Investigating 3D-Printed Carbon–Carbonyl Iron Composites for Electromagnetic Applications
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
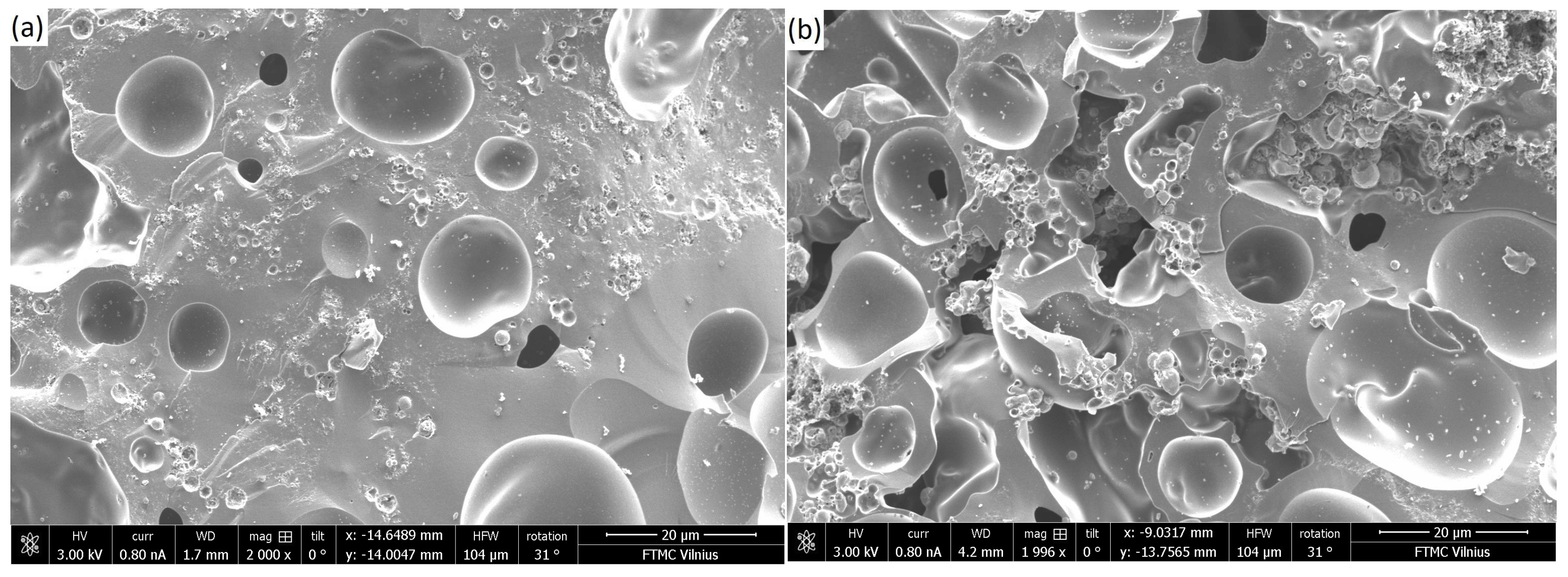
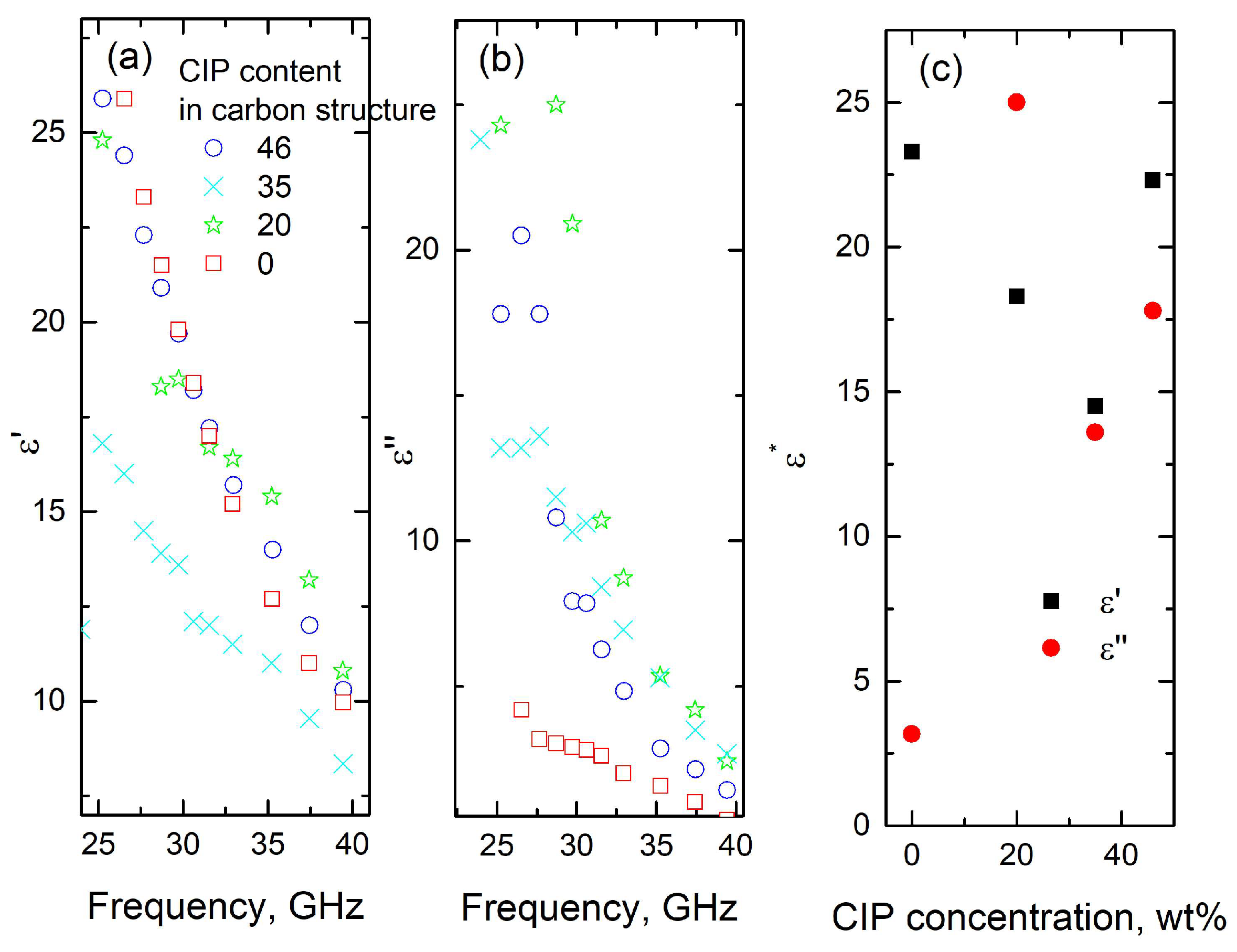
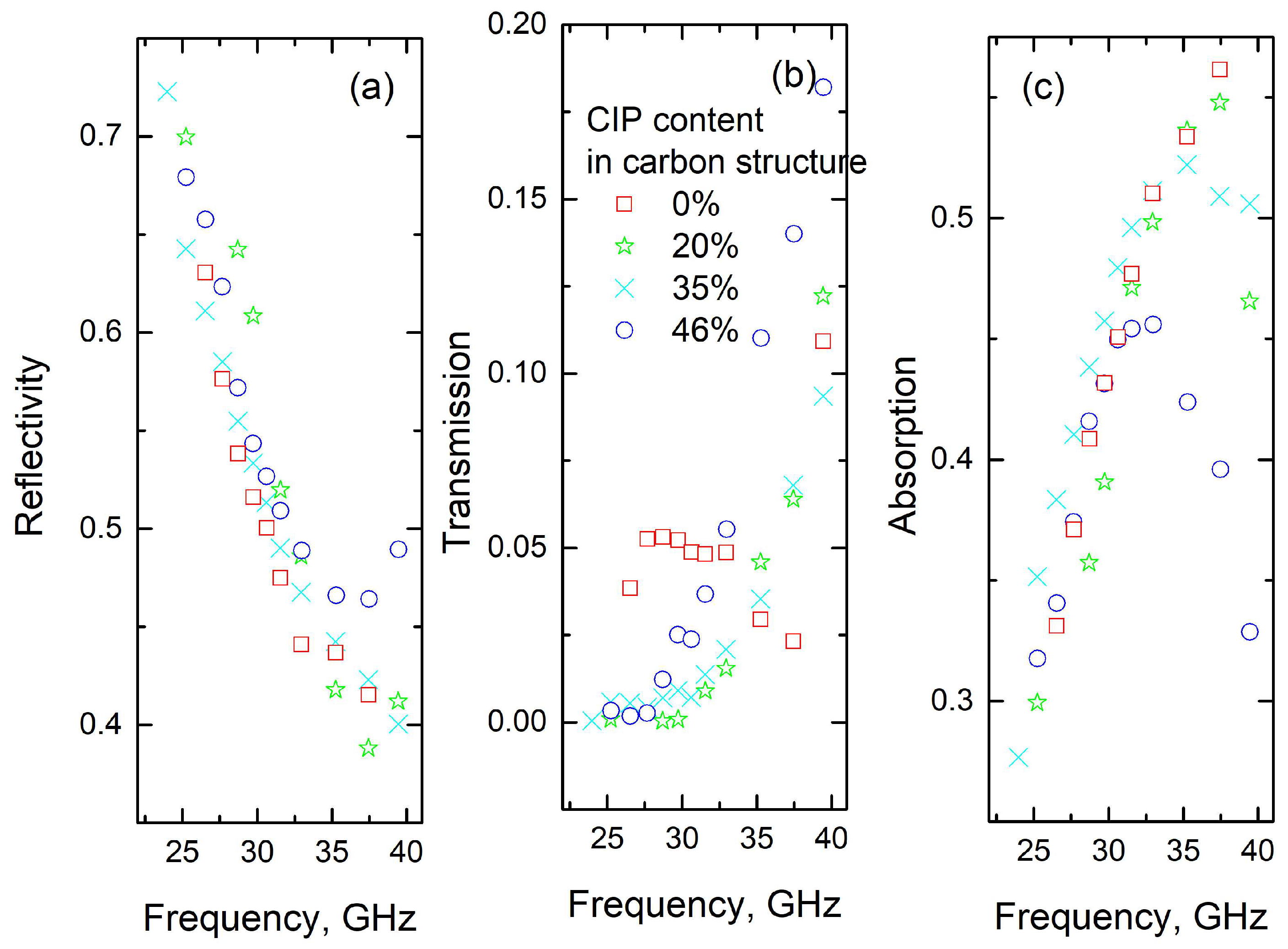
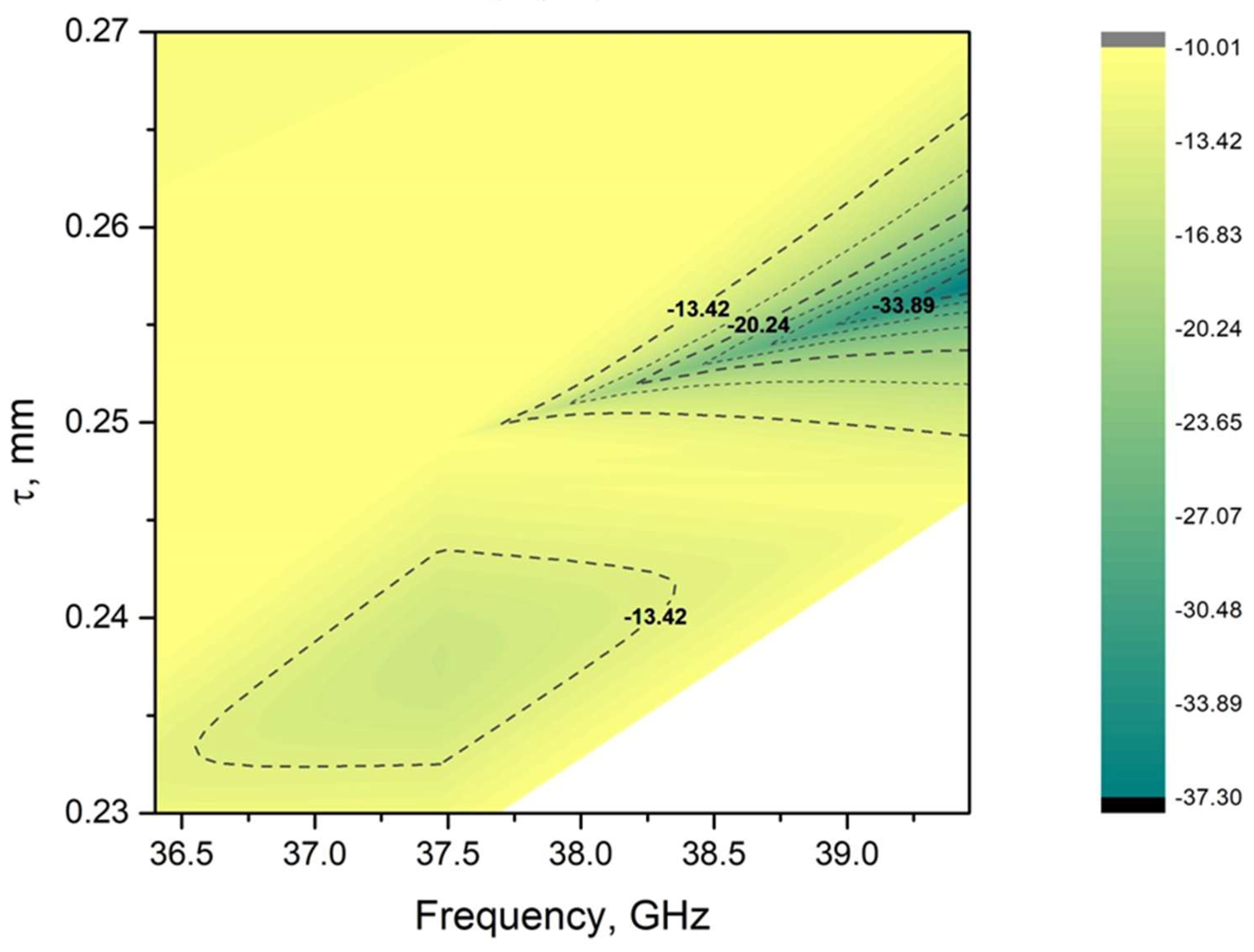
3. Results
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sankaran, S.; Deshmukh, K.; Ahamed, M.B.; Pasha, S.K.K. Recent advances in electromagnetic interference shielding properties of metal and carbon filler reinforced flexible polymer composites: A review. Compos. Part A-Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2018, 114, 49–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snoeck, J.L. Gyromagnetic resonance in ferrites. Nature 1947, 160, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sista, K.S.; Dwarapudi, S.; Kumar, D.; Sinha, G.R.; Moon, A.P. Carbonyl iron powders as absorption material for microwave shielding: A review. J. Alloys Compd. 2021, 853, 157251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.G.; Ren, H.; Zhang, H.Y. Preparation and microwave shielding property of silver-coated carbonyl iron powder. J. Alloys Compd. 2015, 631, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.Z.; Ding, J.; Jiang, H.B.; Chen, L.F.; Ong, C.K. Particle size influence to the microwave properties of iron based magnetic particulate composites. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2005, 285, 233–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinho, M.S.; Gregory, M.L.; Nunes, R.C.R.; Soares, B.G. Performance of radar absorbing materials by waveguide measurements for X- and Ku-band frequencies. Eur. Polym. J. 2002, 38, 2321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Y.; Li, G.; Liu, L.; Liu, S. Electromagnetic properties of carbonyl iron and their microwave absorbing characterization as filler in silicone ruber. Bull. Mater. Sci. 2010, 33, 633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Wei, J.; Yang, Y.; Wang, T.; Li, F. Investigation on peak frequency of the microwave absorption for carbonyl iron/epoxy resin composite. