Novel Molecular Weight Gradient Hyaluronate Dissolving Microneedles for Sustained Intralesional Delivery and Photodynamic Activation of Hematoporphyrin in Port-Wine Stain Therapy
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Compatibility Test of HP Excipients
2.3. Establishment of High Liquid-Phase Analysis Method for HP
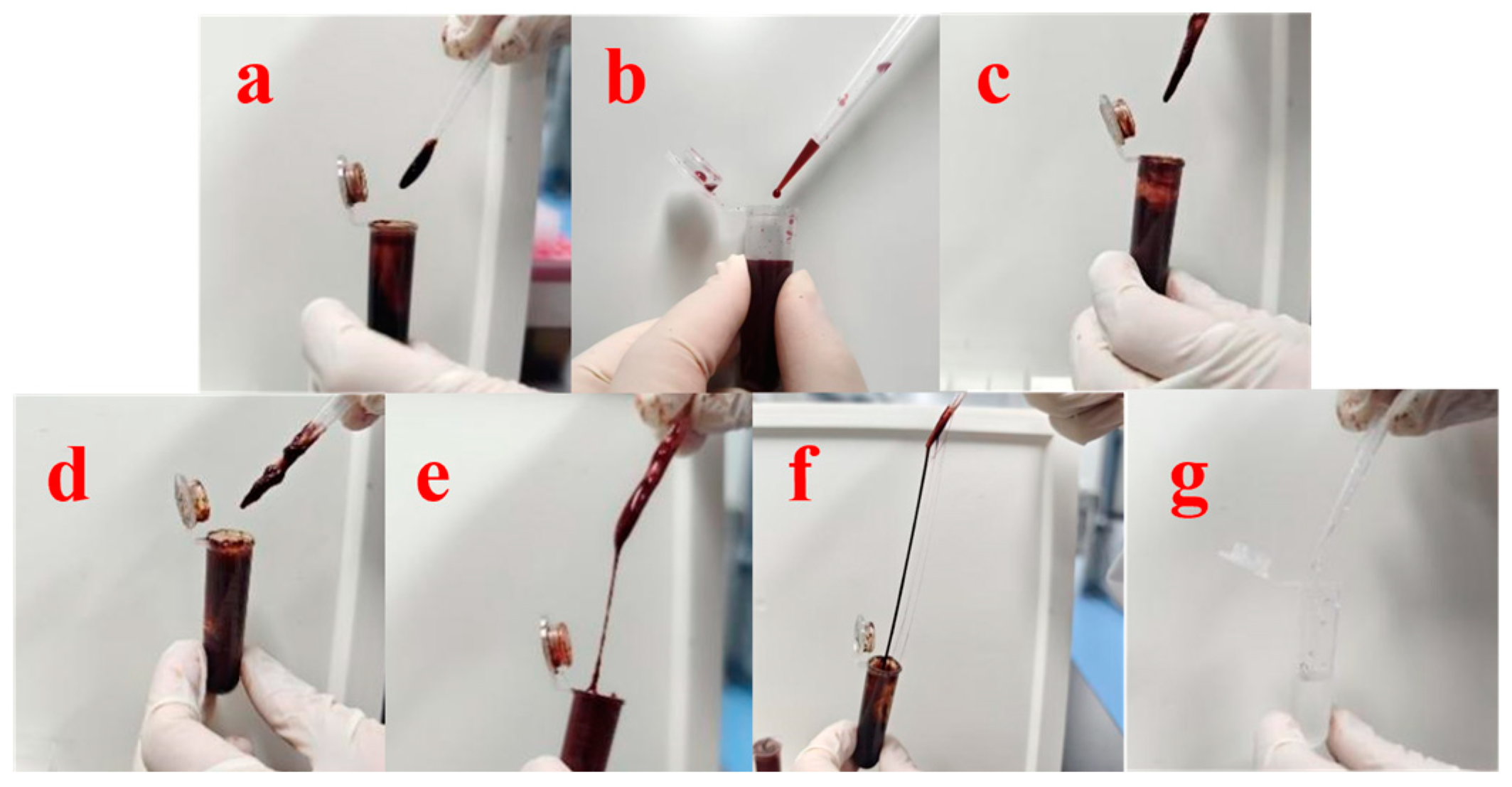
2.4. Preparation of HP-DMNs
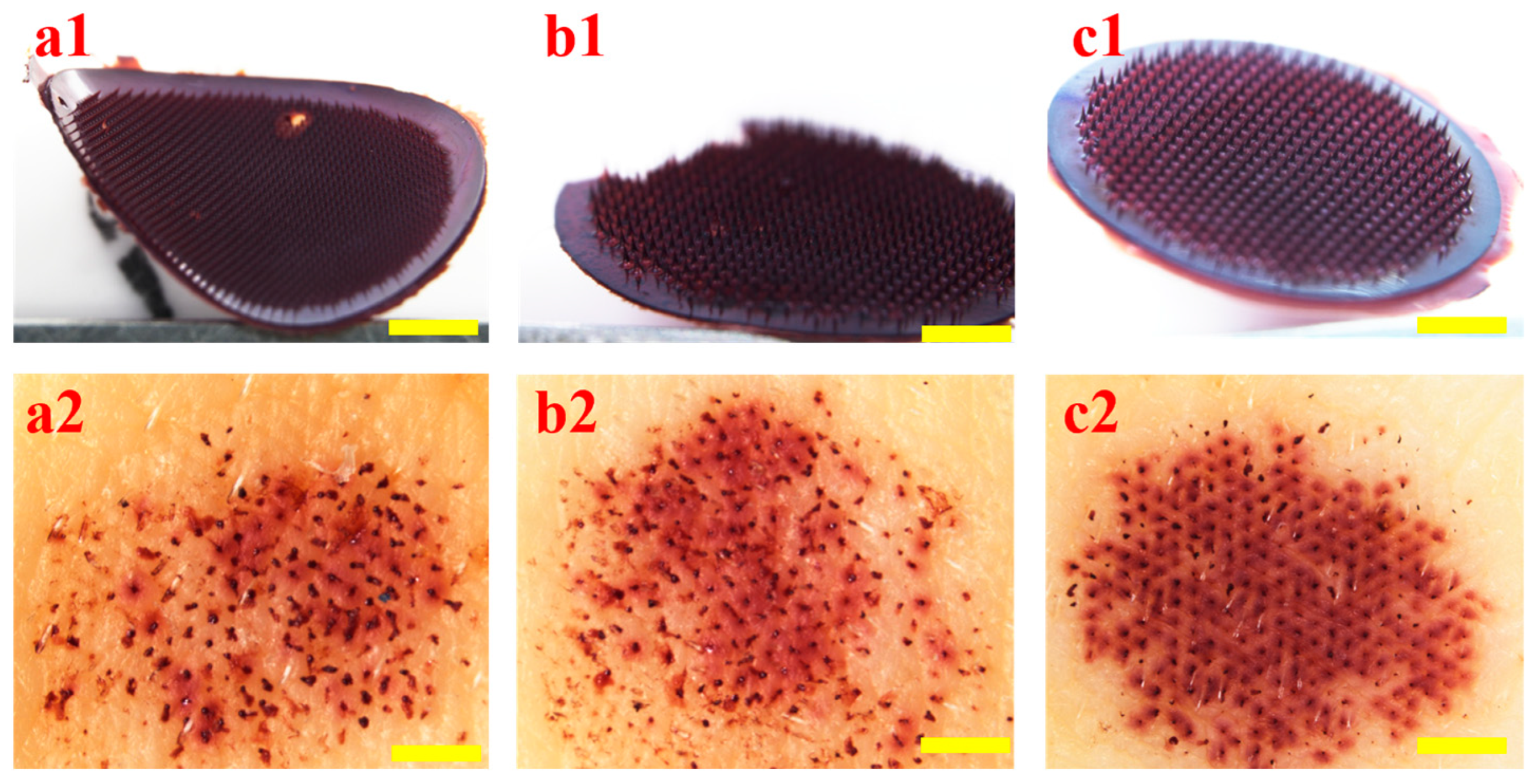
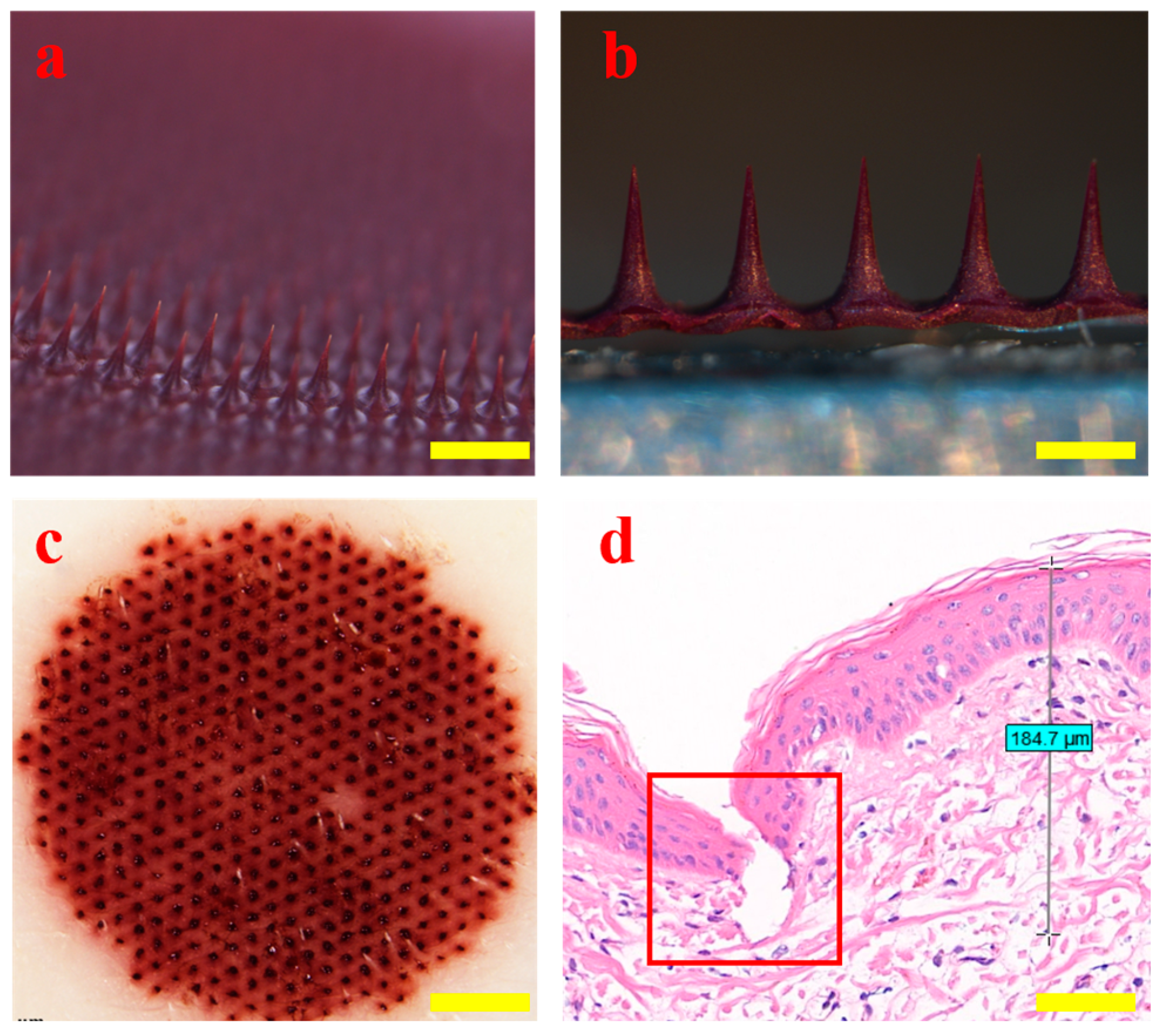
2.5. Morphological Observation and Puncture Performance of HP
2.6. Mechanical Properties of HP-DMNs
2.7. Solubility Test of HP-DMNs
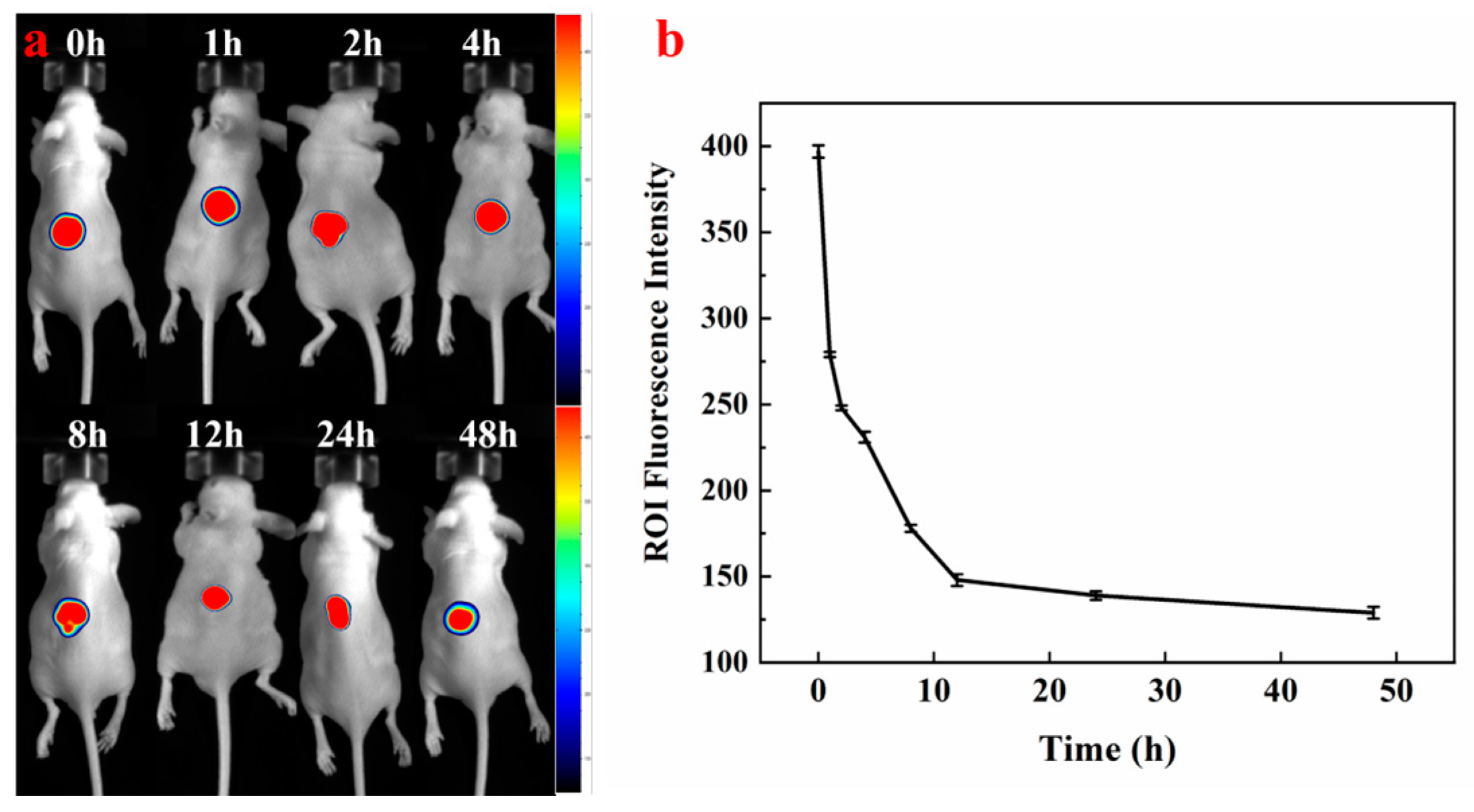
2.8. Distribution of HP-DMNs In Vivo
2.9. In Vitro Release Test of HP-DMNs
2.10. In Vitro Permeation Test of HP-DMNs
2.11. Stability Test of HP Soluble Microneedles
3. Results and Discission
3.1. Compatibility Test Results of HP and Excipients
3.2. HPLC Analysis of HP-DMNs
3.3. Validation of Liquid-Phase Methodology
3.4. Microneedle Matrix Formulation Selection for HP-DMNs
3.5. Morphology and Puncture Performance of HP-DMNs
3.6. Mechanical Strength of HP-DMNs
3.7. Solubility Test Results of HP-DMNs
3.8. In Vivo Fluorescence Imaging of HP-DMNs
