ura, D.P.; Gajek, M.; Marzec, M.M.; Berent, K.; Bernasik, A.; Chiverton, J.P.; Stachewicz, U. Fiber-Based Composite Meshes with Controlled Mechanical and Wetting Properties for Water Harvesting. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 1665–1676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parisi, G.; Szewczyk, P.K.; Narayan, S.; Stachewicz, U. Thermoresponsive Nanofiber Yarns for Water Harvesting Enhanced by Harp System. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 499, 155874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parisi, G.; Szewczyk, P.K.; Narayan, S.; Ura, D.P.; Knapczyk-Korczak, J.; Stachewicz, U. Multifunctional Piezoelectric Yarns and Meshes for Efficient Fog Water Collection, Energy Harvesting, and Sensing. Small Sci. 2024, 4, 2400021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakur, N.; Ranganath, A.S.; Agarwal, K.; Baji, A. Electrospun Bead-On-String Hierarchical Fibers for Fog Harvesting Application. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2017, 302, 1700124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Wang, L.; Xue, Y.; Jiang, L.; Zheng, Y. Bioinspired Tilt-Angle Fabricated Structure Gradient Fibers: Micro-Drops Fast Transport in a Long-Distance. Sci. Rep. 2013, 3, 2927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huan, J.; Chen, M.; Hou, Y.; Zheng, Y. Special Fog Harvesting Mode on Bioinspired Hydrophilic Dual-Thread Spider Silk Fiber. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 473, 145174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, M.J.; Qu, J.G.; Zhang, J.F. Design and Optimization of an Electrostatic Fog Collection System for Water Harvesting: Modeling and Experimental Investigation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2023, 323, 124422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, M.J.; Qu, Z.G.; Zhang, J.F. Experimental Study on Water Collection Performance of Wire-to-Plate Electrostatic Fog Collector at Various Fog Generation Rates and Fog Flow Velocities. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2023, 305, 122465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Li, C.; Li, J.; Yang, W.; Xiao, M.; Zhang, M.; Yang, Y.; Yu, K.; Pan, Y. Efficient Corona Discharge Fog Collector: Multiple Mesh Electrodes with Electric Field Enhances Fog Harvesting. Plasma Chem. Plasma Process. 2022, 42, 1249–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parisi, G.; Szewczyk, P.K.; Narayan, S.; Stachewicz, U. Photoresponsive Electrospun Fiber Meshes with Switchable Wettability for Effective Fog Water Harvesting in Variable Humidity Conditions. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2023, 15, 40001–40010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huan, S.; Liu, G.; Han, G.; Cheng, W.; Fu, Z.; Wu, Q.; Wang, Q. Effect of Experimental Parameters on Morphological, Mechanical and Hydrophobic Properties of Electrospun Polystyrene Fibers. Materials 2015, 8, 2718–2734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gañán-Calvo, A.M.; López-Herrera, J.M.; Herrada, M.A.; Ramos, A.; Montanero, J.M. Review on the Physics of Electrospray: From Electrokinetics to the Operating Conditions of Single and Coaxial Taylor Cone-Jets, and AC Electrospray. J. Aerosol Sci. 2018, 125, 32–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Zhao, S.; Han, L. Fabrication of CA/TPU Helical Nanofibers and Its Mechanism Analysis. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2018, 13, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nezarati, R.M.; Eifert, M.B.; Cosgriff-Hernandez, E. Effects of Humidity and Solution Viscosity on Electrospun Fiber Morphology. Tissue Eng. Part C Methods 2013, 19, 810–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banikazemi, S.; Rezaei, M.; Rezaei, P.; Babaie, A.; Eyvazzadeh-Kalajahi, A. Preparation of Electrospun Shape Memory Polyurethane Fibers in Optimized Electrospinning Conditions via Response Surface Methodology. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2020, 31, 2199–2208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fei, P.; Liao, L.; Cheng, B.; Song, J. Quantitative Analysis of Cellulose Acetate with a High Degree of Substitution by FTIR and Its Application. Anal. Methods 2017, 9, 6194–6201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knapczyk-Korczak, J.; Szewczyk, P.K.; Berniak, K.; Marzec, M.M.; Frąc, M.; Pichór, W.; Stachewicz, U. Flexible and Thermally Insulating Porous Materials Utilizing Hollow Double-Shell Polymer Fibers. Adv. Sci. 2024, 11, 2404154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, C.H.; Kim, C.H.; Tijing, L.D.; Lee, D.H.; Yu, M.H.; Pant, H.R.; Kim, Y.; Kim, C.S. Preparation and Characterization of (Polyurethane/Nylon-6) Nanofiber/ (Silicone) Film Composites via Electrospinning and Dip-Coating. Fibers Polym. 