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2011, 323, 1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, M.; He, Z.; Pang, H. Microwave absorption enhancement of CIP/PANI composites. Synth. Met. 2013, 166, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joseph, N.; Thomas Sebstian, M. Electromagnetic interference shielding nature of PVDF-carbonyl iron composites. Mater. Lett. 2013, 90, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, F.; Brosseau, C.A. A reviewe and analysis of microwave absorption in polymer composites filled with carbonaceous particles. J. Appl. Phys. 2012, 111, 061301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.J.; Wang, Y.; Huang, Y.; Ma, Y.F.; Liu, Z.F.; Cai, J.M.; Zhang, C.D.; Gao, H.J.; Chen, Y.S. Electromagnetic interference shielding of graphene/epoxy composites. Carbon 2009, 47, 922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandler, J.W.K.; Kirk, J.E.; Kinloch, I.A.; Schaffer, M.S.P.; Windle, A.H. Ultra low electrical percolation threshold in carbon-nanotube-epoxy composites. Polymer 2003, 44, 5893–5899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mierczynska, A.; Mayne-LHermite, M.; Boiteux, G.; Jeszka, J.K. Electrical and mechanical properties of carbon nanotube/ultrahigh-molecular-weight polyethylene composites prepared by a filler prelocalization method. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2007, 105, 158–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palaimiene, E.; Macutkevic, J.; Banys, J.; Selskis, A.; Fierro, V.; Celzard, A.; Schaefer, S.; Shenderova, O. Ultra-low percolation threshold in epoxy resin-onion-like carbon composites. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2018, 113, 033105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuilla, T.; Bhadra, S.; Yao, D.; Kim, N.H.; Bose, S.; Lee, J.H. Recent advances in graphene based polymer composites. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2010, 35, 1350–1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Letellier, M.; Macutkevic, J.; Kuzhir, P.; Banys, J.; Fierro, V.; Celzard, A. Electromagnetic properties of model vitreous carbon foam. Carbon 2017, 122, 217–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, H.; Lin, L.; Ji, M.; Zhang, S.; Yang, M.; Fu, Q. Progress on the morphological control of conductive network in conductive polymer composites and the use as electroactive multifunctional materials. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2014, 39, 627–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro-Guttierrez, J.; Palaimiene, E.; Macutkevic, J.; Banys, J.; Kuzhir, P.; Schaefer, S.; Fierro, V.; Celzard, A. Electromagnetic properties of carbon gels. Materials 2019, 12, 4143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bychanok, D.; Li, S.; Sanchez-Sanchez, A.; Gorokhov, G.; Kuzhir, P.; Ogrin, F.Y.; Pasc, A.; Balweg, T.; Mandel, K.; Szczurek, A.; et al. Hollow carbon spheres in microwaves: Bio inspired absorbing coating. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2016, 108, 013701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, N.; Hu, Q.; Wei, R.; Mai, X.; Naik, N.; Pan, D.; Guo, Z.; Shi, Z. Review on electromagnetic shielding properties of carbon based materials and their novel composites: Recent progress, challenges and prospects. Carbon 2021, 176, 88–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theilman, P.; Yun, D.Y.; Asbeck, P.; Park, S.H. Superior electromagnetic interference shielding and dielectric properties of carbon nanotubes composites though the use of high aspect CNTs and three-roll miling. Org. Electron. 2013, 14, 1531–1537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ao, D.; Tang, Y.; Xu, X.; Xiang, X.; Yu, J.; Li, S.; Zu, X. Highly conductive PDMS composite mechanically enhanced with 3D-graphene network for high-performance emi shielding application. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Q.Q.; Hu, Y.M.; Sun, N.; Lei, T.; Qin, S.H.; Yang, Y.Y.; Wu, X.; Cui, Z.Y.; An, M.Z. Fabrication of PVC-based electromagnetic intereference shielding composite film by positively charged SMA enhancing the dispersibility of carbon nanomaterial. Carbon 2024, 231, 119701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spitalsky, Z.; Tasis, D.; Papagelis, K.; Galiotis, C. Carbon nanotube-polymer composites: Chemistry, processing, mechanical and electrical properties. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2010, 35, 357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauhofer, W.; Kovacs, J.Z. A review and analysis of electrical percolation in carbon nanotube polymeric composite. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2009, 69, 1486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Kong, L. High microwave permittivity of multiwalled carbon nanotube composites. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2004, 84, 4956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Ma, H. Highly enhanced electromagnetic wave absorption bandwidth based on reduced graphene oxide-Fe aerogel composites. Nanotechnology 2019, 31, 095711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Ren, Y.; Guo, X.; Zhao, B. Three-dimensional magnetic functionalized graphene composite aerogels for microwave absorption: A review. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2022, 5, 14133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blyweert, P.; Zharov, A.; Meisak, D.; Plyushch, A.; Macutkevič, J.; Banys, J.; Fierro, V.; Celzard, A. Electromagnetic properties of 3D-printed carbon-BaTiO3 composites. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2023, 123, 012903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blyweert, P.; Nicolas, V.; Macutkevic, J.; Fierro, V.; Celzard, A. Tannin-based resins for 3D printing of porous carbon architectures. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 7702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blyweert, P.; Nicolas, V.; Fierro, V.; Celzard, A. Experimental design optimisation of tannin-acrylate photocurable resins for 3D printing of biobased porous carbon architectures. Molecules 2022, 27, 2091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grigas, J. Microwave Dielectric Spectroscopy of Ferroelectrics and Related Materials; Gordon and Breach Science Publishers: London, UK, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Jang, D.; Park, J.E.; Kim, Y. K Evaluation of (CNT@CIP) embedded magneto-resistive sensor based on carbon nanotube and carbonyl iron powder polymer composite. Polymers 2022, 14, 542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klein, C.A. Electrical properties of pyrolytic graphites. Rev. Mod. Phys. 1962, 34, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plyushch, A.; Macutkevic, J.; Svirskas, S.; Banys, J.; Plausinaitiene, V.; Bychanok, D.; Maksimenko, S.A.; Selskis, A.; Sokal, A.; Lapko, K.N.; et al. Silicon carbide/phosphate ceramics composite for electromagnetic shielding applications whiskers vs particles. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2019, 114, 183105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jonsher, A.K. The universal dielectric response. Nature 1977, 267, 673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, B.; Wang, M.; Yao, Z.; Chen, Z.; Chen, P.; Tao, X.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, J. Bimetallic nanoarrays embedded in three-dimensional carbon foam as lightweight and and efficient microwave absorber. Carbon 2022, 191, 486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fante, R.L.; McCormack, M.T. Reflection properties of the Salisburry screen. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 1988, 36, 1443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meisak, D.; Plyushch, A.; Macutkevič, J.; Grigalaitis, R.; Sokal, A.; Lapko, K.N.; Selskis, A.; Kuzhir, P.P.; Banys, J. Effect of temperature on shielding efficiency of phosphate-bonded CoFe2O4-xBaTiO3 multiferroic composite in microwaves. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2023, 24, 1939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Initial CIP Concentration, Φi (wt.%) | Final CIP Concentration, Φf (wt.%) * | Final CIP Concentration, Φv (vol.%) ** | Bulk Density, ρb (g/cm3) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.42 |