3.9. In Vitro Release Test Results of HP-DMNs
3.10. In Vitro Permeation Test Results of HP-DMNs
3.11. Storage Stability of HP-DMNs
4. Conclusions
5. Patents
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| PWS | Port-wine stain |
| HP | Hematoporphyrin |
| PDT | Photodynamic therapy |
| MW | Molecular weight |
| HP-DMNs | Hematoporphyrin dissolving microneedles |
| HP-DMN | Hematoporphyrin dissolving microneedle |
| HA | Sodium hyaluronate |
| EC | Ethyl cellulose |
| CMC | Sodium carboxymethyl cellulose |
| PVP | Polyvinylpyrrolidone |
| PVP-K17 | Polyvinylpyrrolidone-K17 |
| PVP-K90 | Polyvinylpyrrolidone-K90 |
| HPLC | High-performance liquid chromatography |
| H&E | Hematoxylin and eosin |
| PVDF | Polyvinylidene fluoride |
| IVRT | In vitro release test |
| IVPT | In vitro permeation test |
References
- Lyu, J.; Wang, S.; Li, Y.; Zhang, H.; Yang, Q.; Liu, S. Hematoporphyrin Monomethyl Ether-Mediated Photodynamic Therapy for Phakomatosis Pigmentovascularis Type II: A Case Report. Photodiagn. Photodyn. Ther. 2022, 37, 102637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diao, P.; Jiang, X. Clinical application of photodynamic therapy in the treatment of port-wine stains. Bull. Dermatol. 2023, 40, 200–206. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.K.; Ghasri, P.; Aguilar, G.; van Drooge, A.M.; Wolkerstorfer, A.; Kelly, K.M.; Heger, M. An Overview of Clinical and Experimental Treatment Modalities for Port Wine Stains. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2012, 67, 289–304.e29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Wei, G.; Zhang, X.; Xu, F.; Xiong, X.; Zhou, S. A Step-by-Step Multiple Stimuli-Responsive Nanoplatform for Enhancing Combined Chemo-Photodynamic Therapy. Adv. Mater. 2017, 29, 1605357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Yan, Y.; Chen, X.; Fan, H.; Yi, M. Clinical application of hematoporphyrin photodynamic therapy for skin cancer. Jiangxi Med. J. 2022, 57, 1039–1040, 1056. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, F.; Liu, H.; Su, H.; Ren, J.; Wang, W.; Wei, H. Clinical study of hematoporphyrin-mediated photodynamic therapy combined with PD-1 inhibitor in the treatment of esophageal cancer. Chin. J. Laser Med. 2022, 31, 188–193. [Google Scholar]
- Wencheng, L.; Cho, K.; Yamasaki, Y.; Takeshita, S.; Hwang, K.; Kim, D.; Oda, T. Photo-Induced Antibacterial Activity of a Porphyrin Derivative Isolated from the Harmful Dinoflagellate Heterocapsa circularisquama. Aquat. Toxicol. 2018, 201, 119–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Liu, C.; Ouyang, C.; Yan, Y.; Zhao, S. Efficacy and safety of hematoporphyrin photodynamic therapy in the treatment of actinic keratosis. Jiangxi Med. J. 2024, 59, 110–111, 116. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, T.; Wu, H.; Yao, S.Q.; Xu, Q.-H.; Xu, G.Q. Nanocomposites Containing Gold Nanorods and Porphyrin-Doped Mesoporous Silica with Dual Capability of Two-Photon Imaging and Photosensitization. Langmuir 2010, 26, 14937–14942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, J.-E.; Shim, W.-S.; Yang, S.-G.; Kwak, E.-Y.; Chong, S.; Kim, D.-D.; Chung, S.-J.; Shim, C.-K. Liver Cancer Targeting of Doxorubicin with Reduced Distribution to the Heart Using Hematoporphyrin-Modified Albumin Nanoparticles in Rats. Pharm. Res. 2012, 29, 795–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chilakamarthi, U.; Giribabu, L. Photodynamic Therapy: Past, Present and Future. Chem. Rec. 2017, 17, 775–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.-T.; Chen, C.-T.; Yang, J.