2012, 13, 339–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moradi, A.; Szewczyk, P.K.; Roszko, A.; Fornalik-Wajs, E.; Stachewicz, U. Unraveling the Impact of Boron Nitride and Silicon Nitride Nanoparticles on Thermoplastic Polyurethane Fibers and Mats for Advanced Heat Management. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2024, 16, 41475–41486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashid, T.U.; Gorga, R.E.; Krause, W.E. Mechanical Properties of Electrospun Fibers—A Critical Review. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2021, 23, 2100153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, M.; Xiao, J.; Yu, C.; Li, K.; Jiang, L. Hydrophobic/Hydrophilic Cooperative Janus System for Enhancement of Fog Collection. Small 2015, 11, 4379–4384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Li, J.; Zhao, J.; Guo, J.; Zhang, S.; Sherazi, T.A.; Ambreen; Li, S. Bioinspired Superhydrophilic-Hydrophobic Integrated Surface with Conical Pattern-Shape for Self-Driven Fog Collection. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2018, 530, 274–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knapczyk-Korczak, J.; Stachewicz, U. Biomimicking Spider Webs for Effective Fog Water Harvesting with Electrospun Polymer Fibers. Nanoscale 2021, 13, 16034–16051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yue, H.; Zeng, Q.; Huang, J.; Guo, Z.; Liu, W. Fog Collection Behavior of Bionic Surface and Large Fog Collector: A Review. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2022, 300, 102583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Wang, Y.; Qiu, J.; Cao, J.; Zou, Y.; Wang, S.; Jia, D.; Zhou, Y. A Facile Bioinspired Strategy for Accelerating Water Collection Enabled by Passive Radiative Cooling and Wettability Engineering. Mater. Des. 2021, 206, 109829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, S.; Park, Y.; Park, C.H. Preparation of Breathable and Superhydrophobic Polyurethane Electrospun Webs with Silica Nanoparticles. Text. Res. J. 2016, 86, 1816–1827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szewczyk, P.K.; Berniak, K.; Knapczyk-Korczak, J.; Karbowniczek, J.E.; Marzec, M.M.; Bernasik, A.; Stachewicz, U. Mimicking Natural Electrical Environment with Cellulose Acetate Scaffolds Enhances Collagen Formation of Osteoblasts. Nanoscale 2023, 15, 6890–6900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, M.; Hill, R.M.; Rutledge, G.C. A Review of Recent Results on Superhydrophobic Materials Based on Micro- and Nanofibers. J. Adhes. Sci. Technol. 2008, 22, 1799–1817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhushan, B.; Jung, Y.C.; Koch, K. Micro-, Nano- And Hierarchical Structures for Superhydrophobicity, Self-Cleaning and Low Adhesion. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 2009, 367, 1631–1672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szewczyk, P.; Ura, D.; Metwally, S.; Knapczyk-Korczak, J.; Gajek, M.; Marzec, M.; Bernasik, A.; Stachewicz, U. Roughness and Fiber Fraction Dominated Wetting of Electrospun Fiber-Based Porous Meshes. Polymers 2018, 11, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarei, M.; Dabir, B.; Esmaeilian, N.; Warsinger, D.M. Biomimetic Bumpy and Eco-Friendly Slippery Surfaces for Enhanced Dew and Fog Water Harvesting. J. Water Process. Eng. 2025, 70, 106950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Zhang, M.; Li, C.; Gao, C.; Zheng, Y. Excellent Fog-Droplets Collector via Integrative Janus Membrane and Conical Spine with Micro/Nanostructures. Small 2018, 14, 1801335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, Q.; Wang, J.; Zhao, F.; Wang, L. Fog Collection on a Superhydrophobic/Hydrophilic Composite Spine Surface. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 9318–9323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.; Zhou, H.; Wang, H.; Shao, H.; Yan, G.; Lin, T. Novel Water Harvesting Fibrous Membranes with Directional Water Transport Capability. Adv. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 6, 1801529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.; Liu, Y.; Bai, T.; Shi, X.; Li, D.; Feng, L. High-Efficient and Robust Fog Collection through Topography Modulation. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2023, 468, 129747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, H.; Wang, N.; Wang, L.; Bai, H.; Wu, J.; Zheng, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Jiang, L. Bioinspired Electrospun Knotted Microfibers for Fog Harvesting. ChemPhysChem 2012, 13, 1153–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, Y.; Chen, Y.; Xue, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Jiang, L. Water Collection Behavior and Hanging Ability of Bioinspired Fiber. Langmuir 2012, 28, 4737–4743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Venkatesan, H.; Shi, S.; Wang, C.; Cui, M.; Zhang, Q.; Tan, L.; Hu, J. Spider-Capture-Silk Mimicking Fibers with High-Performance Fog Collection Derived from Superhydrophilicity and Volume-Swelling of Gelatin Knots. Collagen