| 5 | 20 | 1 | 0.44 |
| 10 | 35 | 2 | 0.51 |
| 15 | 46 | 4 | 0.67 |
| CIP Concentration, wt.% | Temperature Region, K | σ0, S/cm | E/k, K (meV) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | T < 155 | 7.2 | 137 (11.8) |
| T > 155 | 9.6 | 184 (15.8) | |
| 20 | T < 186 | 2.27 | 302.7 (26) |
| T < 186 | 1.02 | 152.1 (13.1) | |
| 35 | T < 227 | 11.98 | 131.9 (11.3) |
| T > 259 | 11.98 | 186.3 (13) | |
| 46 | T < 220 | 1.79 | 275.6 (23.7) |
| T > 250 | 1.15 | 147.2 (12.6) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tsyhanok, D.; Meisak, D.; Blyweert, P.; Selskis, A.; Macutkevič, J.; Banys, J.; Fierro, V.; Celzard, A. Investigating 3D-Printed Carbon–Carbonyl Iron Composites for Electromagnetic Applications. Polymers 2025, 17, 1009. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17081009
Tsyhanok D, Meisak D, Blyweert P, Selskis A, Macutkevič J, Banys J, Fierro V, Celzard A. Investigating 3D-Printed Carbon–Carbonyl Iron Composites for Electromagnetic Applications. Polymers. 2025; 17(8):1009. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17081009
Chicago/Turabian StyleTsyhanok, Dzmitry, Darya Meisak, Pauline Blyweert, Algirdas Selskis, Jan Macutkevič, Jūras Banys, Vanessa Fierro, and Alain Celzard. 2025. "Investigating 3D-Printed Carbon–Carbonyl Iron Composites for Electromagnetic Applications" Polymers 17, no. 8: 1009. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17081009
APA StyleTsyhanok, D., Meisak, D., Blyweert, P., Selskis, A., Macutkevič, J., Banys, J., Fierro, V., & Celzard, A. (2025). Investigating 3D-Printed Carbon–Carbonyl Iron Composites for Electromagnetic Applications. Polymers, 17(8), 1009. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17081009