-C.; Tsai, T. Spray-Dried Microparticles Containing Polymeric Micelles Encapsulating Hematoporphyrin. AAPS J. 2010, 12, 138–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.; Zeng, Z.; Huang, Z.; Sun, Y.; Huang, Y.; Chen, J.; Ye, J.; Yang, H.; Yang, C.; Zhao, C. Near-Infrared Light-Triggered Degradable Hyaluronic Acid Hydrogel for on-Demand Drug Release and Combined Chemo-Photodynamic Therapy. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 229, 115394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.; Lai, H.; Jiang, J.; Xu, X.; Zeng, Z.; Ren, L.; Liu, Q.; Chen, M.; Zhang, T.; Ding, X.; et al. pH-Activatable Oxidative Stress Amplifying Dissolving Microneedles for Combined Chemo-Photodynamic Therapy of Melanoma. Asian J. Pharm. Sci. 2022, 17, 679–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, Z.; Yu, J.; Quek, Y.J.; Bai, B.; Li, X.; Shou, Y.; Myint, B.; Xu, C.; Tay, A. Design Principles of Microneedles for Drug Delivery and Sampling Applications. Mater. Today 2023, 63, 137–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagarkar, R.; Singh, M.; Nguyen, H.X.; Jonnalagadda, S. A Review of Recent Advances in Microneedle Technology for Transdermal Drug Delivery. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2020, 59, 101923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed Saeed AL-Japairai, K.; Mahmood, S.; Hamed Almurisi, S.; Reddy Venugopal, J.; Rebhi Hilles, A.; Azmana, M.; Raman, S. Current Trends in Polymer Microneedle for Transdermal Drug Delivery. Int. J. Pharm. 2020, 587, 119673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y. Construction of Doxorubicin Prodrug/Hematoporphyrin Co-Assembled Nanoparticles and Investigation of Their Pharmacodynamics and Pharmacokinetics. Master’s Thesis, Shanxi Medical University, Jinzhong, China, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Y. A Preliminary Study of Hematoporphyrin Injection-Mediated Photodynamic Therapy Inducing Autophagy in 4T1 Cells of Mouse Mammary Adenocarcinoma. Master’s Thesis, Jinzhou Medical University, Jinzhou, China, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Shao, M. Experimental Study on Hematoporphyrin Derivative-Induced Lung Adenocarcinoma A549 Cells Transplantation in Nude Mice by Introducing 630nm Laser via Percutaneous Puncture. Master’s Thesis, Qingdao University, Qingdao, China, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- ASTM D1708-13a; Standard Test Method for Polymer-Crete Bonding Strength. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2013.