Leather 2023, 5, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lalia, B.S.; Anand, S.; Varanasi, K.K.; Hashaikeh, R. Fog-Harvesting Potential of Lubricant-Impregnated Electrospun Nanomats. Langmuir 2013, 29, 13081–13088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, H.; Chen, B.; Wang, Y. Enhanced Atmospheric Water Harvesting Performance by Three-Dimensional Carbon Fiber Felt Structure. Langmuir 2024, 40, 12810–12817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, M.; Wang, Y.; Gong, X.; Luo, M.; Yin, X.; Yu, J.; Zhang, S.; Ding, B. Fluorine-Free Nanofiber/Network Membranes with Interconnected Tortuous Channels for High-Performance Liquid-Repellency and Breathability. ACS Nano 2025, 19, 5539–5548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krysiak, Z.J.; Kaniuk, Ł.; Metwally, S.; Szewczyk, P.K.; Sroczyk, E.A.; Peer, P.; Lisiecka-Graca, P.; Bailey, R.J.; Bilotti, E.; Stachewicz, U. Nano- and Microfiber PVB Patches as Natural Oil Carriers for Atopic Skin Treatment. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2020, 3, 7666–7676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stachewicz, U.; Modaresifar, F.; Bailey, R.J.; Peijs, T.; Barber, A.H. Manufacture of Void-Free Electrospun Polymer Nanofiber Composites with Optimized Mechanical Properties. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2012, 4, 2577–2582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sroczyk, E.A.; Berniak, K.; Jaszczur, M.; Stachewicz, U. Topical Electrospun Patches Loaded with Oil for Effective Gamma Linoleic Acid Transport and Skin Hydration towards Atopic Dermatitis Skincare. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 429, 132256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajaram, M.; Heng, X.; Oza, M.; Luo, C. Enhancement of Fog-Collection Efficiency of a Raschel Mesh Using Surface Coatings and Local Geometric Changes. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2016, 508, 218–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurera, D.; Bhushan, B. Designing Bioinspired Surfaces for Water Collection from Fog. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 2019, 377, 20180269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Meng, N.; Babar, A.A.; Wang, X.; Yu, J.; Ding, B. Multi-Bioinspired and Multistructural Integrated Patterned Nanofibrous Surface for Spontaneous and Efficient Fog Collection. Nano Lett. 2021, 21, 7806–7814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerasopoulos, K.; Luedeman, W.L.; Ölçeroglu, E.; McCarthy, M.; Benkoski, J.J. Effects of Engineered Wettability on the Efficiency of Dew Collection. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 4066–4076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Ji, Y.; Li, X.; Hou, K.; Cai, Z. Diatoms Inspired Green Janus Fabric for Efficient Fog Harvesting. Adv. Sustain. Syst. 2025, 9, 2400664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, S.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, T.; Yang, J. A New Janus Mesh Membrane with Ultrafast Directional Water Transportation and Improved Fog Collection. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2024, 202, 129–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chenxi, Y.; Jian, W.; Juan, L.; Haiou, Z.; Tianqing, C.; Zhen, G.; Yingguo, W.; Bo, B. Multibioinspired Design of a Durable Janus Copper Foam with Asymmetric and Cooperative Alternating Wettability for Efficient Fog Harvesting. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2023, 11, 3147–3159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganesh, V.A.; Ranganath, A.S.; Baji, A.; Raut, H.K.; Sahay, R.; Ramakrishna, S. Hierarchical Structured Electrospun Nanofibers for Improved Fog Harvesting Applications. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2017, 302, 1600387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2026 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license.
Share and Cite
Knapczyk-Korczak, J.; Marszalik, K.; Gajek, M.; Stachewicz, U. Hydrophobic Fibers with Hydrophilic Domains for Enhanced Fog Water Harvesting. Polymers 2026, 18, 425. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym18030425
Knapczyk-Korczak J, Marszalik K, Gajek M, Stachewicz U. Hydrophobic Fibers with Hydrophilic Domains for Enhanced Fog Water Harvesting. Polymers. 2026; 18(3):425. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym18030425
Chicago/Turabian StyleKnapczyk-Korczak, Joanna, Katarzyna Marszalik, Marcin Gajek, and Urszula Stachewicz. 2026. "Hydrophobic Fibers with Hydrophilic Domains for Enhanced Fog Water Harvesting" Polymers 18, no. 3: 425. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym18030425
APA StyleKnapczyk-Korczak, J., Marszalik, K., Gajek, M., & Stachewicz, U. (2026). Hydrophobic Fibers with Hydrophilic Domains for Enhanced Fog Water Harvesting. Polymers, 18(3), 425. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym18030425