- ISO 13485:2016; Medical Devices—Quality Management Systems—Requirements for Regulatory Purposes. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2016.
- Demir, Y.K.; Akan, Z.; Kerimoglu, O. Characterization of Polymeric Microneedle Arrays for Transdermal Drug Delivery. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e77289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, L.; Zhang, Z.; Lei, S.; Zhou, J.; Liu, Y.; Yu, X.; Wang, J.; Wan, D.; Shi, J.; Wang, S. A Temperature and pH Dual-Responsive Injectable Self-Healing Hydrogel Prepared by Chitosan Oligosaccharide and Aldehyde Hyaluronic Acid for Promoting Diabetic Foot Ulcer Healing. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 253, 127213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, E.J.; Park, K.; Kim, K.S.; Kim, J.; Yang, J.-A.; Kong, J.-H.; Lee, M.Y.; Hoffman, A.S.; Hahn, S.K. Target Specific and Long-Acting Delivery of Protein, Peptide, and Nucleotide Therapeutics Using Hyaluronic Acid Derivatives. J. Control. Release 2010, 141, 2–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salamanca, C.H.; Barrera-Ocampo, A.; Lasso, J.C.; Camacho, N.; Yarce, C.J. Franz Diffusion Cell Approach for Pre-Formulation Characterisation of Ketoprofen Semi-Solid Dosage Forms. Pharmaceutics 2018, 10, 148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Group | Excipient | Added Content (%) w/w |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | HA | 10 |
| 2 | PVP-K17 | 10 |
| 3 | EC | 10 |
| 4 | CMC | 10 |
| 5 | PVP-K90 | 10 |
| Time (min) | Water Phase (%) | Acetonitrile (%) |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | 55 | 45 |
| 15.00 | 55 | 45 |
| 15.10 | 20 | 80 |
| 25.00 | 20 | 80 |
| 25.10 | 0 | 100 |
| 35.00 | 0 | 100 |
| 35.10 | 55 | 45 |
| 45.00 | 55 | 45 |
| Time | Transit Dose (μg) | Total Transit Dose (24 h) | Total Transmittance (%) | Amount of Residue in Pig Skin (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3 h | 8.36 ± 2.80 | 103.27 | 27.04 | 5.53 |
| 6 h | 20.77 ± 6.63 | |||
| 8 h | 14.96 ± 3.24 | |||
| 24 h | 59.17 ± 2.67 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Peng, X.; Yan, C.; Fan, N.; Sun, C.; Zhang, S.; Gao, Y. Novel Molecular Weight Gradient Hyaluronate Dissolving Microneedles for Sustained Intralesional Delivery and Photodynamic Activation of Hematoporphyrin in Port-Wine Stain Therapy. Polymers 2025, 17, 1238. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17091238
Peng X, Yan C, Fan N, Sun C, Zhang S, Gao Y. Novel Molecular Weight Gradient Hyaluronate Dissolving Microneedles for Sustained Intralesional Delivery and Photodynamic Activation of Hematoporphyrin in Port-Wine Stain Therapy. Polymers. 2025; 17(9):1238. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17091238
Chicago/Turabian StylePeng, Xueli, Chenxin Yan, Nengquan Fan, Chaoguo Sun, Suohui Zhang, and Yunhua Gao. 2025. "Novel Molecular Weight Gradient Hyaluronate Dissolving Microneedles for Sustained Intralesional Delivery and Photodynamic Activation of Hematoporphyrin in Port-Wine Stain Therapy" Polymers 17, no. 9: 1238. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17091238
APA StylePeng, X., Yan, C., Fan, N., Sun, C., Zhang, S., & Gao, Y. (2025). Novel Molecular Weight Gradient Hyaluronate Dissolving Microneedles for Sustained Intralesional Delivery and Photodynamic Activation of Hematoporphyrin in Port-Wine Stain Therapy. Polymers, 17(9), 1238. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17091238







